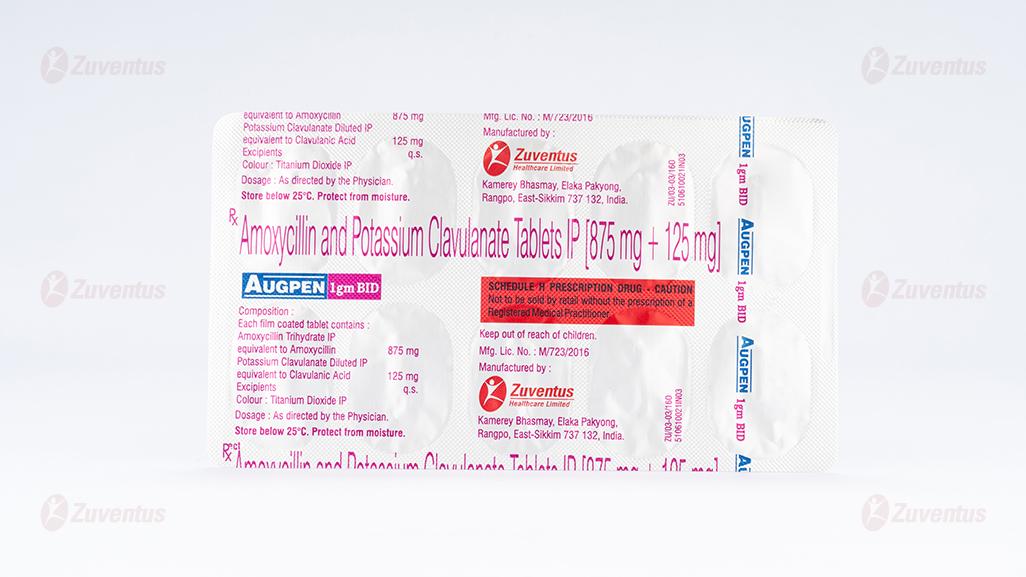
Augpen 1 gm BID Tablets
Therapy Area
Anti Infective
1.0 Generic name
Amoxycillin and Potassium Clavulanate Tablets IP
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Augpen 375
Each film coated tablet contains :
Amoxycillin Trihydrate IP
equivalent to Amoxycillin 250 mg
Potassium Clavulanate Diluted IP
equivalent to Clavulanic Acid 125 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Titanium Dioxide IP
Augpen 625 BID
Each film coated tablet contains :
Amoxycillin Trihydrate IP
equivalent to Amoxycillin 500 mg
Potassium Clavulanate Diluted IP
equivalent to Clavulanic Acid 125 mg
Excipients q.s
Colour : Titanium Dioxide IP
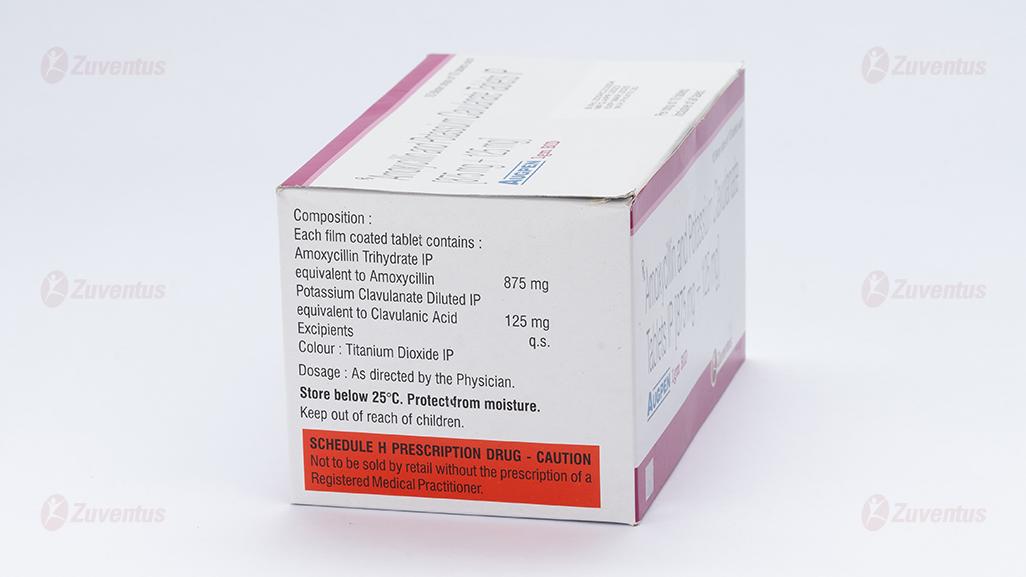
Augpen 1gm BID
Each film coated tablet contains :
Amoxycillin Trihydrate IP
equivalent to Amoxycillin 875 mg
Potassium Clavulanate Diluted IP
equivalent to Clavulanic Acid 125 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Titanium Dioxide IP
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Tablet, [250 mg / 500 mg / 875 mg + 125 mg]
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
- Upper respiratory tract infections
- Lower respiratory tract infections
- Genito-urinary tract infections
- Skin and soft tissue infections
- Bone and joint infections
- Dental infections
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Dosage depends on the age and renal function of the patient and the severity of the infection. To minimise potential gastrointestinal intolerance, administer at the start of a meal. The absorption of Augpen is optimised when taken at the start of a meal. Treatment should not be extended beyond 14 days without review. Therapy can be started parenterally and continued with an oral preparation. Tablets should be swallowed whole without chewing. If required, tablets may be broken in half and swallowed without chewing. Augpen tablets are not recommended in children of 12 years and under.
Adults and children over 12 years
The usual recommended daily dosage is :
| Mild - Moderate infections | One or two Augpen 375 tablet(s) every eight hours or One Augpen 625 mg tablet every 12 hours. |
| Severe infections | One Augpen 1 gm tablet every 12 hours. |
Renal impairment
No adjustment in dose is required in patients with creatinine clearance (CrCl) greater than 30 mL/min. The Augpen 1 gm tablet should only be used in patients with a creatinine clearance (CrCl) rate of more than 30 mL/min.
| CrCl 10 - 30 mL/min | One Augpen 625 mg tablet every 12 hours. |
| CrCl < 10 mL/min | One Augpen 625 mg tablet every 24 hours. |
| Haemodialysis | One Augpen 625 mg tablet every 24 hours, plus a further one tablet during dialysis, to be repeated at the end of dialysis (as serum concentrations of both amoxicillin and Clavulanic Acid are decreased). |
Hepatic impairment
Dose with caution; monitor hepatic function at regular intervals.
4.3 Contraindications
- Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to beta-lactams, e.g. penicillin and cephalosporins.
- Patients with a previous history of Augpen-associated jaundice/hepatic dysfunction.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Before initiating therapy with Augpen, careful enquiry should be made concerning previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillin, cephalosporins or other allergens. Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylactoid and severe cutaneous adverse reactions) have been reported in patients on penicillin therapy. These reactions are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity (see Contraindications). If an allergic reaction occurs, Augpen therapy must be discontinued and appropriate alternative therapy instituted. Serious anaphylactic reactions require immediate emergency treatment with adrenaline. Oxygen, intravenous (I.V.) steroids and airway management (including intubation) may also be required.
Augpen should be avoided if infectious mononucleosis is suspected since the occurrence of a morbilliform rash has been associated with this condition following the use of Amoxycillin. Prolonged use may also occasionally result in overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms. Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with the use of antibiotics and may range in severity from mild to life-threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider its diagnosis in patients who develop diarrhoea during or after antibiotic use. If prolonged or significant diarrhoea occurs or the patient experiences abdominal cramps, treatment should be discontinued immediately and the patient investigated further. Abnormal prolongation of prothrombin time (increased INR) has been reported rarely in patients receiving Augpen and oral anticoagulants. Appropriate monitoring should be undertaken when anticoagulants are prescribed concurrently. Adjustments in the dose of oral anticoagulants may be necessary to maintain the desired level of anticoagulation. Changes in liver function tests have been observed in some patients receiving Augpen. The clinical significance of these changes is uncertain but Augpen should be used with caution in patients with evidence of hepatic dysfunction. Cholestatic jaundice, which may be severe, but is usually reversible, has been reported rarely. Signs and symptoms may not become apparent for up to six weeks after treatment has ceased. In patients with reduced urine output, crystalluria has been observed very rarely, predominantly with parenteral therapy. During the administration of high doses of Amoxycillin, it is advisable to maintain adequate fluid intake and urinary output in order to reduce the possibility of Amoxycillin crystalluria.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Concomitant use of probenecid is not recommended. Probenecid decreases the renal tubular secretion of Amoxycillin. Concomitant use with Augpen may result in increased and prolonged blood levels of Amoxycillin but not of Clavulanate. Concomitant use of Allopurinol during treatment with Amoxycillin can increase the likelihood of allergic skin reactions. There are no data on the concomitant use of Augpen and Allopurinol. In common with other antibiotics, Augpen may affect the gut flora, leading to lower oestrogen reabsorption and reduced efficacy of combined oral contraceptives. In the literature there are rare cases of increased international normalised ratio in patients maintained on Acenocoumarol or warfarin and prescribed a course of Amoxycillin. If co-administration is necessary, the prothrombin time or international normalised ratio should be carefully monitored with the addition or withdrawal of Augpen. In patients receiving Mycophenolate Mofetil, reduction in pre-dose concentration of the active metabolite mycophenolic acid of approximately 50% has been reported following commencement of oral Amoxycillin plus Clavulanic Acid. The change in pre-dose level may not accurately represent changes in overall MPA exposure.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy and lactation
Reproduction studies in animals (mice and rats) with orally and parenterally administered Augpen have shown no teratogenic effects. In a single study in women with preterm, premature rupture of the foetal membrane (pPROM), it was reported that prophylactic treatment with Augpen may be associated with an increased risk of necrotising enterocolitis in neonates. As with all medicines, use should be avoided in pregnancy, especially during the first trimester, unless considered essential by the Physician. Augpen may be administered during the period of lactation. With the exception of the risk of sensitisation, associated with the excretion of trace quantities in breast milk, there are no detrimental effects for the infant.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Adverse effects on the ability to drive or operate machinery have not been observed.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Data from large clinical trials were used to determine the frequency of very common to rare undesirable effects. The frequencies assigned to all other undesirable effects (i.e., those occurring at < 1/10,000) were mainly determined using post-marketing data and refer to a reporting rate rather than a true frequency
Infections and infestations
Common : Mucocutaneous candidiasis
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Rare : Reversible leucopenia (including neutropenia) and thrombocytopenia.
Very rare : Reversible agranulocytosis and haemolytic anaemia. Prolongation of bleeding time and prothrombin time
Immune system disorders
Very rare : Angioneurotic oedema, Anaphylaxis, Serum sickness-like syndrome, Hypersensitivity vasculitis
Nervous system disorders
Uncommon : Dizziness, Headache
Very rare : Reversible hyperactivity, Aseptic meningitis, Convulsions. Convulsions may occur in patients with impaired renal function or in those receiving high doses.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Adults
Very common : Diarrhoea
Common : Nausea, Vomiting
Children
Common : Diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting
All populations
Nausea is more often associated with higher oral dosages. If gastrointestinal reactions are evident, they may be reduced by taking Augpen at the start of a meal.
Uncommon : Indigestion
Very rare : Antibiotic-associated colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis and haemorrhagic colitis), black hairy tongue, superficial tooth discolouration has been reported very rarely in children. Good oral hygiene may help to prevent tooth discolouration as it can usually be removed by brushing.
Hepatobiliary disorders
Uncommon : A moderate rise in AST and/or ALT has been noted in patients treated with beta-lactam class antibiotics, but the significance of these findings is unknown.
Very Rare : Hepatitis and cholestatic jaundice. These events have been noted with other penicillins and cephalosporins.
Hepatic events have been reported predominantly in males and elderly patients and may be associated with prolonged treatment. These events have been very rarely reported in children.
Signs and symptoms usually occur during or shortly after treatment but in some cases may not become apparent until several weeks after treatment has ceased. These are usually reversible. Hepatic events may be severe and in extremely rare circumstances, deaths have been reported. These have almost always occurred in patients with serious underlying disease or taking concomitant medications known to have the potential for hepatic effects.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Uncommon : Skin rash, Pruritus, Urticaria
Rare : Erythema multiforme
Very rare : Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Toxic epidermal necrolysis, Bullous exfoliative-dermatitis, Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS)
If any hypersensitivity dermatitis reaction occurs, treatment should be discontinued
Renal and urinary disorders
Very rare : Interstitial nephritis, Crystalluria
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com
4.9 Overdose
Gastrointestinal symptoms and disturbance of the fluid and electrolyte balances may be evident. Gastrointestinal symptoms may be treated symptomatically with attention to the water-electrolyte balance. Amoxycillin crystalluria, in some cases leading to renal failure, has been observed. Augpen can be removed from the circulation by haemodialysis.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Amoxycillin is a semisynthetic penicillin (beta-lactam antibiotic) that inhibits one or more enzymes (often referred to as penicillin-binding proteins, PBPs) in the biosynthetic pathway of bacterial peptidoglycan, which is an integral structural component of the bacterial cell wall. Inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis leads to weakening of the cell wall, which is usually followed by cell lysis and death.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Amoxycillin is susceptible to degradation by beta-lactamases produced by resistant bacteria and therefore the spectrum of activity of Amoxycillin alone does not include organisms which produce these enzymes. Clavulanic acid is a beta-lactam structurally related to penicillins. It inactivates some beta-lactamase enzymes thereby preventing inactivation of Amoxycillin. Clavulanic acid alone does not exert a clinically useful antibacterial effect.
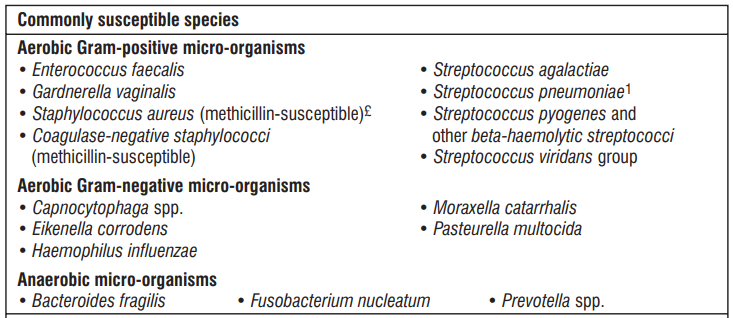
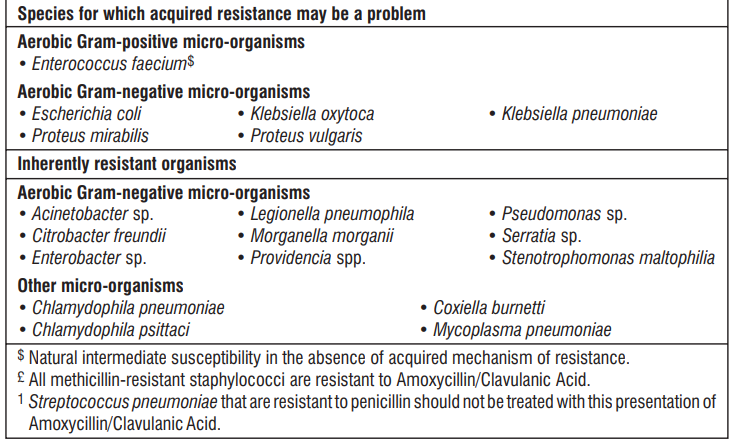
The prevalence of resistance may vary geographically and with time for selected species, and local information on resistance is desirable, particularly when treating severe infections. As necessary, expert advice should be sought when the local prevalence of resistance is such that the utility of the agent in at least some types of infections is questionable.
5.3Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Amoxycillin and Clavulanic Acid, are fully dissociated in aqueous solution at physiological pH. Both components are rapidly and well absorbed by the oral route of administration. Following oral administration, Amoxycillin and Clavulanic Acid are approximately 70% bioavailable. The plasma profiles of both components are similar and the time to peak plasma concentration (Tmax) in each case is approximately one hour.
The pharmacokinetic results for a study, in which Amoxycillin/Clavulanic Acid (250 mg / 125 mg tablets three times daily) was administered in the fasting state to groups of healthy volunteers are presented below.
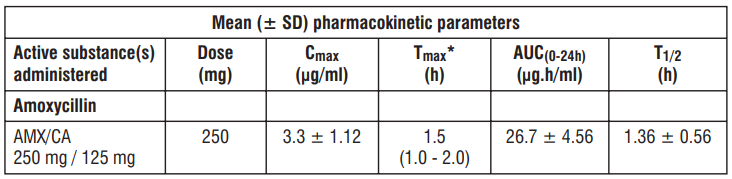
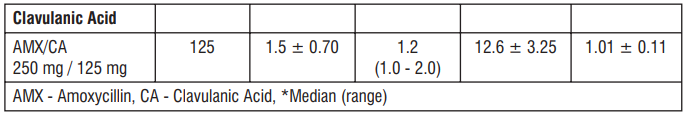
Amoxycillin and Clavulanic Acid serum concentrations achieved with Amoxycillin/Clavulanic Acid are similar to those produced by the oral administration of equivalent doses of Amoxycillin or Clavulanic Acid alone.
Distribution
About 25% of total plasma Clavulanic Acid and 18% of total plasma Amoxycillin is bound to protein. The apparent volume of distribution is around 0.3 - 0.4 l/kg for Amoxycillin and around 0.2 l/kg for Clavulanic Acid. Following intravenous administration, both Amoxycillin and Clavulanic Acid have been found in gall bladder, abdominal tissue, skin, fat, muscle tissues, synovial and peritoneal fluids, bile and pus. Amoxycillin does not adequately distribute into the cerebrospinal fluid.
From animal studies there is no evidence for significant tissue retention of drug-derived material for either component. Amoxycillin, like most penicillins, can be detected in breast milk. Trace quantities of Clavulanic Acid can also be detected in breast milk.
Both Amoxycillin and Clavulanic Acid have been shown to cross the placental barrier
Biotransformation
Amoxycillin is partly excreted in the urine as the inactive penicilloic acid in quantities equivalent to up to 10 to 25% of the initial dose. Clavulanic acid is extensively metabolized in man and eliminated in urine and faeces, and as carbon dioxide in expired air.
Elimination
The major route of elimination for Amoxycillin is via the kidney, whereas for Clavulanic Acid it is by both renal and non-renal mechanisms.
Amoxycillin/Clavulanic Acid has a mean elimination half-life of approximately one hour and a mean total clearance of approximately 25 l/h in healthy subjects. Approximately 60 to 70% of the Amoxycillin and approximately 40 to 65% of the Clavulanic Acid are excreted unchanged in urine during the first 6 h after administration of single Augpen 250 mg / 125 mg or 500 mg / 125 mg tablets. Various studies have found the urinary excretion to be 50 - 85% for Amoxycillin and between 27 - 60% for Clavulanic Acid over a 24-hour period. In the case of Clavulanic Acid, the largest amount of drug is excreted during the first 2 hours after administration.
Concomitant use of probenecid delays Amoxycillin excretion but does not delay renal excretion of Clavulanic Acid
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on studies of safety pharmacology, genotoxicity and toxicity to reproduction
Repeat dose toxicity studies performed in dogs with Amoxycillin/Clavulanic Acid demonstrate gastric irritancy and vomiting, and discoloured tongue.
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with Amoxycillin/Clavulanic Acid.
7.0 Description
Augpen tablet is an oral antibacterial combination consisting of Amoxycillin and the beta-lactamase inhibitor, Clavulanate potassium (the potassium salt of Clavulanic Acid).
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
24 Months
8.3 Packaging information
Augpen 375 : Alu-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets.
Augpen 625 BID : Alu-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets.
Augpen 1gm BID : Alu-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store below 25°C. Protect from moisture
Keep out of reach of children
9.0 Patient counselling information
Patients should be informed that Augpen may be taken every 8 hours or every 12 hours, depending on the dose prescribed. Each dose should be taken with a meal or snack to reduce the possibility of gastrointestinal upset. Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs, including Augpen, should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When Augpen is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may : (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment, and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Augpen or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Counsel patients that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterials, and it usually ends when the antibacterial is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibacterials, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as 2 or more months after having taken their last dose of the antibacterial. If diarrhea is severe or lasts more than 2 or 3 days, patients should contact their physician.
Patients should be aware that Augpen contains a penicillin class drug product that can cause allergic reactions in some individuals.
12.0 Date of revision
29 March 2022
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you (or for your child) only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet
- What Augpen is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you take Augpen
- How to take Augpen
- Possible side effects
- How to store Augpen
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Augpen is and what it is used for
Augpen is an antibiotic and works by killing bacteria that cause infections. It contains two different medicines called amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Amoxicillin belongs to a group of medicines called “penicillins” that can sometimes be stopped from working (made inactive). The other active component (clavulanic acid) stops this from happening.
Augpen is used in adults and children to treat the following infections:
- sinus infections
- urinary tract infections
- skin infections
- dental infections.
2. What you need to know before you take Augpen
Do not take Augpen:
- if you are allergic to amoxicillin, clavulanic acid, penicillin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
- if you have ever had a severe allergic reaction to any other antibiotic. This can include a skin rash or swelling of the face or throat.
- if you have ever had liver problems or jaundice (yellowing of the skin) when taking an antibiotic.
Do not take Augpen if any of the above apply to you. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Augpen.
Warnings and precautions
- have glandular fever
- are being treated for liver or kidney problems
- are not passing water regularly.
If you are not sure if any of the above apply to you, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Augpen.
In some cases, your doctor may investigate the type of bacteria that is causing your infection. Depending on the results, you may be given a different strength of Augpen or a different medicine.
Conditions you need to look out for
Augpen can make some existing conditions worse, or cause serious side effects. These include allergic reactions, convulsions (fits) and inflammation of the large intestine. You must look out for certain symptoms while you are taking Augpen, to reduce the risk of any problems. See ‘Conditions you need to look out for’ in section 4.
Blood and urine tests
If you are having blood tests (such as red blood cell status tests or liver function tests) or urine tests (for glucose), let the doctor or nurse know that you are taking Augpen. This is because Augpen can affect the results of these types of tests.
Other medicines and Augpen
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines.
- If you are taking allopurinol (used for gout) with Augpen, it may be more likely that you will have an allergic skin reaction.
- If you are taking probenecid (used for gout), your doctor may decide to adjust your dose of Augpen.
- If medicines to help stop blood clots (such as warfarin) are taken with Augpen then extra blood tests may be needed.
- Augpen can affect how methotrexate (a medicine used to treat cancer or rheumatic diseases) works.
- Augpen may affect how mycophenolate mofetil (a medicine used to prevent the rejection of transplanted organs) works.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Augpen can have side effects and the symptoms may make you unfit to drive. Do not drive or operate machinery unless you are feeling well.
3. How to take Augpen
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
Adults and Children over 12 years
| Mild - Moderate infections | One AUGPEN 375 mg tablet every 8 hours or One AUGPEN 625 mg tablet every 12 hours. |
Severe infections |
One AUGPEN 1 g tablet every 12 hours |
Children below 12 years preferably be treated with Augpen oral suspension or sachets. Augpen tablets are not recommended.
Patients with kidney and liver problems
- If you have kidney problems the dose might be changed. A different strength or different medicine may be chosen by your doctor.
- If you have liver problems you may have more frequent blood tests to check how your liver is working.
How to take Augpen
- Take with a meal.
- Swallow the tablets whole with a glass of water.
- Space the doses evenly during the day, at least 4 hours apart. Do not take 2 doses in 1 hour.
- Do not take Augpen for more than 2 weeks. If you still feel unwell you should go back to see the doctor.
If you take more Augpen than you should
If you take too much Augpen, signs might include an upset stomach (feeling sick, being sick or diarrhoea) or convulsions. Talk to your doctor as soon as possible. Take the medicine carton or bottle to show the doctor.
If you forget to take Augpen
If you forget to take a dose take it as soon as you remember. You should not take the next dose too soon, but wait around 4 hours before taking the next dose. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop taking Augpen
Keep taking Augpen until the treatment is finished, even if you feel better. You need every dose to help fight the infection. If some bacteria survive they can cause the infection to come back.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. The side effects below may happen with this medicine.
Conditions you need to look out for
Allergic reactions:
- skin rash
- inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis) which may be visible as red or purple raised spots on the skin, but can affect other parts of the body
- fever, joint pain, swollen glands in the neck, armpit or groin
- swelling, sometimes of the face or throat (angioedema), causing difficulty in breathing
- collapse.
➔ Contact a doctor immediately if you get any of these symptoms. Stop taking Augpen. Inflammation of large intestine Inflammation of the large intestine, causing watery diarrhoea usually with blood and mucus, stomach pain and/or fever.
➔ Contact your doctor as soon as possible for advice if you get these symptoms.
Very common side effects
These may affect more than 1 in 10 people
- diarrhoea (in adults).
Common side effects
These may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- thrush (candida - a yeast infection of the vagina, mouth or skin folds)
- feeling sick (nausea), especially when taking high doses
➔ if affected take Augpen with a meal
- vomiting
- diarrhoea (in children).
Uncommon side effects
These may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- skin rash, itching
- raised itchy rash (hives)
- indigestion
- dizziness
- headache.
Uncommon side effects that may show up in your blood tests:
- increase in some substances (enzymes) produced by the liver.
Rare side effects
These may affect up to 1 in 1000 people
- skin rash, which may blister, and looks like small targets (central dark spots surrounded by a paler area, with a dark ring around the edge - erythema multiforme)
➔ if you notice any of these symptoms contact a doctor urgently.
Rare side effects that may show up in your blood tests:
- low number of cells involved in blood clotting
- low number of white blood cells.
Frequency not known
Frequency cannot be estimated from the available data.
- Allergic reactions
- Inflammation of the large intestine
- Inflammation of the protective membrane surrounding the brain (aseptic meningitis)
- Serious skin reactions:
- a widespread rash with blisters and peeling skin, particularly around the mouth, nose, eyes and genitals (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), and a more severe form, causing extensive peeling of the skin (more than 30% of the body surface - toxic epidermal necrolysis)
- widespread red skin rash with small pus-containing blisters (bullous exfoliative dermatitis)
- a red, scaly rash with bumps under the skin and blisters (exanthemous pustulosis).
- flu-like symptoms with a rash, fever, swollen glands, and abnormal blood test results (including increased white blood cells (eosinophilia) and liver enzymes) (Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)).
➔ Contact a doctor immediately if you get any of these symptoms.
- inflammation of the liver (hepatitis)
- jaundice, caused by increases in the blood of bilirubin (a substance produced in the liver) which may make your skin and whites of the eyes appear yellow
- inflammation of tubes in the kidney
- blood takes longer to clot
- hyperactivity
- convulsions (in people taking high doses of Augpen or who have kidney problems)
- black tongue which looks hairy Side effects that may show up in your blood or urine tests:
- severe reduction in the number of white blood cells
- low number of red blood cells (haemolytic anaemia)
- crystals in urine.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
5. How to store Augpen
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date (EXP) which is stated on the carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Do not store above 25°C.
Tablets supplied in pouches should be used within 30 days of opening the pouch.
Store in the original package to protect from moisture.
Do not use if the tablets are chipped or damaged.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Augpen contains
- The active substances are amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Each tablet contains amoxicillin trihydrate equivalent to 250 mg/500 mg/875 mg amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate equivalent to 125 mg of clavulanic acid.