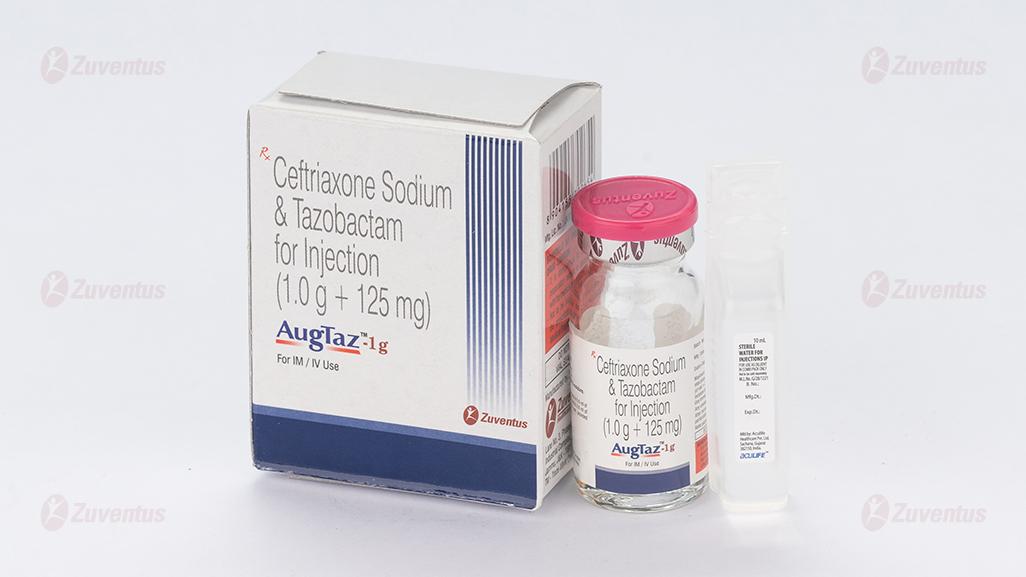
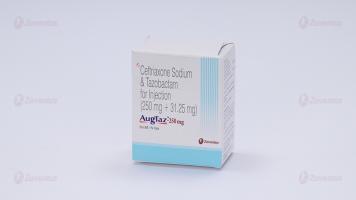
AugTaz Injection 125mg / 250mg / 500mg / 1g
Therapy Area
Anti Bacterial
Composition
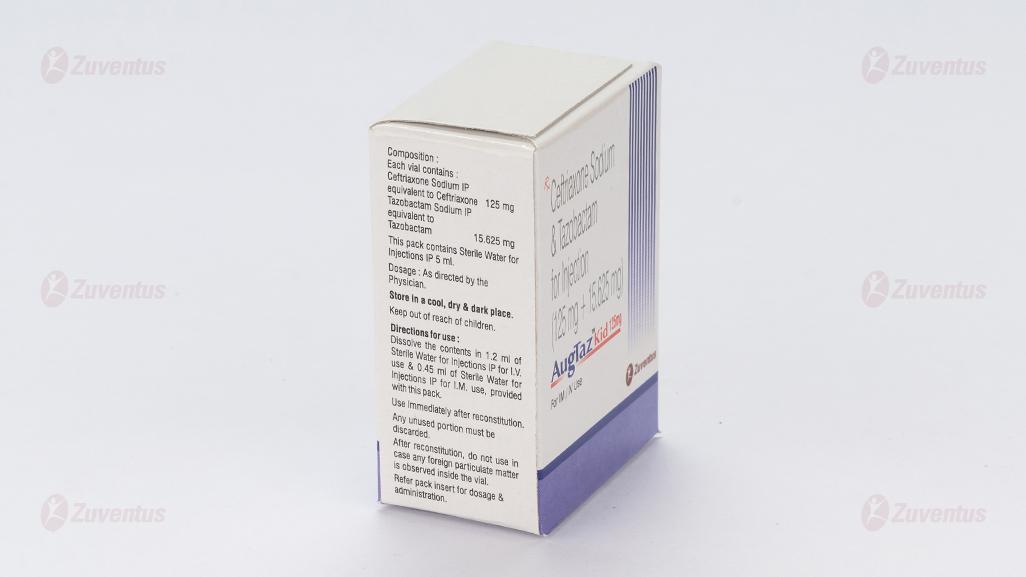
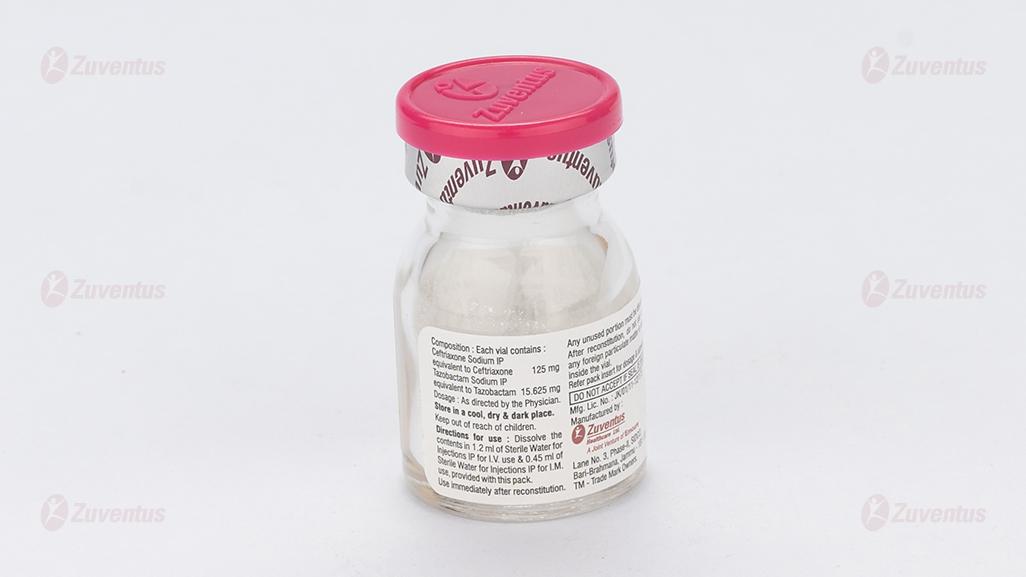
AugTaz-KID 125 mg
Each vial contains :
Ceftriaxone Sodium IP equivalent to Ceftriaxone 125 mg
Tazobactam Sodium IP equivalent to Tazobactam 15.625 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
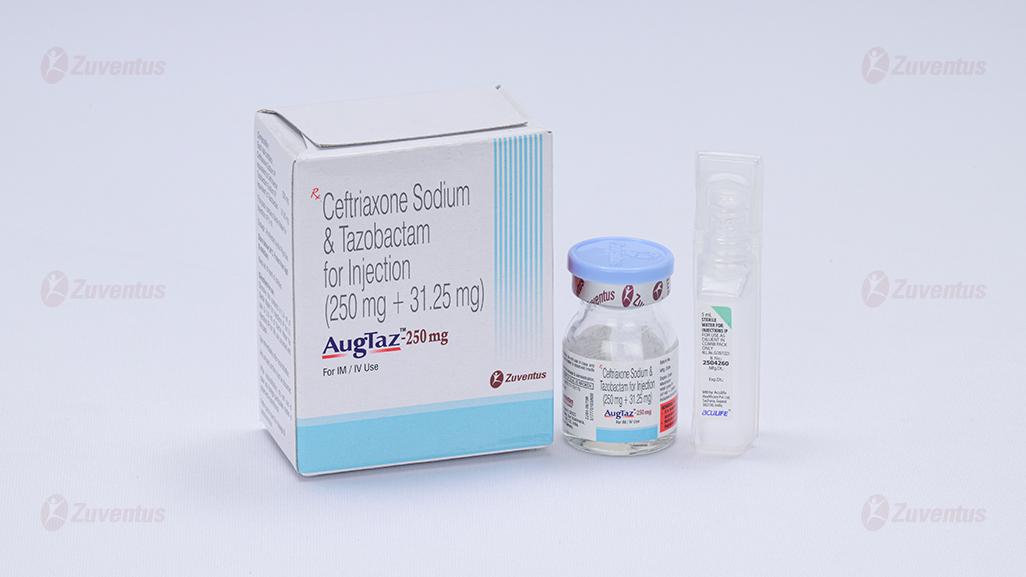
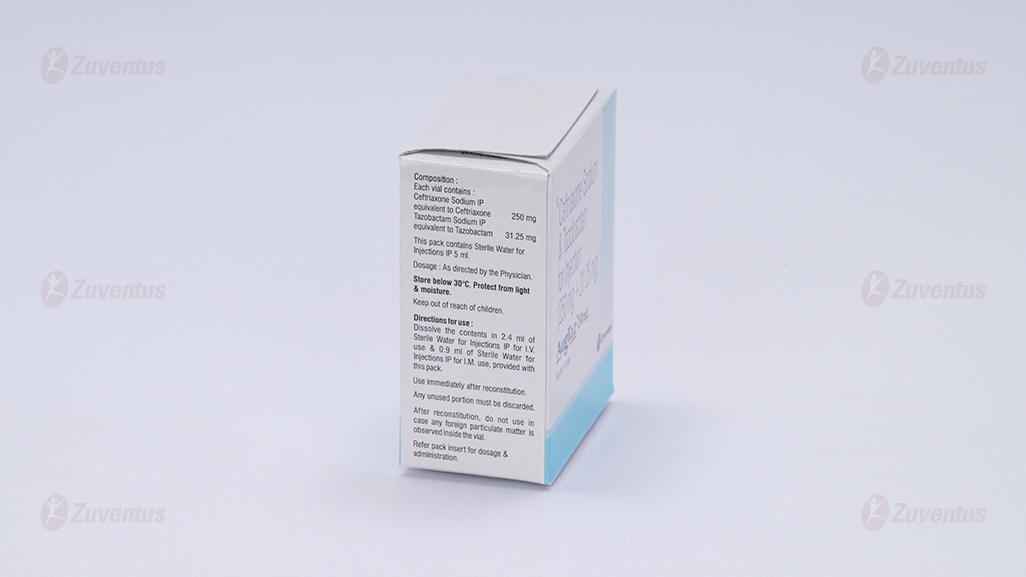
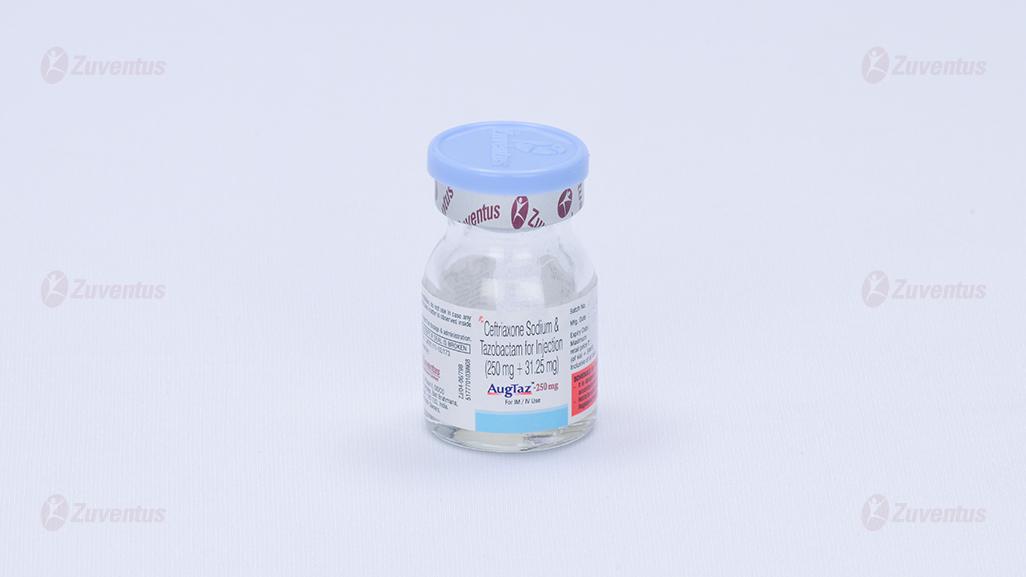
AugTaz-250 mg
Each vial contains :
Ceftriaxone Sodium IP equivalent to Ceftriaxone 250 mg
Tazobactam Sodium IP equivalent to Tazobactam 31.25 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
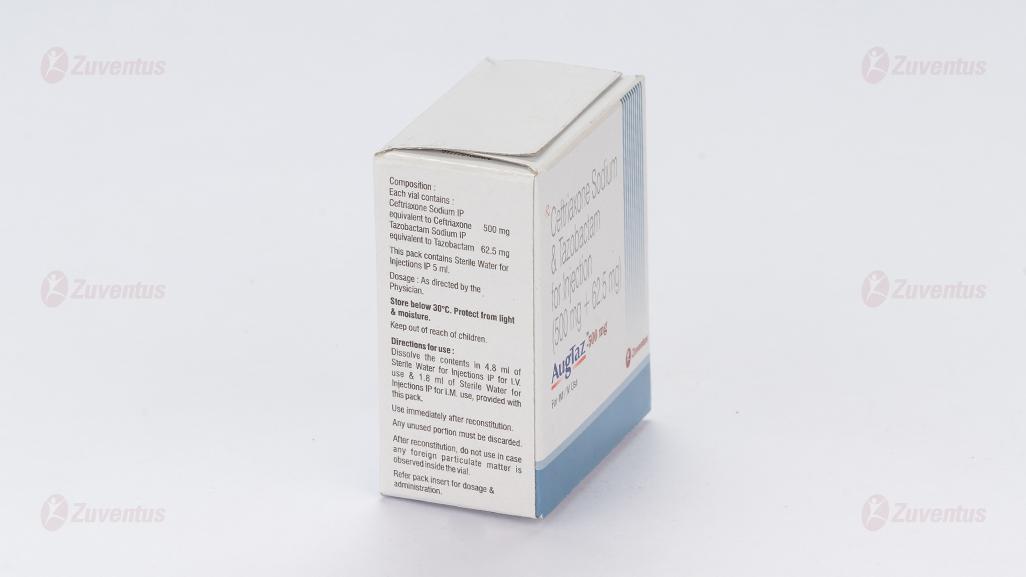
AugTaz-500 mg
Each vial contains :
Ceftriaxone Sodium IP equivalent to Ceftriaxone 500 mg
Tazobactam Sodium IP equivalent to Tazobactam 62.5 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
AugTaz-1 g
Each vial contains :
Ceftriaxone Sodium IP equivalent to Ceftriaxone 1.0 g
Tazobactam Sodium IP equivalent to Tazobactam 125 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 10 ml.
Description
AugTazis a combination of Ceftriaxone, a semi - synthetic third generation broad spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic along with a β- lactamase inhibitor Tazobactam. Tazobactam sodium, a derivative of the penicillin nucleus, is a penicillanic acid sulfone.
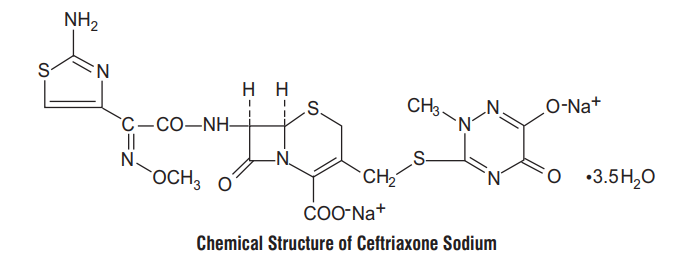
Ceftriaxone Sodium :
Chemical Name : (6R, 7R)-7-[2-(2-Amino-4-thiazolyl) glyoxylamido]-8-oxo-3- Chemical Name : (2S,3S,5R)-3-methyl-7-oxo-3-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-ylmethyl) [[(1,2,5,6-tetrahydro-2-methyl-5,6-dioxo-as-triazin-3-yl)thio]methyl]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo -4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate-4,4-dioxide. [4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 72-(Z)-(O-methyloxime), disodium salt, sesquaterhydrate.
Molecular Formula :C18H16N8Na2O7S3•3.5H2O
Molecular Weight : 661.59
RATIONALE OF THE COMBINATION :
Ceftriaxone is a third generation semi-synthetic parenteral cephalosporin that has excellent activity against variety of gram -ve organisms and some gram +ve organisms like Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, H.influenzae, Neisseria meningitides and members of Enterobacteriaceae. Ceftriaxone is indicated in number of community and hospital acquired infections caused by the susceptible organisms both in adults and in children including neonates. Tazobactam is penicillanic acid sulfone derivative with beta-lactamase inhibitory properties, having good affinity for a variety of both plasmid mediated and chromosomal beta lactamases produced by gram +ve and gram –ve bacteria which are originally sensitive to Ceftriaxone. Therefore, it enhances the activity of penicillins and cephalosporins against many resistant strains of bacteria. It is regarded as more potent than other β-lactamase inhibitors (like sulbactam). Clinical role of Ceftriaxone can be compromised due to increasing proportion of extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producing bacteria which exhibit resistance to Ceftriaxone. To treat such infections Ceftriaxone can be combined with a beta lactamases inhibitor of better efficacy like Tazobactam. The combination of Ceftriaxone and Tazobactam will be effective not only against the beta lactamase producing organisms but also against the originally Ceftriaxone-susceptible bacteria.
Rationale of the Combination
Ceftriaxone is a third generation semi-synthetic parenteral cephalosporin that has excellent activity against variety of gram -ve organisms and some gram +ve organisms like Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, H.influenzae, Neisseria meningitides and members of Enterobacteriaceae. Ceftriaxone is indicated in number of community and hospital acquired infections caused by the susceptible organisms both in adults and in children including neonates. Tazobactam is penicillanic acid sulfone derivative with beta-lactamase inhibitory properties, having good affinity for a variety of both plasmid mediated and chromosomal beta lactamases produced by gram +ve and gram –ve bacteria which are originally sensitive to Ceftriaxone. Therefore, it enhances the activity of penicillins and cephalosporins against many resistant strains of bacteria. It is regarded as more potent than other β-lactamase inhibitors (like sulbactam). Clinical role of Ceftriaxone can be compromised due to increasing proportion of extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producing bacteria which exhibit resistance to Ceftriaxone. To treat such infections Ceftriaxone can be combined with a beta lactamases inhibitor of better efficacy like Tazobactam. The combination of Ceftriaxone and Tazobactam will be effective not only against the beta lactamase producing organisms but also against the originally Ceftriaxone-susceptible bacteria.
Clinical Pharmacology
Ceftriaxone is a parenteral cephalosporin which acts by inhibition of cell wall biosynthesis and thus is bactericidal in its action. It has excellent activity against variety of aerobic and anaerobic, gram-positive and gram-negative pathogens. Tazobactam (sodium) is a new β-lactamase inhibitor with a range of activity that includes extended spectrum plasmid mediated beta lactamases. Tazobactam lacks significant antibacterial activity of its own. It combines irreversibly with the common plasmid-encoded β-lactamases including the extended spectrum group of beta lactamases. By rendering β–lactamase inactive, Tazobactam is able to protect the activity of Ceftriaxone.
Microbiology
MICROBIOLOGY :
AugTaz has been shown to be active against most strains of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections.
Aerobic gram-negative microorganisms
- Escherichia coli
- Haemophilus influenzae (including ampicillin-resistant and β-lactamase producing strains)
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Moraxella catarrhalis (including β--lactamase producing strains)
- Morganella morganii
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae (including penicillinase- and nonpenicillinase-producing strains)
- Neisseria meningitidis
- Proteus spp
- Serratia marcescens
- Ceftriaxone is also active against many strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Aerobic gram-positive microorganisms
- Staphylococcus aureus (including penicillinase-producing strains)
- Staphylococcus epidermidis
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- Viridans group streptococci
Anaerobic microorganisms
- Bacteroides fragilis
- Clostridium species
- Peptostreptococcus species
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Ceftriaxone demonstrates nonlinear dose-dependent pharmacokinetics because of its protein binding. Mean peak plasma concentrations of about 40 and 80 micrograms/mL have been reported 2 hours after intramuscular injection of 0.5 and 1 g of Ceftriaxone respectively. Mean peak plasma concentrations after bolus intravenous injection are about 120 mg/l following a 500 mg dose and about 200 mg/l following a 1g dose.
Distribution
Ceftriaxone is widely distributed in body tissues and fluids. It crosses both inflamed and non-inflamed meninges, generally achieving therapeutic concentrations in the CSF. Tazobactam is widely distributed into tissues and body fluids including, intestinal mucosa, gallbladder, lung, female reproductive tissues (uterus, ovary and fallopian tube) interstitial fluid and bile. The protein binding of Ceftriaxone is 85-95% and that of Tazobactam is 30%.
Metabolism & Excretion
About 40-65% of a dose of Ceftriaxone is excreted unchanged in urine. The remainder is excreted in bile. The plasma half life of Ceftriaxone is not dose-dependent and varies between 6-9 hours. Tazobactam and its metabolite is eliminated primarily by renal excretion with 80% of the administered dose excreted as unchanged drug and the remainder as the single metabolite.
Indications
AugTaz is indicated for the treatment of the following infections when caused by susceptible organisms :
- Respiratory Tract Infections and Pneumonia
- Bacterial Septicemia
- Uncomplicated Gonorrhea (Cervical/Urethral and rectal)
- Surgical Prophylaxis
- Intra-Abdominal Infections
- Urinary Tract Infections (Complicated and Uncomplicated)
- Bone and Joint Infections
- Skin and Skin Structure Infections
- Acute bacterial otitis media
- Meningitis
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Dosage and Administration
Adults
The usual adult daily dose is 1 to 2 grams given once a day (or in equally divided doses twice a day) depending on the type and severity of infection. For infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), the recommended daily dose is 2 to 4 grams, in order to achieve >90% target attainment. The total daily dose should not exceed 4 grams. If Chlamydia trachomatis is a suspected pathogen, appropriate antichlamydial coverage should be added, because ceftriaxone sodium has no activity against this organism. For preoperative use (surgical prophylaxis), a single dose of 1 gram administered intravenously 1/2 to 2 hours before surgery is recommended. Generally, Ceftriaxone Injection therapy should be continued for at least 2 days after the signs and symptoms of infection have disappeared. The usual duration of therapy is 4 to 14 days; in complicated infections, longer therapy may be required. When treating infections caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, therapy should be continued for at least 10 days.No dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with impairment of renal or hepatic function.
Pediatric Patients
For the treatment of skin and skin structure infections, the recommended total daily dose is 50 to 75 mg/kg given once a day (or in equally divided doses twice a day). The total daily dose should not exceed 2 grams. For the treatment of serious miscellaneous infections other than meningitis, the recommended total daily dose is 50 to 75 mg/kg, given in divided doses every 12 hours. The total daily dose should not exceed 2 grams. In the treatment of meningitis, it is recommended that the initial therapeutic dose be 100 mg/kg (not to exceed 4 grams). Thereafter, a total daily dose of 100 mg/kg/day (not to exceed 4 grams daily) is recommended. The daily dose may be administered once a day (or in equally divided doses every 12 hours). The usual duration of therapy is 7 to 14 days.
Neonates
Hyperbilirubinemic neonates, especially prematures, should not be treated with Ceftriaxone Injection. The product may be administered by deep intramuscular injection or as a slow intravenous injection after reconstitution of the solution according to the directions given below. The dosage and mode of administration should be determined by the severity of the infection, susceptibility of the causative organism and the patient’s condition.
Intramuscular injection :Contents of one vial should be dissolved in 0.45 ml of Sterile Water for Injections IP for AugTaz-KID 125 mg of injection, 0.9 ml of Sterile Water for Injections IP for AugTaz-250 mg injection, 1.8 ml of Sterile Water for Injections IP for AugTaz-500 mg injection and 3.6 ml of Sterile Water for Injections IP for AugTaz-1 g injection. The solution should be administered by deep intramuscular injection. Doses greater than 1 g (of Ceftriaxaone) should be divided and injected at more than one site.
Intravenous injection : Contents of one vial should be dissolved in 1.2 ml of Sterile Water for Injections IP for AugTaz-KID 125 mg of injection, 2.4 ml of Sterile Water for Injections IP for AugTaz-250 mg injection, 4.8 ml of Sterile Water for Injections IP for AugTaz-500 mg injection and 9.6 ml of Sterile Water for Injections IP for AugTaz-1 g injection. The solution should be administered over at least 2-4 minutes, directly into the vein or via the tubing of an intravenous infusion
Contraindications
AugTaz should not be given to patients with a history of hypersensitivity to Cephalosporins, Penicillins or β-lactamase inhibitors
Neonates (≤28 days)
For the treatment of skin and skin structure infections, the recommended total daily dose is 50 to 75 mg/kg given once a day (or in equally divided doses twice a day). The total daily dose should not exceed 2 grams. For the treatment of serious miscellaneous infections other than meningitis, the recommended total daily dose is 50 to 75 mg/kg, given in divided doses every 12 hours. The total daily dose should not exceed 2 grams. In the treatment of meningitis, it is recommended that the initial therapeutic dose be 100 mg/kg (not to exceed 4 grams). Thereafter, a total daily dose of 100 mg/kg/day (not to exceed 4 grams daily) is recommended. The daily dose may be administered once a day (or in equally divided doses every 12 hours). The usual duration of therapy is 7 to 14 days.
Warnings and Precautions
Pregnancy : Pregnancy Category B.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women and AugTaz should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers :
Low concentrations of Ceftriaxone are excreted in human milk. Caution should be exercised when Ceftriaxone for injection is administered to a nursing woman
Pediatric Use :
Safety and effectiveness of Ceftriaxone for injection in neonates, infants and pediatric patients have been established. In vitro studies have shown that Ceftriaxone, like some other cephalosporins, can displace bilirubin from serum albumin.
Clostridium difficile :
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with the use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including Ceftriaxone, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
Drug Interactions
Interaction with Calcium - Containing products
Do not use diluents containing calcium, such as Ringer’s solution or Hartmann’s solution, to reconstitute Ceftriaxone vials or to further dilute a reconstituted vial for IV administration because a precipitate can form. Precipitation of Ceftriaxone-calcium can also occur when Ceftriaxone is mixed with calcium-containing solutions in the same IV administration line. Ceftriaxone must not be administered simultaneously with calcium-containing IV solutions, including continuous calcium-containing infusions such as parenteral nutrition via a Y-site. However, in patients other than neonates, Ceftriaxone and calcium-containing solutions may be administered sequentially of one another if the infusion lines are thoroughly flushed between infusions with a compatible fluid. In vitro studies using adult and neonatal plasma from umbilical cord blood demonstrated that neonates have an increased risk of precipitation of Ceftriaxone-calcium.
Probenecid : The elimination of Ceftriaxone is not altered by probenecid.
Aminoglycoside antibiotics and diuretics: No impairment of renal function has so far been observed after concurrent administration of large doses of Ceftriaxone and potent diuretics (e.g.furosemide). There is no evidence that Ceftriaxone increases renal toxicity of aminoglycosides.
Alcohol : No effect similar to that of disulfiram has been demonstrated after ingestion of alcohol subsequent to the administration of Ceftriaxone
Antibiotics : In an in vitro study, antagonistic effects have been observed with the combination of chloramphenicol and Ceftriaxone
Anticoagulants : As Ceftriaxone has an N-methylthiotriazine side-chain, it might have the potential to cause hypoprothrombinaemia resulting in an increased risk of bleeding in patients treated with anticoagulants
Oral Contraceptives : Ceftriaxone may adversely affect the efficacy of oral hormonal contraceptives. Consequently, it is advisable to use supplementary (non-hormonal) contraceptive measures during treatment and in the month following treatment. Based on literature reports Ceftriaxone is incompatible with amsacrine, vancomycin, fluconazole and aminoglycosides.
Interference with Laboratory Tests
In patients treated with Ceftriaxone, the Coombs' test may in rare cases be false-positive
Adverse Effects
Ceftriaxone for injection is generally well tolerated. In clinical trials, the following adverse reactions, which were considered to be related to ceftriaxone for injection therapy or of uncertain etiology, were observed :
Local reactions : Pain, induration, tenderness, phlebitis; General disorders and administration site conditions : Injection site pain; Hypersensitivity : Rash. Less frequently reported were pruritus, fever or chills; Infections and Infestations : Genital fungal infection Hematologic : Eosinophilia, thrombocytosis and leukopenia. Less frequently reported were anemia, hemolytic anemia, neutropenia, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia and prolongation of the prothrombin time; Blood and Lymphatic disorders : Granulocytopenia, coagulopathy; Gastrointestinal : Diarrhea/loose stools. Less frequently reported were nausea or vomiting, and dysgeusia. The onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antibacterial treatment; Hepatic : Elevations of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Less frequently reported were elevations of alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin; Renal : Elevations of the BUN. Less frequently reported were elevations of creatinine and the presence of casts in the urine. Central Nervous System : Headache or dizziness were reported occasionally; Genitourinary : Moniliasis or vaginitis were reported occasionally. Skin and mucous membranes : Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) is reported. Miscellaneous : Diaphoresis and flushing were reported occasionally. Other rarely observed adverse reactions include abdominal pain, agranulocytosis, allergic pneumonitis, anaphylaxis, basophilia, biliary lithiasis, bronchospasm, colitis, dyspepsia, epistaxis, flatulence, gallbladder sludge, glycosuria, hematuria, jaundice, leukocytosis, lymphocytosis, monocytosis, nephrolithiasis, palpitations, a decrease in the prothrombin time, renal precipitations, seizures, and serum sickness. Investigations : Blood creatinine increased.
Cephalosporin class adverse reactions
In addition to the adverse reactions listed above which have been observed in patients treated with ceftriaxone, the following adverse reactions and altered laboratory test results have been reported for cephalosporin class antibiotics :
Adverse reactions
Allergic reactions, drug fever, serum sickness-like reaction, renal dysfunction, toxic nephropathy, reversible hyperactivity, hypertonia, hepatic dysfunction including cholestasis, aplastic anemia, hemorrhage, and superinfection.
Altered laboratory tests
Positive direct Coombs' test, false-positive test for urinary glucose, and elevated LDH. Several cephalosporins have been implicated in triggering seizures, particularly in patients with renal impairment when the dosage was not reduced. If seizures associated with drug therapy occur, the drug should be discontinued. Anticonvulsant therapy can be given if clinically indicated.
Overdosage
In the case of overdose nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea can occur. Ceftriaxone concentration can not be reduced by haemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. There is no specific antidote. Treatment is symptomatic.
Storage
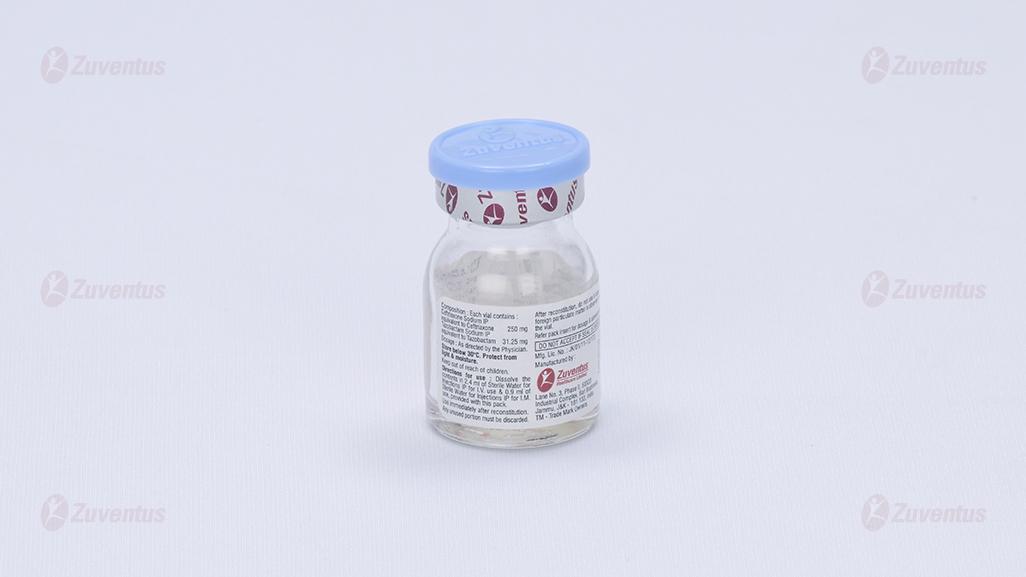
Store below 30°C. Protect from light & moisture
Keep out of reach of children. After reconstitution, do not use in case any foreign particulate matter is observed inside the vial.
Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
Presentation
AugTaz-KID 125 mg : A vial of 140.625 mg with SWFI IP 5 ml.
AugTaz-250 mg : A vial of 281.25 mg with SWFI IP 5 ml.
AugTaz-500 mg : A vial of 562.5 mg with SWFI IP 5 ml.
AugTaz-1 g : A vial of 1.125 g with SWFI IP 10 ml.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
- What AugTaz is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you take AugTaz
- How to take AugTaz
- Possible side effects
- How to store AugTaz
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What AugTaz is and what it is used for
AugTaz is a medicine used to treat a range of bacterial infections. It contains two active substances:
Ceftriaxone, an antibiotic that belongs to the group of “cephalosporins” and which can kill certain bacteria that can cause infection;
Tazobactam, which blocks the action of certain enzymes called beta-lactamases. These enzymes make bacteria resistant to Ceftriaxone by breaking down the antibiotic before it can act. By blocking their action, Tazobactam makes Ceftriaxone more effective at killing bacteria.
AugTaz can be used to treat infections of the:
- Blood (septicaemia)
- Skin and flesh immediately under the skin
- Bones and joints Brain (meningitis)
- Abdomen Urinary tract
- Respiratory tract
- Pneumonia
- Some sexually transmitted infections (gonorrhoea)
It can also be used to prevent and treat infections following surgical operations.
2. What you need to know before you take AugTaz
Do not take AugTaz
- if you are allergic to Ceftriaxone, Tazobactam or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if you are allergic to medicines known as “cephalosporins”.
- if you have had a severe allergic reaction (e.g., severe skin peeling; swelling of the face, hands, feet, lips, tongue or throat; or difficulty swallowing or breathing) to certain other antibiotics (e.g., penicillins or carbapenems).
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking AugTaz if you know you are, or have previously been allergic to cephalosporins, penicillins or other antibiotics.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you develop diarrhoea while taking C-Tri XP.
Infections caused by bacteria that are not sensitive to AugTaz or caused by a fungus can occur during or following treatment with C-Tri XP. Tell your doctor if you think you may have another infection.
Treatment with AugTaz sometimes causes production of antibodies that react with your red blood cells. If you are told that you have an abnormal blood test (called Coombs test) tell your doctor that you are having or have recently had C-Tri XP.
Other medicines and AugTaz
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
Some medicines may interact with Ceftriaxone and Tazobactam. These include:
- Probenecid (a medicine for gout).
- Another antibiotic e.g. chloramphenicol or aminoglycoside antibiotics.
- the contraceptive pill (in which case you will need to take extra contraceptive precautions such as using a condom).
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, or think you may be pregnant, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine. Your doctor will advise if you should receive AugTaz during pregnancy.
If you are breast-feeding, your doctor will advise you on whether you should stop breast-feeding or stop or avoid AugTaz therapy, taking into account the benefit of breast-feeding for the child and the benefit of therapy for you.
3. How to take AugTaz
Your doctor or other healthcare professional will give you this medicine. They will inject this medicine directly into a vein (intravenous) or muscle (intramuscular). Your doctor will decide how much you need and how often the injections should be given. The usual doses are given below but doctors may prescribe different doses depending on the severity and type of your infection, your weight, your age and how well your kidneys are working.
Adults
The dose depends on the type of infection that you have, where the infection is in your body and how serious the infection is. Your doctor will decide on the dose that you need.
The usual adult daily dose is 1 to 2 grams given once in a day (or in equally divided doses twice a day) depending on the type and severity of infection.
AugTaz Injection therapy should be continued for at least 2 days after the signs and symptoms of infection have disappeared. The usual duration of therapy is 4 to 14 days; in complicated infections, longer therapy may be required. When treating infections caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, therapy should be continued for at least 10 days. No dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with impairment of renal or hepatic function.
Pediatric patients
For the treatment of skin infections, the recommended total daily dose is 50 to 75 mg/kg given once a day (or in equally divided doses twice a day). The total daily dose should not exceed 2 grams. For the treatment of serious infections other than meningitis, the recommended total daily dose is 50 to 75 mg/kg, given in divided doses every 12 hours. The total daily dose should not exceed 2 grams. In the treatment of meningitis, it is recommended that the initial therapeutic dose be 100 mg/kg (not to exceed 4 grams). Thereafter, a total daily dose of 100 mg/kg/day (not to exceed 4 grams daily) is recommended. The daily dose may be administered once a day (or in equally divided doses every 12 hours). The usual duration of therapy is 7 to 14 days.
If you take more AugTaz than you should
As this product is given by a doctor or other healthcare professional, it is very unlikely that you will be given too much C-Tri XP. However, if you have any concerns you should let your doctor, nurse or pharmacist know immediately.
If you stop taking AugTaz
If you think you have not been given a dose of C-Tri XP, tell your doctor or other healthcare professional immediately.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. The following side effects may happen with this medicine:
Treatment with ceftriaxone, particularly in elderly patients with serious kidney or nervous system problems may rarely cause decreased consciousness, abnormal movements, agitation and convulsions.
Severe allergic reactions (not known, frequency cannot be estimated from the available data) If you have a severe allergic reaction, tell a doctor straight away.
The signs may include:
- Sudden swelling of the face, throat, lips or mouth. This can make it difficult to breathe or swallow.
- Sudden swelling of the hands, feet and ankles.
Severe skin reactions (not known, frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
If you get a severe skin reaction, tell a doctor straight away. The signs may include:
- A severe rash that develops quickly, with blisters or peeling of the skin and possibly blisters in the mouth (Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis which are also known as SJS and TEN).
- A combination of any of the following symptoms: widespread rash, high body temperature, liver enzyme elevations, blood abnormalities (eosinophilia), enlarged lymph nodes and other body organs involvement (Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms which is also known as DRESS or drug hypersensitivity syndrome).
- Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction which causes fever, chills, headache, muscle pain, and skin rash that is usually self-limiting. This occurs shortly after starting C-Tri treatment for infections with spirochete such as Lyme disease.
Other possible side effects:
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Abnormalities with your white blood cells (such as a decrease of leucocytes and an increase of eosinophils) and platelets (decrease of thrombocytes).
- Loose stools or diarrhoea.
- Changes in the results of blood tests for liver functions.
- Rash.
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Fungal infections (for example, thrush or genital fungal infections).
- A decrease in the number of white blood cells (granulocytopenia).
- Reduction in number of red blood cells (anaemia).
- Problems with the way your blood clots. The signs may include bruising easily and pain and swelling of your joints.
- Headache.
- Dizziness.
- Feeling sick or being sick.
- Pruritis (itching).
- Pain or a burning feeling along the vein where C-Tri has been given. Blisters, deep redness or rash, burned areas, pain, irritation, itching at the injection site.
- A high temperature (fever).
- Abnormal kidney function test (blood creatinine increased).
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- Inflammation of the large bowel (colon). The signs include diarrhoea, usually with blood and mucus, stomach pain and fever.
- Difficulty in breathing (bronchospasm).
- A lumpy rash (hives) that may cover a lot of your body, feeling itchy and swelling.
- Blood or sugar in your urine.
- Oedema (fluid build-up).
- Shivering.
Not known (Frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- A secondary infection that may not respond to the antibiotic previously prescribed
- Form of anaemia where red blood cells are destroyed (haemolytic anaemia).
- Severe decrease in white blood cells (agranulocytosis).
- Convulsions.
- Vertigo (spinning sensation).
- Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis).
- The signs include severe pain in the stomach which spreads to your back.
- Inflammation of the mucus lining of the mouth (stomatitis).
- Inflammation of the tongue (glossitis).
- The signs include swelling, redness and soreness of the tongue. Problems with your gallbladder and/or liver which may cause pain, nausea, vomiting, yellowing of the skin, itching, unusually dark urine and clay coloured stools. A neurological condition that may occur in neonates with severe jaundice (kernicterus).
- Kidney problems caused by deposits of calcium ceftriaxone.
- There may be pain when passing water (urine) or low output of urine.
- A false positive result in a Coombs’ test (a test for some blood problems).
- A false positive result for galactosaemia (an abnormal build-up of the sugar galactose).
AugTaz may interfere with some types of blood glucose tests - please check with your doctor
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine
5. How to store AugTaz
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is printed on the label and carton”. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Store below 30ºC. Store in the original package in order to protect from light and moisture.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What AugTaz looks like and contents of the pack
What AugTaz injection contains:
AugTaz Kid 125 mg
Each vial contains:
Ceftriaxone Sodium equivalent to Ceftriaxone 125 mg
Tazobactam Sodium equivalent to Tazobactam 15.625 mg
AugTaz 250 mg
Each vial contains: Ceftriaxone Sodium equivalent to Ceftriaxone 250 mg
Tazobactam Sodium equivalent to Tazobactam 31.25 mg
AugTaz 500 mg
Each vial contains: Ceftriaxone Sodium equivalent to Ceftriaxone 500 mg
Tazobactam Sodium equivalent to Tazobactam 62.5 mg
AugTaz 1 g
Each vial contains: Ceftriaxone Sodium equivalent to Ceftriaxone 1.0 g
Tazobactam Sodium equivalent to Tazobactam 125 mg
Packing
AugTaz Kid 125 mg: A vial of 140.625 mg with SWFI 5 ml
AugTaz 250 mg: A vial of 281.25 mg with SWFI 5 ml
AugTaz 500 mg: A vial of 562.5 mg with SWFI 5 ml
AugTaz 1 g: A vial of 1.125 g with SWFI 10 ml