Bempeday Tablets
Therapy Area
Lipid lowering agents
1.0 Generic name
Bempedoic Acid Tablets 180 mg
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each film coated tablet contains :
Bempedoic acid 180 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Titanium Dioxide I.P.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Film coated tablets & 180 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
Indicated as an adjunct to diet and maximally tolerated statin therapy for the treatment of adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who require additional lowering of LDL-C.
Limitation of Use : The effect of the drug on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been established
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The recommended dose is one film-coated tablet of 180 mg taken once daily
Concomitant simvastatin therapy
When Bempedoic Acid is coadministered with simvastatin, simvastatin dose should be limited to 20 mg daily (or 40 mg daily for patients with severe hypercholesterolemia and high risk for cardiovascular complications, who have not achieved their treatment goals on lower doses and when the benefits are expected to outweigh the potential risks).
Special populations
Elderly patients
No dose adjustment is necessary in elderly patients.
Patients with renal impairment
No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment. There are limited data available in patients with severe renal impairment (defined as 2 estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] < 30 mL/min/1.73 m ), and patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) on dialysis have not been studied. Additional monitoring for adverse reactions may be warranted in these patients when Bempedoic acid is administered.
Patients with hepatic impairment
No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A or B). No data are available in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child- Pugh C). Periodic liver function tests should be considered for patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Paediatric population
The safety and efficacy of Bempedoic acid in children aged less than 18 years have not yet been established. No data are available.
Method of administration
Each film-coated tablet should be taken orally with or without food. Tablet should be swallowed whole.
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed to any of the excipients listed in section 8.1.
- Pregnancy
- Breast-feeding
- Concomitant use with simvastatin > 40 mg daily
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Potential risk of myopathy with concomitant use of statins Bempedoic acid increases plasma concentrations of statins. Patients receiving bempedoic acid as adjunctive therapy to a statin should be monitored for adverse reactions that are associated with the use of high doses of statins. Statins occasionally cause myopathy. In rare cases, myopathy may take the form of rhabdomyolysis with or without acute renal failure secondary to myoglobinuria, and can lead to fatality. All patients receiving bempedoic acid in addition to a statin should be advised of the potential increased risk of myopathy and told to report promptly any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness. If such symptoms occur while a patient is receiving treatment with bempedoic acid and a statin, a lower maximum dose of the same statin or an alternative statin, or discontinuation of bempedoic acid and initiation of an alternative lipid-lowering therapy should be considered under close monitoring of lipid levels and adverse reactions. If myopathy is confirmed by a creatine phosphokinase (CPK) level > 10× upper limit of normal (ULN), bempedoic acid and any statin that the patient is taking concomitantly should be immediately discontinued. Myositis with a CPK level > 10× ULN was rarely reported with bempedoic acid and background simvastatin 40 mg therapy. Doses of simvastatin > 40 mg should not be used with bempedoic acid.
Increased serum uric acid
Bempedoic acid may raise the serum uric acid level due to inhibition of renal tubular OAT2 and may cause or exacerbate hyperuricaemia and precipitate gout in patients with a medical history of gout or predisposed to gout. Treatment with bempedoic acid should be discontinued if hyperuricaemia accompanied with symptoms of gout appear. Elevated liver enzymes
In clinical trials, elevations of > 3× ULN in the liver enzymes alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) have been reported with bempedoic acid. These elevations have been asymptomatic and not associated with elevations ≥ 2× ULN in bilirubin or with cholestasis and have returned to baseline with continued treatment or after discontinuation of therapy. Liver function tests should be performed at initiation of therapy. Treatment with bempedoic acid should be discontinued if an increase in transaminases of > 3× ULN persists.
Renal impairment
There 2 is limited experience with bempedoic acid in patients with severe renal impairment (defined as eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m ), and patients with ESRD on dialysis have not been studied. Additional monitoring for adverse reactions may be warranted in these patients when bempedoic acid is administered. Hepatic impairment
Patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) have not been studied. Periodic liver function tests should be considered for patients with severe hepatic impairment. Contraception
Women of childbearing potential must use effective contraception during treatment. Patients should be advised to stop taking bempedoic acid before stopping contraceptive measures if they plan to become pregnant.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Effects of other medicinal products on bempedoic acid
Transporter-mediated drug interactions In vitro drug interaction studies suggest bempedoic acid, as well as its active metabolite and glucuronide form, are not substrates of commonly characterised drug transporters with the exception of bempedoic acid glucuronide, which is an OAT3 substrate. Probenecid
Probenecid, an inhibitor of glucuronide conjugation, was studied to evaluate the potential effect of these inhibitors on the pharmacokinetics of bempedoic acid. Administration of bempedoic acid 180 mg with steady-state probenecid resulted in a 1.7-fold increase in bempedoic acid area under the curve (AUC) and a 1.9-fold increase in bempedoic acid active metabolite (ESP15228) AUC. These elevations are not clinically meaningful and do not impact dosing recommendations.
Effects of bempedoic acid on other medicinal products
Statins
The pharmacokinetic interactions between bempedoic acid 180 mg and simvastatin 40 mg, atorvastatin 80 mg, pravastatin 80 mg, and rosuvastatin 40 mg were evaluated in clinical trials. Administration of a single dose of simvastatin 40 mg with steady-state bempedoic acid 180 mg resulted in a 2-fold increase in simvastatin acid exposure. Elevations of 1.4-fold to 1.5-fold in AUC of atorvastatin, pravastatin, and rosuvastatin (administered as single doses) and/or their major metabolites were observed when coadministered with bempedoic acid 180 mg. Higher elevations have been observed when these statins were coadministered with a supratherapeutic 240 mg dose of bempedoic acid. Transporter-mediated drug interactions Bempedoic acid and its glucuronide weakly inhibit OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 at clinically relevant concentrations. Coadministration of bempedoic acid with medicinal products that are substrates of OATP1B1 or OATP1B3 (i.e., bosentan, fimasartan, asunaprevir, glecaprevir, grazoprevir, voxilaprevir, and statins such as atorvastatin, pravastatin, fluvastatin, pitavastatin, rosuvastatin, and simvastatin) may result in increased plasma concentrations of these medicinal products. Bempedoic acid inhibits OAT2 in vitro,which may be the mechanism responsible for minor elevations in serum creatinine and uric acid. Inhibition of OAT2 by bempedoic acid may also potentially increase plasma concentrations of medicinal products that are substrates of OAT2. Bempedoic acid may also weakly inhibit OAT3 at clinically relevant concentrations.
Ezetimibe
Total ezetimibe (ezetimibe and its glucuronide form) and ezetimibe glucuronide AUC and Cmax increased approximately 1.6- and 1.8-fold, respectively, when a single dose of ezetimibe was taken with steady-state bempedoic acid. This increase is likely due to inhibition of OATP1B1 by bempedoic acid, which results in decreased hepatic uptake and subsequently decreased elimination of ezetimibe-glucuronide. Increases in AUC and Cmax for ezetimibe were less than 20%. These elevations are not clinically meaningful and do not impact dosing recommendations. Other interactions studied Bempedoic acid had no effect on the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of metformin or the pharmacokinetics of oral contraceptive norethindrone/ethinyl estradiol.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
Bempedoic acid is contraindicated during pregnancy.
There are no or limited amount of data from the use of bempedoic acid in pregnant women. Studies in animals with bempedoic acid have shown reproductive toxicity. Because bempedoic acid decreases cholesterol synthesis and possibly the synthesis of other cholesterol derivatives needed for normal foetal development, Bempedoic acid may cause foetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Bempedoic acid should be discontinued prior to conception or as soon as pregnancy is recognized.
Women of childbearing potential
Women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception during treatment.
Breast-feeding
It is unknown whether bempedoic acid/metabolites are excreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, women taking Bempedoic acid should not breast-feed their infants. Bempedoic acid is contraindicated during breast-feeding.
Fertility
No data on the effect of Bempedoic acid on human fertility are available. Based on animal studies, no effect on reproduction or fertility is expected with Bempedoic acid.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Bempedoic acid has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
4.8 Undesirable effects
The safety profile of bempedoic acid has been studied in 4 controlled phase 3 clinical studies (N=3,621) including patients with hypercholesterolemia on maximum tolerated statin dose (2 studies; n=3008) and patients on no or low dose statins (2 studies; n=613). The most commonly reported adverse reactions with bempedoic acid during pivotal trials were hyperuricaemia (3.8%), pain in extremity (3.1%), and anaemia (2.5%). More patients on bempedoic acid compared to placebo discontinued treatment due to muscle spasms (0.7% versus 0.3%), diarrhoea (0.5% versus <0.1%), pain in extremity (0.4% versus 0), and nausea (0.3% versus 0.2%), although differences between bempedoic acid and placebo were not significant.
Tabulated list of adverse reactions
Adverse reactions reported with bempedoic acid are displayed by system organ class and frequency in table 1.
Table 1 : Adverse reactions
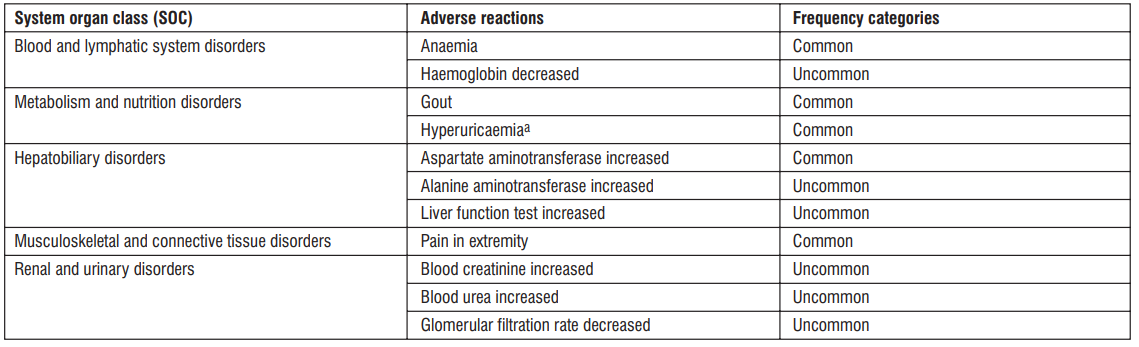
a. Hyperuricaemia includes hyperuricaemia and blood uric acid increased
Description of selected adverse reactions
Hepatic enzyme elevations
Increases in serum transaminases (AST and/or ALT) have been reported with bempedoic acid. In controlled clinical studies, the incidence of elevations (≥ 3× ULN) in hepatic
transaminase levels was 0.7% for patients treated with bempedoic acid and 0.3% for placebo. These elevations in transaminases were not associated with other evidence of liver dysfunction.
Increased serum uric acid
Increases in serum uric acid were observed in clinical trials with bempedoic acid possibly related to inhibition of renal tubular OAT2. In the pooled placebo-controlled trials, a mean increase of 0.8 mg/dL (47.6 micromole/L) in uric acid compared to baseline was observed with bempedoic acid at week 12. The elevations in serum uric acid usually occurred within the first 4 weeks of treatment and returned to baseline following discontinuation of treatment. Gout was reported in 1.4% of patients treated with bempedoic acid and 0.4% of patients treated with placebo. In both treatment groups, patients who reported gout were more likely to have a medical history of gout and/or baseline levels of uric acid above the ULN.
Effects on serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen
Bempedoic acid has been shown to increase serum creatinine and BUN. In the pooled placebo-controlled trials, a mean increase of 0.05 mg/dL (4.4 micromole/L) in serum creatinine and a mean increase of 1.7 mg/dL (0.61 mmol/L) in BUN compared to baseline was observed with bempedoic acid at week 12. The elevations in serum creatinine and BUN usually occurred within the first 4 weeks of treatment, remained stable, and returned to baseline following discontinuation of treatment. The observed elevations in serum creatinine may be associated with bempedoic acid inhibition of OAT2-dependent renal tubular secretion of creatinine, representing a drugendogenous substrate interaction and does not appear to indicate worsening renal function. This effect should be considered when interpreting changes in estimated creatinine clearance in patients on Bempedoic acid therapy, particularly in patients with medical conditions or receiving medicinal products that require monitoring of estimated creatinine clearance.
Decreased haemoglobin Decreases in haemoglobin were observed in clinical trials with bempedoic acid. In the pooled placebo-controlled trials, a decrease in haemoglobin from baseline of ≥ 20 g/L and < lower limit of normal (LLN) was observed in 4.6% of patients in the bempedoic acid group compared with 1.9% of patients on placebo. Greater than 50 g/L and < LLN decreases in haemoglobin were reported at similar rates in bempedoic acid and placebo groups (0.2% versus 0.2%, respectively). The decreases in haemoglobin usually occurred within the first 4 weeks of treatment and returned to baseline following discontinuation of treatment. Among patients who had normal haemoglobin values at baseline, 1.4% in the bempedoic acid group and 0.4% in the placebo group experienced haemoglobin values below LLN while on treatment. Anaemia was reported in 2.5% of patients treated with bempedoic acid and 1.6% of patients treated with placebo.
Elderly population
Of the 3,621 patients treated with bempedoic acid in the placebo-controlled studies, 2,098 (58%) were > 65 years old. No overall difference in safety was observed between elderly and the younger population. Reporting of suspected adverse reactions Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine
4.9 Overdose
Doses up to 240 mg/day (1.3 times the approved recommended dose) have been administered in clinical trials with no evidence of dose limiting toxicity. No adverse events were observed in animal studies at exposures up to 14-fold higher than those in patients treated with bempedoic acid at 180 mg once daily. There is no specific treatment for a Bempedoic acid overdose. In the event of an overdose, the patient should be treated symptomatically, and supportive measures instituted as required
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Bempedoic acid is an adenosine triphosphate citrate lyase (ACL) inhibitor that lowers low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) by inhibition of cholesterol synthesis in the liver. ACL is an enzyme upstream of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway. Bempedoic acid requires coenzyme A (CoA) activation by very long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 1 (ACSVL1) to ETC-1002-CoA. ACSVL1 is expressed primarily in the liver and not in skeletal muscle. Inhibition of ACL by ETC-1002-CoA results in decreased cholesterol synthesis in the liver and lowers LDL-C in blood via upregulation of low-density lipoprotein receptors. Additionally, inhibition of ACL by ETC-1002-CoA results in concomitant suppression of hepatic fatty acid biosynthesis.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Administration of bempedoic acid alone and in combination with other lipid modifying medicinal products decreases LDL-C, non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C), apolipoprotein B (apo B), and total cholesterol (TC) in patients with hypercholesterolaemia or mixed dyslipidaemia. Because patients with diabetes are at elevated risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, the clinical trials of bempedoic acid included patients with diabetes mellitus. Among the subset of patients with diabetes, lower levels of HbA1c were observed as compared to placebo (on average 0.2%). In patients without diabetes, no difference in HbA1c was observed between bempedoic acid and placebo and there were no differences in the rates of hypoglycaemia. Cardiac electrophysiology At a dose of 240 mg (1.3 times the approved recommended dose), bempedoic acid does not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Pharmacokinetic data indicate that bempedoic acid is absorbed with a median time to maximum concentration of 3.5 hours when administered as Bempedoic acid 180 mg tablets. Bempedoic acid pharmacokinetic parameters are presented as the mean [standard deviation (SD)] unless otherwise specified. Bempedoic acid can be considered a prodrug that is activated intracellularly by ACSVL1 to ETC-1002-CoA. The steady-state Cmax and AUC following multiple dose administration in patients with hypercholesterolaemia were 24.8 (6.9) microgram/mL and 348 (120) microgram∙h/mL, respectively. Bempedoic acid steady-state pharmacokinetics were generally linear over a range of 120 mg to 220 mg. There were no time-dependent changes in bempedoic acid pharmacokinetics following repeat administration at the recommended dose, and bempedoic acid steady-state was achieved after 7 days. The mean accumulation ratio of bempedoic acid was approximately 2.3-fold. Concomitant food administration had no effect on the oral bioavailability of bempedoic acid when administered as Bempedoic acid 180 mg tablets. Food slows the absorption rate of bempedoic acid; the absorption rate constant with food is 0.32/h.
Distribution
The bempedoic acid apparent volume of distribution (V/F) was 18 L. Plasma protein binding of bempedoic acid, its glucuronide and its active metabolite, ESP15228, were 99.3%, 98.8% and 99.2%, respectively. Bempedoic acid does not partition into red blood cells. Biotransformation In vitro metabolic interaction studies suggest that bempedoic acid, as well as its active metabolite and glucuronide forms are not metabolised by and do not inhibit or induce cytochrome P450 enzymes. The primary route of elimination for bempedoic acid is through metabolism to the acyl glucuronide. Bempedoic acid is also reversibly converted to an active metabolite (ESP15228) based on aldo-keto reductase activity observed in vitro from human liver. Mean plasma AUC metabolite/parent drug ratio for ESP15228 following repeat-dose administration was 18% and remained constant over time. Both compounds are converted to inactive glucuronide conjugates in vitro by UGT2B7. Bempedoic acid, ESP15228 and their respective conjugated forms were detected in plasma with bempedoic acid accounting for the majority (46%) of the AUC0-48h and its glucuronide being the next most prevalent (30%). ESP15228 and its glucuronide represented 10% and 11% of the plasma AUC0-48h, respectively. The steady-state Cmax and AUC of the equipotent active metabolite (ESP15228) of bempedoic acid in patients with hypercholesterolaemia were 3.0 (1.4) microgram/mL and 54.1 (26.4) microgram∙h/mL, respectively. ESP15228 likely made a minor contribution to the overall clinical activity of bempedoic acid based on systemic exposure and pharmacokinetic properties.
Elimination
The steady-state clearance (CL/F) of bempedoic acid determined from a population PK analysis in patients with hypercholesterolaemia was 12.1 mL/min after once-daily dosing; renal clearance of unchanged bempedoic acid represented less than 2% of total clearance. The mean (SD) half-life for bempedoic acid in humans was 19 (10) hours at steady-state. Following single oral administration of 240 mg of bempedoic acid (1.3 times the approved recommended dose), 62.1% of the total dose (bempedoic acid and its metabolites) was recovered in urine, primarily as the acyl glucuronide conjugate of bempedoic acid, and 25.4% was recovered in faeces. Less than 5% of the administered dose was excreted as unchanged bempedoic acid in faeces and urine combined.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
The standard battery of genotoxicity studies has not identified any mutagenic or clastogenic potential of bempedoic acid. In full lifetime carcinogenicity studies in rodents, bempedoic acid increased the incidence of hepatocellular and thyroid gland follicular tumours in male rats and hepatocellular tumours in male mice. Because these are common tumours observed in rodent lifetime bioassays and the mechanism for tumourigenesis is secondary to a rodent-specific PPAR alpha activation, these tumours are not considered to translate to human risk. Increased liver weight and hepatocellular hypertrophy were observed in rats only and were partially reversed after the 1-month recovery at ≥ 30 mg/kg/day or 4 times the exposure in humans at 180 mg. Reversible, non-adverse changes in laboratory parameters indicative of these hepatic effects, decreases in red blood cell and coagulation parameters, and increases in urea nitrogen and creatinine were observed in both species at tolerated doses. The NOAEL for adverse response in the chronic studies was 10 mg/kg/day and 60 mg/kg/day associated with exposures below and 15 times the human exposure at 180 mg in rats and monkeys, respectively. Bempedoic acid was not teratogenic or toxic to embryos or foetuses in pregnant rabbits at doses up to 80 mg/kg/day or 12 times the systemic exposure in humans at 180 mg. Pregnant rats given bempedoic acid at 10, 30, and 60 mg/kg/day during organogenesis had decreased numbers of viable foetuses and reduced foetal body weight at ≥ 30 mg/kg/day or 4 times the systemic exposure in humans at 180 mg. An increased incidence of foetal skeletal findings (bent scapula and ribs) were observed at all doses, at exposures below the systemic exposure in humans at 180 mg. In a pre- and post-natal development study, pregnant rats administered bempedoic acid at 5, 10, 20 and 30 mg/kg/day throughout pregnancy and lactation had adverse maternal effects at ≥ 20 mg/kg/day and reductions in numbers of live pups and pup survival, pup growth and learning and memory at ≥ 10 mg/kg/day, with maternal exposures at 10 mg/kg/day, less than the exposure in humans at 180 mg. No data are available on the effect of Bempedoic acid on human fertility. Administration of bempedoic acid to male and female rats prior to mating and through gestation day 7 in females resulted in changes in estrous cyclicity, decreased numbers of corpora lutea and implants at ≥ 30 mg/kg/day with no effects on male or female fertility or sperm parameters at 60 mg/kg/day (4 and 9 times the systemic exposure in humans at 180 mg, respectively).
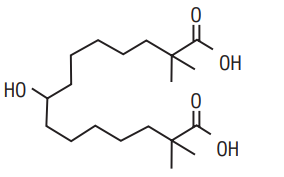
7.0 Description
The chemical name for Bempedoic acid is 8-hydroxy-2,2,14,14tetramethyl-pentadecanedioic acid. The molecular formula is C19H36O5, and the molecular weight is 344.5 grams per mole.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 List of Excipients
Microcrystalline cellulose 101, Microcrystalline cellulose 102, Lactose Monohydrate, Sodium starch glycolate type A, colloidal silicon dioxide, Hydroxy propyl cellulose, Magnesium stearate and Opadry II 85F18422.
8.2 Incompatibilities
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products.
8.3 Packaging information
PVC/PVDC-Alu pack of 10 tablets
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30°C.
Keep out of reach of children
8.5 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
Risk of Hyperuricemia Advise patients of the risk of elevated serum uric acid levels, including development of gout. Inform patients that serum uric acid levels may be monitored during treatment with Bempedoic acid. Patients with signs or symptoms of hyperuricemia should contact their healthcare provider if symptoms occur. Risk of Tendon Rupture Inform patients of the risk of tendon rupture. Advise patients to rest at the first sign of tendinitis or tendon rupture and to immediately contact their healthcare provider if tendinitis or tendon rupture symptoms occur. Risk of Myopathy with Concomitant Use of Simvastatin or Pravastatin Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider(s) if they are taking, or plan to take simvastatin or pravastatin. The risk of myopathy occurring with the use of simvastatin or pravastatin may be increased when taken with Bempedoic acid. Pregnancy Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus based on Bempedoic acid mechanism of action. Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
•Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
•If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
•This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
•If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1.What Bempeday is and what it is used for
2.What you need to know before you take Bempeday
3.How to take Bempeday
4.Possible side effects
5.How to store Bempeday Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Bempeday is and what it is used for
What Bempeday is and how it works Bempeday is a medicine that lowers levels of ‘bad’ cholesterol (also called “LDL-cholesterol”), a type of fat, in the blood. Bempeday contains the active substance bempedoic acid, which is inactive until it enters the liver where it is changed to its active form. Bempedoic acid decreases the production of cholesterol in the liver and increases the removal of LDL-cholesterol from the blood by blocking an enzyme (ATP citrate lyase) needed for the production of cholesterol.
What Bempeday is used for
Bempeday is given to adults with primary hypercholesterolaemia or mixed dyslipidaemia, which are conditions that cause a high cholesterol level in the blood. It is given in addition to a cholesterol lowering diet.
Bempeday is given:
•If you have been using a statin (such as simvastatin, a commonly used medicine that treats high cholesterol) and this does not lower your LDL-cholesterol sufficiently;
•alone or together with other cholesterol-lowering medicines when statins are not tolerated or cannot be used.
2. What you need to know before you take Bempeday
Do not take Bempeday:
•if you are allergic to bempedoic acid or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
•if you are pregnant;
•if you are breast-feeding;
•if you take more than 40 mg of simvastatin daily (another medicine used to lower cholesterol).
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Bempeday:
•if you ever had gout;
•if you have severe kidney problems;
•if you have severe liver problems.
Your doctor may do a blood test before you start taking Bempeday. This is to check how well your liver is working.
Children and adolescents
Do not give Bempeday to children and adolescents under 18 years of age. The use of Bempeday has not been studied in this age group.
Other medicines and Bempeday
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. In particular, tell your doctor if you are taking medicine(s) with any of the following active substances:
•atorvastatin, fluvastatin, pitavastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin (used to lower cholesterol and known as statins).
•The risk of muscle disease may increase when taking both a statin and Bempeday. Tell your doctor immediately about any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness.
•bosentan (used to manage a condition called pulmonary artery hypertension).
•fimasartan (used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure).
•asunaprevir, glecaprevir, grazoprevir, voxilaprevir (used to treat hepatitis C).
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Do not take this medicine if you are pregnant, trying to get pregnant, or think you may be pregnant, as there is a possibility that it could harm an unborn baby. If you get pregnant while taking this medicine, call your doctor immediately and stop taking Bempeday.
• Pregnancy
Before starting treatment, you should confirm you are not pregnant and are using effective contraception, as advised by your doctor. If you use contraceptive pills and suffer from an episode of diarrhoea or vomiting that lasts more than 2 days, you must use an alternative method of contraception (e.g. condoms, diaphragm) for 7 days following resolution of symptoms.
If, after you have started treatment with Bempeday, you decide that you would like to become pregnant, tell your doctor, as your treatment will need to be changed.
• Breast-feeding
Do not take Bempeday if you are breast-feeding because it is not known if Bempeday passes into milk.
Driving and using machines
Bempeday has no or little influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
- Bempeday contains lactose and sodium
- If you have been told by your doctor that you have an intolerance to some sugars, contact your doctor before taking this medicine.
- This medicine contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per tablet, that is to say essentially ‘sodium free’.
3. How to take Bempeday
- Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
- The recommended dose is one tablet once daily.
- Swallow the tablet whole with food or between meals.
If you take more Bempeday than you should
Contact your doctor or pharmacist immediately.
If you forget to take Bempeday
If you notice that you forgot:
• a dose late in a day, take the missed dose and take the next dose at your regular time the next day.
• the previous day’s dose, take your tablet at the regular time and do not make up for the forgotten dose.
If you stop taking Bempeday
Do not stop taking Bempeday without your doctor’s permission as your cholesterol may rise again.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Side effects can occur with the following frequencies:
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
• lower number of red blood cells (anaemia)
• increased levels of uric acid in blood, gout
• pain in shoulders, legs, or arms
• blood test results indicating liver abnormalities
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
• decreased haemoglobin (a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen)
• raised creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (laboratory tests of kidney function)
• decreased glomerular filtration rate (a measure of how well your kidneys are working)
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top right end of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Bempeday
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date, which is stated on the blister and carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
This medicine does not require any special storage conditions.
Do not throw away any medicine via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Bempeday contains
• The active substance is bempedoic acid. Each film-coated tablet contains 180 mg of bempedoic acid.
• The other ingredients are:
Microcrystalline cellulose 101, Microcrystalline cellulose 102, Lactose Monohydrate, Sodium starch glycolate type A, colloidal silicon dioxide, Hydroxy propyl cellulose, Magnesium stearate and Opadry II 85F18422.
Bempeday is available in the following pack sizes:
A blister strip of 10 tablets
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Optimus Pharma Private Limited
Plot No. 73/B,73/B/2, EPIP, Pashamylaram Village,
Patancheru Mandal, Sangareddy District - 502 307,
Telangana, India.