Bevon CD Capsule
Therapy Area
Vitamins/Minerals Supplements
1.0 Generic name
Antioxidants with Omega 3 Fatty Acids Capsules
2. Qualitative and quantitative composition
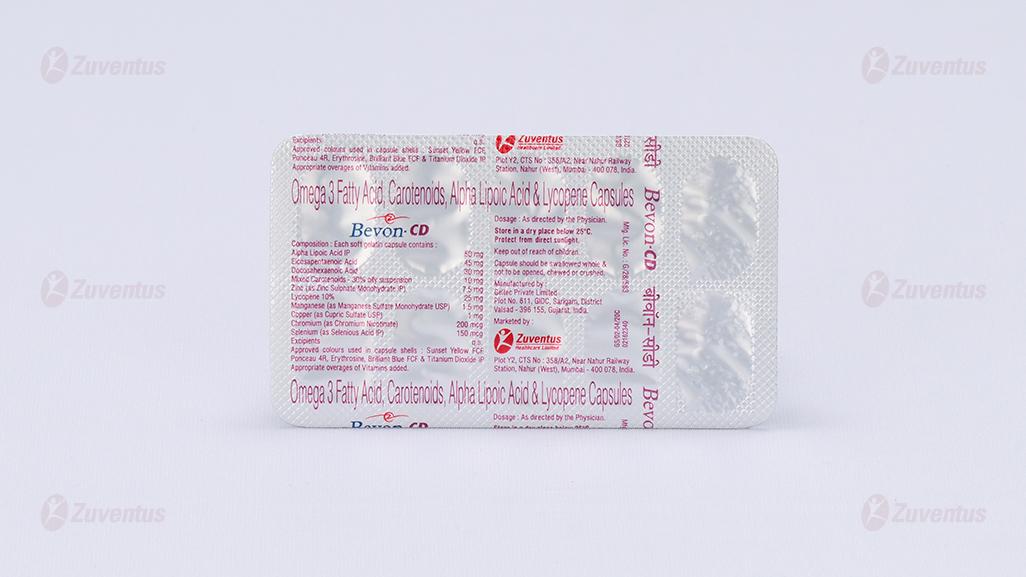
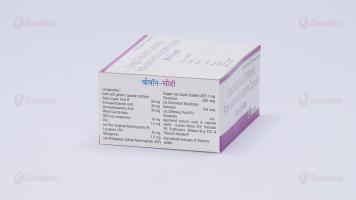
Each soft gelatin capsule contains:
Alpha Lipoic Acid NF 50 mg
Eicosapentaenoic Acid 45 mg
Docosahexaenoic Acid 30 mg
Mixed Carotenoids - 30% oily suspension 10 mg
Zinc 7.5 mg
(as Zinc Sulphate Monohydrate IP)
Lycopene 10% 25 mg
Manganese 1.5 mg (as Manganese Sulfate Monohydrate USP)
Copper (as Cupric Sulfate USP) 1 mg
Chromium 200 mcg
(as Chromium Nicotinate) Selenium 150 mcg
(as Selenium Dioxide USP)
Excipients q.s.
Colours: Sunset Yellow FCF, Ponceau 4R Supra IH, Erythrosine Supra IH, Brilliant Blue FCF IH & Titanium Dioxide IP
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Soft gelatin capsule
Alpha Lipoic Acid (50 mg), Eicosapentaenoic Acid (45 mg), Docosahexaenoic Acid (30 mg), Mixed Carotenoids (10 mg), Zinc (7.5 mg), Lycopene (25 mg), Manganese (1.5 mg), Copper (1 mg), Chromium (200 mcg), Selenium (150 mcg)
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
Antioxidants with Omega 3 Fatty Acids capsules for nutritional supplements in cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adults and the Elderly: One capsule daily, preferably taken after meals. Capsules should be swallowed whole & not to be opened, chewed, or crushed.
4.3 Contraindications
Patients with hypersensitivity reactions to any of its components.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Whilst taking Bevon-CD Capsules both protein and energy are also required to provide complete nutrition in the daily diet.
Other vitamins, minerals or supplements should be taken with this preparation only under medical supervision.
Do not take Bevon-CD Capsules on an empty stomach. Do not exceed the stated dose. Keep out of the reach of children. If symptoms persist, consult your doctor.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Copper: Zinc may inhibit the absorption of copper.
Tetracycline Antibacterials:
Zinc may reduce the absorption of concurrently administered tetracyclines, also the absorption of zinc may be reduced by tetracyclines; when both are being given an interval of at least three hours should be allowed.
Quinolone Antibacterials:
Zinc may reduce the absorption of quinolones; ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin.
Calcium Salts: The absorption of zinc may be reduced by calcium salts.
Iron: The absorption of zinc may be reduced by oral iron, also the absorption of oral iron may be reduced by zinc.
4.6 Use in special populations
Children under 12 years of age
Bevon-CD Capsules are not recommended for this age group.
Pregnancy and lactation
Bevon-CD Capsules may be administered during pregnancy and lactation at the recommendation of the physician.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
None anticipated. Bevon-CD has no influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product.
Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
There are no special recommendations. Administer symptomatic treatment.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA)
It is a potent antioxidant naturally produced in the body and found in foods like spinach, broccoli, and potatoes. It plays a crucial role in energy metabolism and helps regenerate other antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E.
ALA helps neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, which are key factors in cardiovascular diseases. It can improve the function of the endothelium (the inner lining of blood vessels), which is essential for maintaining vascular health. Studies suggest that ALA can help prevent the progression of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the build-up of plaques in the arteries.
ALA has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, which helps in better glucose uptake by cells, thereby lowering blood sugar levels. It can alleviate symptoms of diabetic neuropathy, such as pain and numbness, by reducing oxidative stress and improving nerve function. ALA may help protect against various complications of diabetes, including cardiovascular issues and kidney damage.
Omega-3 fatty acids (Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid)
Omega-3 fatty acids (ω-3 FA) may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in patients with diabetes.
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, are known to lower triglyceride levels, which can reduce the risk of heart disease. They help reduce inflammation, a key factor in the development of atherosclerosis. Regular consumption of omega-3s is associated with a lower risk of myocardial infarction, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
Omega-3 fatty acids may improve insulin sensitivity, helping to manage blood sugar levels. Reduces Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a common issue in diabetes, and omega-3s can help mitigate this.
Mixed Carotenoids
Carotenoids are naturally occurring pigments found in many fruits and vegetables, giving them their vibrant colors. They are powerful antioxidants and play a significant role in human health.
Carotenoids include compounds like beta-carotene, lycopene, lutein, and zeaxanthin. These pigments are found in high concentrations in foods such as carrots, tomatoes, spinach, and kale (leaf cabbage). Carotenoids help reduce oxidative stress, which is a major factor in the development of cardiovascular diseases. They support the health of the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels, which is crucial for maintaining vascular health.
Carotenoids have anti-inflammatory effects that can help prevent atherosclerosis, the build-up of plaques in the arteries. Carotenoids can help reduce blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, which is beneficial for managing diabetes. Higher dietary intake of carotenoids, particularly beta-carotene, has been linked to a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, carotenoids can help protect against complications associated with diabetes.
Zinc
Zinc is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including immune response, protein synthesis, and cell division. Its importance extends to cardiovascular health and diabetes management.
Zinc helps reduce oxidative stress, which is a significant factor in the development of cardiovascular diseases. It supports the proper functioning of the antioxidant system, helping to protect the heart and blood vessels. Zinc can suppress inflammatory mediators, reducing inflammation that contributes to atherosclerosis. Adequate zinc levels are essential for maintaining endothelial function, which is crucial for vascular health.
Zinc is involved in the formation, storage, and release of insulin, making it vital for blood glucose regulation. It acts as a cofactor for enzymes that are crucial in insulin signaling pathways. Zinc helps mitigate oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are common in diabetes and its complications. Adequate zinc levels can reduce the risk of developing complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular issues and neuropathy.
Lycopene
Lycopene is a powerful antioxidant found in red and pink fruits and vegetables, such as tomatoes, watermelon, and pink grapefruit. It is a type of carotenoid, which gives these foods their vibrant color.
Lycopene helps neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, which are key factors in the development of cardiovascular diseases. It supports the health of the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels, which is crucial for maintaining vascular health. Higher blood levels of lycopene have been associated with a significantly lower risk of stroke.
Lycopene helps mitigate oxidative stress, which is a common issue in diabetes and its complications. Some studies suggest that lycopene can improve insulin sensitivity, helping to manage blood sugar levels more effectively. By reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, lycopene can help protect against complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular issues.
Manganese
Manganese is an essential trace mineral that plays a significant role in various bodily functions, including enzyme activation, bone formation, and glucose metabolism. Its importance extends to cardiovascular health and diabetes management.
Manganese is a component of the antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD), which helps protect cells from oxidative damage. This is crucial in preventing cardiovascular diseases. By reducing inflammation, manganese can help prevent the development of atherosclerosis. Adequate manganese levels are associated with better regulation of blood pressure, which is vital for cardiovascular health.
Glucose Metabolism: Manganese is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates and the regulation of blood sugar levels. It helps in the synthesis and secretion of insulin, which is crucial for glucose homeostasis. Low levels of manganese can impair insulin secretion and increase insulin resistance, while adequate manganese intake can improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Manganese helps reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which are common issues in diabetes and its complications.
Copper
Copper is an essential trace mineral that plays a significant role in various physiological processes, including cardiovascular health and diabetes management.
Copper is a component of several antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), which help protect cells from oxidative damage. This is crucial in preventing cardiovascular diseases. Copper helps reduce inflammation, which can prevent the development of atherosclerosis. Adequate copper levels are essential for maintaining proper heart function. Copper deficiency can lead to heart issues such as cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure.
Copper is involved in the metabolism of insulin, which is crucial for blood glucose regulation. It helps in the proper functioning of enzymes that are important for insulin signaling. Copper helps mitigate oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are common in diabetes and its complications.
Chromium
Chromium is an essential trace mineral that plays a vital role in various bodily functions, particularly in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It is often found in foods like whole grains, nuts, broccoli, and meat.
Chromium supplementation has been shown to improve lipid profiles by reducing total cholesterol and triglycerides, which are risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Chromium helps reduce inflammation, which is a key factor in the development of atherosclerosis. Some studies suggest that chromium can help regulate blood pressure, contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
Chromium is known to enhance insulin sensitivity, which helps in better glucose uptake by cells, thereby lowering blood sugar levels. Supplementation with chromium has been shown to improve glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes by reducing fasting blood glucose and insulin levels. Chromium helps mitigate oxidative stress, which is common in diabetes and its complications.
Selenium
Selenium is an essential trace mineral that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including antioxidant defense, thyroid hormone metabolism, and immune function. It is found in foods like nuts, seafood, and whole grains.
Selenium is a component of antioxidant enzymes like glutathione peroxidase, which help protect cells from oxidative damage. This is important in preventing cardiovascular diseases. Selenium helps reduce inflammation, which can prevent the development of atherosclerosis.
Adequate selenium levels are associated with a lower risk of heart disease. Selenium deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular issues.
Selenium may improve insulin sensitivity, helping to regulate blood sugar levels more effectively. By mitigating oxidative stress, selenium can help protect against complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular problems. While selenium has benefits, excessive intake can lead to toxicity and may increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. It’s important to maintain a balanced intake.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Zinc Sulfate (Zinc): Zinc is poorly absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract. It is widely distributed throughout the body. It is excreted in the faeces with traces appearing in the urine.
Manganese Sulfate (Manganese): Manganese salts are poorly absorbed.
Copper Sulfate (Copper): Copper is absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract and its major route of excretion is in the bile.
Selenium: Although it has been established that selenium is essential to human life, very little information is available on its function and metabolism.
Chromium Nicotinate
Most chromium compounds are soluble at the pH of the stomach, but less soluble hydroxides may form as pH is increased. The environment of the gastrointestinal tract and ligands provided by foods and supplements are important for mineral absorption.
Mixed Carotenoids
Carotenoids are fat-soluble compounds, meaning they are absorbed more efficiently when consumed with dietary fats. They are absorbed in the small intestine through passive diffusion and are incorporated into chylomicrons, which are lipoprotein particles that transport dietary lipids. Once absorbed, carotenoids are transported via the lymphatic system into the bloodstream. Carotenoids undergo metabolic conversion in the liver. Carotenoids and their metabolites are primarily excreted through bile and feces. A small amount may also be excreted through urine.
Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA)
ALA is absorbed in the small intestine. Its oral bioavailability is relatively low, around 30%, due to its instability in the stomach and rapid hepatic degradation. Once absorbed, ALA is distributed throughout the body and can cross the blood-brain barrier. It is converted to its reduced form, dihydrolipoic acid (DHLA), in various tissues. ALA undergoes extensive metabolism in the liver. It is reduced to DHLA, which has potent antioxidant properties. Both ALA and DHLA can regenerate other antioxidants like vitamins C and E. ALA and its metabolites are primarily excreted through the kidneys. The compound has a relatively short half-life, which limits its duration of action.
Lycopene
Lycopene absorption occurs via passive diffusion or facilitated by scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SR-B1) in enterocytes, potentially alongside other carotenoids. Partial cleavage by enzymes like Beta-Carotene Oxygenase 1 (BCO1) and Beta-Carotene Oxygenase 2 (BCO2) in enterocytes may occur. Transport involves packaging into chylomicrons, then release into the lymph and portal circulation. Lycopene primarily associates with LDL and is distributed to various organs, notably accumulating in the liver but also present in adipose tissue, adrenal glands, testes, ovaries, kidneys, lungs, skin, and the prostate. Lycopene and its metabolites are primarily eliminated from the body through fecal excretion, a smaller portion may be excreted via urine.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Not available
7.0 Description
Bevon -CD Capsules contains Antioxidants with Omega 3 Fatty Acids.
Alpha Lipoic Acid (50 mg): An antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage and supports energy production in the body.
Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA, 45 mg): An Omega-3 fatty acid that supports heart health, reduces inflammation, and may improve mental health.
Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA, 30 mg): Another Omega-3 fatty acid crucial for brain and eye health, as well as reducing inflammation.
Mixed Carotenoids (10 mg): These are antioxidants that can help protect your cells from damage and support eye health.
Zinc (7.5 mg): An essential mineral that supports immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis.
Lycopene (25 mg): An antioxidant found in tomatoes and other red fruits and vegetables, known for its potential to reduce the risk of certain cancers and support heart health.
Manganese (1.5 mg): A mineral important for bone formation, blood clotting, and reducing inflammation.
Copper (1 mg): Essential for iron metabolism, energy production, and maintaining healthy connective tissues.
Chromium (200 mcg): Helps regulate blood sugar levels by enhancing the action of insulin.
Selenium (150 mcg): An antioxidant that plays a role in DNA synthesis, thyroid function, and protecting the body from oxidative damage and infection.
These ingredients work together to provide a range of health benefits, from supporting heart and boosting your immune system and protecting your cells from damage.
8.0 Pharmaceutical properties
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not Applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on pack
8.3 Packaging information
10 Blister strips of 10 Capsules each
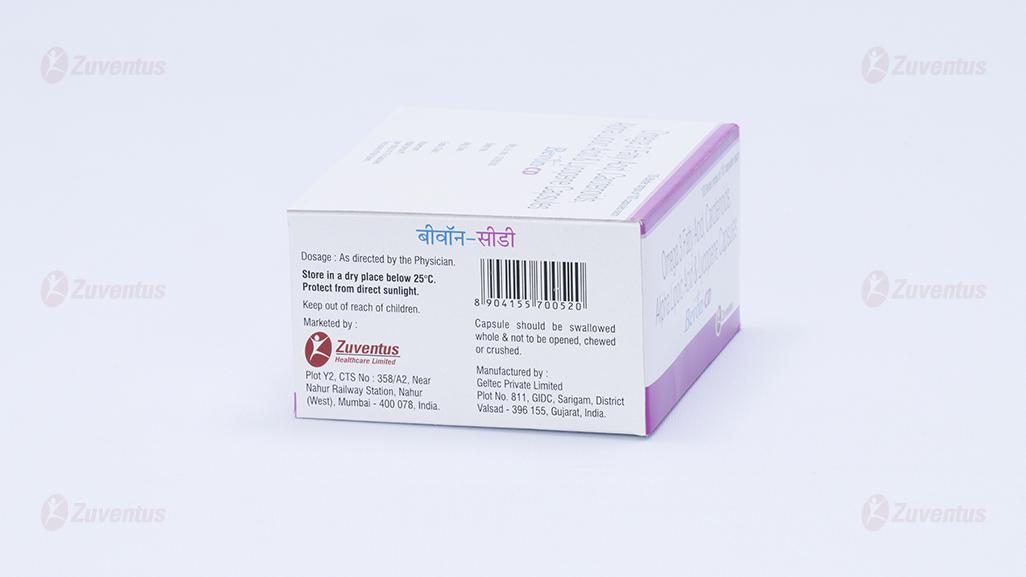
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store in a dry place below 25°C.
Protected from direct sunlight.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient counselling information
The capsule should be swallowed whole and not be opened, chewed, or crushed.
12.0 Date of revision of the text
10th October 2024
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- Ask your pharmacist if you need more information or advice
- You must contact a doctor if your symptoms worsen or do not improve
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1. What Bevon-CD is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you take Bevon-CD capsule
3. How to take Bevon-CD capsule
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store Bevon-CD capsule
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Bevon-CD is and what it is used for
Bevon -CD Capsules contains Antioxidants with Omega 3 Fatty Acids. Bevon-CD Capsule is nutritional supplement rich in antioxidants, designed to support healthy aging and heart health. It enhances immunity and helps manage blood sugar levels. Additionally, the capsule may reduce inflammation and swelling by neutralizing free radicals that cause cellular damage.
Alpha Lipoic Acid (50 mg): An antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage and supports energy production in the body.
Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA, 45 mg): An Omega-3 fatty acid that supports heart health, reduces inflammation, and may improve mental health.
Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA, 30 mg): Another Omega-3 fatty acid crucial for brain and eye health, as well as reducing inflammation.
Mixed Carotenoids (10 mg): These are antioxidants that can help protect your cells from damage and support eye health.
Zinc (7.5 mg): An essential mineral that supports immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis.
Lycopene (25 mg): An antioxidant found in tomatoes and other red fruits and vegetables, known for its potential to reduce the risk of certain cancers and support heart health. Manganese (1.5 mg): A mineral important for bone formation, blood clotting, and reducing inflammation.
Copper (1 mg): Essential for iron metabolism, energy production, and maintaining healthy connective tissues.
Chromium (200 mcg): Helps regulate blood sugar levels by enhancing the action of insulin. Selenium (150 mcg): An antioxidant that plays a role in DNA synthesis, thyroid function, and protecting the body from oxidative damage and infection.
These ingredients work together to provide a range of health benefits, from supporting heart, lowers blood sugar and boosting your immune system and protecting your cells from damage.
2. What you need to know before you take Bevon-CD capsule
Do not take Bevon-CD capsule if:
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in the formulation.
- Whilst taking Bevon-CD capsule, both protein and energy are also required to provide complete nutrition in the daily diet. No other vitamins, minerals or supplements with or without vitamin A should be taken with this preparation except under medical supervision.
Take special care with Bevon-CD Capsule
- Ensure you consume adequate protein and energy in your diet while taking Bevon-CD.
- Consult your doctor before taking other vitamins, minerals, or supplements with Bevon-CD.
- Do not take on an empty stomach.
- Do not exceed the recommended dose.
- Keep out of reach of children.
- If symptoms persist, consult your doctor.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Bevon-CD Capsules may be administered during pregnancy and lactation at the recommendation of the physician.
Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Bevon-CD has no influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
Other medicines and Bevon-CD capsule
Tell your doctor if you are taking or have recently taken/used any of the following medicines as they may interfere with Bevon-CD Capsules:
- Copper: Zinc may inhibit the absorption of copper.
- Tetracycline Antibacterials: Zinc may reduce the absorption of concurrently administered tetracyclines, and the absorption of zinc may be reduced by tetracyclines. An interval of at least three hours should be allowed when both are being given.
- Quinolone Antibacterials: Zinc may reduce the absorption of quinolones such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, norfloxacin, and ofloxacin.
- Calcium Salts: The absorption of zinc may be reduced by calcium salts.
- Iron: The absorption of zinc may be reduced by oral iron, and the absorption of oral iron may be reduced by zinc.
3. How to take Bevon-CD capsule
Adults and Elderly:
- Adults and the elderly: One Bevon-CD capsule daily, preferably after meals.
- Swallow the capsule whole; do not open, chew, or crush it.
In Children
Do not give Bevon-CD Capsules to children aged under 12
If you take more Bevon-CD capsule than you should
If you (or someone else) accidentally take too many tablets, you should tell your doctor at once or contact the nearest accident and emergency department. Show any left-over medicines or the empty packet to the doctor
If you forget to take Bevon-CD capsule
Do not worry. If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as possible, unless it is almost time to take the next dose (within 1-2 hours). Do not take a double dose. Then go on as before.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Bevon-CD capsule can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
Website link: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Bevon-CD capsule
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not take Bevon-CD Capsules after the expiry date which is stated on the carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month after EXP.
Store in a dry place below 25°C. Protected from direct sunlight.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist on how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Bevon-CD capsule contains.
Each soft gelatin capsule contains: Alpha Lipoic Acid (50 mg), Eicosapentaenoic Acid (45 mg), Docosahexaenoic Acid (30 mg), Mixed Carotenoids (10 mg), Zinc (7.5 mg), Lycopene (25 mg), Manganese (1.5 mg), Copper (1 mg), Chromium (200 mcg), Selenium (150 mcg)
Colours: Sunset Yellow FCF, Ponceau 4R Supra IH, Erythrosine Supra IH, Brilliant Blue FCF IH & Titanium Dioxide IP.
Appropriate overages of Vitamins added.
Packaging
Blister strips of 10 Capsules each