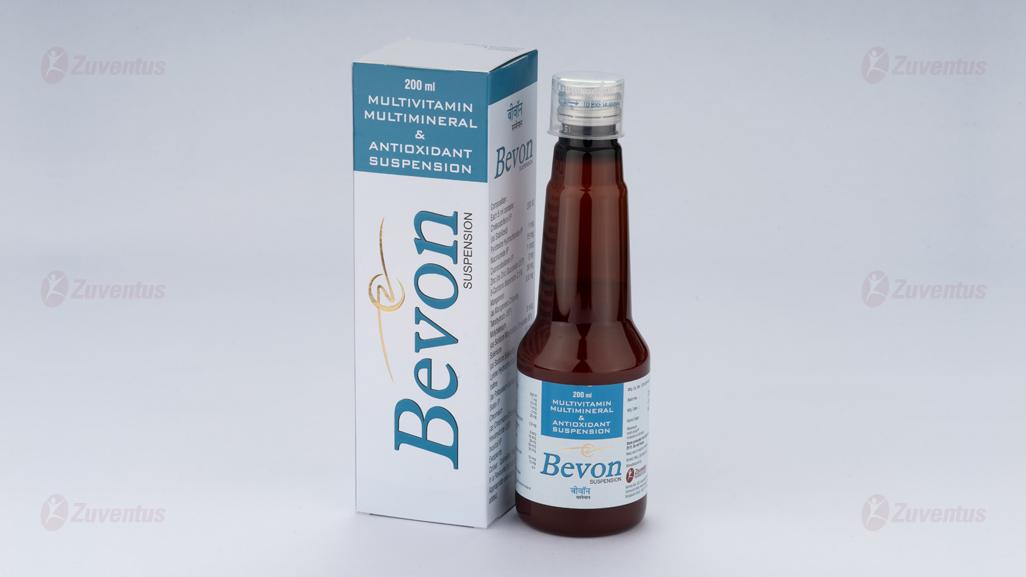
Bevon Suspension
Therapy Area
Vitamins/Minerals Supplements
1.0 Generic name
Multivitamin, Multimineral & Antioxidant Suspension
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
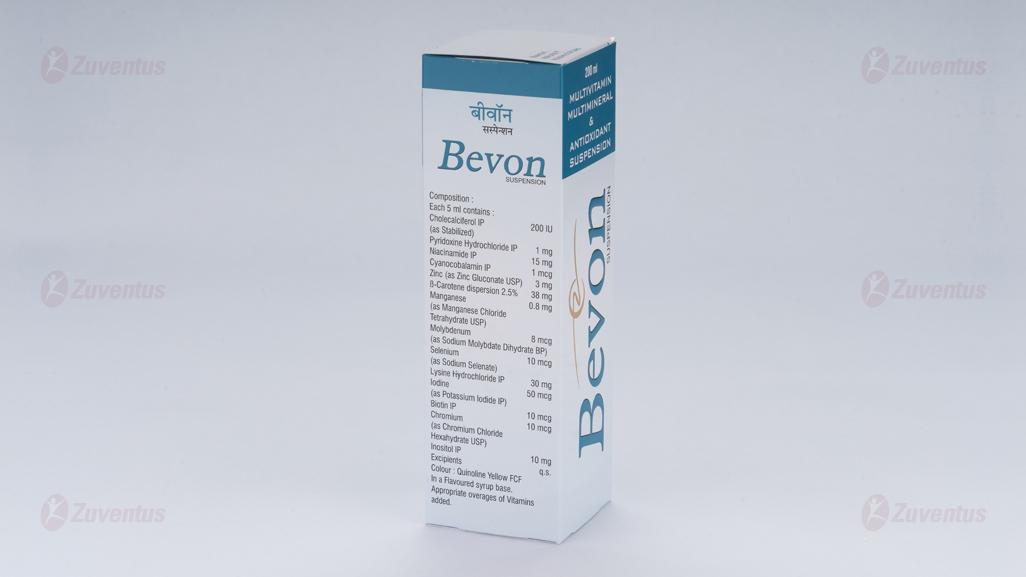
Each 5 ml contains :
- Cholecalciferol IP (As stabilized) 200 IU
- Pyridoxine Hydrochloride IP 1 mg
- Niacinamide IP 15 mg
- Cyanocobalamin IP 1 mcg
- Zinc Sulphate Monohydrate IP
- Equivalent to elemental Zinc 3 mg
- Betacarotene dispersion 2.5% 38 mg
- Manganese Sulfate Monohydrate USP
- Equivalent to elemental Manganese 0.8 mg
- Sodium Molybdate Dihydrate BP
- Equivalent to elemental Molybdenum 8 mcg
- Sodium Selenite Pentahydrate BP
- Equivalent to elemental Selenium 10 mcg
- L-Lysine Hydrochloride USP 30 mg
- Potassium Iodide IP
- Equivalent to elemental Iodine 50 mcg
- Biotin USP 10 mcg
- Chromium Picolinate USP
- Equivalent to elemental Chromium 10 mcg
- Myo-Inositol IP 10 mg
- Excipients q.s.
- Colour : Quinoline Yellow FCF
- In a flavoured syrupy base
- Appropriate overages of vitamins added.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Oral suspension
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For vitamin and mineral deficiency states in adults and children.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
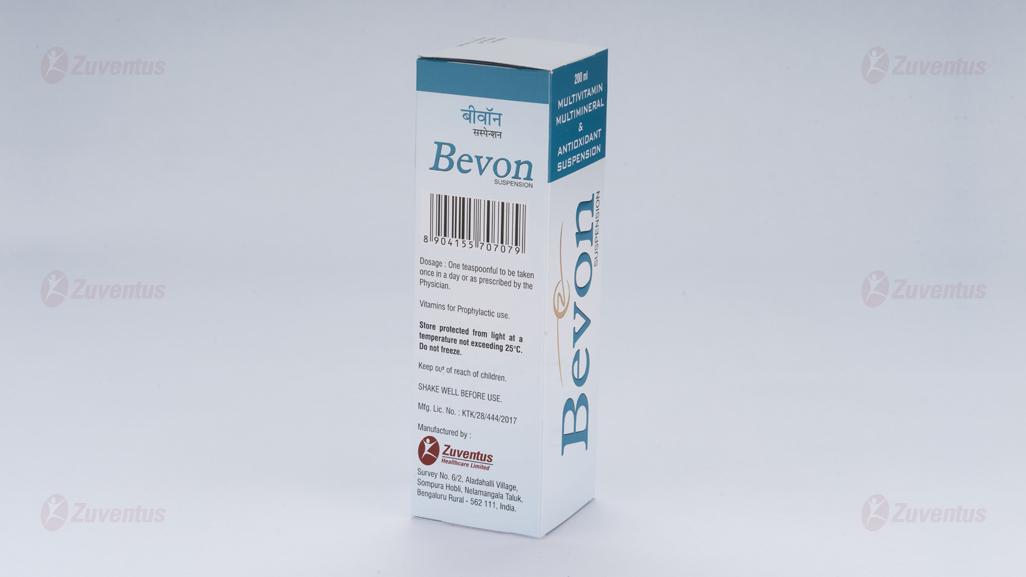
One teaspoonful (5 ml) to be taken once daily.
4.3 Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in the formulation.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
- Whilst taking Bevon Suspension both protein and energy are also required to provide complete nutrition in the daily diet. No other vitamins, minerals or supplements with or without vitamin A should be taken with this preparation except under medical supervision.
- Do not take Bevon Suspension on an empty stomach. Do not exceed the stated dose. Keep out of the reach of children. If symptoms persist, consult your doctor
- Evidence from Randomised Control Trials suggests that high doses (20-30 mg/day) β-carotene intake may increase the risk of lung cancer in current smokers and those previously exposed to asbestos. This high-risk population should consider the potential risks and benefits of Bevon Suspension, which contain 5mg of β-carotene per recommended daily dose, before use.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Zinc sulphate reduce the absorption of tetracyclines.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Bevon suspension may be administered during pregnancy and lactation at the recommendation of the physician.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Not relevant.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Immune system disorders : Hypersensitivity reaction (such as rash) Gastrointestinal disorders : Gastrointestinal disturbances (such as nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain).
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via
email to : medico@zuventus.com
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
No cases of overdosage due to Bevon therapy have been reported. In case of accidental overdose, discontinue use and seek professional assistance immediately. Any symptoms which may be observed due to the ingestion of large quantities of suspension will be due to the fat soluble vitamin content. Gastric lavage may be necessary to remove drug already released into the stomach. Signs and symptoms such as gastrointestinal disorders like diarrhoea may be associated with an overdose of Bevon.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties / Mechanism of action
Cholecalciferol
Vitamin D is required for the absorption of calcium and phosphate from the gastro-intestinal tract and for their transport. Its involvement in the control of calcium metabolism and hence the normal calcification of bones is well documented. Deficiency of Vitamin D in children may result in the development of rickets.
Pyridoxine hydrochloride
The active coenzyme form of vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) is pyridoxal 5 ′-phosphate. Approximately 80% of the body's total vitamin B6 is present as pyridoxal phosphate in muscle. Pyridoxal phosphate is a coenzyme for many enzymes involved in amino acid metabolism. It is also the co-factor for glycogen phosphorylase, where the phosphate group is catalytically important. Vitamin B6 helps the body to make several neurotransmitters. It is needed for normal brain development and function, and helps the body to make the hormones serotonin and norepinephrine, which influence mood, and melatonin, which helps to regulate the body clock. Along with vitamins B12 and B9 (folic acid), B6 helps to control levels of homocysteine in the blood. In addition, vitamin B6 is important in steroid hormone action where it removes the hormone-receptor complex from DNA binding, terminating the action of the hormones. In vitamin B6 deficiency, this results in increased sensitivity to the actions of low concentrations of estrogens, androgens, cortisol and vitamin D.
Niacinamide
Niacin was discovered as a nutrient during studies of pellagra. It is not strictly a vitamin since it can be synthesized in the body from the essential amino acid tryptophan. Two compounds, nicotinic acid and nicotinamide, have the biologic activity of niacin; its metabolic function is as the nicotinamide ring of the coenzymes NAD and NADP in oxidation-reduction reactions. Nicotinamide has important role in DNA repair mechanism.
Cyanocobalamin
Vitamin B12 is found only in foods of animal origin. Vitamin B12 is essential for cellular DNA synthesis and hence contributes to functions of various tissues of the body, formation of myelin sheath, more so the rapidly dividing and proliferating cellular systems such as blood and gastric epithelium. The absorbed inert form of cyanocobalamin is converted into two important active forms. One is methylcobalamininvolved in maturation of red blood corpuscles. The second active form is adenosylcobalamin involved in healthy myelination and neuronal integrity. Methylcobalamin deficiency leads to folate trap resulting in megaloblastic anemia. Deficiency of adenosylcobalamin leads to accumulation of large amount of methylmalonyl-CoA resulting in synthesis and incorporation of nonphysiological fatty acids into neuronal lipids, causing, demyelination, axonal degeneration and neuronal death leading to neurological complications.
Zinc sulfate
Zinc is an essential trace mineral necessary for the proper function of about 300 different enzymes. Therefore, zinc plays a role in virtually all biochemical pathways and physiological processes in the body. Thirty percent of the body's zinc is stored in the bones and 60% in muscles. The other 10% is found in virtually all body tissues. Zinc is important for wound healing, immune system support and to increase fertility (sperm production). It also assists digestion, energy production, growth, cellular repair, collagen synthesis, bone strength, cognitive function, and carbohydrate metabolism (glucose utilization and insulin production). Zinc not only modulates cell-mediated immunity but is also an antioxidant and anti- inflammatory agent. Mild zinc deficiencies are currently thought to cause chronic metabolic derangement leading to or exacerbating immune deficiency, gastrointestinal problems, endocrine disorders, neurologic dysfunction, cancer, accelerated aging, degenerative disease, and more.
Beta carotene
β-carotene is the most prominent and efficient member of the group of carotenoids (natural colorants that occur in the human diet). Carotenoids are red, orange, or yellow, fat-soluble compounds. Alpha, beta, and gamma carotene are considered provitamins because they can be converted to active vitamin A. Beta-carotene is converted to retinol, which is essential for vision and growth. ROS-induced oxidative stress is suggested as being basic to several human diseases. β-carotene has a unique type of antioxidant activity. Beta carotene traps free radicals and studies suggest that it may also reduce tumor development. Studies have shown that vitamin A is essential to the normal growth of epithelial tissues
Manganese sulfate
Manganese is an essential element for humans and is required for growth, development, and maintenance of health. Manganese is necessary for a variety of metabolic functions including those involved in skeletal system development, energy metabolism, activation of certain enzymes, nervous system function, immunological system function, and reproductive hormone function. It is an antioxidant that protects cells from damage due to free radicals. Manganese also plays an essential role in regulation of cellular energy, bone and connective tissue growth and blood clotting. In the brain, Manganese is an important cofactor for a variety of enzymes, including the antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase, as well as enzymes involved in neurotransmitter synthesis and metabolism.
Sodium molybdate dihydrate
Molybdenum belongs to a group of essential microelements. Molybdenum-containing enzymes catalyze basic metabolic reactions in the nitrogen, sulfur, and carbon cycles and are important for variety of metabolic pathways.
Sodium selenite
Selenium is incorporated into selenoproteins that have a wide range of pleiotropic effects, ranging from antioxidant, immune functions and anti-inflammatory effects to the production of active thyroid hormone. Low selenium status has been associated with increased risk of mortality, poor immune function, and cognitive decline. Selenium supplementation has antiviral effects, is essential for male and female reproduction, and reduces the risk of autoimmune thyroid disease. Prospective studies have generally shown some benefit of higher selenium status on the risk of various cancers
L-Lysine
L-Lysine is classified as an essential amino acid. Lysine helps in synthesis of connective tissues such as bone, skin, collagen, and elastin; synthesis of carnitine and resultant conversion of fatty acids to energy; support for healthy growth and development in children; and maintenance of healthy immune function, particularly with regard to antiviral activity.
Iodine (Potassium iodide)
Iodine is an essential constituent of the thyroid hormones.
Biotin
Biotin (Vitamin B7 or H) is a water soluble B vitamin that is essential for bodily health. It helps the body to process fat and sugars, and it helps form a critical process in fat production in the body. Biotin is involved in a number of carboxylase reactions. Biotin is often recommended as a dietary supplement for healthy skin, hair and nails. Biotin deficiency is characterized by development of a fine scaly dermatitis, hair loss, conjunctivitis, ataxia and delayed development.
Chromium picolinate
Chromium is a critical cofactor in the action of insulin. Results from some trials have indicated that chromium supplementation increases muscle gain and fat loss associated with exercise and improves glucose metabolism and the serum lipid profile in patients with or without diabetes. Low chromium levels can increase blood sugar, triglycerides, cholesterol levels, and increase the risk for a number of conditions, such as diabetes and heart disease.
Myo-Inositol
Inositol is an essential molecule found ubiquitously in biological systems. Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate plays an essential role as a secondary messenger in the InsP3/Ca+2 signal transduction pathway, which is responsible for modulating the activity of numerous cellular processes. Biochemical functions elucidated for phosphatidyl inositol in biological membranes include the mediation of cellular responses to external stimuli, nerve transmission, and the regulation of enzyme activity through specific interactions with various proteins.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Cholecalciferol
Cholecalciferol is absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract into the circulation. In the liver, it is hydroxylated to 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, is subject to entero-hepatic circulation and is further hydroxylated to 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol in the renal tubule cells. Vitamin D metabolites are bound to specific plasma proteins.
Pyridoxine hydrochloride
Pyridoxine is absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract and converted to the active pyridoxal phosphate which is bound to plasma proteins. It is excreted in the urine as 4-pyridoxic acid.
Niacinamide
Nicotinic acid is absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract, is widely distributed in the body tissues and has a short half-life.
Cyanocobalamin
Cyanocobalamin is absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract and is extensively bound to specific plasma proteins. A study with labelled Vitamin B12 showed it was quickly taken up by the intestinal mucosa and held there for 2 - 3 hours. Peak concentrations in the blood and tissues did not occur until 8 - 12 hours after dosage with maximum concentrations in the liver within 24 hours. Cobalamins are stored in the liver, excreted in the bile and undergo enterohepatic recycling. Part of a dose is excreted in the urine, most of it in the first eight hours.
Zinc sulfate
Zinc is poorly absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract. It is widely distributed throughout the body. It is excreted in the faeces with traces appearing in the urine.
Beta carotene
Except when liver function is impaired, Vitamin A is readily absorbed. β-carotene (as in Bevon Suspension) is Provitamin A and is the biological precursor to Vitamin A. It is converted to Vitamin A (Retinol) in the liver; retinol is emulsified by bile salts and phospholipids and absorbed in a micellar form. Part is conjugated with glucuronic acid in the kidney and part is metabolised in the liver and kidney, leaving 30 to 50% of the dose for storage in the liver. It is bound to a globulin in the blood. Metabolites of Vitamin A are excreted in the faeces and the urine.
Manganese sulfate
Manganese salts are poorly absorbed.
Sodium molybdate dihydrate
In humans, molybdenum is known to function as a cofactor for four enzymes : Sulfite oxidase catalyzes the transformation of sulfite to sulfate, a reaction that is necessary for the metabolism of sulfur-containing amino acids (methionine and cysteine).
Sodium selenite
Although it has been established that selenium is essential to human life, very little information is available on its function and metabolism
L-Lysine
L-Lysine absorbed from the lumen of the small intestine into the enterocytes by an active transport process.
Potassium iodide
Potassium salts are absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract. Potassium is excreted in the urine, the faeces and in perspiration. Urinary excretion of potassium continues even when intake is low.
Biotin
Following absorption, biotin is stored in the liver, kidney and pancreas.
Chromium picolinate
Most chromium compounds are soluble at the pH of the stomach, but less soluble hydroxides may form as pH is increased. The environment of the gastrointestinal tract and ligands provided by foods and supplements are important for mineral absorption.
Myo-Inositol
Oral ingestion of inositol is registered to generate a maximal plasma concentration of 36 - 45 mcg. The pharmacokinetic profile of inositol was studied in preterm infants and the estimated volume of distribution was reported to be 0.5115 L/kg. It is thought that inositol can be found bound to plasma proteins.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
There are no pre-clinical data of relevance to the prescriber which are additional to that already included in other sections of the prescribing information.
7.0 Description
Bevon suspension contain a comprehensive formula of vitamins, minerals and antioxidants specially designed to support health and wellbeing in adults by unlocking energy and strengthening immunity. Most vitamins, minerals and trace elements are not produced by human body and hence are dependent on dietary supply of these nutrients. Since vitamins, minerals and trace elements are involved in many metabolic processes in the body, an adequate supply of these vital substances contribute to physical and mental well being.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
No major incompatibilities are known
8.2 Shelf-life
18 Months
8.3 Packaging information
A bottle of 200 ml.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Do not freeze.
Keep out of reach of children.
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USE.
9.0 Patient counselling information
Do not take Bevon Suspension :
- if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to any of the ingredients of Bevon suspension.
- if you suffer from hypercalcaemia (high level of calcium in the blood)
Take special care with Bevon Suspension
Before you are given Bevon Suspension tell your doctor, dietician or pharmacist if :
- you are pregnant or thinking of becoming pregnant
- you are a smoker
- you have an asbestos related illness such as asbestosis
- you suffer from thyroid problems.
If any of the above applies to you, or if you are not sure, speak to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Bevon Suspension.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor if you are taking or have recently taken/used any of the following medicines as they may interfere with Bevon suspension :
- Phenytoin (used to treat epilepsy)
- Tetracycline antibiotics (used to treat infections) such as doxycycline and minocycline.
Please tell your doctor if you are taking or have recently taken/used any other medicines including other vitamin or mineral products medicines obtained without a prescription.
12.0 Date of issue
20.04.2022
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully because it contains important information for you.
This medicine is available without prescription. However, you still need to take Bevon Suspension carefully to get the best results from them.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- Ask your pharmacist if you need more information or advice.
- You must contact a doctor, dietician or pharmacist if your symptoms worsen or do not improve.
- If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effect not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor, dietician or pharmacist.
The information in this leaflet has been divided into the following sections:
- What Bevon Suspension are and what they are taken for
- Check before you take Bevon Suspension
- How to take Bevon Suspension
- Possible side effects
- How to store Bevon Suspension
- Further information
1. What Bevon Suspension are and what they are taken for
Bevon Suspension is a multivitamin and mineral supplement. It contains a combination of 14 essential vitamins, minerals and trace elements.
The human body requires a wide variety of vitamins, minerals and trace elements to perform crucial daily tasks such as releasing energy from food and repairing cell damage. During certain illnesses, your body either cannot get or cannot efficiently use all of the vitamins, minerals and trace elements it needs.
Your doctor, dietician or pharmacist will give you Bevon Suspension if your diet cannot provide you with enough vitamins, minerals and trace elements.
Each ml contains the following 14 essential vitamins, minerals and trace elements, each of which plays a vital role in the efficient daily maintenance of many body processes:
Each 5 ml contains:
Cholecalciferol IP (As stabilized) 200 IU
Pyridoxine Hydrochloride IP 1 mg
Niacinamide IP 15 mg
Cyanocobalamin IP 1 mcg
Zinc Sulphate Monohydrate IP Equivalent to elemental Zinc 3 mg
Betacarotene dispersion 2.5% 38 mg
Manganese Sulfate Monohydrate USP Equivalent to elemental Manganese 0.8 mg
Sodium Molybdate Dihydrate BP Equivalent to elemental Molybdenum 8 mcg
Sodium Selenite Pentahydrate BP Equivalent to elemental Selenium 10 mcg
L-Lysine Hydrochloride USP 30 mg
Potassium Iodide IP Equivalent to elemental Iodine 50 mcg
Biotin USP 10 mcg
Chromium Picolinate USP Equivalent to elemental Chromium 10 mcg
Myo-Inositol IP 10 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Quinoline Yellow FCF
In a flavoured syrupy base
The functions of the vitamins found in Bevon Suspension are:
Vitamin D ( cholecalciferol)
Vitamin D has long been known for its important role in regulating body levels of calcium and phosphorus, and in mineralization of bone.
Vitamin A (β-Carotene)
Is essential for growth, maintenance of skin and mucous membranes such as the linings of the mouth, nose, lungs, digestive system, colon and for vision, particularly at night
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
Vitamin B6 helps protein metabolism, along with the maintenance of the nervous and immune systems
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is often called the 'red vitamin' because it is required for regulating blood cells
Biotin
Biotin is needed for normal growth and development of the skin and hair, the maintenance of a healthy nervous system and the healthy functioning of bone marrow
Nicotinamide
Nicotinamide (also known as vitamin B3) is essential for a healthy nervous system
The main functions of the minerals and trace elements are:
Inositol
Inositol is an essential molecule found ubiquitously in biological systems. Biochemical functions elucidated for phosphatidylinositol in biological membranes include the mediation of cellular responses to external stimuli, nerve transmission, and the regulation of enzyme activity through specific interactions with various proteins.
Iodine
Involved in functioning of the thyroid gland which regulates many of the metabolic processes in the body
Zinc
Zinc is required for growth and cell function, bone metabolism, taste, insulin production and the body’s immune system which fights infection.
Manganese
Manganese helps the body to utilise calcium and potassium and maintain the structure of cells.
Selenium
Selenium helps to protect the cells and lipids from free radical damage.
Chromium
Helps the body to use glucose by its action on insulin
Molybdenum
Is involved in the enzyme processes for protein metabolism.
Lysine
L-Lysine is classified as an essential amino acid. Lysine helps in synthesis of connective tissues such as bone, skin, collagen, and elastin; synthesis of carnitine and resultant conversion of fatty acids to energy; support for healthy growth and development in children; and maintenance of healthy immune function
2. Check before you take Bevon Suspension
- Whilst taking Bevon Suspension, both protein and energy are also required to provide complete nutrition in the daily diet. No other vitamins, minerals or supplements with or without vitamin A should be taken with this preparation except under medical supervision.
- Do not take Bevon Suspension: if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to any of the ingredients of Bevon Suspension (see Section 6 Further information)
- Do not take Bevon Suspension on an empty stomach. Do not exceed the stated dose. Keep out of the reach of children. If symptoms persist, consult your doctor.
- Evidence from Randomised Control Trials suggests that high doses (20-30 mg/day) β-carotene intake may increase the risk of lung cancer in current smokers and those previously exposed to asbestos. This high-risk population should consider the potential risks and benefits of Bevon Suspension, which contain 5mg of β-carotene per recommended daily dose, before use.
Take special care with Bevon Suspension
Before you are given Bevon Suspension tell your doctor, dietician or pharmacist if:
- you are a smoker
- you have an asbestos related illness such as asbestosis
- you suffer from thyroid problems.
If any of the above applies to you, or if you are not sure, speak to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Bevon Suspension.
Taking other medicines
Please tell your doctor if you are taking or have recently taken/used any other medicines including other vitamin or mineral products medicines obtained without a prescription.
Zinc sulphate reduce the absorption of tetracyclines
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Bevon suspension may be administered during pregnancy and lactation at the recommendation of the physician.
3. How to take Bevon Suspension
One teaspoonful (5 ml) to be taken once daily.
What to do if you take more Bevon Suspension than you should
If you (or someone else) accidentally take too much suspension, you should tell your doctor at once or contact the nearest accident and emergency department. Show any leftover medicines or the empty bottle to the doctor.
If you forget to take Bevon Suspension
Do not worry. If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as possible, unless it is almost time to take the next dose (within 1-2 hours). Do not take a double dose. Then go on as before.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Bevon Suspension may cause allergic reactions (such as rash), and problems related to your stomach and intestines (such as feeling or being sick and stomach pains).
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Bevon Suspension
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not take Bevon Suspension after the expiry date which is stated on the carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month after EXP.
Do not store above 25ºC. Keep the blister in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist on how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Further information
What is in Bevon Suspension?
The active ingredients in this medicine are: Pyridoxine hydrochloride, Niacinamide, Cyanocobalamin, Folic Acid, Biotin, Beta Carotene, Zinc, selenium, Manganese, Molybdenum, Inositol, Iodine, Chromium, Lysine
Packaging
A bottle of 200 ml