Brophyle N Tablets
Therapy Area
Respiratory
1.0 Generic name
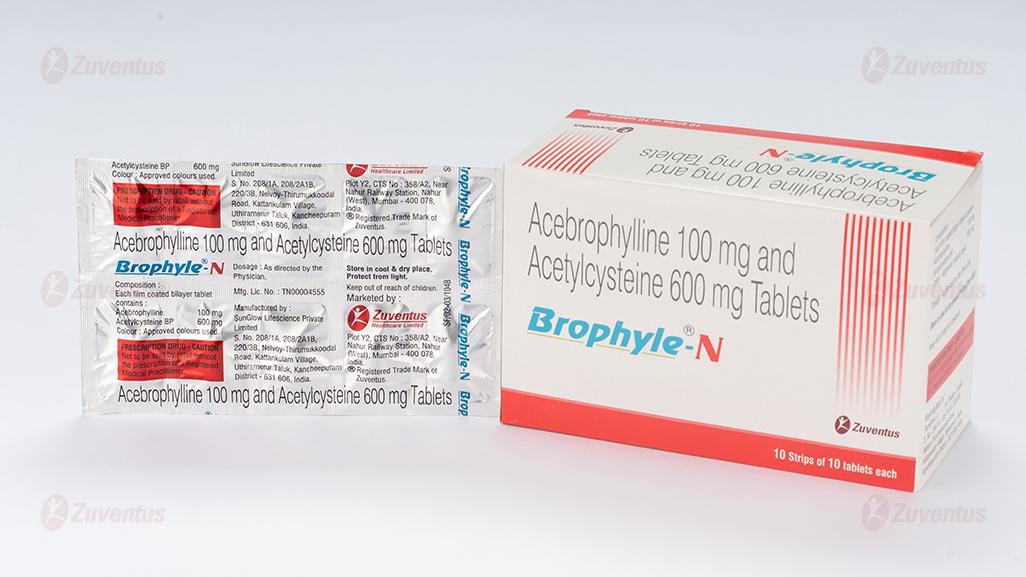
Acebrophylline and Acetylcysteine tablets
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each film coated bilayer tablet contains:
Acebrophylline………………………. 100 mg
Acetylcysteine BP……………………. 600 mg
Colour: Approved colours used.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Tablet Acebrophylline 100 mg and Acetylcysteine 600 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the treatment of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (bronchial asthma, bronchitis, bronchiectasis) emphysema and mucoviscidoses.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adults
One tablet twice daily.
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to ambroxol, acebrophylline, acetylcysteine, theophylline or any other xanthine derivative
- Patients suffering from acute myocardial infarction
- Patients with hypotension, hemodynamic instability, and arrhythmias
- Patients with renal disease or liver disorder
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Careful monitoring is recommended for patients with congestive heart failure, chronic alcoholism, hepatic dysfunction, or viral infections.
Caution should be exercised in patients with cardiac arrhythmias, other cardiovascular diseases, hyperthyroidism or hypertension, gastric and duodenal ulceration or convulsive disorders. Patients with hepatic and renal insufficiency should take it with caution.
Bronchospasms may occur with the use of acetylcysteine especially in patients with asthma. If bronchospasms occur, the medicinal product should be discontinued immediately.
Caution is advised in patients with a history of peptic ulcer, especially when used concomitantly with other medicinal products known to irritate the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract.
Serious skin reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Lyell's syndrome have very rarely been reported in temporal connection with the use of acetylcysteine. In most cases, at least one other suspect medicinal product, which was more likely the cause of the mucocutaneous syndrome could be identified. If cutaneous or mucosal alterations newly occur, immediate medical advice should be sought and the treatment with acetylcysteine should be discontinued immediately.
Bronchial secretions may become more fluid and increase in volume, in particular at the start of the treatment with acetylcysteine. When a patient is unable to cough up the secretions effectively, postural drainage and bronchoaspiration should be performed.
4.5 Drugs interactions
The following reduce clearance and a reduced dosage may therefore be necessary to avoid side-effects: allopurinol, cimetidine, ciprofloxacin, corticosteroids, diltiazem, erythromycin, frusemide, isoprenaline, oral contraceptives, thiabendazole and verapamil, doxycycline, amoxicillin etc.
Xanthines can potentiate hypokalaemia resulting from beta2-agonist therapy, steroids, diuretics and hypoxia. Particular caution is advised in severe asthma. It is recommended that serum potassium levels are monitored in such situations.
No clinically relevant unfavourable interactions with other medications have been reported.
To date, the inactivation of antibiotics by acetylcysteine has been reported only in in-vitro tests, whereby the relevant substances were mixed directly with each other. However, if oral antibiotics are required, it is advised that these should be taken two hours before or after Acetylcysteine.
Acetylcysteine should not be administered concomitantly with antitussive medicinal products.
Acetylcysteine may enhance the vasodilatory effects of nitroglycerin. Caution is advised.
Activated charcoal can decrease the effect of acetylcysteine due to reduced absorption.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
Brophyle N is not recommended in pregnancy as well as during parturition.
Lactation
The safety of Brophyle N is not established during lactation period. Hence the use of acebrophylline is not advisable in lactating mothers.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effect on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Transient nausea and dizziness may occur on taking this drug, but these effects are reversible. On cessation of therapy, these symptoms tend to disappear.
The commonly reported adverse effects with acebrophylline include abdominal discomfort, stomach/abdominal distension, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, heart burn, loss of appetite, esophageal bleeding, rashes, urticaria, itching, drowsiness, difficulty in breathing, leukocytosis, and nasal inflammation. If chills and fevers occur, the drug should be immediately discontinued.
Other rarely reported adverse events include headache, occasional numbness including numbness in arm, insomnia, tachycardia, fatigue, hypertension, albuminuria, glycosuria, hypotension and occasionally hyperglycemia.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Nausea, vomiting (which is often severe), epigastric pain and haematemesis. Pancreatitis if abdominal pain persists. Restlessness, hypertonia, exaggerated limb reflexes and convulsions. Tachycardia is common.
Symptomatic treatment should be provided.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action/ Pharmacodynamic properties
Acebrophylline is a compound which has been found to act as a bronchodilating, mucoregulating and anti-inflammatory drug due to its components theophylline-7-acetate and ambroxol. Theophylline-7-acetate, as with other xanthinic derivatives, has a bronchodilator effect due to inhibition of the intracellular phosphodiesterases, followed by an increase of adenosine monophosphate cyclic levels, which promote the relaxation of bronchial muscles. Ambroxol modifies the mucous gel phase of secretions by decreasing the viscosity and increasing the serous gel phase. It increases the mucociliary clearance by stimulating cilia motility.
Acebrophylline inhibits phospholipase A2 and phosphatidylcholine leading to lesser production of the powerful pro-inflammatory substances like leukotrienes and tumor necrosis factor. By inhibiting the synthesis and release of these inflammatory mediators, acebrophylline reduces inflammation, a key factor in airway obstruction, especially in chronic forms.
Acetylcysteine is a mucolytic.
The mucolytic action is mediated by a reduction in the viscosity of bronchial mucus. This is explained by the depolymerisation with the disulfide bridges between the macromolecules in the mucus being opened.
In addition, acetylcysteine is a precursor of glutathione. Acetylcysteine is a derivative of the natural amino acid cysteine, which serves as a substrate for the synthesis of glutathione in the body.
Apart from the fact that acetylcysteine is able to normalise a state of glutathione depletion, it is able to conjugate with various toxic compounds.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
In healthy volunteers, given 200 mg oral acebrophylline, the two components of the molecule ambroxol and theophylline-7 acetic acid are released in the stomach and absorbed in the intestine, reaching optimal concentrations of ambroxol within 2 hours and of theophylline-7 acetic acid after 1 hour. The plasma half-life varies from 4 to 9 hours after oral administration. The drug is metabolized in the liver and eliminated renally.
Acetylcysteine is rapidly absorbed after oral administration and distributed throughout the organism. The highest tissue concentrations are reached in the liver, kidneys and lungs. Acetylcysteine is mainly deacetylated to cysteine in the liver. Most of this is processed in the amino acid metabolism. Moreover, it forms reversible disulfide compounds with amino acids and proteins with free sulfydryl groups. Finally, high doses are largely converted into inorganic sulfate, which undergoes renal excretion.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Negative interference has been reported between theophylline and erythromycin and in animal’s simultaneous administration of theophylline together with erythromycin estolate at doses that alone are non-toxic enhanced the toxicity of the former, as indicated by the drastic drop in the LD50, i.e. the dose causing the death of half the animals. In similar experimental conditions, acebrophylline was not affected by simultaneous use of erythromycin, and not only was there no reduction in the LD50 but in some cases it was actually higher, indicating the safety of the two components as regards their potential tolerability in patients.
Preclinical data of acetylcysteine based on conventional studies of safety pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenic potential and toxicity to reproduction do not indicate a risk to humans.
7.0 Description
Brophyle – N tablet is a combination of Acebrophylline and Acetylcysteine.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on pack
8.3 Packaging information
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store below 30°C. Protect from light & moisture.
9.0 Patient counselling information
- Brophyle-N Tablet helps in the prevention and treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD).
- It has a smelly odour. This is normal and does not indicate that the medicine has changed.
- It should be taken at the same time each day, preferably in the evening after food.
- Drink plenty of fluids to help loosen the congestion and lubricate your throat while you are taking this medication.
- It does not work right away and should not be used to relieve sudden breathing problems. Use your rescue inhaler to control sudden difficulty in breathing.
- Your doctor may ask you to take regular blood tests to monitor the level of drug in your body to make sure that you are taking the right dose.
- Notify your doctor if you have ever been diagnosed with kidney, liver, or heart disease, or if have a smoking history. Your dose may need to be adjusted.
- Do not discontinue use without consulting your doctor even if you feel better.
12.0 Date of revision
01.10.2024
About leaflet
Please read this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet
1. What Brophyle N tablet is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you use Brophyle N tablet
3. How to use Brophyle N tablet
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store Brophyle N tablet
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Brophyle N Tablet is and what it is used for
Brophyle N tablet contains two active substances: Acebrophylline (100 mg) and Acetylcysteine (600 mg). It is used for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including bronchial asthma, bronchitis, bronchiectasis, emphysema, and mucoviscidoses.
2. What you need to know before you take Brophyle N Tablet
Do not take Brophyle N tablet if you:
- Are allergic to acebrophylline, acetylcysteine, theophylline, or any other xanthine derivative.
- Have had a recent heart attack.
- Have low blood pressure, hemodynamic instability, or arrhythmias.
- Have kidney or liver disease.
Warnings and precautions:
- Monitor carefully if you have congestive heart failure, chronic alcoholism, hepatic dysfunction, or viral infections.
- Use with caution if you have cardiac arrhythmias, other cardiovascular diseases, hyperthyroidism, hypertension, gastric or duodenal ulcers, or convulsive disorders.
- Discontinue use immediately if bronchospasms or serious skin reactions occur.
Important Precautions
- Brophyle-N Tablet helps in the prevention and treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD).
- It has a smelly odour. This is normal and does not indicate that the medicine has changed.
- It should be taken at the same time each day, preferably in the evening after food.
- Drink plenty of fluids to help loosen the congestion and lubricate your throat while you are taking this medication.
- It does not work right away and should not be used to relieve sudden breathing problems. Use your rescue inhaler to control sudden difficulty in breathing.
- Your doctor may ask you to take regular blood tests to monitor the level of drug in your body to make sure that you are taking the right dose.
- Notify your doctor if you have ever been diagnosed with kidney, liver, or heart disease, or if have a smoking history. Your dose may need to be adjusted.
- Do not discontinue use without consulting your doctor even if you feel better.
3. How to take Brophyle N Tablet
Dosage
- Adults: One tablet twice daily.
Method of administration
- Take the tablet with a glass of water, preferably after food.
Brophyle N tablet with other drugs
Brophyle N tablet may interact with other medications, which can affect how it works or increase the risk of side effects. Inform your doctor if you are taking any of the following:
Water pills (diuretics): Furosemide
Medicines for gout: Allopurinol
Antacids: Cimetidine Antibiotics: Ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, amoxicillin, doxycycline, tetracycline, gentamicin, amikacin, neomycin
Blood pressure medications: Diltiazem, verapamil
Heart-related medications: Isoprenaline
Anthelmintics: Thiabendazole
Corticosteroids: Prednisone
Oral contraceptives: Ethinylestradiol
Medicines for chest pain: Glyceryl trinitrate
Cough suppressants: Dextromethorphan, codeine
If you take more Brophyle N tablet than you should
Contact your doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency department immediately.
If you stop using Brophyle N tablet
If you forget to take at the right time, use it as soon as you remember, then carry on as before. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop using Brophyle N tablet
Do not stop your treatment even if you feel better unless told to do so by your doctor.
Do not use in children.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Common side effects:
- Abdominal discomfort, stomach distension, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, heartburn, loss of appetite, esophageal bleeding, rashes, urticaria, itching, drowsiness, difficulty in breathing, leukocytosis, and nasal inflammation.
Rare side effects:
- Headache, occasional numbness, insomnia, tachycardia, fatigue, hypertension, albuminuria, glycosuria, hypotension, and hyperglycemia.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com in and click the tab “Drug Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page. Website link: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Brophyle N Tablet
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- Store below 30°C. Protect from light and moisture.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the pack.
- Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Brophyle N tablet contains:
- Active substances: Acebrophylline (100 mg) and Acetylcysteine (600 mg).