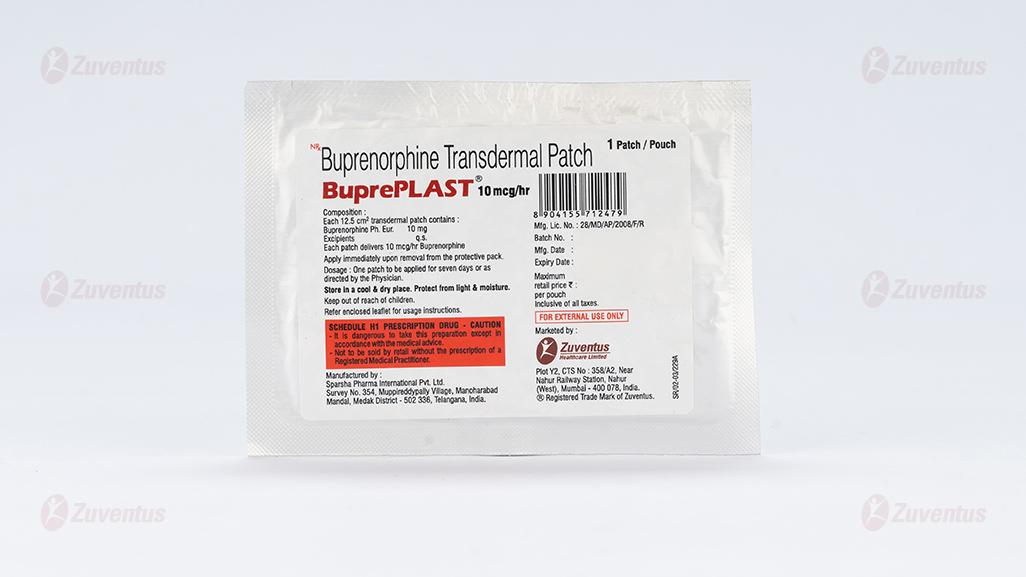
Bupreplast Patch 10 mcg/hr
Therapy Area
Pain management
1.0 Generic name
Buprenorphine Transdermal Patch
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
BuprePLAST 5 mcg/hr
Each 6.25 cm2 transdermal patch contains :
Buprenorphine Ph. Eur. 5 mg
Excipients q.s.
Each patch delivers 5 mcg/hr Buprenorphine
BuprePLAST 10 mcg/hr
Each 12.5 cm2 transdermal patch contains :
Buprenorphine Ph. Eur. 10 mg
Excipients q.s.
Each patch delivers 10 mcg/hr Buprenorphine
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Transdermal Patch
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the treatment of severe opioid responsive pain conditions which are not adequately responding to nonopioid analgesics.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Bupreplast patch should be administered every 7th day. Bupreplast patch is not suitable for the treatment of acute pain.
Patients aged 18 years and over
The lowest Bupreplast patch dose (Bupreplast 5 mcg/hr transdermal patch) should be used as the initial dose. Consideration should be given to the previous opioid history of the patient as well as to the current general condition and medical status of the patient.
Titration
During initiation and titration with Bupreplast, patients should use the usual recommended doses of short acting supplemental analgesics as needed until analgesic efficacy with Bupreplast patch is attained. The dose should not be increased before 3 days, when the maximum effect of a given dose is established. Subsequent dosage increases may then be titrated based on the need for supplemental pain relief and the patient's analgesic response to the patch.
To increase the dose, a larger patch should replace the patch that is currently being worn, or a combination of patches should be applied in different places to achieve the desired dose. It is recommended that no more than two patches are applied at the same time, regardless of the patch strength. A new patch should not be applied to the same skin site for the subsequent 3-4 weeks. Patients should be carefully and regularly monitored to assess the optimum dose and duration of treatment.
Conversion from opioids
Patch can be used as an alternative to treatment with other opioids. Such patients should be started on the lowest available dose (Bupreplast 5 mcg/hr transdermal patch) and continue taking short-acting supplemental analgesics during titration as required.
Patients under 18 years of age
As buprenorphine patch has not been studied in patients under 18 years of age,the use of Bupreplast patch in patients below this age is not recommended.
Elderly
No dosage adjustment of Bupreplast patch is required in elderly patients.
Renal impairment
No special dose adjustment of Bupreplast patch is necessary in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic impairment
Buprenorphine is metabolised in the liver. The intensity and duration of its action may be affected in patients with impaired liver function. Therefore patients with hepatic insufficiency should be carefully monitored during treatment with Bupreplast patch. Patients with severe hepatic impairment may accumulate buprenorphine during Bupreplast patch treatment. Consideration of alternate therapy should be considered, and Bupreplast should be used with caution, if at all, in such patients.
Patch application
Bupreplast should be applied to non-lrritated, Intact skin of the upper outer arm, upper chest, upper back or side of the chest, but not to any parts of the skin with large scars. Bupreplast patch should be applied to a relatively hairless or nearly hairless skin site. If none are available, the hair at the site should be cut with scissors, not shaven.
If the application site must be cleaned, It should be done with clean water only. Soaps, alcohol, oil, lotions of abrasive devices must not be used. The skin must be dry before the patch is applied. Bupreplast should be applied immediately after removal from the sealed sachet. Following removal of the protective layer, the transdermal patch should be pressed firmly in place with the palm of the hand for approximately 30 seconds, making sure the contact is complete, especially around the edges. If the edges of the patch begin to peel off, the edges may be taped down with suitable skin tape.
The patch should be worn continuously for 7 days.
Bathing, showering, or swimming should not affect the patch. If a patch falls off, a new one should be applied.
Duration of administration
Bupreplast should under no circumstances be administered for longer than absolutely necessary. If long-term pain treatment with Bupreplast is necessary in view of the nature and severity to the illness, then careful and regular monitoring should be carried out (If necessary with breaks in treatment) to establish whether and to what extent further treatment is necessary.
Discontinuation
After removal of the patch, buprenorphine serum concentrations decrease gradually and thus the analgesic effect is maintained for a certain amount of time. This should be considered when therapy with Bupreplast is to be followed by other opioids. As a general rule, a subsequent opioid should not be administered within 24 hours after removal of the patch. At present, only limited information is available on the starting dose of other opioids administered after discontinuation of the transdermal patch.
Patients with fever or exposed to external heat
While wearing the patch, patients should be advised to avoid exposing the application site to external heat sources, such as heating pads, electric blankets, heat lamps, sauna, hot tubs, and heated water beds, etc., as an increase in absorption of buprenorphine may occur. When treating febrile patients, one should be aware that fever may also increase absorption resulting in increased plasma concentrations of buprenorphine and thereby increased risk of opioid reactions.
4.3 Contraindications
Buprenorphine patch is contraindicated in :
- Patients with known hypersensitivity to the active substance buprenorphine or to any of the excipients.
- The treatment of opioid dependence and narcotic withdrawal.
- Conditions in which the respiratory centre and function are severely impaired or may become so.
- Patients who are receiving MAO inhibitors or have taken them within the last two weeks.
- Patients suffering from myasthenia gravis
- Patients suffering from delirium tremens
- Pregnancy (see "Warnings & Precautions").
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
- Buprenorphine should be used with particular caution in patients with acute alcohol intoxication, head injury, shock, a reduced level of consciousness of uncertain origin, intracranial lesions or increased intracranial pressure, or in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
- Buprenorphine may lower the seizure threshold in patients with a history of seizure disorder.
- Significant respiratory depression has been associated with buprenorphine, particularly by the intravenous route. A number of overdose deaths have occurred when addicts have intravenously abused buprenorphine, usually with benzodiazepines concomitantly. Additional overdose deaths due to ethanol and benzodiazepines in combination with buprenorphine have been reported.
- Since CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase concentrations of buprenorphine, patients already treated with CYP3A4 inhibitors should have their dose of Buprenorphine carefully titrated since a reduced dosage might be sufficient in these patients.
- Buprenorphine is not recommended for analgesia in the immediate post-operative period or in other situations characterised by a narrow therapeutic index or a rapidly varying analgesic requirement.
- Controlled human and animal studies indicate that buprenorphine has a lower dependence liability than pure agonist analgesics. In humans limited euphorigenic effects have been observed with buprenorphine. This may result in some abuse of the medicinal product and caution should be exercised when prescribing to patients known to have, or suspected of having, a history of drug abuse or alcohol abuse or serious mental illness.
- As with all opioids chronic use of buprenorphine can result in the development of physical dependence. Withdrawal (abstinence syndrome), when it occurs, is generally mild, begins after 2 days and may last up to 2 weeks. Withdrawal symptoms include agitation, anxiety, nervousness, insomnia, hyperkinesia, tremor and gastrointestinal disorders.
- Athletes should be aware that this medicine may cause a positive reaction to sports doping control tests.
- Risk from concomitant use of sedative medicines such as benzodiazepines or related drugs : Concomitant use of Buprenorphine and sedative medicines such as benzodiazepines or related drugs may result in sedation, respiratory depression, coma and death. Because of these risks, concomitant prescribing with these sedative medicines should be reserved for patients for whom alternative treatment options are not possible. If a decision is made to prescribe Buprenorphine concomitantly with sedative medicines, the lowest effective dose should be used, and the duration of treatment should be as short as possible.
- The patients should be followed closely for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation. In this respect, it is strongly recommended to inform patients and their caregivers to be aware of these symptoms.
Serotonin syndrome
Concomitant administration of Buprenorphine and other serotonergic agents, such as MAO inhibitors, selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine re-uptake inhibitors (SNRIs) or tricyclic antidepressants may result in serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition.
If concomitant treatment with other serotonergic agents is clinically warranted, careful observation of the patient is advised, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases.
Symptoms of serotonin syndrome may include mental-status changes, autonomic instability, neuromuscular abnormalities, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms.
If serotonin syndrome is suspected, a dose reduction or discontinuation of therapy should be considered depending on the severity of the symptoms.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Buprenorphine must not be used concomitantly with MAOIs or in patients who have received MAOIs within the previous two weeks. Effect of other active substances on the pharmacokinetics of buprenorphine :
- Buprenorphine is primarily metabolised by glucuronidation and to a lesser extent (about 30%) by CYP3A4.
- Concomitant treatment with CYP3A4 inhibitors may lead to elevated plasma concentrations with intensified efficacy of buprenorphine.
- Studies with the CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole did not produce clinically relevant increases in mean maximum (Cmax) or total (AUC) buprenorphine exposure following buprenorphine with ketoconazole as compared to buprenorphine alone.
- The interaction between buprenorphine and CYP3A4 enzyme inducers has not been studied.
- Co-administration of buprenorphine and enzyme inducers (e.g. phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin and rifampicin) could lead to increased clearance which might result in reduced efficacy.
- Reductions in hepatic blood flow induced by some general anaesthetics (e.g. halothane) and other medicinal products may result in a decreased rate of hepatic elimination of buprenorphine.
Pharmacodynamic interactions
Buprenorphine should be used cautiously with :
- Other central nervous system depressants : other opioid derivatives (analgesics and antitussives containing e.g. morphine, dextropro-poxyphene, codeine, dextromethorphan or noscapine). Certain anti-depressants, sedative H1-receptor antagonists, alcohol, anxiolytics, neuroleptics, clonidine and related substances. These combinations increase the CNS depressant activity. Benzodiazepines : This combination can potentiate respiratory depression of central origin.
- At typical analgesic doses buprenorphine is described to function as a pure mu receptor agonist. In buprenorphine clinical studies subjects receiving full mu agonist opioids (up to 90 mg oral morphine or oral morphine equivalents per day) were transferred to buprenorphine. There were no reports of abstinence syndrome or opioid withdrawal during conversion from entry opioid to buprenorphine.
- Sedative medicines such as benzodiazepines or related drugs The concomitant use of opioids with sedative medicines such as benzodiazepines or related drugs increases the risk of sedation, respiratory depression, coma and death because of additive CNS depressant effect. The dose and duration of concomitant use should be limited Co-administration of Serotonergic medicinal products, such as MAO inhibitors, selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine re-uptake inhibitors (SNRIs) or tricyclic antidepressants as the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition, is increased.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
There are no or limited amount of data from the use of buprenorphine in pregnant women. Studies in animals have shown reproductive toxicity. The potential risk for humans is unknown. Towards the end of pregnancy high doses of buprenorphine may induce respiratory depression in the neonate even after a short period of administration. Prolonged use of buprenorphine during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal. Therefore, buprenorphine should not be used during pregnancy and in women of childbearing potential who are not using effective contraception.
Nursing Mothers
Buprenorphine is excreted in human milk. Studies in rats have shown that buprenorphine may inhibit lactation. Available pharmacodynamic / toxicological data in animals has shown excretion of buprenorphine in milk. Therefore, the use of buprenorphine during lactation should be avoided.
Fertility
No human data on the effect of buprenorphine on fertility are available. In a fertility and early embryonic development study, no effects on reproductive parameters were observed in male or female rats
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Buprenorphine has major influence on the ability to drive and use machines. Even when used according to instructions, buprenorphine patch may affect the patient's reactions to such an extent that road safety and the ability to operate machinery may be impaired. This applies particularly in the beginning of treatment and in conjunction with other centrally acting substances including alcohol, tranquillisers, sedatives and hypnotics. An individual recommendation should be given by the physician. A general restriction is not necessary in cases where a stable
dose is used.
In patients who are affected, such as during treatment initiation or titration to a higher dose, these patients should not drive or use machines, nor for at least 24 hours after the patch has been removed.
This medicine can impair cognitive function and can affect a patient's ability to drive safely. When prescribing this medicine, patients should be told :
- The medicine is likely to affect your ability to drive.
- Do not drive until you know how the medicine affects you.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Serious adverse reactions that may be associated with buprenorphine patch therapy in clinical use are similar to those observed with other opioid analgesics, including respiratory depression (especially when used with other CNS depressants) and hypotension. The following undesirable effects have occurred :
Very common (> 1/10, common (> 1/100, <1/10, uncommon (>/1000, < 1/100), rare (> 1/10,000 < 1/1000), very rare (< 1/10,000 including isolated reports).
Immune system disorders
Uncommon : hypersensitivity
Very rare : anaphylactic reaction, anaphylactoid reaction
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Common : anorexia
Uncommon : dehydration
Psychiatric disorders
Common : confusion, depression, insomnia, nervousness
Uncommon : sleep disorder, restlessness, agitation, depersonalization, euphoric mood, affect lability, anxiety, hallucinations, nightmares
Rare : psychotic disorder, decreased libido
Very rare : drug dependence, mood swings
Nervous system disorders
Very common : headache, dizziness, somnolence Common: paresthesia Uncommon : sedation, dysgeusia, dysarthria, hypoaesthesia, memory impairment, migraine, syncope, tremor, abnormal coordination, disturbance in attention
Rare : balance disorder, speech disorder Very rare: involuntary muscle contractions
Eye disorders
Uncommon : dry eye, blurred vision
Rare : visual disturbance, eyelid oedema, miosis
Ear and labyrinth disorders
Uncommon : tinnitus, vertigo
Very rare : ear pain
Cardiac disorders
Uncommon : angina pectoris, palpitations, tachycardia
Vascular disorders
Common : vasodilation
Uncommon : hypotension, circulatory collapse, hypertension, flushing
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Common : dyspnoea
Uncommon : asthma aggravated, cough, hypoxia, rhinitis, wheezing, hyperventilation, hiccups Rare: respirator y depression, respirator y failure
Gastrointestinal disorders
Very common : constipation, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting
Common : abdominal pain, diarrhoea, dyspepsia
Uncommon : flatulence
Rare : diverticulitis, dysphagia, ileus
Hepatobiliary disorders
Rare : Biliary colic
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Very common : pruritus, erythema
Common : rash, sweating, exanthema
Uncommon : dry skin, face oedema, urticaria Very rare : pustules, vesicles
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Uncommon : Muscle cramp, myalgia, muscular weakness, muscle spasms
Renal and urinary disorders
Uncommon : urinary retention, micturition disorders
Reproductive system and breast disorders
Rare : erectile dysfunction, sexual dysfunction
General disorders and administration site conditions
Very common : application site pruritus, application site reaction
Common : tiredness, asthenia pain, peripheral oedema, application site reaction, erythema at site, rash at site, oedema, chest pain
Uncommon : fatigue, influenza like illness, pyrexia, rigors, malaise, oedema, drug withdrawal syndrome
Rare : application site inflammation
Investigations
Uncommon : alanine aminotransferase increased, weight decreased
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
Uncommon : Accidental injury fall
* In some cases delayed local allergic reactions occurred with marked signs of inflammation. In such cases treatment with buprenorphine patch should be terminated.
Buprenorphine has a low risk of physical dependence. After discontinuation of buprenorphine patch, withdrawal symptoms are unlikely. This may be due to the very slow dissociation of buprenorphine from the opioid receptors and to the gradual decrease of buprenorphine plasma concentrations (usually over a period of 30 hours after removal of the last patch). However, after long-term use of buprenorphine patch, withdrawal symptoms similar to those occurring during opioid withdrawal, cannot be entirely excluded. These symptoms include agitation, anxiety, nervousness, insomnia, hyperkinesia tremor and gastrointestinal disorders.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit / risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to :medico@zuventus.com
Website : https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
Very common : headache, dizziness, somnolence Common: paresthesia Uncommon : sedation, dysgeusia, dysarthria, hypoaesthesia, memory impairment, migraine, syncope, tremor, abnormal coordination, disturbance in attention Rare : balance disorder, speech disorder Very rare: involuntary muscle contractions
4.9 Overdose
Symptoms : Symptoms similar to those of other centrally acting analgesics are to be expected. These include respiratory depression, sedation, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, cardiovascular collapse and marked miosis.
Treatment : Remove any patches from the patient's skin. Establish and maintain a patent airway, assist or control respiration as indicated and maintain adequate body temperature and fluid balance. Oxygen, intravenous fluids, vasopressors and other supportive measures should be employed as indicated.
A specific opioid antagonist such as naloxone may reverse the effects of buprenorphine. The dose of naloxone may be in the range 5 to 12 mg intravenously.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist opioid, acting at the mu opioid receptor. It also has antagonistic activity at the kappa opioid receptor.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Buprenorphine can displace or block morphine binding to µ-receptor thus contributes to reduced opioid dependence. Buprenorphine agonist activity on µ receptor is the primary contributing factor to its analgesic signaling events. Buprenorphine interacts with nociceptin / ORL1 with much lower affinity and thus is unlikely to contribute to analgesic effects at therapeutic doses. Buprenorphine is a potent antagonist of κ-opioid receptor and this interaction could contribute to reduced tolerance and antidepressant like activity.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
There is evidence of enterohepatic recirculation.
Studies in non-pregnant and pregnant rats have shown that buprenorphine passes the blood-brain and placental barriers. Concentrations in the brain (which contained only unchanged buprenorphine) after parenteral administration were 2-3 times higher than after oral administration. After intramuscular or oral administration buprenorphine apparently accumulates in the foetal gastrointestinal lumen - presumably due to biliary excretion, as enterohepatic circulation has not fully developed. Each patch provides a steady delivery of buprenorphine for up to seven days. Steady state is achieved during the first application. After removal of buprenorphine, buprenorphine concentrations decline, decreasing approximately 50% in 12 hours (range 10 - 24 h).
Absorption
Following buprenorphine application, buprenorphine diffuses from the patch through the skin. In clinical pharmacology studies, the median time for “buprenorphine 10 microgram/hour” to deliver detectable buprenorphine concentrations (25 picograms/ml) was approximately 17 hours. Analysis of residual buprenorphine in patches after 7-day use shows 15% of the original load delivered. A study of bioavailability, relative to intravenous administration, confirms that this amount is systemically absorbed. Buprenorphine concentrations remain relatively constant during the 7-day patch application.
Application site
A study in healthy subjects demonstrated that the pharmacokinetic profile of buprenorphine delivered by buprenorphine is similar when applied to upper outer arm, upper chest, upper back or the side of the chest (midaxillary line, 5th intercostal space). The absorption varies to some extent depending on the application site and the exposure is at the most approximately 26 % higher when applied to the upper back compared to the side of the chest.
In a study of healthy subjects receiving buprenorphine repeatedly to the same site, an almost doubled exposure was seen with a 14-day rest period. For this reason, rotation of application sites is recommended, and a new patch should not be applied to the same skin site for 3-4 weeks. In a study of healthy subjects, application of a heating pad directly on the transdermal patch caused a transient 26 - 55% increase in blood concentrations of buprenorphine. Concentrations returned to normal within 5 hours after the heat was removed. For this reason, applying direct heat sources such as hot water bottles, heat pads or electric blankets directly to the patch is not recommended. A heating pad applied to a buprenorphine site immediately after patch removal did not alter absorption from the skin depot.
Distribution
Buprenorphine is approximately 96% bound to plasma proteins. Studies of intravenous buprenorphine have shown a large volume of distribution, implying extensive distribution of buprenorphine. In a study of intravenous buprenorphine in healthy subjects, the volume of distribution at steady state was 430 l, reflecting the large volume of distribution and lipophilicity of the active substance.
Following intravenous administration, buprenorphine and its metabolites are secreted into bile, and within several minutes, distributed into the cerebrospinal fluid. Buprenorphine concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid appear to be approximately 15% to 25% of concurrent plasma concentrations.
Biotransformation and elimination
Buprenorphine metabolism in the skin following buprenorphine application is negligible. Following transdermal application, buprenorphine is eliminated via hepatic metabolism, with subsequent biliary excretion and renal excretion of soluble metabolites. Hepatic metabolism, through CYP3A4 and UGT1A1/1A3 enzymes, results in two primary metabolites, norbuprenorphine and buprenorphine 3-O-glucuronide, respectively. Norbuprenorphine is glucuronidated before elimination. Buprenorphine is also eliminated in the faeces. In a study in post-operative patients, the total elimination of buprenorphine was shown to be approximately 551/h. Norbuprenorphine is the only known active metabolite of buprenorphine.
Effect of buprenorphine on the pharmacokinetics of other active substances
Based on in vitro studies in human microsomes and hepatocytes, buprenorphine does not have the potential to inhibit metabolism catalysed by the CYP450 enzymes CYP1A2, CYP2A6 and CYP3A4 at concentrations obtained with use of buprenorphine 20μg/h transdermal patch. The effect on metabolism catalysed by CYP2C8, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 has not been studied.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
Systemic toxicity and dermal toxicity
In single- and repeat-dose toxicity studies in rats, rabbits, guinea pigs, dogs and minipigs, buprenorphine caused minimal or no adverse systemic events, whereas skin irritation was observed in all species examined. Toxicological data available did not indicate a sensitising potential of the additives of the transdermal patches.
Reproductive and developmental toxicity
No effect on fertility or general reproductive performance was observed in rats treated with buprenorphine. In embryofoetal developmental toxicity studies conducted in rats and rabbits using buprenorphine, no embryofoetal toxicity effects were observed. In a rat pre- and post-natal developmental toxicity study with buprenorphine there was pup mortality, decreased pup body weight and concomitant maternal reduced food consumption and clinical signs.
Genotoxicity
A standard battery of genotoxicity tests indicated that buprenorphine is non-genotoxic.
Carcinogenicity
In long-term studies in rats and mice there was no evidence of any carcinogenic potential relevant for humans.
7.0 Description
Buprenorphine is a semi synthetic derivative of an opiate alkaloid thebaine that is isolated from the poppy Papaver somniferum. Buprenorphine is a hydrophobic molecule and carries a complex chemical structure with multiple chiral centers.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
A pouch of 1 patch.
8.4 Storage and handling instructions
Store in a cool & dry place. Protect from light & moisture.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient counselling information
- These patches contain a strong pain killer.
- Ensure that old patches are removed before applying a new one.
- Patches must not be cut.
- Do not expose the patches to a heat source (such as a hot water bottle).
- Do not soak in a hot bath or take a hot shower whilst wearing a patch.
- If you develop a fever tell your doctor immediately.
- Follow the dosage instructions carefully and only change your patch on the same day and at the same time 7 days later.
- If your breathing becomes shallow and weak take the patch off and seek medical help.
12.0 Date of revision
21 August 2024
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
- What BUPREPLAST is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use BUPREPLAST
- How to use BUPREPLAST
- Possible side effects
- How to store BUPREPLAST
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Bupreplast is and what It is used for
BUPREPLAST contain the active ingredient buprenorphine which belongs to a group of medicines called strong analgesics or ‘painkillers’. They have been prescribed for you by your doctor to relieve moderate, long-lasting pain that requires the use of a strong painkiller. BUPREPLAST should not be used to relieve acute pain.
2. What you need to know before you take Bupreplast
Do not use BUPREPLAST
if you are allergic to buprenorphine or any of the other ingredients of this medicine
if you have breathing problems;
if you are addicted to drugs;
if you are taking a type of medicine known as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (examples include tranylcypromide, phenelzine, isocarboxazid, moclobemide and linezolid), or you have taken this type of medicine in the last two weeks;
if you suffer from myasthenia gravis (a condition in which the muscles become weak);
if you have previously suffered from withdrawal symptoms such as agitation, anxiety, shaking or sweating upon stopping taking alcohol.
BUPREPLAST must not be used to treat symptoms associated with drug withdrawal.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before using BUPREPLAST:
- if you suffer from seizures, fits or convulsions;
- if you have a severe headache or feel sick due to a head injury or increased pressure in your
- skull (for instance due to brain disease). This is because the patches may make symptoms worse or hide the extent of a head injury;
- if you are feeling light-headed or faint;
- if you have severe liver problems;
- if you have ever been addicted to drugs or alcohol;
- if you have a high temperature, as this may lead to larger quantities of the active ingredient being absorbed into the blood than normal.
- if you have depression or other conditions that are treated with antidepressants. The use of these medicines together with BUPREPLAST can lead to serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition (see “Other medicines and BUPREPLAST”).
If you have recently had an operation, please speak to your doctor before using these patches.
Athletes should be aware that this medicine may cause a positive reaction to sports doping control tests.
Children and adolescents
Do not give this medicine to children and adolescents below 18 years.
Other medicines and BUPREPLAST
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
- anti-depressants such as moclobemide, tranylcypromine, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, duloxetine, venlafaxine, amitriptyline, doxepine, or trimipramine. These medicines may interact with BUPREPLAST and you may experience symptoms such as involuntary, rhythmic contractions of muscles, including the muscles that control movement of the eye, agitation, hallucinations, coma, excessive sweating, tremor, exaggeration of reflexes, increased muscle tension, body temperature above 38°C. Contact your doctor when experiencing such symptoms.
- BUPREPLAST must not be used together with a type of medicine known as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (examples include tranylcypromide, phenelzine, isocarboxazid, moclobemide and linezolid), or if you have taken this type of medicine in the last two weeks.
- If you take some medicines such as phenobarbital or phenytoin (medicines commonly used to treat seizures, fits or convulsions), carbamazepine (a medicine to treat seizures, fits or convulsions and certain pain conditions), or rifampicin (a medicine to treat tuberculosis) the effects of BUPREPLAST may be reduced.
- BUPREPLAST may make some people feel drowsy, sick or faint or make them breathe more slowly or weakly. These side effects may be made worse if other medicines that produce the same effects are taken at the same time. These include certain medicines to treat pain, depression, anxiety, psychiatric or mental disorders, medicines to help you sleep, medicines to treat high blood pressure such as clonidine, other opioids (which may be found in painkillers or certain cough mixtures e.g. morphine, dextropropoxyphene, codeine, dextromethorphan, noscapine), antihistamines which make you drowsy, or anaesthetics such as halothane.
- BUPREPLAST must be used with caution if you are also taking benzodiazepines (medicines used to treat anxiety or to help you sleep). This combination may cause serious breathing problems.
Concomitant use of BUPREPLAST and sedative medicines such as benzodiazepines or related drugs increases the risk of drowsiness, difficulties in breathing (respiratory depression), coma and may be life threatening. Because of this, concomitant use should only be considered when other treatment options are not possible.
However, if your doctor does prescribe BUPREPLAST together with sedative medicines the dose and duration of concomitant treatment should be limited by your doctor.
Please tell your doctor about all sedative medicines you are taking, and follow your doctor’s dose recommendation closely. It could be helpful to inform friends or relatives to be aware of the signs and symptoms stated above. Contact your doctor when experiencing such symptoms.
BUPREPLAST with alcohol
Alcohol may make some of the side effects worse and you may feel unwell if you drink alcohol whilst wearing BUPREPLAST. Drinking alcohol whilst using BUPREPLAST may also affect your reaction time.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
There is not sufficient experience regarding the use of buprenorphine in pregnant women. Therefore you should not use BUPREPLAST if you are pregnant or if you could become pregnant during treatment.
Breast-feeding
Buprenorphine, the active substance contained in the transdermal patch, may inhibit milk formation and passes into the breast milk. Therefore, you should not use BUPREPLAST if you are breast-feeding.
Driving and using machines
BUPREPLAST may affect your reactions to such an extent that you may not react adequately or quickly enough in the event of unexpected or sudden occurrences. This applies particularly:
at the beginning of treatment;
if you are taking medicines to treat anxiety or help you sleep;
if your dose is increased.
BUPREPLAST can affect your ability to drive as it may make you sleepy or dizzy.
Do not drive while taking this medicine until you know how it affects you.
It is an offence to drive if this medicine affects your ability to drive.
However, you would not be committing an offence if:
- The medicine has been prescribed to treat a medical or dental problem and
- You have taken it according to the instructions given by the prescriber or in the information provided with the medicine and
- It was not affecting your ability to drive safely
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure whether it is safe for you to drive while taking this medicine.
If you are affected (e.g. feel dizzy, drowsy or have blurred vision), you should not drive or operate machinery whilst using BUPREPLAST, or for 24 hours after removing the patch.
3. How to use Bupreplast
Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
Different strengths of BUPREPLAST are available. Your doctor will decide which strength of BUPREPLAST will suit you best.
During treatment, your doctor may change the patch you use to a smaller or larger one if necessary. Do not cut or divide the patch or use a higher dose than recommended. You should not apply more than two patches at the same time.
If you feel that the effect of the BUPREPLAST is too weak or too strong, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Adults and elderly patients
Unless your doctor has told you differently, attach one BUPREPLAST patch (as described in detail below) and change it every seventh day, preferably at the same time of day.
Your doctor may wish to adjust the dose after 3-7 days until the correct level of pain control has been found. If your doctor has advised you to take other painkillers in addition to the patch, strictly follow the doctor’s instructions, otherwise you will not fully benefit from treatment with BUPREPLAST. The patch should be worn for 3 full days before increasing the dose, this is when the maximum effect of a given dose is established.
Patients with kidney disease/dialysis patients
In patients with kidney disease, no change in dose is necessary.
Patients with liver disease
In patients with liver disease, the effects and period of action of the BUPREPLAST may be affected and your doctor will therefore check on you more closely.
Patients under 18 years of age
BUPREPLAST should not be used in patients below the age of 18 years.
Method of administration
BUPREPLAST transdermal patch is for transdermal use.
BUPREPLAST act through the skin. After application, buprenorphine passes through the skin into the blood.
Before applying the transdermal patch
Apply immediately upon removal from the protective pack.
Choose an area of nonirritated, intact skin on your upper outer arm, upper chest, upper back and side of the chest (See illustrations below). Ask for assistance if you cannot apply the patch yourself.
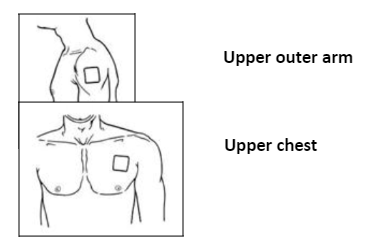

Avoid skin which is red, irritated or has any other blemishes, for instance large scars.
The area of skin you choose must be dry and clean. If necessary, wash it with cold or lukewarm water. Do not use soap, alcohol, oil, lotions or other detergents. After a hot bath or shower, wait until your skin is completely dry and cool. Do not apply lotion, cream or ointment to the chosen area. This might prevent your patch from sticking properly.
Wearing the transdermal patch
You should wear the patch for seven days. Provided that you have applied the patch correctly, there is little risk of it coming off. If the edges of the patch begin to peel off, they may be taped down with a suitable skin tape. You may shower, bathe or swim whilst wearing it.
Do not expose the patch to extreme heat (e.g. heating pads, electric blanket, heat lamps, sauna, hot tubs, heated water beds, hot water bottle, etc) as this may lead to larger quantities of the active ingredient being absorbed into the blood than normal. External heat may also prevent the patch from sticking properly. If you have a high temperature this may alter the effects of BUPREPLAST (see “Warnings and precautions” section above).
In the unlikely event that your patch falls off before it needs changing, do not use the same patch again. Stick a new one on straight away (see “Changing the transdermal patch” below).
Changing the transdermal patch
Take the old transdermal patch off.
Fold it in half with the sticky side inwards.
Open and take out a new patch. Use the empty sachet to dispose of the old patch. Now discard the sachet safely.
Stick a new transdermal patch on a different appropriate skin site (as described above). You should not apply a new patch to the same site for 3-4 weeks.
Remember to change your patch at the same time of day. It is important that you make a note of the time of day.
Duration of treatment
Your doctor will tell you how long you should be treated with the BUPREPLAST. Do not stop treatment without consulting a doctor, because your pain may return and you may feel unwell (see also “If you stop using BUPREPLAST” below).
If you use more BUPREPLAST than you should
As soon as you discover that you have used more patches than you should, remove all patches and call your doctor or hospital straight away. People who have taken an overdose may feel very sleepy and sick. They may also have breathing difficulties or lose consciousness and may need emergency treatment in hospital. When seeking medical attention make sure that you take this leaflet and any remaining patches with you to show to the doctor.
Do not apply additional patches to make up for the forgotten application.
If you stop using BUPREPLAST
If you stop using BUPREPLAST too soon or you interrupt your treatment your pain may return. If you wish to stop treatment, please consult your doctor. They will tell you what can be done and whether you can be treated with other medicines.
Some people may have side effects when they have used strong painkillers for a long time and stop using them. The risk of having effects after stopping BUPREPLAST is very low. However, if you feel agitated, anxious, nervous or shaky, if you are overactive, have difficulty sleeping or digestive problems, tell your doctor.
The pain relieving effect of BUPREPLAST is maintained for some time after removal of the patch. You should not start another opioid analgesic (strong painkiller) within 24 hours after removal of the patch.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Serious side effects that may be associated with BUPREPLAST are similar to those seen with other strong painkillers and include difficulty in breathing and low blood pressure. This medicine can cause allergic reactions, although serious allergic reactions are rare. Remove the patch and tell your doctor immediately if you get any sudden wheeziness, difficulties in breathing, swelling of the eyelids, face or lips, rash or itching especially those covering your whole body. There is a risk that you may become addicted or reliant on BUPREPLAST. In patients treated with buprenorphines, the following other side effects have been reported:
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Headache, dizziness, drowsiness.
- Constipation, feeling or actually being sick.
- Itchy skin
- Rash, redness, itching, inflammation or swelling of the skin at the application site.
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Loss of appetite.
- Confusion, depression, anxiety, difficulty in sleeping, nervousness, shaking (tremors).
- Shortness of breath.
- Abdominal pain or discomfort, diarrhoea, indigestion, dry mouth.
- Sweating, rash, skin eruptions.
- Tiredness, a feeling of unusual weakness, muscle weakness, swelling of hands, ankles or feet.
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Mood swings, restlessness, agitation, a feeling of extreme happiness, hallucinations, nightmares, decreased sexual drive.
- Changes in taste, difficulty in speaking, reduced sensitivity to pain or touch, tingling or numbness.
- Loss of memory, migraine, fainting, problems with concentration or co-ordination.
- Dry eyes, blurred vision.
- A ringing or buzzing sound in the ears, a feeling of dizziness or spinning.
- High or low blood pressure, chest pain, fast or irregular heartbeat.
- Cough, hiccups, wheezing.
- Wind.
- Weight loss.
- Dry skin.
- Spasms, aches and pains.
- Difficulty in beginning the flow of urine.
- Inability to fully empty the bladder.
- Fever.
- An increase in accidental injuries (e.g. falls).
- Withdrawal symptoms such as agitation, anxiousness, sweating or shaking upon stopping using BUPREPLAST.
If you need to have blood tests remind your doctor that you are using BUPREPLAST. This is important because BUPREPLAST may change the way your liver works and this could affect the results of some blood tests.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- Angina (chest pain associated with heart disease).
- Mental disorder.
- Difficulties with balance.
- Swelling of the eyelids or face, a reduction in size of the pupils in the eye.
- Difficulty in breathing, worsening of asthma, over breathing.
- A feeling of faintness, especially on standing up.
- Difficulty in swallowing.
- Local allergic reaction with marked signs of swelling (in such cases treatment should be stopped).
- Swelling and irritation inside the nose.
- Decreased erection, sexual dysfunction.
- A flu like illness.
- Flushing of the skin.
- Dehydration.
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
- Muscle twitching.
- Ear pain.
- Blisters.
Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Seizures, fits or convulsions.
- Inflammation of the bowel wall. Symptoms may include fever, vomiting and stomach pain or discomfort.
- Colicky abdominal pain or discomfort.
- Feeling detached from oneself.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly:
Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top right end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Bupreplast
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and sachet after EXP.
- Store in a cool & dry place. Protect from light & moisture.
- Keep out of reach of children.
- Do not use the patch if the sachet seal is broken.
- Used patches must be folded over on themselves with the adhesive layer inwards, and discarded safely.
- Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What BUPREPLAST contains
BuprePLAST 5 mcg/hr
Each 6.25 cm2 transdermal patch contains :
Buprenorphine Ph. Eur. 5 mg
Excipients q.s.
Each patch delivers 5 mcg/hr Buprenorphine
BuprePLAST 10 mcg/hr
Each 6.25 cm2 transdermal patch contains :
Buprenorphine Ph. Eur. 10 mg
Excipients q.s.
Each patch delivers 10 mcg/hr Buprenorphine
© Zuventus Healthcare Ltd., 2020. All rights reserved.