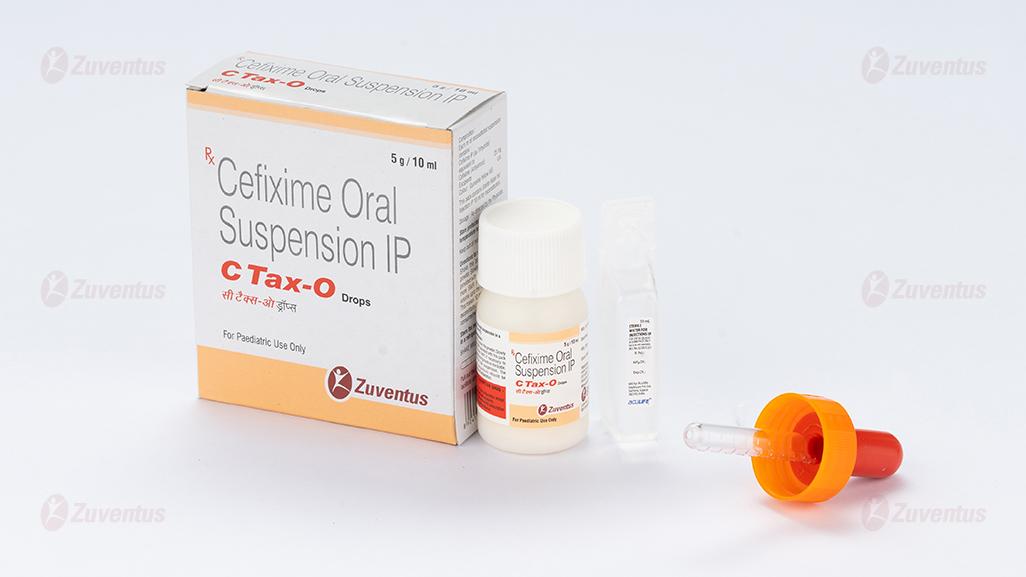
C Tax-O Drops
Therapy Area
Anti Bacterial
1.0 Generic name
Cefixime oral suspension IP
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
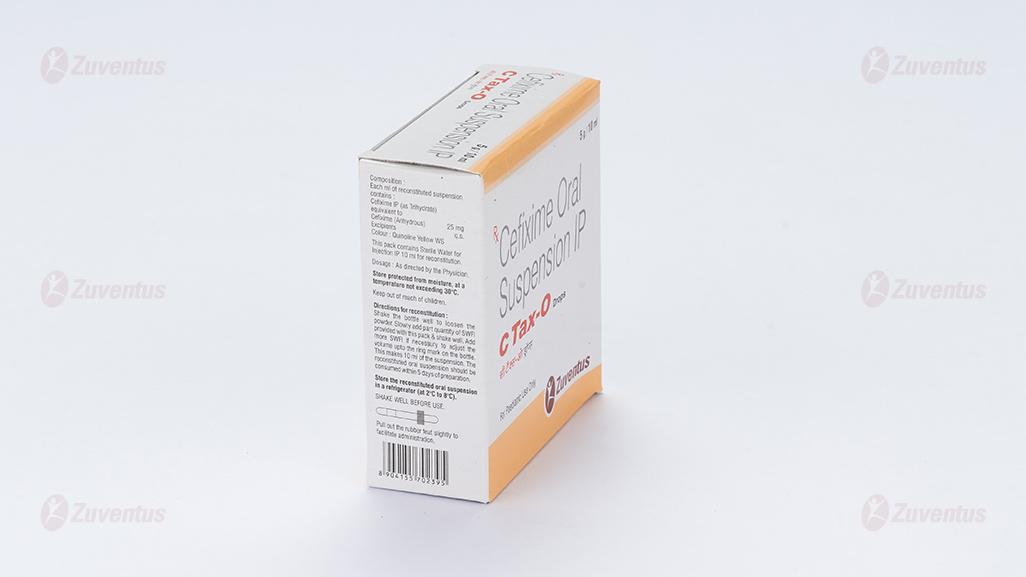
Each ml of reconstituted suspension contains:
Cefixime IP (as Trihydrate)
equivalent to Cefixime (Anhydrous) 25 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Quinoline Yellow WS
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Oral Suspension
25mg/ml
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
- Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections
- Otitis Media
- Pharyngitis and Tonsillitis
- Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis
- Uncomplicated Gonorrhea (cervical/urethral)
- For the treatment of enteric (typhoid) fever
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Pediatric Patients (6 months or older)
The recommended dose is 8 mg/kg/day of the suspension. This may be administered as a single daily dose or may be given in two divided doses, as 4 mg/kg every 12 hours.
Children weighing more than 45 kg or older than 12 years should be treated with the recommended adult dose, 200 to 400 mg daily depending on the severity of infection.
In the treatment of infections due to Streptococcus pyogenes, a therapeutic dosage of cefixime should be administered for at least 10 days.
Safety and effectiveness of cefixime in children aged less than 6 months old have not been established.
Suggested Doses for Pediatric Patients
Renal Impairment
Cefixime may be administered in the presence of impaired renal function. Doses for patients with renal impairment is shown in the table 1.
Table 1: Doses for Patient with Renal Impairment
In patients whose creatinine clearance is less than 20 ml/min, it is recommended that a dose of 200 mg once daily should not be exceeded. The dose and regimen for patients who are maintained on chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis or haemodialysis should follow the same recommendation as that for patients with creatinine clearance of less than 20 ml/min. Neither haemodialysis nor peritoneal dialysis removes significant amounts of drug from the body.
Directions for reconstitution
- Shake the bottle well to loosen the powder.
- Slowly add part quantity of SWFI provided with this pack up to the ring mark on the bottle & shake well.
- Add more SWFI if necessary to adjust the volume up to the ring mark on the bottle.
- This makes 10 ml of the suspension.
- The reconstituted suspension should be consumed within 5 days of preparation.
4.3 Contraindications
Known allergy to cefixime or other cephalosporins.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions (including shock and fatalities) have been reported with the use of cefixime. If this product is to be given to penicillin sensitive patients, caution should be exercised because cross hypersensitivity among beta-lactam antibiotics has been clearly documented and may occur in up to 10% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy. If an allergic reaction to Cefixime for oral suspension occurs, discontinue the drug.
Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhea
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea has been reported with use of Cefixime oral suspension. If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C.difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C.difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Coagulation Effects
Cephalosporins, including Cefixime for oral suspension may be associated with a fall in prothrombin activity. Prothrombin time should be monitored in patients at risk and exogenous vitamin K administered as indicated.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Carbamazepine
Elevated carbamazepine levels have been reported in postmarketing experience when cefixime is administered concomitantly. Drug monitoring may be of assistance in detecting alterations in carbamazepine plasma concentrations.
Warfarin and Anticoagulants
Increased prothrombin time, with or without clinical bleeding, has been reported when cefixime is administered concomitantly.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B
Reproduction studies have been performed in mice and rats at doses up to 40 times the human dose and have revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus due to cefixime. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Labor and Delivery
Cefixime has not been studied for use during labor and delivery. Treatment should only be given if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether cefixime is excreted in human milk. Consideration should be given to discontinuing nursing temporarily during treatment with this drug.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Cefixime has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive or use machines. However, cefixime may cause side effects influencing the capacity of reaction and the ability to drive and use machines.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis and Mouth Ulceration has been seen with Cefixime use.
The most commonly seen adverse reactions were gastrointestinal events, which were reported in 30% of adult
patients on either the twice-daily or the once daily regimen. Individual adverse reactions included diarrhoea (16%), loose or frequent stools (6%), abdominal pain (3%), nausea (7%), dyspepsia (3%), and flatulence (4%).
Diarrhoea has been more commonly associated with higher doses. Other gastrointestinal side effects seen less frequently are vomiting and flatulence. The incidence of gastrointestinal adverse reactions, including diarrhoea and loose stools, in paediatric patients receiving the suspension was comparable with the incidence seen in adult patients receiving tablets.
The following adverse reactions have been reported following the post-approval use of cefixime. Incidence rates were less than 1 in 50 (less than 2%).
Gastrointestinal: pseudomembranous colitis; Hypersensitivity Reactions: Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions (including shock and fatalities), skin rashes, urticaria, drug fever, pruritus, angioedema, and facial edema. Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and serum sickness-like reactions have been reported; Hepatic : Transient elevations in SGPT, SGOT, alkaline phosphatase, hepatitis, jaundice; Renal : Transient elevations in BUN or creatinine, acute renal failure; Central Nervous System : Headaches, dizziness, seizures; Hemic and Lymphatic System : Transient thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, neutropenia, prolongation in prothrombin time, elevated LDH, pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, and eosinophilia; Abnormal Laboratory Tests : Hyperbilirubinemia; Other Adverse Reactions : Genital pruritus, vaginitis, candidiasis, toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Adverse Reactions Reported for Cephalosporin-class Drugs: Allergic reactions, superinfection, renal dysfunction, toxic nephropathy, hepatic dysfunction including cholestasis, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia, hemorrhage, and colitis. Several cephalosporins have been implicated in triggering seizures, particularly in patients with renal impairment when the dosage was not reduced. If seizures associated with drug therapy occur, the drug should be discontinued. Anticonvulsant therapy can be given if clinically indicated.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Gastric lavage may be indicated; otherwise, no specific antidote exists. Cefixime is not removed in significant quantities from the circulation by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Adverse reactions in small numbers of healthy adult volunteers receiving single doses up to 2 g of cefixime did not differ from the profile seen in patients treated at the recommended doses.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Pharmacotherapeutic group: third generation cephalosporin, ATC code: J01DD08
Cefixime is an oral third generation cephalosporin which has marked in vitro bactericidal activity against a wide variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms.
Clinical efficacy has been demonstrated in infections caused by commonly occurring pathogens including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella species, Haemophilus influenzae (beta-lactamase positive and negative), Branhamella catarrhalis (beta-lactamase positive and negative) and Enterobacter species. It is highly stable in the presence of beta-lactamase enzymes.
Most strains of enterococci (Streptococcus faecalis, group D Streptococci) and Staphylococci (including coagulase positive and negative strains and methicillin-resistant strains) are resistant to cefixime. In addition, most strains of Pseudomonas, Bacteroides fragilis, Listeria monocytogenes and Clostridia are resistant to cefixime.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Cefixime is an oral third generation cephalosporin which has marked in vitro bactericidal activity against a wide variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms. Comparative clinical trials of otitis media were conducted in nearly 400 children between the ages of 6 months to 10 years. Streptococcus pneumoniae was isolated from 47% of the patients, Haemophilus influenzae from 34%, Moraxella catarrhalis from 15% and S. pyogenes from 4%. The overall response rate of Streptococcus pneumoniae to cefixime was approximately 10% lower and that of Haemophilus influenzae or Moraxella catarrhalis approximately 7% higher (12% when beta-lactamase positive isolates of H. influenzae are included) than the response rates of these organisms to the active control drugs. In these studies, patients were randomized and treated with either cefixime at dose regimens of 4 mg/kg twice a day or 8 mg/kg once a day, or with a comparator. Sixty-nine to 70% of the patients in each group had resolution of signs and symptoms of otitis media when evaluated 2 to 4 weeks’ post-treatment, but persistent effusion was found in 15% of the patients. When evaluated at the completion of therapy, 17% of patients receiving cefixime and 14% of patients receiving effective comparative drugs (18% including those patients who had Haemophilus influenzae resistant to the control drug and who received the control antibacterial drug) were considered to be treatment failures. By the 2 to 4-week follow-up, a total of 30%-31% of patients had evidence of either treatment failure or recurrent disease.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption: Cefixime suspension, given orally, absorbed about 40% to 50% whether administered with or without food; however, time to maximal absorption is increased approximately 0.8 hours when administered with food. The oral suspension produces average peak concentrations approximately 25% to 50% higher than the tablets, when tested in normal adult volunteers. Two hundred and 400 mg doses of oral suspension produce average peak concentrations of 3 mcg/mL (range 1 to 4.5 mcg/mL) and 4.6 mcg/mL (range 1.9 to 7.7 mcg/mL), respectively, when tested in normal adult volunteers. AUC is greater by approximately 10% to 25% with the oral suspension than with the tablet after doses of 100 to 400 mg, when tested in normal adult volunteers. This increased absorption should be taken into consideration if the oral suspension is to be substituted for the tablet.
Because of the lack of bioequivalence, tablets should not be substituted for oral suspension in the treatment of otitis media. Peak serum concentrations occur between 2 and 6 hours following oral administration of 400 mg of cefixime suspension. Peak serum concentrations occur between 2 and 5 hours following a single administration of 200 mg of suspension.
Distribution: Serum protein binding is concentration independent with a bound fraction of approximately 65%. In a multiple dose study conducted with a research formulation which is less bioavailable than the tablet or suspension, there was little accumulation of drug in serum or urine after dosing for 14 days. Adequate data on CSF levels of cefixime are not available.
Metabolism and Excretion: There is no evidence of metabolism of cefixime in vivo. Approximately 50% of the absorbed dose is excreted unchanged in the urine in 24 hours. In animal studies, it was noted that cefixime is also excreted in the bile in excess of 10% of the administered dose. The serum half-life of cefixime in healthy subjects is independent of dosage form and averages 3 to 4 hours but may range up to 9 hours in some normal volunteers.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before giving your child this medicine, because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your child’s doctor or your pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for your child. Do not pass it on to others.
- It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as your child’s. If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please tell your child’s doctor or your pharmacist
What is in this leaflet:
- What C Tax-O Oral drops is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you give C Tax-O Oral drops to your child
- How to give C Tax-O Oral drops to your child
- Possible side effects
- How to store C Tax-O Oral drops
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What C Tax-O Oral drops is and what it is used for.
C Tax-O Oral drops contains a medicine called cefixime. This belongs to a group of antibiotics called ‘cephalosporins’.
C Tax-O Oral Drops Pack contains the bottle with powder and sterile water for injection [SWFI] which should be mixed for consumption.
C Tax-O Oral drops is used to treat infections caused by bacteria. These include treating infections in the upper respiratory tract (Ear, Nose, Throat, Lung infections) and also in the urinary tract infections.
2. What you need to know before you give C Tax-O Oral drops to your child.
Do not give this medicine to your child and tell their doctor if: Your child is allergic (hypersensitive) to cefixime, any other cephalosporin antibiotics including penicillin or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine (see Section 6: Further information). Signs of an allergic reaction include: a rash, swallowing or breathing problems, swelling of the lips, face, throat and tongue. Do not give this medicine to your child if the above applies to them. If you are not sure, talk to your child’s doctor or your pharmacist before giving C Tax-O Oral drops.
Warnings and precautions
Take special care with C Tax-O Oral drops
Check with your child’s doctor or your pharmacist before giving this medicine if your child:
- Has ever had colitis
- Has allergic tendencies such as asthma, rash or hives
- Has severe kidney problems
- Is under 6 months, as the safety for use has not been established in this group.
If you are not sure if any of the above apply to your child, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before giving this medicine.
Medicines such as C Tax-O Oral drops, make you more susceptible to a condition called “encephalopathy”. You may have sudden involuntary muscle contractions, dizziness, feel less alert or begin to lose consciousness (see section 4).
Other medicines and C Tax-O Oral drops
Please tell your child’s doctor or your pharmacist if your child is taking or has recently taken any other medicines.
This includes medicines you buy without a prescription, including herbal medicines. This is because C Tax-O Oral drops can affect the way some other medicines work. Also some medicines can affect the way C Tax-O Oral drops works.
In particular, tell your child’s doctor if they are taking:
- Medicines to thin the blood such as warfarin
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
This medicine is specially made for children. However, if you are taking this medicine as an adult, you should talk to your doctor before taking this medicine if:
- You are pregnant, might become pregnant or think you may be pregnant
- You are breast-feeding or planning to breast feed
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine if you are pregnant or breast-feeding.
Driving and using machines
This medicine is specially made for children. However, if you are taking this medicine as an adult, you may start to move abnormally, suffer from sudden involuntary muscle contractions, dizziness or feel less alert. If this happens, do not drive or use any tools or machines.
Tests
If your child requires any tests (such as blood or urine tests) while taking this medicine, please make sure your child’s doctor knows that your child is taking C Tax-O Oral drops.
3. How to give C Tax-O Oral drops to your child.
Having this medicine
Always use C Tax-O Oral drops exactly as your child’s doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
The amount of medicine given will depend on the weight and age of your child
- Shake the bottle to loosen the powder.
- Slowly add part quantity of sterile water (SWFI) provided with pack and shake well. Add more SWFI to adjust the level up to the ring mark. This makes 10 ml of the suspension.
- Give this medicine to your child by mouth
- The dose can be given in one go or the dose can be divided into two and given at different times
- If you feel the effect of the medicine is too weak or too strong, do not change the dose yourself, but ask your child’s doctor
- Shake the bottle well before use and make sure the bottle is tightly closed after use
Carefully read the label from the pharmacist. Ask your pharmacist if you are not sure about the dose to give. The medicine should be taken for the prescribed number of days.
How much to give
The usual dose is:
The recommended dose is 8 mg/kg/day. This may be administered as a single daily dose or may be given in two divided doses, as 4 mg/kg every 12 hours.
| 25 mg/ 1 ml | ||
|---|---|---|
| Patient weight (kg) | Dose/Day (mg) | Dose/Day (ml) |
| 5 to 7.5 | 50 | 2 |
| 7.6 to 10 | 80 | 3.2 |
| 10.1 to 12.5 | 100 | 4 |
| 12.6 to 20.5 | 150 | 6 |
| 20.6 to 28 | 200 | 8 |
| 28.1 to 33 | 250 | 10 |
| 33.1 to 40 | 300 | 12 |
| 40.1 to 45 | 350 | 14 |
| 45.1 or greater | 400 | 16 |
Children weighing more than 45 kg or older than 12 years should be treated with the recommended adult dose, 200 to 400 mg daily depending on the severity of infection.
If your child has more C Tax-O Oral drops than they should
If your child has too much of this medicine, talk to your child’s doctor straight away. They may have symptoms of encephalopathy - moving abnormally, sudden involuntary muscle contractions, dizziness or feeling less alert.
If you forget to give C Tax-O Oral drops to your child
If you forget to give your child a dose, give it as soon as you remember it. However, if it is nearly time for the next dose, skip the missed dose. Do not give a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop giving C Tax-O Oral drops to your child
Do not stop giving your child the medicine without talking to your doctor. Your child should not stop taking C Tax-O Oral drops just because he or she feels better. This is because the infection may come back or get worse again. If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, C Tax-O Oral drops can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Tell your doctor straight away or go to the nearest hospital casualty department if you notice any of the following serious side effects – your child may need urgent medical treatment:
If your child has an allergic reaction. The signs may include: a rash, joint pain, swallowing or breathing problems, swelling of your lips, face, throat or tongue
Severe allergic reaction including blistering or bleeding of the skin around the lips, eyes, mouth, nose and genitals or layers of skin peeling off. Also flu-like symptoms, aching muscles and fever. These may be a sign of serious allergies called 'Stevens-Johnson syndrome', 'toxic epidermal necrolysis', "serum sickness like reaction", white blood cell disorder (eosinophilia) or 'drug rash with white blood cell disorder (eosinophilia) and systemic symptoms (DRESS)'
If your child gets a skin rash or skin lesions with a pink/red ring and a pale centre which may be itchy, scaly or filled with fluid. The rash may appear especially on the palms or soles of your feet. These could be signs of a serious allergy to the medicine called ‘erythema multiforme’
If your child gets infections more easily than usual. This could be because of a blood disorder. This normally gets better after stopping the medicine
If your child bruises or bleeds more easily than normal. This could be because of a blood disorder. This normally gets better after stopping the medicine
If your child gets nose bleeds, bleeding gums, chills, tiredness, pale skin (often with a yellow tinge), shortness of breath. This may be due to haemolytic anaemia
Your child may have sudden involuntary muscle contractions, dizziness, feel less alert or begin to lose consciousness. This is called “encephalopathy”
Stop giving your child this medicine and contact the child’s doctor without delay if they get:
Severe watery diarrhoea that will not stop and your child is feeling weak and has a fever. This may be something called ‘Pseudomembranous colitis’.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if any of the following side effects get serious or lasts longer than a few days
Feeling sick (nausea) or being sick (vomiting)
Stomach pains, indigestion or wind
Headaches
Feeling dizzy
Feeling itchy in the genital or vaginal area
Facial swelling
Fever Shortness of breath
Yellowing of the skin
Fits (convulsions) - Frequency not known
Tell your child’s doctor if any of the side effects gets serious or lasts longer than a few days, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet
Blood tests
C Tax-O Oral drops can cause blood clots or changes to the way the liver and kidney work (kidney failure is rare). This would be shown up in blood tests. This is not common and goes back to normal after stopping this medicine.
If you think your child is reacting badly to the medicine or having any problems, then discuss it with the child’s doctor or your pharmacist.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine
5. How to Store C Tax-O Oral drops
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. After the powder has been mixed with water, keep the bottles of medicine in a refrigerator (at 2 ºC to 8 ºC).
Do not freeze.
After being mixed with water, C Tax-O Oral drops can be used for 14 days. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the bottle. Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other Information
What C Tax-O Oral drops contains
Each ml of reconstituted suspension contains:
Cefixime (as Trihydrate) equivalent to
Cefixime (Anhydrous) 25 mg
Packing
C Tax-O Oral Drops: A bottle of 5 g with SWFI IP 10 ml
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Lifetime studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential have not been conducted. Cefixime did not cause point mutations in bacteria or mammalian cells, DNA damage, or chromosome damage in vitro and did not exhibit clastogenic potential in vivo in the mouse micronucleus test. In rats, fertility and reproductive performance were not affected by cefixime at doses up to 25 times the adult therapeutic dose.
7.0 Description
Cefixime is a semisynthetic, cephalosporin antibacterial for oral administration. Chemically, it is (6R,7R)-7-[2-(2-Amino-4-thiazolyl)glyoxylamido]-8-oxo-3-vinyl-5-thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 72-(Z)-[O-(carboxy methyl) oxime]trihydrate. Molecular weight- 507.50 as the trihydrate.
Chemical Formula is C16H15N5O7S2.3H2O
The structural formula for cefixime is:
8.0 Pharmaceutical properties
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not Applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on pack
8.3Packaging information
C Tax-O drops: A bottle of 10 ml. For pediatric use only.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Shake well before use. Store in a cool & dry place. Protect from light. Keep out of reach of children. Store the reconstituted oral suspension in a refrigerator (at 2°C to 8°C).
9.0 Patient counselling information
Counsel patients that antibacterial drugs, including cefixime, should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When cefixime is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed.
Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may: (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by cefixime for oral suspension or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Advise patients that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterial drugs which usually ends when the antibacterial drug is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibacterial drugs, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibacterial drug. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
12.0 Date of revision of the text
20th September 2024