C Tax-O XL 200
Therapy Area
Anti Infective
1.0 Generic name
Cefixime, Cloxacillin & Lactic Acid Bacillus Tablets
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
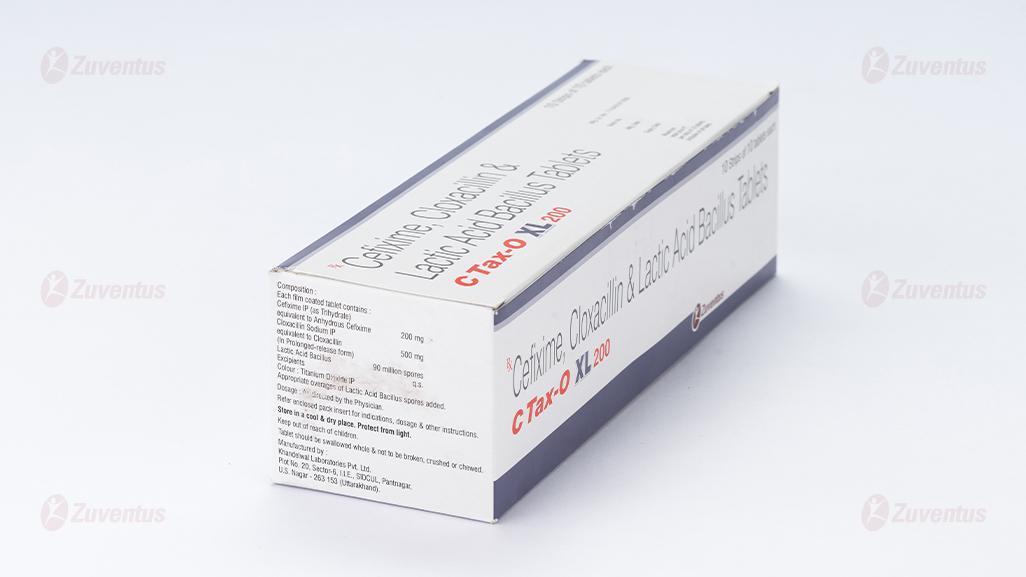
Each film coated tablet contains:
Cefixime IP (as Trihydrate)
equivalent to Anhydrous Cefixime…………... 200 mg
Cloxacillin Sodium IP equivalent to Cloxacillin……………………...500 mg
(In Prolonged-release form)
Lactic Acid Bacillus …………………………90 million spores
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Titanium Dioxide IP
Appropriate overages of Lactic Acid Bacillus spores added.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Film coated tablet
Cefixime (200mg) Cloxacillin (500mg) & Lactic Acid Bacillus (90 million spores)
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic Indication
For the treatment of adult patients with upper & lower respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections.
4.2 Posology and Method of Administration
Adults: the recommended dosage is 1 tablet twice daily. The usual course of treatment is 7 days. This may be continued for up to 14 days if required.
4.3 Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the penicillin, or to cephalosporin antibiotics or to any of the components listed in the formulation.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Cefixime
Encephalopathy: Beta-lactams, including cefixime, predispose the patient to encephalopathy risk (which may include convulsions, confusion, impairment of consciousness, movement disorders), particularly in case of overdose or renal impairment. Severe cutaneous adverse reactions: Severe cutaneous adverse reactions such as toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) have been reported in some patients on cefixime. When severe cutaneous adverse reactions occur, cefixime should be discontinued and appropriate therapy and/or measures should be taken. Cefixime should be given with caution to patients who have shown hypersensitivity to other drugs.
Hypersensitivity to penicillins: As with other cephalosporins, cefixime should be given with caution to patients with a history of hypersensitivity to penicillin, as there is some evidence of partial cross- sensitization between the penicillins and cephalosporins. Patients have had severe reactions (including anaphylaxis) to both classes of drugs. If an allergic effect occurs with cefixime, the drug should be discontinued and the patient treated with appropriate agents if necessary.
Haemolytic anaemia: Drug-induced haemolytic anaemia, including severe cases with a fatal outcome, has been described for cephalosporins (as a class). The recurrence of haemolytic anaemia after re-administration of cephalosporins in a patient with a history of cephalosporin (including cefixime) –associated haemolytic anaemia has also been reported.
Acute renal failure: As with other cephalosporins, cefixime may cause acute renal failure including tubulointerstitial nephritis as an underlying pathological condition. When acute renal failure occurs, cefixime should be discontinued and appropriate therapy and/or measures should be taken.
Renal impairment: Cefixime should be administered with caution in patients with markedly impaired renal function.
Paediatric use: Safety of cefixime in premature or new-born infant has not been established.
Cloxacillin
Hematologic: During long-term therapy, renal, hepatic and hematopoietic functions should be checked periodically.
Hepatic: During long-term therapy, renal, hepatic and hematopoietic functions should be checked periodically.
Immune: Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactoid) reactions have been reported in patients receiving penicillin or cephalosporin
therapy. These reactions are more apt to occur in individuals with a history or sensitivity to multiple allergens. Careful inquiry should be made concerning previous hypersensitivity to reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins or other allergens. If allergic or anaphylactic reactions occurs, discontinue treatment and administer the usual agents, e.g. antihistamines, pressor amines, corticosteroids.
Neurologic: The passage of any penicillin from blood into brain is facilitated by inflamed meninges and during cardiopulmonary bypass. In the presence of such factors, particularly in renal failure when high serum concentration can be attained, CNS adverse effects including myoclonia, convulsive seizures and depressed consciousness can be expected. Although this complication has not been reported with cloxacillin, it should be anticipated.
Renal: During long-term therapy, renal, hepatic and hematopoietic functions should be checked periodically.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Cefixime
Anticoagulants: In common with other cephalosporins, increases in prothrombin times have been noted in a few patients. Care should therefore be taken in patients receiving anticoagulation therapy. Cefixime should be administered with caution to patients receiving coumarin-type anticoagulants, e.g. warfarin potassium. Since cefixime may enhance effects of the anticoagulants, prolonged prothrombin time with or without bleeding may occur.
Other forms of interaction: A false positive reaction for glucose in the urine may occur with Benedict's or Fehling's solutions or with copper sulphate test tablets, but not with tests based on enzymatic glucose oxidase reactions. A false positive direct Coombs test has been reported during treatment with cephalosporin antibiotics, therefore it should be recognised that a positive Coombs test may be due to the drug.
Cloxacillin
Probenecid: As with other penicillins, concurrent administration of probenecid enhances the serum concentration of cloxacillin.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Lactation:
It is not known whether cefixime is excreted in human milk. Consideration should be given to discontinuing nursing temporarily during treatment with this drug.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
In the case of side effects such as encephalopathy (which may include convulsion, confusion, impairment of consciousness, movement disorders), the patient should not operate machines or drive a vehicle.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Cefixime
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis and Mouth ulceration has been reported with Cefixime use.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: eosinophilia, hypereosinophilia, agranulocytosis, leucopenia, neutropenia, granulocytopenia, haemolytic anaemia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytosis.
Gastrointestinal disorders: abdominal pain, diarrhea, dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, flatulence.
Hepatobiliary disorders: jaundice
Infections and infestations: pseudomembranous colitis
Investigations: aspartate aminotransferase increased, alanine aminotransferase increased, blood bilirubin increased, blood urea increased, blood creatinine increased
Nervous system disorders: dizziness, headache, cases of convulsions have been reported with cephalosporins including cefixime, Beta-lactams, including cefixime, predispose the patient to encephalopathy risk (which may include convulsions, confusion, impairment of consciousness, movement disorders), particularly in case of overdose or renal impairment.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: dyspnoea
Renal and urinary disorders: Renal failure acute including tubulointerstitial nephritis as an underlying pathological condition
Immune system disorders, administrative site conditions, skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: anaphylactic reaction, serum sickness-like reaction, drug rash with eaosinophilia and systemic symptoms, pruritus, rash, drug fever, arthralgia, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, angio-oedema, urticaria, pyrexia, face oedema, genital pruritus, vaginitis.
Cloxacillin
It may be expected the most common untoward reactions will be related to sensitivity. They are more likely to occur in individuals who have previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to penicillins and cephalosporins and in those with a history of allergy, asthma, hay fever or urticaria. All degrees of hypersensitivity, including fatal anaphylaxis, have been reported with penicillin.
Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, epigastric discomfort, flatulence and loose stools have been noted in some patients.
Hematologic: Eosinophilia, leucopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic, purpura, neutropenia and agranulocytosis have been reported during therapy with penicillins. These reactions are usually reversible on discontinuation of therapy and are believed to be hypersensitivity phenomena.
Immune: Allergic reactions (rash, urticaria) including wheezing and sneezing have been reported.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
4.9 Overdose
There is a risk of encephalopathy in cases of administration of beta-lactam antibiotics, including cefixime, particularly in case of overdose or renal impairment. Adverse reactions seen at dose levels up to 2 g. Cefixime in normal subjects did not differ from the profile seen in patients treated at the recommended doses. Cefixime is not removed from the circulation in significant quantities by dialysis. No specific antidote exists. General supportive (Gastric lavage) measures are recommended.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Mechanism of action
Cefixime is a 3rd generation oral cephalosporin that has excellent activity against variety of Gram -ve organisms and a few Gram +ve organisms like streptococci spp. but, no activity against staphylococci. Cloxacillin is an acid resistant, β-lactamase resistant isoxazolyl penicillin with a spectrum of activity particularly against staphylococci and streptococci. Cloxacillin is resistant to degradation by penicillinase, thus useful against penicillinase-producing staphylococci.
In order to enhance the antibacterial coverage of cefixime against Gram +ve organisms, the addition of cloxacillin helps in Gram +ve coverage. Thus providing broader spectrum of antibiotic coverage.
Clinical evidence demonstrated the synergistic effect of cloxacillin and cefixime used in combination against S. pneumoniae and H. influenzae, the commonest causes of community-acquired pneumonia. Due to this synergistic activity dosage can be given in reduced frequency, thus increasing patient compliance. The usual dosage for this combination is 200 mg cefixime along with 500 mg cloxacillin to be given twice a day.
Lactobacillus preparations have been shown to offset the detrimental effects on the microflora produced with antibiotic administration. The normal bacterial flora of gut that is disturbed by the antibiotic is replenished by the addition of lactobacillus. Lactobacillus spores maintain or restore gut micro-ecology during or after antibiotic treatment. There is an increasing evidence for the effectiveness of probiotics with antimicrobial therapy in preventing or treating antibiotic associated diarrhea.
Pharmacodynamic properties
Cefixime: Cefixime has marked in vitro bactericidal activity against a wide variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms. As with other cephalosporins, bactericidal action of cefixime results from inhibition of cell-wall synthesis. Clinical efficacy has been demonstrated in infections caused by commonly occurring pathogens including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella species, Haemophilus influenzae (beta-lactamase positive and negative), Branhamella catarrhalis (beta-lactamase positive and negative) and Enterobacter species. It is highly stable in the presence of beta-lactamase enzymes. Most strains of enterococci (Streptococcus faecalis, group D Streptococci) and Staphylococci (including coagulase positive and negative strains and meticillin-resistant strains) are resistant to cefixime. In addition, most strains of Pseudomonas, Bacteroides fragilis, Listeria monocytogenes and Clostridia are resistant to cefixime. Cloxacillin: Cloxacillin exerts a bactericidal action against susceptible microorganisms during the stage of active multiplication. It acts through the inhibition of biosynthesis of cell wall mucopeptides. Cloxacillin displays less intrinsic antibacterial activity and a narrower spectrum than penicillin G.
Lactobacillus: Lactobacillus is an aerobic gram-positive, ubiquitous inhabitant of the human oral cavity, vagina and gastrointestinal tract. It inhibits the colonization of pathogenic bacteria upon the intestinal epithelium. The inhibitory process known as 'competitive exclusion' can be expanded by the competition for the adherence sites of the intestinal mucosa between pathogens and lactobacilli and by the inhibitory substance.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Cefixime: The absolute oral bioavailability of cefixime is in the range of 22-54%. Absorption is not significantly modified by the presence of food. From in vitro studies, serum or urine concentrations of 1 mcg/mL or greater were considered to be adequate for most common pathogens against which cefixime is active. Typically, the peak serum levels following the recommended adult or paediatric doses are between 1.5 and 3 mcg/mL. Little or no accumulation of cefixime occurs following multiple dosing. The pharmacokinetics of cefixime in healthy elderly (age > 64 years) and young volunteers (11-35) compared the administration of 400 mg doses once daily for 5 days. Mean C and AUC values were slightly greater in the elderly. Elderly patients may be given the same max dose as the general population.
Cefixime is predominantly eliminated as unchanged drug in the urine. Glomerular filtration is considered the predominant mechanism. Metabolites of cefixime have not been isolated from human serum or urine.
Serum protein binding is well characterised for human and animal sera; cefixime is almost exclusively bound to the albumin fraction, the mean free fraction being approximately 30%. Protein binding of cefixime is only concentration dependent in human serum at very high concentrations which are not seen 14 following clinical dosing. Transfer of C-labelled cefixime from lactating rats to their nursing offspring through breast milk was quantitatively small (approximately 1.5% of the mothers' body content of cefixime in the pup). No data are available on secretion of cefixime in human breast milk. Placental transfer of cefixime was small in pregnant rats dosed with labelled cefixime.
Cloxacillin: Cloxacillin is stable in an acid medium and is approximately 50% absorbed orally. After an oral dose of 500mg cloxacillin, a peak serum level of about 8 micrograms/mL is reached in about 1 hour. The serum level after i.m. cloxacillin is approximately twice that obtained when the same dose is given orally to fasting adults. Food in the stomach or small intestine reduces absorption and peak serum levels are approximately 50% those obtained after fasting. As with other penicillins, concurrent administration of probenecid enhances the serum concentration. Once absorbed, approximately 94% are bound to plasma proteins. After oral administration, roughly 20% of the dose is excreted in the urine, together with one or more active metabolites as yet unidentified. The half-life of elimination is about 30 minutes.
Lactobacillus: No pharmacokinetic data is available.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
There are no pre-clinical data of relevance to the prescriber which are additional to that already included in other sections.
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
7.0 Description
C Tax-O XL 200 is a combination of three medicines: Cefixime, Cloxacillin, and Lactobacillus.
Cefixime is a semisynthetic, cephalosporin antibacterial for oral administration. Chemically, it is ( 6R,7R)-7-[2-(2-Amino-4-thiazolyl)glyoxylamido]-8-oxo-3-vinyl-5-thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7 2-( Z)-[ O-(carboxy methyl) oxime] trihydrate.
Molecular weight: 507.50 as the trihydrate.
Chemical Formula: C16H15N5O7S2.3H2O The structural formula for cefixime is:
Cloxacillin is a semisynthetic penicillin antibiotic carrying a 3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-carboxamido group at position 6. It is a semi-synthetic penicillin antibiotic which is a chlorinated derivative of [oxacillin].
Molecular Weight: 435.9 g/mol
Molecular Formula:C19H18ClN3O5S
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack
8.3 Packaging information
A strip of 10 tablets
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store in a cool & dry place. Protect from light.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient counselling information
- Counsel patients that antibacterial drugs, including cefixime, should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When cefixime is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may: (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by cefixime for oral suspension or cefixime chewable tablets or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
- Advise patients that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterial drugs which usually ends when the antibacterial drug is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibacterial drugs, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibacterial drug. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
11.0 Date of revision
July 2024
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
- What C Tax-O XL 200 is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you take C Tax-O XL 200
- How to take C Tax-O XL 200
- Possible side effects
- How to store C Tax-O XL 200
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What C Tax-O XL 200 is and what it is used for
C Tax-O XL 200 Tablets is a combination of three medicines: Cefixime, Cloxacillin, and Lactobacillus. Cefixime belongs to a group of antibiotics called ‘cephalosporins’. Cloxacillin is a semisynthetic penicillin antibiotic. It has a role as an antibacterial agent and an antibacterial drug.
Lactic acid bacillus, often referred to as Lactobacillus species, are commonly used probiotics which are considered to be beneficial or "friendly" bacteria. They have shown promise in managing antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) by restoring gut microbiota. Antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the gut, leading to diarrhea. Lactic acid bacillus probiotics help restore this balance by replenishing beneficial bacteria that may have been depleted.
C Tax-O XL 200 is used to treat infections caused by bacteria. These include infections of the: Ear, Nose, sinuses (such as sinusitis), Throat (such as tonsillitis, pharyngitis), Chest and lungs (such as bronchitis, pneumonia), infections involving the skin, subcutaneous tissue, fascia, and muscles.
2. What you need to know before you take C Tax-O XL 200.
Do not take C Tax-O XL 200 if:
You are allergic to cefixime, cloxacillin, any other cephalosporin or penicillin antibiotics or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
Signs of an allergic reaction include: a rash, swallowing or breathing problems, swelling of the lips, face, throat and tongue.
Do not take this medicine if the above applies to you. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking C Tax-O XL 200.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking C Tax-O XL 200 if:
- You have ever had colitis
- You have kidney problems.
If you are not sure if any of the above apply to you, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
Severe skin problems such as Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN), Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) and Acute Generalised Exanthematous Pustulosis (AGEP) have been reported with cefixime. If you develop severe skin reactions or any of the reactions listed in section 4, stop treatment immediately and contact your doctor or healthcare professional.
Other medicines and C Tax-O XL 200
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. This includes medicines you buy without a prescription, including herbal medicines. This is because
C Tax-O XL 200 can affect the way some other medicines work. Also, some medicines can affect the way S C Tax-O XL 200 works.
In particular, tell your doctor if you are taking the following:
- Medicines to thin the blood such as warfarin.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Driving and using machines
This medicine can cause symptoms including fits (convulsions), feeling confused, feeling less alert or aware of things than usual, unusual muscle movements or stiffness. If you experience any of these effects don’t drive or use machinery.
Medical Tests
If you require any tests (such as blood or urine tests) while taking this medicine, please make sure your doctor knows that you are taking C Tax-O XL 200.
3. How to take C Tax-O XL 200.
Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
- Take this medicine by mouth.
- Swallow tablets whole with a drink of water.
- If you feel the effect of the medicine is too weak or too strong, do not change the dose yourself, but ask your doctor.
Carefully read the label from the pharmacist. Ask your pharmacist if you are not sure about the dose to take. The medicine should be taken for the prescribed number of days.
The recommended dose for Adults, Elderly: 1 tablets two times daily.
People with kidney problems
- Your doctor may prescribe a lower dose.
If you take more C Tax-O XL 200 than you should
If you have too much of this medicine, talk to your doctor straight away.
If you forget to take C Tax-O XL 200
If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as you remember it. However, if it is nearly time for the next dose, skip the missed dose. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop taking C Tax-O XL 200
Do not stop taking this medicine without talking to your doctor. You should not stop taking C Tax-O XL 200 just because you feel better. This is because the infection may come back or get worse again.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Tell your doctor straight away or go to the nearest hospital casualty department if you notice any of the following serious side effects – you may need urgent medical treatment:
- You have an allergic reaction. The signs may include: a rash, joint pain, swallowing or breathing problems, swelling of your lips, face, throat or tongue.
- SJS/TEN symptoms may include blistering, peeling or bleeding on any part of the skin (including the lips, eyes, mouth, nose, genitals, hands or feet). Also, flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills or aching muscles.
- DRESS symptoms may include flu-like symptoms and a widespread rash with a high body temperature and enlarged lymph nodes. Abnormal blood test results may include increased levels of liver enzymes and an increase in a type of white blood cell (eosinophilia) and enlarged lymph nodes.
- AGEP symptoms may include a red, scaly, widespread rash with bumps under the skin (including your skin folds, chest, abdomen (including stomach), back and arms) and blisters accompanied by fever.
- Erythema multiforme symptoms include skin rash or skin lesions with a pink/red ring and a pale centre which may be itchy, scaly or filled with fluid. The rash may appear especially on the palms or soles of your feet.
- You get infections more easily than usual. This could be because of a blood disorder. This normally gets better after stopping the medicine.
- You bruise or bleed more easily than normal. This could be because of a blood disorder. This normally gets better after stopping the medicine.
- If your child gets nose bleeds, bleeding gums, chills, tiredness, pale skin (often with a yellow tinge), shortness of breath. This may be due to haemolytic anaemia.
- Changes in the way the kidneys are working or blood in your child’s urine.
- Fits (convulsions)
- A brain condition with symptoms including fits (convulsions), feeling confused, feeling less alert or aware of things than usual, unusual muscle movements or stiffness. This may be something called encephalopathy. This side effect is more likely if you have taken an overdose or you already have a problem with your kidneys. Stop taking this medicine and contact your doctor without delay if you get:
- Severe watery diarrhoea that will not stop and you are feeling weak and have a fever. This may be something called ‘Pseudomembranous colitis’. Tell your doctor or pharmacist if any of the following side effects get serious or lasts longer than a few days:
- Feeling sick (nausea) or being sick (vomiting)
- Stomach pains, indigestion or wind
- Headaches
- Feeling dizzy
- Feeling itchy in the genital or vaginal area
Blood tests
C Tax-O XL 200 can cause blood clots or small changes to the way the liver and kidney work. This would be shown up in blood tests. This is not common and goes back to normal after stopping this medicine.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page. https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store C Tax-O XL 200
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the label and blister pack after EXP. Store below 25°C.
Do not throw away medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What C Tax-O XL 200 contains
Each film coated tablet contains:
Cefixime (as Trihydrate) …………... 200 mg
Cloxacillin ………………………….500 mg
Lactic Acid Bacillus ………………...90 million spores
Packaging information
10 tablets in 1 strip
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Zuventus Healthcare Limited
Zuventus House Plot No. Y2, CTS No: 358/A2,
near Nahur Railway Station, off Raycon IT Park Road,
Nahur West, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400078
This leaflet was last revised in July 2024