C Tax-OF Tablets
Therapy Area
Anti Infective
1.0 Generic name
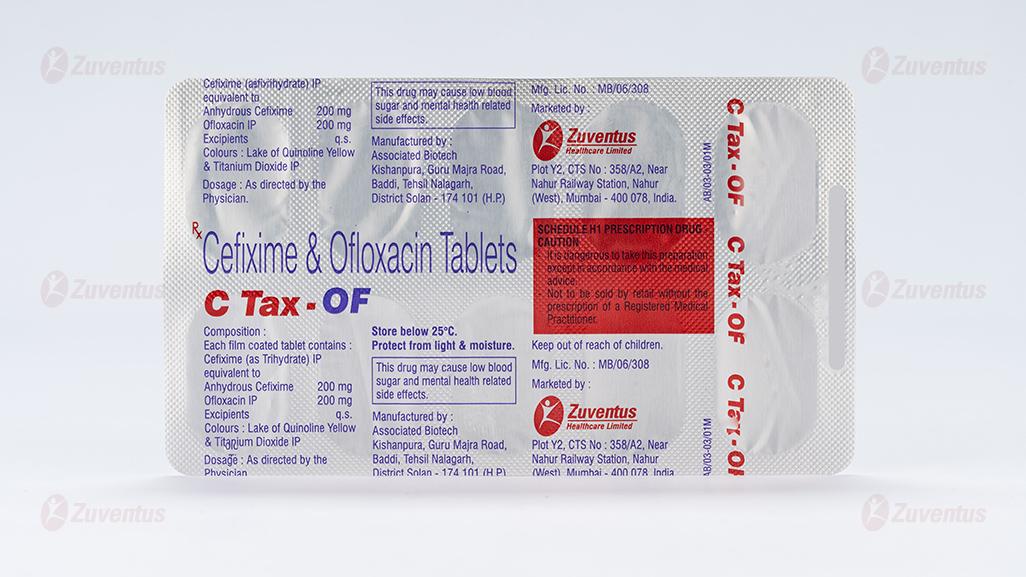
Cefixime & Ofloxacin Tablets
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
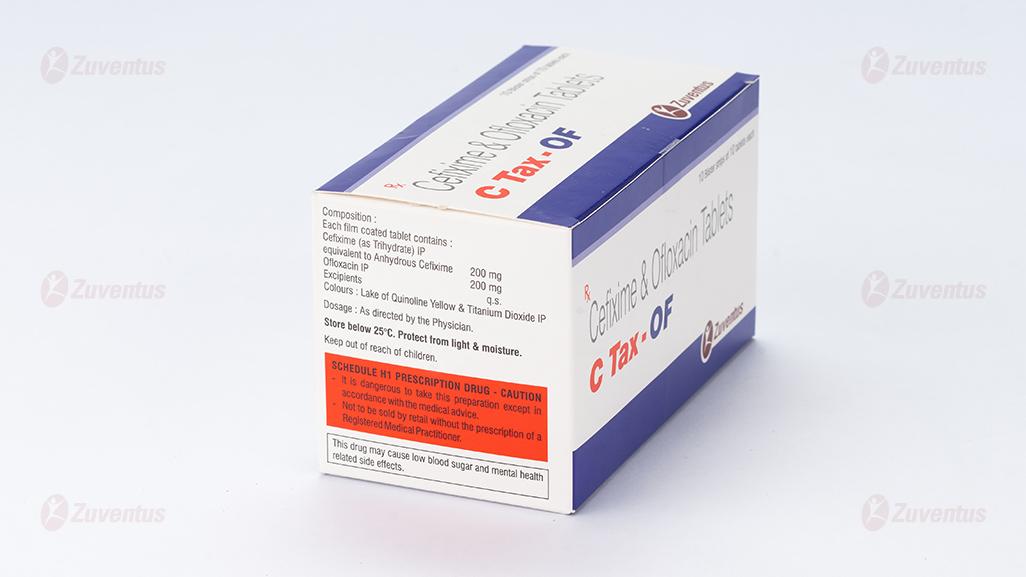
Each film coated tablet contains:
Cefixime (as Trihydrate) IP equivalent to Anhydrous Cefixime 200 mg
Ofloxacin IP 200 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colours: Lake of Quinoline Yellow & Titanium Dioxide IP
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Film coated tablet
Cefixime (200mg) and Ofloxacin (200mg)
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic Indication
For the treatment of patients with typhoid fever and urinary tract infection in adults.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
C Tax-OF adult dose:
1 tablet two times daily.
4.3 Contraindications
- Persons with a history of hypersensitivity associated with the use of ofloxacin or any member of the quinolone group. Patients with known allergy to cefixime or other cephalosporins.
- Patients with a past history of tendinitis related to fluoroquinolone administration.
- Patients with a history of epilepsy or seizures.
- Children or growing adolescents and in pregnant or breast-feeding women, since animal experiments do not entirely exclude the risk of damage to the cartilage of joints in the growing subject
- Patients with latent or actual defects in G6PD activity
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
The drug may cause low blood sugar and mental health related side effects. Low blood sugar levels, also called hypoglycaemia, can lead to coma. The mental health side effects more prominent and more consistent across the systemic fluoroquinolone drug class. The mental health side effects to be added to or updated across all the fluoroquinolones are:
- Disturbances in attention
- Disorientation
- Agitation
- Nervousness
- Memory impairment
- Serious disturbances in mental abilities called delirium
| Condition | Description |
| Hypersensitivity and allergic reactions | Hypersensitivity, severe cutaneous ADRs such as TEN, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) have been reported in some patients. C Tax-OF should be discontinued and appropriate measures should be taken |
| Hypersensitivity to penicillins | As with other cephalosporins, C Tax-OF should be given with caution to patients with a history of hypersensitivity to penicillin, as there is some evidence of cross-allergenicity |
| Hemolytic anaemia | Drug-induced hemolytic anaemia has been seen with cephalosporins (as a class) |
| Renal impairment | It should be used with caution in patients with impaired renal function |
| G6PD deficiency | Patients with G6PD may be predisposed to hemolytic reactions if they are treated with quinolones. Therefore, if C Tax-OF has to be used in these patients, potential occurrence of haemolysis should be monitored |
| Impaired liver function | C Tax-OF should be used with caution in patients with impaired liver function |
| Myasthenia gravis | C Tax-OF is not recommended in patients with a known history of myasthenia gravis |
| Photosensitization | It is recommended that patients should not expose themselves unnecessarily to strong sunlight or to artificial UV rays, during treatment and for 48 hours following treatment discontinuation |
| Superinfection | The prolonged use of C Tax-OF may result in overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms |
| Peripheral neuropathy | C Tax-OF should be discontinued if the patient experiences symptoms of neuropathy |
4.5 Drugs interactions
- Drugs known to prolong QT interval: C Tax-OF should be used with caution in patients receiving drugs known to prolong the QT interval (e.g. anti-arrhythmics, tricyclic antidepressants, macrolides, and antipsychotics).
- Antacids, Sucralfate, Metal Cations: Co-administered magnesium/aluminium antacids, sucralfate, zinc or iron preparations can reduce absorption. Therefore, ofloxacin should be taken 2 hours before such preparations.
- Theophylline, fenbufen or similar NSAIDs: A pronounced lowering of the cerebral seizure threshold may occur when quinolones are given concurrently with theophylline, NSAIDs, or other agents, which lower the seizure threshold. In case of seizures, treatment with C Tax-OF should be discontinued.
- Glibenclamide: Ofloxacin may cause a slight increase in serum concentrations of glibenclamide.
- Probenecid, cimetidine, furosemide and methotrexate: Caution should be exercised when ofloxacin is co-administered with drugs that affect the tubular renal secretion such as probenecid, cimetidine, furosemide and methotrexate.
- Vitamin K antagonists & Anticoagulants: Increased coagulation tests (PT/INR) and/or bleeding have been reported in patients treated with ofloxacin in combination with a vitamin K antagonist (e.g. warfarin). Coagulation tests should be monitored in patients treated with Vitamin-K antagonists. Cefixime should be administered with caution to patients receiving coumarin-type anticoagulants, e.g. warfarin.
- Other forms of interaction: A false positive direct coombs test has been reported during treatment with cephalosporin antibiotics, therefore it should be recognised that a positive coombs test may be due to the drug.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
C Tax-OF should not be used during pregnancy.
Lactation
Breast feeding should be discontinued during treatment with C Tax-OF because of the potential for arthropathy and other serious toxicity in the nursing infants.
Children
C Tax-OF is not indicated for use in children or growing adolescents.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
There have been occasional reports of drowsiness/somnolence, impairment of skills, dizziness/vertigo and visual disturbances, which may impair the patient's ability to concentrate and react, and therefore may constitute a risk in situations where these abilities are of special importance (e.g. driving a car or operating machinery), patients should know how they react to ofloxacin before they drive or operate machinery. These effects may be enhanced by alcohol.
In the case of side effects such as encephalopathy (which may include convulsion, confusion, impairment of consciousness, movement disorders), the patient should not operate machines or drive a vehicle.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Cefixime:
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis and Mouth Ulceration has been reported with Cefixime use.
- The most commonly seen adverse reactions reported were gastrointestinal events (30%) in adult patients
- Individual adverse reactions included Diarrhea-16%, Loose or frequent stools- 6%, Abdominal pain-3%, Nausea-7%, Dyspepsia-3%, Flatulence 4%
Ofloxacin:
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)/ Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) has been reported with Ofloxacin use.
- The most frequently reported adverse events were nausea- 10%, headache- 9%, insomnia- 7%, external genital pruritus in women- 6%, Dizziness-5%, Vaginitis-5%, Diarrhea-4%, Vomiting 4%
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product.
Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Ofloxacin
Important signs of acute over dosage: CNS symptoms such as confusion, dizziness, impairment of consciousness and seizures, increases QT interval, GIT reactions e.g. nausea and mucosal erosions.
In the case of overdose steps to remove any unabsorbed ofloxacin e.g. gastric lavage, administration of adsorbants and sodium sulphate are recommended; antacids are recommended for protection of the gastric mucosa. A fraction of ofloxacin may be removed from the body with haemodialysis.
No specific antidote exists. Elimination of ofloxacin may be increased by forced diuresis. In the event of overdose, symptomatic treatment should be implemented. ECG monitoring should be undertaken, because of the possibility of QT interval prolongation.
Cefixime There is no experience with overdoses with Cefixime. Cefixime is not removed from the circulation in significant quantities by dialysis. No specific antidote exists. General supportive measures are recommended.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic Properties
Cefixime
- is an oral third generation cephalosporin which has marked in vitro bactericidal activity against a wide variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms. Bactericidal action of cefixime results from inhibition of cell-wall synthesis.
- Active against most isolates of the following bacteria both in vitro and in clinical infections:
- Gram-positive bacteria- Streptococcus pneumonia, Streptococcus pyogenes
- Gram-negative bacteria - Haemophilus influenza, Moraxella catarrhalis, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- In vitro bactericidal activity is seen against isolates of the following microorganisms.
- Gram-positive bacteria- Streptococcus agalactiae
- Gram-negative bacteria- Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Proteus vulgaris, Klebsiella pneumonia, Klebsiella oxytoca, Pasteurella multocida, Providencia species, Salmonella species, Shigella species, Citrobacter amalonaticus, Citrobacter diversus, Serratia marcescens
Ofloxacin
- Is a quinolone-carboxylic acid derivative with a wide range of antibacterial activity against both gram negative and gram positive organisms.
- The primary mode of action of the quinolones is the specific inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase. This enzyme is required for DNA replication, transcription, repair and recombination. Its inhibition leads to expansion and destabilisation of the bacterial DNA and hence to cell death.
- Active against most isolates of the following bacteria both in vitro and in clinical infections.
- Gram-Positive Microorganisms- Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible strains), Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible), Streptococcus pyogenes
- Gram-Negative Microorganisms- Citrobacter koseri, Enterobacter aerogenes, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenza, Klebsiella pneumonia, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa,
- Other Microorganisms- Chlamydia trachomatis
- In vitro bactericidal activity is seen against isolates of the following microorganisms
- Gram-positive microorganisms- Staphylococcus epidermidis (methicillin-susceptible strains), Staphylococcus saprophyticu, Streptococcus pneumonia,
- Gram-Negative Microorganisms- Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, Bordetella pertussis, Pasteurella multocida, Enterobacter cloacae, Haemophilus ducreyi, Klebsiella oxytoca, Moraxella catarrhalis, M. morganii, Proteus vulgaris, Providencia rettgeri, P. stuartii, Serratia marcescens
- Other microorganisms- Chlamydia pneumoniae, Gardnerella vaginalis, Legionella pneumophila, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Ureaplasma urealyticum,
- Anaerobic Microorganisms- Clostridium perfringes
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
| Parameter | Cefixime | Ofloxacin |
| Oral bioavailability | 40% to 50% | Approximately 98% |
| Tmax | 2 and 5 hours | 1 to 2 hours |
| Cmax | 2 mcg/mL (range 1 to 4 mcg/mL) | 2.2 mcg/mL |
| Plasma protein binding | Approx. 65%. | Approx. 32% |
| AUC | 34.9 ± 12.2 to 49.5 ± 19.1 mg.h/L | 14.1 mcg.h/mL |
| Half life | Averages 3 to 4 hours but may range up to 9 hours in some healthy volunteers. | Biphasic elimination. Following multiple oral doses at steady-state administration, the half-lives are approximately 4 to 5 hours and 20 to 25 hours. However, the longer half-life represents less than 5% of the total AUC. Accumulation at steady-state can be estimated using a half-life of 9 hours |
| Elimination | Approx. 50% of the absorbed dose is cefixime is also excreted in the bile in excess of 10% of the administered dose. | Mainly by renal excretion |
| Renal impairment | In severe renal impairment (CrCl- 5 to 20 ml/min), the half-life increased to an average of 11.5 hrs. | Dosage adjustment is necessary for elderly and patients with impaired renal function. |
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Preclinical effects in conventional studies of safety pharmacology, acute toxicity, repeated dose toxicity, reproductive studies were observed only at exposures considered sufficiently in excess of the maximum human exposure indicating little relevance to clinical use. Joint toxicity was observed at exposure in the human therapeutic range in juvenile rats and dogs. Ofloxacin exhibits a neurotoxic potential and causes reversible testicular alterations at high doses.
Mutagenicity studies showed no evidence for mutagenicity of ofloxacin. However, like some other quinolones Ofloxacin is phototoxic in animals at exposure in the human therapeutic range. The phototoxic, photomutagenic and photocarcinogenic potential of ofloxacin is comparable with that of other gyrase inhibitors.
Preclinical data from conventional genotoxicity studies reveal no special hazard to humans, carcinogen potential has not been investigated.
Reproduction toxicity
Ofloxacin has no effect on fertility, peri- or postnatal development, and therapeutic doses did not lead to any teratogenic or other embryotoxic effects in animals. Ofloxacin crosses the placenta and levels reached in the amniotic fluid are about 30% of the maximal concentrations measured in maternal serum.
7.0 Description
Cefixime is a semisynthetic, cephalosporin antibacterial for oral administration. Ofloxacin tablets are a synthetic broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent for oral administration.
Cefixime
Chemical Name: (6R,7R)-7-[2-(2-Amino-4-thiazolyl) glyoxylamido]-8-oxo-3-vinyl-5-thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 72-(Z)- [O-(carboxy methyl) oxime] trihydrate
Chemical Formula: C16H15N5O7S2.3H2O
Molecular Weight: 507.50
Structure:
Ofloxacin
Chemical Name: (±)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1- piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7H-pyrido[1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazine6-carboxylic acid
Chemical Formula: C18H20FN3O4
Molecular Weight: 361.4
Structure:
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
None
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack
8.3 Packaging information
A blister strip of 10 tablets.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store below 25°C. Protect from light
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
- Counsel patients that antibacterial drugs should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When C Tax-OF is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may: (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by C Tax- OF or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
- Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they experience pain, swelling, or inflammation of a tendon, or weakness or inability to use one of their joints; rest and refrain from exercise; and discontinue C Tax-OF treatment. The risk of severe tendon disorders with fluoroquinolones is higher in older patients usually over 60 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants;
- Advise patients that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterial drugs which usually ends when the antibacterial drug is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibacterial drugs, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibacterial drug. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
- Advise patients that peripheral neuropathies have been associated with ofloxacin use. If symptoms of peripheral neuropathy including pain, burning, tingling, numbness, and/or weakness develop, they should discontinue treatment and contact their physicians
- photosensitivity/phototoxicity has been reported in patients receiving quinolone antibiotics. Patients should minimize or avoid exposure to natural or artificial sunlight (tanning beds or UVA/B treatment) while taking quinolones. If patients need to be outdoors while using quinolones, they should wear loose-fitting clothes that protect skin from sun exposure and discuss other sun protection measures with their physician. If a sunburn-like reaction or skin eruption occurs, patients should contact their physician.
- if they are diabetic and are being treated with insulin or an oral hypoglycemic drug, to discontinue ofloxacin immediately if a hypoglycemic reaction occurs and consult a physician
- convulsions have been reported in patients taking quinolones, including ofloxacin, and to notify their physician before taking this drug if there is a history of this condition
- if they are diabetic and are being treated with insulin or an oral hypoglycemic drug, to discontinue C Tax-OF immediately if a hypoglycemic reaction occurs and consult a physician
- Patients are advised to inform their physician of any personal or family history of QTc prolongation or proarrhythmic conditions such as hypokalemia, bradycardia, or recent myocardial ischemia; if they are taking any class IA (quinidine, procainamide), or class III (amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic agents. Patients should notify their physicians f they have any symptoms of prolongation of the QTc interval including prolonged heart palpitations or a loss of consciousness.
- Tell the patients if they get any side effects, talk to the doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. Advice patients if they have any further questions, ask the doctor or pharmacist.
12.0 Date of revision of text
05-07-2024
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before your child starts taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for your child. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as your child’s.
- If your child gets any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet?
- What C Tax-OF tablet is and what it is used for?
- What you need to know before you take C Tax-OF tablet?
- How to take C Tax-OF tablet?
- Possible side effects
- How to store C Tax-OF tablet?
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What C Tax-OF tablet is and what it is used for?
C Tax-OF tablet is a combination of two medicines: Cefixime and Ofloxacin. Cefixime belongs to a group of antibiotics called “cephalosporin”. Ofloxacin belongs to a group of medicines called “quinolone antibiotics”.
Cefixime kills bacteria by preventing them from building their cell walls, while ofloxacin kills bacteria by stopping them from making and repairing their DNA. Without a cell wall or functional DNA, the bacteria cannot survive.
C Tax-OF tablets is specifically used for typhoid fever and urinary tract infections in adults.
2. What you need to know before you take C Tax-OF Tablet?
Do not take C Tax-OF Tablet if you:
- Are allergic to cefixime, ofloxacin, cephalosporins, or quinolones. Signs of an allergic reaction include: a rash, swallowing or breathing problems, swelling of your lips, face, throat or tongue.
- Have a history of tendinitis (inflammation or swelling of tendons) or tendon rupture related to fluoroquinolone use.
- Have epilepsy or a history of seizures/fits.
- Are pregnant, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby
- Are breastfeeding.
- If you are under the age of 18 years, or are still growing
- If you suffer from or there is a family history of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (an inherited disorder that affects the red blood cells)
Do not take this medicine if any of the above apply to you. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking C Tax-OF tablets.
Warnings and Precautions:
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking C Tax-OF tablets if any of the following apply:
- if you have been diagnosed with an enlargement or "bulge" of a large blood vessel (aortic aneurysm or large vessel peripheral aneurysm)
- if you have a family history of aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection or congenital heart valve disease, or other risk factors or predisposing conditions (e.g. connective tissue disorders such as Marfan syndrome or Ehlers- Danlos syndrome, Turner syndrome, Sjögren’s syndrome (an inflammatory autoimmune disease) or vascular disorders such as Takayasu arteritis, giant cell arteritis, Behcet’s disease, high blood pressure, or known atherosclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis (a disease of the joints) or endocarditis (an infection of the heart))
- you have or have ever had a history of mental illness.
- you have problems with your liver or kidneys.
- you have heart disease or problems with your heartbeat
- you were born with or have family history of prolonged QT interval (seen on ECG, electrical recording of the heart).
- have salt imbalance in the blood (especially low level of potassium or magnesium in the blood)
- have a weak heart (heart failure)
- have a history of heart attack (myocardial infarction)
- you have an illness of the nervous system called ‘myasthenia gravis’ (muscle weakness)
- you have diabetes or blood sugar problems, as this medication can cause low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
- Avoid strong sunlight or artificial UV rays during and for 48 hours after treatment.
During treatment
When taking this medicine
- If your eyesight becomes impaired or if your eyes seem to be otherwise affected, consult an eye specialist immediately
- If you feel sudden, severe pain in your abdomen, chest or back, which can be symptoms of aortic aneurysm and dissection, go immediately to an emergency room. Your risk may be increased if you are being treated with systemic corticosteroids
- If you start experiencing a rapid onset of shortness of breath, especially when you lie down flat in your bed, or you notice swelling of your ankles, feet or abdomen, or a new onset of heart palpitations (sensation of rapid or irregular heartbeat), you should inform a doctor immediately
- Pain and swelling in the joints and inflammation or rupture of tendons may occur rarely. Your risk is increased if you are elderly (above 60 years of age), have received an organ transplant, have kidney problems or if you are being treated with corticosteroids. Inflammation and ruptures of tendons may occur within the first 48 hours of treatment and even up to several months after stopping of C Tax-OF therapy. At the first sign of pain or inflammation of a tendon (for example in your ankle, wrist, elbow, shoulder or knee), stop taking C Tax-OF, contact your doctor and rest the painful area. Avoid any unnecessary exercise as this might increase the risk of a tendon rupture.
- You may rarely experience symptoms of nerve damage (neuropathy) such as pain, burning, tingling, numbness and/or weakness especially in the feet and legs or hands and arms. If this happens, stop taking C Tax-OF and inform your doctor immediately in order to prevent the development of potentially irreversible condition.
If you are not sure if any of the above apply to you, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking C Tax-OF.
Other medicines and C Tax-OF Tablet:
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
- medicines or dietary supplements that contain iron (for anaemia) or zinc.
- sucralfate used for stomach ulcers.
- antacids used for indigestion that contain magnesium or aluminium.
- corticosteroids, used for treatment of inflammation and swelling or over-active immune system. These may increase the risk of you developing a tendon rupture
- painkillers called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) e.g. ibuprofen or diclofenac, or theophylline, used to treat asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease as these could make you more prone to fits if taken with C Tax-OF tablet.
- glibenclamide, a medicine to control your blood sugar, as the amount of these medicines in the blood may increase and have a greater effect.
- drugs that may affect your kidney function e.g. cimetidine (used for stomach ulcers or indigestion), probenecid (used for gout) and methotrexate (used for rheumatism) as they can increase the level of ofloxacin in the blood.
- medicines to thin your blood, e.g. warfarin.
- water tablets (diuretics) such as furosemide
This medicine should not be taken within two hours of taking iron or zinc tablets, antacids, or sucralfate, as these medicines can stop C Tax-OF tablet from working properly.
If you are due to have urine tests for porphyrin (a pigment in the blood), or for opiates (strong painkillers), tell your doctor or nurse you are taking this medicine.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Do not take C Tax-OF tablet if you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby. If you become pregnant while taking C Tax-OF tablet, stop taking the tablets and contact your doctor immediately.
Driving and using machines
Taking C Tax-OF tablet may make you feel sleepy, dizzy or could affect your eyesight. Do not drive or use machines until you know how this medicine affects you. Drinking alcohol may make these symptoms worse.
3. How to take C Tax-OF Tablet?
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
- For oral use. You should swallow these tablets whole with water. Do not chew them.
- The tablets can be taken with or without food and can be divided into equal doses.
- When taking C Tax-OF, avoid strong sunlight and do not use sun lamps or solaria as your skin may be more sensitive to light.
- If you are taking iron tablets (for anaemia), antacids (for indigestion or heartburn) or sucralfate (for stomach ulcers), it is important not to take these two hours before or after taking C Tax-OF. If you feel the effect of your medicine is too weak or strong, do not change the dose yourself, but ask your doctor.
- When taking C Tax-OF, if your eyesight becomes impaired or if your eyes seem to be otherwise affected, consult an eye specialist immediately
Dosage in Adults:
Take 1 tablet twice daily, as directed by your doctor.
Use in children and adolescents:
Children or adolescents under 18 years of age should not take these tablets.
If you take more C Tax-OF tablet:
If you take more tablets than you should you may become confused and dizzy or lose consciousness, you may have a seizure or fit, and you may feel sick. Contact your doctor or nearest hospital casualty department immediately. Take the container and any remaining tablets with you.
If you forget to take C Tax-OF tablet:
If you forget to take a dose take it as soon as you remember unless it is nearly time for your next dose. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten tablet
If you stop taking C Tax-OF tablet:
Your doctor will tell you how long you need to take your tablets for. Do not suddenly stop taking this medicine without talking to your doctor first. If you stop, your infection may get worse again. If you feel the effect of your medicine is too weak or strong, do not change the dose yourself, but ask your doctor.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side-effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Stop taking C Tax-OF, tell your doctor or go to your nearest hospital casualty department straight away if you have any of the following serious side effects because you may need medical attention:
With Ofloxacin:
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
resistance of infection causing organisms to this treatment, (you may fail to respond to treatment)
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- you have an allergic reaction. Such reactions may appear in the form of anaphylaxis (a severe form of allergic reaction) with symptoms such as: - severe skin rash - swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue or throat (angioedema) - anaphylactic shock (sudden wheezing, swelling of your lips, tongue and throat or body, rash, fainting or difficulties in swallowing)
- inflammation of the bowel, which may cause severe watery diarrhoea, which may have blood in it, possibly with stomach cramps and a high temperature
- swelling of the tendons with the following symptoms; pain, tenderness, sometimes restricted movement (tendonitis). This can lead to tendon rupture, especially of the large tendon at the back of the ankle (Achilles tendon). The risk of this occurring is increased if you are also taking corticosteroids e.g. prednisolone
- numbness or tingling in the hands and feet or being very sensitive to touch, numbness or weakness of the arms and legs
- blurred, double or altered colour vision. If your eyesight becomes impaired or if your eyes seem to be otherwise affected, consult an eye specialist immediately.
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
- a condition in which the amount of oxygen-carrying pigment (haemoglobin) in the blood is below normal or an illness resulting from the destruction of red blood cells with the following symptoms; feeling tired, faint, dizzy, being short of breath when exercising and having pale skin. These may be signs of anaemia or haemolytic anaemia.
- other blood disorders when the numbers of different types of cells in the blood may fall, which may cause fever, chills, sore throat, ulcers in the mouth and throat (leucopenia, agranulocytosis)
- fits (seizures)
- skin rash, which may blister, and looks like small targets (central dark spots surrounded by a paler area, with dark ring around the edge) (erythema multiforme)
- a widespread rash with blisters and skin peeling on much of the body surface (toxic epidermal necrolysis).
- narrowing, blockage or leakage of blood vessels, in exceptional cases leading to severe skin reactions and death of areas of the skin
- severe kidney problems, which may result in your kidneys stopping working. Signs may include a rash, high temperature, general aches and pains, or blood in the urine
- hearing problems or hearing loss
- liver problems, such as inflammation of the liver (hepatitis) or blockage in the bile duct, that may cause your eyes or skin to go yellow (jaundice) or you may notice the following symptoms; nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, feeling generally unwell, fever, itching, light coloured bowel motions, dark coloured urine
With Cefixime:
- liver problems, such as inflammation of the liver (hepatitis) or blockage in the bile duct, that may cause your eyes or skin to go yellow (jaundice) or you may notice the following symptoms; nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, feeling generally unwell, fever, itching, light coloured bowel motions, dark coloured urine
- DRESS symptoms may include flu-like symptoms and a widespread rash with a high body temperature and enlarged lymph nodes. Abnormal blood test results may include increased levels of liver enzymes and an increase in a type of white blood cell (eosinophilia) and enlarged lymph nodes.
- AGEP symptoms may include a red, scaly, widespread rash with bumps under the skin (including your skin folds, chest, abdomen (including stomach), back and arms) and blisters accompanied by fever.
- Erythema multiforme symptoms include skin rash or skin lesions with a pink/red ring and a pale centre which may be itchy, scaly or filled with fluid. The rash may appear especially on the palms or soles of your feet.
- You get infections more easily than usual. This could be because of a blood disorder. This normally gets better after stopping the medicine.
- You bruise or bleed more easily than normal. This could be because of a blood disorder. This normally gets better after stopping the medicine.
- If your child gets nose bleeds, bleeding gums, chills, tiredness, pale skin (often with a yellow tinge), shortness of breath. This may be due to haemolytic anaemia
- A brain condition with symptoms including fits (convulsions), feeling confused, feeling less alert or aware of things than usual, unusual muscle movements or stiffness. This may be something called encephalopathy. This side effect is more likely if you have taken an overdose or you already have a problem with your kidneys.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly:
Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page.
Website link: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store C Tax-OF tablet?
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Do not take this medicine after the expiry date shown on the pack.
The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Store below 25°C. Protect from light & moisture
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What C Tax-OF contains
Each film coated tablet contains:
Cefixime (as Trihydrate) IP equivalent to Anhydrous Cefixime 200 mg
Ofloxacin IP 200 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colours: Lake of Quinoline Yellow & Titanium Dioxide IP
Packaging information
A blister strip of 10 tablets.
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Zuventus Heathcare Ltd. Zuventus House,
Plot Y2, CTS No: 358/A2,
Near Nahur Railway Station,
Nahur (West), Mumbai 400 078.
This leaflet was last revised in July 2024