Coralium-D3 Tablets
Therapy Area
Vitamins/Minerals Supplements
1.0 Generic name
Calcium and Vitamin D3 tablets IP (500 mg + 500 IU)
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
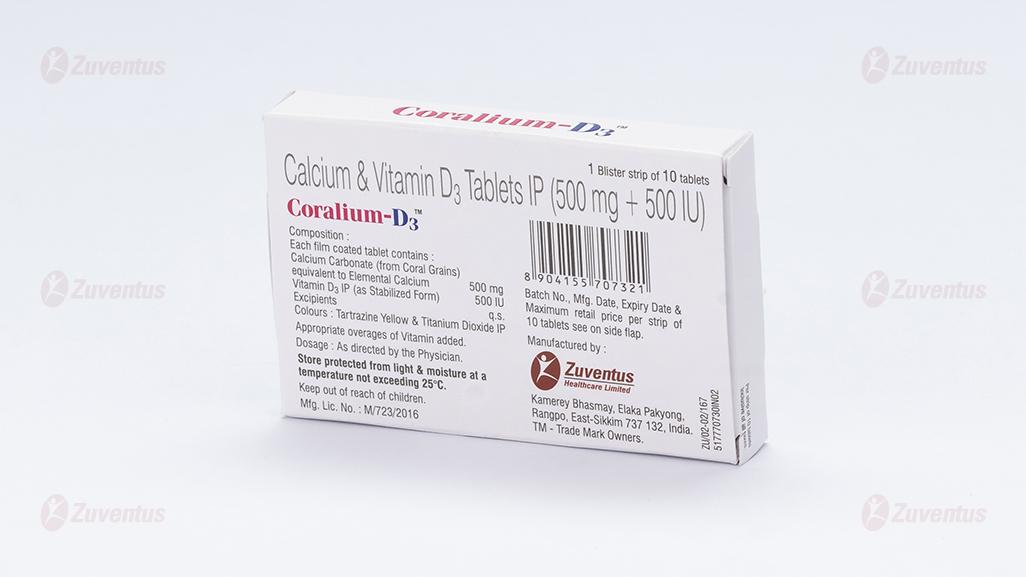
Each film-coated tablet contains:
Calcium Carbonate (from Coral Grains)
equivalent to Elemental Calcium 500 mg
Vitamin D3 IP 500IU
(as Stabilized Granules)
Excipients q.s.
Colours: Tartrazine Yellow & Titanium Dioxide IP
Appropriate overages of Vitamin added.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Film-coated tablets
Calcium and Vitamin D3 tablets IP (500mg + 500IU)
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic Indication
Prevention and treatment of vitamin D and calcium deficiency in elderly. Vitamin D and calcium supplements as an adjunct to specific osteoporosis treatment of patients who are at risk of vitamin D and calcium deficiency.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Posology
Adults and elderly
One tablet once daily or as directed by physician.
Dose reduction should be considered as necessary following the monitoring of calcium levels as indicated in sections 4.4 and 4.5.
Hepatic impairment
No dose adjustment is required.
Renal impairment
Coralium-D3 tablets should not be used in patients with severe renal impairment.
Children and adolescents
Coralium-D3 tablets are not intended for use in children and adolescents.
Method of administration
It is recommended that the film-coated tablet is taken within one and a half hours of a meal with a glass of water or juice, without chewing it. The tablet can be broken in half if needed.
4.3 Contraindications
- Diseases and/or conditions resulting in hypercalcemia and/or hypercalciuria (e.g. myeloma, bone metastases or other malignant bone disease, sarcoidosis; primary hyperparathyroidism).
- Nephrolithiasis/nephrocalcinosis
- Severe renal impairment and renal failure
- Hypervitaminosis D
- Hypersensitivity to the active substances or to any of the excipients present in this tablet.
- Relative contra-indications are osteoporosis due to prolonged immobilization, renal stones, and severe hypercalciuria.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Patients who are already taking thiazide diuretics and/or cardiac glycosides should be referred to their doctor prior to concomitant use (i.e. not suitable for pharmacy supply). Concomitant use should be prescribed with caution due to the increased risk of hypercalcemia.
During long-term treatment, serum calcium levels should be followed and renal function should be monitored through measurements of serum creatinine. Monitoring is especially important in elderly patients on concomitant treatment with cardiac glycosides or diuretics and in patients with a high tendency to calculus formation. In case of hypercalcemia or signs of impaired renal function, the dose should be reduced or the treatment discontinued. It is advisable to reduce or interrupt treatment temporarily if urinary calcium exceeds 7.5 mmol/24 h (300 mg/24 h).
Vitamin D should be used with caution in patients with impairment of renal function and the effect on calcium and phosphate levels should be monitored. The risk of soft tissue calcification should be taken into account. In patients with severe renal insufficiency, vitamin D in the form of cholecalciferol is not metabolized normally and other forms of vitamin D should be used.
Coralium-D3 tablets should be prescribed with caution to patients suffering from sarcoidosis, due to the risk of increased metabolism of vitamin D into its active form. These patients should be monitored with regard to the calcium content in serum and urine.
Coralium-D3 tablets should be used with caution in immobilized patients with osteoporosis due to the increased risk of hypercalcemia.
The content of vitamin D (500 IU) in Coralium-D3 tablets should be considered when prescribing other medicinal products containing vitamin D. Additional doses of calcium or vitamin D should be taken under close medical supervision. In such cases, it is necessary to monitor serum calcium levels and urinary calcium excretion frequently. Milk-alkali syndrome (Burnett's syndrome), i.e. hypercalcemia, alkalosis, and renal impairment can develop when large amounts of calcium are ingested with absorbable alkali.
Allowances should be made for calcium and vitamin D supplements from other sources.
4.5 Drugs interactions
- Thiazide diuretics reduce the urinary excretion of calcium. Due to the increased risk of hypercalcemia, serum calcium should be regularly monitored during the concomitant use of thiazide diuretics.
- Systemic corticosteroids reduce calcium absorption. During concomitant use, it may be necessary to increase the dose of Coralium D3 film-coated tablets.
- Simultaneous treatment with ion exchange resins such as cholestyramine or laxatives such as paraffin oil may reduce the gastrointestinal absorption of vitamin D.
- Calcium carbonate may interfere with the absorption of concomitantly administered tetracycline preparations. For this reason, tetracycline preparations should be administered at least two hours before or four to six hours after oral intake of calcium.
- Hypercalcaemia may increase the toxicity of cardiac glycosides during treatment with calcium and vitamin D. Patients should be monitored with regard to electrocardiogram (ECG) and serum calcium levels.
- If a bisphosphonate or sodium fluoride is used concomitantly with Coralium D3 film-coated tablets, these medicinal products should be administered at least three hours before the intake of Coralium D3 film-coated tablet since gastrointestinal absorption may be reduced.
- Rifampicin, phenytoin, or barbiturates may reduce the activity of vitamin D3, since they increase the rate of its metabolism.
- The absorption of quinolone antibiotics may be impaired if administered concomitantly with calcium. Quinolone antibiotics should be taken two hours before or six hours after intake of calcium.
- Calcium salts may decrease the absorption of iron, zinc or strontium. Consequently, the iron, zinc or strontium preparation should be taken at a distance of two hours from the calcium preparation.
- Calcium salts may reduce the absorption of the estramustin or thyroid hormones. It is recommended that taking CoraliumD3 film-coated tablets be spaced at least 2 hours from these medicines.
- Oxalic acid (found in spinach, sorrel and rhubarb), phosphate, and phytic acid (found in whole cereals) may inhibit calcium absorption through the formation of insoluble compounds with calcium ions. The patient should not take calcium products within two hours of eating foods high in oxalic acid and phytic acid.
4.6 Use in special populations
- Pregnancy
Coralium-D3 tablets may be given during pregnancy in cases of calcium and vitamin D3 deficiency.
During pregnancy the daily dose should not exceed 1500 mg of calcium and 600 IU of vitamin D. Animal studies have shown toxic effects on reproduction at high doses of vitamin D. In pregnant women, all calcium or vitamin D overdose must be avoided as prolonged hypercalcemia in pregnancy may lead to retardation of physical and mental development, supravalvular aortic stenosis and retinopathy in the child. There are no indications that Vitamin D3 at therapeutic doses is teratogenic in humans.
- Breast-feeding
Coralium-D3 tablets can be used during breast-feeding. Calcium and vitamin D pass into breast milk. This should be considered when giving additional vitamin D to the child.
- Fertility
There is no known harmful effect of endogenous levels of calcium and vitamin D in the normal range on fertility. There are no data available on the effect of Coralium D3 film-coated tablets on fertility.
4.7 Effects on the ability to drive and use machines
There are no data on the effect of this product on driving capacity and use of machines. An effect is, however, unlikely.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Adverse reactions are listed below, by system organ class and frequency. Frequencies are defined as: uncommon (>1/1,000 to <1/100); rare (>1/10,000 to <1/1,000); very rare (<1/10,000); not known (cannot be estimated from the available data).
Immune system disorders
Not known: Hypersensitivity reactions including pruritus, wheezing, urticaria, and oropharyngeal swelling have been reported in the post-marketing environment.
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Uncommon: Hypercalcaemia and hypercalciuria.
Very rare: Seen usually only in overdose, see 4.9: Milk-alkali syndrome
Gastrointestinal disorders
Rare: Constipation, flatulence, nausea, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
Very rare: Dyspepsia
Skin and subcutaneous disorders
Rare: Pruritus, rash and urticaria.
Other special population
Patients with renal impairment: potential risk of hyperphosphatemia, nephrolithiasis, and nephrocalcinosis.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
- Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: www.medico@zuventus.com
- Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Overdose can lead to hypervitaminosis and hypercalcemia. Symptoms of hypercalcemia may include anorexia, thirst, nausea, vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain, muscle weakness, fatigue, mental disturbances, polydipsia, polyuria, bone pain, nephrocalcinosis, renal calculi, and in severe cases, cardiac arrhythmias. Extreme hypercalcemia may result in coma and death. Persistently high calcium levels may lead to irreversible renal damage and soft tissue calcification.
Milk-alkali syndrome may occur in patients who ingest large amounts of calcium and absorbable alkali. Symptoms are frequent urge to urinate, continuing headache, continuing loss of appetite, nausea or vomiting, unusual tiredness or weakness, hypercalcemia, alkalosis, and renal impairment.
Treatment of hypercalcemia: The treatment with calcium and vitamin D must be discontinued. Treatment with thiazide diuretics, lithium, vitamin A, vitamin D, and cardiac glycosides must also be discontinued. Emptying of the stomach in patients with impaired consciousness. Rehydration, and, according to severity, isolated or combined treatment with loop diuretics, bisphosphonates, calcitonin, and corticosteroids. Serum electrolytes, renal function, and diuresis must be monitored. In severe cases, ECG and CVP should be followed.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Calcium, combination with vitamin D and/or other drugs
Vitamin D increases the intestinal absorption of calcium. Administration of calcium and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) counteracts the increase of parathyroid hormone (PTH), which is caused by calcium deficiency and causes increased bone resorption.
A clinical study of institutionalized patients suffering from vitamin D deficiency indicated that a daily intake of two tablets of calcium 500 mg/Vitamin D 400 IU for six months normalized the value of the 25-hydroxylated metabolite of Vitamin D3and reduced secondary hyperparathyroidism and alkaline phosphatases.
An 18-month double-blind, placebo-controlled study including 3270 institutionalized women aged 84±6 years who received supplementation of vitamin D (800 IU/day) and calcium phosphate (corresponding to 1200 mg/day of elemental calcium), showed a significant decrease of PTH secretion. After 18 months, an “intent-to-treat” analysis showed 80 hip fractures in the calcium-vitamin D group and 110 hip fractures in the placebo group (p=0.004). A follow-up study after 36 months showed 137 women with at least one hip fracture in the calcium-vitamin D group (n=1176) and 178 in the placebo group (n=1127, p<0.02).
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
- Calcium
Absorption:
The bioavailability of coral calcium is approximately 70% as per study in animals by Japanese Dietetic Society. This is higher as compared to other calcium salts.
Unlike lime and fossilized calcium which are inert, live coral produces calcium in its ionized form. This calcium is able to bypass the digestive process. Hence, calcium and other trace minerals from coral are immediately available to the systems in the human body.
Distribution and metabolism:
99% of the calcium in the body is concentrated in the hard structure of bones and teeth. The remaining 1% is present in the intra- and extracellular fluids. About 50% of the total blood-calcium content is in the physiologically active ionized form with approximately 10% being complexed to citrate, phosphate, or other anions, the remaining 40% being bound to proteins, principally albumin.
Elimination:
Calcium is eliminated through feces, urine, and sweat. Renal excretion depends on glomerular filtration and calcium tubular reabsorption.
- Vitamin D
Absorption:
Vitamin D3 is absorbed in the small intestine.
Distribution and metabolism:
Cholecalciferol and its metabolites circulate in the blood bound to a specific globulin. Cholecalciferol is converted in the liver by hydroxylation to the active form 25-hydroxy cholecalciferol. It is then further converted in the kidneys to 1,25hydroxycolecalciferol. 1,25 hydroxy cholecalciferol is the metabolite responsible for increasing calcium absorption. Vitamin D which is not metabolized is stored in adipose and muscle tissues.
Elimination:
Vitamin D is excreted in feces and urine.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
At doses far higher than the human therapeutic range teratogenicity has been observed in animal studies.
7.0 Description
Coral Calcium (Calcium Carbonate from Coral Grains) is the calcium supplement obtained from the marine coral from Okinawa, Japan. A small sea animal creates coral by ingesting the ionic ocean minerals and secreting them into a coral formation. This natural balance of 72 organic coral minerals are harvested from above sea coral deposits crushed into an ultra-fine powder and sterilized with ozone. Coral Calcium contains up to 40% elemental calcium.
Coral minerals are organic in the sense that they have been previously digested by an animal. It is very difficult for the human body to digest inorganic minerals (similar to eating little rocks). Having been previously digested by the coral polyp, coral minerals are readily absorbable by the human body.
The bioavailability of coral calcium is approximately 70% as per study in animals by Japanese Dietetic Society.
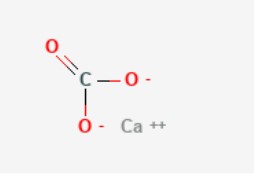
Molecular Formula: CaCO3
Molecular Weight: 100.09 g/mol
Cholecalciferol is a Vitamin D. Cholecalciferol is a steroid hormone produced in the skin when exposed to ultraviolet light or obtained from dietary sources. The active form of cholecalciferol, 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol (calcitriol) plays an important role in maintaining blood calcium and phosphorus levels and mineralization of bone. The activated form of cholecalciferol binds to vitamin D receptors and modulates gene expression. This leads to an increase in serum calcium concentrations by increasing intestinal absorption of phosphorus and calcium, promoting distal renal tubular reabsorption of calcium and increasing osteoclastic resorption.
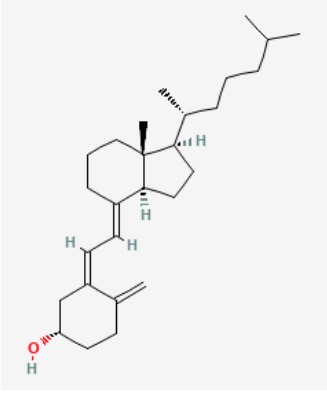
Molecular Formula: C27H44O
Molecular Weight: 384.6 g/mol
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
None stated.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on pack
8.3 Packaging information
1 blister strip of 10 tablets
8.4 Storage and handling instructions
Do not store above 25°C. Store in the original package in order to protect from moisture.
9.0 Patient counselling information
- Take this tablet with food. Take with a full glass of water.
- Children under 12 years and pregnant women should consult a physician.
- Persons with kidney disease, bone disease, malignancies or calcium disorders should not take Vitamin D3 except under the supervision of a physician.
- Mineral oil interferes with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, including vitamin D preparations. Administration of thiazide diuretics to hypoparathyroid patients who are concurrently being treated with vitamin D preparations may cause hypercalcemia.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, or pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4
What is in this leaflet
- What Coralium-D3 Tablets is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Coralium-D3 Tablets
- How to take Coralium-D3 Tablets
- Possible side effects
- How to store Coralium-D3 Tablets
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Coralium-D3 Tablets is and what it is used for
The product is a combination of calcium (as calcium carbonate from coral grains) and Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol).
Coral Calcium is a salt of Calcium derived from fossilized Coral Reefs. It is obtained mainly from Coral Reefs of Okinawa Island, Japan. A small sea animal creates coral by ingesting the ionic ocean minerals and secreting them into a coral formation. This natural balance of 72 organic coral minerals are harvested from above sea coral deposits crushed into an ultra-fine powder and sterilized with ozone.
It is recommended for the prevention and treatment of deficiency of calcium and vitamin D3 which are essential for bone formation and normal bone metabolism. It is also recommended for use as a Vitamin D and calcium supplement alongside specific osteoporosis treatments in people who are at risk of vitamin D and calcium deficiency.
2. What you need to know before you use Coralium-D3 Tablets
Do not take Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets
- if you are allergic to active substances or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets contain hydrogenated soya oil. lf you are allergic to peanuts or soya, do not use this medicinal product.
- if you have kidney stones
- if you have kidney failure or severe renal impairment
- if you have calcium deposits in your kidneys (nephrocalcinosis).
- if you have excessive amounts of vitamin D in the blood
- if you have chronically increased calcium levels in your urine or elevated blood-calcium level
- if you have disturbed parathyroid hormone metabolism
- if you have sarcoidosis (an inflammatory disease of unidentified origin characterized by formation of cell agglomerates (lumps) in different locations.
- if you are an immobilised patient with osteoporosis
- if you are taking thiazide diuretics (to treat high blood pressure)
- if you are taking cardiac glycosides (to treat heart conditions) such as digoxin
- if you are less than 18 years of age.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets
- if you have kidney disease or impaired kidney function
- if you have sarcoidosis (an inflammatory disease of unidentified origin characterized by formation of cell agglomerates (lumps) in different locations)
- if you are prone to the development of kidney stones
- if you are an immobilized patient with osteoporosis
Children and adolescents
Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets are not intended for use in children and adolescents.
Other medicines and Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription.
Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you use:
- other medicines or food supplements containing vitamin D or calcium, because concomitant (accompanying) use of such products with Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets may lead to a significant elevation of blood calcium levels and cause adverse effects that may be harmful. During the treatment with Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets, do not use any other products containing vitamin D or calcium without medical advice.
- thiazide diuretics
- systemic (per os [oral] or injection) corticosteroids (anti-inflammatory drugs)
- cardiac glycosides (used for the treatment of cardiac [heart] failure)
Take special care if you use:
- ion exchange resins such as cholestyramine or laxatives such as paraffin oil, as these medicines may reduce the gastrointestinal absorption of vitamin D.
- tetracycline containing preparations (antibiotics), as calcium carbonate may interfere with their absorption. Therefore, tetracycline preparations should be administered at least two hours before or four to six hours after using of Coralium-D3 film coated tablets.
- bisphosphonate (used for the treatment of osteoporosis) or sodium fluoride is used concomitantly with Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets, these preparations should be administered at least three hours before using Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets.
- Rifampicin (a medicine for tuberculosis), phenytoin (a medicine for epilepsy) and barbiturates (medicines which are used for epilepsy or which help you sleep), as they may make vitamin D3 less effective.
- Quinolone (antibiotics), as calcium may interfere with its absorption. Quinolone antibiotics should be taken two hours before or six hours after intake of calcium.
- Estramustin (a medicine used in chemotherapy), thyroid hormones or medicines containing iron, zinc or strontium, as the amount absorbed may be reduced. They should be taken at least 2 hours before or after Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets.
Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets with food and drink
Oxalic acid (found in e.g. spinach, sorrel and rhubarb), phosphate and phytic acid (found in whole cereals) may inhibit calcium absorption. The patient should not take Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets within two hours after eating foods rich in oxalic acid, phosphate and phytic acid.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine. During pregnancy, the daily intake should not exceed 1500 mg of calcium and 600 IU (International Unit) vitamin D. In pregnant women, overdoses of calcium and vitamin D should be avoided as permanent hypercalcaemia is related to adverse effects on the developing foetus. During pregnancy, Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets should be used in the recommended doses only in cases of calcium and vitamin D3 deficiency. In other cases the daily dose of Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets must not exceed one tablet per day.
Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets can be used during breast-feeding, but your doctor should be informed as calcium and vitamin D gets into the breast milk. This should be considered when giving additional vitamin D to the child. There are no data available on the effect of Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets on fertility.
Driving and using machines
There is no data on the effect of this product on the ability to drive or use machines.
3. How to take Coralium-D3 Tablets
Always use this medicine exactly as described in this leaflet or as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
The recommended dose for adults and the elderly: one tablet per day or as directed by the doctor.
In pregnancy and lactation- should be given as per recommendation of doctor.
It is recommended to take the film-coated tablet within one and a half hours of a meal with a glass of water or juice, without chewing it. The tablet can be broken in half, if needed.
Use in children and adolescents
Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets are not intended for use in children and adolescents under 18 years.
If you take more Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets than you should
Contact your doctor or pharmacist immediately if you have taken too much of this medicine. Remember to keep the pack and any remaining tablets with you.
Taking too much of this medicine may lead to symptoms such as lack of appetite, thirst, nausea, vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain, muscle weakness, fatigue, mental disturbances, excess drinking and excess urination, bone pain, calcification of the kidneys and in severe cases cardiac arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat). In extreme cases, calcium overdose can lead to coma and death. Long-term increased calcium levels in the blood may also lead to irreversible kidney impairment and calcification of soft tissues.
If you forget to take Coralium-D3 film-coated tablets
Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose, as you would not substitute the missing amount but you risk overdosing.
Continue the treatment according to the instructions.
If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Adverse reactions are listed below by classes of organ systems and frequency of occurrence.
Frequency is defined as:
- Uncommon (affects 1 to 10 users in 1,000)
- Rare (affects 1 to 10 users in 10,000)
- Very rare (affects less than 1 in 10,000)
Uncommon: significantly increased blood calcium level (hypercalcaemia)- the symptoms include nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite, constipation, stomach ache, bone pain, extreme thirst. Needing to pass urine more often, muscle weakness, drowsiness and confusion; or markedly increased calcium content of the urine (hypercalciuria).
Rare: constipation, flatulence (wind), nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, itching, rash and urticaria (hives).
Very rare: dyspepsia (indigestion), Milk alkali syndrome (usually only seen in overdose).
Not known: Allergic reactions – symptoms include itching, wheezing, rash, and swelling of the tongue or throat. If you have an allergic reaction stop taking the tablets and seek medical attention immediately.
If you have impaired renal function, you may be at risk of increased amounts of phosphate in the blood, renal stone formation and increased amounts of calcium in the kidneys.
Reporting of side effects
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
- By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Coralium-D3 Tablets
Do not store above 25°C. Store in the original package in order to protect it from moisture.
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton (EXP). The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Coralium-D3 Tablets contains
The active substance is Calcium and Vitamin D3
Composition:
Each film-coated tablet contains:
Calcium Carbonate (from Coral Grains)
equivalent to Elemental Calcium 500 mg
Vitamin D3 IP 500IU
(as Stabilized Granules) Excipients q.s.
Colours: Tartrazine Yellow & Titanium Dioxide IP
Appropriate overages of Vitamin added.
Presentation Packaging: 1 blister strip of 10 Tablets