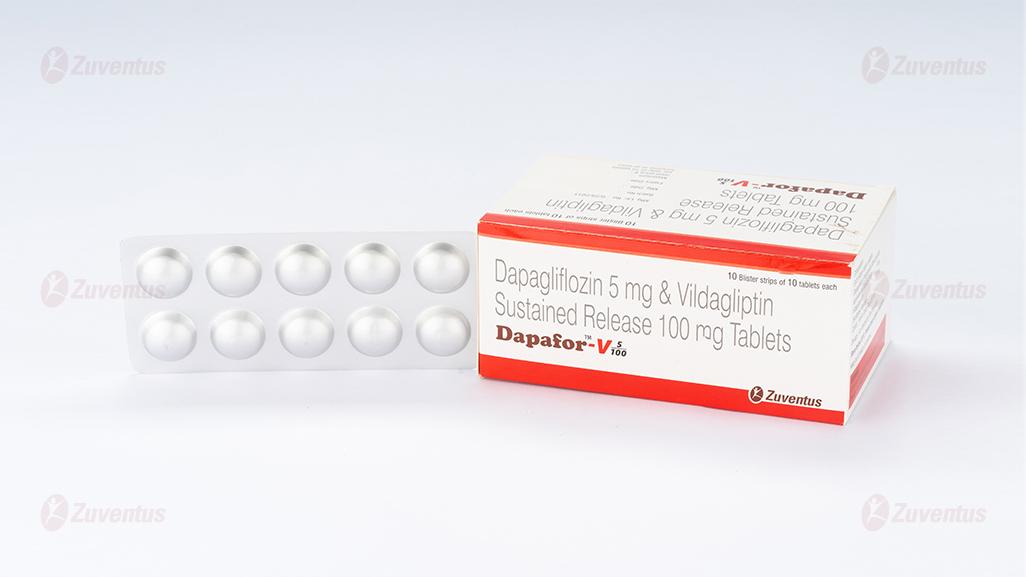
Dapafor V 5/100 mg Tablets
Therapy Area
Anti-diabetic
1.0 Generic name
Vildagliptin (As Sustained Release 100 mg) and Dapagliflozin 5 / 10 mg
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative formula of active ingredients
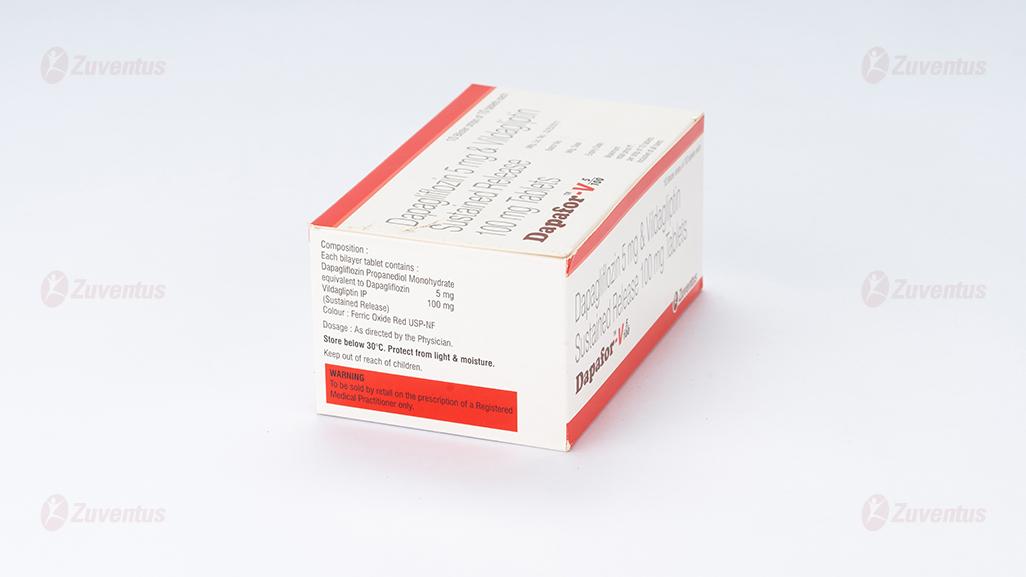
Dapafor-V 5/100 mg
Each bilayered tablet contains :
Dapagliflozin Propanediol Monohydrate
equivalent to Dapagliflozin 5 mg
Vildagliptin IP 100 mg
(As Sustained Release)
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Ferric Oxide Red USP-NF
Dapafor-V 10/100 mg
Each bilayered tablet contains :
Dapagliflozin Propanediol Monohydrate
equivalent to Dapagliflozin 10 mg
Vildagliptin IP 100 mg
(As Sustained Release)
Colour : Ferric Oxide Yellow USP-NF
Excipients q.s.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Bilayer tablets, 5 mg / 100 mg and 10 mg / 100 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
Dapagliflozin and Vildagliptin Sustained Release tablets are indicated for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus who are inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Posology
The recommended dose is one tablet daily. Each tablet contains a fixed dose of dapagliflozin and Vildagliptin (As sustained Release)
Special populations
Renal impairment
No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≥ 50 ml/min). In patients with moderate or severe renal impairment or with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), Dapagliflozin and Vildagliptin SR tablet is not recommended.
Hepatic impairment
This medicinal product must not be used in patients with hepatic impairment
Elderly (≥ 65 years)
This medicinal product should be used with caution as age increases.
Paediatric population
The safety and efficacy of Dapagliflozin and Vildagliptin SR tablets have not yet been established. No data are available.
Method of administration
Dapagliflozin and Vildagliptin SR tablets should be given once daily with meals to reduce the gastrointestinal adverse reactions.
4.3 Contraindications
Dapagliflozin and Vildagliptin SR tablets is contraindicated in patients with: hypersensitivity to the active substances or to any of the excipients used in the manufacturing of the finished product, any type of acute metabolic acidosis, diabetic pre-coma, severe renal failure, dehydration, severe infection, shock, cardiac or respiratory failure, acute alcohol intoxication and alcoholism.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Dapagliflozin
Volume depletion : Before initiating Dapagliflozin, assess volume status and renal function in the elderly, patients with renal impairment or low systolic blood pressure, and in patients on diuretics. Monitor for signs and symptoms during therapy.
Ketoacidosis in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus : Assess patients who present with signs and symptoms of metabolic acidosis for ketoacidosis regardless of blood glucose level. If suspected, discontinue Dapagliflozin, evaluate and treat promptly. Before initiating Dapagliflozin, consider risk factors for ketoacidosis. Patients on Dapagliflozin may require monitoring and temporary discontinuation of therapy in clinical situations known to predispose to ketoacidosis.
Urosepsis and Pyelonephritis : Evaluate for signs and symptoms of urinary tract infections and treat promptly, if indicated.
Hypoglycemia : Consider a lower dose of insulin or the insulin secretagogue to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia when used in combination with Dapagliflozin.
Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum (Fournier's Gangrene) : Serious, life-threatening cases have occurred in patients with diabetes, both females and males. Assess patients presenting with pain or tenderness, erythema, or swelling in the genital or perineal area, along with fever or malaise. If suspected, institute prompt treatment.
Genital Mycotic Infections : Monitor and treat if indicated.
Elderly (≥ 65 years)
Elderly patients may be at a greater risk for volume depletion and are more likely to be treated with diuretics. Elderly patients are more likely to have impaired renal function, and/or to be treated with anti-hypertensive medicinal products that may cause changes in renal function such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE-I) and angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers (ARB). The same recommendations for renal function apply to elderly patients as to all patients.
Lower limb amputations
An increase in cases of lower limb amputation (primarily of the toe) has been observed in long-term, clinical studies in type 2 diabetes mellitus with SGLT2 inhibitors. It is unknown whether this constitutes a class effect. It is important to counsel patients with diabetes on routine preventative foot care.
Vildagliptin
General
Vildagliptin is not a substitute for insulin in insulin-requiring patients. Vildagliptin should not be used in patients with type 1 diabetes or for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Renal impairment
There is limited experience in patients with ESRD on haemodialysis. Therefore Vildagliptin should be used with caution in these patients (see also sections 4.2, 5.1 and 5.2).
Hepatic impairment
Vildagliptin should not be used in patients with hepatic impairment, including patients with pre-treatment ALT or AST > 3x ULN (see also sections 4.2 and 5.2).
Liver enzyme monitoring
Rare cases of hepatic dysfunction (including hepatitis) have been reported. In these cases, the patients were generally asymptomatic without clinical sequelae and liver function test results returned to normal after discontinuation of treatment. Liver function tests should be performed prior to the initiation of treatment with Vildagliptin in order to know the patient's baseline value. Liver function should be monitored during treatment with Vildagliptin at three-month intervals during the first year and periodically thereafter. Patients who develop increased transaminase levels should be monitored with a second liver function evaluation to confirm the finding and be followed thereafter with frequent liver function tests until the abnormality(ies) return(s) to normal. Should an increase in AST or ALT of 3x ULN or greater persist, withdrawal of Vildagliptin therapy is recommended. Patients who develop jaundice or other signs suggestive of liver dysfunction should discontinue Vildagliptin. Following withdrawal of treatment with Vildagliptin and LFT normalisation, treatment with Vildagliptin should not be reinitiated.
Cardiac failure
A clinical trial of vildagliptin in patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class I-III showed that treatment with vildagliptin was not associated with a change in left-ventricular function or worsening of pre-existing congestive heart failure (CHF) versus placebo. Clinical experience in patients with NYHA functional class III treated with vildagliptin is still limited and results are inconclusive (see section 5.1). There is no experience of vildagliptin use in clinical trials in patients with NYHA functional class IV and therefore use is not recommended in these patients.
Skin disorders
Skin lesions, including blistering and ulceration have been reported in extremities of monkeys in non-clinical toxicology studies (see section 5.3). Although skin lesions were not observed at an increased incidence in clinical trials, there was limited experience in patients with diabetic skin complications. Furthermore, there have been post-marketing reports of bullous and exfoliative skin lesions. Therefore, in keeping with routine care of the diabetic patient, monitoring for skin disorders, such as blistering or ulceration, is recommended.
Acute pancreatitis
Use of vildagliptin has been associated with a risk of developing acute pancreatitis. Patients should be informed of the characteristic symptom of acute pancreatitis.
If pancreatitis is suspected, vildagliptin should be discontinued; if acute pancreatitis is confirmed, vildagliptin should not be restarted. Caution should be exercised in patients with a history of acute pancreatitis.
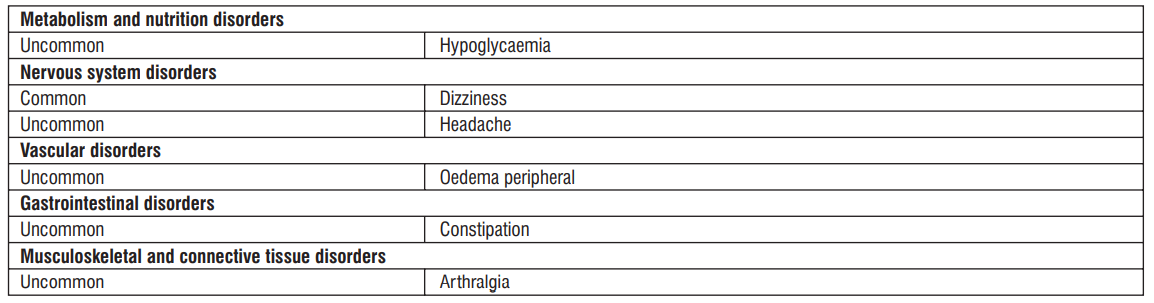
Hypoglycaemia
Sulphonylureas are known to cause hypoglycaemia. Patients receiving vildagliptin in combination with a sulphonylurea may be at risk for hypoglycaemia. Therefore, a lower dose of sulphonylurea may be considered to reduce the risk of hypoglycaemia.
Arthralgia :
We identified cases of severe joint pain associated with the use of DPP-4 inhibitors. Patients started having symptoms from 1 day to years after they started taking a DPP-4 inhibitor. After the patients discontinued the DPP-4 inhibitor medicine, their symptoms were relieved, usually in less than a month. Some patients developed severe joint pain again when they restarted the same medicine or another DPP-4 inhibitor. In such case, Patients should not stop taking their DPP-4 inhibitor medicine, but should contact their health care professional right away if they experience severe and persistent joint pain.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No interaction studies have been performed for Dapagliflozin and Vildaglitpin SR tablets. The following statements reflect the information available on the individual active substances.
Dapagliflozin
Pharmacodynamic interactions
Diuretics
Dapagliflozin may add to the diuretic effect of thiazide and loop diuretics and may increase the risk of dehydration and hypotension.
Insulin and insulin secretagogues
Insulin and insulin secretagogues, such as sulphonylureas, cause hypoglycaemia. Therefore, a lower dose of insulin or an insulin secretagogue may be required to reduce the risk of hypoglycaemia when used in combination with Dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and a known risk of frequent or severe hypoglycaemia, it may be necessary to reduce the insulin dose at the time of initiating treatment with Dapagliflozin to decrease the risk of hypoglycaemia. When needed, insulin dose reduction should be done cautiously to avoid ketosis and DKA.
Pharmacokinetic interactions
The metabolism of Dapagliflozin is primarily via glucuronide conjugation mediated by UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1A9 (UGT1A9). In in vitro studies, Dapagliflozin neither inhibited cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, nor induced CYP1A2, CYP2B6 or CYP3A4. Therefore, Dapagliflozin is not expected to alter the metabolic clearance of co administered medicinal products that are metabolised by these enzymes.
Vildagliptin
Vildagliptin has a low potential for interactions with co-administered medicinal products. Since vildagliptin is not a cytochrome P (CYP) 450 enzyme substrate and does not inhibit or induce CYP 450 enzymes, it is not likely to interact with active substances that are substrates, inhibitors or inducers of these enzymes.
Digoxin (Pgp substrate), warfarin (CYP2C9 substrate)
Clinical studies performed with healthy subjects have shown no clinically relevant pharmacokinetic interactions. However, this has not been established in the target population.
Combination with amlodipine, ramipril, valsartan or simvastatin
Drug-drug interaction studies in healthy subjects were conducted with amlodipine, ramipril, valsartan and simvastatin. In these studies, no clinically relevant pharmacokinetic interactions were observed after co-administration with vildagliptin.
Combination with ACE-inhibitors
There may be an increased risk of angioedema in patients concomitantly taking ACE-inhibitors. As with other oral antidiabetic medicinal products the hypoglycaemic effect of vildagliptin may be reduced by certain active substances, including thiazides, corticosteroids, thyroid products and sympathomimetics.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy
There are no data from the use of Dapagliflozin and Vildagliptin SR tablets or Dapagliflozin in pregnant women. There are no adequate data from the use of vildagliptin in pregnant women. Studies in animals have shown reproductive toxicity at high doses (see section 5.3). The potential risk for humans is unknown. Due to lack of human data, Vildagliptin should not be used during pregnancy.
Breast-feeding
It is unknown whether this medicinal product or dapagliflozin (and / or its metabolites) are excreted in human milk. Available pharmacodynamic / toxicological data in animals have shown excretion of dapagliflozin/metabolites in milk, as well as pharmacologically-mediated effects in nursing offspring. It is unknown whether vildagliptin is excreted in human milk. Animal studies have shown excretion of vildagliptin in milk. Vildagliptin should not be used during breast-feeding.
Fertility
The effect of this medicinal product or Dapagliflozin & Vildagliptin on fertility in humans has not been studied.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Dapagliflozin and Vildagliptin SR tablets have no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Dapagliflozin and Vildagliptin SR tablets have been demonstrated to be bioequivalent with co administered Dapagliflozin and Vildagliptin. There have been no therapeutic clinical trials conducted with Dapagliflozin and Vildagliptin SR tablets. As per reported evidences, following adverse reactions have been identified in the placebo-controlled clinical studies. None were found to be dose-related. Adverse reactions listed below are classified according to frequency and system organ class (SOC). Frequency categories are defined according to the following convention : very common (≥ 1/10), common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10), uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100), rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000), very rare (< 1/10,000), and not known (cannot be estimated from the available data).

Dapagliflozin
Very common : Hypoglycaemia (when used with SU or insulin)
Common : Vulvovaginitis, balanitis and related genital infections, Urinary tract infection
- Dizziness
- Rash
- Back pain
- Dysuria, Polyuria
- Dyslipidaemia
- Haematocrit increased, Creatinine renal clearance decreased during initial treatment
Uncommon : Fungal infection
- Volume depletion, Thirst
- Constipation, Dry mouth
- Nocturia
- Vulvovaginal pruritus, Pruritus genital
- Blood creatinine increased during initial treatment, Blood urea increased
- Weight decreased
Rare : Diabetic ketoacidosis (when used in type 2 diabetes mellitus)
Very rare : Necrotising fasciitis of the perineum (Fournier's gangrene)
- Angioedema
Vildagliptin
Adverse reactions reported in patients who received vildagliptin as monotherapy
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com
4.9 Overdose
Dapagliflozin
Dapagliflozin did not show any toxicity in healthy subjects at single oral doses up to 500 mg (50 times the maximum recommended human dose).
Vildagliptin
Information on the likely symptoms of overdose was taken from a rising dose tolerability study in healthy subjects given Vildagliptin for 10 days. At 400 mg, there were three cases of muscle pain, and individual cases of mild and transient paraesthesia, fever, oedema and a transient increase in lipase levels. At 600 mg, one subject experienced oedema of the feet and hands, and increases in creatine phosphokinase (CPK), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), C-reactive protein (CRP) and myoglobin levels. Three other subjects experienced oedema of the feet, with paraesthesia in two cases. All symptoms and laboratory abnormalities resolved without treatment after discontinuation of the study medicinal product.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group : Drugs used in diabetes, Combinations of oral blood glucose-lowering drugs.
Mechanism of action
Dapagliflozin is a reversible inhibitor of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) that improves glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus by reducing renal glucose reabsorption leading to urinary excretion of excess glucose (glucuresis). SGLT2 is selectively expressed in the kidney. SGLT2 is the predominant transporter responsible for reabsorption of glucose from the glomerular filtrate back into the circulation. Dapagliflozin improves both fasting and post-prandial plasma glucose levels by reducing renal glucose reabsorption leading to urinary excretion of excess glucose. The amount of glucose removed by the kidney through this mechanism is dependent upon the blood glucose concentration and GFR. Dapagliflozin does not impair normal endogenous glucose production in response to hypoglycemia. Dapagliflozin acts independently of insulin secretion and insulin action.
Urinary glucose excretion (glucuresis) induced by Dapagliflozin is associated with caloric loss and reduction in weight. Inhibition of glucose and sodium co-transport by Dapagliflozin is also associated with mild diuresis and transient natriuresis. The effect of vildagliptin layer results in a rapid and complete inhibition of DPP-4 activity, resulting in increased fasting and postprandial endogenous levels of the incretin hormones GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide 1) and GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide).
Vildagliptin
The administration of vildagliptin results in a rapid and complete inhibition of DPP-4 activity, resulting in increased fasting and postprandial endogenous levels of the incretin hormones GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide 1) and GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide).
Pharmacodynamic effects
Dapagliflozin
Increases in the amount of glucose excreted in the urine were observed in healthy subjects and in subjects with type 2diabetes mellitus following the administration of dapagliflozin.
Vildagliptin
By increasing the endogenous levels of these incretin hormones, vildagliptin enhances the sensitivity of beta cells to glucose, resulting in improved glucosedependent insulin secretion. Treatment with vildagliptin sustained release tablets 100 mg daily in patients with type 2 diabetes significantly improved markers of beta cell function including HOMA-β (Homeostasis Model Assessment-β), proinsulin to insulin ratio and measures of beta cell responsiveness from the frequentlysampled meal tolerance test. In non-diabetic (normal glycaemic) individuals, vildagliptin does not stimulate insulin secretion or reduce glucose levels. By increasing endogenous GLP-1 levels, vildagliptin also enhances the sensitivity of alpha cells to glucose, resulting in more glucose-appropriate glucagon secretion.
The enhanced increase in the insulin/glucagon ratio during hyperglycaemia due to increased incretin hormone levels results in a decrease in fasting and postprandial hepatic glucose production, leading to reduced glycaemia. The known effect of increased GLP-1 levels delaying gastric emptying is not observed with vildagliptin treatment.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Dapagliflozin
Absorption : Dapagliflozin was rapidly and well absorbed after oral administration and can be administered with or without food. Geometric mean steady-state Dapagliflozin Cmax and AUCτ values following once daily 10 mg doses of Dapagliflozin were 158 ng/mL and 628 ng.h/mL, respectively. Maximum Dapagliflozin plasma concentrations (Cmax) were usually attained within 2 hours after administration in the fasted state. The Cmax and AUC values increased proportionally to the increment in Dapagliflozin dose. The absolute oral bioavailability of Dapagliflozin following the administration of a 10 mg dose is 78%. Food had relatively modest effects on the pharmacokinetics of Dapagliflozin in healthy subjects. Administration with a high-fat meal decreased Dapagliflozin Cmax by up to 50% and prolonged Tmax by approximately 1 hour, but did not alter AUC as compared with the fasted state. These changes are not considered to be clinically meaningful. Distribution : Dapagliflozin is approximately 91% protein bound. Protein binding was not altered in various disease states (e.g. renal or hepatic impairment). Metabolism : Dapagliflozin is a C-linked glucoside, meaning the aglycone component is attached to glucose by a carbon-carbon bond, thereby conferring stability against glucosidase enzymes. The mean plasma terminal half-life (t1/2) for Dapagliflozin was 12.9 hours following a single oral dose of Dapagliflozin 10 mg to healthy subjects. Dapagliflozin is extensively metabolized, primarily to yield Dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide, which is an inactive metabolite. Dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide accounted for 61% of a 50 mg [14C]-Dapagliflozin dose and was the predominant drug-related component in human plasma, accounting for 42% (based on AUC [0-12 h]) of total plasma radioactivity, similar to the 39% contribution by parent drug. Based on AUC, no other metabolite accounted for >5% of the total plasma radioactivity at any time point measured. Dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide or other metabolites do not contribute to the glucose-lowering effects. The formation of Dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide is mediated by UGT1A9, an enzyme present in the liver and kidney, and CYP-mediated metabolism was a minor clearance pathway in humans. Excretion : Dapagliflozin and related metabolites are primarily eliminated via urinary excretion, of which less than 2% is unchanged Dapagliflozin. After administration of 50 mg [14C]-Dapagliflozin dose, 96% was recovered, 75% in urine and 21% in feces. In feces, approximately 15% of the dose was excreted as parent drug
Vildagliptin
Absorption
Following oral administration in the fasting state, Vildagliptin is rapidly absorbed, with peak plasma concentrations observed at 1.7 hours. Food slightly delays the time to peak plasma concentration to 2.5 hours, but does not alter the overall exposure (AUC). Administration of Vildagliptin with food resulted in a decreased Cmax (19%). However, the magnitude of change is not clinically significant, so that Vildagliptin can be given with or without food. The absolute bioavailability is 85%.
Distribution
The plasma protein binding of Vildagliptin is low (9.3%) and Vildagliptin distributes equally between plasma and red blood cells. The mean volume of distribution of Vildagliptin at steady-state after intravenous administration (Vss) is 71 litres, suggesting extravascular distribution.
Biotransformation
Metabolism is the major elimination pathway for Vildagliptin in humans, accounting for 69% of the dose. The major metabolite (LAY 151) is pharmacologically inactive and is the hydrolysis product of the cyano moiety, accounting for 57% of the dose, followed by the glucuronide (BQS867) and the amide hydrolysis products (4% of dose). In vitro data in human kidney microsomes suggest that the kidney may be one of the major organs contributing to the hydrolysis of Vildagliptin to its major inactive metabolite, LAY151. DPP-4 contributes partially to the hydrolysis of Vildagliptin based on an in vivo study using DPP-4 deficient rats. Vildagliptin is not metabolised by CYP 450 enzymes to any quantifiable extent. Accordingly, the metabolic clearance of Vildagliptin is not anticipated to be affected by co-medications that are CYP 450 inhibitors and/or inducers. In vitro studies demonstrated that Vildagliptin does not inhibit/induce CYP 450 enzymes. Therefore, Vildagliptin is not likely to affect metabolic clearance of co-medications metabolised by CYP 1A2, CYP 2C8, CYP 2C9, CYP 2C19, CYP 2D6, CYP 2E1 or CYP 3A4/5.
Elimination
Following oral administration of [14C] Vildagliptin, approximately 85% of the dose was excreted into the urine and 15% of the dose is recovered in the faeces. Renal excretion of the unchanged Vildagliptin accounted for 23% of the dose after oral administration. After intravenous administration to healthy subjects, the total plasma and renal clearances of Vildagliptin are 41 and 13 l/h, respectively. The mean elimination half-life after intravenous administration is approximately 2 hours. The elimination half-life after oral administration is approximately 3 hours.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Preclinical Pharmacology
Dapagliflozin :
In vivo primary pharmacodynamic studies with Dapagliflozin were carried out in single-dose, dose ranging studies in non-diabetic and diabetic rats or mice in order to evaluate the potency, SGLT2-specificity and duration of action in stimulating urinary glucose excretion, and to describe the secondary consequences of urinary glucose excretion, such as changes in urine volume or blood or plasma glucose effects. Subsequently a multiple-dose study was carried out to evaluate the ability of Dapagliflozin to have sustained effects on urinary glucose excretion, urine volume, and fasting plasma glucose in diabetic rats over a two-week dosing period. Dapagliflozin increased renal glucose excretion in (healthy, non-diabetic) experimental animals. This was accompanied, by osmotic diuresis as measured by increased urine flow. An oral glucose tolerance test was also performed showing that Dapagliflozin was able to significantly reduce glucose area under the curve (AUC), compared to vehicle treatment. A study in knock-out mice lacking the gene for SGLT2 revealed that SGLT2 is indeed the main target for Dapagliflozin at least at lower doses. This study also demonstrated the reversibility of Dapagliflozin's action towards SGLT2. Vildagliptin is a selective and potent inhibitor of DPP-4. The IC50 value for inhibition of human DPP-4 is about 3 nM and similar activity was observed with the rat enzyme, demonstrating the lack of species selectivity. Vildagliptin showed some activity at the related enzymes DPP-8 and DPP-9 (Ki values of 506 nM and 65 nM respectively). Although these values are 253 and 32 times higher than the Ki for DPP-4, activity at Cmax in humans (2.3 μM) is likely. No assays exist allowing evaluation of DPP-8 / DPP-9 inhibition in vivo. The possibility of activity at one or both of these targets is considered a safety concern in relation to the occurrence of skin lesions in monkeys. No, or minimal, inhibition was seen with other related enzymes. In vivo pharmacodynamic studies were performed in rats and monkeys. These studies demonstrated the in vivo inhibition of DPP-4 and increased plasma levels of GLP-1. Studies in diabetic rats and in insulin-resistant monkeys demonstrated a glucose-lowering effect of Vildagliptin. Chronic effects of Vildagliptin were studied in pre-diabetic and insulin-treated diabetic monkeys. Beneficial effects were observed on HbA1c, fasting insulin, fibrinogen and PAI-1.
6.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
6.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
6.2 Special precautions for storage
This medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions.
6.3 Nature and contents of container
Alu-Alu blister. 10 bilayer tablets in non-perforated blisters.
6.4 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements
7.0 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack
8.0 Packaging information
A blister strip of 10 tablets
9.0 Storage condition
Store below 30°C. Protect from light & moisture.
Keep out of reach of children.
12.0 Date of issue
22 June 2022

About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet:
- What Dapafor-V is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you take Dapafor-V
- How to take Dapafor-V
- Possible side effects
- How to store Dapafor-V
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Dapafor-V is and what it is used for
Dapafor-V contains the active substances vildagliptin and dapagliflozin. Each belongs to a group of medicines called “oral anti-diabetics”. These medicines are taken by mouth for diabetes.
Dapafor-V is used for a type of diabetes called “type 2 diabetes mellitus” in adult patients (aged 18 years and older). If you have type 2 diabetes, your pancreas does not make enough insulin or your body is not able to use the insulin it produces properly. This leads to a high level of sugar in your blood. The two active substances in Dapafor-V work in different ways to help control the level of sugar in your blood and remove excess sugar from your body via your urine.
Dapafor-V is used to treat type 2 diabetes when:
- vildagliptin or dapagliflozin alone together with metformin and/or sulphonylurea cannot control your diabetes.
- you are already being treated with vildagliptin and dapagliflozin as single tablets. Your doctor may ask you to switch to this medicine.
It is important to continue to follow the advice on diet and exercise given to you by your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
2. What you need to know before you take Dapafor-V
Do not take Dapafor-V:
- if you are allergic to vildagliptin, dapagliflozin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if you have had a serious allergic reaction to any other similar medicines (for example DPP-4 inhibitors like sitagliptin, linagliptin, alogliptin, or SGLT2 inhibitors like canagliflozin, empagliflozin) that you take to control your blood sugar.
Do not take Dapafor-V if any of the above apply to you. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before taking this medicine.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before taking Dapafor-V, and during treatment:
- if you have or have had a disease of the pancreas called pancreatitis. Possible signs of pancreatitis are listed in section 4.
- if you are on medicines to lower your blood pressure (anti-hypertensives) and have a history of low blood pressure (hypotension). For more information, see section “Other medicines and Dapafor-V” below.
- if you have very high levels of sugar in your blood which may make you dehydrated (lose too much body fluid). Possible signs of dehydration are listed at the top of section 4. Tell your doctor before you start taking Dapafor-V if you have any of these signs.
- if you have or develop nausea (feeling sick), vomiting or fever or if you are not able to eat or drink. These conditions can cause dehydration. Your doctor may ask you to stop taking Dapafor-V until you recover to prevent dehydration.
- if you have moderate or severe liver problem.
- if you experience rapid weight loss, feeling sick or being sick, stomach pain, excessive thirst, fast and deep breathing, confusion, unusual sleepiness or tiredness, a sweet smell to your breath, a sweet or metallic taste in your mouth, or a different odour to your urine or sweat, contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away. These symptoms could be a sign of “diabetic ketoacidosis” – a rare but serious, sometimes life-threatening problem you can get with diabetes because of increased levels of “ketone bodies” in your urine or blood, seen in tests. The risk of developing diabetic ketoacidosis may be increased with prolonged fasting, excessive alcohol consumption, dehydration, sudden reductions in insulin dose, or a higher need of insulin due to major surgery or serious illness.
- if you have “type 1 diabetes” your body does not produce any insulin. Dapafor-V should not be used to treat this condition.
- if you have or have had a serious hypersensitivity (allergic) reaction or is suspected. Signs of a serious allergic reaction are listed in section 4.
- if you often get infections of the urinary tract.
- if you have a history of serious heart disease.
- if you suffer from heart failure or you have other risk factors for developing heart failure such as problems with your kidneys. Your doctor will advise you of the signs and symptoms of heart failure. Symptoms can include, but are not limited to, increasing shortness of breath, rapid increase in weight and swelling of the feet (pedal oedema). You should call your doctor, pharmacist or nurse immediately if you experience any of these symptoms.
- if you have severe joint pain.
- if your body’s ability to fight infections is reduced, for example if you have a disease like AIDS or have undergone an organ transplant.
- if you are taking a medicine to lower your blood sugar, such as sulphonylureas (see “Other medicines and Dapafor-V”).
If any of the above apply to you (or you are not sure), talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before taking Dapafor-V.
Diabetic skin lesions (skin damage such as sores or ulcers) are a common complication of diabetes. Rash has been seen with both vildagliptin and dapagliflozin when given separately (see section 4). You are advised to follow the recommendations for skin care that you are given by your doctor or nurse. Contact your doctor if you encounter blistering of the skin, as it may be a sign for a condition called bullous pemphigoid. Your doctor may ask you to stop Dapafor-V.
Like for all diabetic patients it is important to check your feet regularly and adhere to any other advice regarding foot care given by your health care professional.
Talk to your doctor immediately if you develop a combination of symptoms of pain, tenderness, redness, or swelling of the genitals or the area between the genitals and the anus with fever or feeling generally unwell. These symptoms could be a sign of a rare but serious or even life-threatening infection, called necrotising fasciitis of the perineum or Fournier’s gangrene which destroys the tissue under the skin. Fournier’s gangrene has to be treated immediately.
Kidney function
Your kidneys should be checked before you start taking Dapafor-V. During treatment with this medicine, your doctor will check your kidney function once a year or more frequently if you have worsening kidney function.
Urine tests
Because of how Dapafor-V works, your urine will test positive for sugar while you are on this medicine.
Children and adolescents
Dapafor-V is not recommended for children and adolescents under 18 years of age, because it has not been studied in these patients.
Other medicines and Dapafor-V
Tell your doctor, pharmacist or nurse if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
Especially tell your doctor:
- if you are taking a medicine used to increase the amount of water you pass out of the body (diuretic). Your doctor may ask you to stop taking Dapafor-V. Possible signs of losing too much fluid from your body are listed at the top of section 4.
- if you are taking another medicine that lowers the amount of sugar in your blood such as a sulphonylurea (for example glimepiride). Your doctor may want to lower the dose of this other medicine, to prevent you from getting low blood sugar levels (hypoglycaemia).
- if you are using medicines containing any of the following active substances, that might have an effect on the breakdown of Dapafor-V in your body. Your doctor may ask you to check your blood sugar levels more often while taking these medicines.
- Carbamazepine, phenobarbital or phenytoin. These may be used to control fits (seizures) or chronic pain.
- Dexamethasone – a steroid medicine. This may be used to treat inflammation in different body parts and organs.
- Rifampicin. This is an antibiotic used to treat infections such as tuberculosis. Ketoconazole. This may be used to treat fungal infections.
- Diltiazem. This is a medicine used to treat angina (chest pain) and lower blood pressure. If any of the above apply to you (or if you are not sure), talk to your doctor before taking Dapafor-V.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine. Dapafor-V is not recommended during pregnancy and your doctor will ask you to stop taking this medicine if you become pregnant. Talk to your doctor about the best way to control your blood sugar while you are pregnant.
You should not use Dapafor-V if you are breast-feeding. It is not known if this medicine passes into human breast milk. Talk to your doctor if you would like to or are breast-feeding before taking this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Dapafor-V is not expected to affect you being able to drive a car or use any tools or machines. If you feel dizzy while taking this medicine, do not drive or use any tools or machines. Taking this medicine together with another medicine that lowers your blood sugar, such as a sulphonylurea, can cause too low blood sugar levels (hypoglycaemia). This may cause symptoms such as shaking, sweating and change in vision, and may affect your ability to drive and use machines.
Dapafor-V contains lactose
Dapafor-V contains lactose (milk sugar). If you have been told by your doctor that you have an intolerance to some sugars, contact your doctor before taking this medicine.
Dapafor-V contains sodium
Dapafor-V contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per dose, that is to say essentially ‘sodiumfree’.
3. How to take Dapafor-V
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Check with your doctor, pharmacist or nurse if you are not sure.
How much to take
- The recommended dose is one tablet a day.
Taking this medicine
- Swallow the tablet whole with half a glass of water.
- You can take your tablet with or without food.
- You can take the tablet at any time of the day. However, try to take it at the same time each day. This will help you to remember to take it.
Your doctor may prescribe other medicines to lower the amount of sugar in your blood. Remember to take other medicine(s) as your doctor has told you. This will help get the best results for your health.
Diet and exercise
To control your diabetes, you still need to keep to diet and exercise, even when you are taking this medicine. So it is important to keep following the advice about diet and exercise from your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. In particular, if you are following a diabetic weight control diet, continue to follow it while you are taking Dapafor-V.
If you take more Dapafor-V than you should
If you take more Dapafor-V tablets than you should, talk to a doctor or go to a hospital straight away. Take the medicine pack with you.
If you forget to take Dapafor-V
What to do if you forget to take a tablet.
- If it is less than 12 hours since you should have taken your dose, take a dose of Dapafor-V as soon as you remember. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
- If it is more than 12 hours since you should have taken your dose, skip the missed dose. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
- Do not take a double dose of Dapafor-V to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop taking Dapafor-V
Do not stop taking Dapafor-V without talking to your doctor first. Your blood sugar may increase without this medicine.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Stop taking Dapafor-V and see a doctor straight away if you notice any of the following serious side effects:
Symptoms of a serious allergic reaction (anaphylactic reaction, angioedema) seen rarely, (may affect up to 1 in 1 000 people), which may include:
- rash,
- raised red patches on your skin (hives),
- swelling of the face,lips, tongue, and throat that may cause difficulty in breathing or
- swallowing.
Your doctor may prescribe a medicine to treat your allergic reaction and a different medicine for your diabetes.
Pancreatitis, seen uncommonly (may affect up to 1 in 100 people): severe and persistent pain in the abdomen (stomach area) which might reach through to your back, as well as nausea and vomiting, as it could be a sign of an inflamed pancreas.
Dehydration, (loss of too much fluid from your body), seen uncommonly. These are signs of dehydration:
- very dry or sticky mouth, feeling very thirsty,
- feeling very sleepy or tired, - passing little or no water (urine), - fast heart beat.
Urinary tract infection, seen commonly (may affect up to 1 in 10 people). These are signs of a severe infection of the urinary tract:
- fever and/or chills, burning sensation when passing water (urinating),
- pain in your back or side.
Although uncommon, if you see blood in your urine, tell your doctor immediately.
Low blood sugar levels (hypoglycaemia), seen very commonly (may affect more than 1 in 10 people) if used with other diabetes medicines known to cause hypoglycaemia.
These are the signs of low blood sugar:
shaking, sweating, feeling very anxious, fast heart beat, - feeling hungry, headache, change in vision, - a change in your mood or feeling confused.
Your doctor will tell you how to treat low blood sugar levels and what to do if you get any of the signs above.
Diabetic ketoacidosis, seen rarely.
These are the signs of diabetic ketoacidosis (see also section 2 Warnings and precautions): - increased levels of “ketone bodies” in your urine or blood,
- rapid weight loss,
- feeling sick or being sick,
- stomach pain,
- excessive thirst,
- fast and deep breathing,
- confusion,
- unusual sleepiness or tiredness,
- a sweet smell to your breath,
- a sweet or metallic taste in your mouth or a different odour to your urine or sweat.
This may occur regardless of blood glucose level. Your doctor may decide to temporarily or permanently stop your treatment with Dapafor-V.
Necrotising fasciitis of the perineum or Fournier’s gangrene, a serious soft tissue infection of the genitals or the area between the genitals and the anus, seen very rarely (may affect up to 1 in 10 000 people).
Stop taking Dapafor-V and see a doctor or nurse straight away, if you notice any of the serious side effects above.
Other side effects when taking Dapafor-V alone or in combination with metformin: Very common
- upper respiratory tract infection including: - infection of the upper chest or lungs,
- infection of the sinuses with a feeling of pain and fullness behind your cheeks and eyes (sinusitis),
- inflamed nose or throat (nasopharyngitis) (signs of this may include a cold or a sore throat).
Common
- genital infection (thrush) of your penis or vagina (signs may include irritation, itching, unusual discharge or odour)
- back pain
- passing more water (urine) than usual or needing to pass water more often
- changes in the amount of cholesterol or fats in your blood (shown in tests)
- increases in the amount of red blood cells in your blood (shown in tests)
- decreases in creatinine renal clearance (shown in tests) in the beginning of treatment
- dizziness
- tiredness
- severe joint pain (arthralgia)
- stomach ache and indigestion (dyspepsia)
- nausea
- diarrhoea
- inflamed stomach or gut usually caused by an infection (gastroenteritis)
- headache, muscle pain (myalgia)
- vomiting, inflammation of the stomach (gastritis)
- rash
Uncommon
- thirst
- constipation
- awakening from sleep at night to pass urine
- dry mouth
- weight decreased
- increases in creatinine (shown in laboratory blood tests) in the beginning of treatment
- increases in urea (shown in laboratory blood tests)
- skin rash that may include raised bumps, skin irritation, or unpleasant itchiness
- difficulties in getting or maintaining an erection (erectile dysfunction)
- fungal infection
- hypersensitivity reactions
- itching in the genital area (pruritus genital or vulvovaginal pruritus) or discomfort while urinating
Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- blistering of the skin (bullous pemphigoid)
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Dapafor-V
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date, which is stated on the blister and carton after ‘EXP’. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
This medicine does not require any special storage conditions. Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste.
Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Dapafor-V contains
- The active substances are vildagliptin and dapagliflozin.
Dapafor-V 5/100 mg
Each bilayer tablet contains:
Dapagliflozin Propanediol Monohydrate
equivalent to Dapagliflozin -5 mg
Vildagliptin IP -100 mg (Sustained Release)
Dapafor-V 10/100 mg
Each bilayer tablet contains:
Dapagliflozin Propanediol Monohydrate
equivalent to Dapagliflozin- 10 mg
Vildagliptin IP 100 mg (Sustained Release)
What Dapafor-V looks like and contents of the pack
Dapafor-V 5/100 mg
Colour : Ferric Oxide Red USP-NF
Dapafor-V 10/100 mg
Colour : Ferric Oxide Yellow USP-NF
Pack contains 10 Blister Strips of 10 tablet each.