Efnocar 10 Tablet
Therapy Area
Cardiology
1.0 Generic Name
Efonidipine Hydrochloride Ethanolate Tablets 10 mg / 20 mg / 40 mg
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
EFNOCAR-10
Each film coated tablet contains:
Efonidipine Hydrochloride Ethanolate 10 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Titanium Dioxide IP
EFNOCAR-20
Each film coated tablet contains:
Efonidipine Hydrochloride Ethanolate 20 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Titanium Dioxide IP
EFNOCAR-40
Each film coated tablet contains:
Efonidipine Hydrochloride Ethanolate 40 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Titanium Dioxide IP
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Film coated tablet
10/ 20/40 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic Indication
Efonidipine is indicated for the management of
- Essential hypertension and renal parenchymal hypertension
- Angina
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adults
- Essential hypertension and renal parenchymal hypertension: 20-40 mg orally once daily. A dose of up to 80 mg/day has been reported to be safe and effective in clinical trials.
- Angina: 40 mg/day.
Elderly
Efonidipine should be started with a low dose (20mg/day) and the patient's condition should be monitored. The dose should be halved in case the patient is intolerant to the higher dose.
In Children
Efonidipine is not recommended in infants and children as safety is not established in this group of patients.
4.3 Contraindications
- In patients with known hypersensitivity to Efonidipine or any other component of the formulation
- In pregnant women
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
- Should be administered with caution in patients with hepatic impairment.
- Should be administered with caution in patients with low BP and/or sinus node dysfunction.
- The drug should be withdrawn gradually to prevent rebound hypertension or worsening of angina.
- Administration of the drug may cause hypotension. Under such circumstances appropriate measures should be taken to either reduce the dose or withdraw the drug.
- Should not be taken with grapefruit juice as there may be excessive lowering of blood pressure.
- Dizziness may occur while taking antihypertensive agents. Hence, working on aerial platform, working with dangerous machinery and/or driving should be avoided.
- To be sold by retail on the prescription of Cardiologist / Nephrologist / Endocrinologist and Specialist in General / Internal medicine / Critical Care medicine only.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Concomitant administration of other antihypertensive agent/s may enhance the antihypertensive effect of efonidipine.
- Administration of calcium channel blockers (CCBs) with Cimetidine may cause elevated levels of CCBs.
- Increased levels of CCBs observed when taken concomitantly with grapefruit juice which may result in excessive lowering of blood pressure.
- Efonidipine when taken along with Tacrolimus may cause increased blood levels of Tacrolimus.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
Efonidipine should not be administered in pregnant women.
Nursing Mothers
Efonidipine should not be administered in lactating women.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
If patients taking Efonidipine suffer from dizziness, headache, fatigue or nausea the ability to react may be impaired. Caution is recommended especially at the start of treatment.
4.8 Undesirable effects
The common side effects are hot flushes, palpitations, facial flushing and headache. In addition, elevation in serum total cholesterol, ALT (SGPT), AST (SGOT) and BUN may occur.
Tabulated list of adverse reactions
,!--
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
-->
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to:medico@zuventus.com
Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
4.9 Overdose
In humans, experience with intentional overdose is limited. The stomach should be emptied by aspiration and gastric lavage if the patient reports immediately or up to two hours after overdosage.
Clinically significant hypotension due to Efonidipine overdosage calls for active cardiovascular support including frequent monitoring of cardiac and respiratory function, elevation of extremities, and attention to circulating fluid volume and urine output. A vasoconstrictor may be helpful in restoring vascular tone and blood pressure, provided that there is no contraindication to its use. Intravenous calcium gluconate may be beneficial in reversing the effects of calcium channel blockade.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Efonidipine, a new generation dihydropyridine (DHP) calcium channel blocker, inhibits both L-type and T-type calcium channels.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
- Efonidipine exhibits antihypertensive effect through vasodilatation by blocking L-type and T-type calcium channels.
- Efonidipine has a negative chronotropic effect. Working on sino atrial node cells by inhibiting T-type calcium channel activation, Efonidipine prolongs the late phase-4 depolarization of the sino atrial node action potential and suppresses an elevated HR. The negative chronotropic effect of Efonidipine decreases heart rate, myocardial oxygen demand and increases coronary blood flow.
- Efonidipine increases coronary blood flow by blocking L & T-type calcium channels and attenuates myocardial ischaemia.
- By reducing synthesis and secretion of aldosterone, Efonidipine prevents hypertrophy and remodeling of cardiac myocytes.
- Efonidipine increases glomerular filtration rate without increasing intra-glomerular pressure and filtration fraction. This prevents hypertension induced renal damage.
- Efonidipine prevents Rho-kinase and NF-kB induced renal parenchymal fibrosis and provides long term renal protection.
- Efonidipine suppresses renin secretion from the Juxta Glomerular apparatus in the kidneys. •Efonidipine enhances sodium excretion from the kidneys by suppressing aldosterone synthesis and secretion from the adrenal glands. Aldosterone induced renal parenchymal fibrosis is suppressed by Efonidipine. •Efonidipine prevents NF-kB induced hypertrophy and inflammation in the renal vasculature and protects the kidneys.
- Efonidipine protects against endothelial dysfunction due to its anti-oxidant activity and by restoring nitric oxide bioavailability.
- Efonidipine has anti-atherogenic activity and protects the blood vessels from atherosclerosis.
- Efonidipine lowers blood pressure in cerebral resistance vessels and prevents hypertension induced brain damage.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Peak plasma concentration is achieved in about 1.5 to 3.67 hours after administration. The bioavailability of Efonidipine is ~25% and half-life is approximately 4 hours.
Efonidipine 40mg when administered to healthy volunteers under fasting conditions shows the following pharmacokinetic profile:
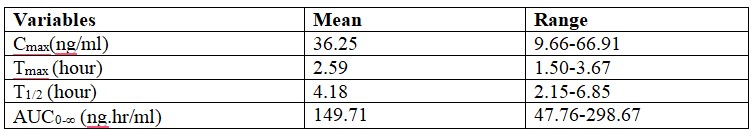
The dissociation constant of Efonidipine from dihydropyridine receptors is very low (0.0042/min/nM), signifying very slow dissociation from the receptors. This explains the long duration of action of Efonidipine.
Metabolism
Efonidipine is primarily metabolized in the liver. The important metabolites are N-dephenylated Efonidipine (DPH), deaminated Efonidipine (AL) and N-debenzylated Efonidipine (DBZ). DBZ and DPH exhibit activity as calcium antagonists. The vasodilating properties of DBZ and DPH were about two-thirds and one-third respectively than that of the parent compound. Results suggest that the majority of the pharmacological effect after oral dosing of Efonidipine hydrochloride in man is due to unchanged compound and its metabolites make a small contribution to the pharmacological effect.
Elimination
Biliary route is the main pathway of excretion. No significant amount of unchanged drug is excreted in urine. In the urine collected for 24 h after an oral dosing, 1.1% of the dose was excreted as deaminated Efonidipine, and 0.5% as a pyridine analogue of deaminated Efonidipine.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
The acute toxicology of efonidipine was studied in male and female mice, rats, and dogs following oral or intravenous administration. The intravenous LD, values in male mice and rats were 77 and 51 mg/kg, respectively. The oral LD, values for efonidipine in mice, rats, and dogs were higher than 1,500 mag. The signs of toxicity observed in mice and rats were depression of spontaneous movement, hypothermia, sedation, piloerection, lying, gasping, and clonic convulsion. The dogs developed mild diarrhea, soft stools, or a temporary decrease in food consumption.
A 13-week oral subacute toxicity study of efonidipine was performed in male or female rats and dogs. Increases in water consumption and urine volume were observed in male and female rats receiving efonidipine at 300 mg/kg/day. Urinalysis revealed a high concentration of Na+ and C1- in the rats receiving 100 or 300 mg/kg/day. Organ weight measurement revealed an increase in liver and heart weight in male animals receiving 10 mg/kg/day or more and in female animals receiving 30 mg/kg/day or more.
Thus, in this study, the noneffective dose level was 3 mg/kg/day in rats. The effects observed at 300 or 100 mg/kg/day in groups of male or female dogs included reversible hyperemia of the sclera. Pathological examination revealed a dose-induced increase in the absolute and relative heart weight in female dogs treated with the drug at 100 mg/kg/day or more. Thus, the maximum noneffective dose of efonidipine in dogs of either sex was estimated to be around 30 mg/kg/day.
An oral chronic toxicity study of efonidipine was carried out in rats and dogs. Efonidipine was administered to rats at a daily dose of 1.5, 7, or 30 mg/kg for one year.
Organ weight measurement revealed an increase or a tendency of increase in heart weight in male or female rats receiving 30 mg/kg/day. A decreased thyroid weight in the males and an elevated liver weight in the females were found in the 30 mg/kg/day group.
Therefore, the noneffective estimated oral dose of efonidipine in rats was 7 mg/kg/day. Efonidipine in a gelatin capsule containing 2.0, 6.5, or 20 mg/kg/day was administered to dogs once daily for one year. The estimated effective dose was ca 20 mg/kg/day and the noneffective dose was ca 6.5 mg/kg/day
7.0 Description
Efonidipine is a novel dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker having anti-hypertensive and anti-anginal properties.
Chemical name: (±) -2 - [benzyl (phenyl) amino] ethyl 1, 4-dihydro-2 ,6-dimethyl- 5-(5,5-dimethyl-2-oxo-1 ,3,2-dioxaphosphorinan-2-yl) -4 - (3-nitrophenyl) -3-pyridinecarboxylate hydrochloride ethanol.
Molecular formula: C34H38 N3O7P • HCl •C2H6O
Molecular mass: 714.18 g/mol
About Leaflet
The name of your medicine is EFNOCAR 10 mg / 20 mg / 40 mg Tablets. We refer to them as EFNOCAR Tablets or EFNOCAR throughout this leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
If you have any more questions, please ask your doctor or your pharmacist.
This medicine has been prescribed for you personally and you should not pass it on to anyone else. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects that are not listed in the leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
In this leaflet:
1. What EFNOCAR Tablets are and what they are used for
2. What you need to know before you take EFNOCAR Tablets
3. How to take EFNOCAR Tablets
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store EFNOCAR Tablets
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Efnocar Tablets Are and What They Are Used for
EFNOCAR Tablets contain the active substance efonidipine which belongs to a group of medicines called calcium antagonists.
EFNOCAR Tablets may be used to treat:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- hypertension caused by kidney disease
- A certain type of chest pain called angina
In patients with high blood pressure, these medicines work by relaxing blood vessels, so that blood passes through them more easily. In patients with angina, EFNOCAR works by improving blood supply to the heart muscle which then receives more oxygen and as a result chest pain is prevented. EFNOCAR Tablets do not immediately relieve chest pain caused by angina.
2. What You Need to Know Before You Take Efnocar Tablets
Do not take EFNOCAR Tablets if you:
- Have ever had an allergic reaction to efonidipine or any of the ingredients in the tablet. An allergic reaction may include a rash, itching, difficulty breathing or swelling of the face, lips, throat or tongue;
- If you are pregnant
Take special care with EFNOCAR Tablets
You should inform you doctor if you have or have had any of the following conditions:
Liver disease;
Recent heart attack;
Heart failure;
Severe increase in blood pressure (Hypertensive crisis).
Use in children and adolescents
EFNOCAR is not recommended in infants and children as safety is not established in this group of patients.
For more information, talk to your doctor.
Taking other medicines and EFNOCAR
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken other medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription.
EFNOCAR may affect or be affected by other medicines, such as:
- Other antihypertensive agent/s (BP lowering drugs)
- Cimetidine (stomach acid reducer)
- Tacrolimus (a drug to suppress immunity)
EFNOCAR may lower your blood pressure even more if you are already taking other medicines to treat your high blood pressure.
If you see another doctor or go into hospital for any reason, tell them that you are taking EFNOCAR Tablets.
Taking EFNOCAR Tablets with food and drink
You should not drink grapefruit juice or eat grapefruit while taking this medicine. Grapefruit and grapefruit juice can lead to an increase in the blood levels of efonidipine, which can cause an unpredictable increase in its blood pressure lowering effect.
Pregnancy
The safety of efonidipine in human pregnancy has not been established. Efonidipine should not be administered in pregnant women.
Breast-feeding
It is not known whether efonidipine is passed into breast milk. Efonidipine should not be administered in breast-feeding women.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
Dizziness may occur while taking antihypertensive agents. Hence, working on aerial platform, working with dangerous machinery and/or driving should be avoided.
3. How to Take Efnocar Tablets
Swallow these tablets with a glass of water at the same time each day. You can take the tablets after meals.
Follow your doctor’s instructions. Check the pharmacy label to see how many tablets to take and how often to take them. If you are still not sure, ask your pharmacist or doctor. The usual doses are described below.
Adults
Essential hypertension and renal parenchymal hypertension: 20-40 mg orally once daily. A dose of up to 80 mg/day has been reported to be safe and effective in clinical trials.
Angina: 40 mg/day.
Children
EFNOCAR is not recommended in infants and children as safety is not established in this group of patients.
Elderly
EFNOCAR should be started with a low dose (20mg/day). Your doctor will closely monitor your response to any decrease in the dose.
Patients with liver disease
Your doctor may give you a different dose to normal.
If you take more EFNOCAR Tablets than you should
If you (or someone else) swallow a lot of tablets all together, or if you think a child has swallowed any of the tablets, contact your nearest hospital casualty department or your doctor immediately. Take your medication and the packaging with you to the doctor or casualty department. If you have taken an overdose, you may you may appear flushed (your skin will look red), or you may feel dizzy or faint. If blood pressure drop is severe enough shock can occur.
If you forget to take EFNOCAR Tablets
If you forget to take a tablet, take one as soon as you remember, unless it is nearly time to take the next one. Never take two doses together. Take the remaining doses at the correct time.
If you stop taking EFNOCAR Tablets
Take this medicine for as long as your doctor tells you to, as you may become unwell if you stop.
4. Possible Side Effects
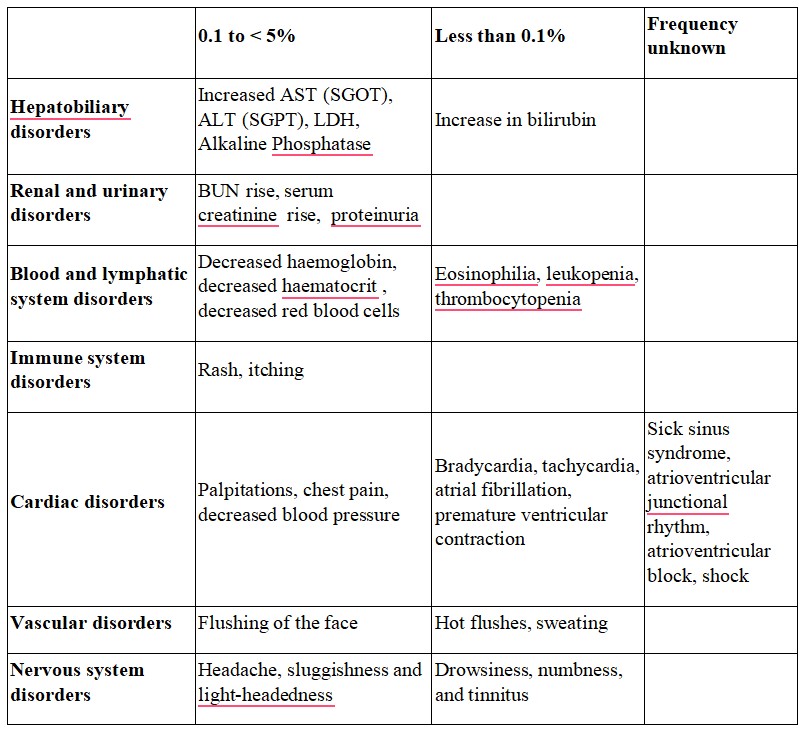
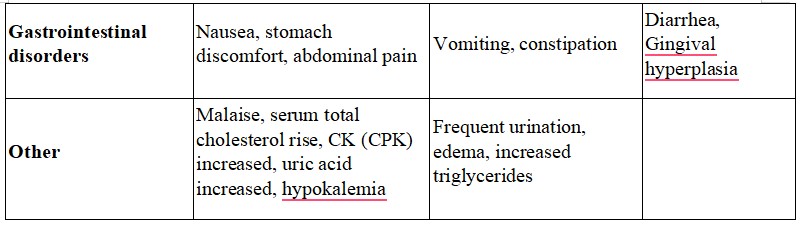
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. The common side effects are hot flushes, palpitations, facial flushing and headache. In addition, elevation in serum total cholesterol, ALT (SGPT), AST (SGOT) and BUN may occur. Other known side effects are as follows. Tell your doctor if you notice or are worried by any of the side effects listed.
Frequency 0.1 to < 5%
Increased AST (SGOT), ALT (SGPT), LDH, Alkaline Phosphatase
BUN rise, serum creatinine rise, proteinuria
Decreased hemoglobin, decreased hematocrit, decreased red blood cells
Rash, itching
Palpitations, chest pain, decreased blood pressure
Flushing of the face
Headache, sluggishness and light-headedness
Nausea, stomach discomfort, abdominal pain
Malaise, serum total cholesterol rise, CK (CPK) increased, uric acid increased, hypokalemia
Frequency Less than 0.1%
- Increase in bilirubin
- Eosinophilia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
- Bradycardia, tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, premature ventricular contraction
- Hot flushes, sweating
- Drowsiness, numbness, and tinnitus
- Vomiting, constipation
- Frequent urination, edema, increased triglycerides
Frequency unknown
- Sick sinus syndrome, atrioventricular junctional rhythm, atrioventricular block, shock
- Diarrhea, Gingival hyperplasia
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice any other effects not listed.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top right end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to Store Efnocar Tablets
Do not use the tablets after the end of the expiry month (use-by date) shown on the product packaging.
Store below 25°C. Protected from light & moisture.
Keep This Medicine Out of the Sight and Reach of Children
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Contents of the Pack and Other Information
What EFNOCAR Tablets contain
- The active substance is Efonidipine Hydrochloride Ethanolate.
Each tablet contains 10 mg / 20 mg / 40 mg of Efonidipine.
- Other ingredients: Excipients q.s.
Marketing authorisation holder:
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd.
Manufacturer responsible for batch release:
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd.
Kamerey Bhasmay, Elaka Pakyong,
Rangpo, East-Sikkim 737 132.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on pack
8.3 Packaging information
10 Blister strips of 10 tablets each
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
- Store below 25°C. Protected from light & moisture.
- Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
Efnocar is a type of medicine known as a calcium channel blocker (CCB). It is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and a type of chest pain called angina. It can be used by itself or with other medicines to treat these conditions. Do not use Efnocar if you are allergic to efonidipine (the active ingredient in Efnocar), or to the inactive ingredients.
Tell your doctor about any prescription and non-prescription medicines you are taking, including natural or herbal remedies. Tell your doctor if you:
- ever had heart disease
- ever had liver problems
- are pregnant, or plan to become pregnant.
- are breast-feeding. Do not breast-feed while taking Efnocar.
You can stop breast-feeding or take a different medicine.
It may be easier to take your dose if you do it at the same time every day, such as with breakfast or dinner, or at bedtime.
While you are taking Efnocar do not stop taking your other prescription medicines, including any other blood pressure medicines, without talking to your doctor.
12.0 Date of revision
09/10/2024


