Efnocar CT 40-12.5 Tablets
Therapy Area
Cardiology
1.0 Generic name
Efonidipine Hydrochloride Ethanolate & Chlorthalidone Tablets [40 mg + 12.5 mg]
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
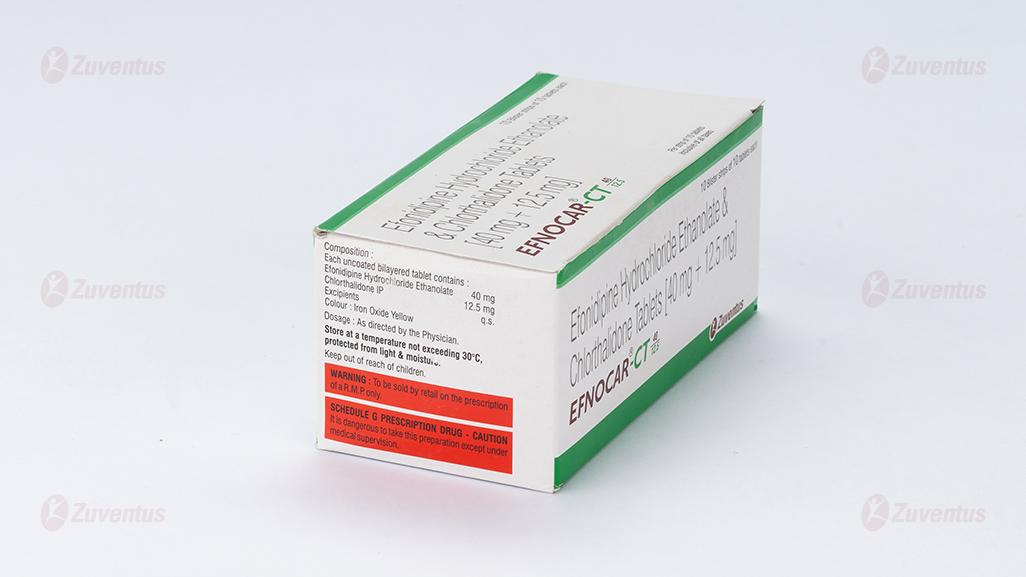
Each uncoated bilayered tablet contains :
Efonidipine Hydrochloride Ethanolate 40 mg
Chlorthalidone IP 12.5 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Iron Oxide Yellow
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Uncoated bilayered tablet [40 mg +12.5 mg]
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
In the management of hypertension.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adult : One tablet per day.
Use in special populations
Geriatric
Efonidipine should be started at low dose (20 mg/day) in elderly. Patient should be carefully observed for development of hypotension. Dose may be halved if there is intolerance to the 20mg/day dosage regimen.
For Chlorthalidone, dose selection for an elderly patient should be done cautiously, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to any of the components of the formulation.
- Anuria, severe renal failure (creatinine clearance lower than 30 mL/min), and severe hepatic failure.
- Refractory hypokalaemia or conditions involving enhanced Potassium loss, hyponatraemia and hypercalcaemia
- Symptomatic hyperuricaemia (history of gout or uric acid calculi).
- Pregnancy
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Efonidipine
- Should be administered with caution in patients with hepatic impairment.
- Dose adjustment may be required in elderly as hypotension can occur.
- Efonidipine may worsen clinical condition in patients with sinus bradycardia, sinus arrest or sinus node dysfunction.
- As dizziness can occur due to hypotensive action, one should be careful while operating machines, with aerial work platforms and driving a motor vehicle.
- Drug should not be stopped abruptly. Discontinuation should be gradual and under supervision of a qualified Physician.
Chlorthalidone
- Hypokalemia and other electrolyte abnormalities, including hyponatremia and hypochloremic alkalosis, are common in patients receiving Chlorthalidone.
- Serum electrolytes should be determined before initiating therapy and at periodic intervals during therapy.
- Thiazide-like diuretics have been shown to increase the urinary excretion of magnesium; this may result in hypomagnesemia
- Calcium excretion is decreased by thiazide-like drugs. Pathological changes in the parathyroidgland with hypercalcemia and hypophosphatemia have been observed in a few patients on Thiazide therapy. The common complications of hyperparathyroidism such as renal lithiasis, bone resorption and peptic ulceration have not been seen.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Efonidipine
- Other anti-hypertensive agents : Efonidipine enhances the antihypertensive action additively and may produce hypotension and shock. Blood pressure should be monitored regularly to adjust dose of concomitant drugs.
- Cimetidine : Cimetidine inhibits CYP450 enzymes involved in metabolism of CCBs. Blood concentration of Calcium channel antagonists increase leading to higher incidence of side effects (hot flushes).
- Grapefruit juice : Grapefruit juice suppresses enzymes metabolizing Calcium channel antagonists (Cytochrome P450) and reduces the clearance. Thus, there is a possibility that blood concentration of the drug may increase and the anti-hypertensive effect is enhanced.
- Tacrolimus : Efonidipine inhibits metabolic enzymes involved in Tacrolimus metabolism and reduces its clearance. So, increase in blood concentration of Tacrolimus can occur.
Chlorthalidone
- Chlorthalidone may add to or potentiate the action of other antihypertensive drugs.
- Insulin requirements in diabetic patients may be increased, decreased or unchanged. Higher dosage of oral hypoglycemic agents may be required
- Chlorthalidone and related drugs may increase the responsiveness to tubocurarine.
- Chlorthalidone and related drugs may decrease arterial responsiveness to norepinephrine. This diminution is not sufficient to preclude effectiveness of the pressor agent for therapeutic use.
- Lithium renal clearance is reduced by Chlorthalidone, increasing the risk of Lithium toxicity.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
Efnocar CT should not be administered to pregnant women and women suspected of being
pregnant
Lactation
Administration to lactating women should be avoided unless benefit significantly surpasses the risk to the child. Mothers on Efnocar CT treatment should avoid breast feeding.
Pediatric
Safety and efficacy of Efnocar CT in low birth weight infants, newborns, infants and children has not been established.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
As dizziness can occur due to hypotensive action, one should be careful while driving a motor vehicle.
4.8 Undesirable effects
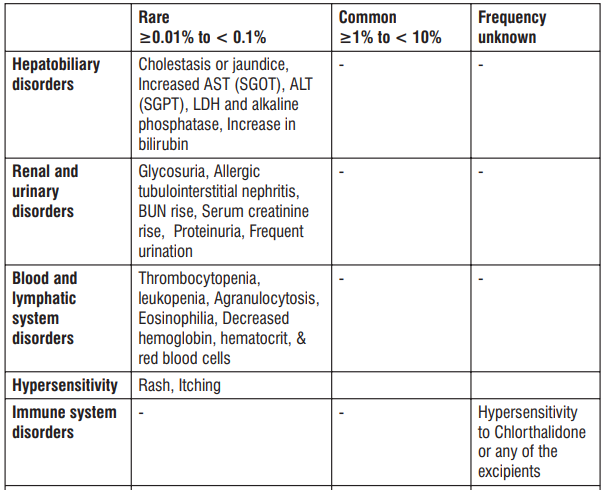
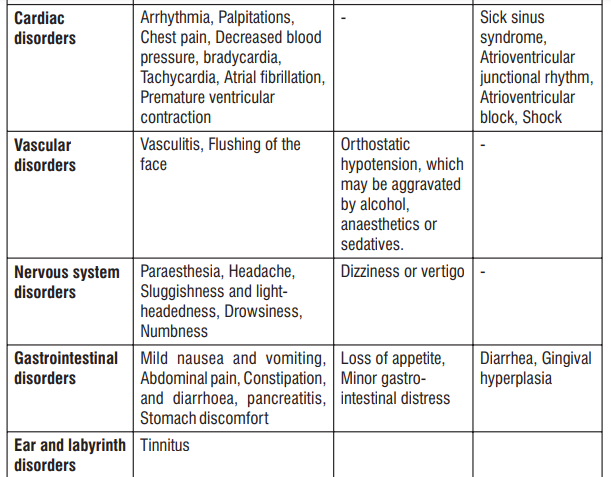
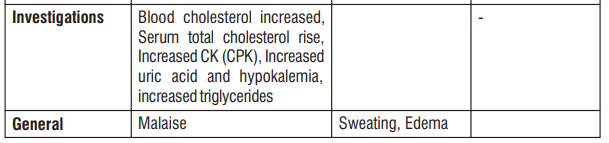
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
In humans, experience with intentional overdose is limited. Dizziness, nausea, somnolence, hypovolaemia, hypotension and electrolyte disturbances associated with cardiac arrhythmias and muscle spasms are some of the signs and symptoms associated with drug overdose. Gastric lavage, emesis or activated charcoal should be employed to reduce absorption. Blood pressure and fluid and electrolyte balance should be monitored and appropriate corrective measures taken. Intravenous fluid and electrolyte replacement may be indicated. Clinically significant hypotension due to drug over dosage calls for active cardiovascular support including frequent monitoring of cardiac and respiratory function, elevation of extremities, and attention to circulating fluid volume and urine output. A vasoconstrictor may be helpful in restoring vascular tone and blood pressure, provided that there is no contraindication to its use. Intravenous Calcium gluconate may be beneficial in reversing the effects of Calcium channel blockade.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Efonidipine, a new generation Dihydropyridine (DHP) is a dual Ca2+ channel blocker that blocks both T-type and L-type Calcium channels. Apart from being a potent antihypertensive, additional T-type Calcium channel inhibition is responsible for its negative chronotropic, renoprotective and cardioprotective effects. Chlorthalidone is a long-acting oral diuretic with antihypertensive activity. The drug produces diuresis with increased excretion of sodium and chloride.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Efonidipine
Efonidipine blocks both, L and T-type Ca++ channels and has an excellent clinical profile. Like other Dihydropyridine CCBs, Efonidipine exhibits anti-hypertensive action due to the blocking of L-type voltage sensitive Calcium channels. These Ca++ channels mediate the entry of extracellular Ca++ into vascular smooth muscle in response to electrical depolarization. In both smooth muscle and cardiac myocytes, Ca++ is a trigger for contraction, albeit by different mechanisms. Apart from being a potent antihypertensive, additional T-type Calcium channel inhibition is responsible for its negative chronotropic, renoprotective and cardioprotective effects. Long term therapy with Efonidipine also has protective and reparative effect on the blood vessels. Efonidipine regulates heart rate (HR) by inhibiting the T-type Calcium channels, which are localized primarily in the SA node and are involved in the pacemaker mechanism of the heart. Efonidipine has been reported to have a negative chronotropic effect, which may be involved in controlling tachycardia. Unlike the conventional types of Calcium antagonists, Efonidipine potently dilates both afferent and efferent arterioles. It leads to a reduction in glomerular pressure; this effect may be a favourable one in regard to renoprotection. Efonidipine also exhibits reno-protective action in renal impairment or chronic renal parenchymal disease. It has been reported that Efonidipine attenuates proteinuria and serum aldosterone level to a great extent in comparison to amlodipine.
Chlorthalidone
Chlorthalidone contain a Sulfonamide group that inhibits carbonic anhydrase activity, which may be associated with lower vascular contractility. It is concentrated in the kidney and secreted into the tubular lumen; therefore, its therapeutic diuretic effects are often achieved with relatively low plasma concentrations. It inhibits the sodium-chloride co transporter in the luminal membrane of the distal convoluted tubule of the ascending loop of Henle, leading to a modest natriuresis and diuresis. Chlorthalidone may have beneficial effects on endothelial function and oxidative stress. It also increases secretion of Potassium and Hydrogen ions and promote increased reabsorption of Calcium through increased expression of a Sodium-Calcium exchange channel. Chlorthalidone may cause more inhibition of carbonic anhydrase as compared to other diuretics (eg. Hydrochlorothiazide), which can lead to lower intracellular pH and cell volume. This effect explains a pleiotropic effect of Chlorthalidone, ie, inhibition of platelet function, which in turn may contribute to this drug’s beneficial effect on cardiovascular outcomes.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
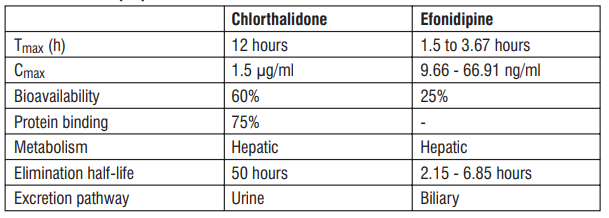
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
No known animal toxicology data
7.0 Description
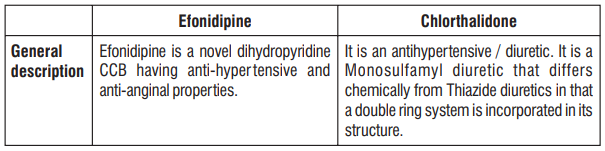
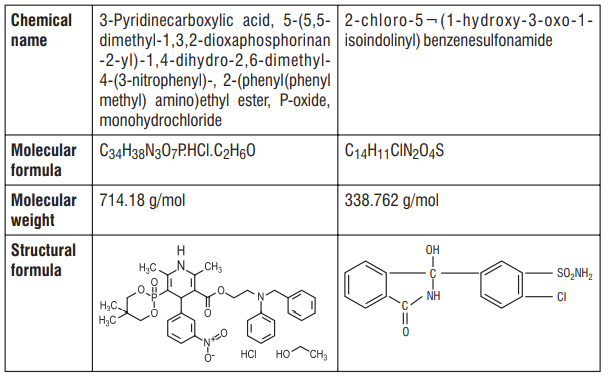
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack
8.3 Packaging information
Alu-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30°C, protected from light & moisture.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient counselling information
Do not take Efnocar CT Tablets if you :
- Have ever had an allergic reaction to Efonidipine, Chlorthalidone or kidney disease, gout, been taking lithium carbonate. An allergic reaction may include a rash, itching, difficulty breathing or swelling of the face, lips, throat or tongue.
- If you are pregnant.
Take special care with Efnocar CT Tablets
You should inform you doctor if you have or have had any of the following conditions :
- Liver disease
- Recent heart attack
- Heart failure
- Severe increase in blood pressure (Hypertensive crisis)
- Symptoms of potassium loss: excess thirst, tiredness, drowsiness, restlessness, muscle pains or cramps, nausea, vomiting or increased heart rate or pulse.
- Symptoms of light-headedness or dizziness.
Use in children and adolescents
Efnocar CT is not recommended in infants and children as safety is not established in this group of patients
For more information, talk to your doctor.
Taking other medicines and Efnocar CT
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken other medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription.
Efnocar CT may affect or be affected by other medicines, such as :
- Other antihypertensive agent/s (BP lowering drugs)
- Cimetidine (stomach acid reducer)
- Tacrolimus (a drug to suppress immunity)
Efnocar CT may lower your blood pressure even more if you are already taking other medicines to treat your high blood pressure.
If you see another doctor or go into hospital for any reason, tell them that you are taking Efnocar CT Tablets.
Taking Efnocar CT Tablets with food and drink
You should not drink grapefruit juice or eat grapefruit while taking this medicine. Grapefruit and grapefruit juice can lead to an increase in the blood levels of Efonidipine, which can cause an unpredictable increase in its blood pressure lowering effect
Efonidipine Hydrochloride Ethanolate and Chlorthalidone Tablets [40mg + 12.5mg]
The name of your medicine is EFNOCAR-CT 40/12.5 Tablets. We refer to them as EFNOCAR-CT Tablets or EFNOCAR-CT throughout this leaflet.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any more questions, please ask your doctor or your pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you personally and you should not pass it on to anyone else. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects that are not listed in the leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
In this leaflet:
1. What EFNOCAR-CT Tablets are and what they are used for
2. What you need to know before you take EFNOCAR-CT Tablets
3. How to take EFNOCAR-CT Tablets
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store EFNOCAR-CT Tablets
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Efnocar-ct Tablets Are and What They Are Used for
EFNOCAR-CT Tablets contain the active substances Efonidipine and Chlorthalidone. Both of these substances help to control high blood pressure.
- Efonidipine belongs to a group of substances called “calcium channel blockers”. Amlodipine stops calcium from moving into the blood vessel wall which stops the blood vessels from tightening.
- Chlorthalidone belongs to a group of medicines known as diuretics which work by increasing the amount of urine passed (a diuretic action), reduces the water in your body, also helping to lower blood pressure.
EFNOCAR-CT Tablets are used to treat High blood pressure.
2. What You Need to Know Before You Take Efnocar-ct Tablets
Do Not Take Efnocar-ct Tablets if You:
- Have ever had an allergic reaction to efonidipine or Chlorthalidone or any of the ingredients in the tablet. An allergic reaction may include a rash, itching, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face, lips, throat, or tongue;
- If you are pregnant
- if you are not passing any urine at all
- if you have severe kidney or liver problems
- if you have low blood levels of potassium which can cause muscle weakness, muscle twitching or abnormal heartbeat
- if you have low blood levels of sodium which can cause tiredness, confusion, muscle twitching, fits or coma
- if you have high blood levels of calcium which can cause loss of appetite, tiredness or muscle weakness
- if you have Addison’s disease (which is a condition where your adrenal gland is not producing enough steroids)
- if you are taking lithium.
If any of the above applies to you, do not take EFNOCAR-CT and talk to your doctor.
Take special care with EFNOCAR-CT Tablets
You should inform you doctor if you have or have had any of the following conditions:
- Liver or kidney disease;
- Recent heart attack
- Heart failure;
- Severe increase in blood pressure (Hypertensive crisis)
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before taking EFNOCAR-CT Tablets:
• if you suffer from any other liver or kidney problems;
• if you are on a low-salt diet;
• if you suffer from diabetes mellitus (increased levels of sugar in the blood);
• if you have high cholesterol levels;
• if you have recently had an anaesthetic;
• if you are elderly.
• If you experience a decrease in vision or eye pain. These could be symptoms of fluid accumulation in the vascular layer of the eye (choroidal effusion) or an increase of pressure in your eye and can happen within hours to a week of taking EFNOCAR-CT Tablets. This can lead to permanent vision loss, if not treated. If you earlier have had a penicillin or sulphonamide allergy, you can be at higher risk of developing this.
If any of the above applies to you, or if you are not sure, speak to your doctor or pharmacist before you take EFNOCAR-CT Tablets.
Other medicines and EFNOCAR-CT Tablets
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines This applies to medicinal products subject to medical prescription or those obtained without a prescription, especially:
other treatments for high blood pressure or heart problems such as:
• ACE inhibitors (for example, lisinopril) beta blockers (for example propranolol hydrochloride)
• methyldopa
• vasodilators (for example bosentan)
• calcium channel blockers (for example amlodipine)
• guanethidine
- corticosteroids such as prednisolone or betamethasone - used to treat allergic and inflammatory diseases and immune reactions
- adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) - used to treat a number of different conditions, including ulcerative colitis (a form of inflammatory bowel disease), Crohn’s disease (a form of chronic inflammatory bowel disease) and rheumatoid arthritis
- corticosteroids such as prednisolone or betamethasone - used to treat allergic and inflammatory diseases and immune reactions
- cytotoxic agents such as cyclophosphamide or methotrexate - used to treat cancer
- asthma treatments such as salbutamol or formoterol
- amphotericin - used to treat infections
- carbenoxolone - used to treat ulcers
- insulin and other treatments for diabetes such as chlorpropamide or glibenclamide
- digoxin – for an irregular heartbeat
- lithium - used to treat mental illness
- anticholinergics such as atropine sulphate or hyoscine (butylbromide) - for abdominal or stomach spasms or cramps
- colestyramine - used to reduce cholesterol levels and prevent heart disease
- amantadine - used to treat Parkinson’s disease or viral infections
- allopurinol - used to treat gout (a complex type of arthritis)
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs) such as aspirin or indometacin - used for pain relief or rheumatism
- ciclosporin - used to treat rheumatic disease or skin complaints or after a transplant
- calcium salts or vitamin D - used for replacement therapy.
- Cimetidine (stomach acid reducer)
- Tacrolimus (a drug to suppress immunity)
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken/used any other medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription.
Use in children and adolescents
EFNOCAR-CT is not recommended in infants and children as safety is not established in this group of patients.
For more information, talk to your doctor.
Taking EFNOCAR-CT Tablets with food and drink
- You should not drink grapefruit juice or eat grapefruit while taking this medicine. Grapefruit and grapefruit juice can lead to an increase in the blood levels of efonidipine, which can cause an unpredictable increase in its blood pressure-lowering effect.
- It is best to take EFNOCAR-CT Tablets in the morning with food. Swallow your tablets whole with a drink of water.
- You should avoid low-salt diets. Taking EFNOCAR-CT Tablets may reduce the amount of salt in your body.
- If you are on a low-salt diet check with your doctor first before taking EFNOCAR-CT Tablets
Pregnancy
The safety of efonidipine in human pregnancy has not been established. EFNOCAR-CT should not be administered in pregnant women.
Breast-feeding
It is not known whether efonidipine is passed into breast milk. EFNOCAR-CT should not be administered in breastfeeding women.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
Dizziness may occur while taking antihypertensive agents. Hence, working on aerial platform, working with dangerous machinery and/or driving should be avoided.
3. How to Take Efnocar-ct Tablets
Your doctor will choose a suitable starting dose for your particular condition and monitor your progress. If necessary, this dose can be increased or reduced.
While you are taking EFNOCAR-CT Tablets, your doctor may want to carry out a number of tests from time to time. This is quite usual and nothing to worry about.
It is best to take EFNOCAR-CT Tablets in the morning with food. Swallow your tablets whole with a drink of water.
Follow your doctor’s instructions. Check the pharmacy label to see how many tablets to take and how often to take them. If you are still not sure, ask your pharmacist or doctor. The usual doses are described below.
Adult: One tablet per day.
Children
EFNOCAR-CT is not recommended in infants and children as safety is not established in this group of patients.
Elderly
Efonidipine should be started at low dose (20 mg/day) in elderly. Patient should be carefully observed for development of hypotension. Dose may be halved if there is intolerance to the 20mg/day dosage regimen.
For Chlorthalidone, dose selection for an elderly patient should be done cautiously, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Patients with liver/kidney disease
Your doctor may give you a different dose than normal.
If you take more EFNOCAR-CT Tablets than you should
If you (or someone else) swallow a lot of tablets all together, or if you think a child has swallowed any of the tablets, contact your nearest hospital casualty department or your doctor immediately. Take your medication and the packaging with you to the doctor or casualty department. If you have taken an overdose, you may you may appear flushed (your skin will look red), or you may feel dizzy or faint. If blood pressure drop is severe enough shock can occur.
If you forget to take EFNOCAR-CT Tablets
If you forget to take a tablet, take one as soon as you remember, unless it is nearly time to take the next one. Never take two doses together. Take the remaining doses at the correct time.
If you stop taking EFNOCAR-CT Tablets
Take this medicine for as long as your doctor tells you to, as you may become unwell if you stop.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Some side effects can be serious and need immediate medical attention
A few patients rarely may experience serious side effects. If any of the following happen, tell your doctor straight away:
Allergic reaction with symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling of face or lips or tongue, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure (feeling of faintness, light-headedness).
Other possible side effects of Efonidipine
The common side effects are hot flushes, palpitations, facial flushing and headache. In addition, elevation in serum total cholesterol, increased liver enzymes may occur.
Other known side effects are as follows. Tell your doctor if you notice or are worried by any of the side effects listed.
- Increased liver enzymes, Jaundice
- Abnormal urine tests
- Decreased haemoglobin,
- Rash, itching
- Palpitations, abnormal heartbeat, chest pain, decreased blood pressure
- Flushing of the face
- Headache, sluggishness and light-headedness
- Nausea, stomach discomfort, abdominal pain
- Malaise, increase serum total cholesterol
- Hot flushes, sweating
- Drowsiness, numbness, and tinnitus
- Vomiting, constipation
- Frequent urination, edema, increased bad cholesterol levels
- Diarrhea, Gingival hyperplasia
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice any other effects not listed.
Chlorthalidone
If you get any of the following effects tell your doctor or pharmacist immediately:
Very common:
- low blood levels of potassium which can cause muscle weakness, muscle twitching or abnormal heartbeat
- increased blood levels of uric acid
- increased blood levels of cholesterol.
Common :
- low levels of sodium which can cause tiredness, confusion, muscle twitching, fits or coma
- low levels of magnesium
- high blood sugar levels which can cause tiredness, weakness or feeling thirsty
- nettle rash, skin rash
- low blood pressure which may make you feel dizzy when you stand up
- dizziness, loss of appetite, upset stomach
- impotence in men.
Rare:
- increased calcium in the blood which can cause agitation, sore eyes, abdominal pain
- sugar in the urine (this would show up when your doctor or nurse tests your urine)
- worsening of diabetes
- yellowing of the skin or eyes caused by liver or blood problems (jaundice)
- increased sensitivity of your skin to sunlight
- abnormal heartbeat the symptoms of which include palpitations and fainting
- pins and needles, headache, feeling or being sick, stomach pain
- constipation, or diarrhoea
- reduction in blood platelets which increases the risk of bruising or bleeding
- severe reduction in the number of white blood cells which makes infection more likely
- an abnormally high amount of eosinophils (type of white blood cell) in the blood
- breathing problems
- problems with your kidneys.
Uncommon side effects
• gout which causes pain and swelling in the joints.
Very rare:
• low levels of chloride in the blood, symptoms include dry mouth, thirst, gastrointestinal disturbances (including nausea, vomiting), weakness, lethargy, drowsiness, restlessness, seizures, confusion, headache, muscle pains or cramps, hypotension
• inflammation of the pancreas which causes severe stomach and back pain.
Frequency unknown:
• Decrease in vision or pain in your eyes due to high pressure (possible signs of fluid accumulation in the vascular layer of the eye or glaucoma).
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to Store Efnocar-ct Tablets
Do not use the tablets after the end of the expiry month (use-by date) shown on the product packaging.
Store below 30°C. Protected from light & moisture.
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Contents of the Pack and Other Information
What EFNOCAR-CT Tablets contain
The active substance is Efonidipine and Chlorthalidone.
Efnocar CT 40/12.5
Each uncoated bilayered tablet contains:
Efonidipine Hydrochloride Ethanolate 40 mg
Chlorthalidone IP 12.5 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Iron Oxide Yellow
Packaging information
Each Alu-Alu blister strips contains 10 tablets.