Efnocar MX 40-25 Tablets
Therapy Area
Cardiology
1.0 Generic name
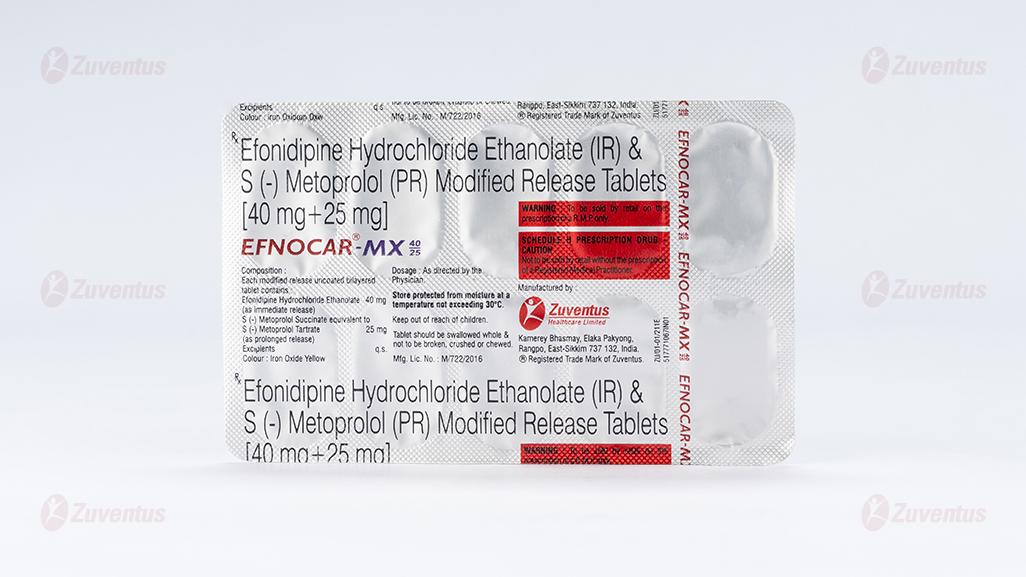
Efonidipine Hydrochloride Ethanolate (IR) & S (-) Metoprolol (PR) Modified Release Tablets [40 mg+25 mg]
2.0 Quantitative and qualitative composition
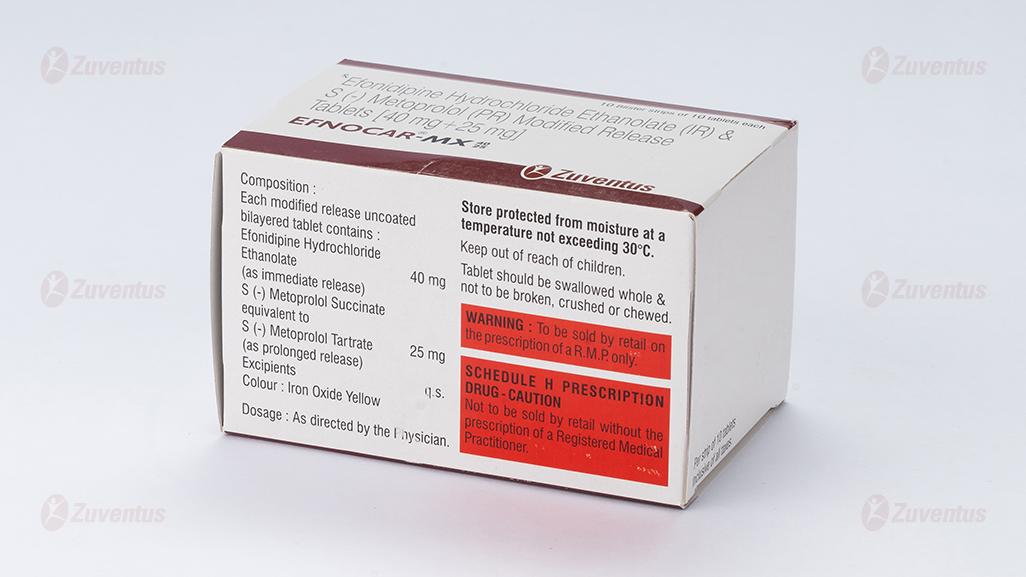
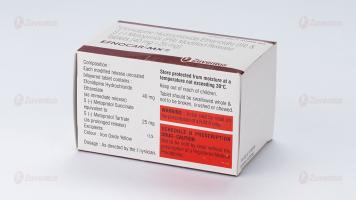
Each modified release uncoated bilayered tablet contains :
Efonidipine Hydrochloride Ethanolate 40 mg
(as immediate release)
S (-) Metoprolol Succinate
equivalent to S (-) Metoprolol Tartrate 25 mg
(as prolonged release)
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Iron Oxide Yellow
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Tablet Efonidipine Hydrochloride and S (-) Metoprolol Succinate [40 mg + 25 mg]
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
It is indicated for the management of hypertension.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adult : The usual recommended dose is 1 tablet daily. It may be increased to 2 tablets per day depending upon the blood pressure control.
4.3 Contraindications
- In patients who are hypersensitive to any component of this product
- Severe bradycardia.
- Second or third degree heart block.
- Cardiogenic shock.
- Decompensated cardiac failure.
- Sick sinus syndrome (unless a permanent pacemaker is in place).
4.4 Warning and precautions
Efonidipine
- Should be administered with caution in patients with hepatic impairment
- Dose adjustment may be required in elderly as hypotension can occur
- Efonidipine may worsen clinical condition in patients with sinus bradycardia, sinus arrest or sinus node dysfunction.
- As dizziness can occur due to hypotensive action, one should be careful while operating machines, with aerial work platforms and driving of a motor vehicle.
- Drug should not be stopped abruptly. Discontinuation should be gradual and under supervision of a qualified Physician.
S (-) Metoprolol
- If an asthmatic uses a β-2 agonist when initiating metoprolol treatment, the dose of the β-2 agonist must be controlled and increased if necessary.
- Metoprolol may reduce the effect of diabetes treatment and mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia
- When prescribing metoprolol to patients with a pheochromocytoma, an alpha blocker must be used before initiating treatment and during the metoprolol treatment.
- Metoprolol treatment may possibly mask the symptoms of thyrotoxicosis.
- In patients with Prinzmetal's angina, β1-selective agents should be used with care, because they may increase the number and duration of angina attacks.
- It is not recommended to discontinue β-blocker treatment during a surgical procedure.
- Metoprolol may also increase both the sensitivity to allergens and the severity of anaphylactic reactions. Adrenalin treatment does not always give the desired therapeutic effect in individuals receiving β-blockers.
- Beta blockers may trigger or exacerbate psoriasis. In the case of increasing bradycardia, the dosage should be reduced, or treatment gradually discontinued.
4.5 Drug interactions
Efonidipine
- Other anti-hypertensive agents : Efonidipine enhances the antihypertensive action additively and may produce hypotension and shock. Blood pressure should be monitored regularly to adjust dose of concomitant drugs.
- Cimetidine : Cimetidine inhibits CYP450 enzymes involved in metabolism of CCBs. Blood concentration of Calcium channel antagonists increase leading to higher incidence of side effects (hot flushes).
- Grapefruit juice : Grapefruit juice suppresses enzymes metabolizing Calcium channel antagonists (Cytochrome P450) and reduces the clearance. Thus, there is a possibility that blood concentration of the drug may increase and the anti-hypertensive effect is enhanced.
- Tacrolimus : Efonidipine inhibits metabolic enzymes involved in Tacrolimus metabolism and reduces its clearance. So, increase in blood concentration of Tacrolimus can occur.
S (-) Metoprolol
- The effects of metoprolol and other antihypertensive drugs on blood pressure are usually additive, and care should be taken to avoid hypotension.
- In the case of the concomitant use of calcium antagonists of the verapamil or diltiazem types, an increase in negative inotropic and chronotropic effects can occur.
- Class I-antiarrhythmic and beta-receptor blockers have additive negative inotropic effects, which can result in serious hemodynamic adverse reactions in patients with impaired left-ventricular function.
- Patients treated with amiodarone can develop severe sinus bradycardia during concomitant treatment with metoprolol.
- NSAID-type antiphlogistics counteract the antihypertensive effect of β-receptor blocking agents.
- CYP2D6 inhibitors such as antidepressants (Fluoxetine, Paroxetine or Bupropion), antipsychotics (Thioridazine), antiarrhythmics (Propafenone), antiretrovirals (Ritonavir), antihistamines (Diphenhydramine), antimalarials (Hydroxychloroquine or Quinidine), antifungals (Terbinafine) and cimetidine increase the plasma concentration of metoprolol.
- Digitalis glycosides in connection with beta-receptor blockers, can increase the atrioventricular conduction time and induce bradycardia.
- MAO inhibitors should be used with caution as concomitant administration with beta-blockers may result in bradycardia and an enhanced hypotensive effect. An increase in the plasma concentrations of metoprolol has been observed when the drug was coadministered with an antacid.
4.6 Special populations
Pregnancy
Efonidipine should not be administered to pregnant women and women suspected of being pregnant. It is recommended that metoprolol should not be administered during pregnancy or lactation unless it is considered that the benefit outweighs the possible risk to the fetus/infant. Should therapy with metoprolol be employed, special attention should be paid to the fetus, neonate and breast fed infant for any undesirable effects such as slowing of the heart rate.
There is an increased risk of cardiac and pulmonary complications in the neonate in the postnatal period. Beta blockers reduce placental perfusion and may cause fetal death and premature birth. Intrauterine growth retardation has been observed after long-time treatment of pregnant women with mild to moderate hypertension. β-blockers have been reported to cause bradycardia in the fetus and the newborn child; there are also reports of hypoglycemia and hypotension in newborn children.
Lactation
Administration to lactating women should be avoided unless benefit significantly surpasses the risk to the child. Mothers on Efonidipine treatment should avoid breast feeding. The concentration of metoprolol in breast milk is approximately three times higher than the one in the mother's plasma. An infant consuming 1 liter of breast milk daily would receive a dose of less than 1 mg of the dr ug. Breastfeeding babies should be monitored for signs of β-blocking if nursing mothers are administered with metoprolol.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Efonidipine / S (-) Metoprolol can have influence on the ability to drive and use machines. Dizziness or drowsiness may occasionally occur when taking Efonidipine / S (-) Metoprolol.
4.8 Undesirable effects
In a double blind, comparative phase III clinical trial conducted on 240 patients, 120 patients were on Efnocar MX 40/25 treatment group and were observed for 3 months. Seven patients of this group experienced mild adverse events like headache, vomiting, fever, hypotension, bradycardia and erythema. All the side effects were resolved without sequelae. Other known side effects observed with the individual ingredients of the formulation are mentioned below :
Efonidipine
Common side effects
The common side effects are hot flushes, palpitations, facial flushing and headache. In addition, elevation in serum total cholesterol, ALT (SGPT), AST (SGOT) and BUN may occur
Uncommon side effects
Hepatobiliary disorders : LDH and alkaline phosphatase, Increase in bilirubin.
Renal and urinary disorders : Serum creatinine rise, Proteinuria, Frequent urination.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders : Decreased hemoglobin, Decreased hematocrit, Decreased red blood cells, Eosinophilia, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopenia.
Hypersensitivity : Rash, Itching
Cardiac disorders : Palpitations, Chest pain, Decreased blood pressure, Bradycardia, Tachycardia, Atrial fibrillation, Premature ventricular contraction, Sick sinus syndrome, Atrioventricular junctional rhythm, Atrioventricular block, Shock.
Nervous system disorders : Sluggishness and light-headedness, Drowsiness, Numbness
Gastrointestinal disorders : Nausea, Stomach discomfort, Abdominal pain, Vomiting, Constipation, Diarrhea, Gingival hyperplasia
Ear and labyrinth disorders : Tinnitus
Investigations : Increased CK (CPK), Increased uric acid and hypokalemia, Increased triglycerides
General : Malaise, Sweating, Edema
S (-) Metoprolol
Since S (-) Metoprolol is the racemic isomer of Metoprolol therefore side effects of Metoprolol may be relevant here
Common side effects
The common side effects are functional dyspnea, fatigue, bradycardia, balance disturbances, palpitations, pronounced blood pressure drop and orthostatic hypotension, very rarely with syncope, cold hands and feet, dizziness, headache, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea and constipation. headache, vomiting, fever, low blood pressure, decrease in heartbeat and skin redness
Uncommon side effects
Hepatobiliary disorders : Abnormal LFT values
Metabolism and nutrition disorders : Weight gain
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders : Bronchospasms, rhinitis
Endocrine disorders: deterioration of latent diabetes mellitus
Cardiac disorders : Temporary exacerbation of symptoms of heart failure, First-degree atrioventricular block,
Precordial pain, Functional heart symptoms, Heart arrhythmia, Conductivity disturbances.
Nervous system disorders : Paresthesia
Psychiatric disorders : Depression, Concentration problems, Drowsiness or insomnia,
Nightmares, Nervousness, Anxiety
Eye disorders : Visual disturbances, Dry or irritated eyes, Conjunctivitis.
Gastrointestinal disorders : Vomiting, Dryness of mouth
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders : Muscle spasms
General disorders and administration site conditions : Oedema
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com, By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
In humans, experience with intentional overdose is limited. Dizziness, nausea, somnolence, hypotension and electrolyte disturbances associated with cardiac arrhythmias, sinus bradycardia, atrioventricular block, heart failure, cardiogenic shock, cardiac arrest, asystole, QT-prolongation (isolated cases), poor peripheral perfusion, loss of consciousness (even coma), nausea, vomiting or cyanosis, bronchospasms and muscle spasms are some of the signs and symptoms associated with drug overdose. Respiratory depression, apnea, fatigue, fine tremor, seizures, sweating, paraesthesias, possible oesophageal spasm, hyperglycaemia, hyperkalaemia, renal effects, transient symptoms of myasthenia are other symptoms associated with drug overdose. The symptoms may be exacerbated by concomitant ingestion of alcohol, antihypertensive agents or barbiturates.
Gastric lavage, emesis or activated charcoal should be employed to reduce absorption. Patients should be admitted to hospital and, generally, should be managed in an intensive care setting, with continuous monitoring of cardiac function, blood gases, and blood biochemistry. Emergency supportive measures such as artificial ventilation or cardiac pacing should be instituted if appropriate. A vasoconstrictor may be helpful in restoring vascular tone and blood pressure, provided that there is no contraindication to its use. Intravenous calcium gluconate may be beneficial in reversing the effects of calcium channel blockade. Even apparently well patients who have taken a small overdose should be closely observed for signs of poisoning for at least 4 hours. In case of severe hypotension, bradycardia or in risk of heart failure, the patient could be given a β-1 agonist intravenously at intervals of 2-5 minutes or as continuous infusion until achieving the desired effect. If a selective β-1 agonist is unavailable, dopamine may be used.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Efonidipine, a new generation dihydropyridine (DHP) is a dual Ca2+ channel blocker that blocks both T-type and L-type calcium channels. Apart from being a potent antihypertensive, additional T-type calcium channel inhibition is responsible for its negative chronotropic, renoprotective and cardioprotective effects S (-) Metoprolol antagonizes β-1-adrenergic receptors in the myocardium, thereby reducing the rate and force of myocardial contraction, and consequently a diminished cardiac output. This agent may also reduce the secretion of renin with subsequent reduction in levels of angiotensin II thus decreasing sympathetic activation, including vasoconstriction and aldosterone secretion.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Efonidipine
Efonidipine blocks both, L and T-type Ca channels and has an excellent clinical profile. Like other dihydropyridine CCBs, Efonidipine exhibits anti-hypertensive action due to the blocking of L-type voltage ++ ++ sensitive calcium channels. These Ca channels mediate the entry of extracellular Ca into vascular ++ smooth muscle in response to electrical depolarization. In both smooth muscle and cardiac myocytes, Ca is a trigger for contraction, albeit by different mechanisms. Apart from being a potent antihypertensive, additional T-type calcium channel inhibition is responsible for its negative chronotropic, renoprotective and cardioprotective effects. Long term therapy with Efonidipine also has protective and reparative effect on the blood vessels.
Efonidipine regulates heart rate (HR) by inhibiting the T-type calcium channels, which are localized primarily in the SA node and are involved in the pacemaker mechanism of the heart. Efonidipine has been reported to have a negative chronotropic effect, which may be involved in controlling tachycardia. Unlike the conventional types of calcium antagonists, Efonidipine potently dilates both afferent and efferent arterioles. It leads to a reduction in glomerular pressure; this effect may be a favourable one in regard to renoprotection. Efonidipine also exhibits reno-protective action in renal impairment or chronic renal parenchymal disease. It has been reported that Efonidipine attenuates proteinuria and serum aldosterone level to a great extent in comparison to amlodipine
S (-) Metoprolol
Metoprolol is a cardioselective β-adrenergic blocking agent. It has a relatively greater blocking effect on β-1-receptors (i.e. those mediating adrenergic stimulation of heart rate and contractility and release of free fatty acids from fat stores) than on β-2-receptors, which are chiefly involved in broncho and vasodilation. Clinical pharmacology studies have confirmed the β-blocking activity of metoprolol in man, as shown by (1) reduction in heart rate and cardiac output at rest and upon exercise, (2) reduction of systolic blood pressure upon exercise, (3) inhibition of isoproterenol-induced tachycardia, and (4) reduction of reflex orthostatic tachycardia. The relative β-1-selectivity of metoprolol has been confirmed by the following : (1) in normal subjects, metoprolol is unable to reverse the β-2-mediated vasodilating effects of epinephrine. This contrasts with the effect of nonselective β-blockers, which completely reverse the vasodilating effects of epinephrine; (2) in asthmatic patients, metoprolol reduces FEV1 and FVC significantly less than a nonselective β-blocker, propranolol, at equivalent β1-receptor blocking doses. S (-) Metoprolol is the chirally pure enantiomer. It is known to exhibit greater affinity and higher β-1 receptor blocking activity than the R isomer with S: R activity ratio being 33:1. The β-1 receptor affinity of S (-) Metoprolol is 500 times greater than that of R (-) Metoprolol.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption and distribution
Peak plasma concentration of Efonidipine is achieved in about 1.5 - 3.67 h after administration. The bioavailability of Efonidipine is ~ 25% and half-life is ~4h. The dissociation constant of Efonidipine from DHP receptors is very low (0.0042/min/nm), signifying very low dissociation from receptors. This causes long duration of action of Efonidipine.
Metoprolol is completely absorbed after an oral dose, peak plasma concentrations occurring 1.5 - 2 hours after dosing. Concomitant intake of food increases bioavailability to approximately 70%. Peak plasma-metoprolol concentrations at steady state with usual doses have been reported as 20 - 340 ng/ml. Only a small fraction of metoprolol (approx. 5 - 10%) binds to plasma proteins. Metoprolol is widely distributed; it crosses the blood-brain barrier, crosses the placenta, and is found in breast milk.
Metabolism
Efonidipine is primarily metabolized in liver. The important metabolites are N-dephenylated Efonidipine (DPH), deaminated Efonidipine (AL) and N-debenzylated Efonidipine (DBZ). DBZ and DPH exhibit activity as calcium antagonists.
Metoprolol is extensively metabolized in the liver; O-dealkylation followed by oxidation and aliphatic hydroxylation. The rate of hydroxylation to α-hydroxymetoprolol is reported to be determined by genetic polymorphism; the half-life of metoprolol in fast hydroxylators is stated to be 3 - 4 hours, whereas in poor hydroxylators it is about 7 hours.
Elimination
Biliary route is the main pathway of excretion of Efonidipine. Only 1.1% of the dose was excreted as deaminated Efonidipine and 0.5% as a pyridine analogue of deaminated Efonidipine in urine collected for 24 h after oral dosing.
The metabolites of metoprolol are excreted in the urine (> 95%) together with only small amounts of unchanged metoprolol. The elimination half-life of metoprolol in plasma is 3.5 hours on average (interval 1 - 9 hours). Total clearance is ~ 1 L/min. Metoprolol is excreted in breast milk.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
No known animal toxicology data
7.0 Description
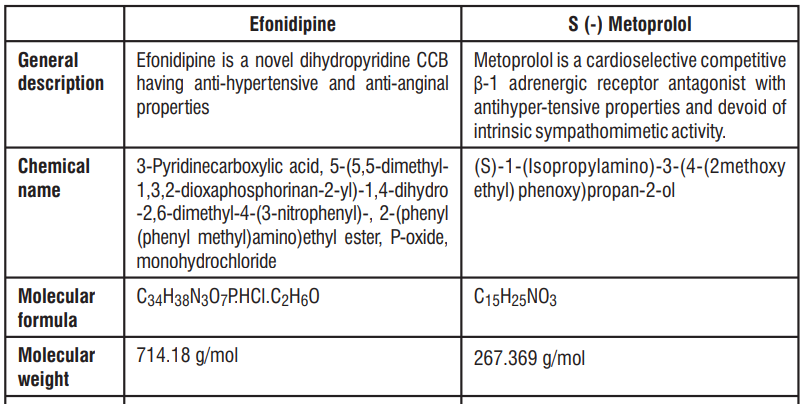
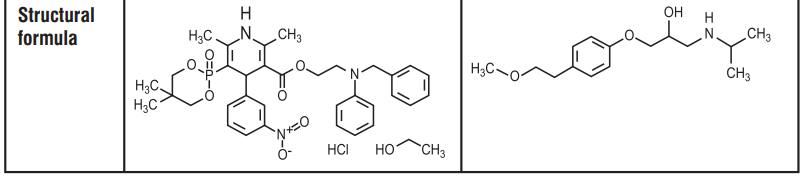
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf life
24 Months
8.3 Packaging information
Alu-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store protected from moisture at a temperature not exceeding 30°C.
Keep out of reach of children. Tablet should be swallowed whole & not to be broken, crushed or chewed
9.0 Patient counselling information
Do not use Efnocar MX if you are allergic to Efonidipine or S (-) Metoprolol. While you are taking Efnocar MX, do not stop taking your other prescription medicines, including any other blood pressure medicines, without talking to your doctor. If you took too much Efnocar MX, call your doctor or Poison Control Centre, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away. Tell your doctor about any prescription and non-prescription medicines you are taking, including natural or herbal remedies.
Tell your doctor if you
- Ever had heart disease
- Ever had liver problems
- Are pregnant, or plan to become pregnant.
- Are breastfeeding. Do not breastfeed while taking Efnocar MX. You can stop breastfeeding or take a different medicine.
- Heart failure patients (if they experience signs or symptoms of worsening heart failure such as weight gain or increasing shortness of breath).
Patients should be advised
- To avoid operating automobiles and machinery or engaging in other tasks requiring alertness until the patient's response to therapy with Efnocar MX tablets has been determined.
- To contact the Physician if any difficulty in breathing occurs
- To inform the physician or dentist before any type of surgery that he or she is taking Efnocar MX tablets.
Efonidipine Hydrochloride Ethanolate (IR) and S (-) Metoprolol (PR) Modified Release Tablets [40 mg + 25 mg]
The name of your medicine is EFNOCAR-MX 40/25 Tablets. We refer to them as EFNOCAR-MX Tablets or EFNOCAR-MX throughout this leaflet.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any more questions, please ask your doctor or your pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you personally and you should not pass it on to anyone else. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects that are not listed in the leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
In this leaflet:
1. What EFNOCAR-MX Tablets are and what they are used for
2. What you need to know before you take EFNOCAR-MX Tablets
3. How to take EFNOCAR-MX Tablets
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store EFNOCAR-MX Tablets
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Efnocar-mx Tablets Are and What They Are Used for
EFNOCAR-MX Tablets contain the active substances Efonidipine (as immediate release) and S (-) Metoprolol (as prolonged release). Both of these substances help to control high blood pressure.
- Efonidipine belongs to a group of substances called “calcium channel blockers”. Amlodipine stops calcium from moving into the blood vessel wall which stops the blood vessels from tightening/contraction.
- S (-) Metoprolol belongs to a group of medicines called beta-blockers. Beta-blockers slow the heartbeat, lessen the force with which the heart muscle contracts, and reduce blood vessel contraction in the heart, brain, and throughout the body.
EFNOCAR-MX Tablets are used in management of High blood pressure.
2. What You Need to Know Before You Take Efnocar-mx Tablets
Do not take EFNOCAR-MX Tablets if you:
- Have ever had an allergic reaction to efonidipine or S (-) Metoprolol or any of the ingredients in the tablet. An allergic reaction may include a rash, itching, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face, lips, throat, or tongue;
- If you are pregnant
- If you have uncontrolled heart failure
- if you are allergic to any other beta-blocker drugs,
- if you have severe asthma or severe attacks of wheezing,
- if you have certain serious heart or blood vessel disorders that shouldn’t be treated with beta-blockers (your doctor should be aware of these),
- if you have low blood pressure,
- if you have been told that you have high blood pressure due to a tumour near your kidney (phaeochromocytoma),
- if you have been told that your blood is more acidic than normal (a condition called metabolic acidosis).
If any of the above applies to you, do not take EFNOCAR-MX and talk to your doctor.
Take special care with EFNOCAR-MX Tablets
You should inform you doctor if you have or have had any of the following conditions:
- Liver or kidney disease
- Hypotension
- Recent heart attack; Heart failure; Severe increase in blood pressure (Hypertensive crisis)
- Drug should not be stopped abruptly. Discontinuation should be gradual and under supervision of a qualified Physician or doctor
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before taking EFNOCAR-MX Tablets if you:
- Suffer from asthma, bronchitis, or any similar lung disorder
- Have problems with your heart (such as slow heart rate) or circulation (taking this medicine may make these worse)
- Have diabetes
- Suffer from any serious liver disease
- Have had a severe allergic reaction to anything
- Suffer from a rare form of angina called Prinzmetal's angina
- will be having an operation that requires a general anesthetic
- Have psoriasis
If any of the above applies to you, or if you are not sure, speak to your doctor or pharmacist before you take EFNOCAR-MX Tablets.
Other medicines and EFNOCAR-MX Tablets
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines This applies to medicinal products subject to medical prescription or those obtained without a prescription, especially:
- Medicines for high blood pressure (including prazosin, clonidine and drugs called calcium channel blockers such as verapamil or diltiazem)
- Other beta-blockers (including those used in the form of eye drops)
- Drugs that affect the peripheral circulation (fingers and toes) such as ergotamine which can be used to treat migraine
- Medicines to treat depression
- Medicines to treat other mental illnesses
- Antiretroviral drugs used to treat AIDS and some other conditions
- Antihistamines (including medicines that you can buy without a prescription for hay fever and other allergies, colds, and other conditions)
- Drugs to prevent malaria
- Medicines to treat fungal infections
- Medicines that affect liver enzymes, such as cimetidine used to treat stomach ulcers and rifampicin used to treat tuberculosis
- Medicines for heart problems including angina, such as amiodarone, digoxin, nitrates and anti-arrhythmic drugs
- Insulin and other drugs to treat diabetes
- Drugs called NSAIDs used to treat pain and inflammation
- A local anesthetic called lidocaine.
- Cimetidine (stomach acid reducer)
- Tacrolimus (a drug to suppress immunity)
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken/used any other medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription.
Use in children and adolescents
EFNOCAR-MX is not recommended in infants and children as safety is not established in this group of patients.
For more information, talk to your doctor.
Taking EFNOCAR-MX Tablets with food, drink, and alcohol
- You should not drink grapefruit juice or eat grapefruit while taking this medicine. Grapefruit and grapefruit juice can lead to an increase in the blood levels of efonidipine, which can cause an unpredictable increase in its blood pressure-lowering effect.
- Be careful when drinking alcohol - it may affect you more than usual
Pregnancy
The safety of efonidipine in human pregnancy has not been established. EFNOCAR-MX should not be administered in pregnant women.
Breast-feeding
It is not known whether efonidipine is passed into breast milk. EFNOCAR-MX should not be administered in breastfeeding women.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
Dizziness may occur while taking antihypertensive agents. Hence, working on aerial platform, working with dangerous machinery and/or driving should be avoided.
3. How to Take Efnocar-mx Tablets
Swallow these tablets with a glass of water at the same time each day. You can take the tablets after meals.
Follow your doctor’s instructions. Check the pharmacy label to see how many tablets to take and how often to take them. If you are still not sure, ask your pharmacist or doctor. The usual doses are described below.
Adult:
The usual recommended dose is one EFNOCAR-MX tablet daily.
It may be increased to 2 tablets per day depending upon the blood pressure control.
If you take more EFNOCAR-MX Tablets than you should
If you (or someone else) swallow a lot of tablets all together, or if you think a child has swallowed any of the tablets, contact your nearest hospital casualty department or your doctor immediately. Take your medication and the packaging with you to the doctor or casualty department. If you have taken an overdose, you may you may appear flushed (your skin will look red), or you may feel dizzy or faint. If blood pressure drop is severe enough shock can occur.
If you forget to take EFNOCAR-MX Tablets
If you forget to take a tablet, take one as soon as you remember, unless it is nearly time to take the next one. Never take two doses together. Take the remaining doses at the correct time.
If you stop taking EFNOCAR-MX Tablets
Take this medicine for as long as your doctor tells you to, as you may become unwell if you stop.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Efonidipine
The common side effects are hot flushes, palpitations, facial flushing and headache. In addition, elevation in serum total cholesterol, liver enzymes ALT may occur.
Other known side effects are as follows. Tell your doctor if you notice or are worried by any of the side effects listed.
Frequency 0.1 to < 5%
- Increased liver enzyme
- BUN rise, serum creatinine rise, proteinuria
- Decreased hemoglobin, decreased hematocrit, decreased red blood cells
- Rash, itching
- Palpitations, chest pain, decreased blood pressure
- Flushing of the face
- Headache, sluggishness and light-headedness
- Nausea, stomach discomfort, abdominal pain
- Malaise, serum total cholesterol rise, CK (CPK) increased, uric acid increased, hypokalemia
Frequency Less than 0.1%
- Increase in bilirubin
- Eosinophilia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
- Bradycardia, tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, premature ventricular contraction
- Hot flushes, sweating
- Drowsiness, numbness, and tinnitus
- Vomiting, constipation
- Frequent urination, edema, increased triglycerides
Frequency unknown
- Sick sinus syndrome, atrioventricular junctional rhythm, atrioventricular block, shock
- Diarrhea, Gingival hyperplasia
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice any other effects not listed.
S (-) Metoprolol
The side effects listed below have been reported.
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
• Headache, dizziness, or unusual tiredness.
• Slow heartbeat.
• Low blood pressure which might make you faint or dizzy.
• Feeling short of breath when exercising.
• Feeling or being sick, stomach ache.
Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
• Sleep disorders such as sleepiness, sleeplessness or nightmares.
• Feeling less alert.
• Coldness, numbness or tingling in your hands and feet.
• Depression.
• Muscle cramps
• Heart failure or irregular heartbeat.
• Water retention (oedema).
• Breathlessness or wheeziness (bronchospasm).
• Diarrhoea or constipation.
• Skin rash and/or itching.
Very rare: may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people
• Weight gain.
• Hallucinations or personality disorders.
• Dry or sore eyes or problems with vision.
• Tinnitus or hearing problems.
• Gangrene.
• Runny nose, dry mouth.
• Changes in the results of liver function tests.
• Bruising or increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight, worsening of psoriasis.
• Increased sweating, loss of hair.
• Impotence or loss of libido.
• Painful joints.
• Chest pain.
The following have also been reported:
• Confusion
• Abnormal levels of certain types of fats such as cholesterol or triglycerides in the blood.
• Abnormal curvature of the penis with painful erections (known as Peyronie’s disease)
• Retroperitoneal fibrosis where abnormal scar tissue occurs behind the membrane that lines the cavity of the abdomen. This may present with pain in the back, groin or lower abdomen.
• Hepatitis.
Do not be alarmed by this list - most people take metoprolol without any problems.
If any of the symptoms become troublesome, or if you notice anything else not mentioned here, please go and see your doctor as they may want to give you a different medicine.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to Store Efnocar-mx Tablets
Do not use the tablets after the end of the expiry month (use-by date) shown on the product packaging.
Store below 30°C. Protected from light & moisture.
Keep This Medicine Out of the Sight and Reach of Children
The tablet should be swallowed whole & not to be broken, crushed, or chewed.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Contents of the Pack and Other Information
What EFNOCAR-MX Tablets contain
- The active substance is Efonidipine and S (-) Metoprolol.
Each modified release uncoated bilayered tablet contains:
Efonidipine Hydrochloride Ethanolate 40 mg
(as immediate release) S (-) Metoprolol Succinate equivalent to S (-) Metoprolol Tartrate 25 mg
(as prolonged release) Excipients q.s. Colour: Iron Oxide Yellow
Packaging information
Alu-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets.