Eslo-D Tablets
Therapy Area
Cardiology
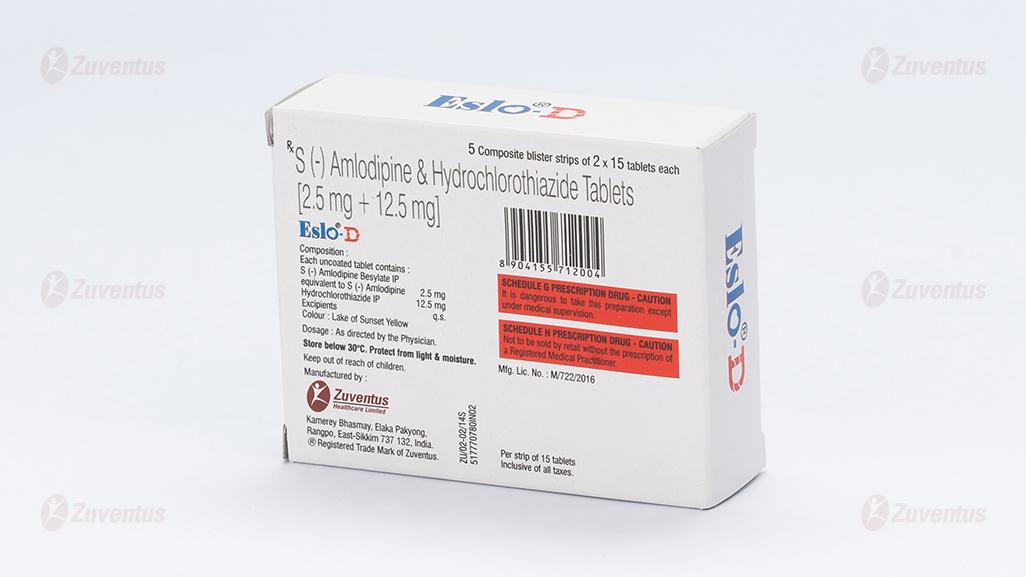
Composition
Each uncoated tablet contains :
S (-) Amlodipine Besylate IP
equivalent to S (-) Amlodipine 2.5 mg
Hydrochlorothiazide IP 12.5 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Lake of Sunset Yellow
Description
S (-) Amlodipine, the chirally pure form of Amlodipine is a calcium channel antagonist belonging to the dihydropyridine class. Hydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic which produces the antihypertensive activity.
Rationale of Combination
The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC 7) states that drug treatment for hypertension should begin with a thiazide-type diuretic in most patients, either alone or in combination with an ACE inhibitor, an ARB, or a CCB. Various studies have been conducted using calcium channel blockers along with the Hydrochlorothiazide and the combination has found to be superior than the individual drugs and there are no adverse drug interactions recorded with the usage of the combination. Therefore combination of S (-) Amlodipine along with a thiazide diuretic is a rationale combination which can be used as a first line treatment of the hypertension.
Clinical Pharmacology
S (-) Amlodipine, the chirally pure form of Amlodipine is a calcium channel antagonist belonging to the dihydropyridine class. The S (-) isomer of Amlodipine is found to possess greater pharmacological effects than R (+) Amlodipine. S (-) Amlodipine is 1000 times more potent than the R (+) isomer in binding to the dihydropyridine receptor. Therefore this is the only form which produces its therapeutic effects. In humans, the dominant effects of Amlodipine are consequent to vasodilation. S (-) Amlodipine lowers peripheral vascular resistance without causing a reflex tachycardia. In patients with angina pectoris S (-) Amlodipine reduces the myocardial oxygen demand by causing a direct vasodilation of the coronary artery and arterioles. Thiazides are moderately potent diuretics and exert their diuretic effect by reducing the reabsorption of electrolytes from the renal tubules, thereby increasing the excretion of Sodium and Chloride ions, and consequently of water. They act mainly at the beginning of the distal tubules. They also reduce carbonic-anhydrase activity so that bicarbonate excretion is increased, but this effect is generally small compared with the effect on Chloride excretion and does not appreciably alter the pH of the urine. Their hypotensive effect is probably partly due to a reduction in peripheral resistance : they also enhance the effects of other antihypertensives.
Pharmacokinetics
Administration of S (-) Amlodipine 2.5 mg as a single dose in the fasting state produced maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) of 8.30 ± 1.071 ng/ ml in 2.73 ± 0.88 hrs. (Tmax). Amlodipine is extensively (about 90%) converted to inactive metabolites via hepatic metabolism with 10% of the parent compound and 60% of the metabolites excreted in the urine. Ex vivo studies have shown that approximately 93% of the circulating drug is bound to plasma proteins in hypertensive patients. The mean AUC0-t value (t = 48 hrs.) of S (-) Amlodipine (2.5 mg) is 95.33 ± 14.45 ng.hr/ml. The AUC0-∞ value is recorded to be 140.91± 28.06 ng.hr/ml. The plasma elimination half life of S (-) Amlodipine has been found to be 31.09 ± 12.65 hrs. Hydrochlorothiazide is fairly rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. It is reported to have a bioavailability of about 65 to 70%. It has been estimated to have a plasma half-life of between about 5 and 15 hours and appears to be preferentially bound to red blood cells. It is excreted mainly unchanged in the urine. Hydrochlorothiazide crossed the placental barrier and is distributed into breast milk.
Indications
For the treatment of mild to moderate hypertension.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to any of the components listed in the formulation
Dosage and Administration:
One tablet to be administered once daily
Overdosage
There are no reported cases of overdosage with the use of S (-) Amlodipine. Overdosage with racemic Amlodipine may cause excessive peripheral vasodilation with marked hypotension and possibly a reflex tachycardia. Hence, caution should be taken in case of an overdosage with S (-) Amlodipine. If massive overdose occurs, active cardiac and respiratory monitoring should be instituted. Frequent blood pressure measurements should be performed. Should hypotension occur, cardiovascular support including elevation of the extremities and the judicious administration of fluids should be initiated. If hypotension remains unresponsive to these conservative measures, administration of vasopressors (such as phenylephrine) should be considered with attention to circulating. If massive overdose occurs, gastric lavage should be employed. As this product is highly plasma protein bound, hemodialysis is not likely to be of benefit. Electrolyte depletion (hypokalaemia, hypochloremia, hyponatraemia) and dehydration are the most common signs and symptoms of Hydrochlorothiazide overdosage. If digitalis has been administered, hypokalaemia may accentuate cardiac arrhythmias. The plasma half-life of Hydrochlorothiazide is 5.6 hours with a subsequent longer terminal half-life. Treatment should be symptomatic and supportive. Therapy should be discontinued and the patient watched closely.
Adverse Reactions
S (-) Amlodipine : Gingival Hypertrophy and Alopecia has been seen with S (-) Amlodipine. On the basis of the clinical data available, only minor side effects have been reported with the use of S (-) Amlodipine. Adverse events reported in less than 5% of the patients included anxiety (0.43%), anorexia (0.43%), irritation (0.43%), headache (2.13%) and facial flushing (2.13%). Caution should be exercised when administering S (-) Amlodipine to patients with impaired hepatic and renal function. Hydrochlorothiazide : Common adverse events seen with Hydrochlorothiazide are as follows : fever, necrotising angiitis (vasculitis, cutaneous vasculitis), jaundice (intrahepatic cholestatic jaundice), pancreatitis, cramping, gastric irritation, glycosuria, hyperglycaemia, hyperuricaemia, hypokalaemia, photosensitivity, sialadenitis, urticaria, toxic epidermal necrolysis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anaemia, haemolytic anaemia, leucopenia, purpura, thrombocytopenia, restlessness, interstitial nephritisrespiratory distress, including pneumonitis, pulmonary oedema, transient blurred vision, xanthopsia, non-melanoma skin cancer (Basal cell carcinoma and Squamous cell carcinoma).
Precautions
Hepatic impairment and renal impairment : No controlled clinical study of S (-) Amlodipine has been performed in patients with hepatic impairment and renal impairment. Clinical studies in patients with normal liver function have shown that there is no elevation in the hepatic enzymes with the use of S (-) Amlodipine. Approximately 90% of S (-) Amlodipine is metabolised in liver therefore a careful dosage adjustment should be considered in cases of hepatic impairment. Since about 10% of the S (-) Amlodipine is excreted unchanged in urine, no dosage adjustment is required in patients with renal impairment. Hydrochlorothiazide should be avoided in patients with severe hepatic impairment, in whom encephalopathy may be precipitated. Diuretics should be given with caution in patients with renal impairment, since they can further reduce renal impairment.
Special Population
Pregnant Women & Nursing Mothers : There is no data available on the use of S (-) Amlodipine in pregnant and lactating women. Hydrochlorothiazide may cross placenta, and there have been reports of neonatal jaundice, thrombocytopenia and electrolyte imbalance following maternal use. Treatment with large doses may inhibit lactation.
Since there are no studies available on the use of the combination in pregnant women, it should be administered only when the potential benefits outweighs the risk to the patient.
Children : Safety and effectiveness of this product in children has not been established.
Drug Interactions
Clinical studies have shown that S (-) Amlodipine when combined with aspirin, nitrates, beta-blockers, statins, ACE inhibitors, H2 blockers, and Proton Pump Inhibitors produced no drug interactions. Usual side effects of S (-) Amlodipine given alone and Hydrochlorothiazide given alone can be expected with the combination, but no known enhancement of the side effect has been observed in the published literature with the combination.
Storage
Store below 30°C. Protect from light & moisture.
Keep out of reach of children.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you:
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1. What Eslo D® is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you take Eslo D®
3. How to take Eslo D®
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store Eslo D®
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Eslo D® is and what it is used for
Eslo D® contains two substances called S (-) Amlodipine and Hydrochlorothiazide. Both of these substances help to control high blood pressure.
Amlodipine belongs to a group of substances called “calcium channel blockers”. Amlodipine also lowers blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels.
Hydrochlorothiazide is one of a group of medicines called thiazide diuretics (“water tablets”). It lowers blood pressure by helping the body to get rid of extra fluid by making your kidneys produce more urine.
The actions of these two substances contribute to decreasing your blood pressure.
Thus, Eslo D® is used to treat high blood pressure.
2. What you need to know before you take Eslo D®
Do not take Eslo D®:
if you are allergic to S(-)Amlodipine, amlodipine, Hydrochlorothiazide, any drug of a related class, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
If you think you may be allergic, talk to your doctor before taking Eslo D®.
if you have severe liver problems or bile problems such as biliary cirrhosis or cholestasis.
If you have severe kidney problems.
if you are more than 3 months pregnant. (It is also better to avoid Eslo D® in early pregnancy, see Pregnancy section).
if you have severe low blood pressure (hypotension).
If the blood flow from your heart is slow or blocked.
This may happen if the blood vessel or valve that takes blood away from your heart becomes narrow (aortic stenosis).
you have a low heart output after a heart attack (acute myocardial infarction).
Low heart output may make you feel short of breath or have swelling in your feet and ankles.
if you have diabetes or impaired kidney function and you are treated with a blood pressure lowering medicine containing aliskiren.
If any of the above applies to you, do not take Eslo D® and talk to your doctor.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor before taking Eslo D® Tablets:
if you have been sick (vomiting or diarrhoea).
if you have liver or kidney problems.
if you have had a kidney transplant or if you had been told that you have a narrowing of your kidney arteries.
if you have a condition affecting the renal glands called “primary hyperaldosteronism”.
if you have had heart failure or have experienced a heart attack.
Follow your doctor’s instructions for the starting dose carefully.
Your doctor may also check your kidney function.
Skin reactions such as sunburn or rash after being in the sun or using a sunbed.
If you have had skin cancer or if you develop an unexpected skin lesion during the treatment.
Treatment with hydrochlorothiazide, particularly long-term use with high doses, may increase the risk of some types of skin and lip cancer (non-melanoma skin cancer).
Protect your skin from sun exposure and UV rays while taking Sevikar HCT.
if your doctor has told you that you have a narrowing of the valves in your heart (called “aortic or mitral stenosis”) or that the thickness of your heart muscle is abnormally increased (called “obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy”).
if you have experienced swelling, particularly of the face and throat while taking other medicines (including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors).
If you get these symptoms, stop taking Eslo D® and contact your doctor straight away.
You should never take Eslo D® again.
if you are taking any of the following medicines used to treat high blood pressure:
- an ACE inhibitor (for example enalapril, lisinopril, ramipril), in particular if you have diabetes-related kidney problems.
- aliskiren.
Your doctor may check your kidney function, blood pressure, and the amount of electrolytes (e.g. potassium) in your blood at regular intervals.
See also information under the heading “Do not take Eslo D®”.
If any of these apply to you, tell your doctor before taking Eslo D®.
Children and adolescents
The use of Eslo D® in children and adolescents is not recommended (aged below 18 years old).
Other medicines and Eslo D® Tablets
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. Your doctor may need to change your dose and/or to take other precautions. In some cases, you may have to stop taking one of the medicines. This applies especially to the medicines listed below:
Eslo D® Tablets may affect or be affected by other medicines, such as:
- ACE inhibitors or aliskiren (see also information under the headings “Do not take Eslo D ®” and “Warnings and precautions”);
- diuretics (which increase the amount of urine you produce);
- lithium (a medicine used to treat some types of depression);
- potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements,
- salt substitutes containing potassium and other substances that may increase potassium levels;
- certain types of painkillers called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) or selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors (COX-2 inhibitors).
- Your doctor may also check your kidney function;
- anticonvulsant agents (e.g. carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, fosphenytoin, primidone). St. John’s wort; nitroglycerin and other nitrates, or other substances called “vasodilators”;
- medicines used for HIV/AIDS (e.g. ritonavir, indinavir, nelfinavir); medicines used to treat fungal infections (e.g. ketoconazole, itraconazole);
- medicines used to treat bacterial infections (such as rifampicin, erythromycin, clarithromycin, telithromycin); verapamil, diltiazem (heart medicines);
- simvastatin (a medicine used to control high cholesterol levels); dantrolene (infusion for severe body temperature abnormalities);
- medicines used to protect against transplant rejection (ciclosporin).
Eslo D® Tablets with food and drink
Grapefruit juice and grapefruit should not be consumed by people who are taking Eslo D® Tablets. This is because grapefruit and grapefruit juice can lead to an increase in the blood levels of the active ingredient S(-)Amlodipine, which can cause an unpredictable increase in the blood pressure-lowering effect of S(-)Amlodipine.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
Pregnancy
You must tell your doctor if you think you are (or might become) pregnant. Your doctor will normally advise you to stop taking Eslo D® before you become pregnant or as soon as you know you are pregnant and will advise you to take another medicine instead of Eslo D®. Eslo D® is not recommended in early pregnancy (first 3 months), and must not be taken when more than 3 months pregnant.
Breast-feeding
Tell your doctor if you are breast-feeding or about to start breast-feeding. Eslo D® is not recommended for mothers who are breastfeeding, and your doctor may choose another treatment for you if you wish to breastfeed, especially if your baby is a newborn or was born prematurely. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
This medicine may make you feel dizzy. This can affect how well you can concentrate. So, if you are not sure how this medicine will affect you, do not drive, use machinery, or do other activities that you need to concentrate on.
3. How to take Eslo D® Tablets
Always take or give this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure. This will help you get the best results and lower the risk of side effects.
The usual dose of Eslo D® is one tablet per day.
− It is preferable to take your medicine at the same time each day.
− Swallow the tablets with a glass of water.
− You can take Eslo D® with or without food. Do not take Eslo D® with grapefruit or grapefruit juice.
Patients with kidney or liver problems
You should tell your doctor if you have kidney or liver problems as your doctor may need to alter the normal dose or medicine.
If you take more Eslo D® than you should
If you have taken too many tablets of Eslo D®, or if someone else has taken your tablets, consult a doctor immediately.
If you forget to take Eslo D®
If you forget to take this medicine, take it as soon as you remember. Then take your next dose at its usual time. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the dose you missed. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten tablet.
If you stop taking Eslo D®
Stopping your treatment with Eslo D® may cause your disease to get worse. Do not stop taking your medicine unless your doctor tells you to.
4. Possible side effects
This medicine can cause side effects like all medicines, although not everybody gets them.
Some side effects can be serious and need immediate medical attention: A few patients have experienced these serious side effects (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people). If any of the following happens, tell your doctor straight away: Allergic reaction with symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling of face or lips or tongue, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure (feeling of faintness, light-headedness).
Other possible side effects of Eslo D®:
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people): blocked nose, sore throat and discomfort when swallowing; headache; swelling of arms, hands, legs, ankles or feet; tiredness; asthenia (weakness); redness and warm feeling of the face and/or neck.
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people): Dizziness; nausea and abdominal pain; dry mouth; drowsiness, tingling or numbness of the hands or feet; vertigo; fast heart beat including palpitations; dizziness on standing up; cough; diarrhoea; constipation; skin rash, redness of the skin; joint swelling, back pain; pain in joints.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people): Feeling anxious; ringing in the ears (tinnitus); fainting; passing more urine than normal or feeling more of an urge to pass urine; inability to get or maintain an erection; sensation of heaviness; low blood pressure with symptoms such as dizziness, light-headedness; excessive sweating; skin rash all over your body; itching; muscle spasm.
If any of these affects you severely, tell your doctor.
Side effects reported with S(-)amlodipine or Hydrochlorothiazide alone and either not observed with Eslo D® or observed with a higher frequency than with Eslo D®:
S(-)Amlodipine
Consult a doctor immediately if you experience any of the following very rare, severe side effects
after taking this medicine:
- Sudden wheeziness, chest pain, shortness of breath or difficulty in breathing.
- Swelling of eyelids, face or lips.
- Swelling of the tongue and throat which causes great difficulty breathing.
- Severe skin reactions including intense skin rash, hives, reddening of the skin over your whole body, severe itching, blistering, peeling and swelling of the skin, inflammation of the mucous membranes (Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis) or other allergic reactions.
- Heart attack, abnormal heart beat.
- Inflamed pancreas, which may cause severe abdominal and back pain accompanied with feeling of being very unwell.
Hydrochlorothiazide
fever, inflammation of blood vessel walls (necrotising angiitis), jaundice, pancreatitis, cramping, gastric irritation, sugar or glucose in urine (Glucosuria), high blood sugar, high level of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricaemia), low level of potassium in your blood (hypokalaemia), photosensitivity, a swollen salivary gland (sialadenitis), skin reactions, agranulocytosis, aplastic anaemia, haemolytic anaemia, leucopenia, purpura, thrombocytopenia, restlessness, interstitial nephritis, respiratory distress, including pneumonitis, pulmonary oedema, transient blurred vision, xanthopsia (color vision deficiency), non-melanoma skin cancer.
If you experience any of these, tell your doctor straight away.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Eslo D®
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and blister. Do not store above 30°C. Store in the original package in order to protect it from moisture. Do not use any Eslo D® pack that is damaged or shows signs of tampering.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Eslo D® tablets contain
The active substances of Eslo D® are S(-)Amlodipine as s(-) Amlodipine besylate and Hydrochlorothiazide.
Each uncoated tablet contains:
S (-) Amlodipine Besylate IP equivalent to S (-) Amlodipine 2.5 mg
Hydrochlorothiazide IP 12.5 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Lake of Sunset Yellow
Presentation/pack size
A composite blister strip of 3 x 10 tablets / 2 x 15 tablets.