Eslo-AT Tablets
Therapy Area
Cardiology
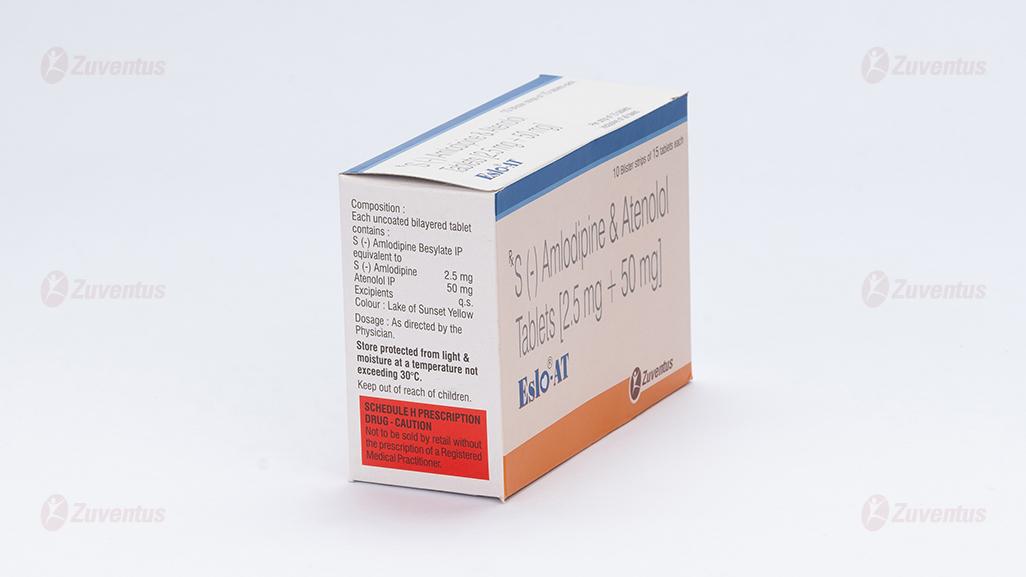
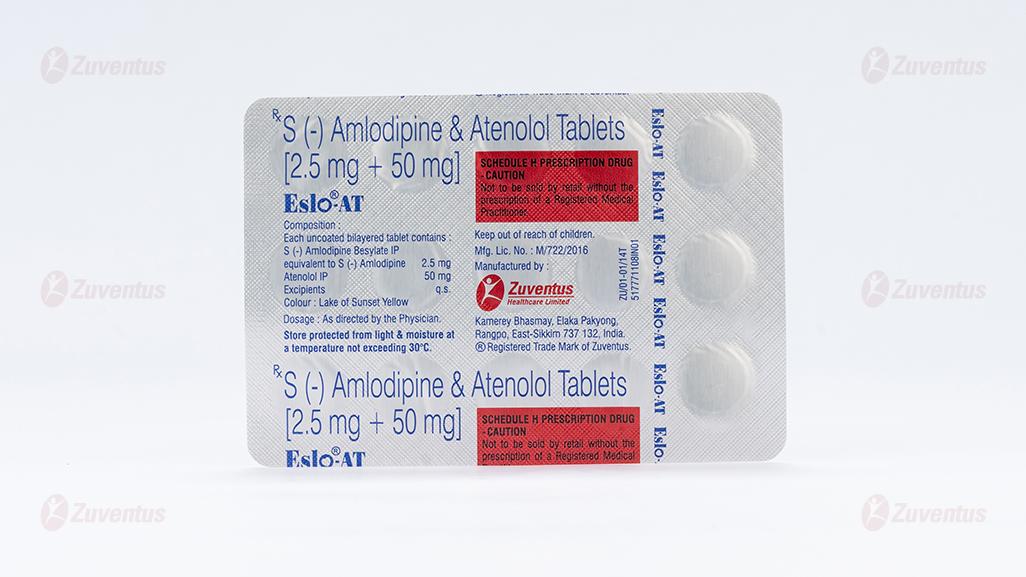
Composition
Each uncoated bilayered tablet contains :
S (-) Amlodipine Besylate IP
equivalent to S (-) Amlodipine 2.5 mg
Atenolol IP 50 mg
Excipients q.s
Colour : Lake of Sunset Yellow
Therapeutic Category
Antihypertensive, antianginal agent
Description:
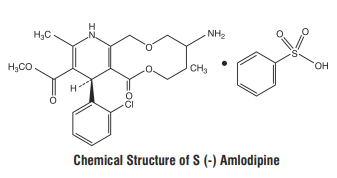
S (-) Amlodipine, the chirally pure form of Amlodipine is a Calcium channel antagonist belonging to the Dihydropyridine class. The chemical name of S (-) Amlodipine is (S)-3-ethyl-5-1-methyl-2-(2- aminoethoxymethyl)-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dih-ydro-6-methyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate. Its empirical formula
is C20H25ClN2O5 C6H6O3S, with a molecular weight of 567.1 g/mol.
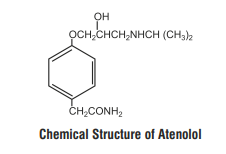
Atenolol is a β1-selective receptor antagonist and produces the antihypertensive activity. It is chemically described as Benzeneacetamide, 4-[2'-hydroxy-3'-[(1-methylethyl) amino] propoxy]. Atenolol has a molecular weight of 266.34 g/mol with molecular formula C14H22N2O3
Clinical Pharmacology :
S (-) Amlodipine, the chirally pure form of Amlodipine is a calcium channel antagonist belonging to the Dihydropyridine class. The S (-) isomer of Amlodipine is found to possess greater pharmacological effects than R (+) Amlodipine. S (-) Amlodipine is 1000 times more potent than the R (+) isomer in binding to the Dihydropyridine receptor. In humans, the dominant effects of Amlodipine are consequent to vasodilation. S (-) Amlodipine lowers peripheral vascular resistance without causing a reflex tachycardia. In patients with angina pectoris S (-) Amlodipine reduces the myocardial oxygen demand by causing a direct vasodilation of the coronary artery and arterioles. Atenolol is a β1-selective receptor antagonist and produces the antihypertensive activity. β-adrenergic antagonists slow the heart rate and decrease myocardial contractility. These agents decrease the effect of catecholamines on the determinants of myocardial oxygen consumption thus improving the relationship between cardiac oxygen supply and demand. Combinations of Amlodipine and Atenolol have been used successfully to treat hypertension and angina. Since S (-) Amlodipine is the chirally pure form of Amlodipine, the combination of S (-) Amlodipine and Atenolol is highly beneficial in the treatment of hypertension and angina.
Pharmacokinetics:
Administration of S (-) Amlodipine 2.5 mg as a single dose in the fasting state produced maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) of 8.30 ± 1.071 ng/ ml in 2.73 ± 0.88 hrs. (Tmax). Amlodipine is extensively (about 90%) converted to inactive metabolites via hepatic metabolism with 10% of the parent compound and 60% of the metabolites excreted in the urine. Ex vivo studies have shown that approximately 93% of the circulating drug is bound to plasma proteins in hypertensive patients. The mean AUC0-t value (t= 48 hrs.) of Tablet S (-) Amlodipine (2.5 mg) is 95.33 ± 14.45 ng.hr/ml. The AUC0-∞ value is recorded to be 140.91± 28.06 ng.hr/ml. The plasma elimination half life of (S) - Amlodipine has been found to be 31.09 ± 12.65 hrs.
Approximately 50% of an oral dose of Atenolol is absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract and the remainder being excreted unchanged in the faeces. Maximum plasma concentrations are reached within two to four hours after a single oral dose and doses of 50 mg and 100 mg produce mean peak plasma concentrations of approximately 300 and 700 ng/mL, respectively. The plasma half-life (t½) is 6-7 hours and Atenolol is effective for at least 24 hours after a single oral dose. Atenolol is 6-16% plasma protein bound and is extensively distributed to extravascular tissues, but only a small amount is found in the central nervous system. Approximately 10% of Atenolol is metabolised in man. Approximately 47% and 53% of an oral dose is eliminated in the urine and faeces respectively.
Indications :
For treatment of Essential Hypertension and Angina Pectoris.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to any of the components of the formulation, sinus bradycardia, second and higher degrees of heart block, cardiogenic shock, hypotension and overt cardiac failure
Dosage and Administration :One tablet to be administered once daily.
Adverse Reactions
Gingival hypertrophy and alopecia has been seen with S (-) Amlodipine. On the basis of the clinical data available, only minor side effects have been reported with the use of S (-) Amlodipine. On the basis of clinical data available, adverse events reported in less than 5% of the patients included anxiety (0.43%), anorexia (0.43%), irritation (0.43%), headache (2.13%) and facial flushing (2.13%). Caution should be exercised when administering S (-) Amlodipine to patients with impaired hepatic and renal function. Common adverse events seen with Atenolol are as follows : Sleep disturbances, purpura, thrombocytopenia, leucopenia, mood changes, depression, anxiety, nightmares, confusion, psychosis, hallucinations, dizziness, headache, paraesthesia of extremities, dry eyes, impaired vision, visual disturbances, bradycardia, heart failure deterioration, precipitation of heart block, cold extremities, postural hypotension which may be associated with syncope, bronchospasmm, gastrointestinal disturbances, constipation, dry mouth, elevations of transaminase levels, hepatic toxicity including intrahepatic cholestasis, alopecia, psoriasiform skin reactions, exacerbation of psoriasis, skin rashes, impotence, fatigue, sweating.
Drug Interactions
Clinical studies have shown that S (-) Amlodipine when combined with aspirin, nitrates, beta-blockers, statins, ACE inhibitors, H2 blockers, and Proton Pump Inhibitors produced no drug interactions. No drug interaction has been reported with the use of Atenolol.
Warnings :
Increased Angina and/or Myocardial Infarction
Rarely, patients, particularly those with severe obstructive coronary artery disease, have developed documented increased frequency, duration and/or severity of angina or acute myocardial infarction on starting calcium channel blocker therapy or at the time of dosage increase. The mechanism of this effect has not been elucidated.
Cardiac Failure
Sympathetic stimulation is necessary in supporting circulatory function in congestive heart failure, and beta blockade carries the potential hazard of further depressing myocardial contractility and precipitating more severe failure. In patients who have congestive heart failure controlled by digitalis and/or diuretics, Atenolol should be administered cautiously. Both digitalis and Atenolol slow AV conduction. In general, calcium channel blockers should also be used with caution in patients with heart failure.
Bronchospastic Diseases
Patients with bronchospastic disease should, in general, not receive beta blockers. Because of its relative β1 selectivity, however, Atenolol may be used with caution in patients with bronchospastic disease who do not respond to, or cannot tolerate, other antihypertensive treatment.
Thyrotoxicosis
Beta-adrenergic blockade may mask certain clinical signs (eg, tachycardia) of hyperthyroidism. Abrupt withdrawal of beta blockade might precipitate a thyroid storm; therefore, patients suspected of developing thyrotoxicosis from which Atenolol therapy is to be withdrawn and should be monitored closely.
Untreated Pheochromocytoma
Atenolol should not be given to patients with untreated pheochromocytoma.
Pregnancy and Fetal Injury
There is no data available on the use of S (-) Amlodipine in pregnant and lactating women. Atenolol can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Atenolol crosses the placental barrier and appears in cord blood. Administration of Atenolol, starting in the second trimester of pregnancy, has been associated with the birth of infants that are small for gestational age. No studies have been performed on the use of Atenolol in the first trimester and the possibility of fetal injury cannot be excluded. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. Neonates born to mothers who are receiving Atenolol at parturition or breast-feeding may be at risk for hypoglycemia and bradycardia. Caution should be exercised when Atenolol is administered during pregnancy or to a woman who is breast-feeding.
Precautions
Hepatic impairment and renal impairment
No controlled clinical study of S (-) Amlodipine has been performed in patients with hepatic impairment and renal impairment. Clinical studies in patients with normal liver function have shown that there is no elevation in the hepatic enzymes with the use of S (-) Amlodipine. Since about 90% of the drug is excreted unchanged in urine, no dosage adjustment is required in patients with hepatic impairment. There is no significant hepatic metabolism of Atenolol and more than 90% of that absorbed reaches the systemic circulation unaltered. Plasma half-life is raised in patients with renal failure with S (-) Amlodipine. Since Atenolol is excreted via the kidneys, the dosage should be adjusted in cases of severe impairment of renal function.
Hence, caution should be taken while administering the combination to such patients.
Children
Safety and effectiveness of this product in children has not been established.
Overdosage
Overdosage with racemic Amlodipine and Atenolol may cause excessive peripheral vasodilation with marked hypotension possibly a reflex tachycardia, acute cardiac insufficiency and bronchospasm. Hence, caution should be taken in case of an overdosage with Eslo AT tablet. If massive overdose occurs, active cardiac and respiratory monitoring should be instituted. Frequent blood pressure measurements should be performed. Should hypotension occur, cardiovascular support including elevation of the extremities and the judicious administration of fluids should be initiated. If hypotension remains unresponsive to these conservative measures, administration of vasopressors (such as phenylephrine) should be considered with attention to circulating volume and urine output. If massive overdose occurs, gastric lavage should be employed. As this product is highly plasma protein bound, hemodialysis is not likely to be of benefit.
Storage
Store protected from light & moisture at a temperature not exceeding 30°C.
Keep out of reach of children.
Presentation
A blister strip of 15 tablets.