Feronia D3 Tablets
Therapy Area
Vitamins/Minerals Supplements
1.0 Generic Name
Ferrous Ascorbate, Folic Acid, Cyanocobalamin, Pyridoxine Hydrochloride & Cholecalciferol Tablets
2.0 Qualitative and Quantitative Composition
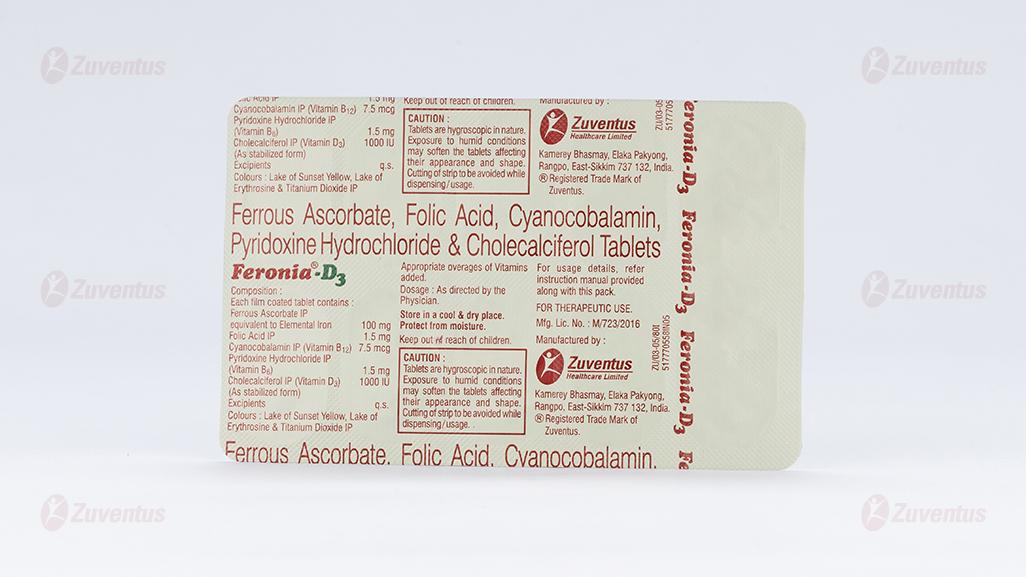
Each film coated tablet contains:
Ferrous Ascorbate IP
equivalent to Elemental Iron 100 mg
Folic Acid IP 1.5 mg
Cyanocobalamin IP 7.5 mcg
(Vitamin B12)
Pyridoxine Hydrochloride IP 1.5 mg
(Vitamin B6)
Cholecalciferol IP 1000 IU (Vitamin D3) (As stabilized form) Excipients q.s. Colours: Lake of Sunset Yellow,
Lake of Erythrosine & Titanium Dioxide IP
3.0 Dosage Form and Strength
Film coated tablet
Ferrous ascorbate (100mg), Folic Acid (1.5mg), Cyanocobalamin (7.5 mcg), Pyridoxine Hydrochloride (1.5 mg), Cholecalciferol IP (1000 IU)
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Treatment and prevention of anemia with multivitamin deficiency
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adults
One tablet to be taken daily orally
Pediatric Population
There is no relevant use of Feronia-D3 Tablets in the pediatric population.
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the active substances or any of the excipients.
- Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, hemosiderosis, haemochromatosis, active peptic ulcer, repeated blood transfusion, regional enteritis and ulcerative colitis.
- Hypercalcaemia and/or hypercalciuria
- Nephrolithiasis (Renal calculi)
- Hypervitaminosis
- Severe renal impairment
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
- CAUTION: Tablets are hygroscopic in nature. Exposure to humid conditions may soften the tablets affecting their appearance and shape. Cutting of strip to be avoided while dispensing /usage.
- Important warning: Contains Iron. Keep out of reach and sight of children, as overdose may be fatal.
- Some post-gastrectomy patients show poor absorption of iron. Care is needed when treating iron deficiency anemia in patients with treated or controlled peptic ulceration. Caution should be exercised when administering folic acid to patients who may have folate dependent tumors.
- Since anemia due to combined iron and vitamin B12 or folate deficiencies may be microcytic in type, patients with microcytic anemia resistant to therapy with iron alone should be screened for vitamin B12 or folate deficiency.
- Cholecalciferol should be used with caution in patients with impairment of renal function and the effect on calcium and phosphate levels should be monitored. The risk of soft tissue calcification should be taken into account. In patients with severe renal insufficiency, vitamin D in the form of Cholecalciferol is not metabolised normally and other forms of vitamin D should be used. Cholecalciferol should not be taken by patients with a tendency to form calcium-containing renal calculi.
- Caution is required in patients receiving treatment for cardiovascular disease
Pediatric population
Feronia D3 Tablets should be kept out of the reach of children.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
- Iron reduces the absorption of penicillamine. Iron compounds impair the bioavailability of fluoroquinolones, levodopa, carbidopa, thyroxine and bisphosphonates.
- Absorption of both iron and antibiotic may be reduced if Feronia D3 is given with tetracycline.
- Absorption of both iron and zinc are reduced if taken concomitantly. Concurrent administration of antacids may reduce absorption of iron. Co- trimoxazole, chloramphenicol, sulphasalazine, aminopterin, methotrexate, pyrimethamine or sulphonamides may interfere with folate metabolism. Serum levels of anticonvulsant drugs may be reduced by administration of folate.
- Oral chloramphenicol delays plasma iron clearance, incorporation of iron into red blood cells and interferes with erythropoiesis.
- Patients treated with cardiac glycosides may be susceptible to high calcium levels and should have ECG parameters and calcium levels monitored. It is recommended to reduce the dose or interrupt treatment if the calcium content in the urine exceeds 7.5 mmol/24 hours (300 mg/24 hours).
- Simultaneous administration of benzothiadiazine derivatives (thiazide diuretics) increases the risk of hypercalcaemia because they decrease the calcium excretion in the urine. The calcium levels in plasma and urine should therefore be monitored for patients undergoing long-term treatment.
- If Cholecalciferol is combined with metabolites or analogues of vitamin D careful monitoring of serum calcium levels is recommended.
- Some inhibition of iron absorption may occur if it is taken with cholestyramine, trientine, tea, eggs or milk.
- Administration of oral iron may increase blood pressure in patients receiving methyldopa.
- Coffee may be a factor in reducing iron bioavailability. Neomycin may alter the absorption of iron.
- Anti-convulsants e.g. phenytoin, phenobarbital, primidone may diminish the effect of Cholecalciferol due to hepatic enzyme induction.
- Rifampicin may reduce the effectiveness of Cholecalciferol due to hepatic enzyme induction.
- Isoniazid may reduce the effectiveness of Colecalciferol due to inhibition of the metabolic activation of Colecalciferol.
- Drugs leading to fat malabsorption, e.g. orlistat, liquid paraffin, cholestyramine, may impair the absorption of Cholecalciferol.
- The cytotoxic agent actinomycin and imidazole antifungal agents interfere with vitamin D activity.
- Concomitant use of glucocorticoids can decrease the effect of vitamin D.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy
The use of Feronia D3 Tablets may be considered during pregnancy, if necessary.
The development of anemia despite prophylaxis with Feronia D3 Tablets calls for investigation. During pregnancy women should follow the advice of their medical practitioner as their requirements may vary depending on the severity of their disease and their response to treatment.
Breast-feeding
It is unknown whether Ferrous Ascorbate and Folic Acid / metabolites are excreted in human milk.
A risk to the newborns/infants cannot be excluded.
Cholecalciferol and its metabolites are excreted in breast milk. Overdose in infants induced by nursing mothers has not been observed. However, when prescribing additional vitamin D to a breast-fed child the practitioner should consider the dose of any additional vitamin D given to the mother.
Fertility
No fertility data is available.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Feronia D3 Tablets has no influence on the ability to drive and use machines. Cholecalciferol has no known side effects that are likely to affect the ability to drive and use or operate machines.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Very rare (<1/10,000)
Very rare (<1/10,000): Rarely allergic reactions may occur. Not known (cannot be estimated from the available data) Not known: Gastrointestinal disorders Gastro-intestinal discomfort, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea. Not known: Renal and urinary disorders Darkening of the stools may occur. Rarely Hypercalcemia, Hypercalciuria
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to:medico@zuventus.com
Website: Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Symptoms
Symptoms and signs of abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea appear within 60 minutes. Cardiovascular collapse with coma may follow. Some improvement may occur after this phase which, in some patients, is followed by recovery. In others, after about 16 hours, deterioration may occur involving diffuse vascular congestion, pulmonary edema, convulsions, anuria, hypothermia, severe shock, metabolic acidosis, coagulation abnormalities and hypoglycemia.
Acute or chronic overdose of Cholecalciferol can cause hypercalcaemia, an increase in the serum and urinary concentrations of calcium. The symptoms of hypercalcaemia are not very specific and consist of nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea often in the early stages and later constipation, anorexia, fatigue, headache, muscle and joint pain, muscle weakness, polydipsia, polyuria formation of renal calculi, nephrocalcinosis, kidney failure, calcification of soft tissues, changes in ECG measurements, arrhythmias and pancreatitis. In rare and isolated cases there are reports that hypercalcaemia is fatal.
Management
Vomiting should be induced immediately, followed as soon as possible by parenteral injection of desferrioxamine mesylate, and then gastric lavage. In the meantime, it is helpful to give milk and/or 5% sodium bicarbonate solution by mouth.
Dissolve 2g desferrioxamine mesylate in 2 to 3ml of water for injections and give intramuscularly. A solution of 5g desferrioxamine in 50 to 100ml of fluid may be left in the stomach. If desferrioxamine is not available, leave 300ml of 1 % to 5 % sodium bicarbonate in the stomach. Fluid replacement is essential.
Recovery may be complicated by long-term sequelae such as hepatic necrosis, pyloric stenosis or acute toxic encephalitis which may lead to CNS damage.
A normalisation of hypercalcaemia due to vitamin D intoxication lasts several weeks. The recommendation for the treatment of hypercalcaemia is the avoidance of any further administration of vitamin D, including supplements, dietary intakes and the avoidance of sunlight. A low calcium or calcium-free diet can also be considered.
Rehydration and the treatment with diuretics e.g. furosemide to ensure adequate diuresis should be considered. Additional treatment with calcitonin or corticosteroids can also be considered.
Phosphate infusions should not be administered to lower hypercalcaemia of hypervitaminosis D because of the dangers of metastatic calcification.
Pediatric population
Acute overdose of oral iron requires emergency treatment. In young children 200-250mg/kg Ferrous Ascorbate is considered to be extremely dangerous.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action/ Pharmacodynamic properties
Iron absorption occurs predominantly in the duodenum and upper jejunum. Iron is oxidized to the Fe3+ state no matter its original form when taken in orally. Gastric acidity as well as solubilizing agents such as ascorbate prevent precipitation of the normally insoluble Fe3+. Intestinal mucosal cells in the duodenum and upper jejunum absorb the iron. The iron is coupled to transferrin (Tf) in the circulation which delivers it to the cells of the body. A feedback mechanism exists that enhances iron absorption in people who are iron deficient. In contrast, people with iron overload dampen iron absorption. A number of dietary factors influence iron absorption. Ascorbate increase iron uptake in part by acting as weak chelators to help to solubilize the metal in the duodenum. Iron is readily transferred from these compounds into the mucosal lining cells.
Cholecalciferol is produced within the skin under the influence of UV radiation including sunlight. In its biologically active form, Cholecalciferol stimulates intestinal calcium absorption, incorporation of calcium into the osteoid, and release of calcium from bone tissue. In the small intestine it promotes rapid and delayed calcium uptake. The passive and active transport of phosphate is also stimulated. In the kidney, it inhibits the excretion of calcium and phosphate by promoting tubular resorption. The production of parathyroid hormone (PTH) in the parathyroids is inhibited directly by the biologically active form of Cholecalciferol. PTH secretion is inhibited additionally by the increased calcium uptake in the small intestine under the influence of biologically active Cholecalciferol.
Elimination: Cholecalciferol and other forms of vitamin D are excreted in feces and urine.
- Iron participates in the second activation step of vitamin D, necessary to make this hormone functional.
- This conversion is done by a renal 25-hydroxyvitamin D 1α-hydroxylase (1α-OHase) enzyme which comprises a CYP-450, a ferredoxin, and a ferredoxin reductase.
- Therefore, less available iron could compromise production of the active form of vitamin D.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Folic Acid is absorbed mainly from the proximal part of the small intestine.
Distribution
The amounts of Folic Acid absorbed from normal diets are rapidly distributed in body tissues.
Biotransformation
Absorption being aided by the acid secretion of the stomach and being more readily affected when the iron is in the ferrous state.
Folic acid rapidly appears in the blood, where it is extensively bound to plasma proteins.
When larger amounts are absorbed, a high proportion is metabolized in the liver to other active forms of folate and a proportion is stored as reduced and methylated folate.
Elimination
Larger amounts of folate are rapidly excreted in the urine and about 4 to 5 micrograms is excreted in the urine daily.
The pharmacokinetics of Cholecalciferol have been widely studied and are well-known. Cholecalciferol from nutritional sources is almost completely absorbed from within the gastro-intestinal tract in the presence of dietary lipids and bile acids. Cholecalciferol is stored in fat cells and its biological half-life is approximately 50 days.
Cholecalciferol is metabolised by microsomal hydroxylase to form 25-hydroxycolecalciferol (25(OH)D3, calcidiol), the primary storage form of vitamin D3. 25(OH)D3 undergoes a secondary hydroxylation within the kidney to form the predominant active metabolite 1,25-hydroxycolecalciferol (1,25(OH)2D3, calcitriol). The metabolites circulate in the blood bound to a specific α -globin.
After a single oral dose of Cholecalciferol, the maximum serum concentrations of the primary storage form are reached after approximately 7 days. 25(OH)D3 is then slowly eliminated with an apparent half-life in serum of about 50 days. Cholecalciferol and its metabolites are excreted mainly in the bile and feces.
After high doses of Cholecalciferol, serum concentrations of 25(OH)D3 may be increased for months. Overdose-induced hypercalcemia may persist for weeks
6.0 Description
This Product (tablet) contains: Ferrous Ascorbate, Folic Acid Cyanocobalamin, Pyridoxine and Cholecalciferol as active ingredients, for the treatment and prevention of Anemia with multivitamin deficiency.
Ferrous Ascorbate is an iron supplement used to treat or prevent low blood levels of iron (such as those caused by anemia or during pregnancy). Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) improves the absorption of iron from the stomach.

Vitamin D promotes calcium absorption in the gut and maintains adequate serum calcium and phosphate concentrations to enable normal bone mineralization and to prevent hypocalcemic tetany.

Folic acid is used to treat anemia caused by folate deficiency. Folic acid is also used as a supplement by women during pregnancy to reduce the risk of neural tube defects (NTDs) in the baby.
Molecular Formula-C19H19N7O6
Molecular Weight- 441.4 g/mol

8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on pack.
8.3 Packaging information
3 Blister strips of 10 tablets each
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store in a cool & dry place. Protect from moisture. Protect from light. Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
- WARNING: Accidental overdose of iron-containing products is a leading cause of fatal poisoning in children under 6. Keep this product out of reach of children. In case of accidental overdose, call a doctor immediately.
- Feronia -D3 Tablet is given to fulfill your nutritional requirement and to prevent any related diseases.
- Avoid taking antacids 2 hours before or after taking Feronia-D3 Tablet as they may make it harder for your body to absorb the medicine.
- Let your doctor know if you are taking any other medications like antihypertensive, antibiotics, or medicines for heart disease or bone disorders.
12.0 Date of revision
25th Sept 2024
Read this entire leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
1. What Feronia D3 Tablets is and what it is used for?
Feronia D3 film-coated Tablets (referred to as Feronia D3 in this leaflet) contains active substances Ferrous Ascorbate 100mg (an iron supplement) and Folic Acid 1.5mg, Cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B12) IP-7.5 mcg, Pyridoxine Hydrochloride (Vitamin B6) IP-1.5 mg, Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) IP-1000 IU. These work together in the medicine.
Feronia D3 belongs to a group of medicines called haematinics and multivitamins supplement.
Feronia D3 works as a supplement. It provides the body with more iron and folic acid, vitamin D3, B12, B6. These are important substances that your body needs to form red blood cells, bone mineralisation. If you do not have the right amount of these substances, it is possible that you may develop anemia, osteoporosis.
Feronia D3 is used to prevent and treat low levels of iron and folic acid, vitamin D, B12, B6 in the blood (such as those caused by anemia or during pregnancy). Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) improves the absorption of iron from the stomach.
2. What you need to know before you take Feronia D3 Tablets?
Do not take Feronia D3:
- if you are allergic to any of the other ingredients of this medicine
- if you are breast-feeding or trying to become pregnant
- if you have been told you suffer from Vitamin B12 deficiency
- if you suffer from a blood disorder
- if you have had or are having repeated blood transfusions
- if you have a stomach ulcer or other digestive conditions such as regional enteritis or ulcerative
colitis
- if you are suffering from anemia that is not due to a lack of iron
- If any of the above applies to you, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor before taking Feronia D3
- if you have been or you are being treated for a stomach ulcer
- if you have had or you have a folate dependent tumour
- if you have had all or part of your stomach removed
Feronia D3 contains iron. Keep out of reach and sight of children, as overdose may be fatal.
Children
There is no relevant use of Feronia D3 in children.
Other medicines and Feronia D3
Tell your doctor if you are taking any other medicines.
- Antibiotics e.g. fluoroquinolones, cotrimoxazole, chloramphenicol, sulphonamides, tetracyclines, neomycin (used for infections)
- Anticonvulsant medicines (used for epilepsy)
- Antacids
- Penicillamine (used for rheumatoid arthritis)
- Sulfasalazine (used for rheumatoid arthritis and bowel disease, e.g. Crohn’s disease)
- Cholestyramine (used for reducing blood cholesterol or control diarrhea)
- Levodopa or Carbidopa (used for Parkinson’s disease)
- Thyroxine (used for thyroid disease)
- Bisphosphonates (used for bone disease)
- Aminopterin and Methotrexate (used for certain cancers)
- Pyrimethamine (used for malaria)
- Trientine (used for Wilson’s disease)
- Methyldopa (used for high blood pressure)
- Zinc
- Any other medicine, including medicines obtained without a prescription
Feronia D3 with food and drink
If you drink tea, coffee or milk or eat eggs at the same time as taking Feronia D3 your body may absorb less of the iron supplement, which may reduce the effect of this medicine.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant, ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine.
Driving and using machines.
There are no known effects on driving or using machines.
3. How to take Feronia D3 Tablets?
Always take Feronia D3 Tablets exactly as your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
The recommended dose for adults
- The usual dose is one tablet each day to be taken by mouth.
Method of administration: For oral administration only.
Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Seek immediate medical help if you have an allergic reaction.
This includes any of the following symptoms:
- Difficulties in breathing
- Swelling of your eyelids, face or lips
- Rash or itching Not known: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
- Upset stomach
- Anorexia (e.g. loss of appetite)
- Sickness
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Darkening of stools
Reporting of side effects: If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page.
Website link: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this product.
5. How should I store Feronia D3 Tablets?
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. An overdose can be fatal.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and blister after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
- Store below 25°C. Keep the blister in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
- Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste.
- Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
- The active substances are Ferrous Ascorbate, Folic Acid, Cyanocobalamin, Pyridoxine and Cholecalciferol
- Each tablet contains Ferrous Ascorbate 100mg, Folic Acid 1.5mg, Cyanocobalamin IP-7.5 mcg, Pyridoxine Hydrochloride IP-1.5 mg, Cholecalciferol IP-1000 IU Pack size: 3 Blister strips of 10 tablets each