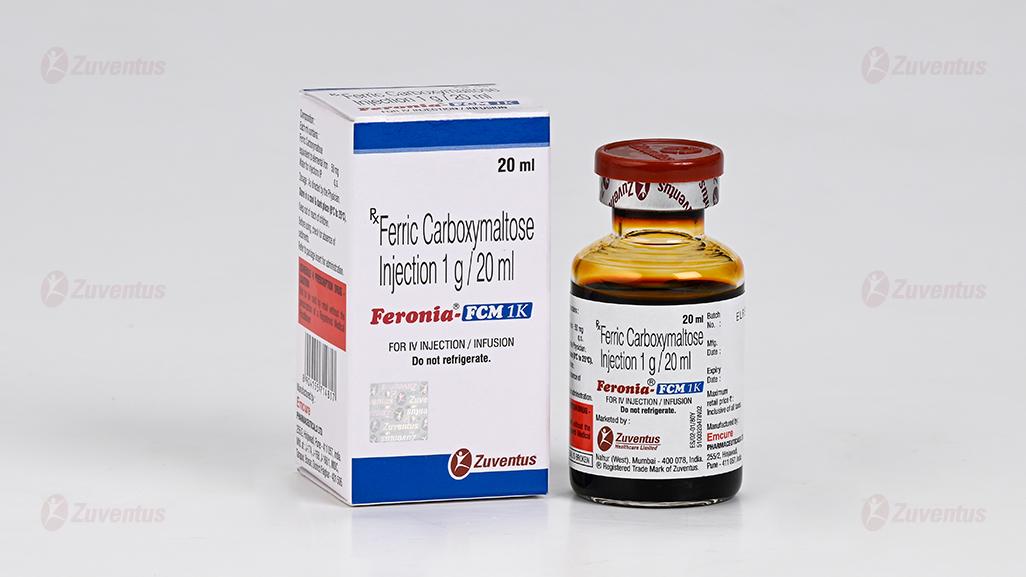
Feronia FCM 1k Injection
Therapy Area
Vitamins/Minerals Supplements
1.0 Generic name
Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection 100 mg / 2 ml, 500 mg / 10 ml & 1 g / 20 ml
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Feronia FCM 100
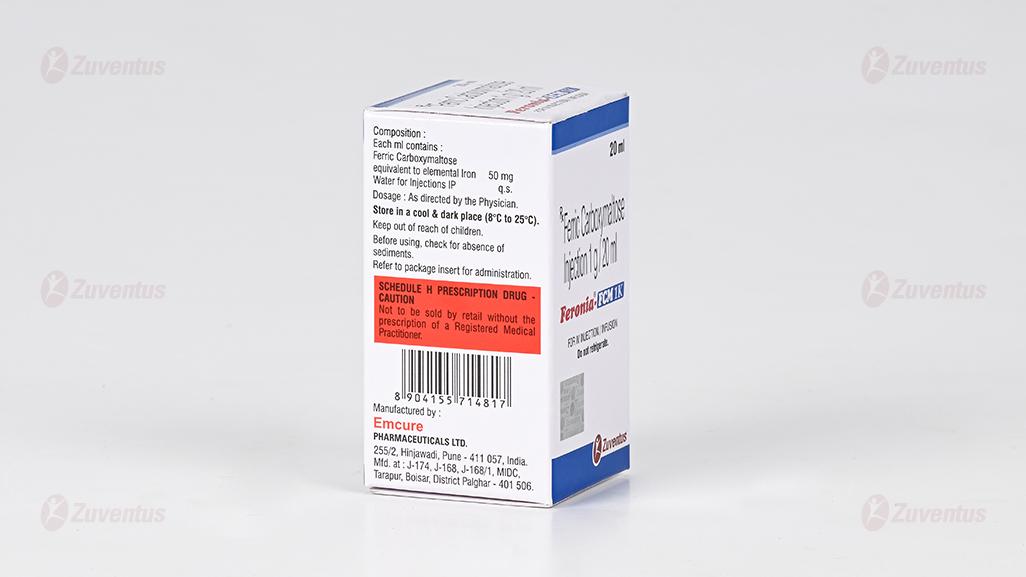
Each ml contains :
Ferric Carboxymaltose
equivalent to elemental Iron 50 mg
Water for Injections IP q.s.
Feronia FCM 500
Each ml contains :
Ferric Carboxymaltose
equivalent to elemental Iron 50 mg
Water for Injections IP q.s.
Feronia FCM 1K
Ferric Carboxymaltose
equivalent to elemental Iron 50 mg
Water for Injections IP q.s.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Injection 100 mg / 2 ml
Injection 500 mg / 10 ml
Injection 1 g / 20 ml
For IV Injection / Infusion
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For treatment of iron deficiency when oral iron preparations are ineffective or cannot be used. The diagnosis must be based on laboratory tests.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Monitor carefully patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions during and following each administration of Ferric Carboxymaltose. Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection should only be administered when staff trained to evaluate and manage anaphylactic reactions is immediately available, in an environment where full resuscitation facilities can be assured. The patient should be observed for adverse effects for at least 30 minutes following each Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection.
Calculation of the cumulative iron dose
The cumulative dose for repletion of iron using Ferric Carboxymaltose is determined based on the patient's body weight and haemoglobin level and must not be exceeded. The following table should be used to determine the cumulative iron dose :
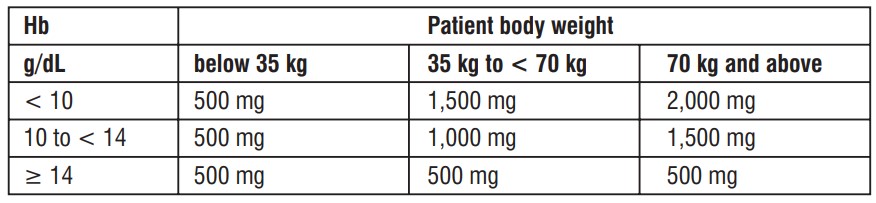
Note :Acumulative iron dose of 500mg should not be exceeded for patientswith bodyweight<35 kg.
Maximum tolerated single dose
A single Ferric Carboxymaltose administration should not exceed :
- 15 mg iron/kg body weight (for administration by intravenous injection) or 20 mg iron/kg body weight (for administration by intravenous infusion).
- 1,000 mg of iron (20 mL Ferric Carboxymaltose).
Do not administer 1000 mg of iron (20 ml) more than once a week.
Post-iron repletion assessments
Re-assessment should be performed by the clinician based on the individual patient's condition. The Hb level should be re-assessed no earlier than 4 weeks post nal Ferric Carboxymaltose administration to allow adequate time for erythropoiesis and iron utilisation.
Special population
Haemodialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease
A single maximum daily injection dose of 200 mg iron should not be exceeded in haemodialysisdependent chronic kidney disease patients.
Paediatric population
The use of Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection has not been studied in children and therefore is not recommended in children under 14 years.
Method of administration
Ferric Carboxymaltose must only be administered by the intravenous route :
- By injection, or
- By infusion, or
- During a haemodialysis session undiluted directly into the venous limb of the dialyser.
Ferric Carboxymaltose must not be administered by the subcutaneous or intramuscular route.
Intravenous injection
Ferric Carboxymaltose may be administered by intravenous injection using undiluted solution. The maximum single dose is 15 mg iron/kg body weight but should not exceed 1,000 mg iron.
Administration rates for intravenous injection of Ferric Carboxymaltose
| Ferric Carboxymaltose | Equivalent iron dose | Administration rate / minimum administration time |
| 2 to 4 mL | 100 to 200 mg | No minimal prescribed time. |
| > 4 to 10 mL | > 200 to 500 mg | 100 mg iron / min |
| > 10 to 20 mL | > 500 to 1,000 mg | 15 minutes |
Intravenous infusion
Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection may be administered by intravenous infusion, in which case it must be diluted. The maximum single dose is 20 mg iron/kg body weight, but should not exceed 1000 mg iron.
In case of infusion, Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection must be diluted only in sterile 0.9% Sodium Chloride Solution as follows :
Dilution plan of Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection for intravenous drip infusion
| Volume of Ferric Carboxymaltose | Equivalent iron dose | Maximum amount of sterile 0.9% Sodium Chloride Solution | Minimum administration time |
| 2 to 4 mL | 100 to 200 mg | 50 mL | No minimal prescribed time |
| > 4 to 10 mL | > 200 to 500 mg | 100 mL | 6 minutes |
| > 10 to 20 mL | > 500 to 1000 mg | 250 mL | 15 minutes |
Note : For stability reasons, dilutions to concentrations less than 2 mg iron/ml are not permissible. Inspect vials visually for sediment and damage before use. Use only those containing sedimentfree, homogeneous solution.
Each vial of Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection is intended for single use only. Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements. Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection must only be mixed with sterile 0.9% Sodium Chloride Solution. No other intravenous dilution solutions and therapeutic agents should be used, as there is the potential for precipitation and/or interaction.
From a microbiological point of view, preparations for parenteral administration should be used immediately after dilution with sterile 0.9% Sodium Chloride Solution.
4.3 Contraindications
The use is contraindicated in cases of :
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance, to Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection or any of its Excipients.
- Known serious hypersensitivity to other parenteral iron products.
- Anaemia not attributed to iron deficiency, e.g. other microcytic anaemia.
- Evidence of iron overload or disturbances in the utilisation of iron.
- First trimester of pregnancy.
4.4 Warning and precautions
Parenterally administered iron preparations can cause hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactoid reactions which may be potentially fatal. Therefore, facilities for cardio-pulmonary resuscitation must be available. Hypersensitivity reactions have also been reported after previously uneventful doses of parenteral iron complexes.
The risk is enhanced for patients with known allergies including drug allergies, including patients with a history of severe asthma, eczema or other atopic allergy. There is also an increased risk of hypersensitivity reactions to parenteral iron complexes in patients with immune or inammator y conditions (e.g. systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis). Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection should only be administered when staff trained to evaluate and manage anaphylactic reactions is immediately available, in an environment where full resuscitation facilities can be assured. Each patient should be observed for adverse effects for at least 30 minutes following each Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection. If hypersensitivity reactions or signs of intolerance occur during administration, the treatment must be stopped immediately. Facilities for cardio respiratory resuscitation and equipment for handling acute anaphylactic / anaphylactoid reactions should be available, including an injectable 1:1000 adrenaline solution. Additional treatment with antihistamines and/or corticosteroids should be given as appropriate.
In patients with liver dysfunction, parenteral iron should only be administered after careful risk/benet assessment. Parenteral iron administration should be avoided in patients with hepatic dysfunction where iron overload is a precipitating factor, in particular Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT). Careful monitoring of iron status is recommended to avoid iron overload. No safety data on haemodialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease patients receiving single doses of more than 200 mg iron are available.
Parenteral iron must be used with caution in cases of acute or chronic infection, asthma, eczema or atopic allergies. It is recommended that the administration of Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection is stopped in patients with ongoing bacteremia. In patients with chronic infection a risk/benet evaluation has to be performed, taking into account the suppression of erythropoiesis. Caution should be exercised to avoid paravenous leakage when administering Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection. Paravenous leakage of Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection at the injection site may lead to brown discolouration and irritation of the skin. In case of paravenous leakage, the administration of Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection must be stopped immediately. As with all parenteral iron preparations the absorption of oral iron is reduced when administered concomitantly.
4.5 Drug interactions
As with all parenteral iron preparations the absorption of oral iron is reduced when administered concomitantly. Therefore, if required, oral iron therapy should not be started for at least 5 days after the last injection of Ferric Carboxymaltose.
4.6 Special populations
Pregnancy
There are no adequate and well-controlled trials of Ferric Carboxymaltose in pregnant women. A careful benet/risk evaluation is required before use during pregnancy and Ferric Carboxymaltose should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary. Treatment with Ferric Carboxymaltose should be conned to the second and third trimester if the benet is judged to outweigh the potential risk for both the mother and the foetus. Animal data suggest that iron released from Ferric Carboxymaltose can cross the placental barrier and that its use during pregnancy may influence skeletal development in the fetus.
Lactation
Clinical studies showed that transfer of iron from Ferric Carboxymaltose to human milk was negligible (≤ 1%). Based on limited data on breast-feeding women it is unlikely that Ferric Carboxymaltose represents a risk to the breast-fed child.
Fertility
There are no data on the effect of Ferric Carboxymaltose on human fertility. Fertility was unaffected following Ferric Carboxymaltose treatment in animal studies.
Pediatric use
The use of Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection has not been studied in children.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection is unlikely to impair the ability to drive and use machines.
4.8 Undesirable effects
The most commonly reported ADR is nausea (occurring in 3.2% of the subjects), followed by
injection/infusion site reactions, hypophosphataemia, headache, ushing, dizziness and hypertension. Injection/infusion site reactions comprise several ADRs which individually are either uncommon or rare. The most serious ADR is anaphylactic reactions (rare); fatalities have been reported.
The following denitions of frequencies are used : Common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10), Uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to <1/100) and Rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000).
Immune system disorders
Uncommon : Hypersensitivity
Rare : Anaphylactoid reactions
Metabolism and nutritional disorders
Common : Hypophosphataemia
Nervous system disorders
Common : Headache, dizziness
Uncommon : Paraesthesia, dysgeusia
Frequency not known (estimated as rare) : Loss of consciousness
Psychiatric disorders
Rare : Anxiety
Cardiac disorders
Uncommon : Tachycardia
Frequency not known (estimated as rare) : Kounis syndrome
Vascular disorders
Common : Hypotension, flushing
Uncommon : Hypertension
Rare : Phlebitis, syncope, presyncope
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Uncommon : Dyspnoea
Rare : Bronchospasm
Gastrointestinal disorders
Common : Nausea
Uncommon : Vomiting, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhoea
Rare : Flatulence
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Uncommon : Pruritus, urticaria, erythema, rash
Rare : Angioedema, pallor, distant skin discolouration
Frequency not known (estimated as rare) : Face oedema
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Uncommon : Myalgia, back pain, arthralgia, muscle spasm
Frequency not known (estimated as rare) : Hypophosphataemic osteomalacia
General disorders and administration site conditions
Common : Injection/infusion site reactions - Includes, but is not limited to, the following preferred terms : injection/infusion site -pain, -haematoma, -discolouration, -extravasation, -irritation, - reaction, (all individual ADRs determined to be uncommon) and -paraesthesia (individual ADR determined to be rare).
Uncommon : Pyrexia, fatigue, chest pain, oedema peripheral, chills, malaise Rare : Rigors, malaise, inuenza like illness (onset may vary from a few hours to several days)
Investigations
Uncommon : Alanine aminotransferase increased, Aspartate aminotransferase increased, gamma-glutamyltransferase increased, blood lactate dehydrogenase increased, blood alkaline phosphatase increased
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Administration of Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection in quantities exceeding the amount needed to correct iron deficit at the time of administration may lead to accumulation of iron in storage sites eventually leading to hemosiderosis. Monitoring of iron parameters such as serum ferritin and transferrin saturation may assist in recognizing iron accumulation. If iron accumulation has occurred, treat according to standard medical practice, e.g. consider the use of an iron chelator.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Ferric Carboxymaltose is a colloidal iron (III) hydroxide in complex with Carboxymaltose, a carbohydrate polymer that releases iron. The complex is designed to provide, in a controlled way, utilisable iron for the iron transport and storage proteins in the body (transferrin and ferritin, respectively).
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group : Iron trivalent, parenteral preparation ATC code : B03AC Using positron emission tomography (PET) it was demonstrated that red cell uptake of 59Fe and 59 52Fe from Ferric Carboxymaltose ranged from 61% to 99%. Red cell utilisation of Fe from radiolabelled Ferric Carboxymaltose ranged from 91% to 99% in subjects with iron deficiency (ID) and 61% to 84% in subjects with renal anaemia at 24 days post-dose. Ferric Carboxymaltose treatment results in an increase in reticulocyte count, serum ferritin levels and TSAT levels to within normal ranges.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Distribution
Positron emission tomography demonstrated that Fe and Fe from Ferric Carboxymaltose was rapidly eliminated from the blood, transferred to the bone marrow, and deposited in the liver and spleen.
After administration of a single dose of Ferric Carboxymaltose of 100 to 1,000 mg of Iron in iron decient subjects, maximum total serum iron levels of 37 µg/mL up to 333 µg/mL are obtained after 15 minutes to 1.21 hours respectively. The volume of distribution was estimated to be 3 L.
Elimination
The iron injected or infused was rapidly cleared from the plasma, the terminal half-life ranged from 7 to 12 hours, the mean residence time (MRT) from 11 to 18 hours. Renal elimination of iron was negligible.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
Preclinical data revealed no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety pharmacology, repeat dose toxicity and genotoxicity. Preclinical studies indicate that iron released from Ferric Carboxymaltose does cross the placental barrier and is excreted in milk in limited, controlled amounts. In reproductive toxicology studies using iron replete rabbits Ferric Carboxymaltose was associated with minor skeletal abnormalities in the fetus. In a fertility study in rats, there were no effects on fertility for either male or female animals. No long-term studies in animals have been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of Ferric Carboxymaltose. No evidence of allergic or immunotoxic potential has been observed. A controlled in-vivo test demonstrated no cross-reactivity of Ferric Carboxymaltose with anti-dextran antibodies. No local irritation or intolerance was observed after intravenous administration.
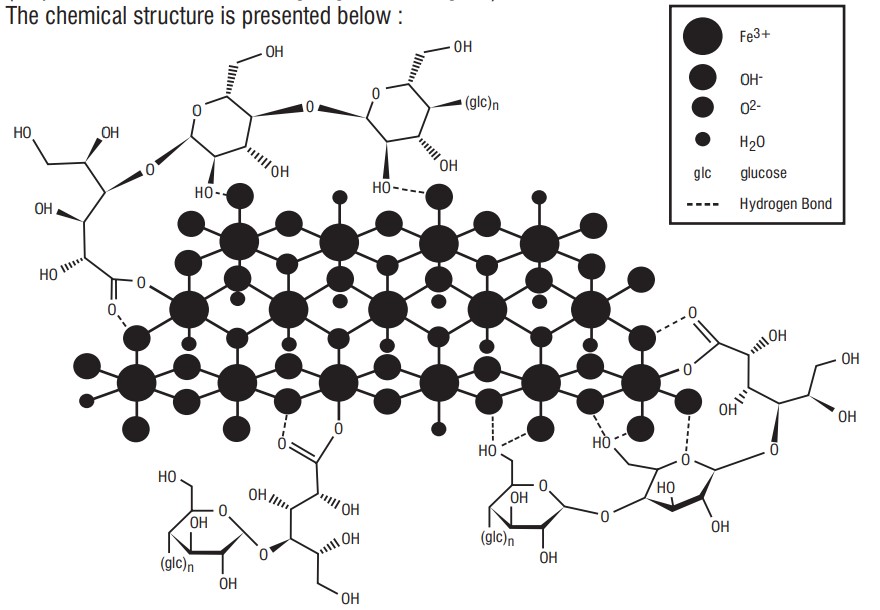
7.0 Description
Ferric Carboxymaltose, an iron replacement product, is an iron carbohydrate complex with the chemical name of polynuclear iron (III)-hydroxide4(R)-(poly-(1→4)-O-α-Dglucopyranosyl)-oxy2(R),3(R),5(R), 6-tetrahydroxy-hexanoate. It has a relative molecular weight of approximately 150,000 Da corresponding to the following empirical formula :
[FeOx(OH)y(H2O)z]n [{(C6H10O5)m (C6H12O7)}l]k where n ≈ 103, m ≈ 8, l≈ 11 and k ≈ 4 (l represents the mean
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
Feronia FCM 100 : A vial of 2 ml.
Feronia FCM 500 : A Vial of 10 ml.
Feronia FCM 1K : A vial of 20 ml.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store in a cool & dark place (8°C to 25°C). Do not refrigerate
Keep out of reach of children.
Before using, check for absence of sediments
9.0 Patient counselling information
Advise the patient to read the patient information leaflet and discuss with the patient the etiology of the iron deficiency anemia and the patient’s iron deficiency anemia treatment options. Advise patients of the risks associated with Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection.
Prior history of reactions to parenteral iron products
Question patients regarding any prior history of reactions to parenteral iron products.
Serious hypersensitivity reactions
Advise patients to report any signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity that may develop during and following Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection administration, such as rash, itching, dizziness, lightheadedness, swelling, and breathing problems.
Pregnancy
Advise pregnant women about the risk of hypersensitivity reactions which may have serious consequences for the fetus. Advise patients who may become pregnant to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
- What Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you receive Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K
- How Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K is administered
- Possible side effects
- How to store Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K?
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K is and what it is used for
Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K is a medicine that contains iron. Medicines that contain iron are used when you do not have enough iron in your body. This is called iron deficiency.
Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K is used to treat iron deficiency when:
oral iron is not effective enough.
you cannot tolerate oral iron.
your doctor decides you need iron very quickly to build up your iron stores.
The doctor will determine whether you have iron deficiency by performing a blood test.
2. What you need to know before you receive Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K
You must not receive Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K
if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to ferric carboxymaltose or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
if you have experienced serious allergic (hypersensitive) reactions to other injectable iron preparations.
if you have anaemia not caused by iron deficiency.
if you have an iron overload (too much iron in your body) or disturbances in the utilization of iron.
Warnings and Precautions
Talk to your doctor or nurse before receiving Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K:
if you have a history of medicine allergy.
if you have systemic lupus erythematosus.
if you have rheumatoid arthritis.
if you have severe asthma, eczema or other allergies.
if you have an infection.
if you have liver disorders.
if you have or have had low levels of phosphate in the blood.
Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K should not be given to children under 14 year of age. Incorrect administration of Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K may cause leakage of the product at the administration site, which may lead to irritation of the skin and potentially long lasting brown discolouration at the site of administration. The administration must be stopped immediately when this occurs.
Other medicines and Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K
Tell your doctor if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines, including medicines obtained without prescription. If Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K is given together with oral iron preparations, then these oral preparations could be less efficient.
Pregnancy
There is limited data from the use of Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K in pregnant women. It is important to tell your doctor if you are pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby. If you become pregnant during treatment, you must ask your doctor for advice. Your doctor will decide whether or not you should be given this medicine.
Breast feeding
If you are breast-feeding, ask your doctor for advice before you are given Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K. It is unlikely that Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K represents a risk to the nursing child.
Driving and using machines
Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K is unlikely to impair the ability to drive or operate machines.
Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K contains sodium
This medicine contains up to 5.5 mg sodium (main component of cooking/table salt) in each mL of undiluted dispersion. This is equivalent to 0.3% of the recommended maximum daily dietary intake of sodium for an adult.
3. How Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K is administered
Your doctor will decide how much Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K to give you, how often you need it and for how long. Your doctor will perform a blood test to determine the dose you need.
Adults and adolescents aged 14 years and older
Your doctor or nurse will administer Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K undiluted by injection, diluted by infusion, or during dialysis:
By injection, you may receive up to 20 mL of Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K, corresponding to 1,000 mg of iron, once a week directly into the vein.
If you are on dialysis, you may receive Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K during a haemodialysis session via the dialyser.
By infusion, you may receive up to 20 mL of Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K, corresponding to 1,000 mg of iron, once a week directly into the vein. Because Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K is diluted with sodium chloride solution for the infusion, it may have a volume of up to 250 mL and will appear as a brown solution.
Children
The use of Ferric Carboxymaltose Injection has not been studied in children and therefore is not recommended in children under 14 years.
If you receive more Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K than you should
As this medicine will be given to you by trained medical staff it is not likely that you will be given too much of this medicine. Overdose can cause accumulation of iron in your body. Your doctor will monitor iron parameters to avoid iron accumulation.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Serious side effects:
Tell your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following signs and symptoms that may indicate a serious allergic reaction: rash (e.g. hives), itching, difficulty breathing, wheezing and/or swelling of the lips, tongue, throat or body, and chest pain which can be a sign of a potentially serious allergic reaction called Kounis syndrome.
In some patients these allergic reactions (affecting less than 1 in 1,000 people) may become severe or life-threatening (known as anaphylactic reactions) and can be associated with heart and circulation problems and loss of consciousness.
Tell your doctor if you develop worsening of tiredness, muscle or bone pain (pain in your arms or legs, joints or back). That may be a sign of a decrease in blood phosphorus which might cause your bones to become soft (osteomalacia). This condition may sometimes lead to bone fractures. Your doctor may also check the levels of phosphate in your blood, especially if you need a number of treatments with iron over time.
Your doctor is aware of these possible side effects and will monitor you during and after the administration of Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K.
Other side effects that you should tell your doctor about if they become serious: Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people): headache, dizziness, feeling hot (flushing), high blood pressure, nausea, and injection/infusion site reactions (see also section 2).
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people): numbness, tingling or prickling sensation on the skin, a change in your taste sensation, high heart rate, low blood pressure, difficulty breathing, vomiting, indigestion, stomach pain, constipation, diarrhoea, itching, hives, redness of the skin, rash, muscle-, joint- and/or back pain, pain in arms or legs, muscle spasms, fever, tiredness, chest pain, swelling of the hands and/or the feet, chills, and a general feeling of discomfort.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people): inflammation of a vein, anxiety, fainting, feeling faint, wheeze, excessive wind (flatulence), rapid swelling of the face, mouth, tongue or throat which may cause difficulty in breathing, paleness, and skin discoloration at other areas of the body than the administration site.
Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data): loss of consciousness and swelling of the face. Flu-like illness (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people) may occur a few hours to several days after injection and is typically characterized by symptoms such as high temperature, and aches and pains in muscles and joints.
Some blood parameters may change temporarily, which could be detected in laboratory tests. The following change in blood parameters is common: decrease in blood phosphorus. The following changes in blood parameters are uncommon: increase in certain liver enzymes called alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyltransferase and alkaline phosphatase, and increase in an enzyme called lactate dehydrogenase.
Ask your doctor for more information.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top right end of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K
Keep Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K after the expiry date which is stated on the label. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Store in the original package in order to protect from light. Do not store above 30°C. Do not freeze. Once the Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K vials have been opened, they should be used immediately. After dilution with sodium chloride solution, the diluted dispersion should be used immediately.
Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K will normally be stored for you by your doctor or the hospital.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K contains
The active substance is ferric carboxymaltose, an iron carbohydrate compound.
The concentration of iron present in the product is 50 mg per millilitre.
Each vial of 2 mL contains ferric carboxymaltose corresponding to 100 mg iron.
Each vial of 10 mL contains ferric carboxymaltose corresponding to 500 mg iron.
Each vial of 20 mL contains ferric carboxymaltose corresponding to 1,000 mg iron.
Feronia FCM 100/ Feronia FCM 500/ Feronia FCM 1K
Each ml contains: Each ml contains:
Ferric Carboxymaltose Ferric Carboxymaltose
equivalent to elemental Iron 50 mg
Water for Injections IP q.s.
What Feronia FCM 100/ 500/1K looks like and contents of the pack
Feronia FCM is supplied in glass vials containing:
Feronia FCM 100: A vial of 2 ml.
Feronia FCM 500: A Vial of 10 ml.
Feronia FCM 1K: A vial of 20 ml.