Feronia XT Suspension
Therapy Area
Vitamins/Minerals Supplements
1.0 Generic Name
Ferrous Ascorbate Suspension
2.0 Qualitative and Quantitative Composition
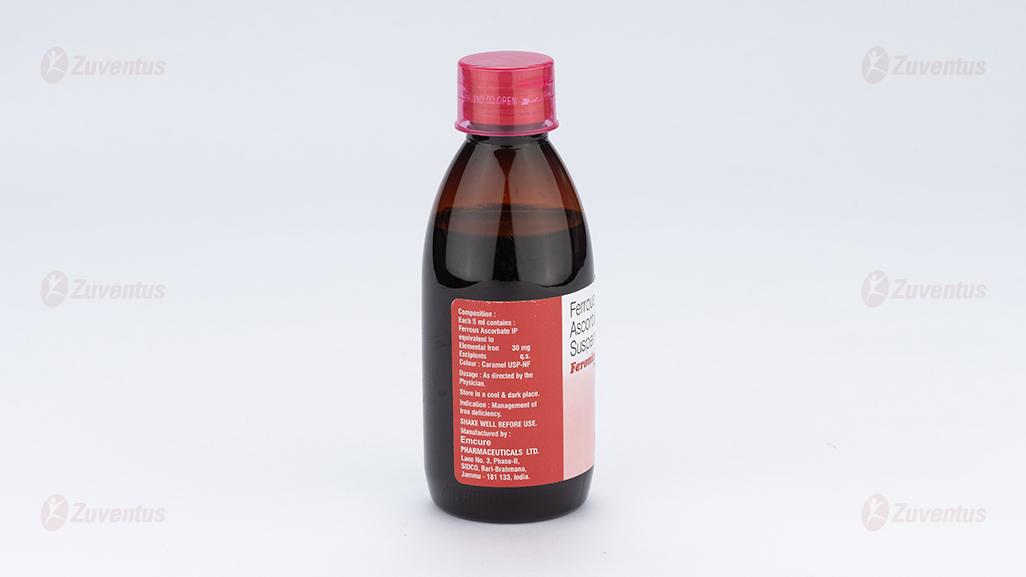
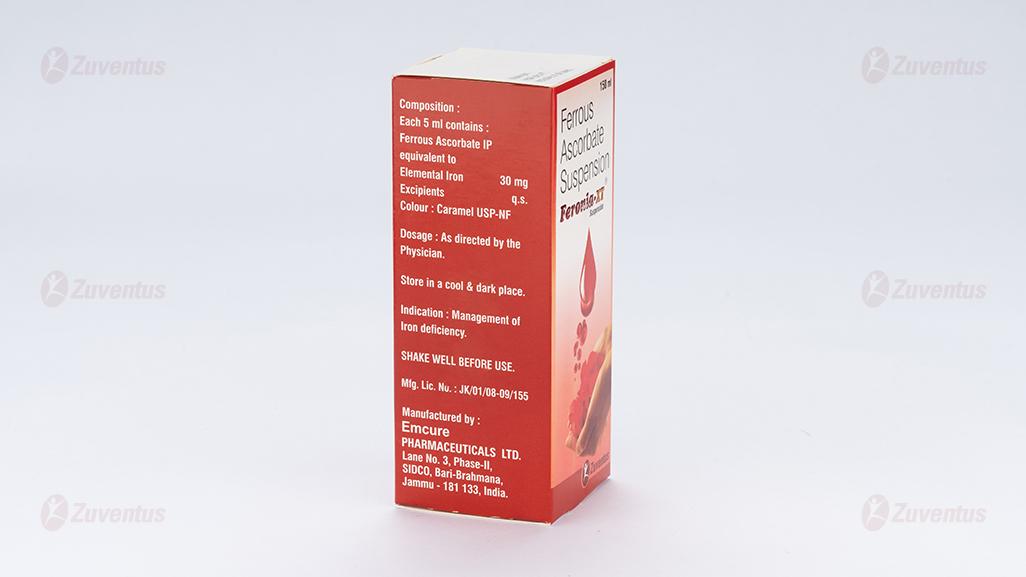
Each 5 ml contains:
Ferrous Ascorbate
equivalent to Elemental Iron 30 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Caramel USP-NF
3.0 Dosage Form and Strength
Suspension
30mg/5ml, 150 ml bottle
4.0 Clinical Particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
Prophylaxis and treatment of iron deficiency anemia.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Prevention of iron deficiency:
Adults and elderly:
Feronia XT Suspension one 5 ml spoonful two to three times a day.
Paediatric population:
6-24 months of age: 12.5mg/day
2-5 years of age: 20-30mg/day
6-11 years of age: 30-60mg/day
Older children: 60mg/day
Premature infants: 5mg elemental iron per day. Iron supplementation in premature infants is only recommended in those of low birth weight who are solely breast fed. Higher doses up to 2mg/kg of elemental iron per day might be needed to cover the needs of growing exclusively breastfed infants. Supplementation should be commenced 4-6 weeks after birth and continued until mixed feeding is established.
Treatment of iron deficiency:
Adults and elderly:
Paediatric population:
Feronia XT Suspension 10 ml three times a day
Full term infants and children: 3 to 6 mg elemental iron/Kg/day given in 2 to 3 divided doses. Total daily dose should not exceed 180 mg elemental iron.
Administration to infants and children should take place under medical advice.
Medical advice should be sought if symptoms do not improve after four weeks of use of this product as these symptoms may reflect an underlying disease process.
Method of administration: Oral
4.3 Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients of the product.
- Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Haemosiderosis, haemochromatosis.
- Active peptic ulcer. Repeated blood transfusions. Regional enteritis and ulcerative colitis. Must not be used in anaemias other than those due to iron deficiency.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
- Some post-gastrectomy patients show poor absorption of iron. Care is required when treating patients with iron deficiency anaemia who have treated or controlled peptic ulceration.
- Duration of treatment of uncomplicated iron deficiency anaemia should not usually exceed 6 months (3 months after reversal of the anaemia has been achieved).
- Because anaemia due to combined iron and Vitamin B12 or folate deficiencies may be microcytic in type, patients with microcytic anaemia resistant to treatment with iron alone should be screened for Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency.
- Paediatric population
- Feronia XT suspension should be kept out of the reach of children.
- Long-term treatment with Feronia XT suspension may increase the risk of dental caries. Adequate dental hygiene must be maintained.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Iron reduces the absorption of penicillamine, bisphosphonates, ciprofloxacin, entacapone, levodopa, levofloxacin, levothyroxine (thyroxine) (give at least 2 hours apart), moxifloxacin, mycophenolate, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, zinc. Absorption of both iron and antibiotic may be reduced if Feronia XT suspension is given with tetracycline. Absorption of oral iron is reduced by calcium salts, magnesium salts (as magnesium trisilicate), Trientine.
Chloramphenicol delays plasma iron clearance, incorporation of iron into red blood cells and interferes with erythropoiesis. Some inhibition of iron absorption may occur if it is taken with cholestyramine, tea, eggs or milk.
Avoid concomitant use of iron with dimercaprol.
Oral iron antagonises hypotensive effect of methyldopa.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
Ferrous ascorbate can be used during pregnancy if clinically indicated.
Lactation
No adverse effects of ferrous ascorbate have been shown in breastfed infants of treated mothers. Feronia XT suspension can be used during breast-feeding if clinically indicated.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The medicine is considered unlikely to impair the ability to drive or to operate machinery safely.
4.8 Undesirable effects
The following adverse reactions are classified by system organ class and ranked under heading of frequency using the following convention:
Not known: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
Gastrointestinal disorders:
The commonest side effects relate to gastrointestinal irritation (nausea, epigastric pain, constipation or diarrhoea). In the event of these ADRs, it may be helpful to reduce the dose or switch to an alternative iron salt.
Darkening of stools, black discoloration of the teeth and allergic reactions (due to metabisulphite in the syrup vehicle) may also occur.
Reporting of side effects
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
4.9 Overdose
Symptoms:
Ingestion of 20 mg/kg elemental iron is potentially toxic and 200-250 mg/kg is potentially fatal. No single method of assessment is entirely satisfactory - clinical features as well as laboratory analysis must be taken into account. The serum iron taken at about 4 hours after ingestion is the best laboratory measure of severity.
Serum Iron
< 3 mg/L (55 micromol/L)
3-5 mg/L (55-90 micromol/L)
> 5 mg/L (90 micromol/L)
Severity
Mild toxicity
Moderate toxicity
Severe toxicity
Early signs and symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhoea. The vomit and stools may be grey or black.In mild cases early features improve but in more serious cases there may be evidence of hypoperfusion (cool peripheries and hypotension), metabolic acidosis and systemic toxicity. In serious cases there can be recurrence of vomiting and gastrointestinal bleeding, 12 hours after ingestion. Shock can result from hypovolaemia or direct cardiotoxicity. Evidence of hepatocellular necrosis appears at this stage with jaundice, bleeding, hypoglycaemia, encephalopathy and positive anion gap metabolic acidosis. Poor tissue perfusion may lead to renal failure. Rarely, gastric scarring causing stricture or pyloric stenosis (alone or in combination) may lead to partial or complete bowel obstruction 2-5 weeks after ingestion.
Management:
Supportive and symptomatic measures include ensuring a clear airway, monitor cardiac rhythm, BP and urine output, establishing IV access and administering sufficient fluids to ensure adequate hydration. Consider whole bowel irrigation. If metabolic acidosis persists despite correction of hypoxia and adequate fluid resuscitation, an initial dose of 50 mmol sodium bicarbonate may be given and repeated as necessary, for adults guided by arterial blood gas monitoring (aim for a pH of 7.4). Consider the use of desferrioxamine, if /the patient is symptomatic (other than nausea), serum iron concentration is between 3-5 mg/L (55-90 micromol/L) and still rising. Haemodialysis does not remove iron effectively but should be considered on a supportive basis for acute renal failure as this will facilitate removal of the iron-desferrioxamine complex.
5.0 Pharmacological Properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Iron bivalent, oral preparations Iron is an essential constituent of the body, and is necessary for haemoglobin formation and the oxidative processes of living tissues. Iron and iron salts should be given for the treatment or prophylaxis of iron deficiency anaemias. Preparations of iron are administered by mouth, by intramuscular or intravenous injection.
Soluble ferrous salts are most effective by mouth. Ferrous ascorbate is an easily absorbed source of iron for replacement therapy. It is a salt of ferrous iron with an organic acid and is less irritant to the gastro-intestinal tract than salts with inorganic acids.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
In the acid conditions of the gastric contents, ferrous ascorbate is dissociated and ferrous ions are liberated. These ions are absorbed in the proximal portion of the duodenum. The ferrous iron absorbed by the mucosal cells of the duodenum is oxidised to the ferric form, and this is bound to protein to form Ferritin.
Distribution
Ferritin in the mucosal cells releases iron into the blood, where it is bound to transferrin and passed into the iron stores - liver, spleen, and bone marrow. These stores are a reserve of iron for synthesis of haemoglobin, myoglobin, and iron containing enzymes.
Elimination
Iron is lost from the body through loss of cells in urine, faeces, hair, skin, sputum, nails, and mucosal cells, and through blood loss.
Ferrous ascorbate has the same pattern of absorption and excretion as dietary iron.
6.0 Nonclinical Properties
Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
As per the toxicity reports, designed to determine the acute oral toxicity of ferrous ascorbate Complex to Sprague Dawley rats. No signs of intoxication were observed in animals treated at the dose level of 2000 mg/kg of the test substance. All animals survived through the study period of 14 days. Animals from control and 2000 mg/kg dose group exhibited normal body weight gain on day 7 and day 14. Gross pathological examination did not reveal any abnormalities attributable to the treatment.
7.0 Description
Ferrous Ascorbate is a synthetic molecule of ascorbic acid and iron and is used as a source of iron for iron deficiency anaemia.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf life
24 months
8.3 Packaging Information
Amber glass bottle with polypropylene, child resistant, tamper evident closure with PET faced Aluminium foil/EPE wads. Pack size: 1 x 150 ml
8.4 Special precautions for storage
Store below 30°C. Protect from light.
8.5 Storage and handing Instructions
No special requirements for disposal. Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
Do not administer Feronia XT suspension
- if the patient is allergic to active substances or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
- if the patient suffers from Vitamin B12 deficiency.
- if the patient suffers from a blood disorder.
- if the patient had or is having repeated blood transfusions.
- if the patient has a stomach ulcer or other digestive conditions such as regional enteritis or ulcerative colitis.
- if the patient is suffering from anemia that is not due to lack of iron.
If any of the above applies to the patient, talk to your doctor.
Talk to your doctor before starting Feronia XT suspension
- if the patient has been or is being treated for a stomach ulcer.
- if the patient had or has folate dependent tumour.
- if the patient had all or part of the stomach removed.
Keep out of reach and sight of children, as overdose of iron may be fatal.
Other medicines and Feronia XT suspension
Tell your doctor if the patient is taking any other medicines.
- Antibiotics e.g. fluoroquinolones, cotrimoxazole, chloramphenicol, sulphonamides, tetracyclines, neomycin (used for infections).
- Anticonvulsant medicines (used for epilepsy).
- Antacids.
- Penicillamine (used for rheumatoid arthritis).
- Sulfasalazine (used for rheumatoid arthritis and bowel disease, e.g. Crohn’s disease).
- Cholestyramine (used for reducing blood cholesterol or control diarrhoea).
- Thyroxine (used for thyroid disease).
- Bisphosphonates (used for bone disease).
- Aminopterin and Methotrexate (used for certain cancers).
- Pyrimethamine (used for malaria).
- Trientine (used for Wilson’s disease).
- Methyldopa (used for high blood pressure).
- Zinc.
- Any other medicine, including medicines obtained without a prescription
Feronia XT suspension with food and drink
If tea, coffee or milk or eggs are taken at the same time as Feronia XT suspension, the body may absorb less of the iron supplement, which may reduce the effect of this medicine.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
-Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
-If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
-This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
-If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet:
1. What Feronia XT Suspension is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you take Feronia XT Suspension
3. How to take Feronia XT Suspension
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store Feronia XT Suspension
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Feronia XT Suspension is and what it is used for
Feronia XT Suspension contains a form of iron called Ferrous ascorbate. Iron is usually found in foods and is necessary for the normal development of red blood cells. A lack of iron affects the development of the red blood cells and causes iron deficiency anaemia.
Ferrous ascorbate suspension is used to prevent or treat iron deficiency anaemia.
The prevention of iron deficiency during pregnancy usually requires a combination of iron and folic acid.
2. What you need to know before you take Feronia XT Suspension
Do not take medicine if:
• You are allergic to Ferrous ascorbate or any of the other ingredients of this medicine, or to any other medicine containing iron
• You have noticed blood in your urine
• You suffer from any form of anaemia, other than iron deficiency anaemia, or from any other condition where your body’s iron is affected (your doctor will be able to advise you)
• You have bronze markings on your skin or you have been told that you have increased stores of iron in your tissues • You are suffering from a recently diagnosed stomach or duodenal ulcer
• You are undergoing repeated blood transfusions
• You suffer from ulcerative colitis or any other inflammatory condition of the bowels. Speak to your doctor if any of these apply to you before you take your medicine.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Ferrous ascorbate suspension if:
• You suffer or have suffered from a peptic ulcer
• You have problems associated with narrowing of your intestine (stricture) or outpocketing of the inner layer of your intestine (diverticular disease)
• You have difficulty in absorbing certain sugars (glucose or galactose)
• You have had some or all of your stomach removed as this may make it difficult for you to absorb iron
• You have diabetes.
If any of these conditions apply to you, speak to your doctor before you take this medicine. Your doctor will want to watch you closely, and will advise you if any additional medicine is required to treat your condition.
Other medicines and Feronia XT Suspension
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines
The effects of any of these medicines or of Ferrous ascorbate suspension may change, particularly if you are taking:
• Certain medicines for treating infections (e.g. chloramphenicol, tetracyclines, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, ofloxacin, norfloxacin)
• Medicines containing zinc, calcium or magnesium salts
• Levothyroxine, used for thyroid gland problems
• Medicines used for a disease known as ‘Parkinson’s disease’ (e.g. levodopa, entacapone).
• Methyl dopa, used for increase in blood pressure
• Antacids used to treat indigestion
• Penicillamine used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
• Colestyramine used to reduce cholesterol and fats in the blood.
• Medicines for bone diseases (bisphosphonates)
• Trientine, used for high copper levels in blood
• Dimercaprol, used for various metal poisonings
• Mycophenolate, used during change of organs (transplant).
Feronia XT Suspension with food and drink
Ferrous ascorbate suspension may be taken with meals. This may help to relieve any stomach related side effects. However, it is advisable not to take your medicine with tea, eggs or milk as this may reduce its effect.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
The prevention of iron deficiency during pregnancy usually requires a combination of iron and folic acid.
3. How to take Feronia XT Suspension
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
It is important to take your medicine at the right time.
The label will tell you how much to take and how often.
The recommended dose is:
Adults and the elderly:
The usual dose to prevent Iron deficiency anemia is one spoonful (5ml) two to three times a day.
Use in children
For children and premature infants, your doctor will decide the dose, according to the age and weight of the child and infant.
Your doctor will advise you on how long you should take the medicine, which is normally not more than six months. It is usually stopped three months after the anemia has been corrected.
If you have to go to another doctor or to the hospital tell them, you are taking Feronia XT Suspension.
If you take more Ferrous ascorbate suspension than you should:
Contact your nearest hospital casualty department or doctor immediately. Take any remaining medicine and this leaflet with you so that the medical staff know exactly what you have taken.
Your medicine is very dangerous if too much is taken by young children and care should be taken to keep the medicine safely out of the reach of children.
If you forget to take your Ferrous ascorbate suspension:
Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
Take your dose as soon as you remember. Then go on as before. If it is almost time for the next dose, then do not take the missed dose at all.
If you stop taking Ferrous ascorbate suspension:
If you are having no problems with Ferrous ascorbate suspension, do not stop taking it until your doctor tells you to.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
All medicines can cause allergic reactions although serious allergic reactions are rare. Any sudden wheeziness, difficulty in breathing, swelling of the eyelids, face or lips, rash or itching (especially affecting your whole body) should be reported to a doctor immediately.
Not known: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
Other side effects may include:
• stomach discomfort
• pain in upper part of the stomach
• vomiting sensation
• difficulty in passing stools
• loose stools.
Also, you might find your stools are darker in colour after you have taken this medicine. This is quite commonly seen with all iron preparations and is normal.
If you use Ferrous ascorbate suspension for a long time the sugar content may increase the risk of tooth decay. It may also result in blackish discolouration of the teeth. This can be reduced by daily brushing of the teeth.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to Store Ferrous Ascorbate Suspension
Important warning: contains iron.
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children, as overdose may be fatal.
Store in cool and dry place. Keep the bottle in the outer carton in order to protect from light. Shake the bottle before use.
Replace the cap after taking your dose.
If you have any of your medicine left after finishing your treatment, return it to your pharmacist.
Do not use this medicine if the bottle is damaged or after the Expiry Date which is stated on the bottle after ‘Exp’. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
REMEMBER
This medicine is for YOU. Never give it to anyone else. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
6. Contents of the Pack and Other Information
The active substance is Ferrous ascorbate. Each 5 ml contains Ferrous ascorbate equivalent to elemental iron 30 mg. Ferrous ascorbate is an iron compound.
What Ferrous ascorbate suspension looks like and contents of pack?
Amber glass bottle with polypropylene, child resistant, tamper evident closure with PET faced Aluminium foil/EPE wads. Pack size: 1 x 150 ml