Floresp Az Nasal Spray
Therapy Area
Respiratory
1.0 Generic name
Azelastine Hydrochloride & Fluticasone Furoate Nasal Spray
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition:
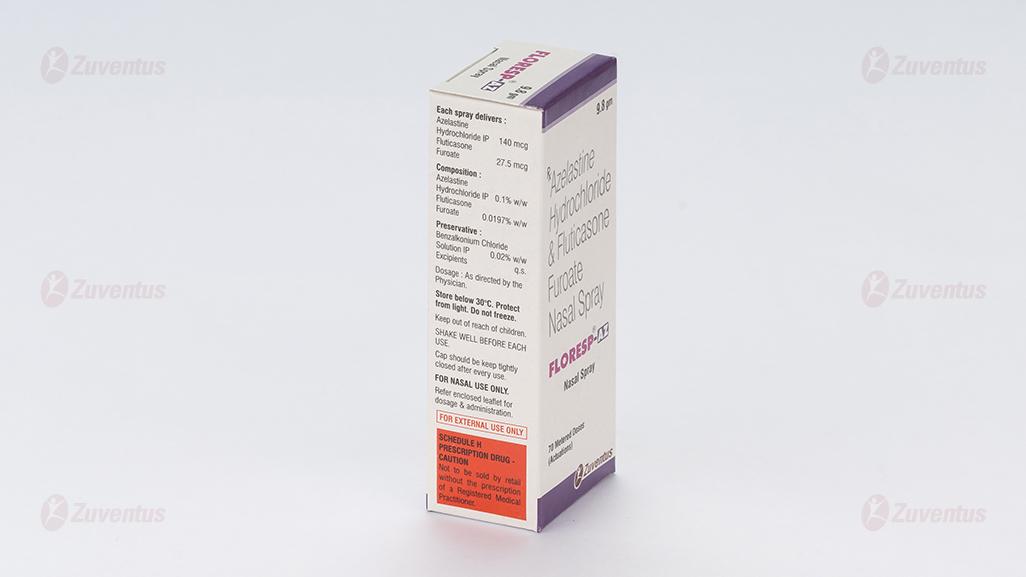
Each spray delivers :
Azelastine Hydrochloride IP 140 mcg
Fluticasone Furoate 27.5 mcg
Composition :
Azelastine Hydrochloride IP 0.1% w/w
Fluticasone Furoate 0.0197% w/w
Preservative :
Benzalkonium Chloride Solution IP 0.02% w/w
Excipients q.s.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Nasal spray
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the relief of the symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis in patients 12 years of age and older.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adults and adolescents (12 years and over)
One spray/nostril twice daily
Hepatic impairment
Azelastine Hydrochloride : Following oral administration, pharmacokinetic parameters were not influenced by age, gender, or hepatic impairment
Fluticasone furoate : Since fluticasone furoate undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism by the hepatic cytochrome P450 isozyme, CYP3A4, the pharmacokinetics of fluticasone furoate may be altered in patients with hepatic impairment. The systemic exposure would be expected to be higher than that observed had the study been conducted after multiple doses and/or in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Therefore, use fluticasone furoate nasal spray with caution in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
5.0 Renal impairment
Azelastine Hydrochloride : Based on oral, single-dose studies, renal impairment (creatinine clearance <50 mL/min) resulted in a 70–75% higher Cmax and AUC compared to normal subjects. Time to maximum concentration was unchanged.
fluticasone furoate : Fluticasone furoate is not detectable in urine from healthy subjects following intranasal dosing. Less than 1% of dose-related material is excreted in the urine. No dosage adjustment is required in patients with renal impairment.
Method of administration
Floresp AZ nasal spray is for administration by the intranasal route only.
The device should be cleaned after each use and the cap replaced.
Directions for use
Following are directions for the use of FLORESP-AZ nasal spray.
Using your nasal spray :
STEP 1
Blow your nose gently
STEP 2
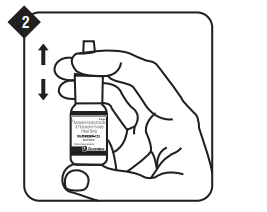
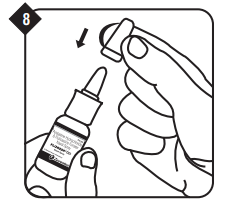
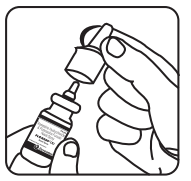
Shake the bottle gently and then remove the protective dust cap.
Hold the bottle as shown with your forefinger and middle finger on either side of the nozzle and your thumb underneath the bottle.
STEP 3
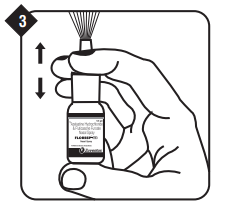
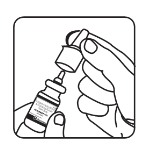
If using for the first time or if you have not used it for a week or more, test the spray.
Testing the spray : With the nozzle pointing away from you, press down a few times as shown until a fine mist comes out of the nozzle.
STEP 4
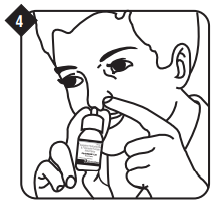
Close one nostril and hold the bottle as shown in step 2. Tilt your head forward slightly and keeping the bottle upright, carefully insert the tip of the nozzle in the other nostril.
STEP 5
Start to breathe in through your nose and while breathing in, press down with your fingers once to release a spray
STEP 6
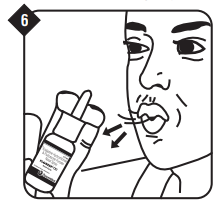
Breathe out through your mouth. Repeat steps 5 and 6 to inhale a second spray.
STEP 7
Repeat steps 4,5 and 6 for the other nostril.
STEP 8
Wipe the nozzle with a clean handkerchief/tissue and replace the protective dust cap.
Cleaning your nasal spray :
Pull the nozzle upwards to detach form the bottle.
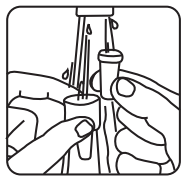
Soak the nozzle and the dust cap in warm water for few minutes
Rinse the nozzle and the dust cap under clean running water
Shake off excess water and allow nozzle and cap to dry at room temperature before refitting onto the bottle.
4.3 Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substances or to any of the excipients
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use Azelastine Hydrochloride
Concurrent use of Azelastine HCl Nasal Solution (Nasal Spray) with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of central nervous system performance may occur.
Fluticasone furoate Systemic corticosteroid effects
Systemic effects of nasal corticosteroid may occur, particularly at high doses prescribed for prolonged periods. These effects are much less likely to occur than with oral corticosteroids and may vary in individual patients and between different corticosteroid preparations. Potential systemic effects may include Cushing's syndrome, Cushingoid features, adrenal suppression, growth retardation in children and adolescents, cataract, glaucoma and more rarely, a range of psychological or behavioural effects including psychomotor hyperactivity, sleep disorders, anxiety, depression or aggression (particularly in children). Treatment with higher than recommended doses of nasal corticosteroids may result in clinically significant adrenal suppression. If there is evidence for higher than recommended doses being used, then additional systemic corticosteroid cover should be considered during periods of stress or elective surgery. Fluticasone furoate 110 micrograms once daily was not associated with hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression in adult, adolescent or paediatric subjects. However the dose of intranasal fluticasone furoate should be reduced to the lowest dose at which effective control of the symptoms of rhinitis is maintained. As with all intranasal corticosteroids, the total systemic burden of corticosteroids should be considered whenever other forms of corticosteroid treatment are prescribed concurrently
If there is any reason to believe that adrenal function is impaired, care must be taken when transferring patients from systemic steroid treatment to fluticasone furoate.
Visual disturbance
Visual disturbance may be reported with systemic and topical corticosteroid use. If a patient presents with symptoms such as blurred vision or other visual disturbances, the patient should be considered for referral to an ophthalmologist for evaluation of possible causes which may include cataract, glaucoma or rare diseases such as central serous chorioretinopathy (CSCR) which have been reported after use of systemic and topical corticosteroids.
Growth retardation
Growth retardation has been reported in children receiving nasal corticosteroids at licensed doses. A reduction in growth velocity has been observed in children treated with fluticasone furoate 110 micrograms daily for one year. Therefore, children should be maintained on the lowest possible efficacious dose which delivers adequate symptom control. It is recommended that the growth of children receiving prolonged treatment with nasal corticosteroids is regularly monitored. If growth is slowed, therapy should be reviewed with the aim of reducing the dose of nasal corticosteroid if possible, to the lowest dose at which effective control of symptoms is maintained. In addition, consideration should be given to referring the patient to a paediatric specialist.
Patients on ritonavir
Concomitant administration with ritonavir is not recommended because of the risk of increased systemic exposure of fluticasone furoate.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Azelastine hydrochloride
Central nervous system depressants
Concurrent use of Azelastine HCl Nasal Solution (Nasal Spray), with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants should be avoided because reductions in alertness and impairment of central nervous system performance may occur.
Erythromycin and ketoconazole
Interaction studies investigating the cardiac effects, as measured by the corrected QT interval (QTc), of concomitantly administered oral azelastine hydrochloride and erythromycin or ketoconazole were conducted. Oral erythromycin (500 mg three times daily for 7 days) had no effect on azelastine pharmacokinetics or QTc based on analyses of serial electrocardiograms. Ketoconazole (200 mg twice daily for 7 days) interfered with the measurement of azelastine plasma concentrations on the analytic HPLC; however, no effects on QTc were observed
Cimetidine
Cimetidine (400 mg twice daily) increased the mean Cmax and AUC of orally administered azelastine hydrochloride (4 mg twice daily) by approximately 65%
Fluticasone furoate
Interaction with CYP3A inhibitors
Fluticasone furoate is rapidly cleared by extensive first pass metabolism mediated by the cytochrome P450 3A4. Based on data with another glucocorticoid (fluticasone propionate), that is metabolised by CYP3A4, coadministration with ritonavir is not recommended because of the risk of increased systemic exposure of fluticasone furoate. Caution is recommended when co-administering fluticasone furoate with potent CYP3A inhibitors including cobicistat-containing products as an increase in the risk of systemic side effects is expected. Co-administration should be avoided unless the benefit outweighs the increased risk of systemic corticosteroid side effects, in which case patients should be monitored for systemic corticosteroid side effects. In a drug interaction study of intranasal fluticasone furoate with the potent CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole there were more subjects with measurable fluticasone furoate concentrations in the ketoconazole group (6 of the 20 subjects) compared to placebo (1 out of 20 subjects). This small increase in exposure did not result in a statistically significant difference in 24 hour serum cortisol levels between the two groups. The enzyme induction and inhibition data suggest that there is no theoretical basis for anticipating metabolic interactions between fluticasone furoate and the cytochrome P450 mediated metabolism of other compounds at clinically relevant intranasal doses. Therefore, no clinical studies have been conducted to investigate interactions of fluticasone furoate on other drugs.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. This combination should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the foetus
Azelastine hydrochloride has been shown to cause developmental toxicity in mice, rats, and rabbits.Hypoadrenalism may occur in infants born of mothers receiving corticosteroids during pregnancy. Such infants should be carefully monitored. In animal studies glucocorticoids have been shown to induce malformations including cleft palate and intra-uterine growth retardation. This is not likely to be relevant for humans given recommended nasal doses which results in minimal systemic exposure.
Nursing mothers
It is not known whether azelastine hydrochloride or fluticasone furoate is excreted in human milk. Hence, caution should be exercised while prescribing this combination to nursing mothers and should only be considered if the expected benefit to the mother is greater than any possible risk to the child.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The occurrence of somnolence has been reported in some patients taking intranasal azelastine hydrochloride. In these cases, the ability to drive and use machines may be impaired by Floresp AZ nasal spray. Alcohol may enhance this effect.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Azelastine hydrochloride
Commonly (1 - 10 %) : a substance-specific bitter taste may be experienced after administration (often due to incorrect method of application, namely tilting the head too far backwards during administration) which, in rare cases, may lead to nausea. Uncommonly (0.1 - 1 %) : a mild, transient irritation of the inflamed nasal mucosa may occur with symptoms such as stinging, itching, sneezing and epistaxis. In very rare cases (< 0.01 %) : hypersensitivity reactions (such as rash, pruritus, urticaria) were reported.
Fluticasone furoate
The most commonly reported adverse reactions during treatment with fluticasone furoate are epistaxis, nasal ulceration and headache. The most serious undesirable effects are rare reports of hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis (less than 1 case per 1000 patients). The following convention has been used for the classification of frequencies : Very common ≥1/10; Common ≥1/100 to <1/10; Uncommon ≥1/1000 to <1/100; Rare ≥1/10,000 to <1/1000; Very rare <1/10,000; Not known (cannot be estimated from the available data).
• Immune system disorders : Rare- Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, and urticaria.
• Nervous system disorders : Common- Headache.
• Eye disorders : Not known- Transient ocular changes, vision blurred.
• Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders : Very common- *Epistaxis, Common- Nasal ulceration, dyspnoea**, Uncommon- Rhinalgia, nasal discomfort (including nasal burning, nasal irritation, and nasal soreness), nasal dryness. Very rare- Nasal septum perforation, Not known- Bronchospasm.
• Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders (Children) : Not known- ***Growth retardation.
6.0 Description of selected adverse reactions
Epistaxis
*Epistaxis was generally mild to moderate in intensity. In adults and adolescents, the incidence of epistaxis was higher in longer-term use (more than 6 weeks) than in short-term use (up to 6 weeks).
Systemic effects Systemic effects of nasal corticosteroids may occur, particularly when prescribed at high doses for prolonged periods. Growth retardation has been reported in children receiving nasal corticosteroids.
**Dyspnoea cases were reported in more than 1% of patients during clinical trials with fluticasone furoate; similar rates were also observed in placebo groups.
Paediatric population
The safety in children under 6 years has not been well established. Frequency, type and severity of adverse reactions observed in the paediatric population are similar to those in the adult population.
Epistaxis
*In paediatric clinical studies of up to 12 weeks duration the incidence of epistaxis was similar between patients receiving fluticasone furoate and patients receiving placebo.
Growth retardation
***In a one-year clinical study assessing growth in pre-pubescent children receiving 110 micrograms of fluticasone furoate once daily, an average treatment difference of -0.27 cm per year in growth velocity was observed compared to placebo.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com
4.9 Overdose
Azelastine hydrochloride
The results of animal studies show that toxic doses can produce CNS symptoms, e.g. excitation, tremor, convulsions. Should these occur in humans, symptomatic and supportive treatment should be instigated as there is no specific antidote. Gastric lavage is recommended if the overdose is recent. With the nasal route of administration overdosage reactions are not anticipated.
Fluticasone furoate
In a bioavailability study, intranasal doses of up to 2640 micrograms per day were administered over three days with no adverse systemic reactions observed. Acute overdose is unlikely to require any therapy other than observation.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Azelastine, a phthalazinone derivative of novel structure, is classified as a potent long acting anti-allergic compound with particularly strong H1 antagonist properties. Fluticasone furoate is a synthetic trifluorinated corticosteroid that possesses a very high affinity for the glucocorticoid receptor and has a potent anti-inflammatory action.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Data from animal studies show that where high levels of azelastine are achieved both inhibition and release of chemical mediators (e.g. leukotriene, histamine, serotonin) involved in allergic reaction occurs. Corticosteroids have been shown to have a wide range of actions on multiple cell types (e.g., mast cells, eosinophils, neutrophils, macrophages, lymphocytes) and mediators (e.g., histamine, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, cytokines) involved in inflammation. Specific effects of fluticasone furoate demonstrated in in vitro and in vivo models included activation of the glucocorticoid response element, inhibition of pro-inflammatory transcription factors such as NFkB, and inhibition of antigen-induced lung eosinophilia in sensitized rats.
Fluticasone furoate has been shown in vitro to exhibit a binding affinity for the human glucocorticoid receptor that is approximately 29.9 times that of dexamethasone and 1.7 times that of fluticasone propionate. The clinical relevance of these findings is unknown.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Azelastine hydrochloride
Absorption : After intranasal administration of 2 sprays per nostril (548 mcg total dose) of 137 mcg azelastine hydrochloride, the mean azelastine peak plasma concentration (C max) is 200 pg/mL, the mean extent of systemic exposure (AUC) is 5122 pg•hr/mL and the median time to reach Cmax (t max) is 3 hours. The systemic bioavailability of azelastine hydrochloride is approximately 40% after intranasal administration.
Distribution : Based on intravenous and oral administration, the steady-state volume of distribution of azelastine is 14.5 L/kg. In vitro studies with human plasma indicate that the plasma protein binding of azelastine and its metabolite, desmethylazelastine, are approximately 88% and 97%, respectively.
Metabolism : Azelastine is oxidatively metabolized to the principal active metabolite, desmethylazelastine, by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. The specific P450 isoforms responsible for the biotransformation of azelastine have not been identified. After a single-dose, intranasal administration of 137 mcg azelastine hydrochloride (548 mcg total dose), the mean desmethylazelastine Cmax is 23 pg/mL, the AUC is 2131 pg•hr/mL and the median tmax is 24 hours. After intranasal dosing of azelastine to steadystate, plasma concentrations of desmethylazelastine range from 20-50% of azelastine concentrations
Elimination : Following intranasal administration of 137 mcg azelastine hydrochloride, the elimination half-life of azelastine is 22 hours while that of desmethylazelastine is 52 hours. Approximately 75% of an oral dose of radiolabeled azelastine hydrochloride was excreted in the feces with less than 10% as unchanged azelastine.
Fluticasone furoate
Absorption : Fluticasone furoate undergoes incomplete absorption and extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver and gut resulting in negligible systemic exposure. The intranasal dosing of 110 micrograms once daily does not typically result in measurable plasma concentrations (<10 pg/mL). The absolute bioavailability for intranasal fluticasone furoate is 0.50 %, such that less than 1 microgram of fluticasone furoate would be systemically available after administration of 110 micrograms.
Distribution : The plasma protein binding of fluticasone furoate is greater than 99 %. Fluticasone furoate is widely distributed with volume of distribution at steady-state of, on average, 608 L.
Biotransformation : Fluticasone furoate is rapidly cleared (total plasma clearance of 58.7 L/h) from systemic circulation principally by hepatic metabolism to an inactive 17β-carboxylic metabolite (GW694301X), by the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP3A4. The principal route of metabolism was hydrolysis of the S-fluoromethyl carbothioate function to form the 17β-carboxylic acid metabolite. In vivo studies have revealed no evidence of cleavage of the furoate moiety to form fluticasone.
Elimination : Elimination was primarily via the faecal route following oral and intravenous administration indicative of excretion of fluticasone furoate and its metabolites via the bile. Following intravenous administration, the elimination phase half-life averaged 15.1 hours. Urinary excretion accounted for approximately 1 % and 2 % of the orally and intravenously administered dose, respectively.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
Azelastine hydrochloride
Two-year carcinogenicity studies in Crl:CD(SD)BR rats and NMRI mice were conducted to assess the carcinogenic potential of azelastine hydrochloride. No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in rats at doses up to 30 mg/kg day (approximately 180 and 160 times the MRHDID 2 for adults and children, respectively, on a mg/m basis). No evidence for tumorigenicity was observed in mice at doses up to 25 mg/kg (approximately 75 and 65 times the MRHDID for adults and children, respectively, 2 on a mg/m basis).
Azelastine hydrochloride showed no genotoxic effects in the Ames test, DNA repair test, mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay, mouse micronucleus test, or chromosomal aberration test in rat bone marrow. There were no effects on male or female fertility and reproductive performance in male and female rats at oral doses up to 30 mg/kg (approximately 180 times the MRHDID 2 in adults on a mg/m basis). At 68.6 mg/kg 2 (approximately 410 times the MRHDID on a mg/m basis), the duration of estrous cycles was prolonged and copulatory activity and the number of pregnancies were decreased. The numbers of corpora lutea and implantations were decreased; however, pre-implantation loss was not increased.
Fluticasone furoate
Findings in general toxicology studies were similar to those observed with other glucocorticoids and are associated with exaggerated pharmacological activity. These findings are not likely to be relevant for humans given recommended nasal doses which results in minimal systemic exposure. No genotoxic effects of fluticasone furoate have been observed in conventional genotoxicity tests. Further, there were no treatment-related increases in the incidence of tumours in two year inhalation studies in rats and mice.
7.0 Description
FLORESP-AZ nasal spray is an antihistamine-corticosteroid combination available as a metered spray formulation for intranasal administration. It contains azelastine hydrochloride, which is a second generation H1 receptorantagonist with potent topical activity, and fluticasone furoate, a synthetic corticosteroid with anti-inflammatory properties.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
FLORESP-AZ sales pack contains 70 metered doses.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
• Store below 30°C. Protect from light. Do not freeze.
• Keep out of reach of children.
• SHAKE WELL BEFORE EACH USE.
• FOR NASAL USE ONLY.
• Refer enclosed leaflet for dosage & administration.
9.0 Patient counselling information
• Local Nasal Effects : Patients should be informed that treatment with Floresp AZ Nasal Spray may lead to adverse reactions, which include epistaxis and nasal ulceration. Candida infection may also occur with treatment with Floresp AZ Nasal Spray. In addition, nasal corticosteroids are associated with nasal septal perforation and impaired wound healing. Patients who have experienced recent nasal ulcers, nasal surgery, or nasal trauma should not use Floresp AZ Nasal Spray until healing has occurred
• Cataracts and Glaucoma : Patients should be informed that glaucoma and cataracts are associated with nasal and inhaled corticosteroid use. Patients should inform his/her health care provider if a change in vision is noted while using Floresp AZ Nasal Spray
• Hypersensitivity Reactions, Including Anaphylaxis : Patients should be aware that hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, and urticaria, may occur after administration of Floresp AZ Nasal Spray. If such reactions occur, patients should discontinue use of Floresp AZ Nasal Spray
• Immunosuppression : Patients who are on immunosuppressant doses of corticosteroids should be warned to avoid exposure to chickenpox or measles and, if exposed, to consult their physician without delay. Patients should be informed of potential worsening of existing tuberculosis, fungal, bacterial, viral or parasitic infections, or ocular herpes simplex
• Use Daily for Best Effect : Patients should use Floresp AZ Nasal Spray on a regular basis for optimal effect.
• Keep Spray Out of Eyes : Patients should be informed to avoid spraying Floresp AZ Nasal Spray in their eyes.
• Potential Drug Interactions : Patients should be advised that coadministration of Floresp AZ Nasal Spray and ritonavir is not recommended and to be cautious if coadministrating with ketoconazole.
• Do not drive, operate machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how Floresp AZ affects you.
• Do not drink alcohol or take other medicines that may cause you to feel sleepy while using Floresp AZ, it may make your sleepiness worse.
• Do not take this medicine, if you are allergic to Fluticasone furoate or Azelastine Hydrochloride.
• If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
• If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
What FLORESP AZ is and what it is used for
What you need to know before you take FLORESP AZ
How to take FLORESP AZ
Possible side effects
How to store FLORESP AZ
Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Floresp Az is and What It is Used for
FLORESP AZ Nasal Spray contains two active substances: azelastine hydrochloride and fluticasone furoate.
Azelastine hydrochloride belongs to a group of medicines called antihistamines. Antihistamines work by preventing the effects of substances such as histamine that the body produces as part of an allergic reaction – thus reducing symptoms of allergic rhinitis.
Fluticasone furoate belongs to a group of medicines called glucocorticoids. Fluticasone furoate works to decrease inflammation caused by allergy (rhinitis) and therefore reduce symptoms of allergy.
FLORESP AZ nasal spray is used to treat symptoms of allergic rhinitis including stuffy, runny or itchy nose, sneezing and watery, itchy or red eyes, in adults and adolescents aged 12 years and over.
Allergy symptoms can occur at specific times of the year and be caused by allergy to pollen from grass or trees (hayfever), or they can occur all year round and be caused by allergy to animals, house-dust mites or moulds to name some of the most common.
2. What You Need to Know Before You Take Floresp Az
Do not use FLORESP AZ
- If you are allergic to fluticasone furoate, Azelastine hydrochloride or any of the other ingredients of this medicine
Warnings and precautions
Children and adolescents
Do not use in children under 12 years old.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before using FLORESP AZ Nasal Spray if:
- You had a recent operation on your nose.
- You have an infection in your nose. Infections of the nasal airways should be treated with antibacterial or antifungal medication. If you are given medication for an infection in your nose you can continue to use FLORESP AZ Nasal Spray to treat your allergies.
- You have tuberculosis or an untreated infection.
- You have a change in vision or a history of increased ocular pressure, glaucoma and/or cataracts. If this applies to you, you will be closely monitored whilst using FLORESP AZ Nasal Spray.
- You suffer from impaired adrenal function. Care must be taken when transferring from systemic steroid treatment to FLORESP AZ Nasal Spray.
- You suffer from a severe liver disease. Your risk of suffering from systemic side effects is increased.
In these cases, your doctor will decide whether you can use FLORESP AZ Nasal Spray.
It is important that you take your dose as stated in section 3 below or as advised by your doctor. Treatment with higher than recommended doses of nasal corticosteroids may result in adrenal suppression, a condition that may produce weight loss, fatigue, muscle weakness, low blood sugar, salt cravings, joint pains, depression and darkening of the skin. If this happens your doctor may recommend another medicine during periods of stress or elective surgery.
To avoid adrenal suppression your doctor will advise you to take the lowest dose at which effective control of your symptoms of rhinitis is maintained.
Taking nasal corticosteroids may when have taken for a long time cause children and adolescents to grow more slowly. The doctor will check your child’s height regularly, and make sure he or she is taking the lowest possible effective dose.
Contact your doctor if you experience blurred vision or other visual disturbances.
If you are unsure whether the above applies to you, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before using FLORESP AZ Nasal Spray.
Other medicines and FLORESP AZ
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, or have recently taken, or might take any other medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription.
It is especially important to tell your doctor if you are taking, or have recently taken any of the following medicines:
steroid tablets or injected steroids
steroid creams
medicines for asthma
ritonavir or cobicistat, used to treat HIV
ketoconazole, used to treat fungal infections
Your doctor will assess whether you should take FLORESP AZ with these medicines. Your doctor may wish to monitor you carefully if you are taking any of these medicines as they may increase the side effects of FLORESP AZ.
FLORESP AZ should not be used at the same time with other nasal sprays containing steroids.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine.
Do not use FLORESP AZ if you are pregnant, or planning to become pregnant, unless your doctor or pharmacist tells you to.
Do not use FLORESP AZ if you are breast feeding unless your doctor or pharmacist tells you to.
Driving and using machines
FLORESP AZ Nasal Spray has minor influence on the ability to drive and use machines. Very rarely, you may experience fatigue or dizziness due to the disease itself or when using FLORESP AZ Nasal Spray. In these cases, do not drive or operate machinery. Please be aware that drinking alcohol may enhance these effects.
FLORESP AZ contains benzalkonium chloride
This medicine contains benzalkonium chloride. Benzalkonium chloride may cause irritation or swelling inside of the nose, especially if used for a long time. Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you feel discomfort when using the spray.
3. How to Use Floresp Az
Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Don’t exceed the recommended dose. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you’re not sure.
Adults and adolescents (12 years and over)
One spray/nostril twice daily. The recommended dosage should not be exceeded.
It is essential to use FLORESP AZ Nasal Spray regularly to gain the full therapeutic benefit.
How to use the nasal spray
Be careful not to get any spray into your eyes. If you do, rinse your eyes with water.
There is a step-by-step guide to using the nasal spray after Section 6 of this leaflet. Follow the guide carefully to get full benefit from using FLORESP AZ.
If you take more FLORESP AZ than you should
talk to a doctor or pharmacist immediately
If you forget to take FLORESP AZ
If you miss a dose, take it when you remember.
If it is nearly the time for your next dose, wait until then. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, or if you have any discomfort using the nasal spray ask your doctor or pharmacist or nurse.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Allergic reactions: get a doctor’s help straight away
Allergic reactions to FLORESP AZ are rare and affect less than 1 person in 1,000. In a small number of people, allergic reactions can develop into a more serious, even life-threatening problem if not treated. Symptoms include:
- becoming very wheezy, coughing or having difficulty with breathing
- suddenly feeling weak or light-headed (which may lead to collapse or loss of consciousness)
- swelling around the face
- skin rashes or redness.
In many cases, these symptoms will be signs of less serious side effects. But you must be aware that they are potentially serious — so, if you notice any of these symptoms: Contact a doctor as soon as possible.
Azelastine Hydrochloride
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
An unpleasant taste in your mouth especially if you tilt your head backwards when you are using the nasal spray. In rare cases the unpleasant taste might cause you to feel sick.
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
Slight irritation of the inside of the nose (stinging, itching), sneezing and epitaxis.
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
Hypersensitivity reactions (such as rash, pruritus, urticaria).
fluticasone furoate
Very common side effects (may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- Nosebleeds (generally minor), particularly if you use FLORESP AZ for more than 6 weeks continuously.
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Nasal ulceration – which may cause irritation or discomfort in your nose. You may also get streaks of blood when you blow your nose.
- Headache.
- Shortness of breath
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Pain, burning, irritation, soreness or dryness in the inside of the nose.
Very rare side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- Small holes (perforations) in the ridge inside the nose that separates the nostrils.
Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- Slowing of growth in children.
- Blurred vision or temporary changes to vision with long term use.
- Chest tightness causing difficulty in breathing.
Nasal corticosteroids can affect the normal production of hormones in your body, particularly if you use high doses for a long time. In children this side effect can cause them to grow more slowly than others.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top right end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to Store Floresp Az
Store below 25°C. Protected from light. Do not freeze.
Keep out of reach of children.
SHAKE WELL BEFORE EACH USE.
FOR NASAL USE ONLY.
6. Contents of the Pack and Other Information
What FLORESP AZ contains
Each spray delivers:
Azelastine Hydrochloride IP 140 mcg
Fluticasone Furoate 27.5 mcg
Composition:
Fluticasone Furoate 0.02% w/v
Azelastine Hydrochloride IP 0.10% w/v
Benzalkonium Chloride IP 0.02% w/v (As preservative)
DIRECTIONS FOR USE
Following are directions for the use of FLORESP AZ nasal spray.
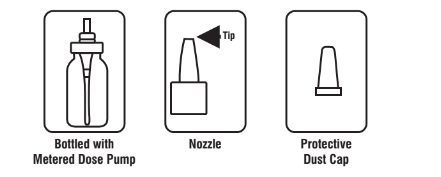
PARTS OF THE NASAL SPRAY
USING YOUR NASAL SPRAY
STEP 1
Blow your nose gently
STEP 2
Shake the bottle gently and then remove the protective dust cap. Hold the bottle as shown with your forefinger and middle finger on either side of the nozzle and your thumb underneath the bottle.
STEP 3
If using for the first time or if you have not used it for a week or more, test the spray. Testing the spray: With the nozzle pointing away from you, press down a few times as shown until a fine mist comes out of the nozzle.
STEP 4
Close one nostril and hold the bottle as shown in step 2. Tilt your head forward slightly and keeping the bottle upright, carefully insert the tip of the nozzle in the other nostril.
STEP 5
Start to breathe in through your nose and white breathing in, press down with your fingers once to release a spray.
STEP 6
Breathe out through your mouth. Repeat steps 5 and 6 to inhale a second spray.
STEP 7
Repeat steps 4,5 and 6 for the other nostril.
STEP 8
Wipe the nozzle with a clean handkerchief/tissue and replace the protective dust cap.

CLEANING YOUR NASAL SPRAY
Pull the nozzle upwards to detach form the bottle.
Soak the nozzle and the dust cap in warm water for few minutes.
Rinse the nozzle and the dust cap under clean running water.
Shake off excess water and allow nozzle and cap to dry at room temperature before refitting onto the bottle.
© Zuventus Healthcare Ltd., 2020. All rights reserved.