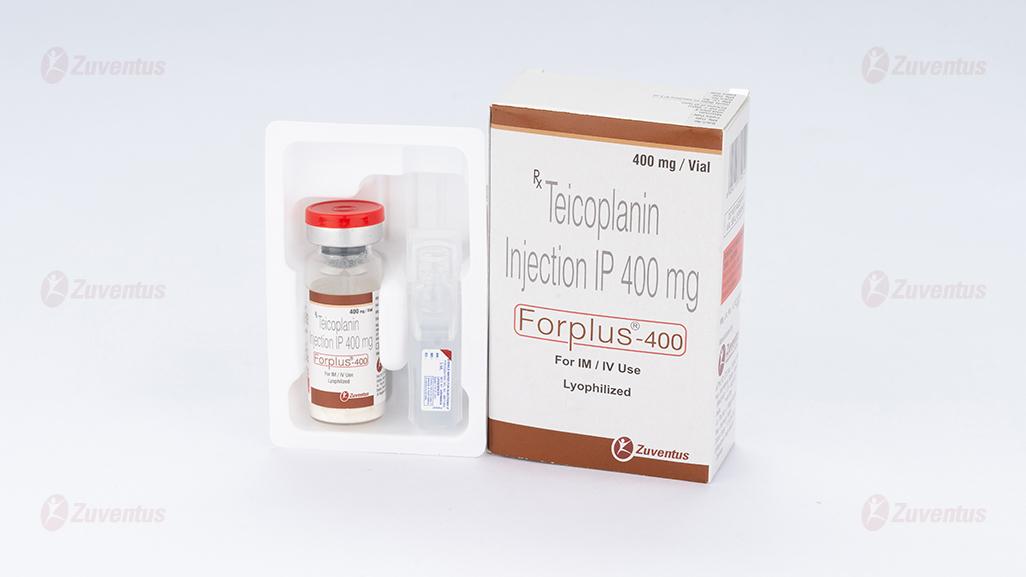
Forplus 400 Injection
Therapy Area
Anti Infective
1.0 Generic Name
Teicoplanin for Injection IP 400 mg
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
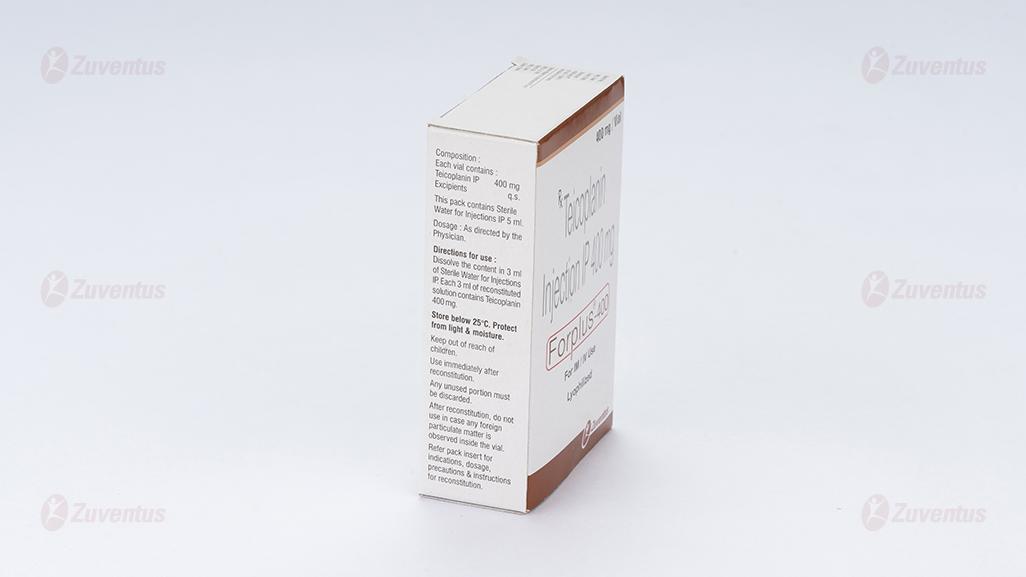
Each Combi - pack contains:
- Teicoplanin Injection IP 400 mg
- Each vial contains: Teicoplanin IP……… 400 mg
- Excipients…………… q.s.
- Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Lyophilized Powder for solution for injection/infusion 400 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1. Therapeutic indication
Glycopeptide antibiotic-use in serious gram +ve infection, staphylococcal infection in patients sensitive or unresponsive to penicillin and cephalosporins CAPD related peritonitis, prophylaxis in orthopaedic surgery at risk of gram +ve infections.
4.2. Posology and method of administration
Posology
The dose and duration of treatment should be adjusted according to the underlying type and severity of infection and clinical response of the patient, and patient factors such as age and renal function.
Adults and elderly patients with normal renal function


1 Measured by FPIA- Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay
Duration of treatment
The duration of treatment should be decided based on the clinical response. For infective endocarditis a minimum of 21 days is usually considered appropriate. Treatment should not exceed 4 months.
Combination therapy
Teicoplanin has a limited spectrum of antibacterial activity (Gram positive). It is not suitable for use as a single agent for the treatment of some types of infections unless the pathogen is already documented and known to be susceptible or there is a high suspicion that the most likely pathogen(s) would be suitable for treatment with teicoplanin.
Clostridium difficile infection-associated diarrhoea and colitis
The recommended dose is 100-200 mg administered orally twice a day for 7 to 14 days.
Elderly population
No dose adjustment is required, unless there is renal impairment.
Adults and elderly patients with impaired renal function
Dose adjustment is not required until the fourth day of treatment, at which time dosing should be adjusted to maintain a serum trough concentration of at least 10 mg/L.
After the fourth day of treatment:
- In mild and moderate renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance 30-80 mL/min) : maintenance dose should be halved, either by administering the dose every two days or by administering half of this dose once a day.
- In severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min) and in haemodialysed patients: dose should be one-third the usual dose, either by administering the initial unit dose every third day or by administering one-third of this dose once a day. Teicoplanin is not removed by haemodialysis.
Patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD)
After a single intravenous loading dose of 6 mg/kg bodyweight, 20 mg/L is administered in the bag of the dialysis solution in the first week, 20 mg/L in different bags the second week and then 20 mg/L in the overnight bag in the third week.
Paediatric population
The dose recommendations are the same in adults and children above 12 years of age.
Neonates and infants up to the age of 2 months
Loading dose
One single dose of 16 mg/kg body weight, administered intravenously by infusion on the first day.
Maintenance dose
One single dose of 8 mg/kg body weight administered intravenously by infusion once a day
Children (2 months to 12 years)
Loading dose: One single dose of 10 mg/kg body weight administered intravenously every 12 hours, repeated 3 times.
Maintenance dose: One single dose of 6-10 mg/kg body weight administered intravenously once a day
METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION
Teicoplanin should be administered by the intravenous or intramuscular route. The intravenous injection may be administered either as a bolus over 3 to 5 minutes or as a 30-minute infusion. Only the infusion method should be used in neonates.
Preparation of Injection:
The powder should be reconstituted strictly in accordance with the instructions below. Errors in reconstitution may result in the formation of a stable foam and delivery of smaller doses.
The entire contents of the accompanying diluent water ampoule should be added slowly down the side wall of the vial of Forplus-400. The vial should be rolled gently between the palms until the powder is completely dissolved, taking care to avoid foam formation. DO NOT SHAKE. If the solution does become foamy, allow to stand for 15 minutes for the foam to subside. Withdraw the entire contents from the vial slowly into a syringe, trying to recover most of the solution by placing the needle in the central part of the stopper.
The reconstituted solution contains :
For a 400 mg vial : 400 mg/3.0 ml of Teicoplanin.
The reconstituted solution may be injected directly, or alternatively diluted with any of the following diluents.
- 0.9% Sodium Chloride Solution
- Compound Sodium Lactate Solution
- 5% Dextrose Solution
- 0.18% Sodium Chloride & 4% Dextrose Solution
In keeping with good clinical pharmaceutical practice reconstituted vials of Forplus-400 should be used immediately and any unused portion discarded. In case if not used immediately, the reconstituted solution should be kept at 2°C to 8°C and used within 24 hours.
Solutions kept longer than 24 hours should be discarded
4.3. Contraindications
Teicoplanin is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug.
4.4. Special warnings and precautions for use
Teicoplanin should not be administered by intraventricular use.
Hypersensitivity reactions
Serious, life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, sometimes fatal, have been reported with teicoplanin (e.g. anaphylactic shock). If an allergic reaction to teicoplanin occurs, treatment should be discontinued immediately and appropriate emergency measures should be initiated. Teicoplanin must be administered with caution in patients with known hypersensitivity to vancomycin, as crossed hypersensitivity reactions, including fatal anaphylactic shock, may occur. However, a prior history of "red man syndrome" with vancomycin is not a contraindication to the use of teicoplanin.
Infusion related reactions
In rare cases (even at the first dose), red man syndrome (a complex of symptoms including pruritus, urticaria, erythema, angioneurotic oedema, tachycardia, hypotension, dyspnoea) has been observed. Stopping or slowing the infusion may result in cessation of these reactions. Infusion related reactions can be limited if the daily dose is not given via bolus injection but infused over a 30-minute period.
Severe bullous reactions
Life-threatening or even fatal cutaneous reactions Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) have been reported with the use of teicoplanin. If symptoms or signs of SJS or TEN (e.g. progressive skin rash often with blisters or mucosal lesions) are present teicoplanin treatment should be discontinued immediately.
Spectrum of antibacterial activity
Teicoplanin has a limited spectrum of antibacterial activity (Gram-positive). It is not suitable for use as a single agent for the treatment of some types of infections unless the pathogen is already documented and known to be susceptible or there is a high suspicion that the most likely pathogen(s) would be suitable for treatment with teicoplanin. The rational use of teicoplanin should take into account the bacterial spectrum of activity, the safety profile and the suitability of standard antibacterial therapy to treat the individual patient. On this basis it is expected that in most instances teicoplanin will be used to treat severe infections in patients for whom standard antibacterial activity is considered to be unsuitable.
Loading dose regimen
Since data on safety are limited, patients should be carefully monitored for adverse reactions when teicoplanin doses of 12 mg/kg body weight twice a day are administered. Under this regimen blood creatinine values should be monitored in addition to the recommended periodic haematological examination. Teicoplanin should not be administered by intraventricular use.
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia has been reported with teicoplanin. Periodic haematological examinations are recommended during treatment, including complete blood cell count.
Nephrotoxicity
Renal failure has been reported in patients treated with teicoplanin. Patients with renal insufficiency, and/or in those receiving teicoplanin in conjunction with or sequentially with other medicinal products with known nephrotoxic potential (aminoglycosides, colistin, amphotericin B, ciclosporin, and cisplatin) should be carefully monitored, and should include auditory tests. Since teicoplanin is mainly excreted by the kidney, the dose of teicoplanin must be adapted in patients with renal impairment.
Ototoxicity
As with other glycopeptides, ototoxicity (deafness and tinnitus) has been reported in patients treated with teicoplanin. Patients who develop signs and symptoms of impaired hearing or disorders of the inner ear during treatment with teicoplanin should be carefully evaluated and monitored, especially in case of prolonged treatment and in patients with renal insufficiency. Patients receiving teicoplanin in conjunction with or sequentially with other medicinal products with known neurotoxic/ototoxic potential (aminoglycosides, ciclosporin, cisplatin, furosemide and ethacrynic acid) should be carefully monitored and the benefit of teicoplanin evaluated if hearing deteriorates. Special precautions must be taken when administering teicoplanin in patients who require concomitant treatment with ototoxic and/or nephrotoxic medicinal products for which it is recommended that regular haematology, liver and kidney function tests are carried out.
Superinfection
As with other antibiotics, the use of teicoplanin, especially if prolonged, may result in overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
4.5. Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
No specific interaction studies have been performed.
Teicoplanin and aminoglycoside solutions are incompatible and must not be mixed for injection; however, they are compatible in dialysis fluid and may be freely used in the treatment of CAPD-related peritonitis. Teicoplanin should be used with care in conjunction with or sequentially with other medicinal products with known nephrotoxic or ototoxic potential. These include aminoglycosides, colistin, amphotericin B, ciclosporin, cisplatin, furosemide, and ethacrynic acid. However, there is no evidence of synergistic toxicity in combinations with teicoplanin. In clinical studies, teicoplanin has been administered to many patients already receiving various medications including other antibiotics, antihypertensives, anaesthetic agents, cardiac medicinal products and antidiabetic agents without evidence of adverse interaction.
Paediatric population- Interaction studies have only been performed in adults.
4.6. Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy
There are a limited amount of data from the use of teicoplanin in pregnant women. Studies in animals have shown reproductive toxicity at high doses. In rats there was an increased incidence of stillbirths and neonatal mortality. The potential risk for humans is unknown. Therefore, teicoplanin should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary. A potential risk of inner ear and renal damage to the foetus cannot be excluded.
Breast-feeding
It is unknown whether teicoplanin is excreted in human milk. There is no information on the excretion of teicoplanin in animal milk. A decision on whether to continue/discontinue breast-feeding or to continue/discontinue therapy with teicoplanin should be made taking into account the benefit of breast-feeding to the child and the benefit of teicoplanin therapy to the mother.
Fertility
Animal reproduction studies have not shown evidence of impairment of fertility.
4.7. Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Teicoplanin has minor influence on the ability to drive and use machines. Teicoplanin can cause dizziness and headache. The ability to drive or use machines may be affected. Patients experiencing these undesirable effects should not drive or use machines.
4.8. Undesirable effects
In the table below all the adverse reactions, which occurred at an incidence greater than placebo and more than one patient are listed using the following convention : Very common (≥1/10); common (≥1/100 to <1/10); uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100); rare (≥1/10,000 to < 1/1000); very rare (<1/10,000), not known (cannot be estimated from the available data). Within each frequency grouping, undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness. Adverse reactions should be monitored when teicoplanin doses of 12 mg/kg body weight twice a day are administered
|
System organ class
|
common (≥1/100 to <1/10); |
uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100); |
rare (≥1/10,000 to < 1/1000); |
not known (cannot be estimated from the available data).
|
|
Infections & infestations
|
|
|
Abcess |
Superinfection (overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms) |
|
Blood & the lymphatic system disorders
|
|
Leucopenia, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia |
|
Agranulocytosis, neutropenia |
|
Immune system disorders
|
|
Anaphylactic reaction (anaphylaxis) |
|
Anaphylactic shock |
|
Nervous system disorders
|
|
Dizziness, headache |
|
Seizures |
|
Ear & Labyrinth disorders
|
|
Deafness, hearing loss, tinnitus, vestibular disorder |
|
|
|
Vascular disorders
|
|
Phlebitis |
|
Thrombophlebitis
|
|
Respiratory, thoracic & mediastinal disorders
|
|
Bronchospasm |
|
|
|
Gastro-intestinal disorders
|
|
Diarrhoea, vomiting, nausea |
|
|
|
Skin & subcutaneous tissue disorders
|
Rash, Erythema, Pruritus |
|
Red man syndrome (e.g. Flushing of the upper part of the body) |
Toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, angioedema, dermatitis exfoliativa, urticaria |
|
Renal & Urinary disorders
|
Pain, Pyrexia |
Raised blood creatinine
|
|
Renal failure
|
|
General disorders & administration site conditions
|
|
|
|
Injection site abcess, chills and rigors |
|
Investigations
|
|
Transaminases increased (transient abnormality of transaminases), blood alkaline phosphatase increased (transient abnormality of alkaline phosphatase), blood creatinine increased (transient rise of serum creatinine)
|
|
|
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9. Overdose Symptoms
Cases of accidental administration of excessive doses to paediatric patients have been reported. In one case agitation occurred in a 29-day-old newborn who had been administered 400 mg intravenously (95 mg/kg). Management Treatment of teicoplanin overdose should be symptomatic. Teicoplanin is not removed by haemodialysis and only slowly by peritoneal dialysis.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Glycopeptide Antibacterials, ATC code : J01XA 02
Mechanism of action
Teicoplanin inhibits the growth of susceptible organisms by interfering with cell-wall biosynthesis at a site different from that affected by beta-lactams. Peptidoglycan synthesis is blocked by specific binding to D-alanyl-D-alanine residues.
Mechanism of resistance
Resistance to teicoplanin can be based on the following mechanisms:
- Modified target structure: This form of resistance has occurred particularly in Enterococcus faecium. The modification is based on exchange of the terminal D-alanine- D-alanine function of the amino-acid chain in a murein precursor with D-Ala-D-lactate, thus reducing the affinity to vancomycin. The responsible enzymes are a newly synthesised D-lactate dehydrogenase or ligase.
- The reduced sensitivity or resistance of staphylococci to teicoplanin is based on the overproduction of murein precursors to which teicoplanin is bound. Cross-resistance between teicoplanin and the glycoprotein vancomycin may occur. A number of vancomycinresistant enterococci are sensitive to teicoplanin (Van-B phenotype).
Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic relationship
Teicoplanin antimicrobial activity depends essentially on the duration of time during which the substance level is higher than the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the pathogen.
Susceptibility
The prevalence of resistance may vary geographically and over time for selected species and local information on resistance is desirable, particularly when treating severe infections. As necessary, expert advice should be sought when the local prevalence of resistance is such that the utility of the agent in at least some types of infections is questionable.
|
Commonly susceptible species Aerobic Gram-positive bacteria Corynebacterium jeikeiuma Enterococcus faecalis Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant strains) Streptococcus agalactiaea Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilisa (Group C & G streptococci) Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus pyogenesa b Streptococci in the viridans group Anaerobic Gram-positive bacteria Clostridium difficilea Peptostreptococcus spp.a |
|
Species for which acquired resistance may be a problem Aerobic Gram-positive bacteria Enterococcus faecium Staphylococcus epidermidis Staphylococcus haemolyticus Staphylococcus hominis |
|
Inherently resistant bacteria All Gram-negative bacteria Other bacteria Chlamydia spp. Chlamydophila spp. Legionella pneumophila Mycoplasma spp |
a No current data were available when the tables were published. The primary literature, standard volumes and treatment recommendations assume sensitivity.
b Collective term for a heterogeneous group of streptococcus species. Resistance rate can vary depending on the actual streptococcus species.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Teicoplanin is administered by parenteral route (intravenously or intramuscularly). After intramuscular administration, the bioavailability of teicoplanin (as compared to intravenous administration) is almost complete (90%). After six daily intramuscular administrations of 200 mg the mean (SD) maximum teicoplanin concentration (Cmax) amounts to 12.1 (0.9) mg/L and occurs at 2 hours after administration. After a loading dose of 6 mg/kg administered intravenously every 12 hours for 3 to 5 administrations, Cmax values range from 60 to 70 mg/L and C are usually above 10 mg/L. After an intravenous loading dose of 12 mg/kg administered every 12 hours for trough 3 administrations, mean values of Cmax and C are estimated to be around 100 mg/L and 20 mg/L, respectively. After a maintenance dose of 6 mg/kg administered once daily Cmax and C values are approximately 70 mg/L and 15 mg/L, trough respectively. After a maintenance dose of 12 mg/kg once daily Ctrough values range from 18 to 30 mg/L.
Distribution
The binding to human serum proteins ranges from 87.6 to 90.8% without any variation in function of the Teicoplanin concentrations. Teicoplanin is mainly bound to human serum albumin. Teicoplanin is not distributed in red cells. The volume of distribution at steady-state (Vss) varies from 0.7 to 1.4 mL/kg. The highest values of Vss are observed in the recent studies where the sampling period was superior to 8 days. Teicoplanin distributed mainly in lung, myocardium and bone tissues with tissue/serum ratios superior to 1. In blister fluids, synovial fluid and peritoneal fluid the tissue/serum ratios ranged from 0.5 to 1.
Elimination of Teicoplanin from peritoneal fluid occurs at the same rate as from serum. In pleural fluid and subcutaneous fat tissue the tissue/serum ratios are comprised between 0.2 and 0.5. Teicoplanin does not readily penetrate into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Biotransformation
Unchanged form of Teicoplanin is the main compound identified in plasma and urine, indicating minimal metabolism. Two metabolites are formed probably by hydroxylation and represents 2 to 3% of the administered dose.
Elimination
Unchanged Teicoplanin is mainly excreted by urinary route (80% within 16 days) while 2.7% of the administered dose is recovered in feces (via bile excretion) within 8 days following administration. Elimination half-life of Teicoplanin varies from 100 to 170 hours in the most recent studies where blood sampling duration is about 8 to 35 days. Teicoplanin has a low total clearance in the range of 10 to 14 mL/h/kg and a renal clearance in the range of 8 to 12 mL/h/kg indicating that Teicoplanin is mainly excreted by renal mechanisms.
Linearity
Teicoplanin exhibited linear pharmacokinetics at dose range of 2 to 25 mg/kg.
Special populations
- Renal impairment: As teicoplanin is eliminated by renal route, Teicoplanin elimination decreases according to the degree of renal impairment. The total and renal clearances of Teicoplanin depends on the creatinine clearance.
- Elderly patients: In the elderly population the Teicoplanin pharmacokinetics is not modified unless in case of renal impairment.
- Paediatric population: A higher total clearance (15.8 mL/h/kg for neonates, 14.8 mL/h/kg for a mean age 8 years) and a shorter elimination half-life (40 hours neonates; 58 hours for 8 years) are observed compared to adult patients.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
Following repeated parenteral administration to the rat and dog, effects on the kidney were observed and were shown to be dose-dependent and reversible. Studies to investigate the potential to cause ototoxicity in the guinea-pig indicate that a mild impairment of cochlear and vestibular function is possible, in the absence of morphological damage.
Subcutaneous administration of teicoplanin at up to 40 mg/kg/day did not affect male and female fertility in the rat. In embryofetal development studies, no malformations were observed following subcutaneous administration of up to 200 mg/kg/day in the rat and intramuscular administration up to 15 mg/kg/day in the rabbit. However, in the rat, there was an increased incidence of stillbirths at doses of 100 mg/kg/day and above and neonatal mortality at 200 mg/kg/day. This effect was not reported at 50 mg/kg/day. A peri and postnatal study in rats showed no effects on the fertility of the F1 generation or on the survival and development of the F2 generation following subcutaneous administration of up to 40 mg/kg/day.
Teicoplanin did not show any potential to cause antigenicity (in mice, guinea-pigs or rabbits), genotoxicity or local irritancy
7.0 Description
Teicoplanin is a novel bactericidal, glycopeptide antibiotic, produced by fermentation of Actinoplanes teichomyceticus. It acts by inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis in the cell wall of gram positive bacteria.

IUPAC Name : Ristomycin A 34-O-[2-(acetylamino)-2-deoxy-beta-Dglucopyranosyl]-22, 31-dichloro-7-demethyl-64-O-demethyl-19-deoxy-56-O-[2- deoxy-2-[(8-methyl-1-oxononyl) amino]-beta-D-glucopyranosyl]-42-O-alpha-Dmannopyranosyl
Molecular Formula : C77H77N9O31Cl2·R
Molecular Weight : 1709.39
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
- Incompatibilities Teicoplanin and aminoglycoside are incompatible when mixed directly and must not be mixed before injection. If teicoplanin is administered in combination therapy with other antibiotics, the preparation must be administered separately. This medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products except those mentioned in method of administration section.
- Shelf-life Refer on the pack.
- Packaging information A vial of 400 mg with SWFI IP 5 ml.
- Storage and handing instructions Store below 25°C. Protect from light & moisture. Keep out of reach of children. It is advisable to use reconstituted vial of Forplus-400 immediately. After reconstitution, do not use in case any foreign particulate matter is observed inside the vial.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
- Finish the prescribed course of Forplus®-400, even if you start to feel better. Stopping it early may cause the infection to return and become more difficult to treat. It is given by an injection or drip into a vein or into a muscle.
- Lactation It is unknown whether teicoplanin is excreted in human milk. There is no information on the excretion of teicoplanin in animal milk. A decision on whether to continue/discontinue breast-feeding or to continue/discontinue therapy with teicoplanin should be made taking into account the benefit of breast-feeding to the child and the benefit of teicoplanin therapy to the mother.
- Diarrhea Advise patients, their families, or caregivers that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterial drugs, including Forplus®-400. Sometimes, frequent watery or bloody diarrhea may occur and may be a sign of a more serious intestinal infection. If severe watery or bloody diarrhea develops, advise patients to contact his or her healthcare provider.
- Development of Resistance Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including Forplus®-400 should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When Forplus®-400 is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Forplus®-400 or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
12.0 Date of revision
1st June 2024
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine because it contains important information for you.
1. Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
2. If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
3. If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1. What For Plus-400 is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you are given For Plus-400
3. How to use For Plus-400
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store For Plus-400
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What For Plus-400 is and what it is used for
Forplus-400 is an antibiotic. It contains a medicine called ‘teicoplanin’. It works by killing the bacteria that cause infections in your body. Forplus-400 is used in adults and children (including newborn babies) to treat bacterial infections of: the skin and underneath the skin - sometimes called ‘soft tissue’ the bones and joints the lung the urinary tract the heart - sometimes called ‘endocarditis’ the abdominal wall - peritonitis the blood, when caused by any of the conditions listed above
2. What you need to know before you are given For Plus-400
Do not use For Plus-400 if:
you are allergic to teicoplanin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine .
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before you are given For Plus-400 if:
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before you are given For Plus-400 if:
- you are allergic to an antibiotic called ‘vancomycin’
- you have had a flushing of your upper part of your body (red man syndrome)
- you have a decrease in platelet count (thrombocytopenia)
- you have kidney problems
- you are taking other medicines which may cause hearing problems and/or kidney problems. You may have regular tests to check if your kidneys and/or liver are working properly.
- If any of the above apply to you (or you are not sure), talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before you are given For Plus-400.
Tests
During treatment you may have tests to check your blood, your kidneys and/or your hearing. This is more likely if:
- your treatment will last for a long time
- you have a kidney problem
- you are taking or may take other medicines that may affect your nervous system, kidneys or hearing.
In people who are given For Plus-400 for a long time, bacteria that are not affected by the antibiotic may grow more than normal - your doctor will check for this.
Other medicines and For Plus-400
Tell your doctor, pharmacist or nurse if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines. This is because For Plus-400 can affect the way some other medicines work. Also, some medicines can affect the way For Plus-400 works. In particular, tell your doctor, pharmacist or nurse if you are taking the following medicines:
- Aminoglycosides as they must not be mixed together with For Plus-400 in the same injection. They may also cause hearing problems and/or kidney problems.
- amphotericin B - a medicine that treats fungal infections which may cause hearing problems and/or kidney problems
- cyclosporin - a medicine that affects the immune system which may cause hearing problems and/or kidney problems
- cisplatin - a medicine that treats malignant tumours which may cause hearing problems and/or kidney problems
- water tablets (such as furosemide) - also called ‘diuretics’ which may cause hearing problems and/or kidney problems.
If any of the above apply to you, (or you are not sure), talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before being given For Plus-400.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant, think that you might be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse for advice before being given this medicine. They will decide whether or not you are given this medicine while you are pregnant. There may be a potential risk of inner ear and kidney problems. Tell your doctor if you are breast-feeding, before being given this medicine. He/she will decide whether or not you can keep breast-feeding, while you are given For Plus-400.
Studies in animal reproduction have not shown evidence of fertility problems.
Driving and using machines
You may have headaches or feel dizzy while being treated with For Plus-400. If this happens, do not drive or use any tools or machines.
3. How to use For Plus-400
The recommended dose is
Adults and children (12 years and over) with no kidney problems Skin and soft tissue, lung and urinary tract infections
- Starting dose (for the first three doses): 6 mg for every kilogram of body weight, given every 12 hours, by injection into a vein or muscle
- Maintenance dose: 6 mg for every kilogram of body weight, given once a day, by injection into a vein or muscle
Bone and joint infections, and heart infections
- Starting dose (for the first three to five doses): 12 mg for every kilogram of body weight, given every 12 hours, by injection into a vein
- Maintenance dose: 12 mg for every kilogram of body weight, given once a day, by injection into a vein or muscle
Infection caused by ‘Clostridium difficile’ bacteria
The recommended dose is 100 to 200 mg by mouth, twice a day for 7 to 14 days.
Adults and elderly patients with kidney problems
If you have kidney problems, your dose will usually need to be lowered after the fourth day of treatment:
- For people with mild and moderate kidney problems - the maintenance dose will be given every two days, or half of the maintenance dose will be given once a day.
- For people with severe kidney problems or on haemodialysis - the maintenance dose will be given every three days, or one-third of the maintenance dose will be given once a day.
Peritonitis for patients on peritoneal dialysis
The starting dose is 6 mg for every kilogram of body weight, as a single injection into a vein, followed by:
- Week one: 20 mg/L in each dialysis bag
- Week two: 20 mg/L in every other dialysis bag
- Week three: 20 mg/L in the overnight dialysis bag.
Babies (from birth to the age of 2 months)
- Starting dose (on the first day): 16 mg for every kilogram of body weight, as an infusion through a drip into a vein.
- Maintenance dose: 8 mg for every kilogram of body weight, given once a day, as an infusion through a drip into a vein.
Children (from 2 months to 12 years)
- Starting dose (for the first three doses): 10 mg for every kilogram of body weight, given every 12 hours, by injection into a vein.
- Maintenance dose: 6 to 10 mg for every kilogram of body weight, given once a day, by injection into a vein.
How For Plus-400 is given
The medicine will normally be given to you by a doctor or nurse.
It will be given by injection into a vein (intravenous use) or muscle (intramuscular use).
It can also be given as an infusion through a drip into a vein.
Only the infusion should be given in babies from birth to the age of 2 months.
If you have more Four Plus-400 than you should
It is unlikely that your doctor or nurse will give you too much medicine. However, if you think you have been given too much For Plus-400 or if you are agitated, talk to your doctor or nurse straight away.
If you forget to have For Plus-400
Your doctor or nurse will have instructions about when to give you For Plus-400. It is unlikely that they will not give you the medicine as prescribed. However, if you are worried, talk to your doctor or nurse.
If you stop having For Plus-400
Do not stop having this medicine without first talking to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Serious side effects
Stop your treatment and tell your doctor or nurse straight away, if you notice any of the following serious side effects - you may need urgent medical treatment:
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- sudden life-threatening allergic reaction - the signs may include: difficulty in breathing or wheezing, swelling, rash, itching, fever, chills
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people)
- flushing of the upper body
Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- blistering of the skin, mouth, eyes or genitals - these may be signs of something called ‘toxic epidermal necrolysis’ or ‘Stevens-Johnson syndrome’ or ‘drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS)’. DRESS appears initially as flu-like symptoms and a rash on the face then an extended rash with a high temperature, increased levels of liver enzymes seen in blood tests and an increase in a type of white blood cell (eosinophilia) and enlarged lymph nodes.
Tell your doctor or nurse straight away, if you notice any of the side effects above. Tell your doctor or nurse straight away, if you notice any of the following serious side effects - you may need urgent medical treatment:
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- swelling and clotting in a vein
- difficulty in breathing or wheezing (bronchospasm)
- getting more infections than usual - these could be signs of a decrease in your blood cell count
Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- lack of white blood cells - the signs may include: fever, severe chills, sore throat or mouth ulcers (agranulocytosis)
- kidney problems or changes in the way your kidneys work - shown in tests
- epileptic fits
Tell your doctor or nurse straight away, if you notice any of the side effects above.
Other side effects
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse if you get any of these:
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Rash, erythema, pruritus
- Pain
- Fever
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- decrease in platelet count.
- raised blood levels of liver enzymes
- raised in blood levels of creatinine (to monitor your kidney)
- hearing loss, ringing in the ears or a feeling that you, or things around you are moving
- feeling or being sick (vomiting), diarrhoea
- feeling dizzy or headache
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- infection (abscess).
Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- problems where the injection was given - such as reddening of the skin, pain or swelling
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top right end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effects with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store For Plus-400
Store at a cool place. Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and label of the vial. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month. This medicine does not require any special storage conditions. Information about storage and the time to use For Plus-400, after it has been reconstituted and is ready to use, are described in the ‘Prescribing information for healthcare professionals.’
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What For Plus-400 contains
- The active substance is teicoplanin. Each vial contains 400 mg teicoplanin.
What For Plus-400 looks like and contents of the pack
Forplus-400 is a powder solution for injection/infusion or oral solution. The powder is spongy, ivory and coloured homogeneous mass.
Pack size:
A vial of 400 mg with SWFI IP 5 ml.