Gutclear 100 ml Syrup
Therapy Area
Gastrointestinal
1.0 Generic name
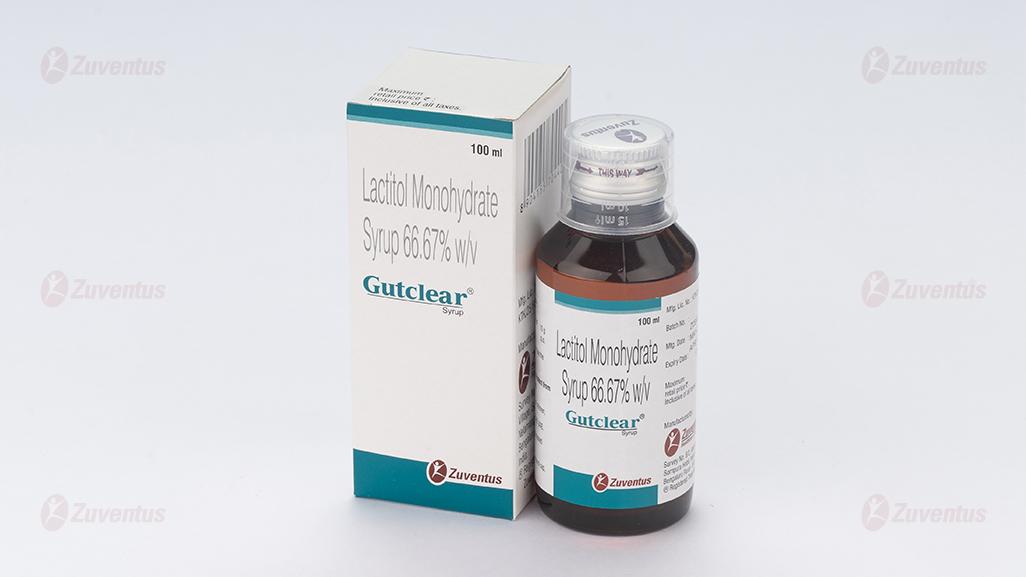
Lactitol Monohydrate Syrup 66.67% w/v
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
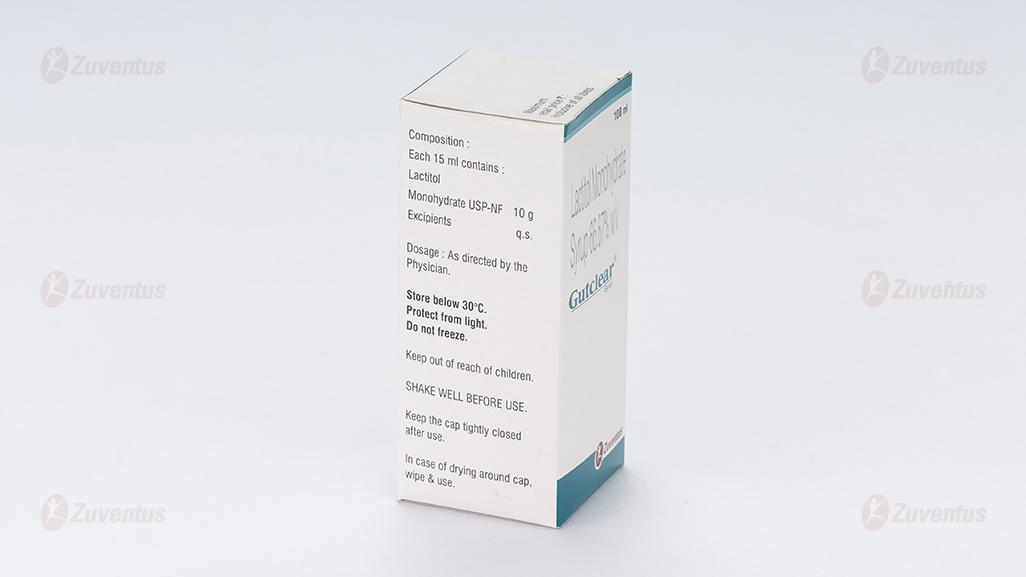
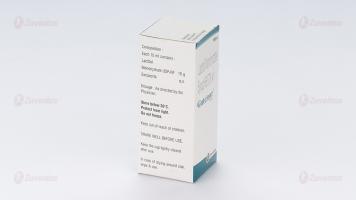
Each 15 ml syrup contains:
Lactitol Monohydrate USP 10 g
Benzoic Acid USP 0.0225 g
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Syrup
10 g/15ml in 100/200 ml bottles
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Gutclear® Syrup is indicated for treatment of chronic constipation and prevention of hepatic encephalopathy.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
In the treatment of constipation, the recommended dose of Gutclear® Syrup is as follows
Adults:
The recommended adult dosage of Gutclear® Syrup is 30 ml (20 grams) orally once daily, preferably with meals.
Reduce the dosage to 15 ml (10 grams) once daily for persistent loose stools.
Pediatrics: 250-400 mg/kg/day
Gutclear® Syrup is given as a single dose with the morning or evening meal, subsequently adjusted to produce one stool daily.
In the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy, Gutclear® Syrup is given in usual oral doses of 500 to 700 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses at meal times. The dose is subsequently adjusted to produce 2 soft stools daily.
Administration Instructions
Doses should be mixed with food or liquid, and it is recommended to drink 1 to 2 glasses of liquid with the meal.
Administer other oral medications at least 2 hours before or 2 hours after Gutclear® Syrup.
4.3 Contraindications
Gutclear® Syrup is contraindicated in:
- Patients with the undiagnosed abdominal pain, colic, bleeding or vomiting
- Patients with intestinal obstruction, ileostomy, colostomy, appendicitis or diverticulitis
- Patients with galactosemia
- Patients hypersensitive to the drug or any other component of the formulation
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
- It is suggested that individuals taking Gutclear® Syrup have their fluid and salt (electrolyte) balance monitored regularly especially in elderly patients on long term treatment.
- Treatment with Gutclear® Syrup may cause accumulation of hydrogen in the bowel; patient should be advised to have a thorough bowel cleansing with a non-fermentable solution.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Reduced Absorption of Other Oral Medications Gutclear® Syrup may reduce the absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. Administer oral medications at least 2 hours before or 2 hours after Gutclear® Syrup [see Dosage and Administration] Gutclear® Syrup should not be administered with other laxatives.
Caution may be exercised in using Gutclear® Syrup with drugs causing potassium loss like loop diuretics.
Gutclear® Syrup can increase digitalis toxicity.
Reduction in acidification effect can be observed if broad spectrum antibacterial agents or antacids are administered along with Gutclear® Syrup.
4.6 Pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy
Lactitol is minimally absorbed systemically following oral administration, and it is unknown whether maternal use will result in fetal exposure to the drug. Available data from case reports on lactitol use in pregnant women are insufficient to evaluate for any drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal developmental studies, no effects on embryo-fetal development were observed with oral administration of lactitol to rats and rabbits during organogenesis at doses much higher than the maximum recommended human dosage. The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the United States general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Gutclear® Syrup should be prescribed only if the potential benefits outweigh the risks to the fetus.
Animal Data
Reproduction studies have been performed in pregnant rats at oral doses of lactitol up to 2 g/kg/day (about 0.93 times the recommended daily human dose based on body surface area) and in pregnant rabbits at oral doses up to 1 g/kg/day (about 0.93 times the recommended daily human dose based on body surface area) administered during the period of organogenesis. These studies did not reveal any evidence of harm to the fetus due to lactitol.
In a pre-and postnatal development study in rats, lactitol, administered from gestation day 6 to lactation day 20, did not cause any adverse effect on pre and postnatal development up to 2 g/kg/day (about 0.93 times the recommended daily human dose based on body surface area).
Lactation
There are no data on the presence of lactitol in human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Lactitol is minimally absorbed systemically following oral administration. It is unknown whether the minimal systemic absorption of lactitol by adults will result in a clinically relevant exposure to breastfed infants. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Gutclear® Syrup and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Gutclear® Syrup or from the underlying maternal condition.
No studies are available on the secretion of lactitol in breast milk.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Lactulose has no or negligible influence on your ability to drive safely or use machines.
Undesirable effects
The most commonly observed adverse effects with Gutclear® Syrup are abdominal cramps, distensionor flatulence during the first 10 days of treatment which are likely to disappear after continued administration. The other less frequent side effects are abdominal pain, diarrhoea, nausea and vomiting, anal pruritus, borborygmii or steatorrhea.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
- Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
- Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.8 Overdose
No data on overdosage of Lactitol is available. If a patient consumes large amount of Lactitol, symptoms of abdominal pain and diarrhea may appear. There may also be electrolyte imbalance. There is no specific antidote known for Lactitol over dosage. Gastric lavage may be instituted at the earliest to remove the remnant drug from the stomach. Patient should be treated symptomatically and electrolyte levels should be monitored periodically.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Mechanism of action
Once ingested, Lactitol is neither hydrolysed nor absorbed in the small intestine. It is passed undigested to the colon and a substantial proportion of orally ingested lactitol becomes substrate for the resident colonic microflora where it is slowly fermented and is converted into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). The liberation of short-chain fatty acids causes a fall in pH of the right colon. The fall in pH results in the formation of an acidic media.
The reduction in intra-luminal pH increases the intra-luminal osmolality. This promotes retention of water within the bowel lumen, softening the stool and increasing the bowel volume. Hydration of the gut content and reduction in intra-luminal pH also results in shorter transit time and the establishment of laxation.
Lactitol decreases blood ammonia concentration by inhibiting both the production and the absorption of ammonia by reducing intestinal pH and shortening the residence time of intestinal contents in the intestinal tract and hence improves hepatic encephalopathy. Lactitol also favors the growth of saccharolytic (healthy) bacteria in the gut.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic Properties
Following a single oral dose of 20-gram Lactitol in healthy adult subjects under fed conditions, the mean ± SD peak serum concentration (Cmax) is 776 ± 253 ng/mL, and the mean ± SD area under the curve (AUC) is 6,019 ± 1,771 ng*hr/mL.
Absorption
Lactitol is minimally absorbed systemically following oral administration. The mean ± SD time to reach peak serum concentration (Tmax) is 3.6 ± 1.2 hours following a single oral dose of 20-gram Lactitol in healthy adult subjects under fed conditions.
Effect of Food
Cmax and AUC values increase greater than 2-fold under fasted conditions compared to fed conditions.
Elimination
The mean half-life of lactitol is 2.4 hours.
Excretion
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Preclinical safety data
A perinatal and postnatal study of lactitol, a hepatic encephalopathy drug was conducted in Sprague-Dawley rats. Female rats were given lactitol orally at dose levels of 0 (control), 0.7, 2.65 and 10 g/kg from day 17 of pregnancy to day 21 after delivery. All pregnant rats per level were allowed to deliver naturally for postnatal examination of their offspring. The high dose caused diarrhea or soft stool in dams. The high dose suppressed the body weight of dams during the perinatal period. The food consumption of dams decreased in the intermediate and high dose groups. The water consumption of dams increased in the high dose group. The high dose caused enlargement of cecum and increase of weights of cecum in dams. The drug failed to affect the delivery of dams and gestation index. However, high dose caused prolongation of gestation period. Two dams in the high dose group failed to nurse their all newborns during early lactation. The drug did not affect the number of live newborns, birth index, external appearance, body weight, viability index, weaning index, and sex ratio of weanlings. Nor did lactitol have any adverse effect on the postnatal development of the first (F1) generation offspring, such as differentiation, emotionality, motor ability, learning ability or reproductive performance. Nor did lactitol have any adverse effect on the second (F2) generation offspring. The results show that the no-effect dose levels of lactitol are 0.7 g/kg for general toxicity in mother animals, 2.65 g/kg for reproductive function in mother animals, and 10 g/kg for their offspring.
7.0 Description
Lactitol is an osmotic laxative for oral use. Lactitol is a simple monosaccharide sugar alcohol. It is a dry, free flowing, white to off-white powder, readily soluble in aqueous solutions. As shown by the structure diagrams, it is an analog of the disaccharide lactulose. Its chemical name is 4-O-β-dGalactopyranosyl-d-glucitol lactitol.

Molecular Formula C12H24O11
Molecular Weight 344.31
Gutclear® Syrup ® (lactitol) for oral solution is available in multi-dose bottles.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 List of excipients
Benzoic Acid and Purified water
8.2 Incompatibilities
Gutclear® Syrup may reduce the absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. Administer oral medications at least 2 hours before or 2 hours after Gutclear® Syrup
8.3 Shelf life
36 months
8.4 Special precautions for storage
Store below 30°C. Protect from light. Do not freeze
8.5 Nature and contents of container
100 ml or 200 ml filled in amber colour pet bottle of 200 ml with a silver pp cap with ep wad and 15 ml measuring cup. One such pack is placed along with a leaflet in a carton.
8.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
Persistent Loose Stools Advise patients to stop Gutclear® Syrup ® Syrup and contact their healthcare provider if they experience persistent loose stools.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
Always take this medicine exactly as described in this leaflet or as your doctor, pharmacist or nurse has told you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- Ask your pharmacist if you need more information or advice.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
- You must talk to a doctor if you do not feel better or if you feel worse.
What is in this leaflet:
- What Gutclear® Syrup is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you take Gutclear® Syrup ® Syrup
- How to take Gutclear® Syrup
- Possible side effects
- How to store Gutclear® Syrup
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Gutclear® Syrup is and What It is Used for
The name of this medicine is Gutclear® Syrup, which contains lactitol. It is a laxative for the treatment of chronic constipation and prevention of hepatic encephalopathy in adults, adolescents and elderly. Lactitol exerts an osmotic effect, causing the influx of water into the small intestine leading to a laxative effect in the colon.
Lactitol promotes retention of water within the bowel lumen, softening the stool and increasing the bowel volume. Hydration of the gut content and reduction in intra-luminal pH also results in shorter transit time and the establishment of laxation.
Lactitol decreases blood ammonia concentration by inhibiting both the production and the absorption of ammonia by reducing intestinal pH and shortening the residence time of intestinal contents in the intestinal tract and hence improves hepatic encephalopathy.
2. What You Need to Know Before You Take Gutclear® Syrup
Do not take Gutclear® Syrup if your doctor has told you that you have:
- Patients with the undiagnosed abdominal pain, colic, bleeding or vomiting.
- Patients with intestinal obstruction, ileostomy, colostomy, appendicitis or diverticulitis.
- Patients with galactosemia (disease which impairs the body's ability to process and produce energy from a sugar called galactose)
- Patients hypersensitive to the drug or any other component of the formulation.
Warnings and Precautions
- It is suggested that individuals taking Gutclear® Syrup have their fluid and salt (electrolyte) balance monitored regularly especially in elderly patients on long term treatment.
- Treatment with Gutclear® Syrup may cause accumulation of hydrogen in the bowel; patient should be advised to have a thorough bowel cleansing with a non-fermentable solution.
Other medicines and Gutclear® Syrup
Gutclear® Syrup should not be administered with other laxatives. Caution may be exercised in using Gutclear® Syrup with drugs causing potassium loss like loop diuretics. Gutclear® Syrup can increase digitalis toxicity. Reduction in acidification effect can be observed if broad spectrum antibacterial agents or antacids are administered along with Gutclear® Syrup.
Pregnancy
Gutclear® Syrup should be prescribed only if the potential benefits outweigh the risks to the fetus.
Lactation
No studies are available on the secretion of Gutclear® Syrup in breast milk. There are no data on the presence of lactitol in human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production.
Driving and using machines
Gutclear® Syrup does not affect your ability to drive or use machines.
3. How to Take Gutclear® Syrup
Always take Lactulose exactly as described in this leaflet or as your doctor or pharmacists have told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
Taking this medicine
- Take Gutclear® Syrup from measuring cup.
- You can mix it with fruit juice or water. It is recommended that you drink plenty of fluids (approximately 6-8 glasses throughout the day).
- Swallow the dose immediately. Do not keep it in your mouth as the sugar content may lead to tooth decay, particularly if the syrup is taken for long periods.
- The syrup takes 2 to 3 days to start working.
- After this time, you may be able to reduce the dose you take according to your needs.
Constipation
Adults and adolescents: The starting dose is 30 ml. After this the dose can be adjusted to 15-30ml.
Use in Children: Use of laxatives in children, infants, and babies should be exceptional and under medical supervision because it can influence the normal reflexes for passing stools. Please do not give the syrup to children (under 14 years) before consulting your doctor for prescription and careful supervision.
Gutclear® Syrup is given as a single dose with the morning or evening meal, subsequently adjusted to produce one stool daily.
Hepatic encephalopathy
Adults: The usual starting dose 30-45 ml in 3 to 4 times a day.
Use in Children: No information is available for treatment of children (new-born to 18 years of age) with hepatic encephalopathy.
Use in elderly patients and patients with renal or hepatic insufficiency: No special dosage recommendations exist.
The dose is subsequently adjusted to produce 2 soft stools daily. Doses should be mixed with food or liquid, and it is recommended to drink 1 to 2 glasses of liquid with the meal.
If you take more Gutclear® Syrup than you should
You may develop excessive diarrhoea, which can lead to dehydration. If this occurs, stop taking Gutclear® Syrup and drink plenty of fluids. If you are worried contact your doctor or pharmacist.
If you forget to take Gutclear® Syrup
Take the dose as soon as you remember to take it.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The most commonly observed adverse effects with Gutclear® Syrup are abdominal cramps, distension or flatulence during the first 10 days of treatment which may likely to disappear after continued administration. The other less frequent side effects in abdominal pain, loose motions, nausea and vomiting, anal itching.
Tell your doctor immediately and stop taking Gutclear® Syrup if you:
Get a serious allergic reaction which causes difficulty in breathing, or swelling of the face, lips, tongue or throat.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Drug Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to Store Gutclear® Syrup
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use Gutclear® Syrup after the expiry date which is stated on the carton. Store below 30°C. Protect from light. Do not freeze.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the Pack and Other Information
What Gutclear® Syrup contains
Each 15 ml contains Lactitol Monohydrate 10 g and Benzoic Acid is 0.0225 g
Gutclear® Syrup is available in 100 or 200ml bottles.