Lafaxid-D Tablets
Therapy Area
Gastrointestinal
1.0 Name of the medicinal product
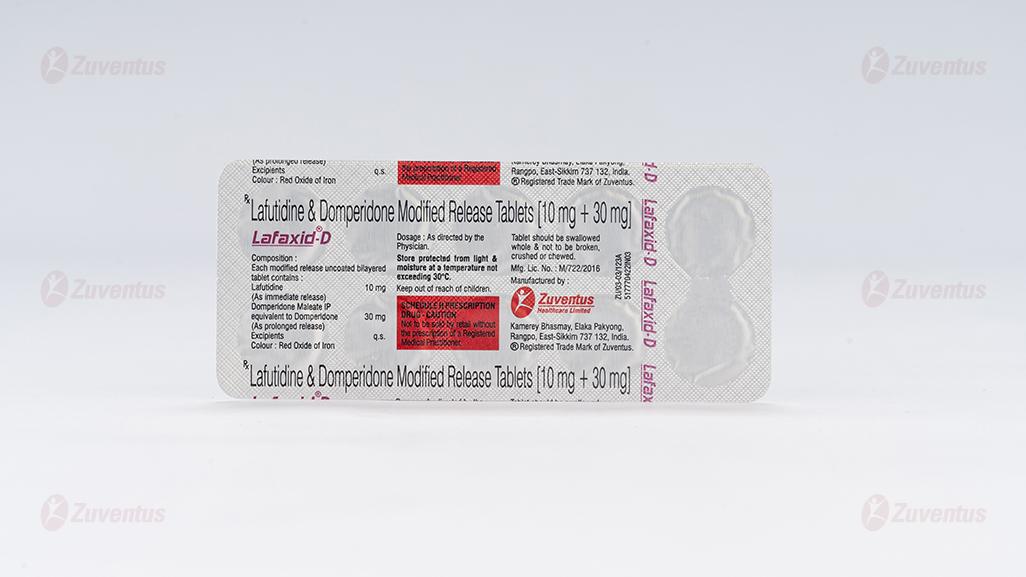
Lafutidine & Domperidone Modified Release Tablets
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
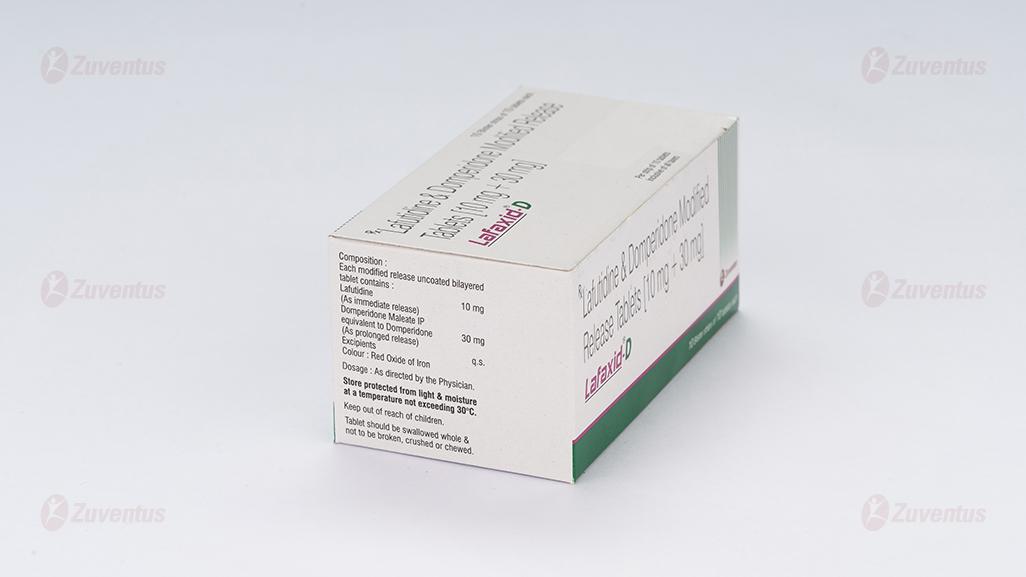
Each modified release uncoated bilayered tablet contains:
Lafutidine (as immediate release) ………………………………… 10 mg
Domperidone Maleate IP
equivalent to Domperidone (as prolonged release) ………………. 30 mg
Excipients q.s.
3.0 Pharmaceutical form & Strength
Tablet Lafutidine & Domperidone (10 mg + 30 mg)
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1Therapeutic indications
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Peptic ulcer
4.2 Posology and method of administration
One tablet once or twice daily.
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
- Prolactin-releasing pituitary tumour (prolactinoma).
- Domperidone should not be used when stimulation of gastric motility could be harmful: gastro-intestinal haemorrhage, mechanical obstruction or perforation.
- In patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment.
- In patients who have known existing prolongation of cardiac conduction intervals, particularly QTc, patients with significant electrolyte disturbances or underlying cardiac disease such as congestive heart failure.
- Co-administration with QT-prolonging drugs.
- Co-administration with potent CYP3A4 inhibitors (regardless of their QT prolonging effects).
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Domperidone
Renal impairment
The elimination half-life of Domperidone is prolonged in severe renal impairment. For repeated administration, the dosing frequency of Domperidone should be reduced to once or twice daily depending on the severity of the impairment. The dose may also need to be reduced. Such patients on prolonged therapy should be reviewed regularly.
Cardiovascular effects
Domperidone has been associated with prolongation of the QT interval on the electrocardiogram.
Epidemiological studies showed that Domperidone was associated with an increased risk of serious ventricular arrhythmias or sudden cardiac death. A higher risk was observed in patients older than 60 years, patients taking daily doses greater than 30 mg, and patients concurrently taking QT-prolonging drugs or CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Treatment with Domperidone should be stopped if signs or symptoms occur that may be associated with cardiac arrhythmia, and the patients should consult their physician. Domperidone should be used at the lowest effective dose in adults and children.
Co-administration of levodopa
Although no dosage adjustment of levodopa is deemed necessary, an increase of plasma levodopa concentration (max 30 - 40%) has been observed when Domperidone was taken concomitantly with levodopa.
Lafutidine
- Careful observation should be made for any changes in hematological, hepatic or renal parameters, and for changes in other factors.
- Since treatment with this product may mask the symptoms of gastric cancer, administration should be made after confirming the tumor is not malignant.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Domperidone
The main metabolic pathway of Domperidone is through CYP3A4. In vitro data suggest that the concomitant use of drugs that significantly inhibit this enzyme may result in increased plasma levels of Domperidone. Separate in vivo pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic interaction studies with oral Ketoconazole or oral Erythromycin in healthy subjects confirmed a marked inhibition of Domperidone's CYP3A4 mediated first pass metabolism by these drugs.
Increased risk of occurrence of QT-interval prolongation, due to pharmacodynamic and/or pharmacokinetic interactions. Concomitant use of the following substances is contraindicated
- Anti-arrhythmics class IA (e.g. Disopyramide, Hydroquinidine, Quinidine)
- Anti-arrhythmics class III (e.g. Amiodarone, Dofetilide, Dronedarone, Ibutilide, Sotalol)
- Certain antipsychotics (e.g. Haloperidol, Pimozide, Sertindole)
- Certain antidepressants (e.g. Citalopram, Escitalopram)
- Certain antibiotics (e.g. Erythromycin, Levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, Spiramycin)
- Certain antifungal agents (e.g. Pentamidine)
- Certain antimalarial agents (in particular Halofantrine, Lumefantrine)
- Certain gastro-intestinal medicines (e.g. Cisapride, Dolasetron, Prucalopride)
- Certain antihistaminics (e.g. Mequitazine, Mizolastine)
- Certain medicines used in cancer (e.g. Toremifene, Vandetanib, Vincamine)
- Certain other medicines (e.g. Bepridil, Diphemanil, Methadone)
- Potent CYP3A4 inhibitors (regardless of their QT prolonging effects), i.e. protease inhibitors
- Systemic azole antifungals
- Some macrolides (Erythromycin, Clarithromycin and Telithromycin)
Concomitant use of the following substances is not recommended
Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors i.e. Diltiazem, Verapamil and some macrolides.
Concomitant use of the following substances requires caution in use
Caution with bradycardia and hypokalaemia-inducing drugs, as well as with the following macrolides involved in QT-interval prolongation: Azithromycin and Roxithromycin (Clarithromycin is contra-indicated as it is a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor).
Levodopa: Increase of plasma levels of levodopa (max 30 - 40%).
The above list of substances is representative and not exhaustive.
Opioids may antagonise the effects of Domperidone on gastric emptying.
Lafutidine
Not known
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
Lafaxid D tablet can be given if benefit to the mother outweighs the risk to the fetus.
Lactation
Not recommended.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Lafaxid-D Tablet may decrease alertness, affect your vision or make you feel sleepy and dizzy. Do not drive if these symptoms occur.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Domperidone
Lafutidine
Constipation, diarrhea, drug rash, nausea or vomiting and dizziness are the adverse reactions observed during clinical trials. Other adverse effects of unknown frequency include abnormal changes in liver function tests, elevation of serum uric acid levels and hypersensitivity reactions (itching, redness of the skin, skin rash).
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorization of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product.
Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Symptoms
Overdose has been reported primarily in infants and children. Symptoms of overdosage may include agitation, altered consciousness, convulsion, disorientation, somnolence and extrapyramidal reactions.
Treatment
There is no specific antidote but in the event of overdose, standard symptomatic treatment should be given immediately. Gastric lavage as well as the administration of activated charcoal, may be useful within 2 hours of overdosage. ECG monitoring should be undertaken, because of the possibility of QT prolongation. Close medical supervision and supportive therapy is recommended. Anticholinergic, anti-parkinson drugs may be helpful in controlling extrapyramidal reactions.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action/ Pharmacodynamic properties
Lafutidine
Lafutidine inhibits acid secretion via histamine H2-receptor blockade. It also possesses a cytoprotective efficacy, which comprises mucin biosynthesis, stimulation of gastric blood flow and promotion of epithelial restitution of damaged mucosa, mediated through capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons and endogenous calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP). It increases the endothelial production of prostacyclin, which inhibits neutrophil activation and reduces inflammation. It also affects gastrointestinal functions by regulating gastrointestinal motility closely relate to changes in the plasma levels of somatostatin, CGRP and secretin.
Domperidone
Domperidone is a dopamine-antagonist with anti-emetic properties. Domperidone does not readily cross the blood-brain barrier. In domperidone users, especially in adults, extrapyramidal side effects are very rare, but domperidone promotes the release of prolactin from the pituitary. Its anti-emetic effect may be due to a combination of peripheral (gastrokinetic) effects and antagonism of dopamine receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone, which lies outside the blood-brain barrier in the area postrema. Animal studies, together with the low concentrations found in the brain, indicate a predominantly peripheral effect of domperidone on dopamine receptors.
Studies in man have shown oral domperidone to increase lower oesophageal pressure, improve antroduodenal motility and accelerate gastric emptying. There is no effect on gastric secretion.
In accordance with ICH-E14 guidelines, a thorough QT study was performed. This study included a placebo, an active comparator and a positive control and was conducted in healthy subjects with up to 80mg per day, 10 or 20mg administered 4 times a day of domperidone. This study found a maximal difference of QTc between domperidone and placebo in LS- means in the change from baseline of 3.4 msec for 20mg domperidone administered 4 times a day on Day 4. The 2-sided 90% CI (1.0 to 5.9 msec) did not exceed 10msec. No clinically relevant QTc effects were observed in this study when domperidone was administered at up to 80mg/day (i.e., more than twice the maximum recommended dosing).
However, two previous drug-drug interaction studies showed some evidence of QTc prolongation when domperidone was administered as monotherapy (10mg 4 times a day). The largest time-matched mean difference of QTcF between domperidone and placebo was 5.4msec (95 % Cl: -1.7 to 12.4) and 7.5msec (95% Cl: 0.6 to 14.4), respectively.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic Properties
Lafutidine
When 10mg of lafutidine is orally administered to normal adult males in fasting conditions, peak plasma concentration of 265.15±49.84 ng/ml is achieved at 0.95±0.24 hours. Lafutidine is metabolized primarily in the liver. In vitro studies showed that lafutidine is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4 and partially metabolized by CYP2D6. Hydroxylated and sulfonyl lafutidine are the major metabolites. Most of the drug is excreted in bile while approximately 20% of the given dosage is excreted in urine. The plasma half-life is 1.92 ± 0.94 hours.
Among the elderly, there was no difference in pharmacokinetics parameters between those with normal renal function and those with deteriorating renal function. In dialytic patients when administered without hemodialysis, the Cmax, AUC and the T1/2 values were 336±40 ng/ml, 2278±306 ng・hr/mL and 6.71±0.30 hours respectively while those after haemodialysis were 226±36 ng/ml, 853±128 ng・hr/mL and 4.57±0.2 hours respectively.
Domperidone
Absorption Domperidone is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with peak plasma concentrations occurring at approximately 1 hr after dosing. The Cmax and AUC values of domperidone increased proportionally with dose in the 10mg to 20mg dose range. A 2-to-3-fold accumulation of domperidone AUC was observed with repeated four times daily (every 5 hr) dosing of domperidone for 4 days.
The low absolute bioavailability of oral domperidone (approximately 15%) is due to an extensive first-pass metabolism in the gut wall and liver. Although domperidone's bioavailability is enhanced in normal subjects when taken after, a meal, patients with gastro-intestinal complaints should take domperidone 15-30 minutes before a meal. Reduced gastric acidity impairs the absorption of domperidone. Oral bioavailability is decreased by prior concomitant administration of cimetidine and sodium bicarbonate. The time of peak absorption is slightly delayed and the AUC somewhat increased when the oral drug is taken after a meal.
Distribution
Oral domperidone does not appear to accumulate or induce its own metabolism; a peak plasma level after 90 minutes of 21ng/ml after two weeks’ oral administration of 30mg per day was almost the same as that of 18ng/ml after the first dose. Domperidone is 91-93% bound to plasma proteins. Distribution studies with radiolabelled drug in animals have shown wide tissue distribution, but low brain concentration. Small amounts of drug cross the placenta in rats.
Metabolism
Domperidone undergoes rapid and extensive hepatic metabolism by hydroxylation and N- dealkylation. In vitro metabolism experiments with diagnostic inhibitors revealed that CYP3A4 is a major form of cytochrome P-450 involved in the N-dealkylation of domperidone, whereas CYP3A4, CYP1A2 and CYP2E1 are involved in domperidone aromatic hydroxylation.
Excretion
Urinary and faecal excretions amount to 31 and 66% of the oral dose respectively. The proportion of the drug excreted unchanged is small (10% of faecal excretion and approximately 1% of urinary excretion). The plasma half-life after a single oral dose is 7-9 hours in healthy subjects but is prolonged in patients with severe renal insufficiency.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Lafutidine
Inhibition of gastric acid secretion
The inhibitory effect on gastric acid secretion 4 hours after administration of lafutidine in the duodenum with the pylorus ligated, was 0.1 times more potent than that of famotidine and 2.3 times more potent than that of cimetidine (in rats). However, the inhibitory effect of lafutidine in response to various stimulants lasted longer than that of famotidine and cimetidine (in rats and dogs).
H2-receptor antagonistic effect
The antagonistic effects of lafutidine on specific binding of tiotidine to H2-receptor in cerebral cortex membrane of guinea pig was 1.9 times stronger than that of famotidine and 85.5 times stronger than that of cimetidine (in vitro).
Effect on acute gsatric mucosal lesions
Lafutidine showed protective effect on gastric mocosal damage induced by various necroctic substances (ammonia, hydrochloric acid-ethanol, ethanol, hydrochloric acid, hydrochloric acid-taurocholic acid), especially on the damage induced by ammonia (in rats).
Effect on acute / chronic ulcers
Lafutidine not only suppressed the occurrence of acute gastric ulcers (water immersion restraint stress, indomethacin, ligated pylorus aspirin, histamine) and acute duodenal ulcers (mepirizole, diethyldithiocarbamate), but also accelarated the healing and suppressed the recurrence of chronic ulcers (acetic acid ulcers, burning ulcers) (in rats).
Domperidone
Electrophysiological in vitro and in vivo studies indicate an overall moderate risk of domperidone to prolong the QTc interval in humans. In in vitro experiments on isolated cells transfected with hERG and on isolated guinea pig myocytes, exposure ratios ranged between 26-47-fold, based on IC50 values inhibiting currents through IKr ion channels in comparison to the free plasma concentrations in humans after administration of the maximum daily dose of 10mg administered 3 times a day. Safety margins for prolongation of action potential duration in in vitro experiments on isolated cardiac tissues exceeded the free plasma concentrations in humans at maximum daily dose (10 mg administered 3 times a day) by 45- fold. Safety margins in in vitro pro-arrhythmic models (isolated Langendorff perfused heart) exceeded the free plasma concentrations in humans at maximum daily dose (10 mg administered 3 times a day) by 9- up to 45- fold. In in vivo models the no effect levels for QTc prolongation in dogs and induction of arrhythmias in a rabbit model sensitized for torsade de pointes exceeded the free plasma concentrations in humans at maximum daily dose (10mg administered 3 times a day) by more than 22-fold and 435-fold, respectively. In the anaesthetized guinea pig model following slow intravenous infusions, there were no effects on QTc at total plasma concentrations of 45.4 ng/mL, which are 3-fold higher than the total plasma levels in humans at maximum daily dose (10mg administered 3 times a day). The relevance of the latter study for humans following exposure to orally administered domperidone is uncertain. In the presence of inhibition of the metabolism via CYP3A4 free plasma concentrations of domperidone can rise up to 3-fold.
At a high, maternally toxic dose (more than 40 times the recommended human dose) teratogenic effects were seen in the rat. No teratogenicity was observed in mice and rabbits.
7.0 Description
Lafaxid-D Tablet is a combination of two drugs: Lafutidine (H2 receptor antagonist) and Domperidone (a dopamine antagonist). Lafutidine works by blocking histamine H2 receptors located on the stomach lining, thereby reduces gastric acid secretion. Domperidone works by increasing the movements and contractions of stomach muscles.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf Life
Refer on pack
8.3 Packaging Information
8.4 Storage and handing Instructions
9.0 Patient counselling information
- Lafaxid-D Tablet helps relieve acidity and heartburn.
- It is a well-tolerated and safe medicine with very low incidence of side effects.
- It should be taken before meals as per the dose and duration prescribed by your doctor.
- Avoid taking soft drinks, citrus fruits like orange and lemon while taking this medicine. These can irritate the stomach and increase acid secretion.
- It may cause dizziness and sleepiness. Don't drive or do anything that requires mental focus until you know how it affects you.
- Avoid consuming alcohol when taking Lafaxid-D Tablet as it may irritate your stomach and also cause excessive drowsiness.
- Inform your doctor if you get watery diarrhoea, fever, or stomach pain that does not go away.
12.0 Date of revision
16.12.2024
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet
- What Lafaxid D Tablet is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you take Lafaxid D Tablet
- How to take Lafaxid D Tablet
- Possible side effects
- How to store Lafaxid D Tablet
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Lafaxid D Tablet is and what it is used for
Lafaxid D Tablet contains two active substances: Lafutidine and Domperidone. Lafutidine is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist that reduces stomach acid secretion. Domperidone is a dopamine antagonist that increases the movements and contractions of stomach muscles.
Lafaxid D Tablet is used to treat
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Peptic ulcer
2. What you need to know before you take Lafaxid D Tablet
Do not take Lafaxid D Tablet if you:
- Are allergic to Lafutidine, Domperidone, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
- Have a prolactin-releasing pituitary tumour (prolactinoma).
- Have moderate or severe liver impairment.
- Have known existing prolongation of cardiac conduction intervals, particularly QTc.
- Have significant electrolyte disturbances or underlying cardiac disease such as congestive heart failure.
- Are taking QT-prolonging drugs or potent CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Warnings and precautions:
- Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Lafaxid D Tablet if you have kidney problems.
- Domperidone may cause serious heart problems. Stop taking it and consult your doctor if you experience symptoms such as palpitations, fainting, or dizziness.
- This medicine may mask the symptoms of gastric cancer. Ensure that your doctor has ruled out malignancy before starting treatment.
Other medicines and Lafaxid D Tablet: Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines, especially:
- Anti-arrhythmics
- Certain antipsychotics and antidepressants
- Certain antibiotics and antifungal agents
- Certain antimalarial agents
- Certain gastrointestinal medicines
- Certain antihistamines
- Medicines used in cancer treatment
- Potent CYP3A4 inhibitors
Pregnancy
Lafaxid D Tablet should not be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding unless the potential benefit outweighs the risks.
Lactation
Not recommended.
Driving and using machines:
Lafaxid-D Tablet may decrease alertness, affect your vision or make you feel sleepy and dizzy. Do not drive if these symptoms occur.
3. How to take Lafaxid D Tablet
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
Dosage:
The recommended dose is one tablet once or twice daily, before meals.
If you use more Lafaxid D Tablet than you should
Tell your doctor if you accidentally use more than you were told.
If you forget to use Lafaxid D Tablet
If you forget to take at the right time, use it as soon as you remember, then carry on as before. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop using Lafaxid D Tablet
Do not stop your treatment even if you feel better unless told to do so by your doctor.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Common side effects
- Dry mouth
- Diarrhoea
- Rash, pruritus
Uncommon side effects
- Loss of libido
- Anxiety
- Somnolence
- Headache
Rare side effects
- Agitation
- Nervousness
Very rare side effects:
- Convulsion
- Extrapyramidal disorder
- Oculogyric crisis
- Ventricular arrhythmias
- Sudden cardiac death
- QTc prolongation
- Torsade de Pointes
- Urticaria
- Angioedema
- Urinary retention
- Galactorrhoea
- Breast pain
- Breast tenderness
- Gynaecomastia
- Amenorrhoea
- Asthenia
- Liver function test abnormal
- Blood prolactin increased
Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Anaphylactic reaction (including anaphylactic shock)
- Constipation
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness
- Abnormal changes in liver function tests
- Elevation of serum uric acid levels
- Hypersensitivity reactions (itching, redness of the skin, skin rash)
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly:
Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Drug Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page.
Website link: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Lafaxid D Tablet
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and blister after EXP.
The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Store in the original package to protect from moisture.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Lafaxid D Tablet contains:
The active substances are Lafutidine (10 mg) and Domperidone (30 mg).
The other ingredients are listed in the full prescribing information.
This leaflet was last revised on: 16 December 2024