Lobetron 0.5 Tablets
Therapy Area
Anti-diabetic
1.0 Generic name
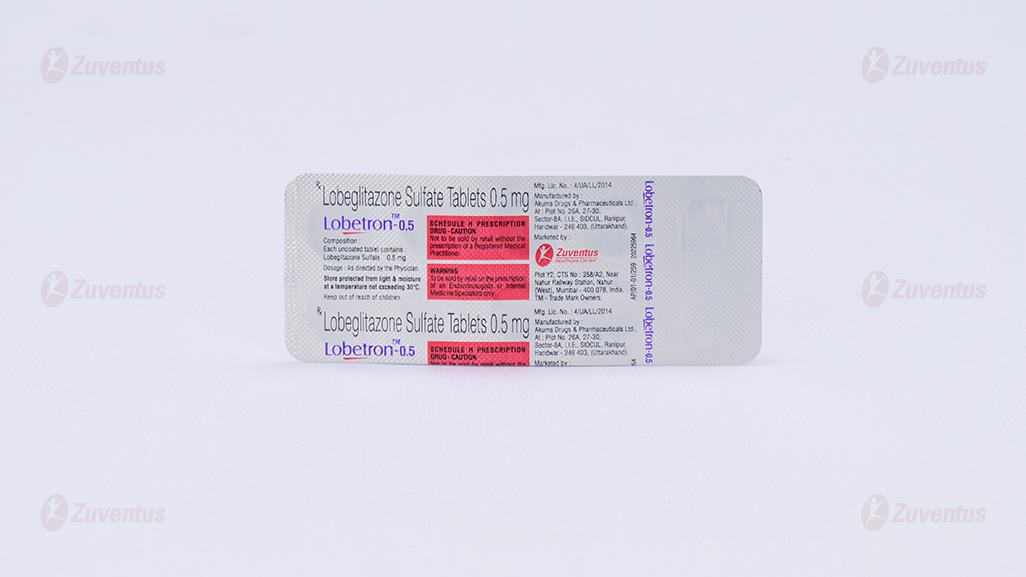
Lobeglitazone Sulfate Tablets 0.5 mg
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
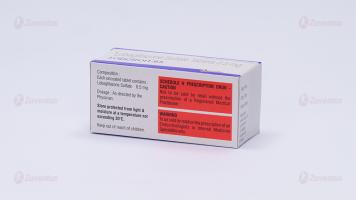
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Lobeglitazone Sulfate 0.5 mg
3.0 Dosage form and Strength
Uncoated Tablet, Lobeglitazone Sulfate 0.5 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
Indicated for treatment of adult type 2 diabetes mellitus patients:
As monotherapy
- Who are inadequately controlled by diet and exercise for whom metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance.
As dual oral therapy in combination with
- Who are inadequately controlled by diet and exercise for whom metformin, despite maximal tolerated dose of metformin monotherapy.
- Who are inadequately controlled by diet and exercise and taking a sulphonyl urea at maximal tolerated dose of sulphonyl urea monotherapy in which metformin is inappropriate because of contraindications or intolerance.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The recommended oral dosage is 1 tablet once daily or as directed by the Physician.
Patients with hepatic impairment
At the beginning of treatment, if the patient shows clinical evidence of active liver disease or increased serum transaminase levels (more than 2.5 times the upper limit of ALT or AST), therapy with this drug should not be initiated.
Liver enzyme monitoring is recommended in all patients before and on a regular basis after starting Lobeglitazone Tablet 0.5 mg therapy.
Patients with renal impairment
Dosage adjustment is not necessary for patients with mild to moderate renal impairment.
Method of administration: For oral use only.
4.3 Contraindications
- known hypersensitivity to Lobeglitazone or its ingredients
- severe heart failure or with a history of heart failure (New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification 1 to 4 heart conditions)
- Liver disorder patients
- Patients with severe renal impairment
- Diabetic ketoacidosis patients, diabetic coma and pre-coma, type 1 diabetes patient
- Before and after surgery, patients with severe infections, patients with severe trauma
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Thiazolidinedione drugs, including Lobeglitazone, may cause or worsen congestive heart failure in some patients and should be administered with the care of a doctor.
After starting treatment with this drug, the patient should be carefully monitored for symptoms and signs of heart failure (including excessive and rapid weight change, dyspnea, and swelling). If these symptoms and signs appear, tests (e.g., echocardiography, chest x- ray, electrocardiogram, related blood tests (NT-proBNP), etc.) are performed to evaluate them. Heart failure should be managed according to current standard treatment regimens, and discontinuation of this drug should be considered.
Patients with severe heart failure (patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class 1 to 4 heart conditions) should not start treatment with this drug. Lobeglitazone Tablet 0.5 mg is not recommended for patients with symptomatic heart failure.
Heart failure and other actions on the heart: Lobeglitazone, like other thiazolidinediones, can cause fluid retention when administered alone or in combination with other antidiabetic drugs such as insulin. Fluid retention can cause or worsen heart failure. Patients should be observed for signs or symptoms of heart failure. When these symptoms and signs appear, heart failure should be managed according to current standard treatment regimens. In addition, discontinuation of this drug should be considered.
Administer carefully to the following patients
- Patients who are administered in combination with other oral hypoglycemic drugs
- Premenopausal women
- Patients with edema
General caution
Diabetes patients should regularly examine vital signs, physical examinations, clinical laboratory tests (blood tests, serum biochemical tests, urine tests), and ophthalmic tests, and closely monitor them.
Edema
In the 24-week monotherapy clinical trial, the incidence of edema was 3.45% in the placebo group and 6.25% in the Lobeglitazone 0.5mg group. In combination therapy clinical trials, it was reported in 1.60% in the 15 mg administration group of pioglitazone and 3.91% in the 0.5 mg Lobeglitazone administration group. Most of the patients with edema were mild to moderate. Thiazolidinediones drugs, including this drug, can cause fluid retention, which can cause or worsen congestive heart failure, so this drug should be administered with caution in patients with congestive heart failure. Patients receiving this drug should be regularly monitored for symptoms and signs of congestive heart failure.
Weight gain
Lobeglitazone tablet has been reported to increase 0.89kg in 24 weeks of monotherapy and 0.92kg in combination therapy clinical trials. The mechanism of weight gain is not clear, but it is speculated that fluid retention and fat accumulation are the cause. Patients with weight gain should be evaluated for fluid accumulation and reactions associated with symptoms such as excessive swelling and congestive heart failure. In addition, since diet control is a way of treating diabetes, it is necessary to educate yourself to strictly adhere to a diet with controlled calories.
Hematology
The average Hemoglobin and Hematocrit levels tended to decrease in patients who received this drug as monotherapy and metformin combination therapy for 24 weeks. The mean reduction was 0.37 g/dl reduction in Hemoglobin monotherapy, 0.54 g/dl reduction in combination therapy, 0.85% reduction in Hematocrit monotherapy, and 1.32% reduction in combination therapy. The white and red blood cells also decreased slightly.
Ovulation
Other thiazolidinediones (thiazolidinediones) have been reported to cause ovulation in some premenopausal women who take this class of drugs. As a result, these patients may have an increased risk of getting pregnant while taking this drug. Therefore, proper contraception should be recommended for premenopausal women. Since clinical trials have not studied this possible action, the frequency of occurrence for this is not known.
Patients with hepatic impairment
Compared with subjects with normal liver function, no significant changes were observed in the pharmacokinetic properties of lobeglitazone and its metabolites in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A/B), Safety and efficacy in patients with hepatic impairment have not been established.
Action on the liver
In patients who received Lobeglitazone tablet as monotherapy for 24 weeks, 2 cases of total ALT increase (1.79%) and 2 cases of AST increase (1.79%), including 1 increase in ALT exceeding the upper limit of normal (0.89%) were reported. Fatty liver was reported in two (1.56%) patients in 24-week combination therapy.
Type 2 diabetes patients may have fatty liver or heart disease with congestive heart failure. Both disorders can cause liver test abnormalities and can lead to other forms of liver disease, many of which can be treated or managed. Therefore, it is recommended to evaluate the patient by obtaining liver test levels (serum ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin) before starting treatment with this drug. In patients with liver test abnormalities, caution should be exercised when starting treatment with Lobeglitazone tablet.
Patients who report symptoms that may indicate liver damage, including fatigue, loss of appetite, discomfort in the right upper abdomen, melanuria or jaundice, perform a liver test quickly. In these clinical situations, if the patient shows abnormal liver test values (ALT or AST that is 2.5 times the upper limit of the normal range), repeat liver function tests within 1 week and if the results are the same, it is necessary to decide whether to discontinue this drug. If you have abnormal liver test levels (ALT, which is more than 3 times the upper limit of the normal range), you should stop treatment with this drug and investigate to determine possible causes. If there is no other cause for abnormal liver examination, these patients should not resume taking this drug. Patients with no other etiology, serum ALT levels greater than 3 times the upper limit of the normal range, and total serum bilirubin levels greater than 2 times the upper limit of normal range should not resume taking this drug as they are at risk of severe drug-induced liver damage. In patients with less elevated serum ALT or bilirubin levels and for other reasons, treatment with this drug may be used with caution.
Macular edema
Macular edema has been reported in diabetic patients receiving thiazolidinedione drugs. Some patients had blurred vision or decreased vision, while others were diagnosed at regular eye exams. Most patients developed peripheral edema when macular edema was diagnosed. Some patients improved symptoms of macular edema after stopping the thiazolidinedione drug. People with diabetes should undergo regular eye examinations by an ophthalmologist according to current standard treatment regimens. Diabetes patients who report any type of visual symptoms should see an ophthalmologist promptly, regardless of the patient's medication or other physical findings.
Fracture
In a long-term clinical trial of other thiazolidinedione drugs, especially female patients, the incidence of fractures was increased. Most of the fractures observed in female patients occurred in the upper and distal lower extremities. Fractures have been reported in both men and women in a post marketing investigation of patients taking other thiazolidinedione-based drugs. No statistically significant difference was observed in change from baseline in the bone mineral density measured by DEXA Scan score between placebo and lobeglitazone treatment over a period of 52 weeks in 170 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. However, during long-term treatment with this drug, the risk of fractures should be considered, and care should be taken to assess and maintain bone health according to current standard treatment regimens.
Macro vascular complications
Clinical trials have not been conducted to determine whether this drug or other diabetes medications reduce the risk of macro vascular complications.
Laboratory tests
Fasting blood glucose (FPG) and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) should be measured on a regular basis to control blood sugar levels and monitor treatment response to this drug. Liver enzyme monitoring is recommended prior to initiating this drug therapy in all patients, after which periodic monitoring is recommended based on the clinical judgment of the physician.
Pediatric population
The safety and efficacy of this drug have not been established in pediatric patients.
Elderly population
In a clinical trial of this drug in patients with type 2 diabetes, 133 of a total of 634 patients for safety analysis were 65 years or older. No significant differences were found in terms of safety between patients over 65 years of age and those under that age. Since physiological functions such as liver and kidney function are generally deteriorated in the elderly, the patient's condition should be observed and this drug should be administered carefully.
Combination use with insulin should be considered with caution in the elderly because of increased risk of serious heart failure. In light of age- related risks (fractures and heart failure), the balance of benefits and risks should be considered carefully both before and during treatment in the elderly.
The application of this drug is effective after sufficient diet and exercise therapy, which are the basics of diabetes treatment, in advance.
4.5 Drugs interactions
This drug did not inhibit the p450 enzyme at clinically relevant doses in the in vitro drug metabolism test, and it was confirmed that it was metabolized by CYP 2C19, 2D6, and 3A4. This drug has been identified as a substrate of CYP2C19, 2D6 enzymes in vitro drug metabolism studies, so that in the presence of CYP2C19 inhibitors such as fluconazole and amiodarone and CYP2D6 inhibitors such as quinidine and paroxetine, blood levels of this drug may be increased.
The results of confirming the interaction of this drug with the following drugs in healthy volunteers are as follows.
Metformin
When 0.5 mg of this drug was administered for 5 days, metformin 1000 mg was administered for 5 days, and the two drugs were administered together for 5 days, the pharmacokinetic properties of the two drugs were randomized and taken sequentially.
Glimepiride
In the results of the drug interaction trial between 0.5 mg and glimepiride 4 mg, this drug did not have a clinically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of glimepiride.
Amlodipine
When 3 mg of amlodipine, a substrate of CYP4A10, one of the main metabolizing enzymes of this drug, and 0.5 mg of this drug were administered alone or in combination, the two drugs did not significantly affect each other's pharmacokinetic properties.
Ketoconazole
As a result of the administration of ketoconazole 3 mg, an inhibitor of CYP4A200, one of the main metabolic enzymes of this drug, alone or in combination with this drug, the geometric mean ratio of Cmax of co-administration for the administration of this drug alone was 1.0227 (90% CI 0.9710 ~ 1.0771), and AUC 0→48h and AUC0→inf were 1.3345 (90% CI 1.2410 ~ 1.4351) and 1.3320 (90% CI 1.2338 ~ 1.4380), respectively, and the metabolic inhibitor ketoconazole increased the degree of exposure of this drug by about 33%.
Warfarin
When 0.5 mg of this drug was administered in combination with 25 mg of warfarin, the two drugs did not affect each other's pharmacokinetic properties.
Sitagliptin
When 0.5 mg of this drug was administered in combination with 100 mg of sitagliptin, the two drugs did not significantly affect each other's pharmacokinetic properties.
Empagliflozin
When 0.5 mg of this drug was co-administered with 25 mg of empagliozin, the two drugs did not affect each other's pharmacokinetic properties.
Dapagliflozin
When 0.5 mg of this drug was administered in combination with 10 mg of dapagliozin, the two drugs did not significantly affect each other's pharmacokinetic properties.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
It is not recommended for use in pregnant women as there are no adequate clinical trial results in pregnant women.
Lactation
It is not known if this drug is secreted in human breast milk. This drug has been reported to be secreted in the milk of rats, so it is not administered to lactating women.
Paediatric patients
The safety and efficacy of this drug have not been established in paediatric patients.
Elderly population
Elderly people generally have reduced physiological functions such as liver and kidney function, so the patient's condition should be observed and administered carefully.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed. However, patients who experience visual disturbance should be cautious when driving or using machines
4.8 Undesirable effects
Table 1 shows the incidence rates and types of adverse reactions reported with a frequency of 1% or more in the group administered with 0.5mg of Lobeglitazone tablet in monotherapy and metformin combination therapy in the 24-week placebo-controlled monotherapy clinical trial and 24-week active drug-controlled metformin combination therapy clinical trial for this drug Table 1. Adverse reactions reported in more than 1% of patients in the placebo- controlled monotherapy clinical trials and active drug-controlled metformin combination therapy clinical trials in the group treated with 0.5mg of Lobeglitazone tablet (regardless of the researcher's causal assessment)
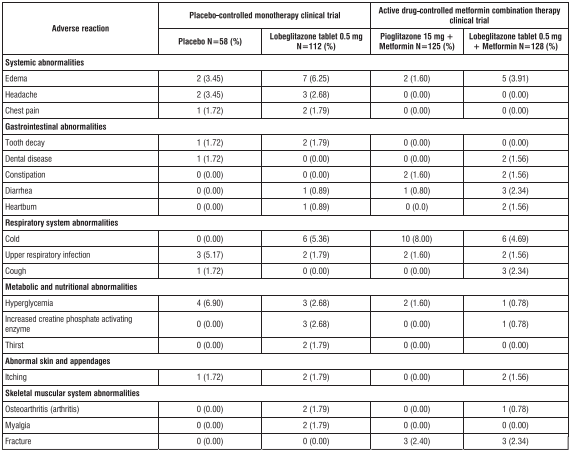
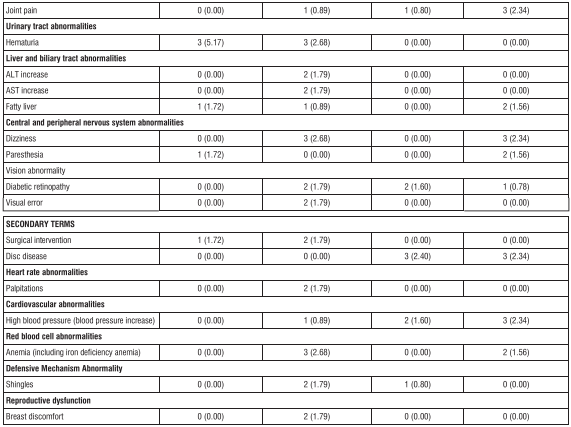
Monotherapy for 52-week extended trial: Among the adverse reactions reported in patients receiving this drug alone for 52 weeks (n=64), regardless of the causal evaluation of the investigator during the extended trial period (24 weeks to 52 weeks), the adverse reactions expressed at a frequency of 2% or more were total reflux esophagitis (2 patients, 3.13%), dental diseases (2 persons, 3.13%), upper respiratory infections (5 persons, 7.81%), dizziness (2 persons, 3.13%), and hyperglycemia (2 persons, 3.13%). Active drug-control metformin combination therapy 52-week extended trial: adverse reactions that occurred in patients who received metformin for 52 weeks in combination with this drug and activity treatment for an extended period (24 weeks to 52 weeks) with an incidence of 2% or more of the reported adverse reactions regardless of the investigator's causal relationship evaluation are shown in Table 2 below.
No clinically significant changes in vital signs or ECG were observed with the administration of Lobeglitazone tablet.
Edema
In the 24-week monotherapy clinical trial, the incidence of edema was 3.45% (2 patients) in the placebo group and 6.25% (7 patients) in the lobeglitazone 0.5mg group, and in the combination therapy clinical trial, 1.60% (2) in the 15mg pioglitazone group Persons), and 3.91% (5 persons) in the group receiving 0.5mg of lobeglitazone. Most of the patients with edema were reported as mild to moderate.
Weight gain
No adverse body weight reactions were reported during the 24-week monotherapy and combination therapy trials. Looking at the overall weight change in the conducted clinical trial, in the 24-week monotherapy clinical trial, the placebo-treated group decreased by about 0.63 kg, and the Lobeglitazone 0.5 mg-administered group increased by about 0.89 kg. In a 24-week combination therapy clinical trial, an increase of about 0.76 kg in the group receiving 15 mg of pioglitazone and about 0.92 kg in the group receiving 0.5 mg of Lobeglitazone was found to increase compared to baseline. In the 24-week combination therapy clinical trial, there was no statistical significance for weight gain between the 15 mg of pioglitazone and the 0.5 mg of Lobeglitazone.
Red blood cells
In the above 24-week monotherapy clinical trial, Lobeglitazone tablet developed anemia in 2 patients (1.79%), iron deficiency anemia in 1 patient (0.89%), and pancytopenia in 1 patient (0.89%). In combination therapy clinical trials, anemia was reported in 2 patients (1.56%). Of these, one patient (0.89%) was evaluated as having a causal relationship with this drug. All erythrocyte-related adverse reactions were mild.
Hypoglycemia
Lobeglitazone tablet did not show hypoglycemia in a 24-week monotherapy trial. In the 24-week combination therapy, it was reported in 1 patient (0.78%) in the Lobeglitazone 0.5mg group and 3 patients (2.4%) in the pioglitazone 15mg group.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Data on overdose in humans are limited. In clinical trials in healthy men, the drug was administered orally up to 7 mg for 4 days and was well tolerated. This drug has been administered in single doses up to 8 mg.
In case of overdose, appropriate adjuvant treatment is given according to the patient's clinical condition. The drug has a high rate of protein binding, so it is not eliminated by hemodialysis.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action/ Pharmacodynamic properties
Lobeglitazone is a thiazolidinedione drug that acts on PPAR (Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma), and does not promote insulin secretion in pancreatic cells, but increases insulin-mediated glucose uptake and metabolism in skeletal muscle.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Single dose and multiple dose pharmacokinetic studies in healthy volunteer demonstrated that lobeglitazone is rapidly and nearly completely absorbed after oral administration reaching peak plasma levels (Tmax) at 1.0 to 3.0 hours It is eliminated mostly by metabolism with negligible urine excretion and has a half-life of 7.8 to 9.8 hours. There was dose proportional increase in plasma concentrations for doses 0.5 mg up to 2 mg. Plasma maximum concentration (Cmax) increase was less than dose proportional for doses more than 2 mg.
Absorption of lobeglitazone may be saturated at doses more than 2 mg. No human studies are available providing data on absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) properties of lobeglitazone. However, ADME information is available from the animal study (Oh ES et al, Clin Ther 2014). In rats, lobeglitazone appeared to be readily absorbed after an oral administration (an absolute bioavailability of ~95%). Following intravenous administration, LB exhibited linear pharmacokinetics in the dose range of 0.5–2 mg/kg. The primary distribution site was the liver but it was also distributed to heart, lungs, and fat tissue. Lobeglitazone, is metabolized primarily by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 isoenzyme. The excretion of LB to the urine, bile, feces, and intestine was insignificant (i.e., <10% of the dose) in rats. Lobeglitazone is highly bound to plasma proteins in-vitro by >99%, mostly albumin. This drug is excreted mainly from the kidney as an unchanged drug.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
(1) Carcinogenicity
As a result of the carcinogenicity test for 2 years, there was no carcinogenicity in mice when administered orally up to 6 mg/kg/day (0.5 times the AUC when administered to humans at 65.2 mg/day). No neoplastic lesions were observed in rat males at 0.24 mg/kg/day (3.25 times higher than clinical AUC), but liposarcoma was observed in subcutaneous and abdominal cavity in females 0.12 mg/kg/day (7.5 times higher than clinical dose AUC). In rat females, the tumor-free dose was 0.06 mg/kg/day (3.72 times the clinical dose).
(2) Genotoxicity
Genotoxicity studies such as return mutation test, chromosomal abnormality test, mouse micronucleus test, etc., did not show mutagenicity.
(3) Repeated administration toxicity
Diffuse hypertrophy of the myocardium was observed in rats administered orally for 26 weeks in males 1 mg/kg/day (13.5 times compared to the clinical dose) and in the female 0.06 mg/kg/day group (3.74 times compared to the clinical dose). At all doses, there was fat deposition around the aorta, brown fat hypertrophy and hyperplasia, and myelolipotic atrophy. The non-toxic dose (NOAEL) is 0.12 mg/kg/day for males and 0.03 mg/kg/day for females, which is 1.67 times and 3.74 times less than the clinical dose.
In a 52-week study of monkeys, 0.8 mg/kg/day (7.54 times the clinical dose) increase in cardiac weight in the oral group. Cardiomyocyte hypertrophy appeared. The non-toxic dose (NOAEL) was 0.2 mg/kg/day, which showed a safety range of 2.1 times compared to the clinical dose.
(4) Reproductive development toxicity
There was no teratogenicity when the drug was administered up to 0.8 mg/kg in rats and 90 mg/kg in rabbits during the organogenesis period. (1.0 times and 5 times, respectively , compared to the daily human dose of 35.8 mg) rat embryo toxicity was observed at 57.0 mg / kg (2.0 times AUC when administered to humans at 5.11 mg / day) and rabbit embryo toxicity (fetal weight, number of living fetuses, embryo absorption water, embryo mortality increase) was observed at more than 2 mg / kg (15.0 times AUC when administered to humans 5.10 mg / day). The non-toxic dose (NOAEL) of embryotoxicity in rats is 9.0 mg/kg (05.0 times the AUC when administered to humans at 5.1 mg/day) and the non-toxic dose (NOAEL) of rabbit embryotoxicity is 3.2 mg/kg (5.0 times the AUC when administered to humans at 5.1 mg/day).
In the pre- and post-natal development and maternal function tests of rats, an increase in the number of stillbirths, a decrease in the proportion of survivors among live births and implantation was observed at 0.2 mg/kg (0.5 times the AUC when administered to humans at 11.2 mg/day). In the next-generation test group, weight loss was observed at 0.05 mg/kg (2.62 times human AUC), cardiac weight gain at 0.1 mg/kg (6.18 times human AUC), and delay in morphological differentiation. The non-toxic dose (NOAEL) of mother and nextgeneration animals is less than or equal to 0.05 mg/kg (0.5 times AUC when administered to humans at 2.62 mg/day).
7.0 Description
The chemical name for Lobeglitazone Sulphate is 5-[[4-[2-[[6-(4-methoxyphenoxy) pyrimidin-4-yl]-methylamino] ethoxy] phenyl] methyl]-1, 3-thiazolidine-2, 4-dione; sulfuric acid. Molecular formula of Lobeglitazone Sulphate is C24H26N4O9S2 and a molecular weight of 578.6 g/mol. The structural formula of Lobeglitazone Sulphate is:

8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable.
8.2 Shelf life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
Alu-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets.
8.4 Storage and handling instructions
Store protected from light & moisture at a temperature not exceeding 30°C.
Keep out of reach of children
9.0 Patient counselling information
- It is important to educate patients to follow the diet and to regularly undergo blood glucose tests and glycated hemoglobin and glucosylated hemoglobin tests. During stressful periods such as fever, trauma, infection, or surgery, medical requirements may change, so patients should be reminded to see a doctor promptly.
- Patients who experience unusual, rapid weight gain or swelling during the period of administration of this drug, or who develop other symptoms of shortness of breath or heart failure, should report these symptoms to their physician immediately.
- Before and after the start of treatment, the patient should be informed that blood tests including liver function will be performed according to the doctor's clinical judgment. Patients should be advised to see a doctor immediately for unexplained nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, loss of appetite, dark urine, and dizziness.
- The patient should be told to take this medication once a day. This medication can be taken with or without meals. If you take one dose a day, you shouldn't double the dose the next day.
- When co-administered with insulin or oral hypoglycemic drugs, the risk of hypoglycemia, its symptoms and treatments, and the conditions that are prone to developing such symptoms should be explained to the patient and his or her family members.
- As with other thiazolidinediones, its therapy can cause ovulation in some premenopausal anovulatory women. As a result, these patients may have an increased risk of pregnancy while taking this drug. Therefore, adequate contraception should be recommended for premenopausal women. Since this possible action has not been studied in clinical trials, the frequency of occurrence is unknown.
12.0 Date of issue
14 July 2023

Plot Y2, CTS No : 358/A2, Near Nahur Railway
Station, Nahur (West), Mumbai - 400 078, India.
TM - Trade Mark Owners.
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1. What LobetronTM-0.5 is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you take LobetronTM-0.5
3. How to take LobetronTM-0.5
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store LobetronTM-0.5
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What LobetronTM-0.5 is and what it is used for
LobetronTM-0.5 tablets contain Lobeglitazone.
- It is an anti-diabetic medicine used to treat type 2 (non-insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus in adults, when metformin is not suitable or has failed to work adequately. This is the diabetes that usually develops in adulthood.
- Lobeglitazone tablets help control the level of sugar in your blood when you have type 2 diabetes by helping your body make better use of the insulin it produces. Your doctor will check whether Lobeglitazone is working 3 to 6 months after you start taking it.
- Lobeglitazone tablets may be used on their own in patients who are unable to take metformin, and where treatment with diet and exercise has failed to control blood sugar or may be added to other therapies (such as insulin, sulphonyl urea) which have failed to provide sufficient control in blood sugar.
2. What you need to know before you take LobetronTM-0.5
Do not take LobetronTM-0.5 if:
- you are allergic to Lobeglitazone or any of the other ingredients of this medicine,
- you have heart failure or have had heart failure in the past,
- you have liver disease,
- you have had diabetic ketoacidosis (a complication of diabetes causing rapid weight loss, nausea or vomiting),
- you have severe kidney disease,
- you have blood in your urine that your doctor has not checked.
- Serious infection or trauma
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Lobeglitazone:
- If you retain water (fluid retention) or have heart problems in particular if you are over 75 years old. If you take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines which can also cause water (fluid retention) and swelling, including celecoxib or etoricoxib, you must also tell your doctor.
- If you have ever had blood in your urine. If you find blood in your urine or have other problems urinating while taking Lobeglitazone, you should contact your doctor.
- If you smoke (or have smoked in the past), have received chemotherapy or radiotherapy (for cancer treatment).
- If you have a special type of diabetic eye disease called macular oedema (swelling of the back of the eye with worsening of your vision).
- If you have cysts on your ovaries (polycystic ovary syndrome). There may be an increased possibility of becoming pregnant because you may ovulate again when you take Lobeglitazone. If this applies to you, use appropriate contraception to avoid the possibility of an unplanned pregnancy.
- If you have a problem with your liver or heart. Before you start taking Lobeglitazone you will have a blood sample taken to check your liver function. This check may be repeated at intervals. Some patients with long-standing type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart disease or previous stroke who were treated with Lobeglitazone and insulin experienced the development of heart failure. Inform your doctor as soon as possible if you experience signs of heart failure such as unusual shortness of breath or rapid increase in weight or localised swelling (oedema).
- Broken bones, a higher number of bone fractures was seen in patients, particularly women taking Lobeglitazone. Your doctor will take this into account when treating your diabetes.
- If you take Lobeglitazone with other medicines for diabetes, it is more likely that your blood sugar could fall below the normal level (hypoglycaemia).
- You may also experience a reduction in blood count (anaemia).
Pediatric population
Use in children is not recommended.
Other medicines and Lobeglitazone
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. You can usually continue to take other medicines whilst you are being treated with Lobeglitazone tablets.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
You should not take Lobeglitazone in pregnancy as it is unsure whether the medicine can affect the growth of your baby.
You should not take Lobeglitazone if you are breast-feeding as it is not known whether it may be present in the milk.
Driving and using machines
Lobeglitazone will not normally affect your ability to drive or use machines but take care if you experience abnormal vision.
3. How to take LobetronTM-0.5
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
The usual recommended dose is 1 tablet (0.5 mg) of Lobeglitazone taken once daily. Swallow your tablet with a glass of water with or without food.
If necessary, your doctor may tell you to take a different dose. When Lobeglitazone tablets are taken in combination with other medicines used to treat diabetes (such as insulin, metformin, glibenclamide, gliclazide) your doctor will tell you whether you need to take a smaller dose of your medicines.
Your doctor will ask you to have blood tests periodically during treatment with Lobeglitazone. This is to check that your liver is working normally.
If you are following a diabetic diet, you should continue with this while you are taking Lobeglitazone.
Your weight should be checked at regular intervals; if your weight increases, inform your doctor.
If you take more Lobeglitazone tablets than you should
If you accidentally take too many tablets, or if someone else or a child takes your medicine, contact your doctor or hospital emergency department immediately. Your blood sugar could fall below the normal level and can be increased by taking sugar. It is recommended that you carry some sugar lumps, sweets, biscuits or sugary fruit juice.
If you forget to take Lobeglitazone tablets
Take Lobeglitazone daily as prescribed. However, if you miss a dose, just carry on with the next dose as normal. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop taking Lobeglitazone tablets
Lobeglitazone should be used every day to work properly. If you stop using Lobeglitazone, your blood sugar may go up. Talk to your doctor before stopping this treatment.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If you notice any of the following side effects, stop taking this medicine and contact your doctor or go to the nearest hospital casualty department straight away.
- Heart failure (when taking Lobeglitazone in combination with insulin): symptoms are unusual shortness of breath or rapid increase in weight or localised swelling (oedema).
- Signs and symptoms include blood in your urine.
- Localised swelling (oedema) (when taking Lobeglitazone in combination with insulin).
- Broken bones (this has been reported in both female and male patients).
- Blurred vision due to swelling (or fluid) at the back of the eye. Also, if you already have blurred vision and the symptom gets worse, talk to your doctor as soon as possible.
- Allergic reactions: symptoms of a serious allergic reaction include hives and swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat that may cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing.
Other possible side effects:
Common
- abnormal vision
- respiratory infection
- weight gain
- numbness
Uncommon
- inflammation of the sinuses (sinusitis)
- difficulty sleeping (insomnia).
Not known: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
- increase in liver enzymes
- allergic reactions
The following additional side effects have been experienced by some patients when Lobeglitazone is taken with other antidiabetic medicines.
Very common
- decreased blood sugar (hypoglycaemia)
Common
- headache
- dizziness
- joint pain
- impotence
- back pain
- shortness of breath
- small reduction in red blood cell count (anemia)
- flatulence
- increase in enzyme levels
Uncommon
- sugar in urine, proteins in urine
- spinning sensation (vertigo)
- sweating
- tiredness
- increased appetite
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effects with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store LobetronTM-0.5
Store protected from light & moisture at a temperature not exceeding 30°C. Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the blister, carton, bottle after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
6. Content of the pack and other information
What LobetronTM-0.5 contains
The active substance is Lobeglitazone. Each tablet contains 0.5 mg of Lobeglitazone (as Sulfate).
What LobetronTM-0.5 looks like and contents of the pack
Alu-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets.