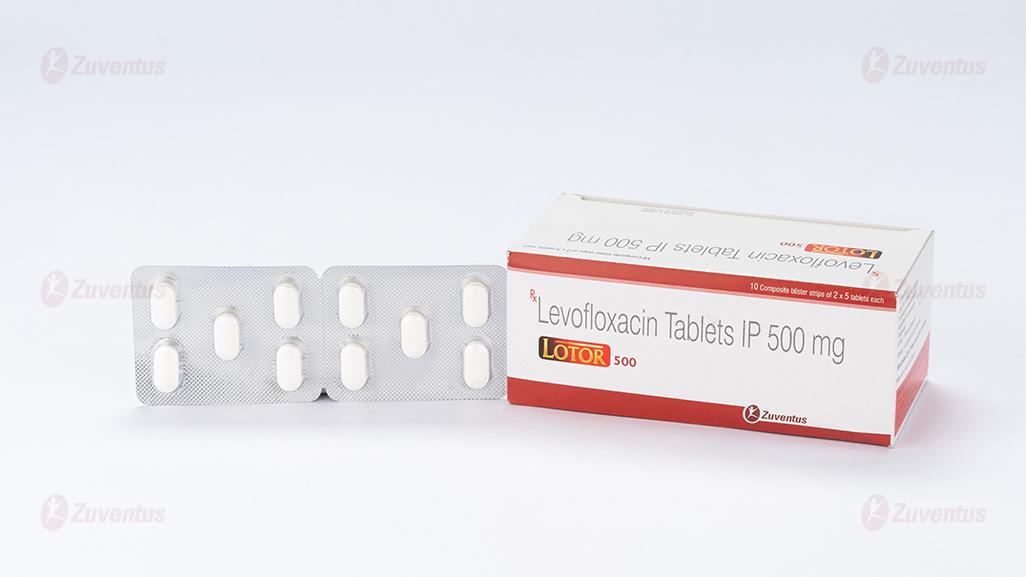
Lotor 500 Tablet
Therapy Area
Anti Bacterial
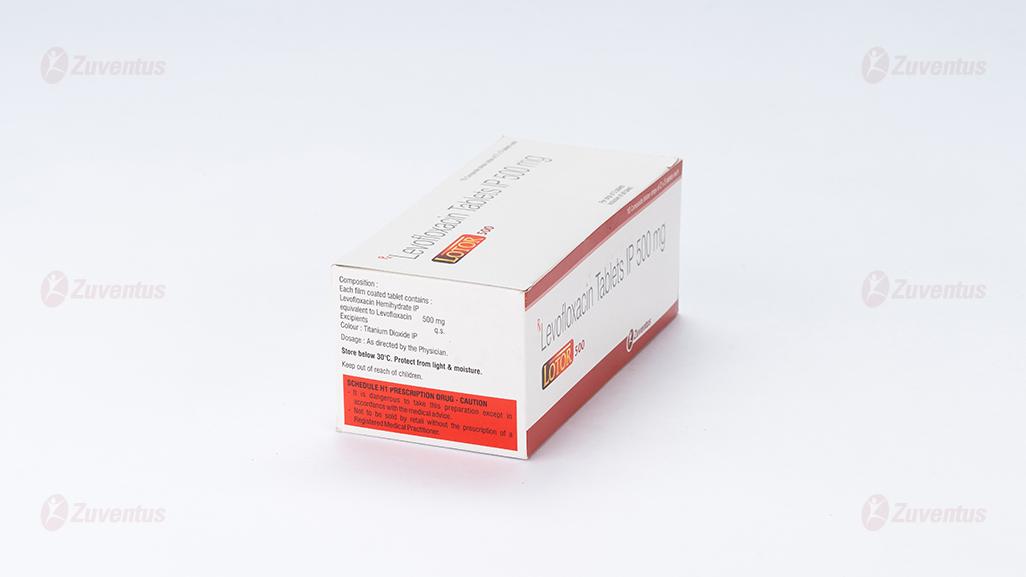
Composition
Each film coated tablet contains :
Levofloxacin Hemihydrate IP
equivalent to Levofloxacin 500 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Titanium Dioxide IP
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacotherapeutic group : quinolone antibacterials, fluoroquinolones, ATC code: J01MA12 Levofloxacin is a synthetic antibacterial agent of the fluoroquinolone class and is the S (-) enantiomer of the racemic active substance ofloxacin.
Mechanism of action
As a fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent, Levofloxacin acts on the DNA-DNA-gyrase complex and topoisomerase IV. PK/PD relationship The degree of the bactericidal activity of Levofloxacin depends on the ratio of the maximum concentration in serum (Cmax) or the area under the curve (AUC) and the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC).
Mechanism of resistance
Resistance to Levofloxacin is acquired through a stepwise process by target site mutations in both type II topoisomerases, DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. Other resistance mechanisms such as permeation barriers (common in Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and efflux mechanisms may also affect susceptibility to Levofloxacin. Cross-resistance between Levofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones is observed. Due to the mechanism of action, there is generally no cross-resistance between Levofloxacin and other classes of antibacterial agents.
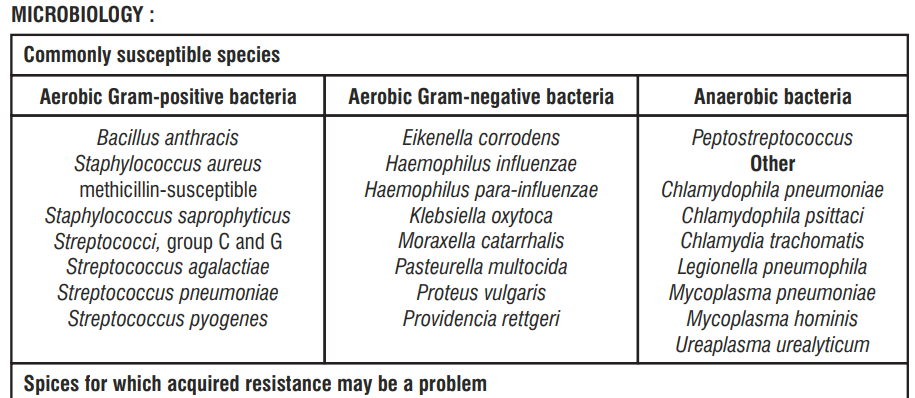
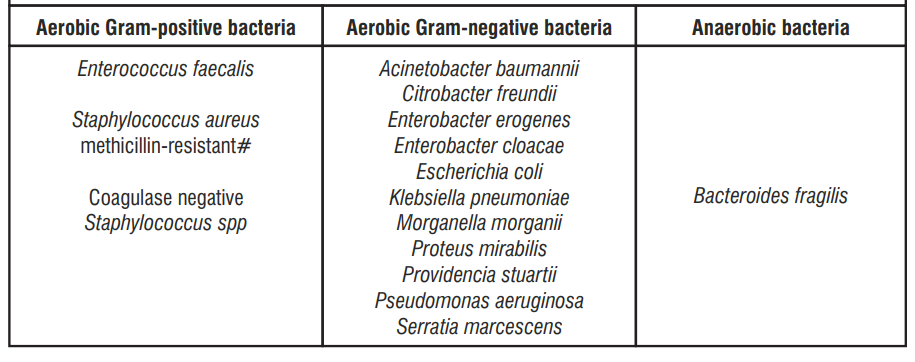
Inherently Resistant Strains
Aerobic Gram-positive bacteria
Enterococcus faecium
# Methicillin-resistant S. aureus are very likely to possess co-resistance to fluoroquinolones, including Levofloxacin.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption
Orally administered Levofloxacin is rapidly and almost completely absorbed with peak plasma concentrations being obtained within 1-2 h. The absolute bioavailability is 99-100%. Food has little effect on the absorption of Levofloxacin. Steady state conditions are reached within 48 hours following a 500 mg once or twice daily dosage regimen.
Distribution
Approximately 30-40% of Levofloxacin is bound to serum protein. The mean volume of distribution of Levofloxacin is approximately 100l after single and repeated 500mg doses, indicating widespread distribution into body tissues. Penetration into tissues and body fluids
Levofloxacin has been shown to penetrate into bronchial mucosa, epithelial lining fluid, alveolar macrophages, lung tissue, skin (blister fluid), prostatic tissue and urine. However, Levofloxacin has poor penetration intro cerebrospinal fluid
Biotransformation
Levofloxacin is metabolised to a very small extent, the metabolites being desmethyl-levofloxacin and Levofloxacin N-oxide. These metabolites account for <5% of the dose and are excreted in urine. Levofloxacin is stereochemically stable and does not undergo chiral inversion.
Elimination
Following oral and intravenous administration of Levofloxacin, it is eliminated relatively slowly from the plasma (t½ : 6 - 8 hours). Excretion is primarily by the renal route (>85% of the administered dose). The mean apparent total body clearance of Levofloxacin following a 500 mg single dose was 175 ± 29.2 ml/min. There are no major differences in the pharmacokinetics of Levofloxacin following intravenous and oral administration, suggesting that the oral and intravenous routes are interchangeable.
Special populations
Subjects with renal insufficiency
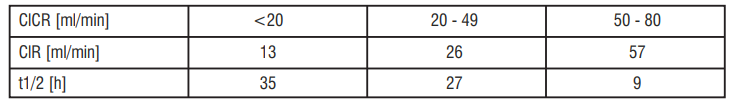
The pharmacokinetics of Levofloxacin are affected by renal impairment. With decreasing renal function, renal elimination and clearance are decreased, and elimination half-lives increased as shown in the table below : Pharmacokinetics in renal insufficiency following single oral 500 mg dose
Indications:
Levofloxacin 500mg film coated tablet is indicated in adults for the treatment of the following infections
• Acute maxillary sinusitis
• Lower respiratory tract infection of chronic bronchitis
• Acute bacterial exacerbation
• Community acquired pneumonia
• Skin & soft tissue infection
• Complicated urinary tract infection or acute pyelonephritis.
• Prostatitis
Contraindications
Lotor tablet is contraindicated in the following situations:
• In patients hypersensitive to Levofloxacin or other quinolones or any of the excipients listed in the formulation.
• In patients with epilepsy.
• In patients with history of tendon disorders related to fluoroquinolone administration.
• In children or growing adolescents.
• During pregnancy.
• In breast-feeding women.
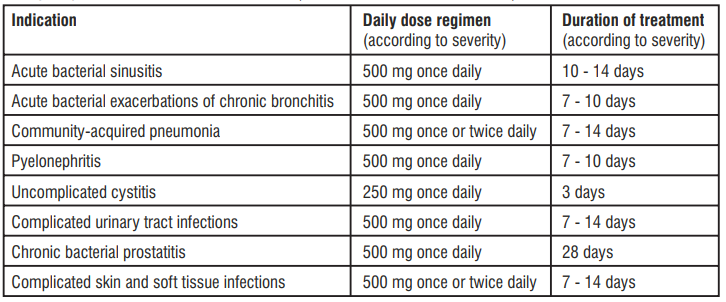
Dosage and Administration
Levofloxacin 500mg film coated tablet are administered once or twice daily. The dosage depends on the type and severity of the infection and the susceptibility of the presumed causative pathogen.
Dosage in patients with normal renal function (creatinine clearance >50 ml/min)
Special populations
Impaired renal function
(creatinine clearance ≤50ml/min)
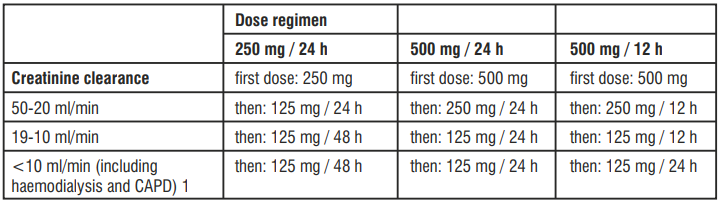
No additional doses are required after haemodialysis or continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD).
Method of Administration:
Levofloxacin 500mg film coated tablet should be swallowed without crushing and with sufficient amount of liquid. They may be divided at the score line to adapt the dose. The tablets may be taken during meals or between meals. Levofloxacin 500mg film coated tablet should be taken at least two hours before or after iron salts, zinc salts, magnesium- or aluminium-containing antacids, or didanosine (only didanosine formulations with aluminium or magnesium containing buffering agents),and sucralfate administration, since reduction of absorption can occur.
Drug Interactions
Effect of other medicinal products on Levofloxacin
Iron salts, zinc-salts, magnesium- or aluminium-containing antacids, didanosine
Levofloxacin absorption is significantly reduced when iron salts, or magnesium- or aluminium-containing antacids, or didanosine (only didanosine formulations with aluminium or magnesium containing buffering agents) are administered concomitantly with Levofloxacin tablets.
Sucralfate
The bioavailability of Levofloxacin 500mg film coated tablet is significantly reduced when administered together with sucralfate.
Theophylline, fenbufen or similar non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
No pharmacokinetic interactions of Levofloxacin were found with theophylline in a clinical study. However a pronounced lowering of the cerebral seizure threshold may occur when quinolones are given concurrently with theophylline, non-steroidal anti-inflammator y drugs, or other agents which lower the seizure threshold. Levofloxacin concentrations were about 13% higher in the presence of fenbufen than when administered alone
Probenecid and cimetidine
Probenecid and cimetidine had a statistically significant effect on the elimination of Levofloxacin. The renal clearance of Levofloxacin was reduced by cimetidine (24%) and probenecid (34%).
Other relevant information
Clinical pharmacology studies have shown that the pharmacokinetics of Levofloxacin were not affected to any clinically relevant extent when Levofloxacin was administered together with the following drugs : calcium carbonate, digoxin, glibenclamide, ranitidine.
Effect of Levofloxacin on other medicinal products
Ciclosporin
The half-life of ciclosporin was increased by 33% when coadministered with Levofloxacin
Vitamin K antagonists
Increased coagulation tests (PT/INR) and/or bleeding, which may be severe, have been reported in patients treated with Levofloxacin in combination with a vitamin K antagonist (e.g. warfarin).
Drugs known to prolong QT interval
Levofloxacin, like other fluoroquinolones, should be used with caution in patients receiving drugs known to prolong the QT interval (e.g Class IA and III antiarrhythmics, tricyclic antidepressants, macrolides and, antipsychotics)
Other relevant information
In a pharmacokinetic interaction study, Levofloxacin did not affect the pharmacokinetics of theophylline (which is a probe substrate for CYP1A2), indicating that Levofloxacin is not a CYP1A2 inhibitor.
Other forms of interactions
Food
There is no clinically relevant interaction with food. Levofloxacin 500mg film coated tablet may therefore be administered regardless of food intake.
Cautions and Precautions
Methicillin-resistant S. aureus are very likely to possess co-resistance to fluoroquinolones, including Levofloxacin. Therefore Levofloxacin is not recommended for the treatment of known or suspected MRSA infections unless laboratory results have confirmed susceptibility of the organism to Levofloxacin (and commonly recommended antibacterial agents for the treatment of MRSA-infections are considered inappropriate). Levofloxacin may be used in the treatment of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis and Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis when these infections have been adequately diagnosed.
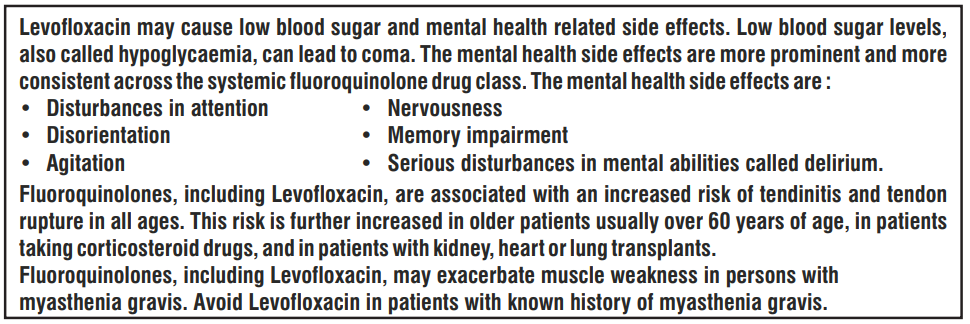
Tendinitis and tendon rupture
Tendinitis may rarely occur. The daily dose should be adjusted in elderly patients based on creatinine clearance. Close monitoring of these patients is therefore necessary if they are prescribed Levofloxacin. All patients should consult their physician if they experience symptoms of tendinitis. If tendinitis is suspected, treatment with Levofloxacin must be halted immediately, and appropriate treatment (e.g. immobilisation) must be initiated for the affected tendon.
Clostridium difficile-associated disease
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, Levofloxacin should be stopped immediately and appropriate treatment initiated without delay. Anti-peristaltic medicinal products are contraindicated in this clinical situation
Patients with G-6- phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
If Levofloxacin has to be used in these patients, potential occurrence of haemolysis should be monitored.
Hypersensitivity reactions
Patients should discontinue treatment immediately and contact their physician or an emergency physician, who will initiate appropriate emergency measures
Severe bullous reactions
Patients should be advised to contact their doctor immediately prior to continuing treatment if skin and/or mucosal reactions occur
Dysglycaemia
In diabetic patients, careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
Prevention of photosensitisation
It is recommended that patients should not expose themselves unnecessarily to strong sunlight or to artificial UV rays (e.g. sunray lamp, solarium), during treatment and for 48 hours following treatment discontinuation in order to prevent photosensitisation.
Patients treated with Vitamin K antagonists
Due to possible increase in coagulation tests (PT/INR) and/or bleeding in patients treated with Levofloxacin in combination with a vitamin K antagonist (e.g. warfarin), coagulation tests should be monitored when these drugs are given concomitantly
Peripheral neuropathy
Levofloxacin should be discontinued if the patient experiences symptoms of neuropathy in order to prevent the development of an irreversible condition.
Hepatobiliary disorders
Patients should be advised to stop treatment and contact their doctor if signs and symptoms of hepatic disease develop such as anorexia, jaundice, dark urine, pruritus or tender abdomen.
Vision disorders
If vision becomes impaired or any effects on the eyes are experienced, an eye specialist should be consulted immediately.
Superinfection
If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
Aortic aneurysm and dissection
Fluoroquinolones should only be used after careful benefit-risk assessment and after consideration of other therapeutic options in patients with positive family history of aneurysm disease, or in patients diagnosed with pre-existing aortic aneurysm and/or aortic dissection, or in presence of other risk factors or conditions predisposing for aortic aneurysm and dissection (e.g. Marfan syndrome, vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Takayasu arteritis, giant cell arteritis, Behcet's disease, hypertension, known atherosclerosis). In case of sudden abdominal, chest or back pain, patients should be advised to immediately consult a physician in an emergency department.
Interference with laboratory tests
In patients treated with Levofloxacin, determination of opiates in urine may give false-positive results. It may be necessary to confirm positive opiate screens by more specific method. Levofloxacin may inhibit the growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and, therefore, may give false-negative results in the bacteriological diagnosis of tuberculosis.
Adverse Effects
Infections and infestations : Uncommon - Fungal infection including Candida infection, pathogen resistance. Blood and lymphatic system disorders : Uncommon - Leukopenia, eosinophilia; Rare - thrombocytopenia, neutropenia; Not known - Pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, haemolytic anaemia. Immune system disorders : Rare - angioedema, a a hpersensitivity; Not known - anaphylactic shock , anaphylactoid shock . Metabolism and nutrition disorders : Uncommon - anorexia; Rare - hypoglycaemia particularly in diabetic patients; Not known - hyperglycaemia, hypoglycaemic coma. Psychiatric disorders : Common - insomnia; Uncommon - anxiety, confusional state, nervousness; Rare - psychotic reactions (with e.g. hallucination, paranoia), depression agitation, abnormal dreams, nightmares; Not known - psychotic disorders with self-endangering behaviour including suicidal ideation or suicide attempt. Nervous system disorders : Common - headache, dizziness; Uncommon - somnolence, tremor, dysgeusia; Rare - convulsion, paraesthesia; Not known - peripheral sensory neuropathy, peripheral sensory motor neuropathy, parosmia including anosmia, dyskinesia extrapyramidal disorder, ageusia syncope, benign intracranial hypertension. Eye disorders : Rare - visual disturbances such as blurred vision; Not known - transient vision loss. Ear and Labyrinth disorders : Uncommon - vertigo; Rare - tinnitus; Not known - hearing loss, hearing impaired. Cardiac disorders : Rare - tachycardia, palpitation; Not known - ventricular tachycardia, which may result in cardiac arrest, ventricular arrhythmia and torsade de pointes (reported predominantly in patients with risk factors of QT prolongation), electrocardiogram QT prolonged. Vascular disorders : Rare - hypotension. Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders : Uncommon - dyspnoea; Not known - bronchospasm, pneumonitis allergic. Gastro-intestinal disorders : Common- diarrhea, vomiting, nausea; Uncommon - abdominal pain, dyspepsia, flatulence, constipation; Not known - diarrhoea – haemorrhagic which in very rare cases may be indicative of enterocolitis, including pseudomembranous colitis, pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary disorders : Common - Hepatic enzyme increased (ALT/AST, alkaline phosphatase, GGT); Uncommon - blood bilirubin increased; Not known - Jaundice and severe liver injury, including cases with fatal acute liver failure, primarily in patients with severe underlying diseases, b hepatitis. Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders : Uncommon- rash, pruritus, urticaria, hyperhidrosis; Not known - toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, photosensitivity reaction, leukocytoclastic vasculitis, stomatitis. Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders : Uncommon - arthralgia, myalgia; Rare - tendon disorders including tendinitis, muscular weakness which may be of special importance in patients with myasthenia gravis; Not known - rhabdomyolysis, tendon rupture (e.g. Achilles tendon), ligament rupture, muscle rupture, arthritis. Renal and Urinary disorders : Uncommon - blood creatinine increased; Rare - renal failure acute. General disorders and administration site conditions : Uncommon - asthenia; Rare - pyrexia; Not known - Pain (including pain in back, chest, and extremities).
Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions may sometimes occur even after the first dose Mucocutaneous reactions may sometimes occur even after the first dose Other undesirable effects which have been associated with fluoroquinolone administration include: attacks of porphyria in patients with porphyria
Overdosage
According to toxicity studies in animals or clinical pharmacology studies performed with supra-therapeutic doses, the most important signs to be expected following acute overdose of Levofloxacin tablets are central nervous system symptoms such as confusion, dizziness, impairment of consciousness and convulsive seizures, increases in QT interval as well as gastro-intestinal reactions such as nausea and mucosal erosions. CNS effects including confusional state, convulsion, hallucination, and tremor have been observed in post marketing experience.
In the event of overdose, symptomatic treatment should be implemented. ECG monitoring should be undertaken, because of the possibility of QT interval prolongation. Antacids may be used for protection of gastric mucosa. Haemodialysis, including peritoneal dialysis and CAPD, are not effective in removing Levofloxacin from the body. No specific antidote exists.
Storage
Store below 30°C. Protect from light & moisture.
Keep out of reach of children
Presenatation
A blister strip of 5 tablets
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist or nurse.
This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet:
1. What LOTOR® is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you take LOTOR®
3. How to take LOTOR®
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store LOTOR®
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What LOTOR® is and what it is used for
LOTOR® tablet contains a drug called levofloxacin. Levofloxacin is an antibiotic which is used to treat bacterial infections of the
- sinuses
- lungs, in people with long-term breathing problems or Pneumonia
- urinary tract, including your kidneys or bladder
- prostate gland, where you have a long lasting infection
- skin and underneath the skin, including muscles. This is sometimes called ‘soft tissue’
2. What you need to know before you take LOTOR®
Do not take LOTOR®, if
- You are allergic to levofloxacin, any other quinolone antibiotic such as moxifloxacin, ciprofloxacin or ofloxacin or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine. Signs of an allergic reaction include: a rash, swallowing or breathing problems, swelling of your lips, face, throat or tongue.
- If your eyesight becomes impaired or if your eyes seem to be otherwise affected, consult an eye specialist immediately.
- You have ever had epilepsy
- You have ever had a problem with your tendons such as tendonitis that was related to treatment with a ‘quinolone antibiotic'. A tendon is the cord that joins your muscle to your skeleton.
- You are a child or a growing teenager
- You are pregnant, trying to become pregnant or are breast-feeding.
Do not take this medicine if any of the above applies to you. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking LOTOR® Tablets.
Warnings and precautions
Before taking this medicine
You should not take fluoroquinolone/quinolone antibacterial medicines, including LOTOR®, if you have experienced any serious adverse reaction in the past when taking a quinolone or fluoroquinolone.
In this situation, you should inform your doctor as soon as possible.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking LOTOR® Tablets if:
You are 60 years of age or older.
You are using corticosteroids, sometimes called steroids.
You have ever had a fit (seizure).
You have had damage to your brain due to a stroke or other brain injury.
You have kidney problems.
You have something known as ‘glucose – 6 – phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency’. You are more likely to have serious problems with your blood when taking this medicine.
You have ever had mental health problems.
You have ever had Heart problems: Caution should be taken when using this kind of medicine, if you were born with or have family history of prolonged QT interval (seen on ECG, electrical recording of the heart), have salt imbalance in the blood (especially low level of potassium or magnesium in the blood), have a very slow heart rhythm (called ‘bradycardia’), have a weak heart (heart failure), have a history of heart attack (myocardial infarction), you are female or elderly or you are taking other medicines that result in abnormal ECG changes.
if you have been diagnosed with an enlargement or "bulge" of a large blood vessel (aortic aneurysm or large vessel peripheral aneurysm).
if you have experienced a previous episode of aortic dissection (a tear in the aorta wall).
if you have a family history of aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection or other risk factors or predisposing conditions (e.g. connective tissue disorders such as Marfan syndrome, or vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, or vascular disorders such as Takayasu arteritis, giant cell arteritis, Behcet’s disease, high blood pressure, or known atherosclerosis).
You are diabetic
You have ever had liver problems
You have myasthenia gravis.
If you feel sudden, severe pain in your abdomen, chest or back, go immediately to an emergency room.
You have ever developed a severe skin rash or skin peeling, blistering and/or mouth sores after taking levofloxacin.
Serious skin reactions
Serious skin reactions including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) have been reported with the use of levofloxacin.
- SJS/TEN can appear initially as reddish target-like spots or circular patches often with central blisters on the trunk. Also, ulcers of mouth, throat, nose, genitals and eyes (red and swollen eyes) can occur. These serious skin rashes are often preceded by fever and/or flu-like symptoms. The rashes may progress to widespread peeling of the skin and life-threatening complications or be fatal.
- DRESS appears initially as flu-like symptoms and a rash on the face then an extended rash with a high body temperature, increased levels of liver enzymes seen in blood tests and an increase in a type of white blood cell (eosinophilia) and enlarged lymph nodes.
If you develop a serious rash or another of these skin symptoms, stop taking levofloxacin and contact your doctor or seek medical attention immediately.
Other warnings
When taking this medicine
Pain and swelling in the joints and inflammation or rupture of tendons may occur rarely. Your risk is increased if you are elderly (above 60 years of age), have received an organ transplant, have kidney problems or if you are being treated with corticosteroids. Inflammation and ruptures of tendons may occur within the first 48 hours of treatment and even up to several months after stopping of LOTOR® Tablets therapy. At the first sign of pain or inflammation of a tendon (for example in your ankle, wrist, elbow, shoulder or knee), stop taking Levofloxacin Tablets, contact your doctor and rest the painful area. Avoid any unnecessary exercise as this might increase the risk of a tendon rupture. You may rarely experience symptoms of nerve damage (neuropathy) such as pain, burning, tingling, numbness and/or weakness especially in the feet and legs or hands and arms. If this happens, stop taking levofloxacin Tablets and inform your doctor immediately in order to prevent the development of potentially irreversible condition.
If you start having severe, persistent and/or bloody diarrhoea during or after treatment with levofloxacin, tell your doctor immediately. This could mean you have serious inflammation of your bowel (pseudomembranous colitis), which can sometimes occur after antibiotic treatment. You may need to stop taking levofloxacin and for your doctor to give you another medicine.
Whilst taking LOTOR® Tablets you are advised to stay out of strong sunlight and not to use a sun lamp. This is because some patients may become more sensitive to light whilst taking the tablets and get a sun-burn like reaction.
Levofloxacin is not an optimal therapy for most severe cases of Pneumococcal pneumonia.
Infections got from a hospital during treatment due to P. aeruginosa may require combination therapy.
Levofloxacin is not effective against infections caused by MRSA. In infections suspicious for MRSA levofloxacin should be combined with an agent approved to treat MRSA infections. If you are not sure if any of the above applies to you, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Levofloxacin Tablets.
If you are not sure if any of the above applies to you, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking LOTOR® Tablets.
Prolonged, disabling and potentially irreversible serious side effects
Fluoroquinolone/quinolone antibacterial medicines, including LOTOR®, have been associated with very rare but serious side effects, some of them being long lasting (continuing months or years), disabling or potentially irreversible. This includes tendon, muscle and joint pain of the upper and lower limbs, difficulty in walking, abnormal sensations such as pins and needles, tingling, tickling, numbness or burning (paraesthesia), sensory disorders including impairment of vision, taste and smell, and hearing, depression, memory impairment, severe fatigue, and severe sleep disorders. If you experience any of these side effects after taking levofloxacin tablets, contact your doctor immediately prior to continuing treatment. You and your doctor will decide on continuing the treatment considering also an antibiotic from another class.
Other medicines and LOTOR®
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. This is because LOTOR® Tablets can affect the way some other medicines work. Also some medicines can affect the way LOTOR® Tablets work. In particular, tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following medicines. This is because it can increase the chance of you getting side effects, when taken with LOTOR® Tablets:
Corticosteroids, sometimes called steroids – used for inflammation. You may be more likely to have inflammation and/or rupture of your tendons.
Warfarin - used to thin the blood. You may be more likely to have a bleed. Your doctor may need to take regular blood tests to check how well your blood can clot.
Theophylline - used for breathing problems. You are more likely to have a fit (seizure) if taken with LOTOR® Tablets
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) - used for pain and inflammation such as aspirin, ibuprofen, fenbufen, ketoprofen and indomethacin. You are more likely to have a fit (seizure) if taken with LOTOR® Tablets
- Ciclosporin - used after organ transplants. You may be more likely to get the side effects of ciclosporin
- Medicines known to affect the way your heart beats. This includes medicines used for abnormal heart rhythm (antiarrhythmics such as quinidine, hydroquinidine, disopyramide, sotalol, dofetilide, ibutilide and amiodarone), for depression (tricyclic antidepressants such as amitriptyline and imipramine), for psychiatric disorders (antipsychotics), and for bacterial infections (‘macrolide’ antibiotics such as erythromycin, azithromycin and clarithromycin)
- Probenecid – used for gout and cimetidine – used for ulcers and heartburn. Special care should be taken when taking either of these medicines with LOTOR® Tablets. If you have kidney problems, your doctor may want to give you a lower dose.
Do not take LOTOR® Tablets at the same time as the following medicines. This is because it can affect the way LOTOR® Tablets work:
Iron tablets (for anemia), zinc supplements, magnesium or aluminum-containing antacids (for acid or heartburn), didanosine, or sucralfate (for stomach ulcers).
Urine tests for opiates
Urine tests may show ‘false-positive’ results for strong painkillers called ‘opiates’ in people taking LOTOR® tablets. If your doctor is due to take a urine test, tell them you are taking LOTOR® tablets.
Tuberculosis tests
This medicine may cause “false negative” results for some tests used in laboratory to search for the bacteria causing tuberculosis.
Taking LOTOR® Tablets with food and drink
Take without regard to meals. Take with water, drink with plenty of water. Taking this product with orange juice can result in reduced quinolone plasma levels.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
You must not take LOTOR® Tablets if you are pregnant, trying to become pregnant or are breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines
You may get side effects after taking this medicine, including feeling dizzy, sleepy, a spinning feeling (vertigo) or changes to your eyesight. Some of these side effects can affect you being able to concentrate and your reaction speed. If this happens, do not drive or carry out any work that requires a high level of attention.
3. How to use LOTOR®
Always take LOTOR® Tablets exactly as your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
Taking this medicine
- Take this medicine by mouth
- Swallow the tablets whole with a drink of water
- The tablets may be taken during meals or at any time between meals
Protect your skin from sunlight
Keep out of direct sunlight while taking this medicine and for 2 days after you stop taking it. This is because your skin will become much more sensitive to the sun and may burn, tingle or severely blister if you do not take the following precautions:
- Make sure you use high factor sun cream
- Always wear a hat and clothes which cover your arms and legs
- Avoid sun beds
If you are already taking iron tablets, zinc supplements, antacids, didanosine or sucralfate
Do not take these medicines at the same time as LOTOR® Tablets. Take your dose of these medicines at least 2 hours before or after LOTOR® Tablets.
How much to take
- Your doctor will decide on how many LOTOR® Tablets you should take
- The dose will depend on the type of infection you have and where the infection is in your body.
- The length of your treatment will depend on how serious your infection is.
- If you feel the effect of your medicine is too weak or strong, do not change the dose yourself, but ask your doctor.
Adults and the elderly
Sinuses infection
- One tablet of LOTOR® 500 mg, once each day
Lungs infection, in people with long-term breathing problems
- One tablet of LOTOR® Tablets 500 mg, once each day
Pneumonia
- One tablet of LOTOR® Tablets 500 mg, once or twice each day
Infection of urinary tract, including your kidneys or bladder
- 1/2 or one tablet of LOTOR® Tablets 500 mg, each day
Prostate gland infection
- One tablet of LOTOR® Tablets 500 mg, once each day
Infection of skin and underneath the skin, including muscles
- Or, one tablet of LOTOR® Tablets 500 mg, once or twice each day
Adults and the elderly with kidney problems
Your doctor may need to give you a lower dose.
Children and adolescents
This medicine must not be given to children or teenagers.
If you take more LOTOR® Tablets than you should
If you accidentally take more tablets than you should, tell a doctor or get other medical advice straight away. Take the medicine pack with you. This is so the doctor knows what you have taken.
The following effects may happen: convulsive fits (seizures), feeling confused, dizzy, less conscious, having tremor and heart problems - leading to uneven heart beats as well as feeling sick (nausea) or having stomach burning.
If you forget to take a dose of LOTOR® Tablets
If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it is nearly time for your next dose.
Do not double-up the next dose to make up for the missed dose.
If you stop taking LOTOR® Tablets
Do not stop taking LOTOR® Tablets just because you feel better. It is important that you complete the course of tablets that your doctor has prescribed for you. If you stop taking the tablets too soon, the infection may return, your condition may get worse or the bacteria may become resistant to the medicine. If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. These effects are normally mild or moderate and often disappear after a short time.
Stop taking Levofloxacin Tablets and see a doctor or go to a hospital straight away if you
notice the following side effect:
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- You have an allergic reaction. The signs may include: a rash, swallowing or breathing problems, swelling of your lips, face, throat, or tongue
Stop taking Levofloxacin Tablets and see a doctor straight away if you notice any of the following serious side effects - you may need urgent medical treatment:
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- Watery diarrhoea which may have blood in it, possibly with stomach cramps and a high temperature. These could be signs of a severe bowel problem
- Pain and inflammation in your tendons or ligaments, which could lead to rupture. The
- Achilles tendon is affected most often
- Fits (convulsions)
- Widespread rash, high body temperature, liver enzyme elevations, blood abnormalities (eosinophilia), enlarged lymph nodes and other body organs involvement (Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms which is also known as DRESS or drug hypersensitivity syndrome).
- Syndrome associated with impaired water excretion and low levels of sodium (SIADH)
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- Burning, tingling, pain or numbness. These may be signs of something called ‘neuropathy’
Other:
Loss of appetite, skin and eyes becoming yellow in colour, dark-coloured urine, itching, or tender stomach (abdomen). These may be signs of liver problems which may include a fatal failure of the liver
Not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data) Serious skin rashes including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. These can appear as reddish target-like macules or circular patches often with central blisters on the trunk, skin peeling, ulcers of mouth, throat, nose, genitals and eyes and can be preceded by fever and flu-like symptoms. If your eyesight becomes impaired or if you have any other eye disturbances whilst taking Levofloxacin Tablets, consult an eye specialist immediately.
Tell your doctor if any of the following side effects gets serious or lasts longer than a few days:
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Sleeping problems
- Headache, feeling dizzy
- Feeling sick (nausea, vomiting) and diarrhoea
- Increase in the level of some liver enzymes in your blood
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Changes in the number of other bacteria or fungi, infection by fungi named Candida, which may need to be treated
- Changes in the number of white blood cells shown up in the results of some blood tests (leukopenia, eosinophilia)
- Feeling stressed (anxiety), feeling confused, feeling nervous, feeling sleepy, trembling, a spinning feeling (vertigo)
- Shortness of breath (dyspnoea)
- Changes in the way things taste, loss of appetite, stomach upset or indigestion (dyspepsia), pain in your stomach area, feeling bloated (flatulence) or constipation
- Itching and skin rash, severe itching or hives (urticaria), sweating too much (hyperhidrosis)
- Joint pain or muscle pain
- Blood tests may show unusual results due to liver (bilirubin increased) or kidney (creatinine increased) problems
- General weakness
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- Bruising and bleeding easily due to a lowering in the number of blood platelets (thrombocytopenia)
- Low number of white blood cells (neutropenia)
- Exaggerated immune response (hypersensitivity)
- Lowering of your blood sugar levels (hypoglycaemia). This is important for people that have diabetes.
- Seeing or hearing things that are not there (hallucinations, paranoia), change in your opinion and thoughts (psychotic reactions) with a risk of having suicidal thoughts or actions
- Feeling depressed, mental problems, feeling restless (agitation), abnormal dreams or nightmares
- Tingly feeling in your hands and feet (paraesthesia)
- Problems with your hearing (tinnitus) or eyesight (blurred vision)
- Unusual fast beating of your heart (tachycardia) or low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Muscle weakness. This is important in people with myasthenia gravis (a rare disease of the nervous system).
- Changes in the way your kidney works and occasional kidney failure which may be due to an allergic kidney reaction called interstitial nephritis.
- Fever, Sharply demarcated, erythematous patches with/without blistering that develop within hours of administration of levofloxacin and heals with postinflammatory residual hyperpigmentation; it usually recurs at the same site of the skin or mucous membrane upon subsequent exposure to levofloxacin
Other side effects include:
- Lowering in red blood cells (anemia): this can make the skin pale or yellow due to damageb of the red blood cells; lowering in the number of all types of blood cells (pancytopenia)
- Fever, sore throat and a general feeling of being unwell that does not go away. This may be due to a lowering in the number of white blood cells (agranulocytosis).
- Loss of circulation (anaphylactic like shock)
- Increase of your blood sugar levels (hyperglycaemia) or lowering of your blood sugar levels leading to coma (hypoglycaemic coma). This is important for people that have diabetes.
- Changes in the way things smell, loss of smell or taste (parosmia, anosmia, ageusia)
- Problems moving and walking (dyskinesia, extrapyramidal disorders)
- Temporary loss of consciousness or posture (syncope)
- Temporary loss of vision
- Impairment or loss of hearing
- Abnormal fast heart rhythm, life-threatening irregular heart rhythm including cardiac arrest, alteration of the heart rhythm (called ‘prolongation of QT interval’, seen on ECG, electrical activity of the heart)
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing (bronchospasm)
- Allergic lung reactions Pancreatitis
- Inflammation of the liver (hepatitis)
- Increased sensitivity of your skin to sun and ultraviolet light (photosensitivity)
- Inflammation of the vessels that carry blood around your body due to an allergic reaction (vasculitis)
- Inflammation of the tissue inside the mouth (stomatitis)
- Muscle rupture and muscle destruction (rhabdomyolysis)
- Joint redness and swelling (arthritis)
- Pain, including pain in the back, chest and extremities
- Attacks of porphyria in people who already have porphyria (a very rare metabolic disease)
- Persistent headache with or without blurred vision (benign intracranial hypertension)
Very rare cases of long lasting (up to months or years) or permanent adverse drug reactions, such as tendon inflammations, tendon rupture, joint pain, pain in the limbs, difficulty in walking, abnormal sensations such as pins and needles, tingling, tickling, burning, numbness or pain (neuropathy), depression, fatigue, sleep disorders, memory impairment, as well as impairment of hearing, vision, and taste and smell have been associated with administration of quinolone and fluoroquinolone antibiotics, in some cases irrespective of pre-existing risk factors.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top right end of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store LOTOR®
This medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and blister strip after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
LOTOR®
Each vial contains:
Each film coated tablet contains:
Levofloxacin Hemihydrate IP
equivalent to Levofloxacin 500 mg.
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Titanium Dioxide IP.