Maxiliv Injection
Therapy Area
Gastrointestinal
1.0 Generic name
Glutathione for injection 600 mg/via
2.0 Quantitative and qualitative composition
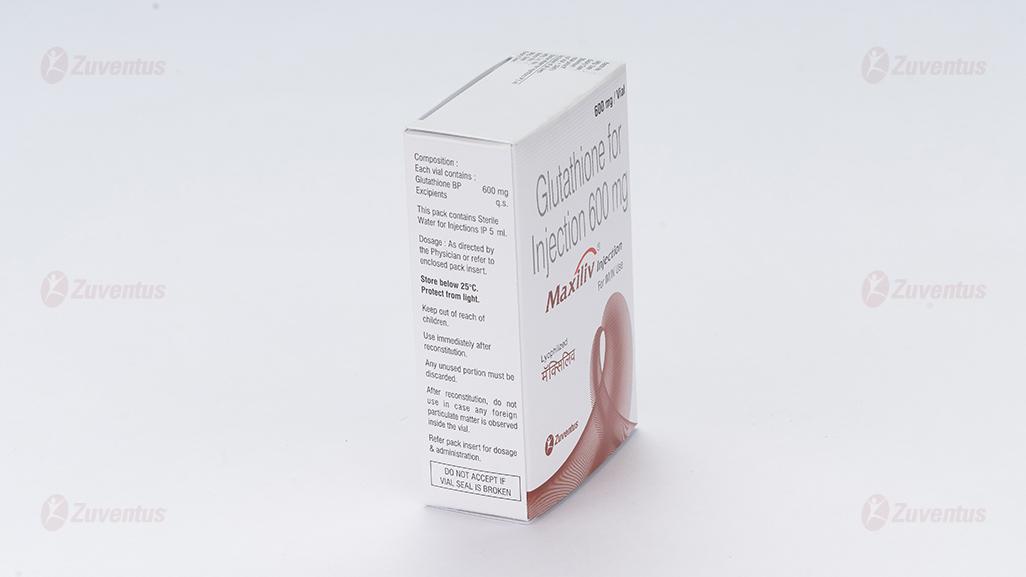
Each vial contains :
Glutathione BP 600 mg
Excipients q.s.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Injection 600 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
- Alcoholic fatty liver
- Alcoholic liver fibrosis
- Alcoholic liver cirrhosis
- Alcoholic hepatitis
- As an add-on to the standard of care in moderate COVID-19 patients
4.2 Posology & method of administration Alcoholic fatty liver, Alcoholic liver fibrosis, Alcoholic liver cirrhosis, Alcoholic hepatitis
The dose of Glutathione injection is dependent on the severity of the disease. In mild to moderate disease : 300 mg to 600 mg daily by slow intramuscular or intravenous injection.
Intravenous drip : Dissolve with 5 ml sterile water for injections; the solution is further diluted into 250 ml or 500 ml with normal saline or 5% glucose solution for intravenous infusion respectively.
Intramuscular injection : Dissolve with 5 ml sterile water for injections. Inject the solution intramuscularly, preferably in the gluteal region.
As an add-on to the standard of care in moderate COVID19 patients
Loading dose : 4 vials of Glutathione (600 mg x 4) followed by.
Maintenance dose : 2 vials (600 mg x 2) every 12 hourly as intravenous injection for maximum of 7 days or earlier till the clinical improvement
4.3 Contraindications
Glutathione injection is contraindicated in the patients who show hypersensitivity to reduced Glutathione.
4.4 Warning And precautions
• Administer Glutathione injection under the supervision of a doctor.
• Keep out of reach of children.
• Administer Glutathione injection intramuscularly only when the need arises. Avoid injecting at the same site repeatedly.
• The products for parenteral use should be visually inspected before administration, in order to detect the presence of particles or an abnormal colour. Do not use in case of turbidity or precipitates.
• Use immediately after reconstitution
4.5 Drug interactions
Vitamin K, Vitamin B12, Calcium pantothenate, and antihistamines can affect the bioavailability of Glutathione.
4.6 Special populations
Pregnancy And Lactation
Glutathione injection should not be administered to a pregnant and lactating woman unless the clinical benefit outweighs the risks.
Pediatric
Glutathione injection should be used with caution in neonates, premature infants, and children, especially when it is administered by intramuscular injection.
Geriatric
For elderly patients, appropriate dose reduction and strict monitoring is required during therapy
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
4.8 Undesirable effects
After intramuscular administration of Glutathione, rare instances of skin rash have been reported which have disappeared after discontinuation of treatment. Mild pain at the injection site has also been reported. As is the case with all intravenous infusions, febrile reactions, infections at the site of injection, venous thrombosis or phlebitis and extravasation may occur.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
No adverse events have been reported after Glutathione intravenous infusion up to 50 mg/kg dosage. No specific antidote is available for the treatment of Glutathione overdosage. Symptomatic treatment should be provided.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Glutathione is an extremely important cell protectant which directly quenches reactive hydroxyl free radicals, other oxygen-centered free radicals, and radical centers on DNA and other biomolecules. It is an essential cofactor for many enzymes which require thiol-reducing equivalents, and helps to keep redox-sensitive active sites on enzymes in the necessary reduced state. Higher-order thiol cell system like metallothioneins, thioredoxins, and other redox regulator proteins are ultimately regulated by reduced form of Glutathione (GSH) levels and the ratio of GSH / GSSG (oxidized GSH). GSH / GSSG balance is crucial for homeostasis, stabilizing cellular biomolecular spectrum, and facilitating cellular performance and survival.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Glutathione (GSH) and its metabolites also interface with energetics and neurotransmitter synthesis, through several prominent metabolic pathways. GSH availability downregulates the pro-inflammatory potential of leukotrienes and other eicosanoids. Recently discovered S-nitroso metabolites generated in-vivo from GSH and NO (Nitric Oxide) further diversity GSH’s impact on metabolism.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Af 2 ter intravenous infusion of 2 g/m of Glutathione, the plasma concentration increases from an average of 6.9 mmol/L to a peak plasma concentration of approximately 334mmol/L. The volume of distribution is approximately 15 L, plasma half-life is approximately 10 minutes, 2 and the average clearance rate is 850 ml/mint/m . After 90 minutes of the first infusion, urinary excretion Glutathione and cysteine increases by 300% and 10% respectively. In addition, after high-dosage intravenous administration (50 mg/kg of body weight), Glutathione shows the following pharmacokinetic parameters in healthy volunteers.
| Parameters | Values |
| Cmax | 1205.8 μM |
| AUC | 12427 μM.min |
| t1/2 | 10.9 min |
| Vd | 0.152 L/kg |
After intramuscular injection, Glutathione reaches peak plasma concentration within 5 hours. Data shows that Glutathione is well distributed in all the organs within a short period of time, with higher concentration in liver, kidney and spleen then in other organs. While the distribution (measured in unit body weight) of GSH in hearts skeletal muscle and brain is not as high as in other organs, the excretion of GSH via these organs is slower. 7 days after the injection, 24 ± 4.2 % of the GSH is excreted in the urine
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
No known animal toxicology data
7.0 Description
Glutathione (GSH) is a physiological tripeptide- a chain of three amino acid- cysteine, glycine and glutamic acid. It is used for the detoxification of electrophilic metabolites. It is a very efficient free radical scavenger, preventing damage to important cellular components caused by reactive oxygen species such as free radicals and peroxides.
Chemical Name : (2S) -2- Amino-4-[1- (carboxymethyl) carbamoyl-(2R)-2-sulfanylethylcarbamoyl] butanoic acid.
Molecular Formula : C10H17N3O6S
Molecular Weight : 307.32 g/mol
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf Life
Refer on the pack
8.3 Packaging information
A vial of 600 mg with SWFI IP 5 ml.
8.4 Storage and handing Instructions Store below 25°C. Protect from light.
Keep out of reach of children.
After reconstitution, do not use in case any foreign particulate matter is observed inside the vial.
9.0 Patient counselling information
• Not to exceed the stated recommended daily dose.
• In case of overdosage, consult your physician.
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
What is in this leaflet
- What Maxiliv Injection is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Maxiliv Injection
- How to use Maxiliv Injection
- Possible side effects
- How to store Maxiliv Injection
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Maxiliv Injection is and what it is used for
Maxiliv contains Glutathione, used for treating alcoholic liver conditions and as an add-on in moderate COVID-19 cases
2. What you need to know before you use Maxiliv Injection
Do not use Maxiliv Injection if you are allergic to it.
Warnings and precautions
- Only a doctor should give you this injection.
- Keep it away from children.
- Use intramuscular injections only when necessary, and don’t inject in the same spot every time.
- Check the liquid before using it. Don’t use it if it looks cloudy or has particles in it.
- Use the injection right after mixing it.
Other medicines and Maxiliv Injection
Some vitamins and allergy medicines can change how well Glutathione works in your body.
Always check with your doctor or pharmacist before starting any new medicine while using Maxiliv Injection.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
This injection should only be used if your doctor thinks the benefits are greater than the risks.
Children
Use this injection carefully in new-borns, premature babies, and children—especially if it’s given into a muscle.
Older adults
Older people may need a lower dose and should be closely monitored during treatment.
3. How to take Maxiliv Injection
For liver conditions (like alcoholic fatty liver, fibrosis, cirrhosis, or hepatitis):
- The dose depends on how serious the condition is.
- For mild to moderate cases: 300 mg to 600 mg once a day.
- It can be given slowly into a muscle or through a vein.
If given through a vein (IV drip):
- Mix the medicine with 5 ml of sterile water.
- Then dilute it further with 250 ml or 500 ml of saline or 5% glucose solution before giving it as a drip.
If given into a muscle (IM injection):
- Mix the medicine with 5 ml of sterile water.
- Inject it into a muscle, preferably in the buttocks.
For moderate COVID-19 patients (as extra support along with regular treatment):
- Starting dose: 4 vials (600 mg each).
- Follow-up dose: 2 vials (600 mg each) every 12 hours.
- Continue for up to 7 days or until the patient gets better.
If you use more Maxiliv Injection than you should
Tell your doctor if you accidentally use more than you were told.
If you stop using Maxiliv Injection
Do not stop your treatment even if you feel better unless told to do so by your doctor.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Skin rash, injection site pain. Febrile reactions, infections, thrombosis, phlebitis, extravasation.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page. Website link: https://www.zuventus.co.in/drug-safety-reporting.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Maxiliv Injection
Store below 25°C. Protect from light.
Keep out of reach of children.
After reconstitution, do not use in case any foreign particulate matter is observed inside the vial.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Maxiliv Injection contains:
Each pack contains a vial of 600 mg Glutathione with 5 ml sterile water for injection.
Pack size: Injection 600 mg/Vial
Revised on 07/25