Maxstine Tablets
Therapy Area
Respiratory
1.0 Generic Name
bilastine
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
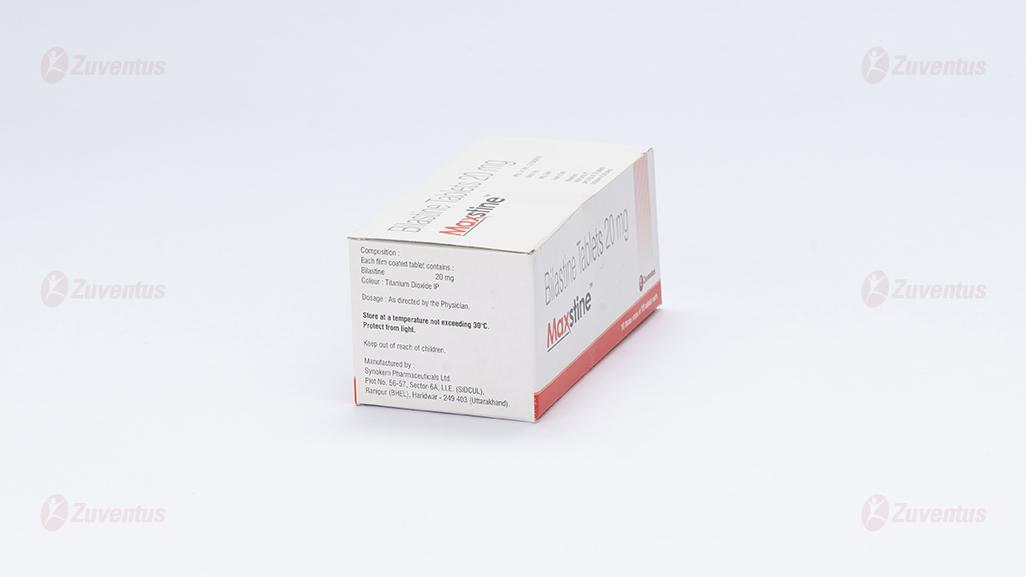
Each film coated tablet contains:
Bilastine 20 mg
Excipients q.s.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Tablet
Bilastine 20mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic Indication
For symptomatic treatment of allergic rhino-conjunctivitis (seasonal and perennial) and urticaria in adults.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adults and adolescents (12 years of age and over)
20 mg bilastine (1 tablet) once daily for the relief of symptoms of allergic rhinoconjunctivitis (SAR and PAR) and urticaria.
The tablet should be taken one hour before or two hours after intake of food or fruit juice
Duration of treatment
For allergic rhino-conjunctivitis the treatment should be limited to the period of exposure to allergens. For seasonal allergic rhinitis treatment could be discontinued after the symptoms have resolved and reinitiated upon their reappearance. In perennial allergic rhinitis continued treatment may be proposed to the patients during the allergen exposure periods. For urticaria the duration of treatment depends on the type, duration and course of the complaints.
Special populations
Elderly
No dosage adjustments are required in elderly patients.
Renal impairment
Studies conducted in adults in special risk groups (renally impaired patients) indicate that it is not necessary to adjust the dose of Bilastine in adults.
Hepatic impairment
There is no clinical experience in adult patients with hepatic impairment. However, since Bilastine is not metabolized and is eliminated as unchanged in urine and faeces, hepatic impairment is not expected to increase systemic exposure above the safety margin in adult patients. Therefore, no dosage adjustment is required in adult patients with hepatic impairment.
Paediatric population
Children 6 to 11 years of age with a body weight of at least 20 kg
Bilastine 10 mg orodispersible tablets and Bilastine 2.5 mg/mL oral solution are appropriate for administration to this population.
Children under 6 years of age and under 20 kg
Bilastine should not be used in this age group
The safety and efficacy of Bilastine in renally and hepatically impaired children have not been established.
Method of administration
Oral use.
The tablet is to be swallowed with water. It is recommended to take the daily dose in one single intake.
4.3 Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in the formulation
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use Paediatric population
Efficacy and safety of Bilastine in children under 2 years of age have not been established and there is little clinical experience in children aged 2 to 5 years, therefore Bilastine should not be used in these age groups. In patients with moderate or severe renal impairment co-administration of Bilastine with P-glycoprotein inhibitors, such as e.g., Ketoconazole, Erythromycin, Cyclosporine, Ritonavir or Diltiazem, may increase plasmatic levels of Bilastine and therefore increase the risk of adverse effects of Bilastine. Therefore, co-administration of Bilastine and P-glycoprotein inhibitors should be avoided in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Interaction studies have only been performed in adults and are summarised below
Interaction with food
Food significantly reduces the oral bioavailability of Bilastine by 30%
Interaction with grapefruit juice
Concomitant intake of Bilastine 20 mg and grapefruit juice decreased Bilastine bioavailability by 30%. This effect may also apply to other fruit juices. The degree of bioavailability decrease may vary between producers and fruits. The mechanism for this interaction is an inhibition of OATP1A2, an uptake transporter for which Bilastine is a substrate. Medicinal products that are substrates or inhibitors of OATP1A2, such as ritonavir or rifampicin, may likewise have the potential to decrease plasma concentrations of Bilastine. Interaction with Ketoconazole or Erythromycin Concomitant intake of Bilastine 20 mg o.d. and Ketoconazole 400 mg o.d. or Erythromycin 500 mg t.i.d. increased Bilastine AUC 2-fold and Cmax 2-3 fold. These changes can be explained by interaction with intestinal efflux transporters, since Bilastine is substrate for P-gp and not metabolised. These changes do not appear to affect the safety profile of Bilastine and ketoconazole or erythromycin, respectively. Other medicinal products that are substrates or inhibitors of P-gp, such as cyclosporine, may likewise have the potential to increase plasma concentrations of Bilastine.
Interaction with Diltiazem
Concomitant intake of Bilastine 20 mg o.d. and Diltiazem 60 mg o.d. increased Cmax of Bilastine by 50%. This effect can be explained by interaction with intestinal efflux transporters, and does not appear to affect the safety profile of Bilastine.
Interaction with Alcohol
The psychomotor performance after concomitant intake of alcohol and 20 mg Bilastine o.d. was similar to that observed after intake of alcohol and placebo.
Interaction with Lorazepam
Concomitant intake of Bilastine 20 mg o.d. and Lorazepam 3 mg o.d. for 8 days did not potentiate the depressant CNS effects of Lorazepam.
Paediatric population
Interaction studies have only been performed in adults. As there is no clinical experience regarding the interaction of Bilastine with other medicinal products, food or fruit juices in children, the results obtained in adult interactions studies should be at present taken into consideration when prescribing Bilastine to children. There are no clinical data in children to state whether changes to the AUC or Cmax due to interactions affect the safety profile of Bilastine.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
There are no or limited amount of data from the use of Bilastine in pregnant women.
Animal studies do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to reproductive toxicity, parturition or postnatal development. As a precautionary measure, it is preferable to avoid the use of Maxstine during pregnancy.
Breast-feeding
The excretion of Bilastine in milk has not been studied in humans. Available pharmacokinetic data in animals have shown excretion of Bilastine in milk. A decision on whether to continue/discontinue breast-feeding or to discontinue/abstain from Maxstine therapy must be made taking into account the benefit of breast-feeding for the child and the benefit of Bilastine therapy for the mother.
Fertility
There are no or limited amount of clinical data. A study in rats did not indicate any negative effect on fertility
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
A study performed in adults to assess the effects of Bilastine on the ability to drive demonstrated that treatment with 20 mg did not affect the driving performance. However, as the individual response to the medicinal product may vary, patients should be advised not to drive or use machines until they have established their own response to Bilastine.
4.8 Undesirable effects
The ADRs most commonly reported by patients (N = 2525) during the clinical development receiving 20 mg Bilastine for the indication of allergic rhinoconjunctivitis or chronic idiopathic urticaria were headache, somnolence, dizziness, and fatigue.
These adverse events occurred with a comparable frequency in patients receiving placebo.
Frequencies are assigned as follows : Very common (≥ 1/10), Common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10), Uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to < 1/100), Rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000), Very rare (< 1/10,000) Not known (cannot be estimated from the available data)
ADRs at least possibly related to Bilastine and reported in more than 0.1% of the patients receiving 20 mg Bilastine during the clinical development (N = 1697) are listed below.
Infections and infestations
Uncommon - Oral herpes.
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Uncommon - Increased appetite.
Psychiatric disorders
Uncommon - Anxiety, Insomnia
Nervous system disorders
Common - Somnolence, Headache.
Uncommon- Dizziness.
Ear and labyrinth disorders
Uncommon - Tinnitus, Vertigo.
Cardiac disorders
Uncommon - Right bundle branch block, Sinus arrhythmia, Electrocardiogram QT prolonged.
Respiratory disorders
Uncommon - Dyspnoea, Nasal discomfort, Nasal dryness.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Uncommon - Nausea, Stomach, Discomfort Abdominal pain, Diarrhoea Dry
Mouth, Dyspepsia, Gastritis.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Uncommon - Pruritus.
General disorders
Uncommon - Fatigue, Thirst, Pyrexia, Asthenia.
Investigations
Uncommon - Increased gammaglutamyltransferase, increased ALT and AST, increased Blood creatinine, increased Blood TG, Increased weight.
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data)
Palpitations, Tachycardia, Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. Anaphylaxis, Angioedema, Rash, Oedema/local swelling and Erythema) and vomiting have been observed during the post-marketing period.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Information regarding acute overdose of Bilastine is retrieved from the experience of clinical trials conducted during the development and the postmarketing surveillance. In clinical trials, after administration of Bilastine at doses 10 to 11 times the therapeutic dose (220 mg as single dose; or 200 mg/day for 7 days) to 26 adult healthy volunteers frequency of treatment emergent adverse events was two times higher than with placebo. The adverse reactions most frequently reported were dizziness, headache and nausea. No serious adverse events and no significant prolongation in the QTc interval were reported. The information collected in the post-marketing surveillance is consistent with that reported in clinical trials.
Critical evaluation of Bilastine ‘S multiple dose (100 mg x 4 days) effect on ventricular repolarization by a “thorough QT/QTc cross-over study” involving 30 healthy adult volunteers did not show significant QTc prolongation. There are no data for overdose in children.
In the event of overdose symptomatic and supportive treatment is recommended.
There is no known specific antidote to Bilastine.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Bilastine is a non-sedating, long-acting histamine antagonist with selective peripheral H1 receptor antagonist affinity and no affinity for muscarinic receptors. Bilastine inhibited histamine-induced wheal and flare skin reactions for 24 hours following single doses.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
In clinical trials performed in adult and adolescent patients with allergic rhinoconjunctivitis (seasonal and perennial), Bilastine 20 mg, administered once daily for 14 - 28 days, was effective in relieving symptoms such as sneezing, nasal discharge, nasal itching, nasal congestion, ocular itching, tearing and ocular redness. Bilastine effectively controlled symptoms for 24 hours. In chronic idiopathic urticaria patients, Bilastine 20 mg once daily for 28 days was effective in relieving the itching intensity and the number and size of wheals, as well as the patient's discomfort due to urticaria. Patients improved their sleep conditions and their quality of life.
No clinically relevant prolongation of QTc interval or any other cardiovascular effect has been observed in the clinical trials performed with Bilastine, even at doses of 200 mg daily (10 times the clinical dose) for 7 days in 9 subjects, or even when co-administered with P-gp inhibitors, such as ketoconazole (24 subjects) and erythromycin (24 subjects). Additionally, a thorough QT study including 30 volunteers has been performed.
In clinical trials at 20 mg once daily dose, the CNS safety profile of Bilastine was similar to placebo and the incidence of somnolence was not statistically different from placebo. Bilastine at doses of up to 40 mg q.d. did not affect psychomotor performance in clinical trials and did not affect driving performance in a standard driving test.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Bilastine is rapidly absorbed after oral administration with a time to maximum plasma concentration of around 1.3 hours. No accumulation was observed. The mean value of Bilastine oral bioavailability is 61%.
Distribution
In vitro and in vivo studies have shown that Bilastine is a substrate of P-gp and OATP. Bilastine does not appear to be a substrate of the transporter BCRP or renal transporters OCT2, OAT1 and OAT3. Based on in vitro studies, Bilastine is not expected to inhibit the following transporters in the systemic circulation : P-gp, MRP2, BCRP, BSEP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OATP2B1, OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, OCT2, and NTCP, since only mild inhibition was detected for P-gp, OATP2B1 and OCT1, with an estimated IC50 ≥ 300 µM, much higher than the calculated clinical plasma Cmax and therefore these interactions will not be clinically relevant. However, based on these results inhibition by Bilastine of transporters present in the intestinal mucosa, e.g. P-gp, cannot be excluded. At therapeutic doses Bilastine is 84 - 90% bound to plasma proteins.
Biotransformation
Bilastine did not induce or inhibit activity of CYP450 isoenzymes in vitro studies.
Elimination
In a mass balance study performed in healthy adult volunteers, after administration of a single dose of 20 mg 14C-bilastine, almost 95% of the administered dose was recovered in urine (28.3%) and faeces (66.5%) as unchanged Bilastine, confirming that Bilastine is not significantly metabolized in humans. The mean elimination half-life calculated in healthy volunteers was 14.5 h.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
Non-clinical data with Bilastine reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity and carcinogenic potential.
In reproduction toxicity studies effects of Bilastine on the foetus (pre-and postimplantation loss in rats and incomplete ossification of cranial bones, sternebrae and limbs in rabbits) were only observed at maternal toxic doses. The exposure levels at the NOAELs are sufficiently in excess (> 30 fold) to the human exposure at the recommended therapeutic dose.
In a lactation study, Bilastine was identified in the milk of nursing rats administered a single oral dose (20 mg/kg). Concentrations of Bilastine in milk were about half of those in maternal plasma. The relevance of those results for humans is unknown.
In a fertility study in rats, Bilastine administered orally up to 1000 mg/kg/day did not induce any effect on female and male reproductive organs. Mating, fertility and pregnancy indices were not affected.
As seen in a distribution study in rats with determination of drug concentrations by autoradiography, Bilastine does not accumulate in the CNS.
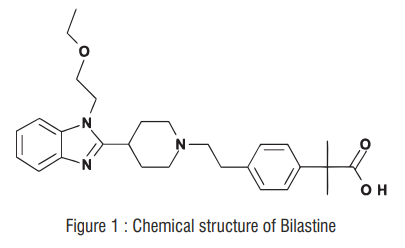
7.0 Description
Bilastine (Figure 1) is a novel, benzimidazole–piperidine derivative that is a highly selective second-generation H1 antihistamine.
Molecular formula : C28H37N3O3
Molecular weight : 463.622 g/mol
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
No incompatibility study have been found.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
Alu-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30°C. Protect from light.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient counselling information
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription. In particular, please discuss with your doctor if you are taking any of the following medicines :
• Ketoconazole (an antifungal medicine)
• Erythromycin (an antibiotic)
• Diltiazem (to treat angina)
• Cyclosporine (to reduce the activity of your immune system, thus avoiding transplant rejection or reducing disease activity in autoimmune and allergic disorders, such as psoriasis, atopic dermatitis or rheumatoid arthritis)
• Ritonavir (to treat AIDS)
• Rifampicin (an antibiotic)
Maxstine with food, drink and alcohol
These tablets should not be taken with food or with grapefruit juice or other fruit juices, as this will decrease the effect of Bilastine. To avoid this, you can :
• Take the tablet and wait for one hour before taking food or fruit juice or
• If you have taken food or fruit juice, wait for two hours before taking the tablet.
Bilastine, at the recommended dose (20 mg), does not increase the drowsiness produced by Alcohol.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for your child. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even
- if their signs of illness are the same as your child’s.
- If your child gets any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side
- effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1. What MAXSTINE is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you take MAXSTINE
3. How to take MAXSTINE
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store MAXSTINE
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What MAXSTINE is and what it is used for
MAXSTINE contains the active substance bilastine which is an antihistamine. MAXSTINE is used to relieve the symptoms of hayfever (sneezing, itchy, runny, blocked-up nose and red and watery eyes) and other forms of allergic rhinitis. It may also be used to treat itchy skin rashes (hives or urticaria).
MAXSTINE 20 mg tablet is indicated in adults and adolescents (12 years and over)
2. What you need to know before you take MAXSTINE 20 mg tablets
Do not take MAXSTINE
if you are allergic to bilastine or any of the other ingredients of this medicine
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before using MAXSTINE if you have moderate or severe renal impairment and in addition you are taking other medicines (see “Other medicines and MAXSTINE”).
Children
Do not give this medicine to children under 12 years of age. Do not exceed the recommended dose. If symptoms persist, consult your doctor.
Other medicines and MAXSTINE
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription.
In particular, please discuss with your doctor if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- Ketoconazole (an antifungal medicine)
- Erythromycin (an antibiotic)
- Diltiazem (to treat angina)
- Cyclosporine (to reduce the activity of your immune system, thus avoiding transplant rejection or reducing disease activity in autoimmune and allergic disorders, such as psoriasis, atopic dermatitis or rheumatoid arthritis)
- Ritonavir (to treat AIDS)
- Rifampicin (an antibiotic)
MAXSTINE with food, drink and alcohol
These tablets should not be taken with food or with grapefruit juice or other fruit juices, as this will decrease the effect of bilastine. To avoid this, you can:
- take the tablet and wait for one hour before taking food or fruit juice or
- if you have taken food or fruit juice, wait for two hours before taking the tablet.
Bilastine, at the recommended dose (20 mg), does not increase the drowsiness produced by alcohol.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
There are no or limited amount of data from the use of bilastine in pregnant women and during breast-feeding and on the effects on fertility.
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
It has been demonstrated that bilastine 20 mg does not affect the driving performance in adults. However, the response from each patient to the medicine may be different.
Therefore, you should check how this medicine affects you, before driving or operating machinery.
3. How to take MAXSTINE
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist have told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
The recommended dose in adults, including the elderly and adolescents aged 12 years and over, is 1 tablet (20 mg) a day.
- The tablet is for oral use.
- The tablet must be taken one hour before or two hours after intake of food or fruit juice (see section 2, MAXSTINE with food, drink and alcohol”).
- Swallow your tablet with a glass of water.
Regarding the duration of treatment, your physician will determine the type of disease you are suffering from and will determine for how long you should take MAXSTINE.
Use in children
Other forms of this medicine - oral solution - may be more suitable for children 6 to 11 years of age with a body weight of at least 20 kg ask your doctor or pharmacist. Do not give this medicine to children under 6 years of age with a body weight below 20 kg since no sufficient data are available.
If you take more MAXSTINE than you should
If you, or anyone else, have taken too many MAXSTINE tablets, contact your doctor or pharmacist immediately or go to the emergency department of your nearest hospital.
Please remember to take this medicine pack or this leaflet with you.
If you forget to take MAXSTINE
Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you forget to take your dose on time, take it as soon as possible, and then go back to your regular dosing schedule.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. If you experience symptoms of an allergic reaction the signs of which may include difficulty in breathing, dizziness, collapsing or losing consciousness, swelling of your face, lips, tongue or throat, and/or swelling and redness of the skin, stop taking the medicine and seek urgent medical advice straight away.
Other side effects that may be experienced in adults and adolescents are:
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- Headache
- Drowsiness
- Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- abnormal ECG heart tracing
- blood tests which show changes in the way the liver is working
- dizziness
- stomach pain
- tiredness
- increased appetite
- irregular heartbeat
- increased weight
- nausea (the feeling of being sick)
- anxiety
- dry or uncomfortable nose
- belly pain
- diarrhoea
- gastritis (inflammation of the stomach wall)
- vertigo (a feeling of dizziness or spinning)
- feeling of weakness
- thirst
- dyspnoea (difficulty in breathing )
- dry mouth
- indigestion
- itching
- cold sores (oral herpes)
- fever
- tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- difficulty in sleeping
- blood tests which show changes in the way kidney is working
- blood fats increased
Frequency not known: cannot be estimated from the available data
- palpitations (feeling your heart beat)
- tachycardia (fast heart beat)
- vomiting
Side effects that may be experienced in children are:
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- rhinitis (nasal irritation)
- allergic conjunctivitis (eye irritation)
- headache
- stomach pain (abdominal /upper abdominal pain)
Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- eye irritation
- dizziness
- loss of consciousness
- diarrhoea
- nausea (the feeling of being sick)
- lip swelling
- eczema
- urticaria (hives)
- fatigue
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top right end of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store MAXSTINE
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and the blisters after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Store below 30°C. Protected from light & moisture.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What MAXSTINE contains
Each film coated tablet contains:
Bilastine 20 mg
Excipients q.s.
© Zuventus Healthcare Ltd., 2020. All rights reserved.