Maxtra P Tablet
Therapy Area
Respiratory
1.0 Generic name
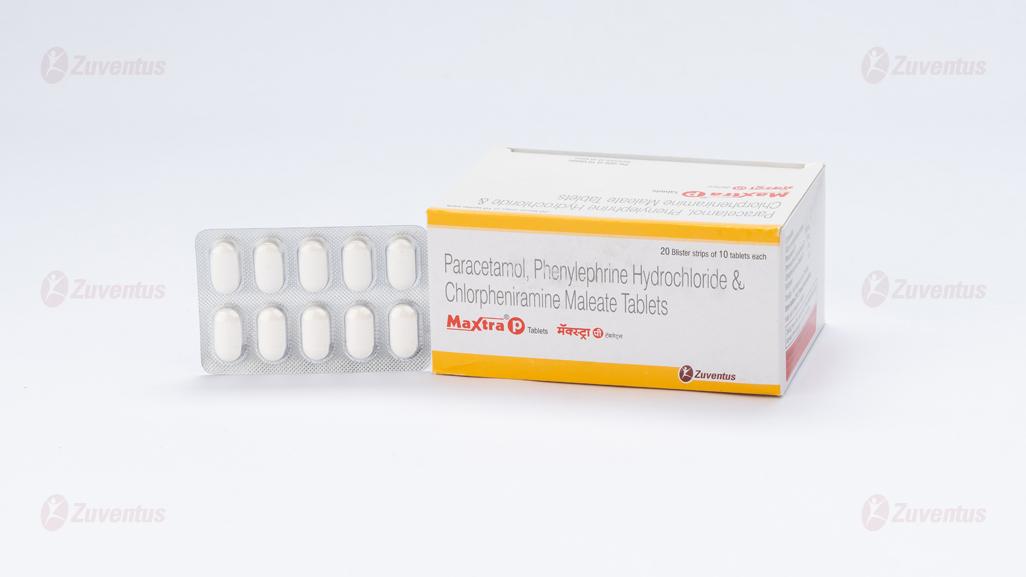
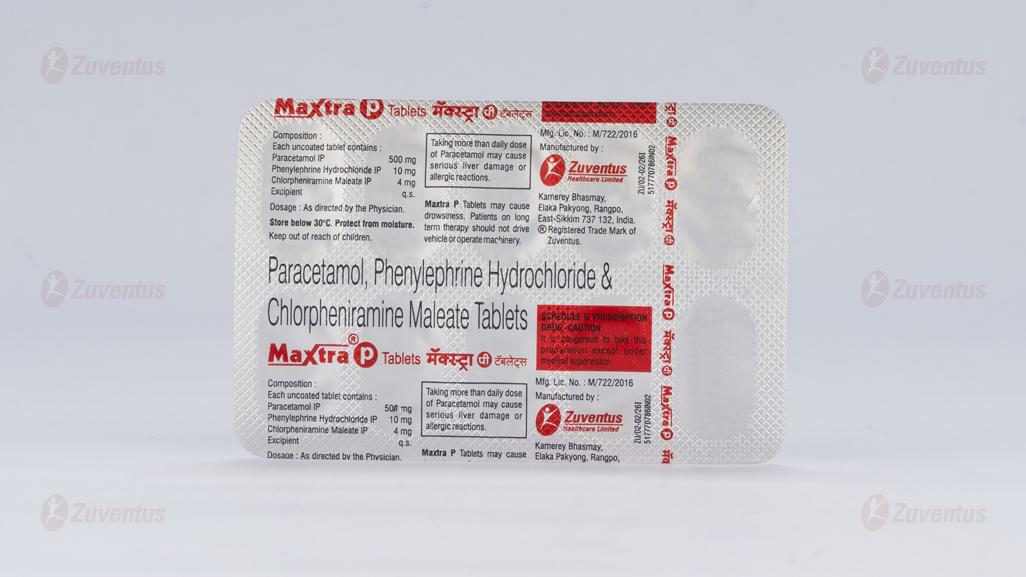
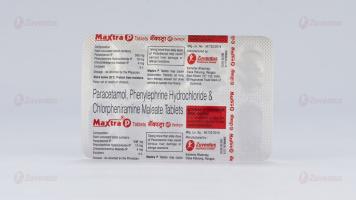
Paracetamol, Phenylephrine Hydrochloride & Chlorpheniramine Maleate Tablets
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
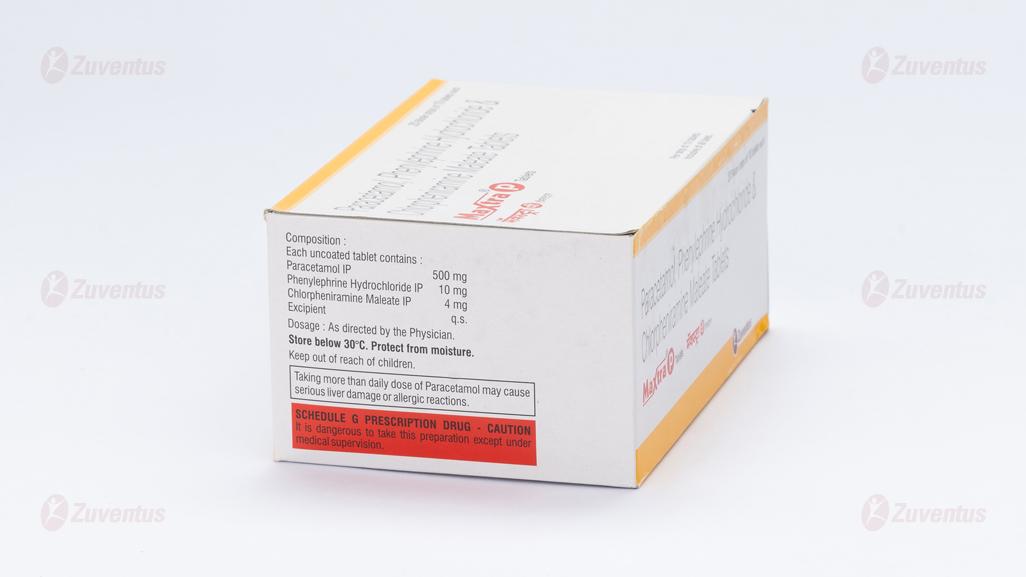
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Paracetamol IP 500 mg
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride IP 10 mg
Chlorpheniramine Maleate IP 4 mg
Excipient q.s.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Tablets, Paracetamol 500 mg, Phenylephrine Hydrochloride 10 mg and Chlorpheniramine Maleate 4 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For symptomatic treatment of common cold and flu-like syndrome.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adults and children 12 years of age and older : Take 1 tablet every 4 to 6 hours.
4.3 Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients of the formulation.
• Avoid in patients with cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, closed angle glaucoma, hyperthyroidism, prostatic enlargement and phaeochromocytoma.
• Taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), (certain drugs for depression, psychiatric or Parkinson’s disease), or for 2 weeks after stopping the MAOI drug.
• Patients with peripheral or mesenteric vascular thrombosis, because ischemia may be increased and the area of infarction extended with the use of Phenylephrine.
• Premature or full-term neonates.
• Patients with hepatocellular insufficiency and in patients with hepatic failure or active liver disease as the formulation contains Paracetamol.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Especially in infants and small children, antihistamines in overdosage may cause hallucinations, convulsions and death. Antihistamines may diminish mental alertness. In young children, they may produce excitation.
• General : This product should be used with caution in patients with a history of narrow-angle glaucoma, gastrointestinal obstruction, or urinary bladder neck obstruction (enlarged prostate), a breathing problem such as emphysema or chronic bronchitis.
• Because of its sympathomimetic component, this product should be used with caution in patients with diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, or thyroid disease.
• Care is advised in the administration of Paracetamol to patients with alcohol dependency and severe renal or severe hepatic impairment. The hazards of overdose are greater in those with noncirrhotic alcoholic liver disease. Do not exceed the recommended dose.
• If symptoms persist consult your doctor.
• Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
• Do not take with any other Paracetamol-containing products.
• Immediate medical advice should be sought in the event of an overdose, even if you feel well, because of the risk of delayed, serious liver damage.
4.5 Drugs interactions
• Avoid using with any other drug containing Acetaminophen.
• Avoid use if you are now taking monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) (drugs for depression, psychiatric, or emotional conditions, or Parkinson's disease), or for 2 weeks after stopping the MAOI drug.
• Anticoagulants : the effect of Warfarin and other coumarins may be enhanced by prolonged regular use of Paracetamol with increased risk of bleeding. Occasional doses have no significant effect.
• Metoclopramide, Domperidone : may increase speed of absorption of Paracetamol.
• Colestyramine : May reduce absorption if given within one hour of Paracetamol.
• Imatinib : restriction or avoidance of concomitant regular Paracetamol use should be taken with Imatinib.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy category C. It is not known whether this product can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. This product should be given to pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Labor and delivery
Use of sympathomimetic amines during late pregnancy or during labor may cause fetal anoxia and bradycardia by increasing contractibility of the uterus and decreasing uterine blood flow
Nursing mothers
Because of the higher risk of intolerance of antihistamines in infants in general, and in new-borns in particular, this product is contraindicated in nursing mothers
Pediatrics
The use of antihistamines is not recommended in new-borns and infants. This age group may be at a higher risk than others because of an increased susceptibility to anticholinergic effects such as CNS excitation, and an increased tendency toward convulsion. In older children, antihistamines may cause a paradoxical reaction characterized by hyperexcitability. Very young children may be more sensitive to the effects of sympathomimetics.
Geriatrics
The elderly (60 years or older) may be more susceptible to the vasopressor effects of sympathomimetics. Confusion, hallucinations, seizures and CNS depression may be more likely to occur in geriatric patients taking sympathomimetics. Antihistamines may cause confusion, dizziness, sedation, hypotension, hyperexcitability, and anticholinergic side effects such as dryness of the mouth and urinary retention in geriatric patients. If these symptoms occur and continue, or are severe, medication should probably be discontinued.
4.7 Effects on the ability to drive and use machines
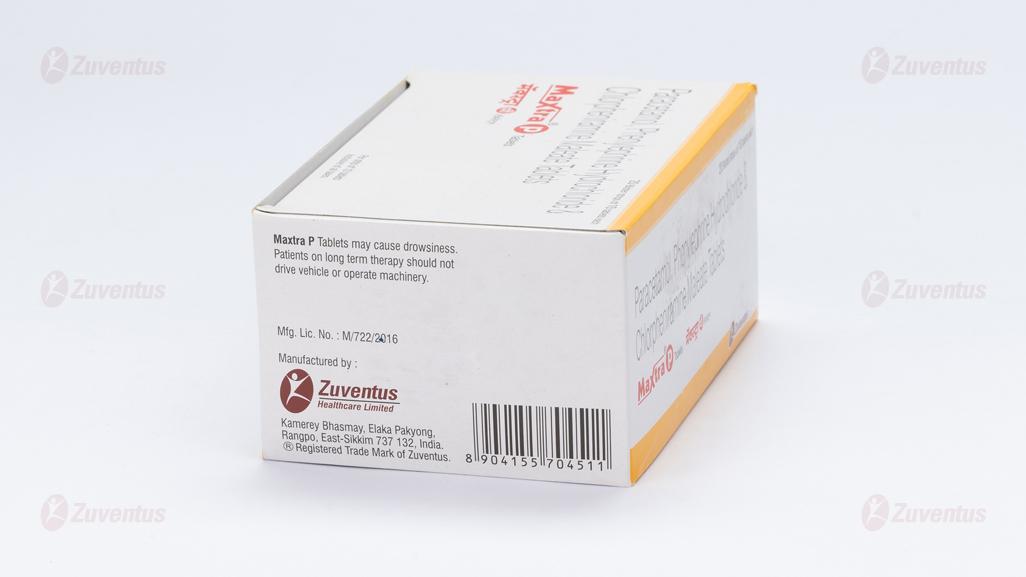
Maxtra P Tablet may decrease alertness, affect your vision or make you feel sleepy and dizzy. Do not drive if these symptoms occur.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Phenylephrine may cause restlessness, anxiety, nervousness, weakness, dizziness, precordial pain or discomfort, tremor, respiratory distress, pallor or blanching of the skin, or a pilomotor response. Over dosage of Phenylephrine may cause hypertension, headache, seizures, cerebral hemorrhage, palpitation, paresthesia, or vomiting. Phenylephrine can cause severe peripheral and visceral vasoconstriction, reduced blood flow to vital organs, decreased renal perfusion, and probably reduced urine output and metabolic acidosis. Severe vasoconstrictive effects may be most likely to occur in hypovolemic patients. Phenylephrine can cause severe bradycardia and decreased cardiac output
The adverse effects of Paracetamol include allergic dermatitis, angioedema, drug-induced hepatitis, hepatitis, leukopenia, maculopapular rash, fixed drug eruption, neutropenic disorder, thrombocytopenic disorder, urticaria, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, nausea, dyspepsia, and fatigue and chest pain.
Most common adverse effects of Chlorpheniramine are drowsiness and thick bronchial secretions. Other side effects include abdominal pain with cramps, allergic reactions, anorexia, blurred vision, dizziness, dry nose, dry throat, excitement, headache disorder, hyperhidrosis, impaired cognition, nervousness, nightmares, skin photosensitivity, skin rash etc.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit / risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Initiate general symptomatic and supportive measures in all cases of over dosages where necessary.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action / pharmacodynamic properties
Phenylephrine is sympathomimetic post-synaptic α1–adrenergic receptor agonist with low cardioselective beta receptor affinity and minimal central nervous stimulant activity. It is a recognised decongestant and acts by vasoconstriction to reduce oedema and nasal swelling.
Chlorpheniramine is a potent antihistamine (H1-antagonist).
Antihistamines diminish or abolish the actions of histamine in the body by competitive reversible blockade of histamine H1-receptor sites on tissues. Chlorpheniramine also has anticholinergic activity. Antihistamines act to prevent the release of histamine, prostaglandins and leukotrienes and have been shown to prevent the migration of inflammatory mediators. The actions of Chlorpheniramine include inhibition of histamine on smooth muscle, capillary permeability and hence reduction of oedema and wheal in hypersensitivity reactions such as allergy and anaphylaxis. Paracetamol may act predominantly by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis in the central nervous system (CNS) and to a lesser extent, through a peripheral action by blocking pain-impulse generation. The peripheral action may also be due to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis or to inhibition of the synthesis or actions of other substances that sensitise pain receptors to mechanical or chemical stimulation.
Antipyretic : Paracetamol probably produces antipyresis by acting centrally on the hypothalamic heat-regulation centre to produce peripheral vasodilation resulting in increased blood flow through the skin, sweating and heat loss. The central action probably involves inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis in the hypothalamus.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Paracetamol is readily absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract with peak plasma concentrations occurring about 30 minutes to 2 hours after ingestion. It is metabolised in the liver and excreted in the urine mainly as the glucuronide and sulfate conjugates. Less than 5% is excreted as unchanged Paracetamol. The elimination half-life varies from about 1 to 4 hours. Plasma-protein binding is negligible at usual therapeutic concentrations but increases with increasing concentrations.
A minor hydroxylated metabolite which is usually produced in very small amounts by mixed-function oxidases in the liver and which is usually detoxified by conjugation with liver glutathione may accumulate following Paracetamol over dosage and cause liver damage.
Phenylephrine is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, but has reduced bioavailability by the oral route due to first-pass metabolism. It retains activity as a nasal decongestant when given orally, the drug distributing through the systemic circulation to the vascular bed of the nasal mucosa. When taken by mouth as a nasal decongestant Phenylephrine is usually given at intervals of 4 - 6 hours. Chlorpheniramine is well absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract, following oral administration. The effects develop within 30 minutes, are maximal within 1 to 2 hours and last 4 to 6 hours. The plasma half-life has been estimated to be 12 to 15 hours. Chlorpheniramine is metabolised to the monodesmethyl and didesmethyl derivatives. About 22% of an oral dose is excreted unchanged in the urine.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
No studies have been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential of this product.
7.0 Description
Maxtra P tablet is a combination of anti-allergic Chlorpheniramine Maleate, analgesic/antipyretic Paracetamol and decongestant Phenylephrine Hydrochloride.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
PVC/PVDC-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets.
8.4 Storage and handling instructions
Store below 30°C. Protect from moisture.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient counselling information
• It may cause dizziness and sleepiness. Don't drive or do anything that requires mental focus until you know how it affects you.
• Avoid consuming alcohol when taking this medicine as it may cause excessive drowsiness.
• Do not take it with any other medicine containing Paracetamol (drugs for pain / fever or cough-and-cold) without asking your doctor first.
• Inform your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to conceive or breastfeeding.
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
In this leaflet:
1. What Maxtra-P Tablet is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you take Maxtra-P Tablet
3. How to take Maxtra-P Tablet
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store Maxtra-P Tablet
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Maxtra-P Tablet is and what it is used for
Maxtra-P Tablet contains a combination of ingredients which are effective in relieving the symptoms associated with colds and flu, including relief of aches and pains, sore throats, headache, nasal congestion and lowering of temperature.
Paracetamol is a painkiller and reduces your temperature when you have a fever.
Phenylephrine hydrochloride is a decongestant which unblocks your nose and sinuses helping you breathe more easily.
This medicine also contains Chlorphenamine Maleate, which belongs to a group of medicines called antihistamines, which act to relieve the symptoms of allergic reactions.
2. Check before you take Maxtra-P Tablet
Do not take Maxtra-P Tablet:
- If you have ever had an allergic reaction to any of the ingredients
- If you have kidney or liver problems, overactive thyroid, diabetes, high blood pressure or heart or circulation disease
- If you have an enlarged prostate
- If you have phaeochromocytoma or glaucoma
- If you are taking tricyclic antidepressants (e.g. imipramine or amitriptyline) or if you are taking or have taken within the last two weeks monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) (e.g. moclobemide) prescribed for depression
- If you are taking beta blockers
- If your child is under 12 years of age
Take special care with Maxtra-P Tablet
- Contains paracetamol. Taking too much paracetamol can cause serious harm to your liver.
- Do not drive or operate machinery. This product may cause dizziness. If affected do not drive or operate machinery.
- Do not drink alcohol (beer, wine, spirits etc) while taking this product.
Ask your doctor before you take this medicine
- If you have a blood vessel disease such as Raynaud’s Phenomenon
- If you have an enlarged prostate
- If you have epilepsy, heart or circulation disease, liver problems
- If you have a severe infection as this may increase the risk of metabolic acidosis
- Signs of metabolic acidosis include:
- Deep, rapid, difficult breathing
- Feeling sick (nausea), being sick (vomiting)
- Loss of appetite
- If you have high blood pressure or glaucoma
- If you have asthma, bronchitis or bronchiectasis
- If you have an overactive thyroid
- If you have difficulty passing urine
- If you have an obstruction in their intestine
- If you have a rare blood disease called porphyria
Contact a doctor immediately if you get a combination of these symptoms.
If you are taking other medicines
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Maxtra-P Tablet if you are taking any prescribed medicines; particularly
- Drugs containing Acetaminophen
- Metoclopramide or domperidone (for nausea [feeling sick] or vomiting [being sick])
- Ergotamine or methylsergide (for migraine)
- Colestyramine (to lower blood cholesterol)
- Drugs to lower blood pressure
- Appetite suppressants or stimulants
- Drugs to treat depression such as tricyclic antidepressants (e.g. Amitriptyline) tranquillisers or other medicines for mental problems
- Drugs to treat heart disease (e.g. Digoxin)
- If you take blood thinning drugs (anticoagulants e.g. Warfarin)
- Other antihistamines
- Strong painkillers
- Sleeping tablets
- Phenytoin (for epilepsy)
- Atropine
Driving and using machines: This medicine may cause drowsiness. If affected do not drive or operate machinery. Avoid alcoholic drink
Pregnancy and breast feeding
Do not use if you are pregnant or breast feeding unless advised by a doctor.
3. How to take Maxtra-P Tablet
- For oral use only.
- Swallow whole with water.
- Do not chew. Do not give to children under 12 years.
Adults and children 12 years of age and older: Take 1 tablet every 4 to 6 hours.
Do not take more than the amount recommended above.
If symptoms do not go away within 5 days talk to your pharmacist or doctor.
If you take too much: Talk to your doctor or go to your nearest hospital casualty department straight away. Take the medicine and this leaflet with you.
- Leave at least 4 to 6 hours between doses.
- Do not take more than eight capsules (4 doses) in any 24 hours period.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Maxtra-P Tablet can have side effects, but not everybody gets them. A small number of people have had side effects.
Stop taking this medicine and tell your doctor immediately if you experience:
- Allergic reactions which may be severe such as skin rash and itching sometimes with swelling of the mouth or face or shortness of breath.
- Very rare cases of serious skin reactions have been reported.
- Skin rash or peeling, or mouth ulcers, sensitivity to sunlight, other allergic reactions
- Breathing problems. These are more likely if you have experienced them before when taking other painkillers such as ibuprofen or aspirin.
- Unexplained bruising or bleeding.
- Reoccuring fevers or infections.
- Nausea, sudden weight loss, loss of appetite
- Visual disturbances. This is rare but is more likely in those with glaucoma.
- Difficulty passing water. This is more likely to occur in men with an enlarged prostate gland.
- Drowsiness (which may make your child fall asleep)
- Dizziness, blurred vision, headaches, fits
- Dry mouth, difficulty in passing urine, sweating
- Indigestion, stomach pain, loss of appetite
- Tremors, muscle pain or weakness, impaired movement or co-ordination, pins and needles
- Change in heart rate, palpitations, low blood pressure, ringing in the ears, hair loss
- Blood problems such as anaemia, weariness
- Sleep disturbance
- Liver problems (which may cause yellowing of the skin or eyes)
- Chest pain
- Cough, phlegm on the chest – these may be caused by thickened bronchial secretions (mucous) in your lungs
- Difficulty concentrating, irritability, depression
- Hyperactivity in children
- Confusion in the elderly
These reactions are rare.
The following side effects may occur. Tell your doctor if you get them.
- Raised blood pressure, headache, dizziness, difficulty sleeping, nervousness, anxiety, diarrhoea or sickness.
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Maxtra-P Tablet
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30º C
Keep out of reach of children.
Protect from light.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Maxtra-P Tablet contains
Each uncoated tablet contains:
Paracetamol 500 mg
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride 10 mg
Chlorpheniramine Maleate 4 mg
Packing
PVC/PVDC-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets.