MAXTRA® Tablets
Therapy Area
Respiratory
1.0 Generic Name
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride / Chlorpheniramine Maleate
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
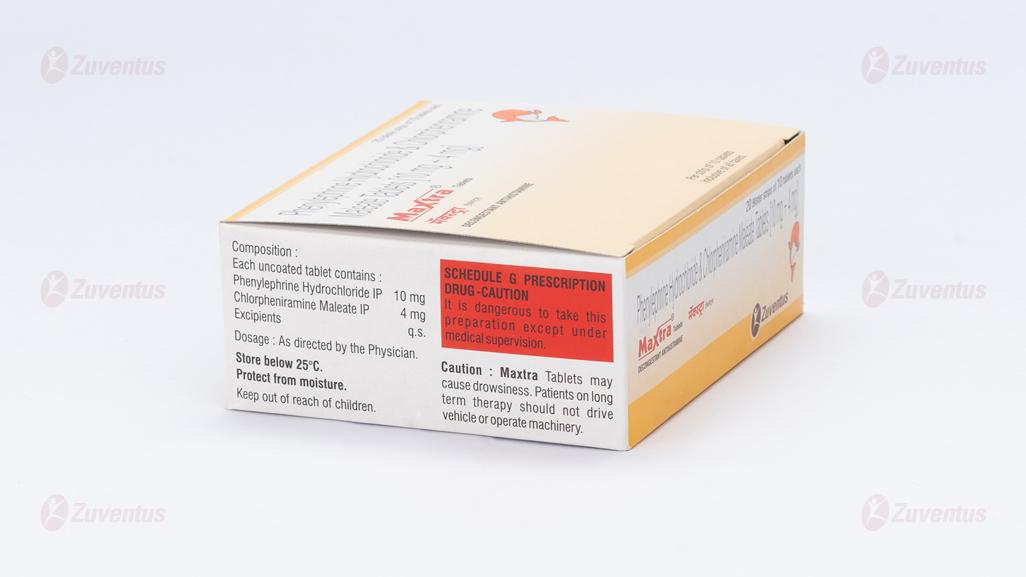
Each uncoated tablet contains
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride 10 mg
Chlorpheniramine Maleate 4 mg
Excipients q.s.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Tablet.
10mg/4mg.
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
Treatment of cough and cold with nasal congestion.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The recommended dosage of MAXTRA® for the treatment of cough and cold with nasal congestion in adults and children 12 years of age and older is 1 tablet every 4 to 6 hours and in children 6 to under 12 years of age is ½ tablet every 4 to 6 hours.
4.3 Contraindications
The tablets are contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to antihistamines or to any of the tablet ingredients. The anticholinergic properties of chlorphenamine are intensified by monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). The tablets are therefore contraindicated in patients who have been treated with MAOIs within the last fourteen days. Avoid in patients with cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, closed angle glaucoma, hyperthyroidism, prostatic enlargement and phaeochromocytoma. Patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or within 14 days of ceasing such treatment
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Chlorphenamine, in common with other drugs having anticholinergic effects, should be used with caution in epilepsy; raised intra-ocular pressure including glaucoma; prostatic hypertrophy; severe hypertension or cardiovascular disease; bronchitis, bronchiectasis or asthma; hepatic impairment; renal impairment. Children and the elderly are more likely to experience the neurological anticholinergic effects and paradoxical excitation (e.g., Increased energy, restlessness, nervousness).
The anticholinergic properties of chlorphenamine may cause drowsiness, dizziness, blurred vision and psychomotor impairment in some patients which may seriously affect ability to drive and use machinery.
The effects of alcohol may be increased and therefore concurrent use should be avoided. Should not be used with other antihistamine containing products, including antihistamine containing cough and cold medicines.
Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine. This medicine should be used with caution in patients with occlusive vascular disease including Raynaud's Phenomenon.
Do not take for longer than 7 days, unless your doctor agrees.
If symptoms do not go away talk to your doctor.
Keep all medicines out of the reach of children.
Warning: Do not exceed the stated dose.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Should not be given to patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or within 14 days of stopping such treatment. May enhance the effects of anticholinergic drugs such as tricyclic antidepressants. May increase the possibility of arrhythmias in digitalised patients. May enhance the cardiovascular effects of other sympathomimetic amines (e.g. decongestants). This medicine should not be taken together with vasodilators, Beta-blockers or enzyme inducers such as alcohol.
Concurrent use with hypnotics or anxiolytics may cause an increase in sedative effects, therefore medical advice should be sought before taking MAXTRA® concurrently with these medicines.
Chlorphenamine inhibits phenytoin metabolism and can lead to phenytoin toxicity.
The anticholinergic effects of chlorphenamine are intensified by MAOIs (see Contraindications).
4.6 Use in special populations (such as pregnant women, lactating women, paediatric patients, geriatric patients etc.)
Pregnancy
The safety of this medicine during pregnancy has not been established but in view of a possible association of foetal abnormalities with first trimester exposure to phenylephrine, the use of the product during pregnancy should be avoided. In addition, because phenylephrine may reduce placental perfusion, the product should not be used in patients with a history of pre-eclampsia. Similarly, there are no adequate data from the use of chlorphenamine maleate in pregnant women. The potential risk for humans is unknown. Use during the third trimester may result in reactions in the newborn or premature neonates. Not to be used during pregnancy unless considered essentially by a physician.
Lactation
The safety of this medicine during lactation has not been established. Chlorphenamine maleate and other antihistamine may inhibit lactation and may be secreted in breast milk. Not to be used during lactation unless considered essential by a physician. In view of the lack of data on the use of phenylephrine during lactation, this medicine should not be used during breast feeding.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The anticholinergic properties of chlorphenamine may cause drowsiness, dizziness, blurred vision and psychomotor impairment, which can seriously hamper the patients' ability to drive and use machinery.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Chlorpheniramine Maleate
Specific estimation of the frequency of adverse events for OTC products is inherently difficult (particularly numerator data). Adverse reactions which have been observed in clinical trials and which are considered to be common (occurring in ≥1% to <10% of subjects) or very common (occurring in ≥10% of subjects) are listed below. The frequency of other adverse reactions identified during post-marketing use is unknown.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
Unknown: haemolytic anaemia, blood dyscrasias
Immune system disorders:
Unknown: allergic reaction, angioedema, anaphylactic reactions
Metabolism and nutritional disorders:
Unknown: anorexia
Psychiatric disorders:
Unknown: confusion*, excitation*, irritability*, nightmares*, depression
Nervous system disorders*:
Very common: sedation, somnolence
Common: disturbance in attention, abnormal coordination, dizziness headache
Eye Disorders:
Common: blurred vision
Ear and labyrinth disorders:
Unknown: tinnitus
Cardiac disorders:
Unknown: palpitations, tachycardia, arrythmias
Vascular disorders:
Unknown: Hypotension
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:
Unknown: thickening of bronchial secretions
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Common: nausea, dry mouth
Unknown: vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, dyspepsia
Hepatobiliary disorders:
Unknown: hepatitis, jaundice
Skin and subcutaneous disorders:
Unknown: exfoliative dermatitis, rash, urticaria, photosensitivity
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders:
Unknown: muscle twitching, muscle weakness
Renal and urinary disorders:
Unknown: urinary retention
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Common: fatigue Unknown: chest tightness
*Children and the elderly are more likely to experience the neurological anticholinergic effects and paradoxical excitation (eg. increased energy, restlessness, nervousness).
Phenylephrine hydrochloride
Adverse effects may include tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmias, palpitations, hypertension, nausea, vomiting, headache and occasionally urinary retention in males.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product.
Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions at www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Chlorpheniramine Maleate
Symptoms and signs
The estimated lethal dose of chlorphenamine is 25 to 50mg/kg body weight. Symptoms and signs include sedation, paradoxical excitation of the CNS, toxic psychosis, convulsions, apnoea, anticholinergic effects, dystonic reactions and cardiovascular collapse including arrhythmias.
Treatment
Symptomatic and supportive measures should be provided with special attention to cardiac, respiratory, renal and hepatic functions and fluid and electrolyte balance. If overdosage is by the oral route, treatment with activated charcoal should be considered provided there are no contraindications for use and the overdose has been taken recently (treatment is most effective if given within an hour of ingestion). Treat hypotension and arrhythmias vigorously. CNS convulsions may be treated with i.v. diazepam. Haemoperfusion may be used in severe cases.
Phenylephrine hydrochloride
Symptoms of overdosage include irritability, restlessness, palpitations, hypertension, difficulty in micturition, nausea, vomiting, thirst and convulsions. In severe overdosage gastric lavage and aspiration should be performed. Symptomatic and supportive measures should be undertaken, particularly with regard to cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Convulsions should be controlled with intravenous diazepam. Chlorpromazine may be used to control marked excitement and hallucinations. Severe hypertension may need to be treated with an alpha-adrenoreceptor blocking drug, such as phentolamine. A beta blocker may be required to control cardiac arrhythmias.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Chlorpheniramine Maleate
Chlorphenamine is a potent antihistamine (H1-antagonist).
Antihistamines diminish or abolish the actions of histamine in the body by competitive reversible blockade of histamine H1-receptor sites on tissues. Chlorphenamine also has anticholinergic activity.
Antihistamines act to prevent the release of histamine, prostaglandins and leukotrienes and have been shown to prevent the migration of inflammatory mediators. The actions of chlorphenamine include inhibition of histamine on smooth muscle, capillary permeability and hence reduction of oedema and wheal in hypersensitivity reactions such as allergy and anaphylaxis.
Phenylephrine hydrochloride
Phenylephrine is a sympathomimetic agent with mainly direct effects on adrenergic receptors. It has predominantly alpha adrenergic activity and is without stimulating effects on the central nervous system. The sympathomimetic effect of phenylephrine produces vasoconstriction which in turn relieves nasal congestion.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Chlorpheniramine Maleate
Chlorphenamine is well absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract, following oral administration. The effects develop within 30 minutes, are maximal within 1 to 2 hours and last 4 to 6 hours. The plasma half-life has been estimated to be 12 to 15 hours.
Chlorphenamine is metabolised to the monodesmethyl and didesmethyl derivatives. About 22% of an oral dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. Only trace amounts have been found in the faeces.
Phenylephrine hydrochloride
Phenylephrine is readily absorbed after oral administration but is subject to extensive presystemic metabolism, much of which occurs in the enterocytes. As a consequence, systemic bioavailability is only about 40%. Following oral administration, peak plasma concentrations are achieved in 1-2 hours. The mean plasma half-life is in the range 2-3 hours. Penetration into the brain appears to be minimal.
Following absorption, the drug is extensively metabolised in the liver. Both phenylephrine and its metabolites are excreted in the urine.
The volume of distribution is between 200 and 500 litres, but there are no data on the extent of plasma protein binding.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
No additional data of relevance.
7.0 Description
MAXTRA® tablet contains phenylephrine hydrochloride (a nasal decongestant) and chlorpheniramine maleate (an antihistamine). Each uncoated tablet contains: Phenylephrine Hydrochloride, IP, 10 mg; Chlorpheniramine Maleate, IP, 4 mg; and Excipients (q.s.)
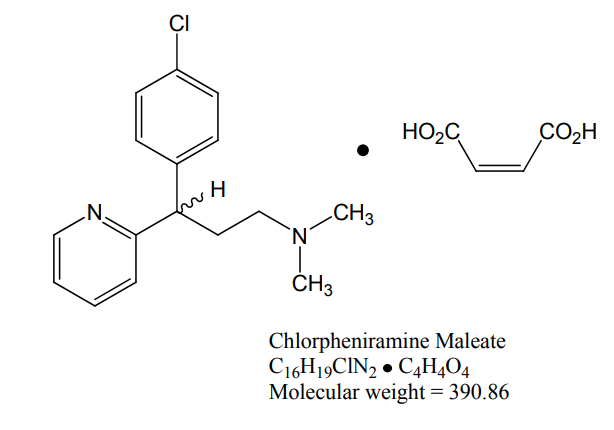
Chlorpheniramine Maleate
Chlorpheniramine maleate is 2-pyridinepropanamine, g-( as the following chemical structu 4-chlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-, (Z)-2 - butenedioate (1:1) and has the following chemical structure:
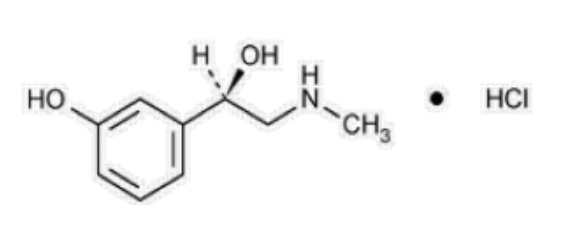
Phenylephrine hydrochloride
Phenylephrine is an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor agonist. The chemical name of phenylephrine hydrochloride is (-)-m-hydroxy-α-[(methylamino)methyl]benzyl alcohol hydrochloride, and its structural formula is depicted below:
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on pack.
8.3 Packaging information
20 Blister strips of 10 tablets in each strip
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store below 25°C. Protect from moisture.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
Caution: Maxtra Tablets may cause drowsiness. Patients on long term therapy should not drive vehicle or operate machinery.
Do Not Use
if you are now taking a prescription monoamine oxadise inhibitor (MAOI) (certain drugs for depression, psychiatric, or emotional conditions, or Parkinson’s disease), or for 2 weeks after stopping the MAOI drug. If you do not know if your prescription drug contains an MAOI, ask a doctor or pharmacist before taking this product.
Ask a doctor before use if you have
- a breathing problem such as emphysema or chronic bronchitis
- glaucoma
- trouble urinating due to an enlarged prostate gland
- diabetes
- heart disease
- high blood pressure
- thyroid disease
Ask a doctor or pharmacist before use if you are
- taking sedatives or tranquilizers
When using this product
- do not use more than directed
- may cause excitability, especially in children
- may cause drowsiness; alcohol, sedatives or tranquilizers may increase drowsiness
- avoid alcoholic beverages and use caution when driving a motor vehicle or operating machinery
Stop use and ask a doctor if
- nervousness, dizziness, or sleeplessness occur
- symptoms do not improve within 7 days or are accompanied by fever
If pregnant or breast-feeding
ask a health professional before use.
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
- What MAXTRA® tablet is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you are given MAXTRA® tablets
- How MAXTRA® tablets is given
- Possible side effects
- How to store MAXTRA® tablets
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What MAXTRA® tablets is and what it is used for
MAXTRA® tablet contains: Chlorphenamine Maleate which belongs to a group of medicines called antihistamines, which act to relieve the symptoms of allergies. Phenylephrine Hydrochloride, a decongestant, which acts to relieve a blocked nose. MAXTRA® tablets is used to treat cough and cold with nasal congestion.
2. What you need to know before you take MAXTRA®
Do not take MAXTRA® tablets:
- If you are allergic to any of the ingredients in this medicine or any other antihistamines (listed in section 6)
- If you have heart or circulatory problems
- If you have high blood pressure (including that due to a tumour near your kidney)
- If you have diabetes, glaucoma or an overactive thyroid
- If you are taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (for depression), or have taken them within the last 14 days
- If you have an intolerance to some sugars, unless your doctor tells you to (this medicine contains lactose)
- If you are a man with prostate problems
- If you are pregnant or breastfeeding
Other important information
Do not drink alcohol (e.g. wine, beer, spirits) whilst taking this medicine.
Other medicines and MAXTRA® tablets
This medicine contains phenylephrine.
Do not take with any other medicines that contain phenylephrine.
Before you take these capsules, make sure that you tell your pharmacist about ANY other medicines you might be using at the same time, particularly the following:
- Digoxin (for heart problems)
- Medicines for high blood pressure
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Sleeping tablets, medicines for anxiety, antidepressants
- Phenytoin (for epilepsy)
- Other antihistamines, including those in cough and cold medicines, that make you sleepy
- Other decongestants
If you are unsure about interactions with any other medicines, talk to your pharmacist. This includes medicines prescribed by your doctor and medicine you have bought for yourself, including herbal and homeopathic remedies.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking MAXTRA® tablets:
- If you have epilepsy
- If you have liver or kidney problems
- If you have heart problems, severe high blood pressure
- If you have asthma, bronchitis or other lung problems
- If you have raised pressure in your eye (glaucoma)
- If you are a man with prostate problems
If you are not sure if any of the above apply to you, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine. Driving and using machines This medicine may cause drowsiness, dizziness or blurred vision. You should not drive or operate machinery until you are sure you are not affected.
3. How to take MAXTRA® tablets
Check the foil is not broken before use. If it is, do not take that tablet.
If you are elderly your doctor or pharmacist may advise you to take fewer tablets. If this applies to you follow their instructions.
- Swallow the tablet with a drink of water.
- Do not give to children under 6 years.
- Do not take more than the amount recommended above.
- Do not take this medicine for more than 7 days, unless your doctor tells you to.
- If symptoms do not go away talk to your doctor
The recommended dose is:
Adults and children 12 years of age and older
- Take 1 tablet every 4 to 6 hours
Children 6 to under 12 years of age
- Take ½ tablet every 4 to 6 hours
If you take more MAXTRA® tablets than you should
If you have too much of this medicine, talk to your doctor straight away. Take your medicine and this leaflet with you.
4. Possible side effects
Most people will not have problems, but some may get some of these.
If you get any of these serious side effects, stop taking the medicine. See a doctor at once:
- Difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue or throat (severe allergic reaction)
If you get any of the following side effects see your pharmacist or doctor:
- Drowsiness which may cause you to fall asleep, sleepiness, feeling tired
- Lack of concentration, dizziness, headache, blurred vision
- Feeling sick, being sick, dry mouth, heartburn, diarrhoea, stomach pain
- Loss of appetite, difficulty in passing urine, ringing in the ears
- Other allergic reactions including skin peeling, itchy red skin rash, sensitivity to sunlight
- Changes in heart rate, palpitations, low blood pressure (you may feel faint), tightness of the chest
- Fast or irregular heartbeat, high blood pressure
- Thickened bronchial secretions (which may cause a cough or phlegm)
- Liver problems including hepatitis and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Blood problems such as anaemia
- Muscle weakness, twitching, lack of co-ordination
- Depression, irritability, nightmares
- Confusion in the elderly
- Hyperactivity in children
- Skin rash
- Occasionally, difficulty in passing urine (in men)
Very young children and elderly adults may be more likely to have some of these side effects.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store MAXTRA® tablets
Do not store above 25°C.
Store in the original package.
Keep this medicine in a safe place out of the sight and reach of children, preferably in a locked cupboard.
Use by the date on the end flap of the carton or on the foil edge.
Do not throw away medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
10 tablets in each Blister strips of Maxtra®
What MAXTRA® Tablets contains
Each uncoated tablet contains:
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride IP (10 mg), Chlorpheniramine Maleate IP (4 mg), Excipients (q.s.)
Details Manufacturer
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd. Plot Y2, CTS No: 358/A2, Near Nahur Railway Station, Nahur (West),
Mumbai - 400 078, India. ® Registered Trade Mark of Zuventus.
This leaflet was last revised in June 2024.