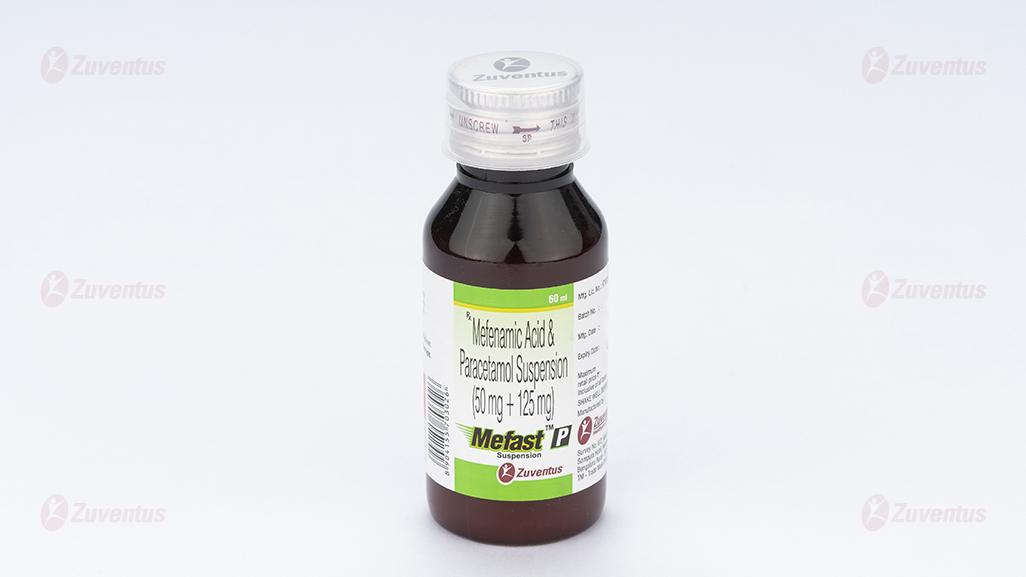
Mefast-P Suspension
Therapy Area
Pain management
1.0 Generic name
Mefenamic Acid & Paracetamol Suspension
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each 5 ml contains :
Mefenamic Acid IP 50 mg
Paracetamol IP 125 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Sunset Yellow FCF
In a flavoured syrupy base
3.0 Dosage form and Strength
Suspension, Mefenamic Acid & Paracetamol Suspension (50 mg + 125 mg)
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
Mefast P Suspension is indicated for fever and pain.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Mefast P Suspension should be taken preferably with or after food. The recommended dosage in children is given up to three times daily, usually not to exceed one week.
| Age | Usual Dose |
|---|---|
| 6 months to 2 years | 5 ml |
| 2 years to 5 years | 10 ml |
| 5 years to 9 years | 15 ml |
| 9 years to 12 years | 20 ml |
4.3 Contraindications
• Patients with known hypersensitivity to mefenamic acid, paracetamol or to any of the excipients
• Patients who have experienced asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, rarely fatal, anaphylactic-like reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients
• For the treatment of peri-operative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery
• In patients with acute active ulceration or chronic inflammation of either the upper or lower gastrointestinal tract
• In patients with pre-existing renal disease
• In severe hepatic impairment
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Mefast P Suspension should be used cautiously during following conditions:
• Cardiovascular Thrombotic Effects: shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal.
• Hypertension
• Congestive Heart Failure
• Renal and hepatic impairment
• Asthma
• Monitor blood counts and liver function during long-term therapy
• Drowsiness may affect ability to perform skilled tasks
• Elderly, advanced renal disease
4.5 Drugs interactions
Paracetamol
• Anticoagulant drugs (warfarin) - dosage may require reduction if paracetamol and anticoagulants are taken for a prolonged period of time.
• Paracetamol absorption is increased by substances that increase gastric emptying, e.g. metoclopramide.
• Paracetamol absorption is decreased by substances that decrease gastric emptying, e.g. propantheline, antidepressants with anticholinergic properties, and narcotic analgesics.
• Paracetamol may increase chloramphenicol concentrations
• The risk of paracetamol toxicity may be increased in patients receiving other potentially hepatotoxic drugs or drugs that induce liver microsomal enzymes such as alcohol and anticonvulsant agents
• Paracetamol excretion may be affected and plasma concentrations altered when given with probenecid
• Cholestyramine reduces the absorption of paracetamol if given within 1 hour.
• Antivirals: Regular use of paracetamol possibly reduces metabolism of Zidovudine (increased risk of neutropenia).
Mefenamic Acid
• Mefenamic Acid enhances activity of oral anticoagulants but rarely significant.
• Increased cyclosporine, lithium toxicity and convulsions reported with ciprofloxacin.
• Absorption is increased by Magnesium Hydroxide antacids.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate or well controlled studies in pregnant women. Mefenamic acid should be used in pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Although paracetamol have shown no ill effects in human pregnancy, the combination should not be used in late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, mefenamic acid may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
Labour and Delivery
In rat studies with NSAIDs, as with other drugs known to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, an increased incidence of dystocia, delayed parturition, and decreased pup survival occurred. The effects of mefenamic acid on labour and delivery in pregnant women are unknown.
Nursing Mothers
Trace amounts of mefenamic acid may be present in breast milk and transmitted to the nursing infant. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from mefenamic acid, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Geriatric use
Clinical studies of combination did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. As with other NSAIDs, caution should be exercised in treating the elderly (65 years and older). This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Patients should be cautioned against engaging in activities requiring complete mental alertness, and motor coordination such as operating machinery until their response to Mefast P Suspension is known.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Fixed Drug Eruption (FDE) has been associated with Paracetamol use.
Difficulty in breathing or swallowing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue or throat, severe itching of the skin with a red rash or raised lumps, blistering of the mouth, eyes, or genital region, patchy areas of rash, peeling skin or any of the following reactions:
• Severe or worsening diarrhoea
• Passing blood in stools (faeces/motions)
• Passing black tarry stools
• Vomiting any blood or dark particles that look like coffee grounds
Abdominal pain, dyspepsia, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, GI ulcers, oedema, bronchospasm, headache, drowsiness, insomnia, visual disturbances, CHF, hypertension, tachycardia, syncope, urticaria, rash, thrombocytopenia, aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, tinnitus, elevated liver enzymes, abnormal renal function. Potentially Fatal: Autoimmune hemolytic anemia; convulsions (overdosage).
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Symptoms following acute NSAIDs, overdoses are usually limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which are generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding can occur. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression and coma may occur, but are rare. Anaphylactoid reactions have been reported with therapeutic ingestion of NSAIDs, and may occur following an overdose. Patients should be managed by symptomatic and supportive care following a NSAID overdose. There are no specific antidotes. Emesis and/or activated charcoal (60 to 100 g in adults, 1 to 2 g/kg in children) and/or osmotic cathartic may be indicated in patients seen within 4 hours of ingestion with symptoms or following a large overdose (5 to 10 times the usual dose). In addition, administration of oral methionine or intravenous N-acetylcysteine (NAC) which may have a beneficial effect up to at least 48 hours after the over-dose may be required. Administration of intravenous NAC is most beneficial when initiated within 8 hours of overdose ingestion. Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Mefenamic acid binds the prostaglandin synthetase receptors COX-1 and COX-2, inhibiting the action of prostaglandin synthetase. As these receptors have a role as a major mediator of inflammation and/or a role for prostanoid signaling in activity-dependent plasticity, the symptoms of pain are temporarily reduced. Paracetamol act primarily in the CNS, increasing the pain threshold by inhibiting both isoforms of cyclooxygenase, COX-1, COX-2, and COX-3 enzymes involved in prostaglandin (PG) synthesis. The antipyretic properties of acetaminophen are likely due to direct effects on the heat-regulating centres of the hypothalamus resulting in peripheral vasodilation, sweating and hence heat dissipation.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Mefenamic acid belongs to the family of drugs called fenamates, which are aspirin-like drugs that are derivatives of N-phenylanthranilic acid. In tests of anti-inflammatory activity, mefenamic acid is about half as potent as phenylbutazone. Mefenamic acid has antipyretic and analgesic properties and displays a central as well as a peripheral action. Mefenamic acid appears to owe these properties to its capacity to inhibit cyclo-oxygenase (COX).
Paracetamol is a widely used analgesic and antipyretic drug that is used for the relief of fever, headaches, and other minor aches and pains. It is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu medications and many prescription analgesics. It is extremely safe in standard doses, but because of its wide availability, deliberate or accidental overdoses are not uncommon. Paracetamol, unlike other common analgesics such as aspirin and ibuprofen, has no anti-inflammatory properties or effects on platelet function, and it is not a member of the class of drugs known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs. At therapeutic doses Paracetamol does not irritate the lining of the stomach nor affect blood coagulation, kidney function, or the fetal ductus arteriosus (as NSAIDs can). Like NSAIDs and unlike opioid analgesics, Paracetamol does not cause euphoria or alter mood in any way. Paracetamol and NSAIDs have the benefit of being completely free of problems with addiction, dependence, tolerance and withdrawal.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Mefenamic acid is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Peak plasma concentrations occur about 2 to 4 hours after ingestion. The plasma elimination half-life is reported to be about 2 to 4 hours. Mefenamic acid is more than 90% bound to plasma proteins. It is distributed into breast milk. Mefenamic acid is metabolised by the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP2C9 to 3-hydroxymethyl Mefenamic acid, which may then be oxidised to 3- carboxymefenamic acid. Over 50% of a dose may be recovered in the urine, as unchanged drug or, mainly, as conjugates of Mefenamic acid and its metabolites.
Paracetamol is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract with peak plasma concentrations occurring about 10 to 60 minutes after oral doses. Paracetamol is distributed into most body tissues. It crosses the placenta and is present in breast milk. Plasma-protein binding is negligible at usual therapeutic concentrations but increases with increasing concentrations. The elimination half-life of paracetamol varies from about 1 to 3 hours. Paracetamol is metabolised mainly in the liver and excreted in the urine mainly as the glucuronide and sulfate conjugates. Less than 5% is excreted as unchanged paracetamol. A minor hydroxylated metabolite (Nacetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine), is usually produced in very small amounts by cytochrome P450 isoenzymes (mainly CYP2E1 and CYP3A4) in the liver and kidney. It is usually detoxified by conjugation with glutathione but may accumulate after paracetamol over dosage and cause tissue damage.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
No known animal toxicology data
7.0 Description
Mefenamic acid (2-(2,3-dimethylphenyl) aminobenzoic acid) is a non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug with a molecular formula of and molecular weight of 241.285 g/mol. Paracetamol (N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) acetamide) is an analgesic with a molecular formula of C8H9NO2 and molecular weight of 151.17 g/mol.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
A bottle of 60 ml.
8.4 Storage and handling instructions
Store below 30°C. Protect from light. Do not freeze.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient counselling information
• Ensure the prescribed dose of Mefast P Suspension is taken as directed.
• Not to exceed the stated recommended daily dose.
• Shake Mefast P suspension well before use each time.
• If pregnant or breast-feeding, ask a health professional before use. Instruct pregnant women not to take Mefast P Suspension especially in the last 3 months of pregnancy as it may cause harm to the foetus and during labour (delivery) because it may delay the labour and increases risk of bleeding.
• Not to use with any other drug containing paracetamol (prescription or over-the-counter - OTC). Users to ask a doctor or pharmacist, if they are not sure about presence of paracetamol in the drug taken for other illnesses.
• Ask the patient to report any adverse events.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others.
- It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours. If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1. What MEFAST P® suspension is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you are given MEFAST P® suspensions
3. How MEFAST P® suspensions is given
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store MEFAST P® suspensions
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What MEFAST P® is and what it is used for
MEFAST P® is a suspension that contains:
Mefenamic acid, which belongs to a group of medicines called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), act to relieve the symptoms of pain. Paracetamol, an anti-pyretic, analgesic, acts to relieve pain and reduce fever.
This product is intended for children but may be given to adults.
Mefast P Suspension is used for fever and pain treatment. It can help to relieve:
- symptoms of inflammation, such as redness and swelling
- pain and discomfort caused by arthritis, muscular or rheumatic disorders
- headache or toothache
- pain after operations, trauma - fever in children
- painful or heavy periods in girls.
2. What you need to know before you take MEFAST P®
Do not take MEFAST P® Suspension
- if you are allergic to mefenamic acid, paracetamol, to any other anti-inflammatory medicines (such as aspirin, ibuprofen, celecoxib), or to any of the other ingredients (listed in section 6)
- if you have, or have ever had, stomach or intestinal conditions such as peptic ulcer, bleeding in the stomach or severe gastritis
- if you have an inflammatory bowel disease (e.g. ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease)
- if you have severe heart, liver or kidney problems
- if you have just had heart bypass surgery
- if you are more than 6 months pregnant.
If any of the above apply to you, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your pharmacist or doctor:
Mefenamic acid
Before taking the suspension, tell your doctor if you:
- are taking any other NSAIDs (e.g. ibuprofen, diclofenac)
- are taking any other anti-inflammatory medicines including steroids (e.g. prednisolone)
- are taking aspirin or medicines that thin the blood (e.g. warfarin, clopidogrel)
- are taking antidepressants called selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs) (e.g. paroxetine)
- have kidney or liver problems. Your doctor may check your kidney or liver function before and during treatment
- have stomach or digestive tract problems or if you ever had an upset stomach after taking pain killers such as aspirin. Bleeding in the stomach or gut can occur in patients taking Mefenamic Acid
- have a bleeding disorder or if you are going to have a major operation. Mefenamic Acid can affect the clotting of your blood. It can make you bleed more and for longer than usual
- have asthma, or a history of asthma, as this medicine may cause breathing difficulties
- have a connective tissue disorder, e.g. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- have epilepsy
- are dehydrated (thirsty with dry skin, dark urine, dry mouth, headache)
- have heart problems, previous stroke or think that you might be at risk of these conditions (e.g. if you have high blood pressure, diabetes or high cholesterol or are a smoker). Additional monitoring may be carried out by your doctor.
Medicines such as Mefenamic Acid may be associated with a small increased risk of heart attack or stroke. Any risk is more likely with high doses and prolonged treatment. Do not exceed the recommended dose or duration of treatment.
Paracetamol
- If your child has liver or kidney problems
- If your child takes any other medicines (see “If your child takes other medicines”)
Other medicines and MEFAST P®
Mefenamic acid
Some medicines may be affected by Mefenamic Acid or they may affect how well Mefenamic Acid will work. Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking:
- medicines that can increase the chance of getting ulcers or a bleed in the stomach or gut, such as:
- corticosteroids used to treat arthritis and inflammation
- medicines such as anti-platelet agents, used to thin the blood (e.g. warfarin, aspirin, clopidogrel)
- antidepressants called selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs) (e.g. paroxetine)
- any other anti-inflammatory medicines (e.g. diclofenac, celecoxib)
- aspirin including low doses of aspirin used to prevent your blood from clotting in certain heart conditions
- medicines used for high blood pressure (e.g. atenolol, ramipril, valsartan)
- diuretics (water tablets) or heart medicines (e.g. digoxin, sotalol, diltiazem)
- some diabetic medicines (e.g. glipizide, glibenclamide)
- medicines which suppress the immune system (e.g. ciclosporin, tacrolimus, methotrexate)
- lithium, a medicine used to treat mood swings and some types of depression
- a medicine usually prescribed through hospitals, called mifepristone (taken within the last 12 days)
- quinolone antibiotics (antibiotics used to treat infections)
- aminoglycoside antibiotics, used under medical
- supervision in hospitals
- zidovudine, a medicine used for HIV
- probenecid, a medicine used in special cases, to protect the kidneys
- medicines which bind to protein in the blood - (check with your pharmacist).
Paracetamol
Before you give this medicine, make sure that you tell your pharmacist about ANY other medicines you might be giving your child at the same time, particularly the following:
- Domperidone or metoclopramide (for feeling sick or being sick)
- Colestyramine (to reduce blood fat levels)
- Medicines to thin the blood (e.g. warfarin)
- Medicines for epilepsy (e.g. barbiturates)
If you are unsure about interactions with any other medicines, talk to your pharmacist or doctor. This includes medicines prescribed by your doctor and medicine you have bought for your child, including herbal and homeopathic remedies.
Blood tests
Your doctor may test your blood during treatment.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine.
Pregnancy
Mefenamic acid will be passed to your unborn baby. You should not take Mefenamic Acid during the first 6 months of pregnancy unless absolutely necessary and advised by your doctor. If you need treatment during this period or while you are trying to get pregnant, the lowest dose for the shortest time possible should be used. If taken for more than a few days from 20 weeks of pregnancy onward, Mefenamic Acid can cause kidney problems in your unborn baby that may lead to low levels of amniotic fluid that surrounds the baby (oligohydramnios) or narrowing of a blood vessel (ductus arteriosus) in the heart of the baby. If you need treatment for longer than a few days, your doctor may recommend additional monitoring.
DO NOT take the suspension in the last 3 months of pregnancy as it may harm your unborn child and cause problems at delivery. It can cause kidney and heart problems in your unborn baby. It may affect your and your baby’s tendency to bleed and cause labour to be later or longer than expected.
Breast-feeding
Mefenamic acid passes into breast milk and can affect the baby. You should not take the suspension while breast-feeding unless advised by your doctor.
Fertility
DO NOT take the suspension if you are trying to become pregnant, as it may make it more difficult to get pregnant. You should inform your doctor if you are planning to become pregnant or if you have problems becoming pregnant
Driving and using machines
Mefenamic acid may cause drowsiness, dizziness, fatigue or affect your vision. If any of these occur do not drive, use machinery, or perform any tasks that may require you to be alert.
3. How to take MEFAST P®
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Your doctor will decide on the appropriate dose to suit your condition. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
- Shake the bottle before taking the medicine.
- Take the suspension with or immediately after a meal.
- After taking the suspension, rinse the mouth
– this medicine contains sucrose which may be harmful to the teeth if taken for more than 2 weeks.
- Do not drink alcohol while taking Mefenamic Acid.
Alcohol and smoking can irritate the stomach and make some of the side effects worse.
Dosages
Adults and the elderly
This medicine is intended for children. Contact your doctor for dosage advice if you are an adult taking this suspension.
Elderly patients are at a higher risk of side effects and should take the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible time, with additional monitoring carried out by their doctor.
Use in children
The recommended dose may be given up to 3 times per day.
| Age | Usual Dose |
|---|---|
| 6 months to 2 year | 5 ml |
| 2 - 5 years | 10 ml |
| 5 - 9 years | 15 ml |
| 9 - 12 years | 20 ml |
Do not take Mefenamic Acid for more than 7 days unless advised to do so by your doctor.
If you take more MEFAST P® than you should
If you take more of the suspension than you should, you may harm your stomach, kidneys and you may get seizures (fits).
Symptoms of overdose may also include headache, nausea, stomach pain, vomiting, rarely diarrhoea, disorientation, excitation, coma (loss of consciousness for a period of time), tiredness, ringing in the ears, fainting and occasionally convulsions.
1. Tell your doctor, pharmacist or nearest hospital casualty department immediately.
2. Take the bottle and any remaining suspension with you so that people can see what you have taken.
3. Do this even if you feel well.
If you forget to take
If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as you remember, but if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and continue as usual.
Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose. If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Most people will not have problems, but some may get some.
Mefenamic acid
Stop taking the suspension and seek medical help immediately if you have any of the following allergic reactions:
- difficulty breathing or swallowing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue or throat
- severe itching of the skin, with a red rash or raised lumps
- blistering of the mouth, eyes, and genital region, patchy areas of rash, peeling skin or any of the following reactions
- diarrhoea
- passing blood in your stools (faeces/motions)
- passing black tarry stools vomiting any blood or dark particles that look like coffee grounds.
Seek immediate medical attention if you have any of the following symptoms:
indigestion or heartburn, abdominal pain (pain in your stomach) or other abnormal stomach symptoms, nausea (feeling sick), vomiting
any unusual bruising or bleeding, for example nose-bleeds, pinpoint red spots on the skin, unusual purple bruise-like rash on the skin or in the mouth
signs of anaemia such as feeling tired, breathless, and looking pale
fever, sore throat, mouth ulcers, repeated infections or infections that will not go away. This may be due to a low level of white blood cells
seizures (fits)
signs of low sodium levels such as headache, nausea, vomiting, tiredness, muscle cramps
sudden headache, stiff neck, fever, sensitivity to bright light, drowsiness and muscle pain, with or without a rash
fever, rash, nausea, aches and pains, passing more or less urine than usual, passing red urine or passing urine at night. This may be due to changes in your kidneys
sudden loss or blurring of vision, loss of colour vision, eye pain which worsens with eye movement
headache, in particular on waking in the morning. This may be due to high blood pressure
pain behind the ribs radiating towards the back, often worse when lying down, nausea, vomiting, fever. This may be due to inflammation of your pancreas
yellowing of your skin or eyes, pale faeces and dark urine, unexplained persistent nausea, stomach problems, loss of appetite or unusual tiredness. This may be due to changes in your liver
low body temperature (below 35ºC), feeling cold with pale-looking skin, especially in children.
Tell your doctor if you get any of the following side effects:
head-spins (vertigo)
hallucinations
rapid heartbeat (palpitations)
mental confusion
constipation or bloating
blurred vision, eye irritation
feeling ill (malaise)
ringing or buzzing in the ears (tinnitus)
depression
inability to sleep
nervousness
sweating
fatty stools
loss of appetite
ear pain
numbness or tingling in hands or feet
sudden poor blood sugar control if you have diabetes. Your doctor or pharmacist can measure your sugar levels
asthma or asthma that is worse than usual
swelling of your hands and feet (around the ankles)
sore mouth (pain or ulcers on the tongue, cheeks, lips, throat or gums)
dizziness, drowsiness, feeling lethargic and tired
signs of low blood pressure such as light-headedness
reactions to the sun. Your skin may become red, painful and swollen - do not sunbathe, use a sun bed, or expose your skin to artificial UV light.
Medicines such as Mefenamic Acid may be associated with a small increased risk of heart attack or stroke.
Urine tests: Tell the doctor if you are having urine tests, as your medicine may affect the results.
Paracetamol
If your child gets any of these serious side effects, stop giving the medicine. See a doctor at once:
- Difficulty in breathing, swelling of the face, neck, tongue or throat (severe allergic reactions)
- Very rare cases of serious skin reactions have been reported. This may include peeling,
- blistering and lesions of the skin.
- If your child gets any of the following side effects, see your pharmacist or doctor.
- Other allergic reactions (e.g. skin rash)
- Unusual bruising, or infections such as sore throats. This may be a sign of very rare changes in the blood
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store MEFAST P®
Do not store above 25°C.
Store in the original package.
Keep this medicine in a safe place out of the sight and reach of children, preferably in a locked cupboard.
Use by the date on the end flap of the carton or on the foil edge. Do not throw away medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What MEFAST P® contains
Each 5 ml suspension contains:
Mefenamic Acid, IP, 50 mg; Paracetamol, IP, 125 mg; and Flavoured suspension base (q.s.)
A bottle of 60 ml.