Montefex Tablets
Therapy Area
Respiratory
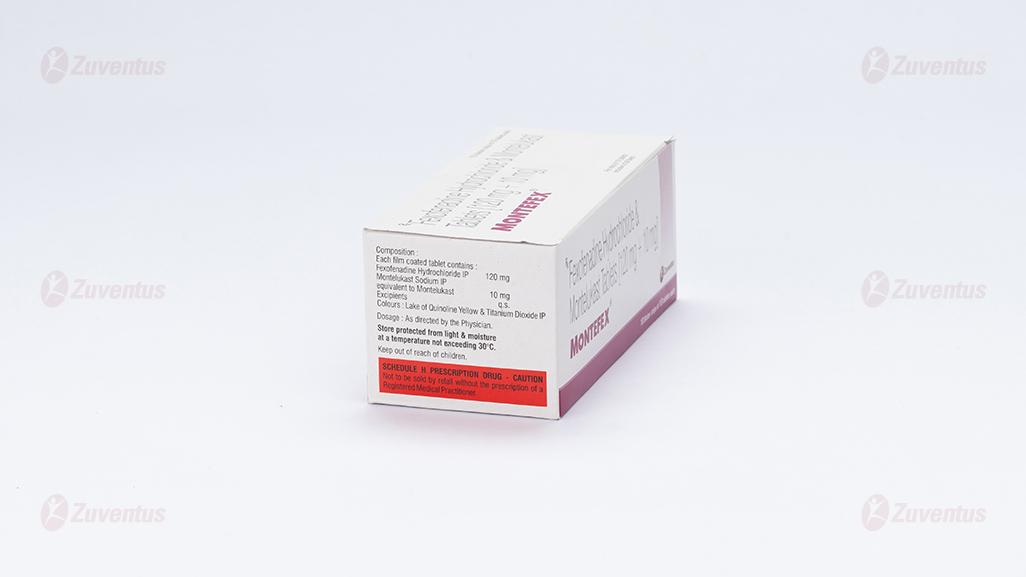
Composition
Each film coated tablet contains :
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride IP 120 mg
Montelukast Sodium IP equivalent to Montelukast 10 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colours : Lake of Quinoline Yellow & Titanium Dioxide IP
Description
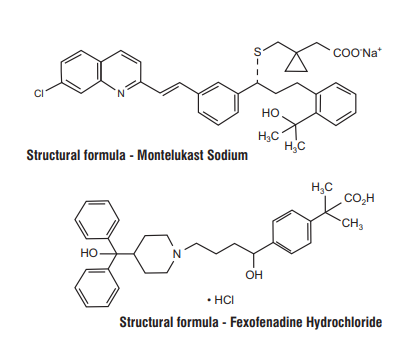
Montefex tablets are a combination of Montelukast Sodium and Fexofenadine Hydrochloride.
Montelukast Sodium
Montelukast Sodium is a selective and orally active leukotriene receptor antagonist that inhibits the cysteinyl leukotriene CysLT1 receptor.
Chemical Name : [R-(E)]-1-[[[1-[3-[2-(7-chloro-2-quinolinyl) ethenyl]phenyl]-3-[2-(1-hydroxy-1- methylethyl)phenyl]propyl] thio]methyl]cyclopropaneacetic acid, monosodium salt.
Molecular Formula : C35H35ClNNaO3S
Molecular Weight : 608.18
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride is a histamine H1-receptor antagonist.
Chemical Name : (±)-4-[1-hydroxy-4-[4-(hydroxydiphenylmethyl)-1-piperidinyl]-butyl]-α, α-dimethyl benzeneacetic acid hydrochloride.
Molecular Formula : C32H39NO4•Hcl
Molecular Weight : 538.13
MECHANISM OF ACTION :
Montelukast Sodium
Pharmacotherapeutic group : Other systemic drugs for obstructive airway diseases, Leukotriene receptor antagonists ATC-code : R03D C03
Mechanism of Action
The cysteinyl leukotrienes (LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4) are products of arachidonic acid metabolism and are released from various cells, including mast cells and eosinophils. These eicosanoids bind to cysteinyl leukotriene (CysLT) receptors. The CysLT type-1 (CysLT1) receptor is found in the human airway (including airway smooth muscle cells and airway macrophages) and on other pro-inflammatory cells (including eosinophils and certain myeloid stem cells). CysLTs have been correlated with the pathophysiology of asthma and allergic rhinitis. In asthma, leukotriene-mediated effects include airway edema, smooth muscle contraction, and altered cellular activity associated with the inflammatory process. In allergic rhinitis, CysLTs are released from the nasal mucosa after allergen exposure during both early-and late-phase reactions and are associated with symptoms of allergic rhinitis. Montelukast is an orally active compound that binds with high affinity and selectivity to the CysLT1 receptor in preference to other airway receptors, such as the prostanoid, cholinergic, or β-adrenergic receptor. Montelukast inhibits physiologic actions of LTD4 at the CysLT1 receptor without any agonist activity.
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride
Pharmacotherapeutic group : Antihistamines for systemic use, ATC code: R06A X26
Mechanism of action
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride is a non-sedating H1 antihistamine. Fexofenadine is a pharmacologically active metabolite of terfenadine.
Clinical efficacy and safety
Human histamine wheal and flare studies following single and twice daily doses of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride demonstrate that the medicinal product exhibits an antihistaminic effect beginning within one hour, achieving maximum at 6 hours and lasting 24 hours. There was no evidence of tolerance to these effects after 28 days of dosing. A positive dose-response relationship between doses of 10 mg to 130 mg taken orally was found to exist. In this model of antihistaminic activity, it was found that doses of at least 130 mg were required to achieve a consistent effect that was maintained over a 24 hour period. Maximum inhibition in skin wheal and flare areas were greater than 80%. Clinical studies conducted in seasonal allergic rhinitis have shown that a dose of 120 mg is sufficient for 24 hour efficacy. No significant differences in QTc intervals were observed in seasonal allergic rhinitis patients given Fexofenadine Hydrochloride up to 240 mg twice daily for 2 weeks when compared to placebo. Also, no significant change in QTc intervals was observed in healthy subjects given Fexofenadine Hydrochloride up to 60 mg twice daily for 6 months, 400 mg twice daily for 6.5 days and 240 mg once daily for 1 year, when compared to placebo. Fexofenadine at concentrations 32 times greater than the therapeutic concentration in man had no effect on the delayed rectifier K+ channel cloned from human heart.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Montelukast Sodium
Absorption
Montelukast is rapidly absorbed following oral administration. For the 10-mg film-coated tablet, the mean peak plasma concentration (Cmax) is achieved 3 hours (Tmax) after administration in adults in the fasted state. The mean oral bioavailability is 64%. The oral bioavailability and Cmax are not influenced by a standard meal. Safety and efficacy were demonstrated in clinical trials where the 10-mg film-coated tablet was administered without regard to the timing of food ingestion.
Distribution
Montelukast is >99% bound to plasma proteins. The steady-state volume of distribution of Montelukast averages 8-11 liters. Studies in rats with radiolabeled Montelukast indicate minimal distribution across the blood-brain barrier. In addition, concentrations of radiolabeled material at 24 hours post dose were minimal in all other tissues.
Biotransformation
Montelukast is extensively metabolized. In studies with therapeutic doses, plasma concentrations of metabolites of Montelukast are undetectable at steady state in adults and children. In vitro studies using human liver microsomes indicate that CYP450 3A4, 2A6 and 2C9 are involved in the metabolism of Montelukast. Based on further in vitro results in human liver microsomes, therapeutic plasma concentrations of Montelukast do not inhibit CYP450 3A4, 2C9, 1A2, 2A6, 2C19, or 2D6. The contribution of metabolites to the therapeutic effect of Montelukast is minimal.
Elimination
The plasma clearance of Montelukast averages 45 ml/min in healthy adults. Following an oral dose of radiolabeled Montelukast, 86% of the radioactivity was recovered in 5-day fecal collections and <0.2% was recovered in urine. Coupled with estimates of Montelukast oral bioavailability, this indicates that Montelukast and its metabolites are excreted almost exclusively via the bile. In several studies, the mean plasma half-life of Montelukast ranged from 2.7 to 5.5 hours in healthy young adults. The pharmacokinetics of Montelukast is nearly linear for oral doses up to 50 mg. During once-daily dosing with 10-mg Montelukast, there is little accumulation of the parent drug in plasma (14%).
Special populations
No dosage adjustment is necessary for the elderly or mild to moderate hepatic insufficiency. Studies in patients with renal impairment have not been undertaken. Because Montelukast and its metabolites are eliminated by the biliary route, no dose adjustment is anticipated to be necessary in patients with renal impairment. There are no data on the pharmacokinetics of Montelukast in patients with severe hepatic insufficiency (Child-Pugh score >9). With high doses of Montelukast (20- and 60-fold the recommended adult dose), decrease in plasma theophylline concentration was observed. This effect was not seen at the recommended dose of 10 mg once daily.
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride
Absorption
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride is rapidly absorbed into the body following oral administration, with Tmax occurring at approximately 1-3 hours post dose. The mean Cmax value was approximately 427 ng/ml following the administration of a 120 mg dose once daily.
Distribution
Fexofenadine is 60-70% plasma protein bound.
Biotransformation and elimination
Fexofenadine undergoes negligible metabolism (hepatic or non-hepatic), as it was the only major compound identified in urine and faeces of animals and man. The plasma concentration profiles of Fexofenadine follow a bi-exponential decline with a terminal elimination half-life ranging from 11 to 15 hours after multiple dosing. The single and multiple dose pharmacokinetics of Fexofenadine are linear for oral doses up to 120 mg BID. A dose of 240 mg BID produced slightly greater than proportional increase (8.8%) in steady state area under the curve, indicating that Fexofenadine pharmacokinetics are practically linear at these doses between 40 mg and 240 mg taken daily. The major route of elimination is believed to be via biliary excretion while up to 10% of ingested dose is excreted unchanged through the urine.
Special populations
Studies in special risk groups (older people, renally or hepatically impaired patients) indicate that it is not necessary to adjust the dose of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride in these patients.
Indications :
For treatment of allergic rhinitis in adults only
Dosage and Method of Administration :
Adults (> 15 yrs) : one tablet once daily
Warnings and Precautions
Montelukast Sodium
In rare cases, patients on therapy with anti-asthma agents including Montelukast may present with systemic eosinophilia, sometimes presenting with clinical features of vasculitis consistent with Churg-Strauss syndrome, a condition which is often treated with systemic corticosteroid therapy. These cases usually, but not always, have been associated with the reduction or withdrawal of oral corticosteroid therapy. The possibility that leukotriene receptor antagonists may be associated with emergence of Churg-Strauss syndrome can neither be excluded nor established. Physicians should be alert to eosinophilia, vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients. Patients who develop these symptoms should be reassessed and their treatment regimens evaluated. Treatment with Montelukast does not alter the need for patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma to avoid taking aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Neuropsychiatric Events
Neuropsychiatric events have been reported in adult, adolescent, and pediatric patients taking Montelukast. Post-marketing reports with Montelukast use include agitation, aggressive behavior or hostility, anxiousness, depression, disorientation, disturbance in attention, dream abnormalities, hallucinations, insomnia, irritability, memory impairment, restlessness, somnambulism, suicidal thinking and behavior (including suicide), and tremor. The clinical details of some post-marketing reports involving Montelukast appear consistent with a drug-induced effect. Patients and prescribers should be alert for neuropsychiatric events. Patients should be instructed to notify their prescriber if these changes occur. Prescribers should carefully evaluate the risks and benefits of continuing treatment with Montelukast if such events occur.
Eosinophilic Conditions
Patients with asthma on therapy with Montelukast may present with systemic eosinophilia, sometimes presenting with clinical features of vasculitis consistent with Churg-Strauss syndrome, a condition which is often treated with systemic corticosteroid therapy. These events have been sometimes associated with the reduction of oral corticosteroid therapy. Physicians should be alert to eosinophilia, vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients. A causal association between Montelukast and these underlying conditions has not been established.
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride
As with most new medicinal products there is only limited data in the older people and renally or hepatically impaired patients. Fexofenadine Hydrochloride should be administered with care in these special groups. Patients with a history of or ongoing cardiovascular disease should be warned that, antihistamines as a medicine class have been associated with the adverse reactions, tachycardia and palpitations.
Effects on ability to drive and use machines
On the basis of the pharmacodynamic profile and reported adverse reactions it is unlikely that Fexofenadine Hydrochloride tablets will produce an effect on the ability to drive or use machines. In objective tests, Fexofenadine has been shown to have no significant effects on central nervous system function. This means that patients may drive or perform tasks that require concentration. Montelukast is not expected to affect a patient's ability to drive a car or operate machinery. However, in very rare cases, individuals have reported drowsiness or dizziness. However, in order to identify sensitive people who have an unusual reaction to medicinal products, it is advisable to check the individual response before driving or performing complicated tasks.
Adverse Effects
Montelukast Sodium
Very common (≥ 1/10) :Upper respiratory infection
Common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10) : Diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, Elevated levels of serum transaminases (ALT, AST), Rash, and Pyrexia.
Uncommon (≥1/1,000 to < 1/100) : Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, Dream abnormalities including nightmares, insomnia, somnambulism, irritability, anxiety, restlessness, agitation including aggressive behaviour or hostility, depression, Dizziness, drowsiness paraesthesia/hypoesthesia, seizure, Epistaxis, Dry mouth, dyspepsia Bruising, urticaria, pruritus, Arthralgia, myalgia including muscle cramps, Asthenia/fatigue, malaise, oedema.
Rare (≥ 1/10,000 to < 1/1,000) : Increased bleeding tendency, Tremor, Palpitations, Angiooedema,
Very rare(< 1/10,000) : Hepatic eosinophilic infiltration, Hallucinations, suicidal thinking and behaviour (suicidality), Churg-Strauss Syndrome (CSS), Hepatitis (including cholestatic, hepatocellular, and mixed-pattern liver injury), Erythema nodosum erythema multiforme.
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride
The following frequency rating has been used, when applicable : Very common ≥1/10 ; Common ≥1/100 and <1/10; Uncommon ≥1/1,000 and <1/100; Rare ≥1/10,000 and <1/1,000; Very rare <1/10,000 and not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data). Within each frequency grouping, undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness. In adults, the following undesirable effects have been reported in clinical trials, with an incidence similar to that observed with placebo :
Common
Nervous system disorders : headache, drowsiness, dizziness
Gastrointestinal disorders : Common: nausea
General disorders and administration site conditions
Uncommon : fatigue In adults, the following undesirable effects have been reported in post-marketing surveillance. The frequency with which they occur is not known (can not be estimated from available data) :
Immune system disorders : Hypersensitivity reactions with manifestations such as angioedema, chest tightness, dyspnoea, flushing and systemic anaphylaxis
Psychiatric disorders : Insomnia, nervousness, sleep disorders or nightmares/excessive dreaming
Cardiac disorders : Tachycardia, palpitations Gastrointestinal disorders : Diarrhoea
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders : Rash, urticaria, pruritus
Drug Interactions
Montelukast Sodium
Montelukast may be administered with other therapies routinely used in the prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma. In drug-interactions studies, the recommended clinical dose of Montelukast did not have clinically important effects on the pharmacokinetics of the following medicinal products : theophylline, prednisone, prednisolone, oral contraceptives (ethinyl estradiol/ norethindrone 35/1), terfenadine, digoxin and warfarin. The area under the plasma concentration curve (AUC) for Montelukast was decreased approximately 40% in subjects with co-administration of phenobarbital. Since Montelukast is metabolised by CYP 3A4, 2C8, and 2C9, caution should be exercised, particularly in children, when Montelukast is co-administered with inducers of CYP 3A4, 2C8, and 2C9, such as phenytoin, phenobarbital and rifampicin. In vitro studies have shown that Montelukast is a potent inhibitor of CYP 2C8. However, data from a clinical drug-drug interaction study involving Montelukast and Rosiglitazone (a probe substrate representative of medicinal products primarily metabolized by CYP 2C8) demonstrated that Montelukast does not inhibit CYP 2C8 in vivo. Therefore, Montelukast is not anticipated to markedly alter the metabolism of medicinal products metabolised by this enzyme (e.g., Paclitaxel, Rosiglitazone, and Repaglinide.) In vitro studies have shown that Montelukast is a substrate of CYP 2C8, and to a less significant extent, of 2C9, and 3A4. In a clinical drug-drug interaction study involving Montelukast and Gemfibrozil (an inhibitor of both CYP 2C8 and 2C9) gemfibrozil increased the systemic exposure of Montelukast by 4.4-fold. No routine dosage adjustment of Montelukast is required upon co-administration with Gemfibrozil or other potent inhibitors of CYP 2C8, but the physician should be aware of the potential for an increase in adverse reactions. Based on in vitro data, clinically important drug interactions with less potent inhibitors of CYP 2C8 (e.g., Trimethoprim) are not anticipated. Co-administration of Montelukast Sodium and Fexofenadine Hydrochloride with Itraconazole, a strong inhibitor of CYP 3A4, resulted in no significant increase in the systemic exposure of Montelukast.
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride
Fexofenadine does not undergo hepatic biotransformation and therefore will not interact with other medicinal products through hepatic mechanisms. Co-administration of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride with Erythromycin or Ketoconazole has been found to result in a 2-3 times increase in the level of Fexofenadine in plasma. The changes were not accompanied by any effects on the QT interval and were not associated with any increase in adverse reactions compared to the medicinal products given singly. Animal studies have shown that the increase in plasma levels of Fexofenadine observed after coadministration of Erythromycin or Ketoconazole appears to be due to an increase in gastrointestinal absorption and either a decrease in biliary excretion or gastrointestinal secretion, respectively. No interaction between Fexofenadine and Omeprazole was observed. However, the administration of antacid containing Aluminium and Magnesium Hydroxide gels 15 minutes prior to Fexofenadine Hydrochloride caused a reduction in bioavailability, most likely due to binding in the gastrointestinal tract. It is advisable to leave 2 hours between administration of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride and Aluminium and Magnesium Hydroxide containing antacids
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Montelukast Sodium : Animal studies do not indicate harmful effects with respect to effects on pregnancy or embryonal/fetal development. Limited data from available pregnancy databases do not suggest a causal relationship between Montelukast and Malformations (i.e. limb defects) that have been rarely reported in worldwide post marketing experience.
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride : There are no adequate data from the use of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride in pregnant women. Limited animal studies do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to effects on pregnancy, embryonal/foetal development, parturition or postnatal development.
Montefex Tablets may be used during pregnancy only if it is considered to be clearly essential.
Lactation
Montelukast Sodium : Studies in rats have shown that Montelukast is excreted in milk. It is not known if Montelukast is excreted in human milk.
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride : There are no data on the content of human milk after administering Fexofenadine Hydrochloride. However, when Terfenadine was administered to nursing mothers, Fexofenadine was found to cross into human breast milk. Therefore Montefex Tablets are not recommended for mothers breast-feeding their babies.
Paediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Montefex Tablets in paediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
There is no data on the geriatric use of this combination. However, the following data is available on the individual components :
Montelukast : No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between the elderly subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but the greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Fexofenadine : In subjects aged 65 years and above, the reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the geriatric and younger subjects. This drug is substantially excreted by the kidneys and, hence, the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
Overdose
No published data is available on the overdosage of this combination. However, overdosage has been reported with individual component.
Montelukast Sodium
No specific information is available on the treatment of overdose with Montelukast. In chronic asthma studies, Montelukast has been administered at doses up to 200 mg/day to patients for 22 weeks and in short term studies, up to 900 mg/day to patients for approximately one week without clinically important adverse experiences. There have been reports of acute overdose in post-marketing experience and clinical studies with Montelukast. These include reports in adults and children with a dose as high as 1000 mg (approx. 61 mg/kg in a 42 month old child). The clinical and laboratory findings observed were consistent with the safety profile in adults and paediatric patients. There were no adverse experiences in the majority of overdose reports. The most frequently occurring adverse experiences were consistent with the safety profile of Montelukast and included abdominal pain, somnolence, thirst, headache, vomiting, and psychomotor hyperactivity. It is not known whether Montelukast is dialysable by peritoneal- or haemodialysis.
Fexofenadine Hydrochloride
Dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue and dry mouth have been reported with overdose of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride. Single doses up to 800 mg and doses up to 690 mg twice daily for 1 month or 240 mg once daily for 1 year have been administered to healthy subjects without the development of clinically significant adverse reactions as compared with placebo. The maximum tolerated dose of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride has not been established. Standard measures should be considered to remove any unabsorbed medicinal product. Symptomatic and supportive treatment is recommended. Haemodialysis does not effectively remove Fexofenadine Hydrochloride from blood.
Storage
Store protected from light & moisture at a temperature not exceeding 30°C.
Keep out of reach of children.
Presentation:
A blister strip of 10 tablets