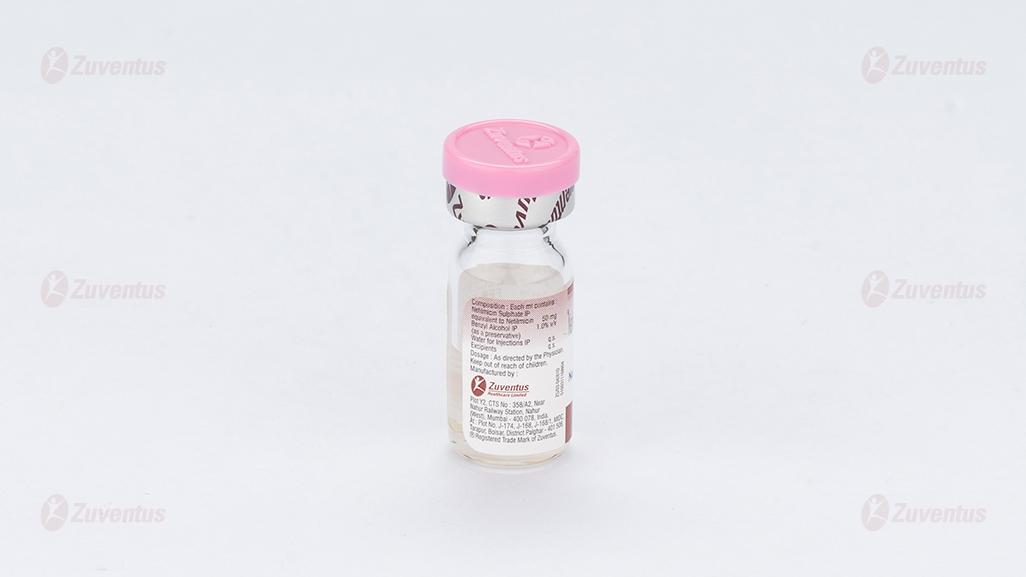
Netromax 50 mg Injection
Therapy Area
Anti Infective
1.0 Name of the medicinal product
Netilmicin injection [10mg / 25mg /50mg / 150mg / 300mg]
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each ml contains:
Netilmicin Sulfate IP equivalent to Netilmicin 10mg / 25mg /50mg / 75mg / 100mg
Preservatives:
Benzyl alcohol IP 1.0% v/v
Water for injection IP q.s.
Excipients q.s.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
IM and IV
10mg / 25mg / 50mg / 150mg / 300mg of Netilmicin
4.0 Clinical Particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the treatment of complicated UTIs, bacteremia, septicemia including neonatal sepsis, gonococcal infection, skin and soft tissue infections, intra-abdominal infections (peritonitis/abscess), serious respiratory tract infections (pneumonia, lung abscess, cystic fibrosis), genitourinary tract infections, bone and joint infections, burns, wounds, peri-operative infections, gastrointestinal tract infections, endocarditis, CNS infections (meningitis and ventriculitis), surgical prophylaxis.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
- The recommended dosage for intravenous and intramuscular administration is identical.
- The patient’s pretreatment body weight should be measured for calculation of correct dosage. Aminoglycoside dosage in obese patients should be based on an estimate of lean body mass.
- Netromax Injection should not be physically premixed with other drugs but should be administered separately in accordance with the recommended route of administration and dosage schedule.
- It is desirable to measure peak and trough Netilmicin serum concentrations to assure adequate but not excessive levels. With the administration of Netromax Injection in two or three daily doses, the peak concentration, measured 30 minutes to 1 hour after administration, is expected to be in the range of 4 to 12 mcg/ml: dosage should be adjusted to avoid prolonged peak serum concentrations above 16 mcg/ml. Trough concentrations (just prior to the next dose) above 4 mcg/ml are to be avoided. With once daily administration of Netromax Injection, peak concentrations between 20-30 mcg/ml can be anticipated.
- The usual duration of treatment for all patients is 7 to 14 days.
- In complicated infections, a longer course of therapy may be necessary. Although prolonged courses of Netilmicin have been well tolerated, it is important that patients treated beyond the usual time period be monitored carefully for changes in renal, auditory and vestibular function. Dosage should be reduced if clinically indicated.
Intramuscular (I.M.) Administration:
Patients with Normal Renal Function:
Adults
- The recommended dosage of Netromax Injection for patients with urinary tract or non-life threatening systemic infections with normal renal function is 4.0 – 6.0 mg/kg/day given in three equal doses every eight hours, two equal doses every twelve hours or once daily.
- In general, within this dose range, the lower dosage will be used for urinary tract infections and the higher dosage for systemic infections. For both uses, the dosage should be adjusted depending on severity of infection and patient condition.
- For adults weighing 40-60 kg, a dose of 100 mg may be given every twelve hours. For adults smaller or larger than the above range, dosage should be calculated in mg/kg of lean body weight.
OR
- For adults weighing 50-90kg, 300 mg once a day or 150 mg may be given every twelve hours or 100 mg every eight hours. For adults weighing less or more than the above range, dosage should be calculated in mg/kg of lean body weight.
- For patients with life-threatening infections, dosages upto 7.5 mg/kg/day may be administered in three equal doses every eight hours. This dosage should be reduced to 6 mg/kg/day or less as soon as clinically indicated, usually within 48 hours.
For Pediatric Patients
- Premature or Full-term Neonate One Week of Age or Less: 6 mg/kg/ day or 3 mg/kg/every 12 hourly.
- Neonates over One Week of Age and Infants: 7.5 to 9.0 mg/kg once a day or 2.5 to 3.0 mg/kg administered every eight hours.
- Children: 6.0 to 7.5 mg/kg/once a day or 2.0 to 2.5 mg/kg/8 hourly
Patients with Impaired Renal Function:
- Dosage must be adjusted in patients with impaired renal function. Whenever possible, Netilmicin serum concentrations should be monitored. Dosage schedules are not intended as rigid recommendations, but are provided as guidance for selecting dosage when the measurement of Netilmicin serum levels is not feasible.
- If serum assay determinations are not available and renal function is stable, serum creatinine and creatinine clearance values are the most reliable, readily available indicators of the degree of renal impairment as a guide for dosage adjustment.
- Variable Frequency Regimen: One method of adjustment is to increase the interval between the usual doses administered. Since the serum creatinine concentration has a high correlation with the Netilmicin serum half-life, this laboratory test may provide guidance for adjustment of the interval between doses. The interval between doses (in hours) may be approximated by multiplying the serum creatinine level (mg/ 100ml) by 8. For example, a patient weighing 60 kg with a serum creatinine level of 3.0 mg/100ml could be given 120 mg (2mg/kg) every 24 hours (3.0x8).
- Variable Dosage Regimen: In patients with serious systemic infections and renal impairment, it may be desirable to administer the antibiotic more frequently but in reduced dosage. In such patients, Netilmicin serum concentrations should be measured.
Suggested methods are:
- After the usual initial or loading dose, a rough guide for determining reduced dosage at eight-hour intervals is to divide the normally recommended dose by the serum creatinine level (Table). For example, after an initial dose of 120 mg (2 mg/kg), a patient weighting 60 kg with a serum creatinine level of 3.0 mg/ 100 ml could be given 40 mg every eight hours (120, 3).
- If the rate of creatinine clearance is known, the maintenance dose to be administered every 8 hours may be calculated using the following formula:
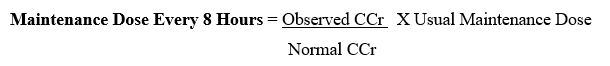
The initial or loading dose is the same as that recommended for a patient with normal renal function.
Table 1. Dosage Adjustment Guide for Patients with Renal Impairment
(Dosage at Eight-Hour Intervals after the Usual Initial Dose)
|
Serum Creatinine (mg/100 ml) |
Approximate Creatinine Clearance Rate ml/min/1.73m2 |
Percent of Usual Dose |
|
<1.0 |
>100 |
100 |
|
1.1 - 1.3 |
70 - 100 |
80 |
|
1.4 – 1.6 |
55 -70 |
65 |
|
1.7 – 1.9 |
45 - 55 |
55 |
|
2.0 - 2.2 |
40 - 45 |
50 |
|
2.3 - 2.5 |
35 – 40 |
40 |
|
2.6 – 3.0 |
30 – 35 |
35 |
|
3.1 – 3.5 |
25 – 30 |
30 |
|
3.6 – 4.0 |
20 – 25 |
25 |
|
4.1 – 5.1 |
15 – 20 |
20 |
|
5.2 – 6.6 |
10 - 15 |
15 |
|
6.7 – 8.0 |
< 10 |
10 |
The above dosage schedules are provided as dosage guides when the measurement of Netilmicin serum levels is not feasible.
Deteriorating renal function may require a greater reduction in dosage than that specified in the guidelines for patients with stable renal impairment.
INTRAVENOUS (IV) ADMINISTRATION:
- The intravenous administration of Netilmicin may be particularly useful for treating patients with septicemia or those in shock.
- It may also be the preferred route of administration for some patients with congestive heart failure, hematologic disorders, severe burns or those with reduced muscle mass.
- For intravenous administration in adults, a single dose of Netromax Injection may be diluted in 50 to 200 ml of sterile normal saline or in a sterile solution of dextrose 5% in water; in infants and children the volume of diluent should be dependent on the patient’s fluid requirements. The solution may be infused over a period of one-half to two hours.
- In certain circumstances, a dose may be injected directly into a vein or IV tubing slowly over a period of 3 to 5 minutes.
Netromax Injection is physically compatible with the following parenteral solutions:
- Sterile Water for Injection,
- Normal Saline,
- 5% Dextrose and 0.9% Sodium Chloride,
- Ringer’s Injection
- Lactated Ringer’s Injection with 5% Dextrose.
SPECIFIC DOSAGE REGIMENS:
Gonorrhea in Males and Females:
A single intramuscular injection of 300 mg Netromax Injection is recommended. The injection (100 mg/ml) should be made deep in the upper outer quadrant of the gluteal muscle, with one-half dose in each buttock. Dosage adjustments using lean body weight are recommended for small or large patients.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI):
Patients with uncomplicated UTI, particularly if chronic and recurrent and without evidence of renal insufficiency may be treated with a single daily dose of 3 mg/kg, for example 150-200 mg, of Netilmicin administered intramuscularly for 7 to 10 days.
Hemodialysis:
In adults with renal failure undergoing hemodialysis, the amount of Netilmicin removed from the blood may vary depending upon several factors, including the dialysis method used. An eight-hour hemodialysis may reduce serum concentrations of Netilmicin by approximately 63%. The recommended dose at the end of each dialysis period is 2 mg/kg. In children, a dose of 2 to 2.5 mg/kg may be administered, depending upon the severity of infection.
4.3 Contraindications
Hypersensitivity or serious toxic reactions to Netromax or other aminoglycosides.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
- Evidence of ototoxicity or nephrotoxicity requires dosage adjustment or discontinuance of the drug. As with other aminoglycosides, on rare occasions changes in renal and eighth cranial nerve function may not manifest until after completion of therapy.
- Aminoglycoside serum concentrations should be monitored when feasible to assure adequate levels and to avoid potentially toxic levels. When monitoring peak concentrations of Netilmicin, adjust dosage so that prolonged levels above 16 mcg/ml are avoided.
- When trough concentrations are monitored (just prior to the next dose), they should be in the range of 0.5 to 2 mcg/ml at the recommended dosage. Trough concentrations above 4 mcg/ml are to be avoided. Excessive peak and/or trough aminoglycoside serum concentrations may increase the risk of renal and eighth cranial nerve toxicities.
- In patients with extensive body surface burns, altered pharmacokinetics may result in reduced serum concentrations of aminoglycosides. Measurement of Netilmicin serum concentrations is particularly important in these patients as a basis for dosage adjustment.
- Concurrent and/or sequential systemic or topical use of other potentially neurotoxic and/or nephrotoxic drugs, such as cisplatin, bacitracin, polymyxin B, colistin, cephaloridine, amphotericin B, kanamycin, acyclovir, gentamicin, amikacin, sisomicin, tobramycin, neomycin, streptomycin, paromomycin, viomycin and vancomycin should be avoided. Advanced age and dehydration may increase patient risk of toxicity.
- Concurrent use of Netilmicin with potent diuretics, such as ethacrynic acid or furosemide, should be avoided since these diuretics by themselves may cause ototoxicity. In addition, when administered intravenously, diuretics may enhance aminoglycoside toxicity by altering the antibiotic concentration in serum and tissue.
- Neurotoxic or nephrotoxic antibiotics may be absorbed in significant quantities from body surfaces after local irrigation or application. The potential toxic effect of antibiotics administered in this fashion should be considered.
- Increased nephrotoxicity has been reported following concomitant administration of aminoglycoside with some cephalosporins.
- Although neuromuscular blockade and respiratory paralysis have not been a problem in clinical trials, they have been reported in animals receiving Netilmicin at doses considerably above those clinically recommended. The possibility of these phenomena occurring in man should be considered, particularly if aminoglycosides are administered to patients receiving neuromuscular blocking agents, such as succinylcholine, tubocurarine or decamethonium; anesthetics or massive transfusions of citrate-anti-coagulated blood. If neuromuscular blockade occurs, calcium salts may reverse it.
- Aminoglycosides should be used with caution in patients with neuromuscular disorders, such as myasthenia gravis, Parkinsonism or infant botulism since these drugs theoretically may aggravate muscle weakness because of their potential curare-like effects on the neuromuscular junction.
- Elderly patients may have reduced renal function which may not be evident in the results of routine screening tests, such as BUN or serum creatinine. A creatinine clearance determination may be more useful. Monitoring of renal function during Netilmicin treatment as with other aminoglycosides is particularly important in these patients.
- A Fanconi-like syndrome, with aminoaciduria and metabolic acidosis, has been reported in some adults and infants treated with Netilmicin sulfate.
- Cross-allergenicity among aminoglycosides has been demonstrated.
- In vitro mixing of an aminoglycoside with beta-lactam-type antibiotics (penicillins or cephalosporins) may result in a significant mutual inactivation. Even when an aminoglycoside and a penicillin-type drug are administered separately by different routes, a reduction in aminoglycoside serum half-life or serum levels has been reported in patients with impaired renal function and in some patients with normal renal function. Usually such inactivation of the aminoglycoside is clinically significant only in patients with severely impaired renal function.
- Treatment with netilmicin sulfate may result in overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms. If this occurs, appropriate therapy is indicated.
4.5 Drug interactions
- Cisplatin
- Bacitracin
- Polymyxin B
- Colistin
- Cephaloridine
- Amphotericin B
- Kanamycin
- Acyclovir
- Gentamicin
- Amikacin
- Sisomicin
- Tobramycin
- Neomycin
- Streptomycin
- Paromomycin
- Viomycin
- Vancomycin
- Potent diuretics (such as ethacrynic acid or furosemide)
- Beta-lactam-type antibiotics (penicillins or cephalosporins)
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
Aminoglycoside antibiotics cross the placenta and may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. There have been reports of total irreversible bilateral congenital deafness in children whose mothers received aminoglycosides, including Netilmicin during pregnancy. If Netilmicin is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking Netilmicin, she should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Lactation
Studies in nursing mothers indicate that small amounts of Netilmicin sulfate are excreted in breast milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug.
4.7 Effects on the ability to drive and use machines
Netilimicin has moderate influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Nephrotoxicity: Adverse renal effects, generally mild in nature, have been reported infrequently after Netilmicin administration. They occur more frequently in the elderly, in patients with a history of renal impairment, in patients treated for longer periods or with larger than the recommended dosage, and are most often reversible.
Neurotoxicity: Unlike other aminoglycosides, incidence of vestibular and cochlear toxicity with Netromax Injection is very low. Impairment of vestibular function may be transient due to compensatory mechanisms. The rarely reported cochlear impairment is usually irreversible. These adverse effects occur primarily in patients with renal impairment and in patients treated with high doses and/ or prolonged periods. Other factors may increase the risk of aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity. Symptoms of aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity are often transient and may include dizziness, vertigo, and tinnitus, roaring in the ears and hearing loss. The latter is usually manifested by diminution of high-tone acuity.
The risk of toxic reactions is low in patients with normal renal function who do not receive Netromax Injection either at higher doses or for longer periods of time than recommended. Some patients who have had previous neurotoxic reactions to other aminoglycosides have been treated safely with Netromax Injection.
Other rarely reported adverse reactions: Headache, malaise, visual disturbances, disorientation, tachycardia, hypotension, palpitations, thrombocytosis, paresthesia, rash, chills, fever, fluid retention, vomiting and diarrhea. Very rarely, anaphylaxis has been reported.
Laboratory abnormalities: Increased blood sugar; increased alkaline phosphatase; increased AST (SGOT) or ALT (SGPT); bilirubin; increased potassium; other abnormal liver function tests; decreased hemoglobin, WBCs and platelets; eosinophilia, anemia and increase in prothrombin time.
Injection site or local reaction: While local tolerance of Netromax Injection is generally excellent, there has been an occasional report of pain at the injection site or local reaction. In a randomized comparative clinical trial of netilmicin and amikacin, pain associated with intramuscular injections was significantly milder with netilmicin than with amikacin.
Reporting of side effects
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
In the event of overdose or toxic reaction, hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis will aid in the removal of Netilmicin sulfate from the blood. However, the rate of removal is considerably less by peritoneal dialysis. These procedures are of particular importance for patients with impaired renal function.
5.0 Pharmacological Properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Netilmicin is a rapidly acting bactericidal aminoglycoside antibiotic which acts by inhibiting normal protein synthesis in susceptible organisms. Aminoglycosides are taken up into sensitive bacterial cells by an active transport process which is inhibited in anaerobic, acidic, or hyperosmolar environments. Within the cell they bind to the 30S and to some extent to the 50S, subunits of the bacterial ribosome, inhibiting protein synthesis and generating errors in the transcription of the genetic code. The overall effect is irreversible and lethal for the bacterial cell.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
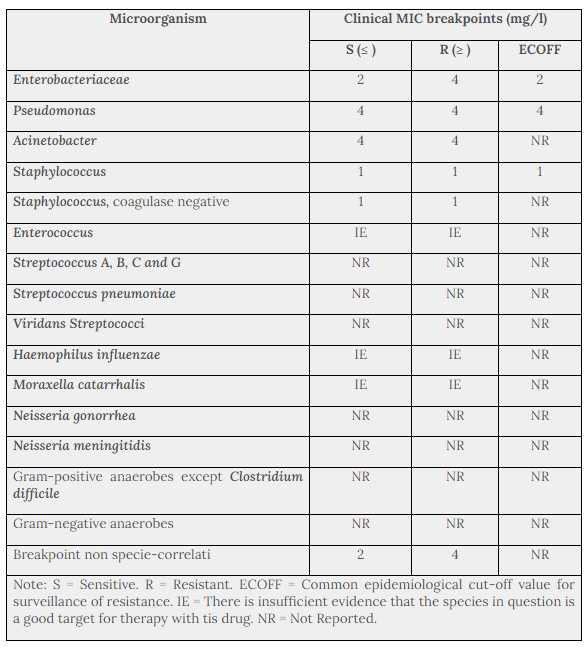
Table 1 provides MIC breakpoints, separating susceptible from intermediate susceptible organisms, and intermediate from resistant organisms, based on data from EUCAST. The prevalence of resistance may vary geographically and with time for selected species and local information on resistance is desirable, particularly when treating severe infections. As necessary, expert advice should be sought when the local prevalence of resistance is such that the utility of the agent in at least some types of infections is questionable. The following information gives only an approximate guidance on probabilities whether bacteria will be susceptible to netilmicin.
The breakpoint definitions classifying isolates as susceptible or resistant are useful in predicting clinical efficacy of antibiotics that are administered systemically. The frequency of overall aminoglycoside resistance may be up to 50% of all staphylococci in some European countries.
Table 1. Species-Related Clinical MIC Breakpoints (EUCAST 2012)
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
After intramuscular injection of Netilmicin, peak plasma concentrations are achieved within 0.5 to 1 hour, and concentrations of about 7 mcg/ml have been reported following doses of 2 mg/kg; similar concentrations are obtained after intravenous infusion of the same dose over 1 hour. Peak concentrations after rapid intravenous injection may transiently be 2 or 3 times higher than those following infusion. Standard, once-daily doses may produce transient peak concentrations of 20 to 30 mcg/ml. In multiple dosing studies, Netilmicin in usual doses every 12 hours produced steady-state concentrations on the second day which were less than 20% of those seen after the first dose. The half-life of Netilmicin is usually 2.0 to 2.5 hours. About 80% of a dose is excreted in the urine within 24 hours.
6.0 Nonclinical Properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
The aminoglycosides as a class of antibiotics are known to have the potential to cause significant nephrotoxic and ototoxic effects, some of which may be irreversible. Fertility, teratogenicity and postnatal studies of netilmicin in rats and rabbits have not provided any significant evidence of toxicity of netilmicin, particularly following ocular administration.
7.0 Description
Netromax Injection contains netilmicin sulfate, a semi-synthetic, water-soluble antibiotic of the aminoglycoside group.
Molecular formula: (C21H41N5O7)25H2SO4
Molecular weight : 1441.54
Netilmicin Sulfate structural formula:
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
None
8.2 Shelf life
Refer to the pack.
8.3 Packaging Information
Vials of 10mg per ml
Vials of 25mg per ml
Vials of 50mg per ml
Vials of 150mg per 2ml
Vials of 300mg per 3ml
8.4 Storage and handling instructions
Store below 30ºC. Do not freeze.
Keep out of reach of children.
Do not use in case any foreign particulate matter is observed inside the vial.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
- Patients treated with aminoglycosides should be under close clinical observation because of the potential toxicity associated with their use.
- Monitoring of renal and eighth cranial nerve functions is recommended during therapy, particularly for patients with known or suspected reduced renal function either at onset of therapy or during therapy.
- Urine should be examined for decreased specific gravity, increased protein excretion and the presence of cells or casts.
- Blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine or creatinine clearance should be determined periodically. When feasible, serial audiograms are recommended, particularly in high-risk patients.
- Aminoglycoside serum concentrations should be monitored when feasible to assure adequate levels and to avoid potentially toxic levels. When monitoring peak concentrations of Netilmicin, adjust dosage so that prolonged levels above 16 mcg/ml are avoided.
- When trough concentrations are monitored (just prior to the next dose), they should be in the range of 0.5 to 2 mcg/ml at the recommended dosage. Trough concentrations above 4 mcg/ml are to be avoided. Excessive peak and/or trough aminoglycoside serum concentrations may increase the risk of renal and eighth cranial nerve toxicities.
- In patients with extensive body surface burns, altered pharmacokinetics may result in reduced serum concentrations of aminoglycosides. Measurement of Netilmicin serum concentrations is particularly important in these patients as a basis for dosage adjustment.
- Advanced age and dehydration may increase patient risk of toxicity.
- Patients should be well hydrated during treatment.
- Netromax Injection contains sodium metabisulfite and sodium sulfite; these may cause allergic-type reactions including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in certain susceptible people. Sulfite sensitivity is observed more frequently in asthmatic than in non-asthmatic people.
11.0 Date of revision of the text
This leaflet was last revised in May 2024.
About Leaflet
The name of your medicine is NetromaxTM-10/25/50/150/300. We refer to them as Netromax or Netromax injection throughout this leaflet.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1. What Netromax injection is and what they are used for
2. What you need to know before you take Netromax injection
3. How Netromax injection is given
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store Netromax injection
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Netromax injections are and what they are used for
Netromax injections contain Netilmicin sulfate, a semi-synthetic, water-solution antibiotic of the aminoglycoside group. Netilmicin acts by inhibiting normal protein synthesis in susceptible organisms.
Netromax injection is used in the treatment of the following conditions:
- Complicated UTIs, Genitourinary tract infections
- Bacteremia, Septicemia including neonatal sepsis,
- Gonococcal infection
- Skin and soft tissue infections, Burns, wounds
- Intra-abdominal infections (peritonitis/abscess)
- Serious respiratory tract infections (pneumonia, lung abscess, cystic fibrosis)
- Bone and joint infections
- Gastrointestinal tract infections, Endocarditis
- CNS infections (meningitis and ventriculitis)
- Peri-operative infections, Surgical prophylaxis
2. What you need to know before you take Netromax injections
Do not take Netromax injections:
If you are allergic to Netromax or other aminoglycosides antibiotics.
Precautions
Use Netromax injections with caution in-
- Patients treated with aminoglycosides because this drug may cause toxicity
- Patients with known or suspected reduced kidney function either at the start of therapy or during therapy
- Patient with signs of damage to kidney or ear
- In patients with extensive body surface burns
- Patient who is using Concurrently and/or topically other drugs which can cause damage to kidney and inner ear
- Patient taking cephalosporins
- Patient with muscle weakness
- Elderly patient, Dehydrated patient
Other medicines and Netromax Injection
Tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken or might take/use any other medicines. Special care is needed if you are taking/using other medicines, as some could interact with Netilmicin for example:
- Diuretics (water tablets) such as furosemide and ethacrynic acid
- Other antibiotics that can affect your kidneys, hearing or balance
- Anaesthetics or muscle-relaxing drugs
- Indomethacin (an anti-inflammatory medicine)
- Other antibiotics called beta-lactamases such as penicillins or cephalosporins
- Platinum compounds used in chemotherapy such as cisplatin
Pregnancy and breast-feeding If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Pregnancy: Do not take Netromax injections if you are pregnant or trying to become pregnant as this drug may cause harm to your growing baby in the womb. Tell your doctor, immediately, if you become pregnant during treatment with Netromax injections.
Breast-feeding: Do not take Netromax injections if you are breastfeeding because the active substance of Netromax injections passes into breast milk and could harm your baby.
Driving and using machines
Do not drive or use machines.
3. How Netromax injection is given
Netromax injection is usually given by a doctor or nurse. The recommended dosage for intravenous and intramuscular administration is similar. The usual duration of treatment for all patients is 7 to 14 days. In complicated infections, a longer course of therapy may be necessary. Although prolonged courses of Netilmicin have been well tolerated, it is important that patients treated beyond the usual time period be monitored carefully for changes in renal, auditory and vestibular function. Dosage should be reduced if clinically indicated.
Intramuscular Administration:
Patients with Normal Kidney Function
Adults:
- The recommended dosage of Netromax Injection for patients with urinary tract or non-life threatening infections with normal kidney function is 4.0 – 6.0 mg/kg/day given in three equal doses every eight hours, two equal doses every twelve hours, or once daily.
- The dosage should be adjusted depending on the severity of infection and patient condition.
- For adults weighing 40-60 kg, a dose of 100 mg may be given every twelve hours. For adults smaller or larger than the above range, dosage should be calculated in mg/kg of lean body weight.
For Pediatric Patients
- Premature or Full-term Neonate One Week of Age or Less: 6 mg/kg/ day or 3 mg/kg/every 12 hourly.
- Neonates over One Week of Age and Infants: 7.5 to 9.0 mg/kg once a day or 2.5 to 3.0 mg/kg administered every eight hours.
- Children: 6.0 to 7.5 mg/kg/once a day or 2.0 to 2.5 mg/kg/8 hourly
Patients with Impaired Renal Function:
- Dosage must be adjusted in patients with impaired renal function.
Specific dosage regimens:
- Gonorrhea (Sexually transmitted infection) in Males and Females:
A single intramuscular injection of 300 mg Netromax Injection is recommended.
- Urinary Tract Infections:
For Patients with Urinary tract infection, a single daily dose of 3 mg/kg, for example, 150-200 mg, of Netilmicin is administered intramuscularly for 7 to 10 days.
- Hemodialysis:
The recommended dose at the end of each dialysis period is 2 mg/kg. In children, a dose of 2 to 2.5 mg/kg may be administered, depending upon the severity of the infection.
If you take more Netromax injections than you should
If you accidentally take more Netromax injections, then you should tell your doctor immediately or contact your nearest accident and emergency department. Show any left-over medicines or the empty packet to the doctor.
Intravenous (IV) Administration:
- The intravenous administration of Netilmicin may be particularly useful for treating patients with septicemia or those in shock.
- It may also be the preferred route of administration for some patients with congestive heart failure, hematologic disorders, severe burns or those with reduced muscle mass.
- For intravenous administration in adults, a single dose of Netromax Injection may be diluted in 50 to 200 ml of sterile normal saline or in a sterile solution of dextrose 5% in water; in infants and children the volume of diluent should be dependent on the patient’s fluid requirements. The solution may be infused over a period of one-half to two hours.
- In certain circumstances, a dose may be injected directly into a vein or IV tubing slowly over a period of 3 to 5 minutes.
If you forget to take Netromax injections
If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as possible, unless it is almost time to take the next dose. Do not take a double dose. Then go on as before.
If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
If you are given too much or too little Netromax Injection
This medicine will be given to you in a hospital, under the supervision of a doctor. It is unlikely that you will be given too much or too little, however, tell your doctor or nurse if you have any concerns.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If you get any of the following effects tell your doctor or pharmacist immediately:
- Effects on kidney: Netromax injection may cause little damage to the kidney.
- Effects on the nervous system: As compared to another aminoglycoside antibiotic, the chances of having damage to the inner ear using Netromax injection are very low.
- Other rarely reported side effects: Headache, weakness, disturbance in vision of eyes, increased heart rate, Low BP, Irregular heartbeat, increase in platelet count, abnormal tingling or pricking sensation, rash, chills, fever, fluid retention, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Very rarely anaphylaxis has been reported.
- Changes in laboratory reports: Increased blood sugar; increased liver enzyme; increased potassium; other abnormal liver function tests; decreased iron in blood, White Blood Cells, and platelets, anemia, and increase in time taken by your blood to form a clot.
- Injection site or local reaction: Pain at the injection site or local reaction may occur.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Netromax Injection
Store below 300C. Do not freeze. Do not use it in case any foreign particulate matter is observed inside the vial. Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of Children. The color of Netromax injection varies from water white to pale yellow. A dark yellow solution should not be used. Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Netromax injection contain
The active substance is Netilmicin.
Composition:
Each ml contains:
Netilmicin Sulfate IP equivalent to Netilmicin 10mg / 25mg /50mg / 75mg / 100mg
Preservatives:
Benzyl alcohol IP 1.0% v/v
(As a preservative)
Water for injection IP q.s.
Excipients q.s.
Presentation/pack size
Netromax-10: a vial of 10mg/1ml
Netromax-25: a vial of 25mg/1ml
Netromax-50: a vial of 50mg/1ml
Netromax-150: a vial of 150mg/2ml
Netromax-300: a vial of 300mg/3ml
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Zuventus Healthcare Limited
Zuventus House, Plot Y2, CTS No.: 358/A2,
Near Nahur Railway Station,
Nahur (W), Mumbai, 400078 Maharashtra, India.
This leaflet was last revised in 05/2024.