Normet Tablet
Therapy Area
Anti Infective
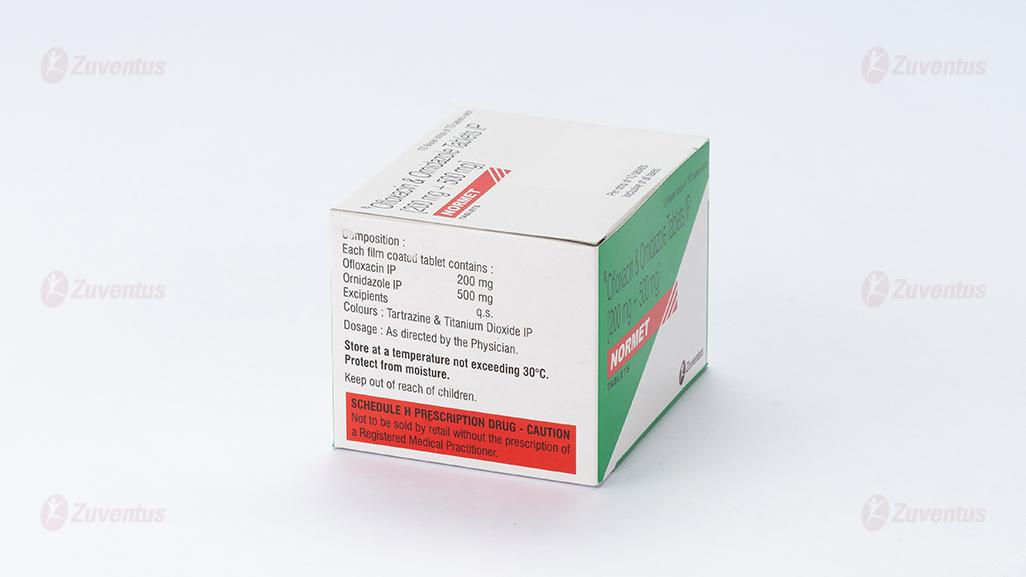
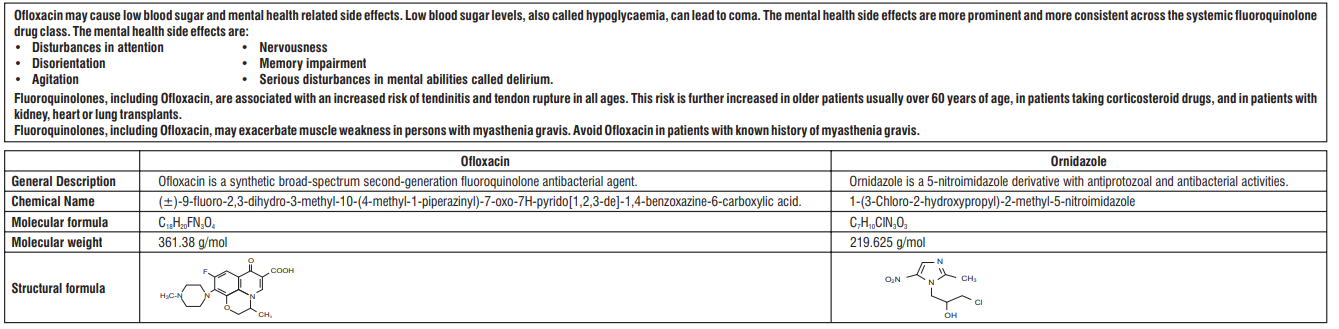
Composition
Each film coated tablet contains :
Ofloxacin IP 200 mg
Ornidazole IP 500 mg
Excipients q.s
Colours : Tartrazine & Titanium Dioxide IP
Rationale of the combination
The rationale of combination is based on the fact that quinolones and nitroimidazole derivatives act synergistically. Combinations of fluoroquinolones with other antimicrobial agents have been extensively investigated. Combinations of fluoroquinolones with nitroimidazole,show synergy against Enterobacteriaceae and gram-positive bacteria. Combination covers all treatment related aspects and to widen the spectrum of activity of these two agents.
Pharmacodynamics:
Ofloxacin inhibits bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting bacterial topoisomerases, particularly DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV and shows bactericidal action. Ornidazole is a 5-nitroimidazole derivative active against protozoa and anaerobic bacteria. It is converted to reduction products that interact with DNA to cause destruction of the helical DNA structure and strand, leading to a protein synthesis inhibition and cell death in susceptible organisms.

Microbiology:
Ofloxacin
Therapeutic doses of Ofloxacin are devoid of pharmacological effects on the voluntary or autonomic nervous system. According to DIN 58 940, the following limits apply for Ofloxacin : Susceptible (S)≤ 1 mg/L, Intermediate (I) = 2 mg/L, Resistant (R) ≥ 4 mg/L.
Range of acquired bacterial resistance to Ofloxacin is as follows :
Normally susceptible
Aerobic Gram-positive micro-organisms : S. aureus - methicillin-sensitive (0.3-12.6%), S. pyogenes (2-5%)
Aerobic Gram-negative micro-organisms : Acinetobacter spp (0.3-7.3%), Citrobacter spp. (3-15%), Enterobacter spp. (2-13%), E. coli (1-8%), H. influenzae (1%), Klebsiella spp. (1-10%), Moraxella spp. (0-0.2%), Morganella morganii (0-6.9%), N. gonorrhoeae (25%) Proteus spp. (1-15%), Serratia marcescens (2-2.4%)
Others : Chlamydia spp, L. pneumophila
Intermediately susceptible :
Aerobic Gram-positive micro-organisms : S. pneumoniae (70%), Providentia (17.1%)
Aerobic Gram-negative micro-organisms : E. faecalis (50%), P. aeruginosa (20-30%), Serratia spp. (20-40%)
Ornidazole
Ornidazole is effective against Trichomonas vaginalis, Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia lamblia (Giardia intestinalis), and also against certain anaerobic bacteria such as Bacteroides and Clostridium spp., Fusobacterium spp., and anaerobic cocci.
INDICATION :
For treatment of diarrhea of mixed infection in adult only
Contraindications:
Normet is contraindicated in the following situations:
• Known hypersensitivity to nitroimidazoles and/or Ofloxacin, any other fluoroquinolone antibacterial, or to any excipients listed in formulation.
• In patients with a history of epilepsy or an existing central nervous system disorder with a lowered seizure threshold.
• In patients with a history of tendon disorders related to fluoroquinolone administration
• Pregnant or breastfeeding women.
• In patients with latent or actual defects in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity because they may be prone to hemolytic reactions when treated with quinolone antibacterial agents.
Dosage and Administration :
One tablet of Normet is recommended as twice-daily therapy.
Use in Special Populations
Hepatic impairment
• Ofloxacin should be used with caution in patients with impaired liver function, as liver damage may occur.In patients with liver cirrhosis, the Ornidazole elimination half-life is longer (22 versus 14 hours) and clearance lower (35 versus 51 ml/min) than in healthy subjects. The dosing interval should be doubled in patients with severe hepatic impairment.Hence,Normet should be used with caution in patients with hepatic impairment.
Renal impairment
• Since Ofloxacin is eliminated primarily via the kidneys, the dose should be adjusted in patients with impaired renal function. The pharmacokinetics of Ornidazole is unaltered in renal impairment.
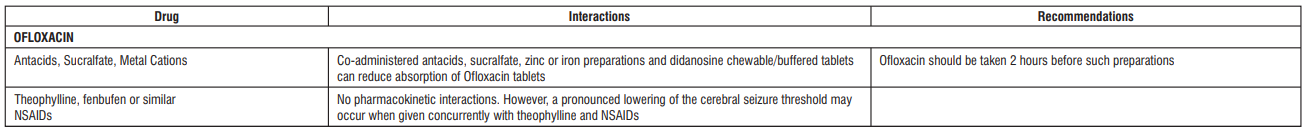
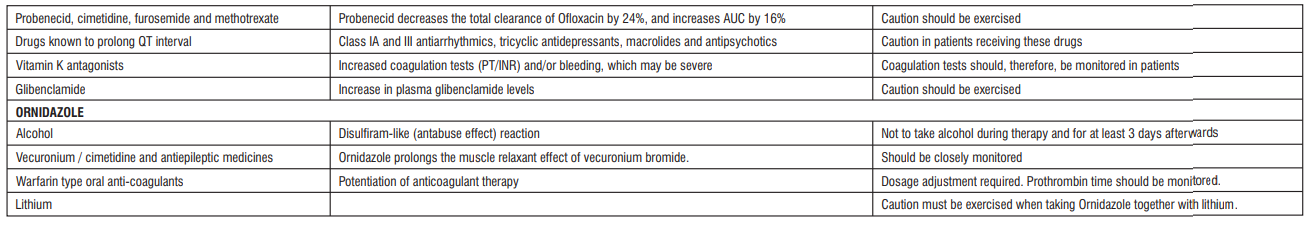
Drug Interactions:
Warnings and Precautions
Ofloxacin
Methicillin-resistant S. Aureus- Ofloxacin is not recommended for the treatment of known or suspected MRSA infections unless laboratory results have confirmed susceptibility of the organism to Ofloxacin
Resistance to fluoroquinolones of E. Coli- Prescribers are advised to take into account the local prevalence of resistance in E. coli to fluoroquinolones.
Severe bullous reactions- Patients should be advised to contact their doctor immediately prior to continuing treatment if skin and/or mucosal reactions occur
Tendonitis- If tendinitis is suspected, treatment with Ofloxacin must be halted immediately, and appropriate treatment must be initiated.
Hypersensitivity- Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions can progress to life-threatening shock
Diseases caused by Clostridium difficile- If pseudo-membraneous colitis is suspected, treatment should be discontinued immediately.
Patients with impaired renal function- Since Ofloxacin is eliminated primarily via the kidneys, the dose should be adjusted in patients with impaired renal function
Patients with history of psychotic disorder- Ofloxacin should be used with caution in patients with a history of psychotic disorder or in patients with psychiatric disease.
Patients with impaired liver function- Patients should be advised to stop treatment and contact their doctor if signs and symptoms of hepatic disease develop
Patients treated with vitamin K antagonists- Coagulation tests should be monitored when these drugs are given concomitantly
Myasthenia gravis- not recommended in patients with a known history of myasthenia gravis.
Superinfection- If secondary infection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures be taken
Prevention of photosensitisation- patients should not expose themselves unnecessarily to strong sunlight or to artificial UV rays for 48 hours following treatment
QT interval prolongation- Caution with known risk factors for prolongation of the QT interval.
Dysglycaemia- Careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
Peripheral neuropathy- Ofloxacin should be discontinued if the patient experiences symptoms of neuropathy
Interference with laboratory tests- In patients treated with Ofloxacin, determination of opiates or porphyrin levels in urine may give false-positive results.
Vision disorders- If vision becomes impaired, an eye specialist should be consulted immediately
ORNIDAZOLE
Caution should be exercised in patients with diseases of the CNS, e.g. epilepsy or multiple sclerosis. The effect of other medicines can be intensified or impaired.
Adverse Effects :
Ofloxacin
Frequencies are defined using the following convention: uncommon (≥ 1/1,000, < 1/100), rare (≥
1/10,000, < 1/1,000), very rare (< 1/10,000), not known (cannot be estimated from the available
data). * postmarketing experience
Stevens-Johnson syndrome / Toxic epidermal necrolysis is reported adverse drug reaction
associated with the use of Ofloxacin.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders : Very rare- Anaemia, Haemolytic anaemia, Leucopenia,
Eosinophilia, Thrombocytopenia, Not known- Agranulocytosis, Bone marrow failure, Pancytopenia
Immune system disorders : Rare- Anaphylactic reaction*, Anaphylactoid reaction*, Angioedema,
Very rare- Anaphylactic shock*, Anaphylactoid shock
Metabolism and Nutrition disorders : Rare- Anorexia, Not known- Hypoglycaemia in diabetics
treated with hypoglycaemic agents, Hyperglycaemia, Hypoglycaemic coma
Psychiatric disorders : Uncommon- Agitation, Sleep disorder, Insomnia, Rare- Psychotic disorder
(for e.g. hallucination), Anxiety, Confusional state, Nightmares, Depression, Not known-
Psychotic disorder and depression with self-endangering behaviour including
suicidal ideation or suicide attempt, Nervousness
Nervous system disorders : Uncommon- Dizziness, Headache, Rare- Somnolence, Paraesthesia,
Dysgeusia, Parosmia, Very rare- Peripheral sensory neuropathy*, Peripheral sensory motor
neuropathy*, Convulsion*,Extra-pyramidal symptoms or other disorders of
muscular coordination, Not known- Tremor, Dykinesia, Ageusia, Syncope
Eye disorders : Uncommon- Eye irritation, Rare- Visual disturbance, Not known- Uveitis
Ear and labyrinth disorders : Uncommon- Vertigo, Very rare- Tinnitus, Hearing loss, Not known-
Hearing impaired
Cardiac disorders : Rare- Tachycardia, Not known- Ventricular arrhythmias and torsades de
pointes, ECG QT prolonged
Vascular disorders : Rare- Hypotension
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders : Uncommon- Cough, Nasopharyngitis, Rare-
Dyspnoea, Bronchospasm, Not known- Allergic pneumonitis, Severe dyspnoea
Gastrointestinal disorders : Uncommon- Abdominal pain, Diarrhoea, Nausea, Vomiting, Rare-
Enterocolitis, sometimes haemorrhagic, Very rare- Pseudomembranous colitis*, Not known-
Dyspepsia, Flatulence, Constipation, Pancreatitis
Hepatobiliary disorders : Rare- Hepatic enzymes increased (ALAT, ASAT, LDH, gamma-GT and/or
alkaline phosphatase), Blood bilirubin increased , Very rare- Jaundice cholestatic, Not known-
Hepatitis, which may be severe*, Severe liver injury, including cases with
acute liver failure, sometimes fatal, have been reported with Ofloxacin, primarily in patients
with underlying liver disorders
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders : Uncommon- Pruritus, Rash, Rare- Urticaria, Hot
flushes, Hyperhidrosis Pustular rash, Very rare- Erythema multiforme, Toxic epidermal
necrolysis, Photo-sensitivity reaction, Drug eruption, Vascular purpura, Vasculitis, which
can lead in exceptional cases to skin necrosis,Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Acute generalised
exanthemous pustulosis, Drug rash, Stomatitis, Exfoliative dermatitis
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders : Rare- Tendonitis, Very rare- Arthralgia,
Myalgia, Tendon rupture (e.g. Achilles tendon) which may occur within 48 hours of treatment
start and may be bilateral, Not known- Rhabdomyolysis and/or Myopathy, Muscle
tear, Muscle rupture, Ligament rupture, Arthritis
Renal and urinary disorders : Rare- Serum creatinine increased, Very rare- Acute renal failure,
Not known- Acute interstitial nephritis
Congenital, familial and genetic disorders : Not known- Attacks of porphyria in patients with
porphyria
General disorders and administration site conditions : Not known- Asthenia, Pyrexia, Pain
(including pain in back, chest and extremities)
Ornidazole
Diseases of the Vascular and Lymph System Rare : leucopaenia
Nervous System Disorders - Very rare : somnolence, headache, dizziness, tremor, rigidity, coordination impairments, seizures, fatigue, vertigo, temporary loss of consciousness and sensory or mixed peripheral neuropathy.
Gastrointestinal Disorders Uncommon : nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, epigastric discomfort, dry mouth, loss of appetite. Rare: impairment of the sense of taste
Hepatobiliary Diseases Unknown : jaundice, abnormal liver function tests Skin and subcutaneous tissue diseases Rare: pruritus and skin reactions
Overdosage and Treatment
Ofloxacin
Symptoms : The most important signs to be expected following acute overdose are CNS symptoms such as confusion, dizziness, impairment of consciousness and convulsive seizures increases in QT interval as well as gastrointestinal reactions such as nausea and mucosal erosions.
Management : In the case of overdose steps to remove any unabsorbed Ofloxacin e.g. gastric lavage, administration of adsorbants and sodium sulphate, if possible during the first 30 minutes, are recommended; antacids are recommended for protection of the gastric mucosa. ECG monitoring should be undertaken, because of the possibility of QT interval prolongation. Antacids may be used for protection of gastric mucosa. A fraction of Ofloxacin may be removed from the body with haemodialysis. Peritoneal dialysis and CAPD are not effective in removing Ofloxacin from the body. No specific antidote exists. Elimination of Ofloxacin may be increased by forced diuresis.
Ornidazole
In cases of overdosage, the symptoms mentioned under undesirable effects occur in a more severe form. No specific antidote is known. The administration of diazepam is recommended if cramps occur
Storage
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30°C. Protect from moisture
Keep out of reach of children
Presenatation
A blister strip of 10 tablets.