Nukast 10 mg Tablet
Therapy Area
Respiratory
1.0 Generic name
Montelukast Sodium & Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride Tablets [10 mg + 5 mg]
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
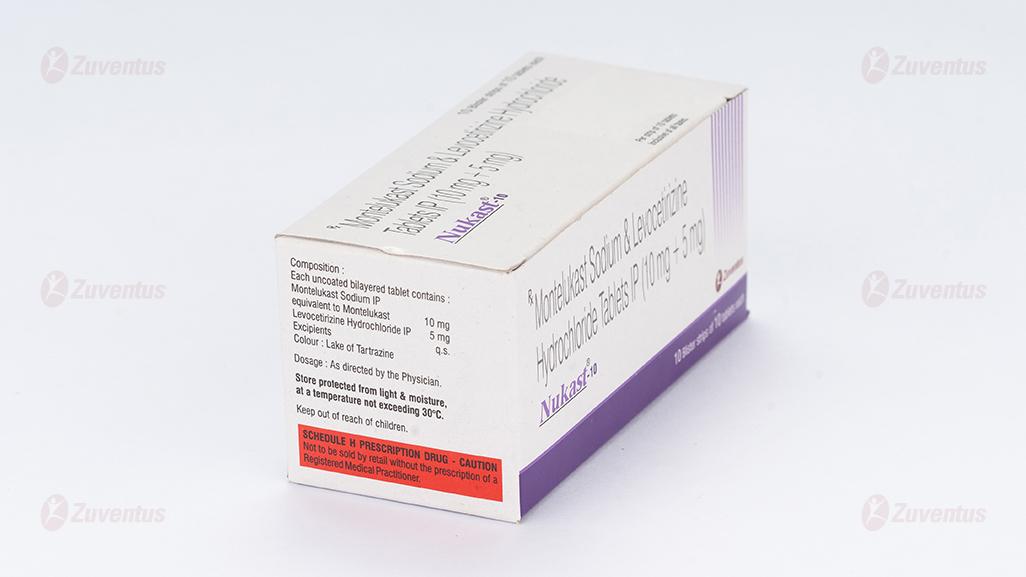
Each uncoated bilayered tablet contains :
Montelukast Sodium
Equivalent to Montelukast 10 mg
Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride USP 5 mg
Excipients q.s.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Tablet, Montelukast Sodium & Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride Tablets [10 mg + 5 mg]
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the treatment of allergic rhinitis in adults only.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
4.3 Contraindications
- Patients who are hypersensitive to any of the component of the product.
- Patients with severe renal impairment at less than 10 ml/min creatinine clearance.
- Patients undergoing haemodialysis.
4.4 Warning and precautions
Montelukast
Acute Asthma
Montelukast is not indicated for use in the reversal of bronchospasm in acute asthma attacks, including status asthmaticus. Patients should be advised to have appropriate rescue medication available. Therapy with Montelukast can be continued during acute exacerbations of asthma. While the dose of inhaled corticosteroid may be reduced gradually under medical supervision, Montelukast should not be abruptly substituted for inhaled or oral corticosteroids. There are no data demonstrating that oral corticosteroids can be reduced when Montelukast is given concomitantly. Patients who have exacerbations of asthma after exercise should have available for rescue a short-acting inhaled beta2- agonist.
Concomitant corticosteroid use
While the dose of inhaled corticosteroid may be reduced gradually under medical supervision, Montelukast should not be abruptly substituted for inhaled or oral corticosteroids
Aspirin sensitivity
Patients with known Aspirin sensitivity should continue avoidance of Aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents while taking Montelukast. Although Montelukast is effective in improving airway function in asthmatics with documented aspirin sensitivity, it has not been shown to truncate bronchoconstrictor response to aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in Aspirin-sensitive asthmatic patients.
Eosinophilic conditions
Patients on therapy with Montelukast may present with systemic eosinophilia sometimes presenting with clinical features of vasculitis consistent with Churg-Strauss syndrome, a condition, which is often treated with systemic corticosteroid therapy. These events usually, but not always, have been associated with the reduction of oral corticosteroid therapy. Physicians should be alert to eosinophilia, vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients. A causal association between, Montelukast and these underlying conditions has not been established.
Neuropsychiatric events
Neuropsychiatric events have been reported in adult, adolescent, and pediatric patients taking Montelukast. Post-marketing reports with Montelukast use include agitation, aggressive behavior or hostility, anxiousness, depression, disorientation, obsessive-compulsive symptoms, dream abnormalities, hallucinations, insomnia, irritability, memory impairment, restlessness, somnambulism, suicidal thinking and behavior (including suicide), and tremor. The clinical details of some post-marketing reports involving Montelukast appear consistent with a drug-induced effect. Patients and prescribers should be alert for neuropsychiatric events. Patients should be instructed to notify their prescriber if these changes occur. Prescribers should carefully evaluate the risks and benefits of continuing treatment with Montelukastif such events occur
Phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuric patients should be informed about the presence of Phenylalanine (a component of Aspartame) in this product.
Levocetirizine
Somnolence
In clinical trials the occurrence of somnolence, fatigue, and asthenia has been reported in some patients under therapy with Levocetirizine. Patients should be cautioned against engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness, and motor coordination such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle after ingestion of Levocetirizine. Concurrent use of Levocetirizine with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of central nervous system performance may occur.
Urinary retention
Urinary retention has been reported post marketing with Levocetirizine. Levocetirizine should be used with caution in patients with predisposing factors of urinary retention (e.g. spinal cord lesion, prostatic hyperplasia) as Levocetirizine may increase the risk of urinary retention. Discontinue Levocetirizine if urinary retention occurs.
4.5 Drug interactions
Montelukast
Montelukast may be administered with other therapies routinely used in the prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma. In drug-interaction studies, the recommended clinical dose of Montelukast did not have clinically important effects on the pharmacokinetics of the following drugs : Theophylline, Prednisone, Prednisolone, Oral contraceptives (Norethindrone 1 mg / Ethinyl estradiol 35 mcg), Terfenadine, Digoxin and Warfarin, Gemfibrozil, Itraconazole, Thyroid hormones, Sedative hypnotics, Non-steroidal antiinflammatory agents, Benzodiazepines, Decongestants and CYP450 enzyme inducers. The area under the plasma concentration curve (AUC) for Montelukast was decreased approximately 40% in subjects with co-administration of phenobarbital. Since Montelukast is metabolised by CYP 3A4, caution should be exercised, particularly in children, when Montelukast is co-administered with inducers of CYP3A4, such as phenytoin, phenobarbital and rifampicin. Although additional specific interaction studies were not performed, Montelukast was used concomitantly with a wide range of commonly prescribed drugs in clinical studies without evidence of clinical adverse interactions. These medications included thyroid hormones, sedative hypnotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, benzodiazepines, and decongestants.
In vitro studies have shown that Montelukast is a potent inhibitor of CYP 2C8. However, data from a clinical drug-drug interaction study involving Montelukast and rosiglitazone (a probe substrate representative of medicinal products primarily metabolised by CYP 2C8) demonstrated that Montelukast does not inhibit CYP 2C8 in vivo. Therefore, Montelukast is not anticipated to markedly alter the metabolism of medicinal products metabolised by this enzyme (e.g., Paclitaxel, Rosiglitazone and Repaglinide.)
In vitro studies have shown that Montelukast is a substrate of CYP 2C8, and to a less significant extent, of 2C9, and 3A4. In a clinical drug-drug interaction study involving Montelukast and gemfibrozil (an inhibitor of both CYP 2C8 and 2C9) gemfibrozil increased the systemic exposure of Montelukast by 4.4-fold. No routine dosage adjustment of Montelukast is required upon co-administration with Gemfibrozil or other potent inhibitors of CYP2C8, but the Physician should be aware of the potential for an increase in adverse reactions. Based on in vitro data, clinically important drug interactions with less potent inhibitors of CYP 2C8 (e.g., trimethoprim) are not anticipated. Co-administration of Montelukast with Itraconazole, a strong inhibitor of CYP 3A4, resulted in no significant increase in the systemic exposure of Montelukast.
Levocetirizine
In vitro data on metabolite interaction indicate that Levocetirizine is unlikely to produce, or be subject to metabolic interactions. Levocetirizine at concentrations well above Cmax level achieved within the therapeutic dose ranges is not an inhibitor of CYP isoenzymes 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2A1, 2D6, 2E1, and 3A4, and is not an inducer of UGT1A or CYP isoenzymes 1A2, 2C9 and 3A4.
No in vivo drug-drug interaction studies have been performed with Levocetirizine. Drug interaction studies have been performed with racemic Cetirizine.
Antipyrine, Azithromycin, Cimetidine, Erythromycin, Ketoconazole, Theophylline, and Pseudoephedrine
Pharmacokinetic interaction studies performed with racemic Cetirizine demonstrated that Cetirizine did not interact with Antipyrine, Pseudoephedrine, Erythromycin, Glipizide and Diazepam, Azithromycin, Ketoconazole and Cimetidine. There was a small decrease (~16%) in the clearance of Cetirizine caused by a 400 mg dose of Theophylline. It is possible that higher Theophylline doses could have a greater effect. The extent of absorption of Levocetirizine is not reduced with food although the rate of absorption is decreased.
Ritonavir
Ritonavir increased the plasma AUC of Cetirizine by about 42% accompanied by an increase in half-life (53%) and a decrease in clearance (29%) of Cetirizine. The disposition of ritonavir was not altered by concomitant Cetirizine administration. In sensitive patients the simultaneous administration of Cetirizine or Levocetirizine and alcohol or other CNS depressants may have effects on the central nervous system, although it has been shown that the racemate Cetirizine does not potentiate the effect of Alcohol.
4.6 Special populations
Pregnancy
There are no adequate and well controlled studies of either Montelukast or Levocetirizine in pregnant women.
Hence this combination should not be used during pregnancy
Lactation
Since Levocetirizine is excreted in breast-milk the combination is not recommended during lactation.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Patients should be cautioned against engaging in activities requiring complete mental alertness, and motor coordination such as operating machinery until their response to Nukast Tablets is known.
4.8 Undesirable effects
There is no data available on undesirable effects of this combination. However, side effects have been reported with individual molecules.
Montelukast
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 5% and greater than placebo; listed in descending order of frequency) in controlled clinical trials were: upper respiratory infection, fever, headache, pharyngitis, cough, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, otitis media, influenza, rhinorrhea, sinusitis, otitis.
Montelukast has been evaluated in 280 paediatric patients 2 to 14 years of age in a 2-week, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group safety study. Montelukast administered once daily in the evening had a safety profile similar to that of placebo. In this study, the following events occurred with a frequency ≥ 2% and at an incidence greater than placebo : headache, otitis media, pharyngitis, and upper respiratory infection. The safety in patients 2 to 14 years of age with perennial allergic rhinitis is supported by the safety in patients 2 to 14 years of age with seasonal allergic rhinitis. The safety in patients 6 to 23 months of age is supported by data from pharmacokinetic and safety and efficacy studies in asthma in this pediatric population and from adult pharmacokinetic studies. The following adverse reactions have been reported in post-marketing use :
Blood and lymphatic system disorders : Increased bleeding tendency. Immune system disorders : Hypersensitivity reactions including Anaphylaxis, Hepatic eosinophilic infiltration.
Psychaitric disorders :
Agitation including aggressive behaviour or hostility, Anxiousness, Depression, Disorientation, Dream abnormalities, Hallucinations, Insomnia, Irritability, Restlessness, Somnambulism, Suicidal thinking and behaviour (including suicide), Tremor.
Nervous system disorder : Drowsiness, Paresthesia / hypoesthesia, Seizure. Respiratory, Thoracic and mediastinal disorder, Epistaxis.
Cardiac disorders : Palpitations.
Gastro-intestinal disorders : Diarrhoea, Dry mouth, Dyspepsia, Nausea, Vomiting.
Hepatobiliary disorders : Elevated levels of serum transminases (ALT, AST), Rare cases of cholestatic hepatitis, Hepatocellular liver injury and mixed-pattern liver injury have been reported in patients treated with Montelukast.
Most of these occurred in combination with other confounding factors, such as use of other medications, or when Montelukast was administered to patients who had underlying potential for liver disease, such as alcohol use or other forms of hepatitis
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders : Angioedema, Bruising, Urticaria, Pruritus, Rash, Erythema nodosum.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders : Arthralgia, Myalgia including muscle cramps.
General disorders and administration site conditions : Asthenia/fatigue, Malaise, Oedema. Patients with asthma on therapy with Montelukast may present with systemic eosinophilia. Sometimes presenting with clinical features of vasculitis consistent with Churg-Strauss syndrome, a condition which is often treated with systemic corticosteroid therapy. These events usually, but not always, have been associated with the reduction of oral corticosteroid therapy. Physicians should be alert to eosinophilia, vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients
Levocetirizine
Use of Levocetirizine has been associated with somnolence, fatigue, nasopharyngitis, dry mouth and pharyngitis in subjects 12 years of age and older. Further uncommon incidences of adverse reactions like asthenia, abdominal pain, syncope and weight- increase were observed. Adverse reactions reported in ≥ 2% of paediatric subjects aged 1 - 6 years exposed to Levocetirizine 1.25 mg twice daily in a 2-week placebo-controlled clinical trial were pyrexia, diarrhoea, vomiting and otitis media while in paediatric subjects 6 - 12 years of age exposed to Levocetirizine 5 mg once daily in placebo-controlled clinical trials 4 and 6 weeks in duration were pyrexia, cough, somnolence, epistaxis. In paediatric subjects 6 months to 11 months receiving 1.25 mg Levocetirizine once daily in a 2-week placebo controlled double blind safety trial the common side effects (≥ 3% subjects) were diarrhoea and constipation. In addition to the adverse reactions reported during clinical studies and listed above very rare cases of the following adverse drug reactions have been reported in post-marketing experience :
Immune system disorders : Hypersensitivity including anaphylaxis.
Psychiatric disorders : Aggression, Agitation, Hallucination, Depression.
Nervous System disorders : Convulsion.
Eyes disorders : Visual disturbances.
Cardiac disorders : Palpitations, tachycardia.
Respiratory,
Thoracic, and mediastinal disorders : Dyspnoea.
Gastrointestinal disorders : Nausea, Vomiting.
Hepatobiliary disorders : Hepatitis.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders : Angioneurotic edema, Fixed drug eruption, Pruritus, Rash urticaria.
Musculoskeletal, connective tissues, and bone disorders : Myalgia.
Investigations : Weight Increased, Abnormal liver functions tests.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important.
It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via
email to : medico@zuventus.com
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
There is no data reported on the overdosage of this combination. In case of overdosage the stomach should be emptied by aspiration and gastric lavage if the patient reports immediately.
Treatment should be symptomatic and supportive.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action / pharmacodynamic properties
Montelukast The cysteinyl leukotrienes (LTC4, LTD4, LTE4) are potent inflammatory eicosanoids released from various cells including mast cells and eosinophils. These important pro-asthmatic mediators bind to cysteinyl leukotriene (CysLT) receptors. The CysLT type-1 (CysLT1) receptor is found in the human airway (including airway smooth muscle cells and airway macrophages) and on other pro-inflammatory cells (including eosinophils and certain myeloid stem cells). CysLTs have been correlated with the pathophysiology of asthma and allergic rhinitis. In allergic rhinitis, CysLTs are released from the nasal mucosa after allergen exposure during both early- and late-phase reactions and are associated with symptoms of allergic rhinitis. Intranasal challenge with CysLTs has been shown to increase nasal airway resistance and symptoms of nasal obstruction. Montelukast is an orally active compound that binds with high affinity and selectivity to the CysLT1 receptor. Montelukast inhibits physiologic actions of LTD4 at the CysLT1 receptor without any agonist activity. Levocetirizine Pharmacodynamic studies in healthy volunteers demonstrate that, at half the dose Levocetirizine has comparable activity to Cetirizine, both in the skin and in the nose. Pharmacokinetic / pharmacodynamic relationship 5 mg Levocetirizine provide a similar pattern of inhibition of histamine-induced wheal and flare than 10 mg Cetirizine. As for Cetirizine, the action on histamine-induced skin reactions was out of phase with the plasma concentrations. ECGs did not show relevant effects of Levocetirizine on QT interval.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Montelukast
Absorption
Montelukast is rapidly absorbed following oral administration. For the 5 mg tablet, the Cmax is achieved in 2 hours after administration in adults in the fasted state. The mean oral bioavailability is 73% and is decreased to 63% by a standard meal.
Distribution
Montelukast is more than 99% bound to plasma proteins. The steady-state volume of distribution of Montelukast averages 8 - 11 liters.
Metabolism
Montelukast is extensively metabolized. In studies with therapeutic doses, plasma concentrations of metabolites of Montelukast are undetectable at steady state in adults and children. In vitro studies using human liver microsomes indicate that cytochrome P450 3A4, 2A6 and 2C9 are involved in the metabolism of Montelukast. Based on further in vitro results in human liver microsomes, therapeutic plasma concentrations of Montelukast do not inhibit cytochromes P450 3A4, 2C9, 1A2, 2A6, 2C19, or 2D6.
Elimination
The plasma clearance of Montelukast averages 45 ml/min in healthy adults. Following an oral dose of radiolabeled Montelukast, 86% of the radioactivity was recovered in 5-day faecal collections and < 0.2% was recovered in urine. Coupled with estimates of Montelukast oral bioavailability, this indicates that Montelukast and its metabolites are excreted almost exclusively via the bile.
Levocetirizine
The pharmacokinetics of Levocetirizine are linear, dose- and time-independent with low inter-subject variability.
Absorption
Levocetirizine is rapidly and extensively absorbed following oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are achieved 0.9 h after dosing. Steady state is achieved after two days. Peak concentrations are typically 270 ng/ml and 308 ng/ml following a single and a repeated 5 mg o.d. dose, respectively. The extent of absorption is dose-independent and is not altered by food, but the peak concentration is reduced and delayed.
Distribution
Levocetirizine is 90% bound to plasma proteins. The distribution of Levocetirizine is restrictive, as the volume of distribution is 0.4 l/kg.
Metabolism
Metabolic pathways include aromatic oxidation, N- and O- dealkylation and taurine conjugation. Dealkylation pathways are primarily mediated by CYP 3A4 while aromatic oxidation involved multiple and/or unidentified CYP isoforms. Levocetirizine had no effect on the activities of CYP isoenzymes 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1 and 3A4 at concentrations well above peak concentrations achieved following a 5 mg oral dose. Due to its low metabolism and absence of metabolic inhibition potential, the interaction of Levocetirizine with other substances, or vice-versa, is unlikely.
Elimination
The plasma half-life in adults is 7.9 ± 1.9 hours. The mean apparent total body clearance is 0.63 ml/min/kg. The major route of excretion of Levocetirizine and metabolites is via urine, accounting for a mean of 85.4% of the dose. Excretion via feces accounts for only 12.9% of the dose. Levocetirizine is excreted both by glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
No known animal toxicology data.
7.0 Description
Montelukast selectively antagonizes leukotriene D4 (LTD4) at the cysteinyl leukotriene receptor, CysLT1, in the human airway thereby preventing airway edema, bronchoconstriction, enhanced secretion of thick, viscous mucus and nasal congestion. It is a safe and effective treatment for patients with allergic rhinitis and allergic asthma. Levocetirizine is the R-enantiomer and the active form of cetirizine. It is an orally active, potent, selective and long acting H1-histamine receptor antagonist with no anticholinergic activity. It blocks the binding of histamine to H1 receptors thus preventing its systemic effects, such as vasodilation, edema, mucous secretion, and smooth muscle contraction. This results in providing relief from the symptoms of allergic rhinitis and asthma including sneezing, itching, rhinorrhea, dyspnea, bronchial hypersensitivity and mucus accumulation. It has been demonstrated by recent studies that the treatment of Allergic rhinitis and asthma with concomitant administration of an anti-leukotriene (Montelukast) and an antihistamine (Levocetirizine), shows significantly better symptom relief and additional improvement in quality of life when compared with each agent given alone.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
24 Months
8.3 Packaging information
1 x 10 Tablets
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store protected from light and moisture at a temperature not exceeding 30°C.
KEEP AWAY FROM THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
9.0 Patient counselling information
Do not take Nukast if you
- Are allergic to Montelukast, Levocetirizine or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
- If you suffer from severe kidney failure (severe renal failure with creatinine clearance below 10 ml/min). Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Nukast
- If your asthma or breathing gets worse, tell your doctor immediately.
- This oral medicine is not meant to treat acute asthma attacks. If an attack occurs, follow the instructions your doctor has given you. Always have your inhaled rescue medicine for asthma attacks with you.
- It is important that you or your child take all asthma medications prescribed by your doctor.
- This medicine should not be substituted for other asthma medications your doctor has prescribed for you.
- Any patient on anti-asthma medicines should be aware that if you develop a combination of symptoms such as a flu-like illness, pins and needles or numbness of arms or legs, worsening of pulmonary symptoms, and/or rash, you should consult your doctor.
- If you suffer from epilepsy or are at risk of convulsions, please ask your doctor for advice as use of may make seizures worse. If you are likely to be unable to be unable to empty your bladder (due to conditions such as a spinal cord injury or enlarged prostate), please ask your doctor for advice. If you are scheduled for allergy testing, ask your doctor if you should stop taking Nukast for several days before testing. This medicine may affect your allergy test results.
Patients should be aware that various neuropsychiatric events (for example behaviour and mood related changes) have been reported in adults, adolescents and children with Nukast. If you develop such symptoms while taking Nukast you should consult your doctor.
Tell your doctor if you are taking the following medicines before starting Nukast :
- Phenobarbital (used for treatment of epilepsy)
- Phenytoin (used for treatment of epilepsy)
- Rifampicin (used to treat tuberculosis and some other infections)
- Gemfibrozil (used for treatment of high lipid levels in plasma)
If you suffer from mild to moderate kidney failure, your doctor may prescribe a lower dose according to the severity of your kidney disease. Patients who only have impaired liver function should take the usual prescribed dose. Patients who have both impaired liver and kidney function may be given a lower dose depending on the severity of the kidney disease.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
- What Nukast-10 is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you take Nukast-10
- How to take Nukast-10
- Possible side effects
- How to store Nukast-10
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Nukast-10 is and what it is used for
Nukast-10 is a combination of two active substances, Montelukast and Levocetirizine in one tablet. Both of these substances help to control seasonal allergies/allergic rhinitis.
Montelukast is a leukotriene receptor antagonist that blocks substances called leukotrienes. Leukotrienes cause narrowing and swelling of airways in the lungs and also cause allergy symptoms. By blocking leukotrienes, Montelukast helps control asthma and improves seasonal allergy symptoms (also known as hay fever or seasonal allergic rhinitis).
Levocetirizine dihydrochloride is the active ingredient of Levocetirizine 5 mg film-coated tablets.
Levocetirizine is an anti-allergic medication. For the treatment of signs of illness (symptoms) associated with:
- allergic rhinitis (including persistent allergic rhinitis);
- nettle rash (urticaria).
What are seasonal allergies?
Seasonal allergies (also known as hay fever or seasonal allergic rhinitis) are an allergic response often caused by airborne pollens from trees, grasses and weeds. The symptoms of seasonal allergies typically may include: stuffy, runny, itchy nose; sneezing; watery, swollen, red, itchy eyes.
2. What you need to know before you take Nukast-10
Do not take Nukast-10
- If you are allergic to montelukast, levocetirizine dihydrochloride, to cetirizine, to hydroxyzine or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- If you have a severe kidney disease requiring dialysis
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Nukast-10.
- If your asthma or breathing gets worse, tell your doctor immediately.
- Oral Montelukast are not meant to treat acute asthma attacks. If an attack occurs, follow the instructions your doctor has given you. Always have your inhaled rescue medicine for asthma attacks with you.
- It is important that you or your child take all asthma medications prescribed by your doctor. Montelukast should not be substituted for other asthma medications your doctor has prescribed for you.
- Any patient on anti-asthma medicines should be aware that if you develop a combination of symptoms such as a flu-like illness, pins and needles or numbness of arms or legs, worsening of pulmonary symptoms, and/or rash, you should consult your doctor.
- You should not take acetyl-salicylic acid (aspirin) or anti-inflammatory medicines (also known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs) if they make your asthma worse.
- If you are likely to be unable to empty your bladder (with conditions such as spinal cord injury or enlarged prostate), please ask your doctor for advice.
- If you suffer from epilepsy or are at risk of convulsions, please ask your doctor for advice as use of Levocetirizine 5mg film-coated tablets may cause seizure aggravation.
- If you are scheduled for allergy testing, ask your doctor if you should stop taking Levocetirizine 5mg film-coated tablets for several days before testing. This medicine may affect your allergy test results.
Patients should be aware that various neuropsychiatric events (for example behaviour and mood-related changes) have been reported in adults, adolescents and children with montelukast (see section 4). If you develop such symptoms while taking Montelukast, you should consult your doctor.
Children and adolescents
Do not give this medicine to children. There are different form (s) of this medicine available for paediatric patients under 18 years of age based on age range.
Other medicines and Nukast-10
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken or might take any other medicines including those obtained without a prescription.
Some medicines may affect how Montelukast works, or Montelukast may affect how other medicines work.
Tell your doctor if you are taking the following medicines before starting Montelukast:
- Phenobarbital (used for treatment of epilepsy)
- Phenytoin (used for treatment of epilepsy)
- Rifampicin (used to treat tuberculosis and some other infections)
- Gemfibrozil (used for treatment of high lipid levels in plasma)
Taking Nukast-10 with food and drink
Nukast-10 may be taken with or without food. Caution is advised if Nukast-10 Tablets is taken at the same time as alcohol or other agents acting on the brain. In sensitive patients, the concurrent administration of Levocetirizine and alcohol or other agents acting on the brain may cause additional reductions in alertness and impairment of performance.
Pregnancy and breast feeding
If you are pregnant or breast feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Pregnancy
Your doctor will assess whether you can take Nukast-10 during this time.
Breast-feeding
It is not known if Nukast-10 appears in breast milk. You should consult your doctor before taking Montelukast if you are breast-feeding or intend to breast feed.
Driving and using machines
Some patients being treated with Nukast-10 (Levocetirizine) may experience somnolence/drowsiness, tiredness and exhaustion. Use caution when driving or operating machinery until you know how this medicine affects you. However, special tests have revealed no impairment of mental alertness, the ability to react or the ability to drive in healthy test persons after taking levocetirizine in the recommended dosage.
3. How to take Nukast -10
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
- You should take only one tablet of Nukast -10 once a day as prescribed by your doctor.
- It should be taken even when you have no symptoms or have an acute asthma attack.
For adults and adolescents 15 years of age and older:
The recommended dose is one Nukast -10 tablet to be taken daily in the evening.
If you are taking Nukast-10, be sure that you do not take any other products that contain the same active ingredient, montelukast or Levocetirizine.
This medicine is for oral use.
You can take Nukast -10 with or without food.
If you take more Nukast-10 than you should
Contact your doctor immediately for advice.
If you take more Nukast-10 tablets than you should somnolence can occur in adults. Children may initially show excitation and restlessness followed by somnolence. If you think you have taken an overdose of Nukast-10, please tell your doctor who will then decide what action should be taken.
The other most frequently occurring symptoms reported with overdose in adults and children included abdominal pain, sleepiness, thirst, headache, vomiting, and hyperactivity.
If you forget to take Nukast-10
Try to take Montelukast as prescribed. However, if you miss a dose, just resume the usual schedule of one tablet once daily.
Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop taking Nukast-10
Nukast-10 can treat your allergic rhinitis only if you continue to take it. It is important to continue taking Nukast-10 for as long as your doctor prescribes. It will help control your allergic rhinitis/asthma.
Stopping treatment should have no negative effects. However, rarely pruritus (intense itching) may occur if you stop taking Levocetirizine, even if those symptoms were not present before treatment initiation. The symptoms may resolve spontaneously. In some cases, the symptoms may be intense and may require treatment to be restarted. The symptoms should resolve when the treatment is restarted.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Special dosage instructions for specific populations:
Renal and hepatic impairment
Patients with impaired kidney function may be given a lower dose according to the severity of their kidney disease and in children the dose will also be chosen on the basis of body weight; the dose will be determined by your doctor.
Patients who have a severe kidney disease requiring dialysis must not take Nukast-10 tablets. Patients who only have impaired liver function should take the usual prescribed dose.
Patients who have both impaired liver and kidney function may be given a lower dose depending on the severity of the kidney disease, and in children the dose will also be chosen on the basis of body weight; the dose will be determined by your doctor
Elderly patients aged 65 years and above
No adaptation of the dose is necessary in elderly patients, provided their renal function is normal.
Use in Children
Nukast-10 tablets are not recommended for children under 18 years of age.
How long should you take Nukast-10 Tablets
The duration of use depends on the type, duration and course of your complaints and is determined by your physician
4. Possible side effects:
MONTELUKAST:
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
In clinical studies with montelukast 10 mg film-coated tablets, the most commonly reported side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people) thought to be related to montelukast were:
- Abdominal pain, Headache
These were usually mild and occurred at a greater frequency in patients treated with montelukast than placebo (a pill containing no medication).
Serious side effects
Talk with your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following side effects, which may be serious, and for which you may need urgent medical treatment.
Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- Allergic reactions including swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and/or throat which may cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing
- Behaviour and mood related changes: agitation including aggressive behaviour or hostility, depression
- Seizure
Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
- Increased bleeding tendency, Tremor, Palpitations
Very rare: may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people
- Combination of symptoms such as flu-like illness, pins and needles or numbness of arms and legs, worsening of pulmonary symptoms and/or rash (see Section 2)
- Low blood platelet count
- Behaviour and mood related changes: hallucinations, disorientation, suicidal thoughts and actions
- Swelling (inflammation) of the lungs
- Severe skin reactions (erythema multiforme) that may occur without warning
- Inflammation of the liver (hepatitis)
Other side effects while the medicine has been on the market
Very common: may affect more than 1 in 10 people
- Upper respiratory infection
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- Diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting,Rash ,Fever,Elevated liver enzymes
Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- Behaviour and mood related changes: dream abnormalities, including nightmares, trouble sleeping, sleepwalking, irritability, feeling anxious, restlessness
- Dizziness, drowsiness, pins and needles/numbness
- Nosebleed, Dry mouth, indigestion
- Bruising, itching, hives, Joint or muscle pain, muscle cramps
- Bedwetting in children, Weakness/tiredness, feeling unwell, swelling
Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
- Behaviour and mood related changes: disturbance in attention, memory impairment, uncontrolled muscle movements
Very rare: may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people
- Tender red lumps under the skin, most commonly on your shins (erythema nodosum)
- behaviour and mood related changes: obsessive-compulsive symptoms, stuttering
LEVOCETIRIZINE
Common: (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- dry mouth,headache ,tiredness,somnolence/drowsiness
Uncommon: (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
exhaustion and abdominal pain
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Drug Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician
5. How to store Nukast -10
Store protected from light and moisture at a temperature not exceeding 30°C. Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the blister after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last date of that month.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Nukast -10 contains:
Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each uncoated bilayered tablet contains:
Montelukast Sodium
Equivalent to Montelukast -10 mg
Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride USP -5 mg
Excipients q.s.
Each strip of Nukast-10 contains 10 Tablets