Polares Drops
Therapy Area
Anti Infective
1.0 Name of the medicinal product
Cefpodoxime Oral Suspension IP
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each ml of reconstituted suspension contains :
Cefpodoxime Proxetil IP
equivalent to Cefpodoxime 25 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Quinoline Yellow WS
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 10 ml for reconstitution.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Dry Suspension, 25 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Acute bronchitis, exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, bronchiolitis pneumonia, sinusitis, recurrent chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis, acute otitis.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Posology
Cefpodoxime Proxetil Drop, should be administered orally with food to enhance absorption.
The recommended dosages, durations of treatment, and applicable patient population are as described in the following chart.
Infants and Pediatric Patients (age 2 months through 12 years)
| Type of Infection | Total Daily Dose | Dose Frequency | Duration |
| Acute otitis media | 10 mg/kg/day (Max 400 mg/day) | 5 mg/kg Q 12 h (Max 200 mg/dose) | 5 days |
| Pharyngitis and/or tonsillitis | 10 mg/kg/day (Max 200 mg/day) | 5 mg/kg/dose Q 12h (Max 100 mg/dose | 5 to 10 days |
| Acute maxillary sinusitis | 10 mg/kg/day (Max 400 mg/day) | 5 mg/kg Q 12 hours (Max 200 mg/dose) | 10 days |
Patients with Renal Dysfunction
For patients with severe renal impairment (<30 mL/min creatinine clearance), the dosing intervals should be increased to Q 24 hours. In patients maintained on hemodialysis, the dose frequency should be 3 times/week after hemodialysis.
Patients with Cirrhosis
Cefpodoxime pharmacokinetics in cirrhotic patients (with or without ascites) are similar to those in healthy subjects. Dose adjustment is not necessary in this population
4.3 Contraindications
• Cefpodoxime is contraindicated in patients with a known allergy to cefpodoxime or to the cephalosporin group of antibiotics.
• previous history of immediate and / or severe hypersensitivity reaction (anaphylaxis) to penicillin or other betalactam antibiotic.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Before therapy with cefpodoxime proxetil is instituted, careful inquiry should be made to determine whether the patient has had previous hypersensitivity reactions to cefpodoxime, other cephalosporins, penicillins, or other drugs. If cefpodoxime is to be administered to penicillin sensitive patients, caution should be exercised because cross hypersensitivity among beta-lactam antibiotics has been clearly documented and may occur in up to 10% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy. If an allergic reaction to cefpodoxime proxetil occurs, discontinue the drug. Serious acute hypersensitivity reactions may require treatment with epinephrine and other emergency measures, including oxygen, intravenous fluids, intravenous antihistamine, and airway management, as clinically indicated.
General precautions
In patients with transient or persistent reduction in urinary output due to renal insufficiency, the total daily dose of cefpodoxime proxetil should be reduced because high and prolonged serum antibiotic concentrations can occur in such individuals following usual doses. Cefpodoxime, like other cephalosporins, should be administered with caution to patients receiving concurrent treatment with potent diuretics. As with other antibiotics, prolonged use of cefpodoxime proxetil may result in overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms. Repeated evaluation of the patient’s condition is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken. Prescribing Cefpodoxime Proxetil, in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug resistant bacteria.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Antacids
Concomitant administration of high doses of antacids (sodium bicarbonate and aluminum hydroxide) or H2 blockers reduces peak plasma levels by 24% to 42% and the extent of absorption by 27% to 32%, respectively. The rate of absorption is not altered by these concomitant medications. Oral anti-cholinergics (e.g., propantheline) delay peak plasma levels (47% increase in Tmax), but do not affect the extent of absorption (AUC).
Probenecid
As with other beta-lactam antibiotics, renal excretion of cefpodoxime was inhibited by probenecid and resulted in an approximately 31% increase in AUC and 20% increase in peak cefpodoxime plasma levels.
Nephrotoxic drugs
Although nephrotoxicity has not been noted when cefpodoxime proxetil was given alone, close monitoring of renal function is advised when cefpodoxime proxetil is administered concomitantly with compounds of known nephrotoxic potential.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Cephalosporins, including cefpodoxime proxetil, are known to occasionally induce a positive direct Coombs’ test
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy
There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies of cefpodoxime proxetil use in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Labor and Delivery
Cefpodoxime proxetil has not been studied for use during labor and delivery
Lactation
Cefpodoxime is excreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious reactions in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
It may cause dizziness. Driving or operating machinery is to be avoided
4.8 Undesirable effects
In clinical trials using multiple doses of cefpodoxime proxetil granules for oral drop, 2128 pediatric patients (93% of whom were less than 12 years of age) were treated with the recommended dosages of cefpodoxime (10 mg/kg/day Q 24 hours or divided Q 12 hours to a maximum equivalent adult dose). There were no deaths or permanent disabilities in any of the patients in these studies. Twenty-four patients (1.1%) discontinued medication due to adverse events thought possibly- or probably-related to study drug. Primarily, these discontinuations were for gastrointestinal disturbances, usually diarrhea, vomiting, or rashes.
Adverse events thought possibly- or probably-related, or of unknown relationship to cefpodoxime proxetil for oral drop in multiple dose clinical trials (N=2128 patients treated with cefpodoxime) were:
Incidence Greater Than 1% were:
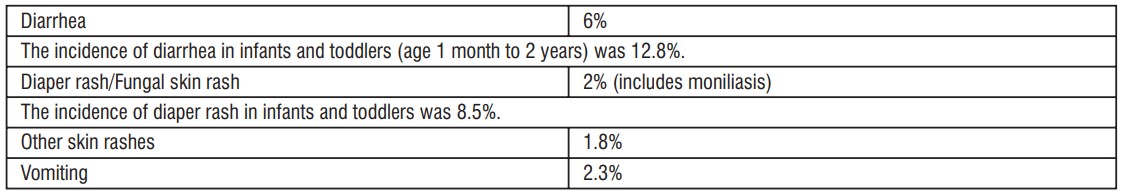
Incidence Less Than 1%
Body: Localized abdominal pain, abdominal cramp, headache, monilla, generalized abdominal pain, asthenia, fever, fungal infection
Digestive: Nausea, monilia, anorexia, dry mouth, stomatitis, pseudomembranous colitis. Hemic & Lymphatic: Thrombocythemia, positive direct Coombs' test, eosinophilla, leukocytosis, leukopenia, prolonged partial thromboplastin time, thrombocytopenic purpura.
Metabolic & Nutritional: Increased SGPT
Musculo-Skeletal: Myalgia
Nervous: Hallucination, hyperkinesia, nervousness, somnolence. Respiratory: Epistaxis, rhinitis
Skin: Fixed drug eruption (FDE), skin moniliasis, urticaria, fungal dermatitis, acne, exfoliative dermatitis, maculopapular rash.
Special Senses: Taste perversion.
Laboratory Changes
Significant laboratory changes that have been reported in adult and pediatric patients in clinical trials of cefpodoxime proxetil, without regard to drug relationship, were:
Hepatic: Transient Increases in AST (SGOT), ALT (SGPT), GGT, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, and LDH
Hematologic: Eosinophilia, leukocytosis, lymphocytosis, granulocytosis, basophilia, mono- cytosis, thrombocytosis, decreased hemoglobin, decreased hematocrit, leukopenia, neu- tropenia, lymphocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocythemia, positive Coombs' test, and prolonged PT, and PTT.
Serum Chemistry: Hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, hypoalbuminemia, hypoproteinemia, hyperkalemia, and hyponatremia.
Renal: Increases in BUN and creatinine.
Most of these abnormalities were transient and not clinically significant
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: https://www.zuventus.com
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
In acute rodent toxicity studies, a single 5 g/kg oral dose produced no adverse effects. In the event of serious toxic reaction from overdosage, hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis may aid in the removal of cefpodoxime from the body, particularly if renal function is compromised.
The toxic symptoms following an overdose of beta-lactam antibiotics may include nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, and diarrhea.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Cefpodoxime is a bactericidal agent that acts by inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cefpodoxime has activity in the presence of some betalactamases, both penicillinases and cephalosporinases, of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Resistance to Cefpodoxime is primarily through hydrolysis by beta-lactamase, alteration of penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), and decreased permeability.
Cefpodoxime has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following bacteria, both in vitro and in clinical infections
Gram-positive Bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible strains, including those producing penicillinases)
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Streptococcus pneumoniae (excluding penicillin-resistant isolates)
Streptococcus pyogenes
Gram-negative Bacteria
Escherichia coli
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Proteus mirabilis
Haemophilus influenzae (including beta-lactamase producing isolates)
Moraxella catarrhalis
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (including penicillinase-producing isolates)
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. At least 90 percent of the following microorganisms exhibit an in vitro minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) less than or equal to the susceptible breakpoint for cefpodoxime. However, the efficacy of cefpodoxime in treating clinical infections due to these microorganisms has not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
Gram-positive Bacteria
Streptococcus agalactiae
Streptococcus spp. (Groups C, F, G)
Gram-negative Bacteria
Citrobacter diversus
Klebsiella oxytoca
Proteus vulgaris
Providencia rettgeri
Haemophilus parainfluenzae
Anaerobic Gram-positive Bacteria
Peptostreptococcus magnus
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
In adult subjects, a 100 mg dose of oral suspension produced an average peak cefpodoxime concentration of approximately 1.5 mcg/mL (range: 1.1 to 2.1 mcg/mL), which is equivalent to that reported following administration of the 100 mg tablet. Time to peak plasma concentration and area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) for the oral suspension were also equivalent to those produced with film-coated tablets in adults following a 100 mg oral dose.
The pharmacokinetics of cefpodoxime were investigated in 29 patients aged 1 to 17 years. Each patient received a single, oral, 5 mg/kg dose of cefpodoxime oral suspension. Plasma and urine samples were collected for 12 hours after dosing. The plasma levels reported from this study are as follows:
Cefpodoxime Plasma Levels (mcg/mL) In Fasted Patients (1 to 17 Years of Age) After Suspension Administration

Dose did not exceed 200 mg
Distribution
Protein binding of cefpodoxime ranges from 22 to 33% in serum and from 21 to 29% in plasma
Effects of Decreased Renal Function
Elimination of cefpodoxime is reduced in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (<50 mL/min creatinine clearance). In subjects with mild impairment of renal function (50 to 80 mL/min creatinine clearance), the average plasma half-life of cefpodoxime was 3.5 hours. In subjects with moderate (30 to 49 mL/min creatinine clearance) or severe renal impairment (5 to 29 mL/mincreatinine clearance), the half-life increased to 5.9 and 9.8 hours, respectively. Approximately 23% of the administered dose was cleared from the body during a standard 3-hour hemodialysis procedure.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
No known animal toxicology data
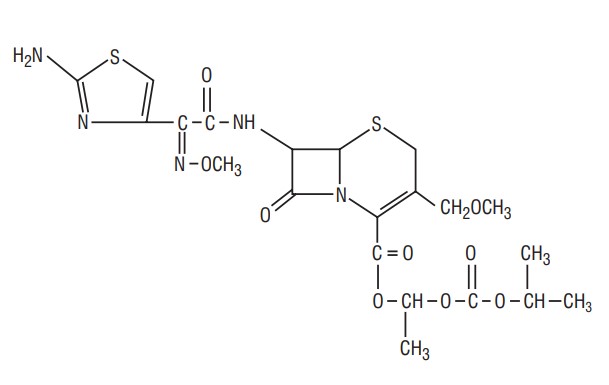
7.0 Description
Cefpodoxime proxetil is an orally administered, extended spectrum, semi-synthetic antibiotic of the cephalosporin class. The chemical name is (RS)-1(iso-propoxycarbonyloxy) ethyl (+) (6R,7R)-7-[2-(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-2- {(Z)methoxyimino} acetamido]-3-methoxymethyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate. Its empirical formula is C21H27N5O9S2 and its structural formula is represented below:
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
A bottle of 4 g / 10 ml.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Preserve in tight containers, at a temperature not exceeding 30°C
Keep out of reach of children.
Store the reconstituted oral suspension in a refrigerator (at 2°C to 8°C).
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including Cefpodoxime Proxetil, should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When Cefpodoxime Proxetil, is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed.
Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may
(1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and
(2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Cefpodoxime Proxetil, or other antibacterial drugs in the future. Diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start giving this medicine to your child because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist. This medicine has been prescribed for your child only.
- Do not pass it on to others.
- It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as your child’s.
- If your child gets any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
- This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
- What Polares Drops is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you give Polares Drops
- How to give Polares Drops
- Possible side effects
- How to store Polares Drops
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Polares Drops is and what it is used for
Polares Drops contains cefpodoxime, which is an antibiotic. It belongs to a group of antibiotics that are called cephalosporins. These types of antibiotics are similar to penicillin.
Cefpodoxime kills bacteria and it can be used against various sorts of infections.
Like all antibiotics, cefpodoxime is only effective against some types of bacteria. So, it is only suitable for treating some types of infection.
Polares Drops can be used to treat:
- Sinus infections
- Throat infections – e.g. Tonsil infection, Pharyngitis
- Chest infections such as bronchitis and lung infections (pneumonia)
- Ear infection (acute otitis media)
2. What you need to know before you give Polares Drops
Do not give Polares Drops if your child:
- is allergic to cefpodoxime or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- is allergic to any other cephalosporin type of antibiotic.
- has ever had a severe allergic reaction to any sort of penicillin antibiotic.
- suffers from phenylketonuria.
- is less than 28 days (4 weeks) old.
- is four weeks to three months of age and has kidney problems.
Not all people who are allergic to penicillins are also allergic to cephalosporins. However, your child should not be given this medicine if they have ever had a severe allergic reaction to any penicillin. This is because they might also be allergic to this medicine.
If you are not sure about anything, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before giving Polares Drops if your child:
- has ever had an allergic reaction to any antibiotic.
- has any other allergies, e.g. hay fever, asthma
- has ever been told that their kidneys do not work very well. Also, if your child is having any sort of treatment (like dialysis) for kidney failure. Your child may take cefpodoxime but you may need to give a lower dose.
- has ever had inflammation of their bowel, called colitis or any other severe disease affecting their gut.
- has, or has recently had, severe diarrhoea and sickness (vomiting).
- has diabetes and you routinely test their urine, this medicine can alter the results of urine tests for sugar (such as Benedict's or Fehling's tests). Other tests may have to be used to monitor their diabetes while they are taking this medicine. – if they have signs of diseases of the skin or mucous.
During treatment
- This medicine can alter the results of some blood tests (such as cross-matching blood and the Coombs' test). It is important to tell the doctor that your child is taking this medicine if they have to have any of these tests.
- Your child’s doctor might have to monitor their blood liver enzymes levels as this medicine may increase their values.
- Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if your child suffers from severe diarrhoea or being sick especially if they are also taking other medicines.
- If your child gets other infections such as thrush, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Other medicines and Polares Drop
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if your child is taking, has recently taken or might take any other medicines.
This medicine can be affected by other medicines that are removed by the kidneys. This is especially if these other medicines also affect how well kidneys work. There are many medicines that can do this, so you should check with your doctor or pharmacist before giving this medicine.
In particular, tell your doctor or pharmacist if your child is taking:
- Antibiotics called aminoglycosides (such as gentamicin) or other antibiotics such as chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracycline or sulfonamides (e.g. co-trimoxazole).
- Water tablets or injections (diuretics) such as furosemide used to increase the flow of water (urine). It might be necessary to check the kidneys often during treatment. This can be done with blood and urine tests.
- Antacids (used to treat indigestion) and medicines for treating ulcers (such as ranitidine or cimetidine): Give antacids and medicines for ulcers 2-3 hours after this medicine as they may reduce the effect of cefpodoxime when taken at the same time.
- Probenecid as it may slow down the kidneys’ ability to get rid of cefpodoxime.
- Coumarin anti-coagulants such as warfarin (used to thin the blood) as their effect may be increased by cefpodoxime.
Polares Drops with food
Give this medicine with meals. This is because it helps this medicine to be absorbed into the body.
Driving and using machines
Your child may get dizzy, light-headed or in more extreme cases experience convulsions, confusion, change of consciousness and movement disorders when taking this medicine. This may affect their ability to ride bikes etc.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
This section may not be applicable to children.
3. How to give Polares Drops
Always give this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
The dispensing label will tell you how much of this medicine you should give and how often you should give it. Please read it carefully. The dose your doctor prescribes depends on the type of infection and how bad the infection is. It also depends on how well the kidneys are working. Your doctor will explain this to you.
Adults and children (≥12 years)
This suspension is not usually recommended for adults and children (≥11 years). Ask your doctor or pharmacist for alternate formulation of same drug.
Infants and Pediatric Patients (age 2 months through 12 years)
- The daily amount is worked out according to the weight of the child.
- Give each dose every 12 hours with a meal.
- The exact dose will have been worked out by the doctor and shown on the label.
- The following table provides a guide to usual doses:
| Type of Infection | Total Daily Dose | Dose Frequency | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ear infection (Acute otitis media) | 10 mg/kg/day (Max 400 mg/day) | 5 mg/kg every 12 h (Max 200 mg/dose) | 5 days |
| Throat infection (Pharyngitis and/or tonsillitis) | 10 mg/kg/day (Max 200 mg/day) | 5 mg/kg/dose every 12h (Max 100 mg/dose) | 5 to 10 days |
| Sinus Infection (sinusitis) | 10 mg/kg/day (Max 400 mg/day) | 5 mg/kg every 12 hours (Max 200 mg/dose) | 10 days |
Directions for reconstitution
Shake the bottle well to loosen the granules. Also enclosed SWFI (Sterile Water for Injection) up to the ring mark on the bottle and shake well. Add more SWFI if necessary to adjust the volume up to the ring mark. This makes 10 ml of suspension.
The reconstituted suspension should be consumed within 14 days of preparation.
Always remember to shake the bottle before measuring out each dose.
If you give more Polares Drop
If you or your child have taken more of this medicine than you should, talk to your doctor straight away or go to the nearest hospital accident and emergency department. Your child may be unable to concentrate, lack energy and experience a decrease in consciousness. These effects are more likely to occur if your child has kidney problems. Take the medicine with you in the carton, so that staff will know exactly what has been taken.
If you forget to give Polares Drops
If you forget to give a dose of this medicine at the right time, give it as soon as you remember. Do not give a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop giving Polares Drops
It is important that you give this medicine until you finish giving the prescribed course. You should not stop giving the medicine just because your child looks or feels better. If you stop too soon, the infection may start up again. If the person being treated still feels unwell at the end of the prescribed course of treatment, or feels worse during treatment, tell your doctor.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If you notice any of the following side effects, stop giving this medicine and contact your doctor or take your child to the nearest hospital casualty department straight away:
- A reduction of white blood cells that may cause an increase in the number of new infections that your child gets, such as sore throat or mouth ulcers, or damage to red blood cells, that may cause your child to feel tired and breathless with possible yellowing of the skin.
- Severe allergic reactions which may cause sudden wheeziness and tightness of chest swelling of eyelids, face or lips, loss of consciousness (fainting).
- Severe skin rashes which may include peeling of the skin (Toxic epidermal necrolysis) or that can blister (bullous dermatitis) and may involve the eyes, mouth and throat and genitals (Stevens-Johnson syndrome).
- A course of cefpodoxime can increase the chance that your child gets other types of infection. For example, thrush may occur (white patches on the tongue or a creamy white discharge from the penis or vagina) or severe diarrhoea which may be bloody with stomach pain.
- Liver damage causing jaundice (this may show as a yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes)
- Sudden severe dull pain around the top of the stomach which radiates to the back, feeling and being sick, which may be due to inflammation of the pancreas.
- A disease that affects the function or structure of your brain (encephalopathy). The symptoms might include among others difficulty with memory or focusing and changes in personality.
Other possible side effects
Very Common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Headaches.
- Stomach pain.
- Diarrhoea. If you have severe diarrhoea or if you see blood in your diarrhoea you should stop taking this medicine and talk to your doctor immediately.
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Dizziness.
- Bloating, feeling or being sick (nausea, vomiting), flatulence (wind).
- Loss of appetite.
- Changes in blood tests that check how your liver is working.
- Skin rash, hives, itching Ringing in the ears.
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Skin and mucosa skin allergic reactions.
- Pins and needles.
Weakness, tiredness and a feeling of generally being unwell.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- Increases in some types of white blood cells, reduced number of small cells that are needed for clotting of the blood, which may cause easy bruising or bleeding.
- Increases in the numbers of small cells that are needed for clotting of the blood, which may show up in blood tests.
- Changes in the way that the kidney is working, which may show up in blood tests.
Very rare (may affect less than 1 in 1,000 people)
- Reduction of red blood cells (haemolytic anaemia)
Not Known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
Fresh, red blood in your stools (haematochezia)
- Purplish-red patches.
- Kidney problems.
During treatment
If your child is having a blood test for any reason, tell the person who is taking their blood sample that you are giving this medicine as it may affect their result.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Polares Drops
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date, which is stated on the bottle after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Before being made up into a solution, do not store above 25ºC. Store in the original package.
Once made up into a solution, store the medicine in a refrigerator (2-8 ºC) and do not use any remaining medicine after 14 days.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Polares dry suspension contains
Polares Drops
Each ml contains:
Cefpodoxime Proxetil IP equivalent to Cefpodoxime 25 mg
This pack contains sterile water for injection IP 10 ml for reconstitution.
What Polares Drops looks like and contents of the pack
A bottle of 4 g / 10 ml.
This pack contains sterile water for injection IP 10 ml for reconstitution.