Polvolt
Therapy Area
Pain management
1.0 Generic name
Polmacoxib Capsules 2 mg
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
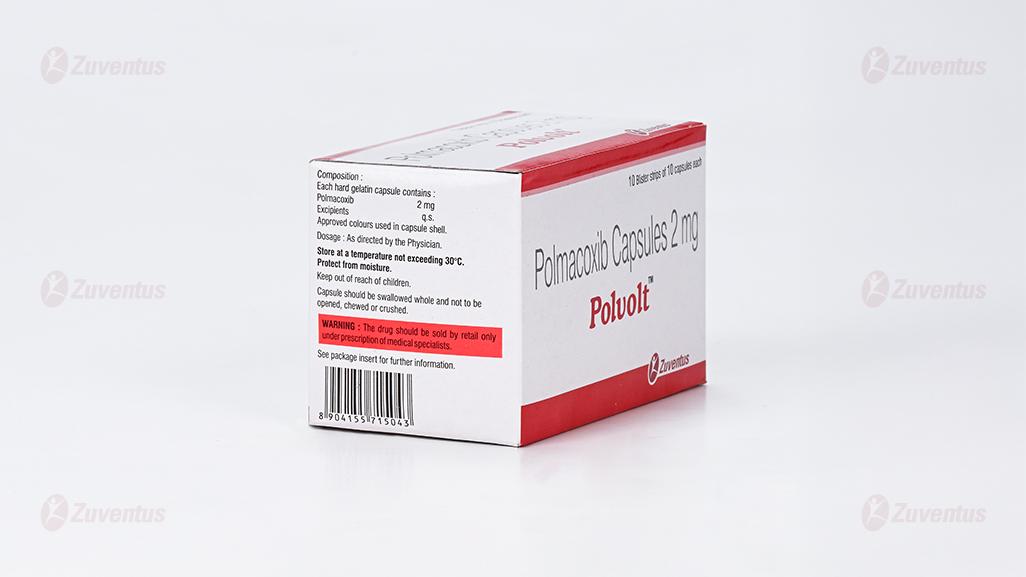
Each hard gelatin capsule contains :
Polmacoxib 2 mg
Excipients q.s
Approved colours used in capsule shell
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Polmacoxib 2 mg capsules for oral use.
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Polmacoxib capsules is indicated for the treatment of idiopathic (primary) osteoarthritis of hip / knee.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adults
The recommended dose of Polmacoxib is 2 mg once daily after a meal, should not exceed 2 mg/day. If there is no therapeutic benefit at the recommended dose, administration of this drug should be discontinued and appropriate alternative treatment methods should be considered.
Patients with hepatic and renal impairment
This drug should not be administered because there is no administration experience.
Recommendations for use in cardiovascular disorders
The potential risks and benefits of Polamcoxib and other alternative therapies should be considered before administering Polmacoxib.
As the dose and duration of exposure increases, the risk of cardiovascular disease increases.
The efficacy of this drug for more than 6 weeks and the safety of long-term administration of more than 6 months have not been established, and adverse reactions such as hypertension, angina pectoris, and edema may occur when administering this drug.
Therefore, when administering this drug, the patient's symptom relief and response to treatment should be reevaluated regularly at least monthly.
4.3 Contraindications
- Patients who have a history of hypersensitivity reactions or a history of this drug and its components.
- Patients with allergic reactions to Sulfonamide.
- Patients with a history of asthma, acute rhinitis, nasal polyps, angioedema, urticaria or allergic reactions to Aspirin or other non-steroidal anti-inammatory drugs (including COX-2 inhibitors).
- Patients with uncontrolled hypertension (systolic blood pressure above 140 mmHg or higher and/or diastolic blood pressure above 90 mmHg or higher).
- Patients with edema or fluid retention.
- Patients with renal and hepatic impairment.
- Patients with active peptic ulcer or gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Patients with inflammatory bowel disease such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis.
- Patients with congestive heart failure (NYHA II - IV).
- Established ischemic heart disease, peripheral arterial disease and/or cerebrovascular disease.
- Pregnant women or women who may be pregnant.
- Nursing mother.
- Treatment of pain before and after coronary artery bypass graft (CABG).
- Patients with hyperkalemia.
- Patients with a blood clotting disorder or receiving anticoagulants.
Carefully administer to the following patients
- Patients with bronchial asthma.
- Heart failure patients or patients with such a history of it.
- High blood pressure (hypertension) patients or patients with such a history of it.
- Patients with a history of edema.
- Patients taking diuretics or ACE inhibitors.
- Patients at risk of hypovolemia
- Dehydration patients.
- Elderly.
- Patients with a history of peptic ulcer or gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Patients with high risk factors for adverse cardiovascular events (such as heart attack, stroke, etc.) (e.g. high blood pressure, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, smoking, etc.) patients with cardiovascular system or a history.
- Patients with difficult metabolism by CYP3A4.
- Women planning pregnancy (taking this drug may impair female fertility).
- Diabetics.
4.4 Warnings and precautions
Warning
If a person who regularly drinks three or more drinks daily who needs to take this medicine or other antipyretic analgesics, they must consult a doctor or pharmacist. When these people take this drug, gastrointestinal bleeding can occur.
Cardiovascular risk
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesic drugs including Polmacoxib, may increase the risk of severe cardiovascular thrombosis, myocardial infarction and stroke which can be fatal. Depending on the duration of administration, dosage and underlying cardiovascular risk factors, these risks may be increased and may be more risky in patients with cardiovascular disease. To minimize the potential risk of adverse cardiovascular events in patients treated with Polmacoxib, it should be used for the shortest possible time at the minimum effective dose. Doctors and patients should carefully monitor the onset of these cardiovascular symptoms, even if there is no history of cardiovascular disease. Patients have signs and/or symptoms of significant cardiovascular toxicity and these symptoms (chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, obscured pronunciation) it is important to know in advance what measures to take if this occurs. As a result of clinical trials of this drug, adverse reactions of prothrombin time prolongation have been reported, but this drug has not been studied for its action on platelets, so it cannot be used as a substitute for aspirin as a prophylactic treatment for the cardiovascular system.
Gastrointestinal risk
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including Polmacoxib, may increase the risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events including gastric or intestinal bleeding, ulcers and perforation, which can be fatal. These adverse reactions can occur without warning symptoms during the administration period. Older people may be at greater risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events. As the duration of administration increases, the likelihood of serious gastrointestinal adverse events may increase, but short-term administration does not completely exclude these risks. While taking Polmacoxib, you should carefully monitor for symptoms and signs of gastrointestinal ulcer or bleeding, and immediately if you suspect any suggestive symptoms or severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions, including pain, indigestion, black stools, and hematomes. Additional evaluation and treatment should be performed. In high-risk patients, alternative treatments not related to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be considered.
Effect on clinical test values
- If symptoms or signs of anemia or blood loss appear due to long-term administration of this drug, hemoglobin or hematocrit test should be performed.
- Patients who take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including this drug, for a long time should have regular complete blood count (CBC) and physical and chemical tests.
- Clinical examinations (urinalysis, blood tests, kidney function tests, liver function tests, electrocardiogram tests, fecal occult blood tests, etc.) should be performed regularly or as necessary, and if any abnormalities are confirmed, appropriate treatment such as withdrawal or suspension of administration should be performed.
- If clinical symptoms or systemic signs (e.g. eosinophilia, rash) associated with liver disease or renal disease are present, or abnormal liver function tests or renal function test results persist or worsen, administration of this drug should be discontinued.
Gastrointestinal adverse reactions
Extreme caution should be exercised when prescribing NSAIDs, including this drug, to patients with a history of ulcerative disease or gastrointestinal bleeding.
In patients with a history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding, the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding increased by more than 10-fold with NSAIDs compared to patients without these risk factors.
Other risk factors for increased gastrointestinal bleeding include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants, concomitant use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or aspirin, alcohol consumption, smoking, advanced age, and poor health.
Since most of the spontaneous reports of fatal gastrointestinal adverse events are in the elderly and infirm, special care should be taken when administering this drug to these patients.
Hypertension
Non-steroidal anti-inammatory drugs, including this drug, may cause hypertension or worsen existing hypertension, which may increase the incidence of adverse cardiovascular events, so patients with uncontrolled hypertension should not be administered.
Patients taking thiazide diuretics or loop diuretics may have a reduced response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including this drug, should be administered with caution in patients with high blood pressure. Blood pressure should be closely monitored at the beginning of administration and during the administration of this drug. If there is a significant increase in blood pressure during the administration of this drug, alternative treatment should be considered.
Congestive heart failure and edema
Fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients taking NSAIDs, including this drug. This drug should not be given to patients with edema or fluid retention.
Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis can cause deterioration of renal function and fluid retention, so this drug should be administered with caution in patients with a history of heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction, or hypertension.
In addition, patients who are taking diuretics or who are at risk of hypovolemia for other reasons should also be careful when administering this drug.
Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including this drug may cause renal papillary necrosis or other kidney damage.
In addition, since the role of prostaglandins in maintaining renal blood flow is important, special care should be taken in patients with heart failure, patients with renal failure, patients with liver failure, patients receiving diuretic ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor antagonists, and the elderly. When the medication is discontinued, most people return to their pre-treatment state.
Advanced renal disease
No controlled clinical trials have been conducted on the use of this drug in patients with advanced renal disease. Therefore, administration of this drug is not recommended for patients with advanced renal disease. If administration of this drug is to be initiated, the patient's renal function should be closely monitored.
Administration of NSAIDs, including this drug, may cause an increase in liver function levels. These abnormal test values may worsen, change or be temporary as treatment continues.
In addition, severe liver-related adverse reactions, including jaundice, fatal fulminant hepatitis, hepatic necrosis, and liver failure (some of which are fatal), have been reported infrequently with NSAIDs, including this drug.
In patients with symptoms and/or signs suggestive of abnormal liver function or abnormal liver function test results, continue to carefully observe whether liver function deteriorates during the administration period, and if abnormal liver function test results (more than 3 times the upper limit of normal) are continuously observed, or clinical symptoms or systemic signs related to liver disease (e.g. eosinophilia, rash) are observed, the administration of this drug is stopped.
Anaphylactic reactions
As with other NSAIDs, pseudo-anaphylactic reactions can occur in patients who have never been exposed to the drug.
This combination of symptoms typically occurs in asthma patients with or without nasal polyps or presenting with potentially fatal severe bronchospasm after administration of aspirin or other NSAIDs. In the event of such a similar anaphylactic reaction, first aid should be administered.
Skin reactions
- This drug is a Sulfonamide class of drugs, which can cause serious adverse skin reactions such as exfoliative dermatitis, mucosal eye syndrome (Stevens-Johnson syndrome) and toxic epidermal necrosis (Riell's syndrome), which can be fatal.
- These serious adverse reactions can occur without warning symptoms and may occur in patients with no history of sulfa allergy. In most cases, these adverse reactions occur within the first month of administration.
- Patients should be aware of the symptoms and symptoms of serious skin manifestations and should stop taking the drug at the first symptoms and signs of hypersensitivity reactions such as skin rashes, mucosal lesions or blisters, fever, and itching.
Some people with asthma may be sensitive to aspirin. The use of aspirin in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma may be associated with severe bronchospasm, which can be fatal.
Cross-reactivity involving bronchospasm between Aspirin and other NSAIDs has been repor ted in these aspirin-sensitive patients. Therefore, this drug should not be administered to these aspirin-sensitive patients and should be used with caution in asthma patients.
This drug cannot be used as a substitute for corticoid preparations or as a drug to treat corticoid deciency. Abrupt discontinuation of corticosteroids may result in worsening of corticosteroid-responsive disease. If this drug is to be administered to patients who have been taking corticosteroids for a long time, the dose should be reduced gradually.
Due to the pharmacological properties of this drug, it is possible to indiscriminate other symptoms and signs of fever and inflammation, thereby delaying the diagnosis of infectious complications under painful and non-infectious conditions.
Patients with severe dehydration should be carefully monitored after hydration.
This drug is not administered because its safety and efficacy in acute pain relief (postoperative or post-tooth extraction) have not been established.
This drug should be avoided in combination with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs other than low-dose aspirin (less than 1 mg per day), regardless of the dose administered.
Patients who are receiving antiplatelet therapy should not stop the treatment, so this drug is not administered. Patients with autoimmune diseases [e.g. patients with systemic erythematosus lupus (SLE) and mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD)] may have an increased risk of developing aseptic meningitis when taking NSAIDs, including this drug.
In the case of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including this drug, hyperkalemia may occur in diabetic patients or when co-administered with drugs that increase bloodpotassium levels, so regular monitoring of potassium levels is necessary in such cases.
Transient infertility has been reported in women taking NSAIDs for a long time.
4.5 Drug interactions
Since this drug is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4 in the liver, caution should be exercised when co-administered with drugs that inhibit CYP3A4.
Ketoconazole
Concurrent administration of Ketoconazole 400 mg with Polmacoxib inhibits the metabolism of CYP3A4, AUC is 1.3 fold higher when given the drug in combination, lower dosage than the typical dosage amount is worth considering. In addition, the drugs when administered in combination of Ketoconazole Tmax median was 71.9 hours, when administered alone was 9 hours, because the extended portion of the time, note that administration of the ketoconazole in combination, the therapeutic response time may be delayed. Concurrent administration with the antifungal agent Ketoconazole, which also interferes with many CYP isoforms, led to a 29% increase of Polmacoxib plasma concentration.
CYP enzymes
Drug-drug interactions with diuretics Acetazolamide, Furosemide, Hydrochlorothiazide or Antiepileptic drugs as it inhibits the metabolism of cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2D6 substrates, affects the metabolism of cytochrome P450, with the isoform CYP3A being involved.
The main exposure in the blood concentration of the clinical dose of these drugs in the study CYP enzymes (CYP1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, etc.) showed that it does not inhibit the action. In vivo because the bar exam studies, should consult with your doctor when administered in combination with other drugs.
ACE inhibitors or angiotensin Ⅱ receptor antagonists
NSAIDs including about ACE inhibitor or angiotensin Ⅱ receptor antagonist, where in it may be reduced in hypertensive effect of the drug and ACE inhibitor or angiotensin Ⅱ because of administering the antagonist in combination. If so, you should keep these interactions in mind. In patients with impaired renal function (e.g. dehydrated patients or the elderly), co-administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including Polmacoxib, in combination with an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor antagonist may generally increase the risk of reversible acute renal failure. Therefore, care should be taken when administering such a combination, especially to the elderly. Shall be supplied to the patient adequate water, it should be regularly monitored for renal function after starting this combination therapy.
Diuretics
In the case of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesics including this drug, it was confirmed that the natriuretic effect of Furosemide and Thiazide diuretics may be reduced in some patients by inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis in the kidney. Therefore, during co-administration of these drugs and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including Polmacoxib, signs of kidney failure should be closely monitored.
NSAIDS and Aspirin
There is no consistent evidence that combination with Aspirin may reduce the risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic reactions associated with the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including Polmacoxib. Selective COX-2 inhibitors of low-dose Aspirin (325 mg or less), can be administered together, about a monotherapy gastrointestinal adverse events than (gastrointestinal ulcer) reported that the increased incidence of other gastrointestinal complications. Since this drug has not been studied for its action on platelets, it cannot be a substitute for aspirin as a prophylactic treatment for the cardiovascular system.
Lithium
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can increase the concentration of serum Lithium and decrease the application rate of Lithium by inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandins in the kidney. Therefore, when a combination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesics and Lithium is administered, the signs of toxicity of Lithium should be carefully observed.
Methotrexate
NSAIDs delay the excretion of Methotrexate when administered in the combination, haematological toxicity of fatal Methotrexate can be increased in anti-cancer therapy (15 mg/week or more), Methotrexate is not administered in combination, when used in combination low-dose Methotrexate dose should be administered carefully, and consider the appropriate monitoring for toxicity associated with Methotrexate.
Coumarin-based anticoagulants
Warfarin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesics may exhibit synergistic effects on gastrointestinal bleeding. It can increase your risk of bleeding.
As a result of clinical trials of Polmacoxib, adverse reactions of prothrombin time prolongation were reported, and serious bleeding related to prothrombin time prolongation, which may be fatal, was reported in patients who co-administered selective COX-2 inhibitors and Warfarin. Should not be administered in combination. Especially, it was reported more in the elderly.
Cyclosporine or Tacrolimus
The nephrotoxicity of Cyclosporine or Tacrolimus may be increased by co-administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesics with Cyclosporine or Tacrolimus, so renal function should be monitored when co-administered with these drugs.
Aspirin
In addition to low-dose Aspirin (less than 325 mg per day), co-administration with other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may increase the risk of adverse reactions and should not be administered in combination.
Corticosteroids
There is a risk of increased gastrointestinal adverse events (e.g. Ulcers, bleeding). It is especially dangerous for the elderly (65 years or older).
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
It has been reported that this drug does not delay delivery in rats. However, the effect of this drug on delivery and childbirth in pregnant women is unknown.
Risk summary
There is no clinical data for administering this drug to pregnant women. In animal studies (rabbits and rats), administration of Polmacoxib has shown reproductive toxicity, including teratogenicity, but the potential risk of human pregnancy is unknown. Also, this drug, like other drugs that inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, may cause uterine asthenia or premature obstruction of the foetal arterial duct when administered at the end of pregnancy. If pregnancy is conrmed while taking Polmacoxib, stop taking Polmacoxib.
Maternal and/or embryo / fetal risk
In rabbit embryo / foetal development tests, the incidence of foetal abnormalities such as rib fusion and sternal segment fusion and ventricular septal defects rarely increased when administered orally over 3 mg/kg/day dose. In the embryo / foetal development test of rats, when 3 mg/kg/day dose was administered orally, the 13th rib length in the foetus was shorter than that of the control group or the low dose group, which is statistically significant that can be observed in the foetus. It was a phenomenon. In addition, there were no changes in mean number of luteal bodies, mean number of implants, and number of survival times in all administration groups. The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesic drugs may interfere or delay follicular rupture due to its mechanism of action, which may cause reversible infertility in some women. Therefore, in the case of women having difficulty conceiving or undergoing infertility testing, discontinuation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesic drugs, including this drug, should be considered.
The inhibitory action of prostaglandin synthesis may adversely affect pregnancy. Epidemiologic studies have shown that the risk of natural abortion increases after taking drugs that inhibit prostaglandin synthesis in early pregnancy. Animal studies have shown that implantation failure increases when drugs that inhibit prostaglandin synthesis are administered. Polmacoxib was found to significantly reduce the average number of luteal bodies, implantation and surviving embryos when administered at a dose of 1 mg/kg/day or more in rats.
Lactation
It has been confirmed that Polmacoxib can be transferred to the breast milk of rats at a concentration similar to or slightly higher than that of plasma and transmitted to the foetus. Many drugs not only transfer into breast milk, but if they do, serious adverse reactions may occur in infants. Therefore, taking into account the importance of drug administration to nursing mothers, lactation should be stopped or drug administration should be discontinued.
Paediatric use
Safety and effectiveness of Polmacoxib in paediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
Geriatric use
Elderly people are likely to have decreased renal function, liver function, and especially heart function, so appropriate observation is required when administering Polmacoxib to the elderly.
In patients with arthritis age 70 or older, the blood drug concentration of is 1.4 times higher than that in ar thritis patients aged 40 to 69 years, so it should be administered carefully.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Patients who experience dizziness, drowsiness, etc. after taking this drug should avoid driving or handling machinery
4.8 Undesirable effects
The safety of this drug was evaluated in 601 patients with osteoarthritis. In osteoarthritis patients, the maximum duration of administration of this drug was 24 weeks, and the most common patients were 2 to 3 weeks. According to the clinical trials of placebo or the active and reference formulations, the most frequent of which at least stop the medication due to adverse reactions was indigestion and epigastric pain. The most commonly reported TEAEs with the treatment of Polmacoxib were associated with GI and general disorders. All adverse reactions reported in the clinical trial of Polmacoxib in osteoarthritis patients, regardless of the causal relationship with this drug are as follows:-
Infection
Common : Nasopharyngitis. Uncommon : Pneumonia, ringworm, bronchitis, cellulitis, boil, shingles, influenza, syphilis, urinary tract infection, nail fungus.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Common : Epigastric pain, diarrhoea, indigestion, nausea, abdominal pain. Uncommon : Vomiting, bowel movement disorder, irritable bowel syndrome, stool discoloration, food poisoning, gastric ulcer, gingivitis, tooth disorder, dry mouth, enteritis, upper abdominal discomfort, gastritis, abdominal discomfort, lower abdominal pain, aphthous stomatitis, constipation, gastroesophageal reflux disease, colon polyps, esophagitis.
General disorders and administration site conditions
Common : Chest discomfort, facial swelling, oedema, peripheral swelling. Uncommon : Fatigue, systemic oedema, influenza-like disease, weight gain, asthenia, thirst, bruise, abrasion, laceration, traffic accident, spinal cord compression fracture, chills, fever, insect bite, concussion, ligament rupture, ligament sprain, wound, wrist fracture.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Uncommon : Swelling of the face, hives, erythema, neuro dermatitis, itching, general itching, dry eczema.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Uncommon : Arthralgia, back pain, flat feet, joint swelling, neck pain, limb pain, musculoskeletal pain, muscle spasms
Investigation
Uncommon : Heat sensation, drug overdose, increased neutrophils, decreased unsaturated iron binding capacity, prothrombin time, haemoglobin decreased, increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT), Increased blood creatinine, increased aspartate aminotransferase, increased creatine phosphate activator.
increased aspartate aminotransferase, increased creatine phosphate activator.
Nervous system disorders
Common : Headache.
Uncommon : Insomnia, paraesthesia, conscious depression, dizziness, drowsiness, dullness, Alzheimer's type dementia.
Benign and malignant neoplasms
Uncommon : Colon adenoma.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Common : Anaemia.
Uncommon : Skin papilloma.
Immune system disorder
Uncommon : Eosinophilia, hypersensitivity reaction.
Metabolic and nutritional system
Uncommon : Chemical allergy, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, hyperkalaemia.
Mental disorder
Uncommon : Depressed mood, major depression.
Visual impairment
Uncommon : Eye edema, swelling of the eyelids, blepharitis, eyelid cramps, dry eyes, keratitis, macular hole.
Ear and maze disorders
Uncommon : Ear discomfort, positional dizziness.
Heart disorder
Uncommon : Palpitations, angina, right leg block, myocardial ischemia.
Vascular disorder
Common : Increase in blood pressure.
Uncommon : Arrhythmia, high blood pressure, facial flushing, abnormal blood pressure.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Common : Coughing, difficulty breathing Uncommon : Asthma, runny nose, oropharyngeal pain, wet cough, rhinitis, allergic rhinitis
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit / risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com
Website : http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Symptoms caused by excessive administration of NSAIDs is usually lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting and upper abdominal pain etc., can be recovered as a co-therapy. Gastrointestinal bleeding can also occur, and in rare cases, high blood pressure, acute renal failure, respiratory depression and coma can occur.
Usually symptomatic and adjuvant treatment is performed, and there is no specific antidote.
Vomiting, activated carbon (60 to 100 g for adults, 1 to 2 g per kg of children), and osmotic diarrhea can be used if symptoms appear within 4 hours of taking the drug or are taken in very large amounts.
Hemodialysis, forced diuresis, alkalized of urine, the treatment such as blood perfusion is not useful because of the high protein bonding ratio of the drug.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action / pharmacodynamic properties
Polmacoxib is not only a selective COX-2 inhibitor but also a potent inhibitor of carbonic anhydrases (CAs). Both CA I and CA II are highly expressed in the GI tract and kidneys, organs that are also thought to be the sites at which selective COX-2 inhibitors show their side effects. By inhibition assays, we show that both CA I and CA II are strongly inhibited by Polmacoxib, while CA II also demonstrates direct competition with COX-2. To understand, at the molecular level, how Polmacoxib interacts with CA I and II, we solved the first crystal structures of CA I and CA II in complex with Polmacoxib, at 2.0 Å and 1.8 Å, respectively. Interestingly, three Polmacoxib molecules bind to the active site of CA I, whereas only one molecule binds CA II. In the active site, the three molecules of Polmacoxib organize itself along hydrophobic interaction as “stack-on-formation”, and fully occupy a cone-shaped active pocket in CA I. The binding mode of Polmacoxib to CA II was found different than its binding to Celecoxib and Valdecoxib. Our results provide structural insight into inhibition of CA I and CA II by Polmacoxib, to assess its potential clinical efficacy.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
In non-clinical pharmacokinetic studies, this drug showed a high distribution in whole blood compared to plasma, and in clinical studies, drug exposure in whole blood was observed to be 80 to 100 times higher than in plasma.
Absorption
In a single oral dose clinical trial for healthy adults, the blood exposure Cmax of this drug increased in proportion to the dose increase, but the AUC (ng h/mL) increased more than the dose increase rate. The maximum plasma t concentration (Cmax) observed in the same clinical trial reached a median value of about 5.5 to 72 hours after administration, and the blood concentration was expected to reach a steady state about 20 days after the start of administration. The half-life of a single 5 mg dose of this drug was approximately 5 days.
Distribution
In vitro tests, the binding rate of human plasma protein of this drug was observed to be about 92% and the distribution rate to whole blood was about 98%. In a clinical trial of a single dose of 8 mg loading dose followed by a 2-day repeat dose of 6 mg in healthy adults, the drug exposure (AUC ) of whole blood was about 50 ~ 70 times higher than that of plasma. At this time, the average t Cmax in the steady state was 2,054 ng / mL in whole blood and 40 ~ 51 ng/mL in plasma.
Metabolism
This drug is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4. When a single oral administration of this dr ug was administered to healthy adults, Phase I and Phase II metabolites were identied in the plasma and urine of the subjects. Phase I metabolites were detected in both plasma and urine of the subjects, and glucuronic acid conjugates were detected only in urine. No other reactive metabolites were detected.
Excretion
Af 14 ter a single oral administration of [ C]-radiolabelled this drug to male and female monkeys, the total radioactivity detected in the excretions collected up to 168 hours was about 70.4% of the dose, and the radioactivity recovered by intravenous administration was 54.5 ~67.7% higher than the highest 13%. In addition, when administered orally, the cumulative radioactivity in feces was 38.5 ~ 49.4%, and the cumulative radioactivity in urine was 20.8 ~ 32.1%, and radioactivity was detected in both feces and urine of monkeys. The ratio of metabolites in the radioactivity recovered from monkey feces was more than 99%, and the parent drug detected in the feces was less than 0.9% of the dose. In a clinical trial of repeated administration of 2 mg for 6 days after 8 mg loading dose in healthy adults, the half-reduction period was about 6 to 7 days in whole blood and about 5 to 6 days in plasma.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
(1) Safety pharmacological test
In rats to evaluate the effect on the central nervous system and respiratory system, and in monkeys to evaluate the effect on the circulatory system, up to 30 mg/kg of this drug was orally administered, and no effect of this drug administration was observed.
(2) Repeated administration toxicity test
As a result of toxicity tests performed in rats and monkeys by repeated oral administration, which is the clinical route of administration, the non-toxic dose (NOAEL) was observed to be less than 26.1 mg/kg/day in males, 25.0 mg/kg/day in females, and 3.39 mg/kg/day in monkeys at 1 weeks in the rat 25-week trial. Digestive tract disorders with inflammation and ulceration were mainly observed as common toxicity symptoms in rats and monkeys.
(3) Genotoxicity test
In the reversion mutation test using bacteria and the mouse micronucleus test, this drug did not show mutagenicity, but in the chromosomal abnormality test using CHO cells at 200 μg/mL, an increase in the frequency of cells with chromosomal abnormalities was observed in the presence of a metabolic active system.
(4) Carcinogenicity test
Tumors were not induced when this drug was orally administered to rats at doses of 1 mg/kg for males and 0.3 mg/kg for females for 102 weeks and 91 weeks, respectively. It represents a safety margin of 2.8 times and 3.0 times, respectively, compared to the recommended dose of 2 mg exposure. Tumors were not induced when this drug was orally administered to mice at a dose of up to 6mg/kg for 78 weeks, and the exposure at week 26 (AUC0-24h) at the highest dose used in the study was compared to the exposure at the clinically recommended dose of 2mg for males and females, respectively. 2.7-fold and 3.4-fold margins of safety.
7.0 Description
Polmacoxib, an orally-active tissue-selective COX-2 inhibitor and binds to enzyme arbonic anhydrase. It is chemically described as Benzenesulfonamide, 4-[3-(3-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-2-furanyl] with a molecular formula of C18H16FNO4S and a molecular weight of 361.40 g/mol.

8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
None
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packing information
Alu-Alu blister strip of 10 capsules.
8.4 Storage and handling instructions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30oC. Protect from moisture.
Keep out of reach of children. Capsule should be swallowed whole and not to be opened, chewed or crushed.
9.0 Patient counselling information
Advise the patient to read the approved patient labeling. Before administering this drug, the potential risks and benefits of this drug and other alternative therapies should be considered. As the dose and duration of exposure increases, the cardiovascular risk increases. Therefore, administer the lowest effective dose for the shortest period possible. The efficacy of this drug for more than 6 weeks and the safety of long-term administration of more than 6 months have not been established, and adverse reactions such as hypertension, angina pectoris, and edema may occur when administering this drug. Therefore, when administering this drug, the efficacy of this drug for more than 6 weeks and the safety of long-term administration for more than6 months have not been established. Therefore, at least monthly, whether to continue administration according to the patient's symptom relief and response to treatment should be re-evaluated. In patients with significant risk factors for cardiovascular events (e.g. hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, smoking), it should be administered after careful consideration.
Elderly
When administering this drug to the elderly or patients with cardiac dysfunction, medically appropriate management should be continued. If symptoms worsen during treatment, appropriate measures such as discontinuation of treatment should be taken.
When administering this drug to the elderly or patients with cardiac dysfunction, medically appropriate management should be continued. If symptoms worsen during treatment, appropriate measures such as discontinuation of treatment should be taken.
Gastrointestinal adverse reactions
Extreme caution should be exercised when prescribing NSAIDs, including this drug, to patients with a history of ulcerative disease or gastrointestinal bleeding.
In patients with a history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding, the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding increased more than 10-fold when treated with NSAIDs compared to patients without these risk factors. Other risk factors for increased gastrointestinal bleeding include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or aspirin, alcohol consumption, smoking, old age, and poor health.
Since most of the spontaneous reports of fatal gastrointestinal adverse reactions are in the elderly and infirm, special care should be taken when administering this drug to these patients.
Hypertension
NSAIDs, including this drug, can cause hypertension or aggravate pre-existing hypertension, which may increase the incidence of adverse cardiovascular events. Therefore, this drug should not be administered to patients with uncontrolled hypertension. do.
Patients taking Thiazide diuretics or loop diuretics may have a reduced response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs.
NSAIDs, including this drug, should be administered with caution in hypertensive patients. Blood pressure should be closely monitored at the beginning and during treatment with this drug. Alternative treatment should be considered if blood pressure rises significantly during treatment with this drug.
Congestive heart failure and edema
Fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including this drug. This drug should not be administered to patients with edema or fluid retention. Because inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis can lead to deterioration of renal function and fluid retention, this drug should be administered with caution in patients with a history of heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction, or hypertension.
n addition, caution should be exercised when administering this drug in patients taking diuretics or at risk of hypovolemia for other reasons.
NSAID’s
When taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including this drug for a long time, renal papillary necrosis or other kidney damage may occur. In addition, since the role of prostaglandin in maintaining renal blood flow is important, special attention is required in patients with heart failure, renal failure, liver failure, patients receiving diuretic ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor antagonists, and the elderly. When the drug is discontinued, most patients return to their pre-treatment state.
Advanced renal disease
No controlled clinical trials have been conducted on the use of this drug in patients with advance adrenal disease. Therefore, administration of this drug is not recommended for patients with advanced renal disease. If treatment with this drug is to be initiated, the patient's renal function should be closely monitored.
Liver function
Administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including this drug may cause an increase in liver function levels. These abnormal laboratory values may worsen, remain unchanged, or be transient as treatment continues. In addition, there have been rare reports of severe liver-related adverse reactions, including jaundice, fatal fulminant hepatitis, hepatic necrosis, and hepatic failure (some fatal), with NSAIDs including this drug. Patients with symptoms and/or signs suggestive of liver function abnormalities, or patients with abnormal liver function test results, should be continuously and carefully monitored for deterioration of liver function during the administration period, and abnormal liver function test results (up to 3 upper limit of normal) Dosage should be discontinued if liver disease-related clinical symptoms or systemic signs (e.g. eosinophilia, rash) are observed.
Hematology
If symptoms or signs of anemia or blood loss appear due to long-term administration of this drug, hemoglobin or hematocrit should be tested. Selective COX-2 inhibitors do not generally affect platelet count, prothrombin time (PT), or partial thromboplastin time (PTT), and do not inhibit platelet aggregation at recommended doses. Adverse reactions have been reported, so caution should be exercised. 10) Patients taking NSAIDs, including this drug, for a long period of time should have a complete blood count (CBC) and physicochemical tests performed regularly. If clinical symptoms or systemic signs (e.g. eosinophilia, rash) associated with liver or renal disease develop, or if abnormal liver or renal function test results persist or worsen, the drug should be discontinued.
Anaphylactic reactions
Similar to other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesics, similar anaphylactic reactions can occur in patients who have never been exposed to drugs. These complex symptoms typically occur in asthma patients with or without nasal polyps or with potentially fatal severe bronchospasm after administration of Aspirin or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. First aid measures should be taken in the event of such an anaphylactic reaction.
Skin reactions
This medicine as a sulfonamide-based drugs, deprived dermatitis, skin, mucous membranes should syndrome (Stevens - Johnson syndrome) and toxic epidermal bars with (Riel's syndrome) can cause serious skin adverse events such as, which can be fatal there is. These serious adverse reactions can occur without warning symptoms and can also occur in patients with no history of sulfa drug allergy. In most cases, these adverse reactions occur within the first month of administration. Patients should be aware of the signs and symptoms of significant skin manifestations and should be discontinued at the first symptoms and signs of hypersensitivity reactions such as skin rash, mucosal lesions or blisters, fever and itching.
Asthma patients
Some people with asthma may be sensitive to aspirin. Aspirin Sensitization The use of Aspirin in patients with asthma may be associated with severe bronchospasm, which can be fatal. Cross-reactions involving bronchospasm between Aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have been reported in these Aspirin-sensitive patients. Therefore, this drug is administered and do not have such Aspirin-sensitive patients, should be with caution for patients with asthma.
Corticosteroids
This drug cannot be used as a substitute for corticosteroids or as a drug to treat corticoid deficiency. Sudden discontinuation of corticosteroids can lead to exacerbation of corticosteroid - reactive disorders. If you are taking this drug to patients who have been taking corticosteroids for a long time, you should gradually decrease the dose.
Diagnosis of infectious complications Due to the pharmacological nature of this drug, it may delay the diagnosis of infectious complications under painful and non-infectious conditions by making other symptoms and signs of fever and inflammation invisible.
Dehydration
In patients with severe dehydration symptoms, the drug should be administered after hydration and carefully observed.
Pain relief
Do not administer this drug as the safety and efficacy for acute pain relief (pain relief after surgery or tooth extraction) have not been established.
Myocardial infarction and stroke
The incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke was found in two large-scale controlled clinical trials for the treatment of pain from the first 10 to 14 days immediately after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) with other selective COX-2 inhibitors used for postoperative pain.
Clinical test
Conduct clinical tests [urinalysis, blood tests, renal function tests, liver function tests, electrocardiogram (EKG) and the fecal occult blood test, etc.] regularly or as needed, and if abnormalities are found, take appropriate measures such as withdrawal or discontinuation of the drug.
Combination with NSAIDS
This drug should be avoided in combination with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs other than low-dose Aspirin (less than 325 mg per day), regardless of the dose administered.
Driving or handling machinery
Patients who experience dizziness, drowsiness, etc. after taking this drug should avoid driving or handling machinery.
Aspirin
Results of clinical trials have been reported about the adverse reactions prothrombin time extension, the drug is not because the bar acts conducted research on platelets as a preventative therapy for cardiovascular drugs can be a substitute for aspirin. Patients receiving anti-platelet therapy, so should not stop the treatment, do not administer this medicine.
Symptomatic treatment
Note that treatment with anti-inflammatory analgesics is symptomatic, not causative therapy.
Cross-sensitivity
Patients who are susceptible to one non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesic can likewise show sensitivity to other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesics.
Autoimmune diseases
Autoimmune diseases (e.g. systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) patients) may have a risk of aseptic meningitis when taking NSAIDs, including Polmacoxib. In the case of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesics including this drug, hyperkalemia may occur in diabetic patients or when coadministered with drugs that increase blood potassium levels, so in such cases, regular observation of potassium levels is necessary
Infertility
Temporary infertility has been reported in women who take non-steroidal anti-inammatory drugs for a long time.
Diet
This drug has not been carried out clinical trials on dietary inuences, authorized usage, by complying with the capacity to be administered after a meal.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again. If you have any further questions, please ask your doctor or pharmacist. This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours. If you get any side effects, talk to you doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet:
1.What PolvoltTM Capsules is and what it is used for
2.What you need to know before you take PolvoltTM Capsules
3.How to take PolvoltTM Capsules
4.Possible side effects
5.How to store PolvoltTM Capsules
6.Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Polvolt Capsules is and what it is used for
PolvoltTM capsules contain Polmacoxib and it belongs to a class of medicines called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). All non-steroidal anti-inflammatory painkillers including PolvoltTM capsules. Polmacoxib is a drug that reduces pain and inflammation caused by osteoarthritis by inhibiting the COX-2 enzyme. Pain reduction is the main function. In addition to reducing pain and inflammation caused by osteoarthritis, drugs belonging to (NSAIDs) may, in rare cases, cause serious side effects such as myocardial infarction or stroke. To minimize the potential risk of adverse reactions, use the lowest effective dose possible. It should be used for the shortest period. Those taking long-term non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and people with heart disease and heart disease may suffer from myocardial infarction or stroke.
Polmacoxib capsules are indicated for the treatment of idiopathic (primary) osteoarthritis of the hip/knee. Osteoarthritis (degenerative) is the most common disease that occurs in joints, where the ends of bones meet. Cartilage surrounds the joints and acts as a cushion. Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease that causes wear and tear and damage to joints and bones. Symptoms of degenerative arthritis include pain, stiffness, and swelling may be felt in the joint area, and as it progresses, physical dysfunction may occur. Symptoms commonly occur in weight-bearing joints like knees, hips and hand joints. Degenerative arthritis occurs with age, and obesity and is more common when there is damage to the joints. Commonly occurs more often in women than men.
2. What you need to know before you take Polvolt Capsules
DO NOT take PolvoltTM Capsules if you:
- If you have hypersensitivity reaction or history of hypersensitivity to the components of PolvoltTM Capsules. (listed in section 6)
- If you have an allergic reaction to sulphonamides.
- If you a history of asthma, acute rhinitis, nasal polyps, angioedema, urticaria, or allergic reactions to aspirin or other NSAIDs (including COX-2 inhibitors).
- Patients with high blood pressure that is not well controlled despite taking antihypertensive drugs.
- Patients with edema or fluid retention.
- Patients with hepatic impairment.
- Patients with renal impairment.
- Patients with active peptic ulcer or gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Patients with inflammatory bowel disease such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis.
- Congestive heart failure patients (NYHA II - IV)
- Patients with established ischemic heart disease, peripheral arterial disease, and/or cerebrovascular disease.
- Women who are pregnant or may be pregnant.
- Nursing mothers.
- Treatment of pain occurring before and after coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG).
- Patients with hyperkalaemia (increased potassium levels).
- Patients with blood coagulation disorders or receiving anticoagulants.
Warnings and Precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking PolvoltTM Capsules.
- Patients with bronchial asthma.
- Patients with heart failure or a history of it.
- Patients with high blood pressure or a history of it.
- Patients with a history of edema.
- Patients taking diuretics or ACE inhibitors.
- Patients at risk of hypovolemia.
- Dehydrated patients.
- Elderly people.
- Patients with a history of peptic ulcer or gastrointestinal bleeding.
- People with high risk factors for adverse cardiovascular events (heart attack, stroke, etc.).
- Patients (e.g. high blood pressure, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, smoking, etc.), patients with cardiovascular disease or its history.
- Patients with difficult metabolism due to ketoconazole (CYP3A4).
- Women planning to become pregnant (taking this drug may impair female fertility).
- Diabetics.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can cause ulcers and bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract at any time while taking them. There are potential risks that may cause it.
- The risk of ulcers and bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract appears to be higher in people who:
- Those taking “corticosteroids” and “anticoagulants”
- Long-term users of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Smoker
- Heavy and frequent drinkers
- Elderly people
- Unhealthy people
Medicines such as PolvoltTM Capsules may be associated with a small increased risk of heart attack (myocardial infarction) or stroke. Any risk is more likely with high doses and prolonged treatment. Do not exceed the recommended dose or duration of treatment.
If you have heart problems, a previous stroke, or think that you might be at risk of these conditions (for example if you have high blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol or are a smoker) you should discuss your treatment with your doctor or pharmacist.
Serious gastrointestinal side effects such as bleeding, ulceration, and perforation can occur at any time with or without warning symptoms in patients treated with NSAIDs. If any sign of gastrointestinal bleeding occurs, PolvoltTM Capsules should be stopped immediately.
Other medicines and PolvoltTM Capsules
Tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
Tell your doctor if you are taking:
- Ketoconazole
- CYP enzymes
- ACE inhibitors or angiotensin Ⅱ receptor antagonists
- Diuretics
- NSAIDS and Aspirin
- Lithium
- Methotrexate
- Coumarin-based anticoagulants
- Cyclosporine or Tacrolimus
- Aspirin
- Corticosteroids
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
Do not take PolvoltTM Capsules, if you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby.
You should inform your doctor if you have problems becoming pregnant. NSAIDs may make it more difficult to become pregnant.
PolvoltTM Capsules should not be used if you are breast-feeding. It has been confirmed that Polmacoxib can be transferred to the breast milk of rats at a concentration similar to or slightly higher than that of plasma and transmitted to the fetus.
Pediatric use
The safety and effectiveness of Polmacoxib in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
Geriatric use
PolvoltTM capsules should be administered carefully in elderly people.
Driving and using machines
PolvoltTM capsules may cause dizziness or drowsiness. So, you should not drive or operate heavy machinery if you feel dizzy or not fully alert.
3. How to take Polvolt Capsules
Always take PolvoltTM Capsules exactly as your doctor told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure. Check the pharmacist's label for the dose recommended for you.
The recommended adult dose is one PolvoltTM capsule (2mg) once daily after a meal. The daily dose should not exceed 2 mg/day. Capsules should be swallowed whole and not to be opened, chewed, or crushed. PolvoltTM Capsules are not recommended for use in children.
If you take more PolvoltTM Capsules than you should-
- If you take more capsules than you should (an overdose), seek medical attention immediately. Immediately go to the emergency room of a nearby hospital.
- Symptoms of overdosage of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory painkillers generally include lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, etc. can be restored to normal with auxiliary treatment.
- Gastrointestinal bleeding may also occur, and in rare cases, hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression, and coma may occur.
If you forget to take PolvoltTM Capsules-
Do not take a double dose to make up for the forgotten dose. Take your capsule as soon as you remember and continue to take your medicine as usual, but do not take more than one capsule a day.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. The most commonly reported side effects of Polmacoxib were associated with GI and general disorders.
Rare but serious side effects may include:
- Myocardial infarction,
- Stroke, High blood pressure,
- Generalized edema (fluid retention) due to heart failure,
- Kidney disease, including kidney failure
- Gastrointestinal bleeding and ulcers
- Decreased red blood cells (anemia)
- Life-threatening skin reactions
- Life-threatening allergic reactions
- Liver disease, including liver failure
- Asthma
Other side effects may include: Abdominal pain, Constipation, Diarrhea, bloating, Gas, Heartburn, Nausea, Vomiting, Dizziness
If you experience any of the following symptoms, call for an emergency immediately.
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
- Chest pain
- Weakness in one part or one side of the body
- Swelling of the face or throat
If you experience the following symptoms, stop taking the drug and consult your doctor.
- Nausea
- When you feel more tired and weak than usual
- Itching
- Skin or eyes turn yellow
- Abdominal pain
- Flu-like symptoms
- Vomiting blood
- Bloody stool or black, sticky stool like tar.
- Skin rash or blisters accompanied by fever
- Abnormal weight gain
- Swelling of the arms, legs, hands, and feet
If any of the side effects become serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician
5. How to store Polvolt Capsules
Keep out of reach of children.
PolvoltTM Capsule should be swallowed whole and not to be opened, chewed or crushed.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What PolvoltTM Capsule contains
Each hard gelatin capsule contains:
Polmacoxib 2 mg
Excipients q.s.
What PolvoltTM Capsules looks like and contents of the pack
Alu-Alu blister strip of 10 capsules.