Rabifast IV
1.0 Name of the medicinal product
Rabeprazole Injection IP
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
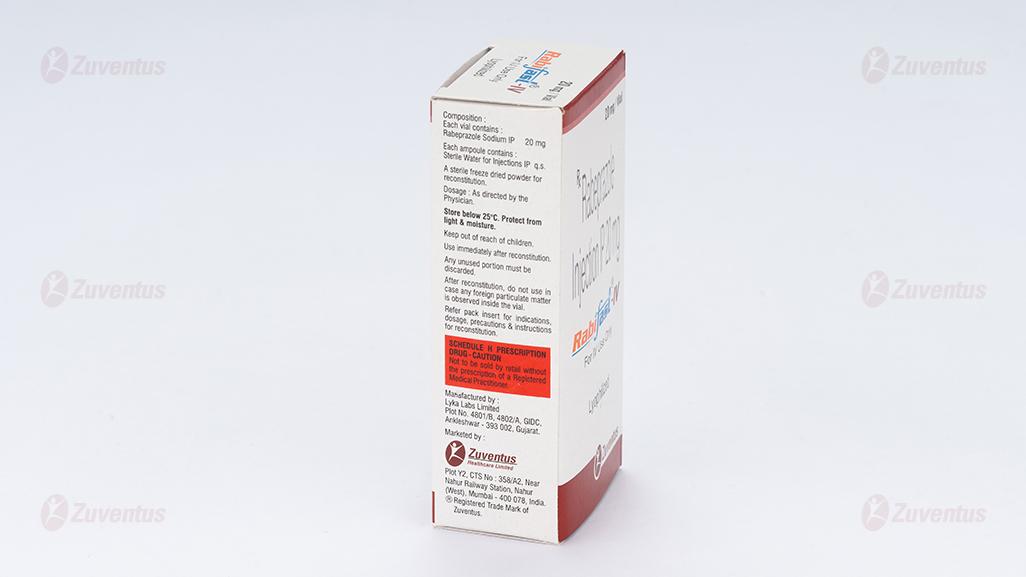
Each vial contains:
Rabiprazole Sodium IP 20 mg
Each ampoule contains
Sterile Water for Injections IP q.s
A sterile freeze dried powder for reconstitution.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Powder for solution for infusion.
20 mg
4.0 CLINICAL PARTICULARS
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the treatment of gastritic & deodenal ulcer, gastroesophagal reflux disease (GERD) as an alternative to oral therapy in patients who are unable to take oral proton pump inhibitor.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
The intravenous administration is recommended only in cases where the oral administration is not indicated. As soon as an oral therapy is possible, the intravenous therapy should be discontinued.
Recommended dose is intravenous administration of the content of one vial (20 mg Rabeprazole) once daily.
Parenteral routes of administration other than intravenous are not recommended.
Injection: The content of the vial needs to be reconstituted with 5 ml Sterile Water for Injections IP, which should be given slowly over 5 - 15 min.
Infusion: For intravenous infusion the reconstituted solution should be further diluted and administered as short-term infusion over 15 - 30 min.
Compatibility with various I.V. fluids: Rabeprazole I.V. is compatible with Sterile Water for Injections IP and 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection IP. No other solvent or infusion fluid must be used for administration of Rabeprazole I.V. injection.
Reconstitution: To reconstitute add 5 ml of Sterile Water for Injections IP to make a solution. After preparation, the reconstituted solution must be used within 4 hours and the unused portion discarded. As with all parenteral admixtures, the reconstituted or further diluted solution should be examined for change in colour, precipitation, haziness or leakage. The unused portion should be discarded. pH of the reconstituted solution: Between 11.2-12.5.
4.3 Contraindications
Rabeprazole is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to Rabeprazole, substituted benzimidazoles or to any component of the formulation
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
- Presence of gastric malignancy: Symptomatic response to therapy with Rabeprazole does not preclude the presence of gastric malignancy.
- Renal impairment: No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with renal impairment.
- Hepatic impairment: No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. Due to the lack of clinical data on Rabeprazole in patients with severe hepatic impairment, caution should be exercised in those patients.
4.5 Drug interactions
Drugs metabolized by CPY450: Studies in healthy subjects have shown that Rabeprazole does not have clinically significant interactions with other drugs metabolized by the CYP450 system, such as warfarin and theophylline given as single oral doses, diazepam as a single intravenous dose, and phenytoin given as a single intravenous dose (with supplemental oral dosing).
Warfarin: There have been reports of increased INR and prothrombin time in patients receiving proton pump inhibitors, including Rabeprazole, and warfarin concomitantly. Increases in INR and prothrombin time may lead to abnormal bleeding and even death.
Cyclosporine: In vitro incubations employing human liver microsomes indicated that Rabeprazole inhibited cyclosporine metabolism with an IC50 of 62 μM, a concentration that is over 50 times higher than the Cmax in healthy volunteers following 14 days of dosing with 20 mg of Rabeprazole. This degree of inhibition is similar to that by omeprazole at equivalent concentrations.
Compounds dependent on gastric pH for absorption: Co-administration of Rabeprazole 20 mg QD resulted in an approximately 30% decrease in the bioavailability of ketoconazole and increases in the AUC and Cmax for digoxin of 19% and 29%, respectively. Therefore, patients may need to be monitored when such drugs are taken concomitantly with Rabeprazole. Concomitant use of atazanavir and proton pump inhibitors is not recommended. Coadministration of atazanavir with proton pump inhibitors is expected to substantially decrease atazanavir plasma concentrations and thereby reduce its therapeutic effect.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Breast-feeding
Since many drugs are excreted in milk, caution should be exercised when Rabeprazole is administered to a nursing mother.
Pediatric use
The safety and effectiveness of Rabeprazole in pediatric patients has not been established.
Geriatric use
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects.
4.7 Effects on the ability to drive and use machines
Based on the pharmacodynamic properties and the adverse events profile, it is unlikely that Rabifast would cause an impairment of driving performance or compromise the ability to use machinery. If however, alertness is impaired due to somnolence, it is recommended that driving and operating complex machinery be avoided.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Worldwide, over 2900 patients have been treated with oral Rabeprazole in Phase II-III clinical trials involving various dosages and durations of treatment.
The most commonly reported adverse reactions observed in patients included pain, pharyngitis, flatulence, infection, and constipation. Other adverse reactions observed include headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, dry mouth, dizziness, peripheral edema, hepatic enzyme increase, hepatitis, hepatic encephalopathy, myalgia, and arthralgia. Proton Pump Inhibitors associated with acute kidney injury.
Reporting of side effects
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to:medico@zuventus.com
Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page.
Website link: https://www.zuventus.co.in/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
There has been no experience with large overdoses of Rabeprazole.
No specific antidote for Rabeprazole is known. Rabeprazole is extensively protein bound and is not readily dialyzable. In the event of overdosage, treatment should be symptomatic and supportive.
5.0 PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Rabeprazole belongs to a class of antisecretory compounds (substituted benzimidazole proton-pump inhibitors) that do not exhibit anticholinergic or histamine-2-receptor antagonist properties, but suppress gastric acid secretion by inhibiting the gastric H+/K+-ATPase at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cell. Because this enzyme is regarded as the acid (proton) pump within the parietal cell, Rabeprazole has been characterized as a gastric proton-pump inhibitor. Rabeprazole blocks the final step of gastric acid secretion.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
In gastric parietal cells, Rabeprazole is protonated, accumulates, and is transformed to an active sulfenamide. When studied in vitro, Rabeprazole is chemically activated at pH 1.2 with a half-life of 78 seconds.
The anti-secretory effect begins within one hour after oral administration of 20 mg Rabeprazole. The median inhibitory effect of Rabeprazole on 24 hour gastric acidity is 88% of maximal after the first dose.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
The plasma concentration time profile of Rabeprazole after intravenous administration of a single 20 mg dose is biphasic, with a terminal half-life of 1.02 ± 0.63 hrs. Peak plasma concentration of 1646.07 ± 461.27 ng/mL is obtained within 0.14 ± 0.08 hrs of administration. Intravenous infusion of 20 mg Rabeprazole over five minutes results in a four-fold increase in peak concentration and a more rapid elimination as compared to the same oral dose. The AUC0-t and AUC0-∞ are 1297.70 ± 357.07 and 1289.83 ± 356.52 ng*h/mL, respectively. The total body clearance of Rabeprazole is 282.93 ± 98.01 mL/min.
Rabeprazole is extensively metabolized. The thioether and sulphone are the primary metabolites measured in human plasma. These metabolites are not observed to have significant antisecretory activity. In vitro studies have demonstrated that Rabeprazole is metabolized in the liver primarily by cytochromes P450 3A (CYP3A) to a sulphone metabolite and cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) to desmethyl Rabeprazole. The thioether metabolite is formed non-enzymatically by reduction of Rabeprazole. CYP2C19 exhibits a known genetic polymorphism due to its deficiency in some sub-populations (e.g. 3 to 5% of Caucasians and 17 to 20% of Asians). Rabeprazole metabolism is slow in these sub-populations; therefore, they are referred to as poor metabolizers of the drug.
6.0 Nonclinical Properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Non-clinical effects were observed only at exposures sufficiently in excess of the maximum human exposure that make concerns for human safety negligible in respect of animal data.
Studies on mutagenicity gave equivocal results. Tests in mouse lymphoma cell line were positive, but in vivo micronucleus and in vivo and in vitro DNA repair tests were negative. Carcinogenicity studies revealed no special hazard for humans.
7.0 Description
RABIFAST-IV contains Rabeprazole, a substituted benzimidazole that inhibits gastric acid secretion.
IUPAC Name: Sodium;2-[[4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl]methylsulfinyl]-benzimidazol-1-ide
Molecular Formula: C18H20N3NaO3S
Molecular Weight: 381.4 g/mol
Structure:

9.0 Patient Counselling Information
Adverse Reactions
Advise patients to report to their healthcare provider if they experience any signs or symptoms consistent with:
- Injection Site Reactions
- Potential for Exacerbation of Zinc Deficiency
- Acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis
- Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhea
- Bone Fracture
- Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
- Cutaneous and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Hepatic Effects
- Hypomagnesemia and Mineral Metabolism
Drug Interactions
- Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider of any other medications they are currently taking, including rilpivirine-containing products and high dose methotrexate.
Pregnancy
- Advise a pregnant woman of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy.
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
12.0 Date of revision of the text
This leaflet was last revised in July 2024.