Revostat FB
Therapy Area
Cardiology
1. GENERIC NAME
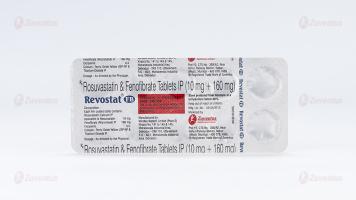
Rosuvastatin & Fenofibrate Tablets IP (10 mg + 160 mg)
2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each film coated tablet contains:
Rosuvastatin Calcium IP
equivalent to Rosuvastatin ………….. 10 mg
Fenofibrate (Micronised) IP………… 160 mg
Excipients……………………………. q.s.
Colours: Ferric Oxide Yellow USP-NF & Titanium Dioxide IP
3. DOSAGE FORM AND STRENGTH
Film-coated tablet 10mg/160mg
4. CLINICAL PARTICULARS
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the treatment of combined hyperlipidemia in patients with normal hepatic and renal function.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
One Revostat®FB tablet once daily or as directed by the Physician.
4.3 Contraindications
- Patients who are hypersensitivity to any component of this product.
- Patients with active liver disease or renal impairment.
- Patients with preexisting gall bladder disease.
- Pregnancy and lactation.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Liver Dysfunction
It is recommended that liver enzyme tests be performed before the initiation of REVOSTAT®FB, and if signs or symptoms of liver injury occur.
Increases in serum transaminases [AST (SGOT) or ALT (SGPT)] have been reported with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, including REVOSTAT®FB. In most cases, the elevations were transient and resolved or improved on continued therapy or after a brief interruption in therapy. There were two cases of jaundice, for which a relationship to rosuvastatin therapy could not be determined, which resolved after discontinuation of therapy. There were no cases of liver failure or irreversible liver disease in these trials.
In a pooled analysis of placebo-controlled trials, increases in serum transaminases to greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal occurred in 1.1% of patients taking REVOSTAT®FB versus 0.5% of patients treated with placebo. There have been rare post-marketing reports of fatal and non-fatal hepatic failure in patients taking statins, including REVOSTAT®FB. If serious liver injury with clinical symptoms and/or hyperbilirubinemia or jaundice occurs during treatment with REVOSTAT®FB, promptly interrupt therapy. If an alternate etiology is not found, do not restart REVOSTAT®FB.
REVOSTAT®FB should be used with caution in patients who consume substantial quantities of alcohol and/or have a history of chronic liver disease. Active liver disease, which may include unexplained persistent transaminase elevations, is a contraindication to the use of REVOSTAT®FB.
Hepatic insufficiency
In a study in subjects with varying degrees of hepatic impairment there was no evidence of increased exposure to REVOSTAT®FB other than in the 2 subjects with the most severe liver disease (Child-Pugh scores of 8 and 9). In these subjects, systemic exposure was increased by at least 2-fold compared with subjects with lower Child-Pugh scores. Its recommended that the liver enzyme tests be performed before and after 12 weeks following both the initiation of therapy and any elevation of dose thereafter.
Renal effects
An assessment of renal function should be considered during routine follow-up of patients treated with higher dose.
Skeletal muscle
Effects on skeletal muscle e.g. uncomplicated myalgia, myopathy and rhabdomyolysis, have been reported in patients treated with REVOSTAT®FB. Patients who develop any signs or symptoms suggestive of myopathy should have their CK levels measured. REVOSTAT®FB therapy should be discontinued if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected.
An increase in the incidence of myositis and myopathy has been seen in patients receiving other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors together with cyclosporin, fibric acid derivatives, including gemfibrozil, nicotinic acid, azole antifungals and macrolide antibiotics.
REVOSTAT®FB should be prescribed with caution in patients with pre-disposing factors for myopathy, such as renal impairment, advanced age and hypothyroidism, or situations where an increase in plasma levels may occur.
REVOSTAT®FB should be temporarily withheld in any patient with an acute serious condition suggestive of myopathy or predisposing to the development of renal failure secondary to rhabdomyolysis (e.g. sepsis, hypotension, major surgery, trauma, severe metabolic, endocrine and electrolyte disorders; or uncontrolled seizures).
4.5 Drug Interaction
Rosuvastatin:
Cyclosporin: Rosuvastatin steady state AUC increased up (0-t) to 7-fold over that seen in healthy volunteers administered the same dose.
Gemfibrozil: Concomitant use of Rosuvastatin and gemfibrozil resulted in a 2-fold increase in Rosuvastatin C and AUC.
Protease Inhibitor: Co-administration of Rosuvastatin with certain protease inhibitors given in combination with ritonavir has different effects on roasuvastatin exposure. The protease inhibitor combinations lopinavir/ritonavir and atazanavir/ritonavir increase Rosuvastatin exposure up to threefold. For these combination the dose of Rosuvastatin is restricted to low dose.
Coumarin Anticoagulants: Rosuvastatin significantly increased INR (International Normalized Ratio) in patients receiving coumarin anticoagulants. Therefore, caution should be excercised when coumarin anticoagulants are given in conjunction with Rosuvastatin. In patients taking coumarin anticoagulants and Rosuvastatin concomitantly INR should be determined before starting Rosuvastatin and frequently enough during early therapy to ensure that no significant alteration of INR occurs.
Niacin: The skeletal muscle effects may be enhanced with Rosuvastatin in used with combination Niacin; a reduction in Rosuvastatin dosage should be considered.
Fenofibrate:
Oral Anticoagulants: Caution should be exercised when coumarin anticoagulants are given along with fenofibrate. The dosage of anticoagulant should be reduced to maintain the prothrombin time/INR.
Cyclosporine: Because cyclosporine can produce nephrotoxicity with decreases in creatinine clearance and rises in serum creatinine and because renal excretion is the primary elimination route of fibrate drugs including Fenofibrate, there is a risk that an interaction will lead to deterioration.
4.6 Use in Special Population
Age and sex: There was no clinically relevant effect on age or sex by this combination.
Race: Population pharmacokinetic analysis revealed no clinically relevant differences in pharmacokinetics among Caucasian, Hispanic and Black or Afro-Caribbean groups. However, in asian patients there is 2 fold median exposure in AUC and C of rosuvatstatin.
Renal insufficiency: The lowest possible dose should be administered in renal insufficiency (mild, moderate and severe). As the drug concentration increases more than 2-fold raise in this case.
Pregnancy and Lactation: The safety of this combination, during pregnancy and breast-feeding has not been established. Women of childbearing potential should use appropriate contraceptive measures.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No effect of Fenofibrate was noted. Studies to determine the effect of Rosuvastatin on the ability to drive and use machines have not been conducted. However, based on its pharmacodynamic properties, Rosuvastatin is unlikely to affect this ability. When driving vehicles or operating machines, it should be taken into account that dizziness may occur during treatment.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Rosuvastatin
Rosuvastatin is generally well tolerated. The adverse events seen with Rosuvastatin are generally mild and transient. In controlled clinical trials less than 4% of Rosuvastatin treated patients were withdrawn due to adverse events. The adverse reactions seen with Revostat are generally mild and transient. In controlled clinical trials, less than 4% of Revostat-treated patients were withdrawn due to adverse reactions.
The frequencies of adverse events are ranked according to the following:
Common (> 1/100, < 1/10); Uncommon (> 1/1000, < 1/100); Rare (> 1/10 000, < 1/1000).
Nervous system disorders:
Common: headache, dizziness and memory loss
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Common: constipation, nausea, abdominal pain
Musculoskeletal, connective tissue and bone disorders:
Common: myalgia
Rare: myopathy, rhabdomyolysis
General disorders:
Common: asthenia Skin disorders: Uncommon: pruritis, rash, urticaria
Rare: hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema.
The incidence of adverse drug reactions tends to increase with increasing dose.
Skeletal muscle effects: Rhabdomyolysis, which may occasionally be associated with impairment of renal function, has been reported with Rosuvastatin.
Renal effects: Proteinuria Laboratory effects: A dose-related increase in liver transaminases and CK has been observed in patients taking Rosuvastatin. Abnormal urinalysis testing (dipstick-positive proteinuria with haematuria) has been seen in patients taking Rosuvastatin. The protein detected was mostly tubular in origin. In most cases, proteinuria decreases or disappears spontaneously on reduction of dose.
Fenofibrate
Adverse events reported by 2% or more of patients treated with Fenofibrate during the double-blind, placebo-controlled trials, regardless of causality, are listed in the table below. Adverse events led to discontinuation of treatment in 5% of patients treated with Fenofibrate and in 3% treated with placebo. Increases in liver function tests were the most frequent events, causing discontinuation of Fenofibrate treatment in 1.6% of patients in double-blind trials.
|
BODY SYSTEM |
Adverse Event |
Fenofibrate (N = 439) |
Placebo (N = 365) |
|
BODY AS A WHOLE |
Abdominal Pain |
4.60% |
4.40% |
|
Back Pain |
3.40% |
2.50% |
|
|
Headache |
3.20% |
2.70% |
|
|
Asthenia |
2.10% |
3% |
|
|
Flu Syndrome |
2.10% |
2.70% |
|
|
DIGESTIVE |
Liver Function Tests Abnormal |
7.50% |
1.40% |
|
Diarrhea |
2.30% |
1.90% |
|
|
Nausea |
2.10% |
1.40% |
|
|
METABOLIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDERS |
SGPT Increased |
3% |
1.60% |
|
Creatine Phosphokinase Increased |
3% |
1.40% |
|
|
SGOT Increased |
3.40% |
0.50% |
|
|
RESPIRATORY |
Respiratory Disorder |
6.20% |
5.50% |
|
Rhinitis |
2.30% |
1.10% |
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: Website: https://www.zuventus.co.in/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
There is no specific treatment in the event of overdose. In the event of overdose, the patient should be treated symptomatically and supportive measures instituted as required. If indicated, elimination of unabsorbed drug should be achieved by emesis or gastric lavage; usual precautions should be observed to maintain the airway. Hemodialysis is unlikely to be of benefit.
5. Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Rosuvastatin
Rosuvastatin is a selective and competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme that converts 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A to mevalonate, a precursor for cholesterol. The primary site of action of rosuvastatin is the liver, the target organ for cholesterol lowering. Rosuvastatin increases the number of hepatic LDL receptors on the cell-surface, enhancing uptake and catabolism of LDL and it inhibits the hepatic synthesis of VLDL, thereby reducing the total number of VLDL and LDL particles.
Fenofibrate
By activation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor α (PPARα), Fenofibrate increases lipolysis and elimination of triglyceride rich particles from plasma by activating lipoprotein lipase and reducing production of apoprotein C-III (an inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase activity).
5.2 Pharmacodynamic effects
Rosuvastatin
Rosuvastatin is a selective and competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase. Rosuvastatin increases the number of hepatic LDL receptors on the cell-surface, enhancing uptake and catabolism of LDL and it inhibits the hepatic synthesis of VLDL, thereby reducing the total number of VLDL and LDL particles.
Fenofibrate
By activation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor α (PPARα), Fenofibrate increases lipolysis and elimination of triglyceride rich particles from plasma by activating lipoprotein lipase and reducing production of apoprotein C-III (an inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase activity). The resulting fall in triglycerides produces an alteration in the size and composition of LDL from small, dense particles (which are thought to be atherogenic due to their susceptibility to oxidation), to large buoyant particles. These larger particles have a greater affinity for cholesterol receptors and are catabolized rapidly. Activation of PPARα (Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha) also induces an increase in the synthesis of apoproteins AI, AII and HDL-cholesterol.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Rosuvastatin
After oral administration peak plasma levels occur 5 hours after dosing. The half-life is 19 hours and does not increase with increasing dose. Rosuvastatin is approximately 90% bound to plasma proteins, mostly albumin. The parent compound, accounts for greater than 90% of the circulating active HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor activity. Rosuvastatin undergoes limited metabolism in humans (approximately 10%), mainly to the N-desmethyl form, and 90% is eliminated as unchanged drug in the faeces with the remainder being excreted in the urine.
Fenofibrate
Peak plasma levels of fenofibric acid occur within 6 to 8 hours after administration, the absorption is increased when administered with food. Serum protein binding was approximately 99%, it is rapidly hydrolyzed by esterases to the active metabolite fenofibric acid; no unchanged Fenofibrate is detected in plasma. Fenofibric acid is primarily conjugated with glucuronic acid and then excreted in urine and its half-life is 20 hours.
6. Nonclinical Properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Rosuvastatin
In a 104-week carcinogenicity study in rats at dose levels of 2, 20, 60, or 80 mg/kg/day by oral gavage, the incidence of uterine stromal polyps was significantly increased in females at 80 mg/kg/day at systemic exposure 20 times the human exposure at 40 mg/day based on AUC. Increased incidence of polyps was not seen at lower doses.
In a 107-week carcinogenicity study in mice given 10, 60, or 200 mg/kg/day by oral gavage, an increased incidence of hepatocellular adenoma/carcinoma was observed at 200 mg/kg/day at systemic exposures 20 times the human exposure at 40 mg/day based on AUC. An increased incidence of hepatocellular tumors was not seen at lower doses.
Rosuvastatin was not mutagenic or clastogenic with or without metabolic activation in the Ames test with Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli, the mouse lymphoma assay, and the chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese hamster lung cells. Rosuvastatin was negative in the in vivo mouse micronucleus test.
In rat fertility studies with oral gavage doses of 5, 15, 50 mg/kg/day, males were treated for 9 weeks prior to and throughout mating and females were treated 2 weeks prior to mating and throughout mating until gestation day 7. No adverse effect on fertility was observed at 50 mg/kg/day (systemic exposures up to 10 times the human exposure at 40 mg/day based on AUC). In testicles of dogs treated with rosuvastatin at 30 mg/kg/day for one month, spermatidic giant cells were seen. Spermatidic giant cells were observed in monkeys after 6-month treatment at 30 mg/kg/day in addition to vacuolation of seminiferous tubular epithelium. Exposures in the dog were 20 times and in the monkey 10 times the human exposure at 40 mg/day based on body surface area. Similar findings have been seen with other drugs in this class.
Fenofibrate
Carcinogenesis: Two dietary carcinogenicity studies have been conducted in rats with fenofibrate. In the first 24-month study, Wistar rats were dosed with fenofibrate at 10 mg/kg/day, 45 mg/kg/ day, and 200 mg/kg/day, approximately 0.3 times, 1 times, and 6 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD), based on body surface area comparisons (mg/m2). At a dose of 200 mg/kg/day (at 6 times the MRHD), the incidence of liver carcinoma was significantly increased in both sexes. A statistically significant increase in pancreatic carcinomas was observed in males at 1 and 6 times the MRHD; an increase in pancreatic adenomas and benign testicular interstitial cell tumors was observed in males at 6 times the MRHD. In a second 24-month study in a different strain of rats (Sprague-Dawley), doses of 10 mg/kg/day and 60 mg/kg/day (0.3 and 2 times the MRHD) produced significant increases in the incidence of pancreatic acinar adenomas in both sexes and increases in testicular interstitial cell tumors in males at 2 times the MRHD.
A 117-week carcinogenicity study was conducted in rats comparing three drugs: fenofibrate 10 mg/kg/day and 60 mg/kg/day (0.3 and 2 times the MRHD), clofibrate (400 mg/kg/day; 2 times the human dose), and gemfibrozil (250 mg/kg/day; 2 times the human dose, based on mg/m2 surface area). Fenofibrate increased pancreatic acinar adenomas in both sexes. Clofibrate increased hepatocellular carcinomas in males and hepatic neoplastic nodules in females. Gemfibrozil increased hepatic neoplastic nodules in males and females, while all three drugs increased testicular interstitial cell tumors in males.
In a 21-month study in CF-1 mice, fenofibrate 10 mg/kg/day, 45 mg/kg/day, and 200 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.2 times, 1 times, and 3 times the MRHD on the basis of mg/m2 surface area) significantly increased the liver carcinomas in both sexes at 3 times the MRHD. In a second 18-month study at 10 mg/kg/day, 60 mg/kg/day, and 200 mg/kg/day, fenofibrate significantly increased the liver carcinomas in male mice and liver adenomas in female mice at 3 times the MRHD.
Electron microscopy studies have demonstrated peroxisomal proliferation following fenofibrate administration to the rat. An adequate study to test for peroxisome proliferation in humans has not been done, but changes in peroxisome morphology and numbers have been observed in humans after treatment with other members of the fibrate class when liver biopsies were compared before and after treatment in the same individual.
Mutagenesis: Fenofibrate has been demonstrated to be devoid of mutagenic potential in the following tests: Ames, mouse lymphoma, chromosomal aberration and unscheduled DNA synthesis in primary rat hepatocytes.
Impairment of Fertility: In fertility studies rats were given oral dietary doses of fenofibrate, males received 61 days prior to mating and females 15 days prior to mating through weaning which resulted in no adverse effect on fertility at doses up to 300 mg/kg/day (approximately 10 times the MRHD, based on mg/m2 surface area comparisons).
7. Description
REVOSTAT®FB is a combination of Rosuvastatin and Fenofibrate.
Rosuvastatin is a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG CoA)-reductase inhibitor.
ChemicalName:bis[(E)-7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-[methyl(methylsulfonyl)amino]pyrimidin-5-yl](3R,5S)-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid]
Molecular Formula: (C22H27FN3O6S)2Ca Molecular Weight: 1,001.14.
Structure:
Fenofibrate is a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha agonist.
Chemical Name: 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl) phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoic acid, l-methylethyl ester
Molecular Formula: C20H21O4Cl
Molecular Weight: 360.83
Structure:
8. Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on pack.
8.3 Packaging information
10 Blister strips of 10 tablets each
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store protected from moisture at a temperature below 30°C.
Keep out of reach of children.
9. Patient Counselling Information
Myopathy and Rhabdomyolysis
Advise patients that REVOSTAT®FB may cause myopathy and rhabdomyolysis. Inform patients that the risk is also increased when taking certain types of medication and they should discuss all medication, both prescription and over-the-counter, with their healthcare provider. Instruct patients to promptly report any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever.
Hepatic Dysfunction
Inform patients that REVOSTAT®FB may cause liver enzyme elevations and possibly liver failure. Advise patients to promptly report fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine or jaundice.
Increases in HbA1c and Fasting Serum Glucose Levels
Inform patients that increases in HbA1c and fasting serum glucose levels may occur with REVOSTAT®FB. Encourage patients to optimize lifestyle measures, including regular exercise, maintaining a healthy body weight, and making healthy food choices.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform patients that serious hypersensitivity reactions, such as anaphylaxis and angioedema, have been reported with fibrates. Advise patients to report immediately any signs or symptoms suggesting allergic reaction, and to discontinue drug until they have consulted prescribing physicians.
Pregnancy
Advise pregnant patients and patients who can become pregnant of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy to discuss if REVOSTAT®FB should be discontinued.
Lactation
Advise patients that breastfeeding during treatment with REVOSTAT®FB is not recommended.
Concomitant Use of Antacids
When taking REVOSTAT®FB with an aluminum and magnesium hydroxide combination antacid, administer REVOSTAT®FB at least 2 hours before the antacid.
Missed Doses
If a dose is missed, advise patients not to take an extra dose. Just resume the treatment with the next dose.
12. Date of revision
14th January 2025.
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side, effects talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet?
1) What Revostat®FB is and what it is used for
2) What you need to know before you take Revostat®FB
3) How to take Revostat®FB
4) Possible side effects
5) How to store Revostat®FB
6) Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Revostat®FB is and what it is used for
Revostat®FB is a combination of Rosuvastatin which belongs to a group of medicines called statins and Fenofibrate which belongs to the class of medications called fibrates. You have been prescribed Revostat®FB because you have a high cholesterol level.
Why it is important to keep taking Revostat®FB
Revostat®FB is used to correct the levels of fatty substances in the blood called lipids, the most common of which is cholesterol in patients with normal liver and kidney function. There are different types of cholesterol found in the blood – ‘bad’ cholesterol (LDL-C) and ‘good’ cholesterol (HDL-C).
- Revostat®FB can reduce the ‘bad’ cholesterol and increase the ‘good’ cholesterol.
- It works by helping to block your body’s production of ‘bad’ cholesterol. It also improves your body’s ability to remove it from your blood.
For most people, high cholesterol does not affect the way they feel because it does not produce any symptoms. However, if it is left untreated, fatty deposits can build up in the walls of your blood vessels causing them to narrow. Sometimes, these narrowed blood vessels can get blocked which can cut off the blood supply to the heart or brain leading to a heart attack or a stroke. By lowering your cholesterol levels, you can reduce your risk of having a heart attack, a stroke or related health problems.
You need to keep taking Revostat®FB, even if it has got your cholesterol to the right level, because it prevents your cholesterol levels from creeping up again and causing build-up of fatty deposits. However, you should stop if your doctor tells you to do so, or you have become pregnant.
2. What you need to know before you take Revostat®FB
Do not take Revostat®FB:
- If you have ever had an allergic reaction to Revostat®FB, or to any of its ingredients.
- If you are pregnant or breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking Revostat®FB stop taking it immediately and tell your doctor. Women should avoid becoming pregnant while taking Revostat®FB by using suitable contraception.
- If you have liver disease.
- If you have severe kidney problems.
- If you have preexisting gall bladder disease
If any of the above applies to you (or you are in doubt), please go back and see your doctor.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Revostat®FB.
- If you have problems with your kidneys.
- If you have problems with your liver.
- If you may have an inflamed liver (hepatitis) - signs include yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes (jaundice) and an increase in liver enzymes (shown in blood tests), stomach pain and itching.
- If you have an under-active thyroid gland (hypothyroidism).
- If you have had repeated or unexplained muscle aches or pains, a personal or family history of muscle problems, or a previous history of muscle problems when taking other cholesterol-lowering medicines. Tell your doctor immediately if you have unexplained muscle aches or pains, especially if you feel unwell or have a fever. Also, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you have a muscle weakness that is constant.
- If you have or have had myasthenia (a disease with general muscle weakness including in some cases muscles used when breathing), or ocular myasthenia (a disease causing eye muscle weakness) as statins may sometimes aggravate the condition or lead to the occurrence of myasthenia.
- If you have ever developed a severe skin rash or skin peeling, blistering and/or mouth sores after taking Revostat®FB or other related medicines.
- If you regularly drink large amounts of alcohol.
- If your thyroid gland is not working properly.
- If you take other medicines called fibrates to lower your cholesterol. Please read this leaflet carefully, even if you have taken other medicines for high cholesterol before.
- If you take medicines used to treat the HIV infection e.g. ritonavir with lopinavir and/or atazanavir, please see “Other medicines and Revostat®FB”.
- If you are taking or have taken in the last 7 days a medicine called fusidic acid (a medicine for bacterial infection), orally or by injection. The combination of fusidic acid and Revostat®FB can lead to serious muscle problems (rhabdomyolysis), please see “Other medicines and Revostat®FB”.
- If you are over 70 (as your doctor needs to choose the right start dose of Revostat®FB to suit you)
- If you have severe respiratory failure.
- If you are of Asian origin – that is Japanese, Chinese, Filipino, Vietnamese, Korean and Indian. Your doctor needs to choose the right start dose of Revostat®FB to suit you.
- Stop taking Revostat®FB and see a doctor straight away if you get:
- unexplained cramps
- painful, tender or weak muscles while taking this medicine
This is because this medicine may cause muscle problems, which may be serious.
These problems are rare but include muscle inflammation and breakdown. This can cause kidney damage or even death.
Your doctor may do a blood test to check your muscles before and after starting treatment.
The risk of muscle breakdown is higher in some patients.
In particular, tell your doctor if:
- You are over 70 years old
- You have kidney problems
- You have thyroid problems
- You or a close family member has a muscle problem which runs in the family
Serious skin reactions including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) have been reported in association with Revostat®FB treatment. Stop using Revostat®FB and seek medical attention immediately if you notice any of the symptoms described in section 4.
In a small number of people, statins can affect the liver. This is identified by a simple test which looks for increased levels of liver enzymes in the blood. For this reason, your doctor will usually carry out this blood test (liver function test) before and during treatment with Revostat®FB.
While you are on this medicine your doctor will monitor you closely if you have diabetes or are at risk of developing diabetes. You are likely to be at risk of developing diabetes if you have high levels of sugars and fats in your blood, are overweight and have high blood pressure.
Children and adolescents
- If the patient is below 18 years of age: The Revostat®FB tablet is not suitable for use in children and adolescents below 18 years of age.
Other medicines and Revostat®FB
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines
Tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following:
- cyclosporin (used for example, after organ transplants),
- warfarin, clopidogrel or ticagrelor (or any other drug used for thinning the blood),
- fibrates (such as gemfibrozil, fenofibrate) or any other medicine used to lower cholesterol (such as ezetimibe),
- niacin
- indigestion remedies (used to neutralise acid in your stomach),
- erythromycin (an antibiotic), fusidic acid (an antibiotic an oral contraceptive (the pill),
- regorafenib (used to treat cancer),
- darolutamide (used to treat cancer),
- capmatinib (used to treat cancer),
- hormone replacement therapy,
- fostamatinib (used to treat low platelet counts),
- febuxostat (used to treat and prevent high blood levels of uric acid),
- teriflunomide (used to treat multiple sclerosis),
- any of the following drugs used to treat viral infections, including HIV or hepatitis C infection, alone or in combination (please see Warnings and precautions): ritonavir, lopinavir, atazanavir, sofosbuvir, voxilaprevir, ombitasvir, paritaprevir, dasabuvir, velpatasvir, grazoprevir, elbasvir, glecaprevir, pibrentasvir.
The effects of these medicines could be changed by Revostat®FB or they could change the effect of Revostat®FB.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Do not take Revostat®FB if you are pregnant or breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking Revostat®FB stop taking it immediately and tell your doctor. Women should avoid becoming pregnant while taking Revostat®FB by using suitable contraception.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
Most people can drive a car and operate machinery while using Revostat®FB – it will not affect their ability. However, some people feel dizzy during treatment with Revostat®FB. If you feel dizzy, consult your doctor before attempting to drive or use machines.
3. How to take Revostat®FB
Always take this medicine as your doctor has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
The recommended dose is one tablet a day in adults.
Taking your tablets
Swallow each tablet whole with a drink of water.
Take Revostat®FB once daily.
Try to take your tablet at the same time every day to help you to remember it.
Regular cholesterol checks
It is important to go back to your doctor for regular cholesterol checks, to make sure your cholesterol has reached and is staying at the correct level.
If you take more Revostat®FB than you should
Contact your doctor or nearest hospital for advice.
If you go into hospital or receive treatment for another condition, tell the medical staff that you’re taking Revostat®FB.
If you forget to take Revostat®FB
Don’t worry, just take your next scheduled dose at the correct time. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop taking Revostat®FB
Talk to your doctor if you want to stop taking Revostat®FB. Your cholesterol levels might increase again if you stop taking Revostat®FB.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
It is important that you are aware of what these side effects may be. They are usually mild and disappear after a short time.
Stop taking Revostat®FB and seek medical help immediately if you have any of the following allergic reactions:
- Difficulty in breathing, with or without swelling of the face, lips, tongue and/or throat.
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue and/or throat, which may cause difficulty in swallowing.
- Severe itching of the skin (with raised lumps).
- Reddish non-elevated, target-like or circular patches on the trunk, often with central blisters, skin peeling, ulcers of mouth, throat, nose, genitals and eyes. These serious skin rashes can be preceded by fever and flu-like symptoms (Stevens-Johnson syndrome).
- Widespread rash, high body temperature and enlarged lymph nodes (DRESS syndrome or drug hypersensitivity syndrome).
Also, stop taking Revostat®FB and talk to your doctor immediately:
- If you have any unusual aches or pains in your muscles which go on for longer than you might expect. Muscle symptoms are more common in children and adolescents than in adults. As with other statins, a very small number of people have experienced unpleasant muscle effects and rarely these have gone on to become a potentially life threatening muscle damage known as rhabdomyolysis.
- If you experience muscle rupture.
- If you have lupus-like disease syndrome (including rash, joint disorders and effects on blood cells).
- If you have severe skin rash which reddens, peels and swells and looks like a severe burn
- If you have long-term lung problems
- If you have complications of gallbladder stones
Common possible side effects (these may affect between 1 in 10 and 1 in 100 patients):
- Headache, stomach pain, diarrhoea, wind (flatulence), feeling sick (nausea), being sick (vomiting), constipation, feeling sick, muscle pain, feeling weak, dizziness.
- raised levels of liver enzymes in the blood - shown in tests
- increase in homocysteine (too much of this amino acid in the blood has been associated to a higher risk of coronary heart disease, stroke and peripheral vascular disease, although a causal link has not been established
- An increase in the amount of protein in the urine - this usually returns to normal on its own without having to stop taking your Revostat®FB tablets
- Diabetes. This is more likely if you have high levels of sugars and fats in your blood, are overweight and have high blood pressure. Your doctor will monitor you while you are taking this medicine.
Uncommon possible side effects (these may affect between 1 in 100 and 1 in 1,000 patients):
- Rash, itching or other skin reactions.
- cramps or painful, tender or weak muscles - these may be signs of muscle inflammation or breakdown, which can cause kidney damage or even death
- stomach pain - this may be a sign that your pancreas is inflamed (pancreatitis)
- chest pain and feeling breathless - these may be signs of a blood clot in the lung (pulmonary embolism)
- pain, redness or swelling in the legs - these may be signs of a blood clot in the leg (deep vein thrombosis)
Rare possible side effects (these may affect between 1 in 1,000 and 1 in 10,000 patients):
- Severe allergic reaction – signs include swelling of the face, lips, tongue and/or throat, difficulty in swallowing and breathing, a severe itching of the skin (with raised lumps). If you think you are having an allergic reaction, then stop taking Revostat®FB and seek medical help immediately.
- Muscle damage in adults – as a precaution, stop taking Revostat®FB and talk to your doctor immediately if you have any unusual aches or pains in your muscles which go on for longer than expected.
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), or an increase in liver enzymes - these may be signs of an inflamed liver (hepatitis)
- Increase in liver enzymes in the blood.
- Bleeding or bruising more easily than normal due to low level of blood platelets.
- Lupus-like disease syndrome (including rash, joint disorders and effects on blood cells).
Very rare possible side effects (these may affect less than 1 in 10,000 patients):
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), hepatitis (an inflamed liver), traces of blood in your urine, damage to the nerves of your legs and arms (such as numbness), joint pain, memory loss and breast enlargement in men (gynaecomastia).
Side effects of unknown frequency may include:
- Diarrhoea (loose stools), cough, shortness of breath, oedema (swelling), sleep disturbances, including insomnia and nightmares, sexual difficulties, depression, breathing problems, including persistent cough and/or shortness of breath or fever, tendon injury and muscle weakness that is constant.
- Myasthenia gravis (a disease causing general muscle weakness including in some cases muscles used when breathing), Ocular myasthenia (a disease causing eye muscle weakness). Talk to your doctor if you experience weakness in your arms or legs that worsens after periods of activity, double vision or drooping of your eyelids, difficulty swallowing, or shortness of breath.
Reporting of side effects:
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: Website: https://www.zuventus.co.in/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Revostat®FB
Store protected from moisture at a temperature below 30°C.
Keep out of reach of children.
Contents of the pack and other information
What Revostat®FB looks like and contents of the pack
Revostat®FB
Composition:
Each film-coated tablet contains:
Rosuvastatin Calcium IP
equivalent to Rosuvastatin …………..……..10mg
Fenofibrate (Micronised) IP ………………. 160 mg
Excipients………………………………….. qs
Colours: Ferric Oxide Yellow USP-NF & Titanium Dioxide IP
Presentation/pack size
10 Blister strips of 10 tablets each
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Zuventus Healthcare Limited
Zuventus House, Plot Y2, CTS No.: 358/A2,
Near Nahur Railway Station,
Nahur (W), Mumbai, 400078 Maharashtra, India
This leaflet was last revised in 01/2025