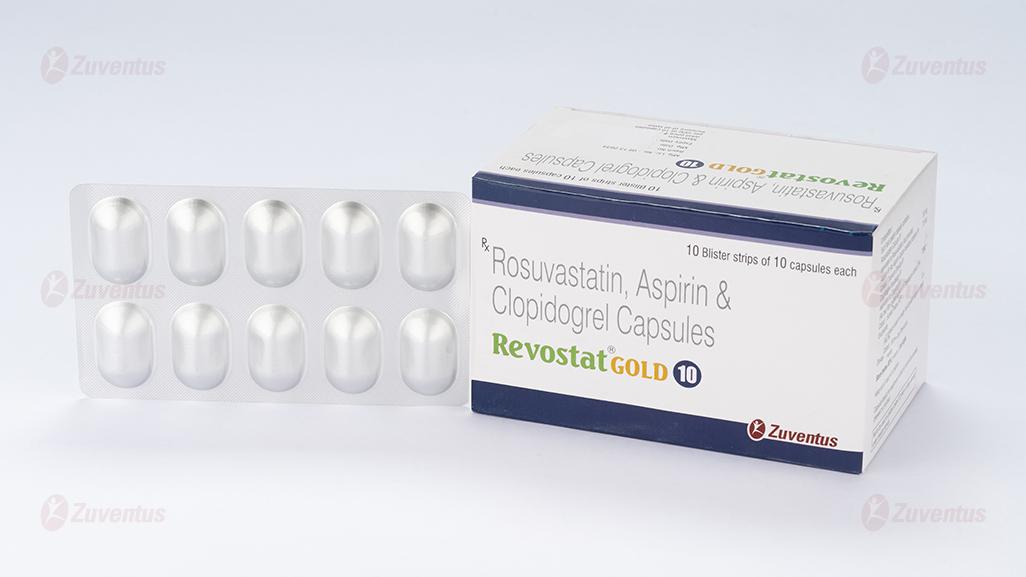
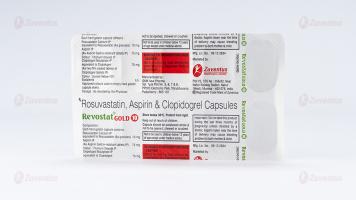
Revostat Gold 10 Capsules
Therapy Area
Cardiology
1. Generic Name
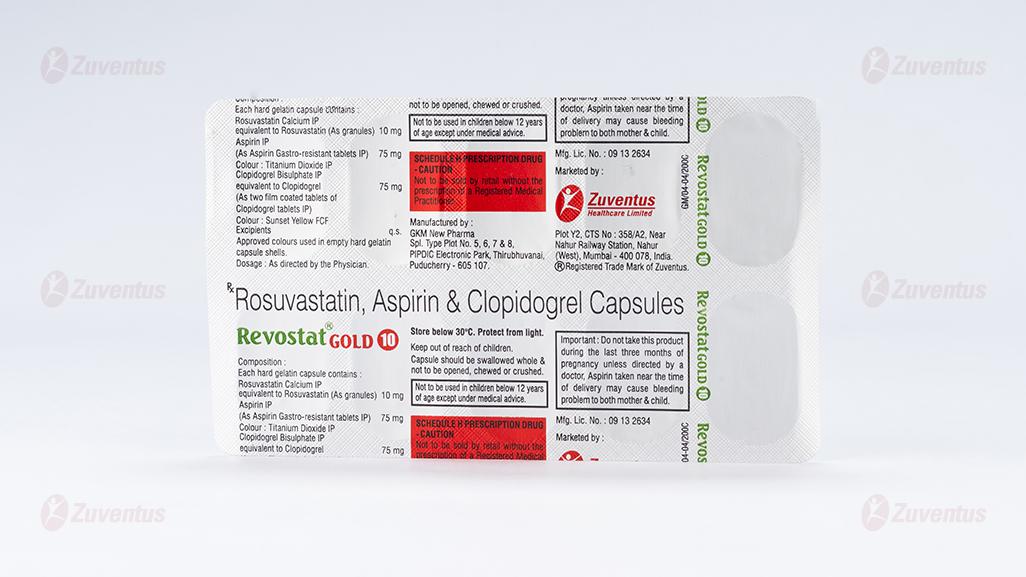
Rosuvastatin, Aspirin & Clopidogrel Capsules (10 + 75 + 75 mg)
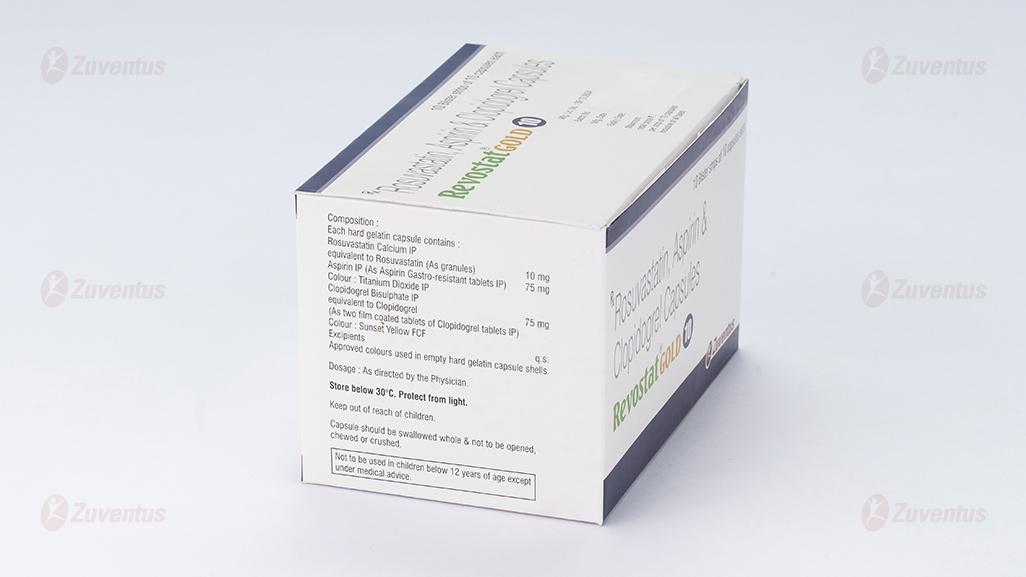
2. Qualitative and quantitative composition
REVOSTAT GOLD® 10
Each hard gelatin capsule contains:
Rosuvastatin Calcium IP equivalent to
Rosuvastatin (As granules) - 10 mg
Aspirin IP - 75 mg
Colour: Titanium Dioxide IP
Clopidogrel Bisulphate IP equivalent to
Clopidogrel IP - 75 mg
Colour: Sunset yellow FCF
Excipients - q.s
Approved colours used in empty hard gelatin capsule shells.
3.Dosage form and strength
Hard Gelatin Capsules.
10 / 75 / 75 mg.
4. Clinical particulars
4.1. Therapeutic indication
REVOSTAT GOLD® is indicated for the treatment of dyslipidaemia associated with atherosclerotic arterial disease with risk of myocardial infarction, stroke or peripheral vascular disease.
4.2. Posology and method of administration
Before treatment initiation the patient should be placed on a standard cholesterol-lowering diet that should continue during treatment. The dose should be individualised according to the goal of therapy and patient response, using current consensus guidelines.
REVOSTAT GOLD® may be given at any time of day, with or without food.
ROSUVASTATIN
Treatment of hypercholesterolaemia
The recommended start dose is 5 or 10 mg orally once daily in both statin-naive or patients switched from another HMG CoA reductase inhibitor. The choice of start dose should take into account the individual patient's cholesterol level and future cardiovascular risk as well as the potential risk for adverse reactions. A dose adjustment to the next dose level can be made after 4 weeks, if necessary. In light of the increased reporting rate of adverse reactions with the 40 mg dose compared to lower doses, a final titration to the maximum dose of 40 mg should only be considered in patients with severe hypercholesterolaemia at high cardiovascular risk (in particular those with familial hypercholesterolaemia), who do not achieve their treatment goal on 20 mg, and in whom routine follow-up will be performed. Specialist supervision is recommended when the 40 mg dose is initiated.
Use in the elderly
A start dose of 5 mg is recommended in patients >70 years. No other dose adjustment is necessary in relation to age.
Dosage in patients with renal insufficiency
No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment. The recommended start dose is 5 mg in patients with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance <60 ml/min). The 40 mg dose is contraindicated in patients with moderate renal impairment. The use of rosuvastatin in patients with severe renal impairment is contraindicated for all doses.
Dosage in patients with hepatic impairment
There was no increase in systemic exposure to rosuvastatin in subjects with Child-Pugh scores of 7 or below. However, increased systemic exposure has been observed in subjects with Child-Pugh scores of 8 and 9. In these patients an assessment of renal function should be considered. There is no experience in subjects with Child-Pugh scores above 9. Rosuvastatin is contraindicated in patients with active liver disease.
Race
Increased systemic exposure has been seen in Asian subjects. The recommended start dose is 5 mg for patients of Asian ancestry. The 40 mg dose is contraindicated in these patients.
Genetic polymorphisms
Specific types of genetic polymorphisms are known that can lead to increased rosuvastatin exposure. For patients who are known to have such specific types of polymorphisms, a lower daily dose of rosuvastatin is recommended.
Dosage in patients with pre-disposing factors to myopathy
The recommended start dose is 5 mg in patients with predisposing factors to myopathy.
The 40 mg dose is contraindicated in some of these patients.
Concomitant therapy
Rosuvastatin is a substrate of various transporter proteins (e.g. OATP1B1 and BCRP). The risk of myopathy (including rhabdomyolysis) is increased when rosuvastatin is administered concomitantly with certain medicinal products that may increase the plasma concentration of rosuvastatin due to interactions with these transporter proteins (e.g. ciclosporin and certain protease inhibitors including combinations of ritonavir with atazanavir, lopinavir and/or tipranavir;). Whenever possible, alternative medications should be considered, and, if necessary, consider temporarily discontinuing rosuvastatin therapy. In situations where co-administration of these medicinal products with rosuvastatin is unavoidable, the benefit and the risk of concurrent treatment and rosuvastatin dosing adjustments should be carefully considered.
ASPIRIN
Elderly
In general, acetylsalicylic acids should be used with caution in elderly patients who are more prone to adverse events. The usual adult dose is recommended in the absence of severe renal or hepatic insufficiency. Treatment should be reviewed at regular intervals.
Paediatric population
Acetylsalicylic acid should not be administered to children and adolescents younger than 16 years, except on medical advice where the benefit outweighs the risk
CLOPIDOGREL
Adults and elderly
Clopidogrel should be given as a single daily dose of 75 mg.
In patients suffering from acute coronary syndrome:
- −Non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction): clopidogrel treatment should be initiated with a single 300-mg loading dose and then continued at 75 mg once a day (with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) 75 mg-325 mg daily). Since higher doses of ASA were associated with higher bleeding risk it is recommended that the dose of ASA should not be higher than 100 mg. The optimal duration of treatment has not been formally established. Clinical trial data support use up to 12 months, and the maximum benefit was seen at 3 months.
- −ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction: clopidogrel should be given as a single daily dose of 75 mg initiated with a 300-mg loading dose in combination with ASA and with or without thrombolytics. For patients over 75 years of age clopidogrel should be initiated without a loading dose. Combined therapy should be started as early as possible after symptoms start and continued for at least four weeks. The benefit of the combination of clopidogrel with ASA beyond four weeks has not been studied in this setting.
In patients with atrial fibrillation, clopidogrel should be given as a single daily dose of 75 mg. ASA (75-100 mg daily) should be initiated and continued in combination with clopidogrel.
If a dose is missed:
- −Within less than 12 hours after regular scheduled time: patients should take the dose immediately and then take the next dose at the regular scheduled time.
- −For more than 12 hours: patients should take the next dose at the regular scheduled time and should not double the dose.
- Paediatric population
- Clopidogrel should not be used in children because of efficacy concerns.
- Renal impairment
- Therapeutic experience is limited in patients with renal impairment.
- Hepatic impairment
- Therapeutic experience is limited in patients with moderate hepatic disease who may have bleeding diatheses.
Method of administration
For oral use.
4.3. Contraindications
ROSUVASTATIN
REVOSTAT GOLD® must not be used in the following conditions:
- in patients with hypersensitivity to rosuvastatin or to any of the excipients.
- in patients with active liver disease including unexplained, persistent elevations of serum transaminases and any serum transaminase elevation exceeding 3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN).
- in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <30 ml/min).
- in patients with myopathy.
- in patients receiving concomitant combination of sofosbuvir / velpatasvir / voxilaprevir
- in patients receiving concomitant ciclosporin.
- during pregnancy and lactation and in women of childbearing potential not using appropriate contraceptive measures.
- The 40 mg dose is contraindicated in patients with pre-disposing factors for myopathy/rhabdomyolysis. Such factors include:
- moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 60 ml/min)
- hypothyroidism
- personal or family history of hereditary muscular disorders
- previous history of muscular toxicity with another HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor or fibrate
- alcohol abuse
- situations where an increase in plasma levels may occur
- Asian patients
- concomitant use of fibrates.
ASPIRIN
- Hypersensitivity to salicylic acid compounds or prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors (e.g. certain asthma patients who may suffer an attack or faint) or to any of the excipients;
- Active, or history of recurrent peptic ulcer and/or gastric/intestinal haemorrhage, or other kinds of bleeding such as cerebrovascular haemorrhages;
- Haemorrhagic diathesis; coagulation disorders such as haemophilia and thrombocytopenia;
- Severe hepatic impairment;
- Severe renal impairment;
- Gout;
- Doses >100 mg/day during the third trimester of pregnancy;
- Methotrexate used at doses >15mg/week
CLOPIDOGREL
- Severe hepatic impairment.
- Active pathological bleeding such as peptic ulcer or intracranial haemorrhage.
4.4. Special warnings and precautions for use
ROSUVASTATIN
Renal Effects
Proteinuria, detected by dipstick testing and mostly tubular in origin, has been observed in patients treated with higher doses of rosuvastatin, in particular 40 mg, where it was transient or intermittent in most cases. Proteinuria has not been shown to be predictive of acute or progressive renal disease. The reporting rate for serious renal events in post-marketing use is higher at the 40 mg dose. An assessment of renal function should be considered during routine follow-up of patients treated with a dose of 40 mg.
Skeletal Muscle Effects
Effects on skeletal muscle e.g. myalgia, myopathy and, rarely, rhabdomyolysis have been reported in rosuvastatin-treated patients with all doses and in particular with doses > 20 mg. Very rare cases of rhabdomyolysis have been reported with the use of ezetimibe in combination with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. A pharmacodynamic interaction cannot be excluded and caution should be exercised with their combined use. As with other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, the reporting rate for rhabdomyolysis associated with rosuvastatin in post-marketing use is higher at the 40 mg dose.
Creatine Kinase Measurement
Creatine Kinase (CK) should not be measured following strenuous exercise or in the presence of a plausible alternative cause of CK increase which may confound interpretation of the result. If CK levels are significantly elevated at baseline (>5xULN) a confirmatory test should be carried out within 5 – 7 days. If the repeat test confirms a baseline CK >5xULN, treatment should not be started.
Before Treatment
Rosuvastatin, as with other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, should be prescribed with caution in patients with pre-disposing factors for myopathy/rhabdomyolysis. Such factors include:
- renal impairment
- hypothyroidism
- personal or family history of hereditary muscular disorders
- previous history of muscular toxicity with another HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor or fibrate
- alcohol abuse
- age >70 years
- situations where an increase in plasma levels may occur
- concomitant use of fibrates.
In such patients the risk of treatment should be considered in relation to possible benefit and clinical monitoring is recommended. If CK levels are significantly elevated at baseline (>5xULN) treatment should not be started.
Whilst on Treatment
Patients should be asked to report inexplicable muscle pain, weakness or cramps immediately, particularly if associated with malaise or fever. CK levels should be measured in these patients. Therapy should be discontinued if CK levels are markedly elevated (>5xULN) or if muscular symptoms are severe and cause daily discomfort (even if CK levels are ≤5xULN). If symptoms resolve and CK levels return to normal, then consideration should be given to re-introducing rosuvastatin or an alternative HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor at the lowest dose with close monitoring. Routine monitoring of CK levels in asymptomatic patients is not warranted. There have been very rare reports of an immune-mediated necrotising myopathy (IMNM) during or after treatment with statins, including rosuvastatin. IMNM is clinically characterised by proximal muscle weakness and elevated serum creatine kinase, which persist despite discontinuation of statin treatment.
In clinical trials, there was no evidence of increased skeletal muscle effects in the small number of patients dosed with rosuvastatin and concomitant therapy. However, an increase in the incidence of myositis and myopathy has been seen in patients receiving other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors together with fibric acid derivatives including gemfibrozil, ciclosporin, nicotinic acid, azole antifungals, protease inhibitors and macrolide antibiotics. Gemfibrozil increases the risk of myopathy when given concomitantly with some HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Therefore, the combination of rosuvastatin and gemfibrozil is not recommended. The benefit of further alterations in lipid levels by the combined use of rosuvastatin with fibrates or niacin should be carefully weighed against the potential risks of such combinations. The 40 mg dose is contraindicated with concomitant use of a fibrate.
Rosuvastatinn must not be co-administered with systemic formulations of fusidic acid or within 7 days of stopping fusidic acid treatment. In patients where the use of systemic fusidic acid is considered essential, statin treatment should be discontinued throughout the duration of fusidic acid treatment. There have been reports of rhabdomyolysis (including some fatalities) in patients receiving fusidic acid and statins in combination. Patients should be advised to seek medical advice immediately if they experience any symptoms of muscle weakness, pain or tenderness. Statin therapy may be re-introduced seven days after the last dose of fusidic acid. In exceptional circumstances, where prolonged systemic fusidic acid is needed, e.g. for the treatment of severe infections, the need for co-administration of rosuvastatin and fusidic acid should only be considered on a case by case basis and under close medical supervision.
Rosuvastatin should not be used in any patient with an acute, serious condition suggestive of myopathy or predisposing to the development of renal failure secondary to rhabdomyolysis (e.g. sepsis, hypotension, major surgery, trauma, severe metabolic, endocrine and electrolyte disorders; or uncontrolled seizures).
Liver Effects
As with other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, rosuvastatin should be used with caution in patients who consume excessive quantities of alcohol and/or have a history of liver disease.
It is recommended that liver function tests be carried out prior to, and 3 months following, the initiation of treatment. Rosuvastatin should be discontinued or the dose reduced if the level of serum transaminases is greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal. The reporting rate for serious hepatic events (consisting mainly of increased hepatic transaminases) in post-marketing use is higher at the 40 mg dose. In patients with secondary hypercholesterolaemia caused by hypothyroidism or nephrotic syndrome, the underlying disease should be treated prior to initiating therapy with rosuvastatin.
Race
Pharmacokinetic studies show an increase in exposure in Asian subjects compared with Caucasians.
Protease Inhibitors
Increased systemic exposure to rosuvastatin has been observed in subjects receiving rosuvastatin concomitantly with various protease inhibitors in combination with ritonavir. Consideration should be given both to the benefit of lipid lowering by use of rosuvastatin in HIV patients receiving protease inhibitors and the potential for increased rosuvastatin plasma concentrations when initiating and up titrating rosuvastatin doses in patients treated with protease inhibitors. The concomitant use with certain protease inhibitors is not recommended unless the dose of rosuvastatin is adjusted.
Lactose Intolerance
Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine.
Interstitial Lung Disease
Exceptional cases of interstitial lung disease have been reported with some statins, especially with long-term therapy. Presenting features can include dyspnoea, non-productive cough and deterioration in general health (fatigue, weight loss and fever). If it is suspected a patient has developed interstitial lung disease, statin therapy should be discontinued.
Diabetes Mellitus
Some evidence suggests that statins as a class raise blood glucose and in some patients, at high risk of future diabetes, may produce a level of hyperglycaemia where formal diabetes care is appropriate. This risk, however, is outweighed by the reduction in vascular risk with statins and therefore should not be a reason for stopping statin treatment. Patients at risk (fasting glucose 5.6 to 6.9 mmol/l, BMI >30 kg/m2, raised triglycerides, hypertension) should be monitored both clinically and biochemically according to national guidelines.
In the JUPITER study, the reported overall frequency of diabetes mellitus was 2.8% in rosuvastatin and 2.3% in placebo, mostly in patients with fasting glucose 5.6 to 6.9 mmol/l.
ASPIRIN
Aspirin Tablets is not suitable for use as an anti-inflammatory / analgesic / antipyretic.
Recommended for use in adults and adolescents from 16 years of age. This medicinal product is not recommended for use in adolescents/children under 16 years unless the expected benefits outweigh the risks. Acetylsalicylic acid may be a contributory factor in the causation of Reye's Syndrome in some children.
There is an increased risk of haemorrhage particularly during or after operative procedures (even in cases of minor procedures, e.g. tooth extraction). Use with caution before surgery, including tooth extraction. Temporary discontinuation of treatment may be necessary.
Aspirin Tablets is not recommended during menorrhagia where it may increase menstrual bleeding.
Aspirin Tablets is to be used with caution in cases of hypertension and when patients have a past history of gastric or duodenal ulcer or haemorrhagic episodes or are undergoing therapy with anticoagulants.
Patients should report any unusual bleeding symptoms to their physician. If gastrointestinal bleeding or ulceration occurs the treatment should be withdrawn.
Acetylsalicylic acid should be used with caution in patients with moderately impaired renal or hepatic function (contraindicated if severe), or in patients who are dehydrated since the use of NSAIDs may result in deterioration of renal function. Liver function tests should be performed regularly in patients presenting slight or moderate hepatic insufficiency.
Acetylsalicylic acid may promote bronchospasm and asthma attacks or other hypersensitivity reactions. Risk factors are existing asthma, hay fever, nasal polyps or chronic respiratory diseases. The same applies for patients who also show allergic reaction to other substances (e.g. with skin reactions, itching or urticaria).
Serious skin reactions, including Steven-Johnsons syndrome, have rarely been reported in association with the use of acetylsalicylic acid. Aspirin Tablets should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash, mucosal lesions, or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Elderly patients are particularly susceptible to the adverse effects of NSAIDs, including acetylsalicylic acid especially gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation which may be fatal. Where prolonged therapy is required, patients should be reviewed regularly.
Concomitant treatment with Aspirin Tablets and other drugs that alter haemostasis (i.e. anticoagulants such as warfarin, thrombolytic and antiplatelet agents, anti-inflammatory drugs and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) is not recommended, unless strictly indicated, because they may enhance the risk of haemorrhage. If the combination cannot be avoided, close observation for signs of bleeding is recommended.
Caution should be advised in patients receiving concomitant medications which could increase the risk of ulceration, such as oral corticosteroids, selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors and deferasirox.
Acetylsalicylic acid should be avoided in late pregnancy and generally during breast feeding.
Acetylsalicylic acid in low doses reduces uric acid excretion. Due to this fact, patients who tend to have reduced uric acid excretion may experience gout attacks.
The risk of hypoglycaemic effect with sulfonylureas and insulins may be potentiated with Aspirin Tablets taken at over dosage.
CLOPIDOGREL
Bleeding and haematological disorders
Due to the risk of bleeding and haematological adverse reactions, blood cell count determination and/or other appropriate testing should be promptly considered whenever clinical symptoms suggestive of bleeding arise during the course of treatment. As with other antiplatelet agents, clopidogrel should be used with caution in patients who may be at risk of increased bleeding from trauma, surgery or other pathological conditions and in patients receiving treatment with ASA, heparin, glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) including Cox-2 inhibitors, or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), or CYP2C19 strong inducers or other medicinal products with bleeding risk such as pentoxifyllin). Patients should be followed carefully for any signs of bleeding including occult bleeding, especially during the first weeks of treatment and/or after invasive cardiac procedures or surgery. The concomitant administration of clopidogrel with oral anticoagulants is not recommended since it may increase the intensity of bleedings.
If a patient is to undergo elective surgery and antiplatelet effect is temporarily not desirable, clopidogrel should be discontinued 7 days prior to surgery. Patients should inform physicians and dentists that they are taking clopidogrel before any surgery is scheduled and before any new medicinal product is taken. Clopidogrel prolongs bleeding time and should be used with caution in patients who have lesions with a propensity to bleed (particularly gastrointestinal and intraocular).
Patients should be told that it might take longer than usual to stop bleeding when they take clopidogrel (alone or in combination with ASA), and that they should report any unusual bleeding (site or duration) to their physician.
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) has been reported very rarely following the use of clopidogrel, sometimes after a short exposure. It is characterised by thrombocytopenia and microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia associated with either neurological findings, renal dysfunction or fever. TTP is a potentially fatal condition requiring prompt treatment including plasmapheresis.
Acquired haemophilia
Acquired haemophilia has been reported following use of clopidogrel. In cases of confirmed isolated activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT) prolongation with or without bleeding, acquired haemophilia should be considered. Patients with a confirmed diagnosis of acquired haemophilia should be managed and treated by specialists, and clopidogrel should be discontinued.
Recent ischaemic stroke
In view of the lack of data, clopidogrel cannot be recommended during the first 7 days after acute ischaemic stroke.
Cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19)
Pharmacogenetics: In patients who are poor CYP2C19 metabolisers, clopidogrel at recommended doses forms less of the active metabolite of clopidogrel and has a smaller effect on platelet function. Tests are available to identify a patient's CYP2C19 genotype.
Since clopidogrel is metabolised to its active metabolite partly by CYP2C19, use of medicinal products that inhibit the activity of this enzyme would be expected to result in reduced drug levels of the active metabolite of clopidogrel. The clinical relevance of this interaction is uncertain. As a precaution, concomitant use of strong or moderate CYP2C19 inhibitors should be discouraged.
Use of medicinal products that induce the activity of CYP2C19 would be expected to result in increased drug levels of the active metabolite of clopidogrel and might potentiate the bleeding risk. As a precaution concomitant use of strong CYP2C19 inducers should be discouraged.
CYP2C8 substrates
Caution is required in patients treated concomitantly with clopidogrel and CYP2C8 substrate medicinal products.
Cross-reactions among thienopyridines
Patients should be evaluated for history of hypersensitivity to thienopyridines (such as clopidogrel, ticlopidine, prasugrel), since cross-reactivity among thienopyridines has been reported. Thienopyridines may cause mild to severe allergic reactions such as rash, angioedema, or haematological cross-reactions such as thrombocytopaenia and neutropaenia. Patients who had developed a previous allergic reaction and/or haematological reaction to one thienopyridine may have an increased risk of developing the same or another reaction to another thienopyridine. Monitoring for signs of hypersensitivity in patients with a known allergy to thienopyridines is advised.
Renal impairment
Therapeutic experience with clopidogrel is limited in patients with renal impairment. Therefore, clopidogrel should be used with caution in these patients.
Hepatic impairment
Experience is limited in patients with moderate hepatic disease who may have bleeding diatheses. Clopidogrel should, therefore, be used with caution in this population.
4.5. Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
ROSUVASTATIN
Effect of co-administered medicinal products on rosuvastatin
Transporter protein inhibitors: Rosuvastatin is a substrate for certain transporter proteins including the hepatic uptake transporter OATP1B1 and efflux transporter BCRP. Concomitant administration of rosuvastatin with medicinal products that are inhibitors of these transporter proteins may result in increased rosuvastatin plasma concentrations and an increased risk of myopathy.
Ciclosporin: During concomitant treatment with rosuvastatin and ciclosporin, rosuvastatin AUC values were on average 7 times higher than those observed in healthy volunteers (see Table 1). Rosuvastatin is contraindicated in patients receiving concomitant ciclosporin. Concomitant administration did not affect plasma concentrations of ciclosporin.
Protease inhibitors: Although the exact mechanism of interaction is unknown, concomitant protease inhibitor use may strongly increase rosuvastatin exposure (see Table 1). For instance, in a pharmacokinetic study, co-administration of 10 mg rosuvastatin and a combination product of two protease inhibitors (300 mg atazanavir/100 mg ritonavir) in healthy volunteers was associated with an approximately three-fold and seven-fold increase in rosuvastatin AUC and Cmax respectively. The concomitant use of rosuvastatin and some protease inhibitor combinations may be considered after careful consideration of rosuvastatin dose adjustments based on the expected increase in rosuvastatin exposure.
Gemfibrozil and other lipid-lowering products: Concomitant use of rosuvastatin and gemfibrozil resulted in a 2-fold increase in rosuvastatin Cmax and AUC. Based on data from specific interaction studies no pharmacokinetic relevant interaction with fenofibrate is expected, however a pharmacodynamic interaction may occur. Gemfibrozil, fenofibrate, other fibrates and lipid lowering doses (> or equal to 1 g/day) of niacin (nicotinic acid) increase the risk of myopathy when given concomitantly with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, probably because they can produce myopathy when given alone. The 40 mg dose is contraindicated with concomitant use of a fibrate. These patients should also start with the 5 mg dose.
Ezetimibe: Concomitant use of 10 mg rosuvastatin and 10 mg ezetimibe resulted in a 1.2-fold increase in AUC of rosuvastatin in hypercholesterolaemic subjects (Table 1). A pharmacodynamic interaction, in terms of adverse effects, between rosuvastatin and ezetimibe cannot be ruled out.
Antacid: The simultaneous dosing of rosuvastatin with an antacid suspension containing aluminium and magnesium hydroxide resulted in a decrease in rosuvastatin plasma concentration of approximately 50%. This effect was mitigated when the antacid was dosed 2 hours after rosuvastatin. The clinical relevance of this interaction has not been studied.
Erythromycin: Concomitant use of rosuvastatin and erythromycin resulted in a 20% decrease in AUC and a 30% decrease in Cmax of rosuvastatin. This interaction may be caused by the increase in gut motility caused by erythromycin.
Cytochrome P450 enzymes: Results from in vitro and in vivo studies show that rosuvastatin is neither an inhibitor nor an inducer of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes. In addition, rosuvastatin is a poor substrate for these isoenzymes. Therefore, drug interactions resulting from cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism are not expected. No clinically relevant interactions have been observed between rosuvastatin and either fluconazole (an inhibitor of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4) or ketoconazole (an inhibitor of CYP2A6 and CYP3A4).
Interactions requiring rosuvastatin dose adjustments (see also Table 1): When it is necessary to co-administer rosuvastatin with other medicinal products known to increase exposure to rosuvastatin, doses of rosuvastatin should be adjusted. Start with a 5 mg once daily dose of rosuvastatin if the expected increase in exposure (AUC) is approximately 2-fold or higher. The maximum daily dose of rosuvastatin should be adjusted so that the expected rosuvastatin exposure would not likely exceed that of a 40 mg daily dose of rosuvastatin taken without interacting medicinal products, for example a 20 mg dose of rosuvastatin with gemfibrozil (1.9-fold increase), and a 10 mg dose of rosuvastatin with combination ritonavir/atazanavir (3.1-fold increase).
If medicinal product is observed to increase rosuvastatin AUC less than 2-fold, the starting dose need not be decreased but caution should be taken if increasing the rosuvastatin dose above 20mg.
|
Table 1 Effect of co-administered medicinal products on rosuvastatin exposure (AUC; in order of decreasing magnitude) from published clinical trials |
||
|
2-fold or greater than 2-fold increase in AUC of rosuvastatin |
||
|
Interacting drug dose regimen |
Rosuvastatin dose regimen |
Change in rosuvastatin AUC* |
|
Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir (400 mg-100 mg-100 mg) + Voxilaprevir (100 mg) once daily for 15 days |
10mg single dose |
7.4 -fold ↑ |
|
Ciclosporin 75 mg BID to 200 mg BID, 6 months |
10 mg OD, 10 days |
7.1-fold ↑ |
|
Darolutamide 600 mg BID, 5 days |
5mg, single dose |
5.2-fold ↑ |
|
Regorafenib 160 mg, OD, 14 days |
5 mg, single dose |
3.8-fold ↑ |
|
Atazanavir 300 mg/ritonavir 100 mg OD, 8 days |
10 mg, single dose |
3.1-fold ↑ |
|
Velpatasvir 100 mg OD |
10 mg, single dose |
2.7-fold ↑ |
|
Ombitasvir 25 mg/paritaprevir 150 mg/ Ritonavir 100 mg OD/ dasabuvir 400 mg BID, 14 days |
5 mg, single dose |
2.6-fold ↑ |
|
Grazoprevir 200 mg/elbasvir 50 mg OD, 11 days |
10 mg, single dose |
2.3-fold ↑ |
|
Glecaprevir 400 mg/pibrentasvir 120 mg OD, 7 days |
5 mg OD, 7 days |
2.2-fold ↑ |
|
Lopinavir 400 mg/ritonavir 100 mg BID, 17 days |
20 mg OD, 7 days |
2.1-fold ↑ |
|
Clopidogrel 300 mg loading, followed by 75 mg at 24 hours |
20 mg, single dose |
2-fold ↑ |
|
Gemfibrozil 600 mg BID, 7 days |
80 mg, single dose |
1.9-fold ↑ |
|
Less than 2-fold increase in AUC of rosuvastatin |
||
|
Interacting drug dose regimen |
Rosuvastatin dose regimen |
Change in rosuvastatin AUC* |
|
Eltrombopag 75 mg OD, 5 days |
10 mg, single dose |
1.6-fold ↑ |
|
Darunavir 600 mg/ritonavir 100 mg BID, 7 days |
10 mg OD, 7 days |
1.5-fold ↑ |
|
Tipranavir 500 mg/ritonavir 200 mg BID, 11 days |
10 mg, single dose |
1.4-fold ↑ |
|
Dronedarone 400 mg BID |
Not available |
1.4-fold ↑ |
|
Itraconazole 200 mg OD, 5 days |
10 mg, single dose |
**1.4-fold ↑ |
|
Ezetimibe 10 mg OD, 14 days |
10 mg, OD, 14 days |
**1.2-fold ↑ |
|
Decrease in AUC of rosuvastatin |
||
|
Interacting drug dose regimen |
Rosuvastatin dose regimen |
Change in rosuvastatin AUC* |
|
Erythromycin 500 mg QID, 7 days |
80 mg, single dose |
20% ↓ |
|
Baicalin 50 mg TID, 14 days |
20 mg, single dose |
47% ↓ |
|
*Data given as x-fold change represent a simple ratio between co-administration and rosuvastatin alone. Data given as % change represent % difference relative to rosuvastatin alone. Increase is indicated as “↑”, decrease as “↓”. **Several interaction studies have been performed at different rosuvastatin dosages, the table shows the most significant ratio AUC = area under curve; OD = once daily; BID = twice daily; TID = three times daily; QID = four times daily |
||
The following medical product/combinations did not have a clinically significant effect on the AUC ratio of rosuvastatin at coadministration:
Aleglitazar 0.3 mg 7 days dosing; Fenofibrate 67 mg 7 days TID dosing; Fluconazole 200mg 11 days OD dosing; Fosamprenavir 700 mg/ritonavir 100 mg 8 days BID dosing; Ketoconazole 200 mg 7 days BID dosing; Rifampin 450 mg 7 days OD dosing; Silymarin 140 mg 5 days TID dosing.
Effect of rosuvastatin on co-administered medicinal products
Vitamin K antagonists: As with other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, the initiation of treatment or dosage up-titration of rosuvastatin in patients treated concomitantly with vitamin K antagonists (e.g. warfarin or another coumarin anticoagulant) may result in an increase in International Normalised Ratio (INR). Discontinuation or down-titration of rosuvastatin may result in a decrease in INR. In such situations, appropriate monitoring of INR is desirable.
Oral contraceptive/hormone replacement therapy (HRT): Concomitant use of rosuvastatin and an oral contraceptive resulted in an increase in ethinyl estradiol and norgestrel AUC of 26% and 34%, respectively. These increased plasma levels should be considered when selecting oral contraceptive doses. There are no pharmacokinetic data available in subjects taking concomitant rosuvastatin and HRT, therefore, a similar effect cannot be excluded. However, the combination has been extensively used in women in clinical trials and was well tolerated.
Other medicinal products:
Digoxin: Based on data from specific interaction studies no clinically relevant interaction with digoxin is expected.
Fusidic Acid: Interaction studies with rosuvastatin and fusidic acid have not been conducted. The risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis may be increased by the concomitant administration of systemic fusidic acid with statins. The mechanism of this interaction (whether it is pharmacodynamic or pharmacokinetic, or both) is yet unknown. There have been reports of rhabdomyolysis (including some fatalities) in patients receiving this combination. If treatment with systemic fusidic acid is necessary, rosuvastatin treatment should be discontinued throughout the duration of the fusidic acid treatment.
Paediatric population: Interaction studies have only been performed in adults. The extent of interactions in the paediatric population is not known.
ASPIRIN
Contraindicated combinations
Methotrexate (used at doses >15 mg/week):
The combined drugs, methotrexate and acetylsalicylic acid, enhance haematological toxicity of methotrexate due to the decreased renal clearance of methotrexate by acetylsalicylic acid. Therefore, the concomitant use of methotrexate (at doses >15 mg/week) with Aspirin Tablets is contraindicated. Not recommended combinations
Uricosuric agents, e.g. probenecid
Salicylates reverse the effect of probenecid. The combination should be avoided. Combinations requiring precautions for use or to be taken into account
Anticoagulants e.g. coumarin, heparin, warfarin
Increased risk of bleeding due to inhibited thrombocyte function, injury of the duodenal mucosa and displacement of oral anticoagulants from their plasma protein binding sites. The bleeding time should be monitored.
Anti-platelet agents (e.g clopidogrel and dipyridamole) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs; such as sertraline or paroxetine) Increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Antidiabetics, e.g. sulfonylureas
Salicylics may increase the hypoglycaemic effect of sulfonylureas.
Digoxin and lithium
Acetylsalicylic acid impairs the renal excretion of digoxin and lithium, resulting in increased plasma concentrations. Monitoring of plasma concentrations of digoxin and lithium is recommended when initiating and terminating treatment with acetylsalicylic acid. Dose adjustment may be necessary
Diuretics and antihypertensives
NSAIDs may decrease the antihypertensive effects of diuretics and other antihypertensive agents. As for other NSAIDs concomitant administration with ACE-inhibitors increases the risk of acute renal insufficiency.
Diuretics: Risk of acute renal failure due to the decreased glomerual filtration via decreased renal prostaglandin synthesis. Hydrating the patient and monitoring renal function at the start of the treatment is recommended.
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (acetazolamide)
May result in severe acidosis and increased central nervous system toxicity
Systemic corticosteroids
The risk of gastrointestinal ulceration and bleeding may be increased when acetylsalicylic acid and corticosteroids are co-administered.
Methotrexate (used at doses <15 mg/week):
The combined drugs, methotrexate and acetylsalicylic acid, may increase haematological toxicity of methotrexate due to decreased renal clearance of methotrexate by acetylsalicylic acid. Weekly blood count checks should be done during the first weeks of the combination. Enhanced monitoring should take place in the presence of even mildly impaired renal function, as well, as in elderly.
Other NSAIDs
Increased risk of ulcerations and gastrointestinal bleeding due to synergistic effects.
Ibuprofen
Experimental data suggest that ibuprofen may inhibit the effect of low dose acetylsalicylic acid on platelet aggregation when they are dosed concomitantly. However, the limitations of these data and the uncertainties regarding extrapolation of ex vivo data to the clinical situation imply that no firm conclusions can be made for regular ibuprofen use, and no clinically relevant effect is considered to be likely for occasional ibuprofen use.
Metamizole
Metamizole may reduce the effect of acetylsalicylic acid on platelet aggregation, when taken concomitantly. Therefore, this combination should be used with caution in patients taking low dose aspirin for cardioprotection.
Ciclosporin, tacrolimus
Concomitant use of NSAIDs and ciclospoin or tacrolimus may increase the nephrotoxic effect of ciclosporin and tacrolimus. The renal function should be monitored in case of concomitant use of these agents and acetylsalicylic acid.
Antacids
The excretion of acetylsalicylic acid is increased by alkaline urine, which can occur with some antacids.
Alcohol
Concomitant administration of alcohol and acetylsalicylic acid increases the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
CLOPIDOGREL
Medicinal products associated with bleeding risk: There is an increased risk of bleeding due to the potential additive effect. The concomitant administration of medicinal products associated with bleeding risk should be undertaken with caution.
Oral anticoagulants: the concomitant administration of clopidogrel with oral anticoagulants is not recommended since it may increase the intensity of bleedings. Although the administration of clopidogrel 75 mg/day did not modify the pharmacokinetics of S-warfarin or International Normalised Ratio (INR) in patients receiving long-term warfarin therapy, coadministration of clopidogrel with warfarin increases the risk of bleeding because of independent effects on hemostasis.
Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors: clopidogrel should be used with caution in patients who receive concomitant glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors.
Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA): ASA did not modify the clopidogrel-mediated inhibition of ADP-induced platelet aggregation, but clopidogrel potentiated the effect of ASA on collagen-induced platelet aggregation. However, concomitant administration of 500 mg of ASA twice a day for one day did not significantly increase the prolongation of bleeding time induced by clopidogrel intake. A pharmacodynamic interaction between clopidogrel and acetylsalicylic acid is possible, leading to increased risk of bleeding. Therefore, concomitant use should be undertaken with caution. However, clopidogrel and ASA have been administered together for up to one year.
Heparin: in a clinical study conducted in healthy subjects, clopidogrel did not necessitate modification of the heparin dose or alter the effect of heparin on coagulation. Co-administration of heparin had no effect on the inhibition of platelet aggregation induced by clopidogrel. A pharmacodynamic interaction between clopidogrel and heparin is possible, leading to increased risk of bleeding. Therefore, concomitant use should be undertaken with caution.
Thrombolytics: the safety of the concomitant administration of clopidogrel, fibrin or non-fibrin specific thrombolytic agents and heparins was assessed in patients with acute myocardial infarction. The incidence of clinically significant bleeding was similar to that observed when thrombolytic agents and heparin are co-administered with ASA.
NSAIDs: in a clinical study conducted in healthy volunteers, the concomitant administration of clopidogrel and naproxen increased occult gastrointestinal blood loss. However, due to the lack of interaction studies with other NSAIDs it is presently unclear whether there is an increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding with all NSAIDs. Consequently, NSAIDs including Cox-2 inhibitors and clopidogrel should be co-administered with caution.
SSRIs: since SSRIs affect platelet activation and increase the risk of bleeding, the concomitant administration of SSRIs with clopidogrel should be undertaken with caution.
Other concomitant therapy:
Inducers of CYP2C19
Since clopidogrel is metabolised to its active metabolite partly by CYP2C19, use of medicinal products that induce the activity of this enzyme would be expected to result in increased drug levels of the active metabolite of clopidogrel.
Rifampicin strongly induces CYP2C19, resulting in both an increased level of clopidogrel active metabolite and platelet inhibition, which in particular might potentiate the risk of bleeding. As a precaution, concomitant use of strong CYP2C19 inducers should be discouraged.
Inhibitors of CYP2C19
Since clopidogrel is metabolised to its active metabolite partly by CYP2C19, use of medicinal products that inhibit the activity of this enzyme would be expected to result in reduced drug levels of the active metabolite of clopidogrel. The clinical relevance of this interaction is uncertain. As a precaution, concomitant use of strong or moderate CYP2C19 inhibitors should be discouraged. Medicinal products that are strong or moderate CYP2C19 inhibitors include, for example, omeprazole and esomeprazole, fluvoxamine, fluoxetine, moclobemide, voriconazole, fluconazole, ticlopidine, carbamazepine, and efavirenz.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI)
Omeprazole 80 mg once daily administered either at the same time as clopidogrel or with 12 hours between the administrations of the two drugs decreased the exposure of the active metabolite by 45% (loading dose) and 40% (maintenance dose). The decrease was associated with a 39% (loading dose) and 21% (maintenance dose) reduction of inhibition of platelet aggregation. Esomeprazole is expected to give a similar interaction with clopidogrel.
Inconsistent data on the clinical implications of this pharmacokinetic (PK)/pharmacodynamic (PD) interaction in terms of major cardiovascular events have been reported from both observational and clinical studies. As a precaution, concomitant use of omeprazole or esomeprazole should be discouraged. Less pronounced reductions of metabolite exposure has been observed with pantoprazole or lansoprazole.
The plasma concentrations of the active metabolite was 20% reduced (loading dose) and 14% reduced (maintenance dose) during concomitant treatment with pantoprazole 80 mg once daily. This was associated with a reduction of the mean inhibition of platelet aggregation by 15% and 11%, respectively. These results indicate that clopidogrel can be administered with pantoprazole. There is no evidence that other medicinal products that reduce stomach acid such as H2 blockers or antacids interfere with antiplatelet activity of clopidogrel.
Other medicinal products: A number of other clinical studies have been conducted with clopidogrel and other concomitant medicinal products to investigate the potential for pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic interactions. No clinically significant pharmacodynamic interactions were observed when clopidogrel was co-administered with atenolol, nifedipine, or both atenolol and nifedipine. Furthermore, the pharmacodynamic activity of clopidogrel was not significantly influenced by the co- administration of phenobarbital or oestrogen.
The pharmacokinetics of digoxin or theophylline were not modified by the co-administration of clopidogrel. Antacids did not modify the extent of clopidogrel absorption. Data from the CAPRIE study indicate that phenytoin and tolbutamide which are metabolised by CYP2C9 can be safely co-administered with clopidogrel.
CYP2C8 substrate medicinal products: Clopidogrel has been shown to increase repaglinide exposure in healthy volunteers. In vitro studies have shown the increase in repaglinide exposure is due to inhibition of CYP2C8 by the glucuronide metabolite of clopidogrel. Due to the risk of increased plasma concentrations, concomitant administration of clopidogrel and drugs primarily cleared by CYP2C8 metabolism (e.g., repaglinide, paclitaxel) should be undertaken with caution.
Apart from the specific medicinal product interaction information described above, interaction studies with clopidogrel and some medicinal products commonly administered in patients with atherothrombotic disease have not been performed. However, patients entered into clinical trials with clopidogrel received a variety of concomitant medicinal products including diuretics, beta blockers, ACEI, calcium antagonists, cholesterol lowering agents, coronary vasodilators, antidiabetic agents (including insulin), antiepileptic agents and GPIIb/IIIa antagonists without evidence of clinically significant adverse interactions.
A significantly lower exposure to clopidogrel active metabolite and reduced platelet inhibition have been demonstrated in HIV-infected patients treated with ritonavir- or cobicistat-boosted anti-retroviral therapies (ART). Although the clinical relevance of these findings is uncertain, there have been spontaneous reports of HIV-infected patients treated with boosted ART, who have experienced re-occlusive events after de-obstruction or have suffered thrombotic events under a clopidogrel loading treatment schedule. Exposure of clopidogrel and average platelet inhibition can be decreased with concomitant use of ritonavir. Therefore, concomitant use of clopidogrel with boosted ART should be discouraged.
As with other oral P2Y12 inhibitors, co-administration of opioid agonists has the potential to delay and reduce the absorption of clopidogrel presumably because of slowed gastric emptying. The clinical relevance is unknown. Consider the use of a parenteral antiplatelet agent in acute coronary syndrome patients requiring co-administration of morphine or other opioid agonists.
4.6. Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
ROSUVASTATIN
Rosuvastatin is contraindicated in pregnancy and lactation. Women of child bearing potential should use appropriate contraceptive measures. Since cholesterol and other products of cholesterol biosynthesis are essential for the development of the foetus, the potential risk from inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase outweighs the advantage of treatment during pregnancy. Animal studies provide limited evidence of reproductive toxicity. If a patient becomes pregnant during use of this product, treatment should be discontinued immediately.
Rosuvastatin is excreted in the milk of rats. There are no data with respect to excretion in milk in humans.
ASPIRIN
Pregnancy
Low doses (up to 100 mg/day):
Clinical studies indicate that doses up to 100 mg/day for restricted obstetrical use, which require specialised monitoring, appear safe.
Doses of 100- 500 mg/day:
There is insufficient clinical experience regarding the use of doses above 100 mg/day up to 500 mg/day. Therefore, the recommendations below for doses of 500 mg/day and above apply also for this dose range.
Doses of 500 mg/day and above:
Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis may adversely affect the pregnancy and/or the embryo/foetal development. Data from epidemiological studies suggest an increased risk of miscarriage and of cardiac malformation and gastroschisis after use of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor in early pregnancy. The absolute risk for cardiovascular malformation was increased from less than 1%, up to approximately 1.5 %. The risk is believed to increase with dose and duration of therapy. In animals, administration of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor has been shown to result in increased pre- and post-implantation loss and embryo-foetal lethality. In addition, increased incidences of various malformations, including cardiovascular, have been reported in animals given a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor during the organogenetic period. During the first and second trimester of pregnancy, acetylsalicylic acid should not be given unless clearly necessary. If acetylsalicylic acid is used by a woman attempting to conceive, or during the first and second trimester of pregnancy, the dose should be kept as low and duration of treatment as short as possible.
During the third trimester of pregnancy, all prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors may expose the foetus to:
- cardiopulmonary toxicity (with premature closure of the ductus arteriosus and pulmonary hypertension);
- renal dysfunction, which may progress to renal failure with oligo- hydroamniosis;
- the mother and the neonate, at the end of pregnancy, to:
- possible prolongation of bleeding time, an anti-aggregating effect which may occur even at very low doses.
- inhibition of uterine contractions resulting in delayed or prolonged labour.
Consequently, acetylsalicylic acid at doses of 100 mg/day and higher is contraindicated during the third trimester of pregnancy.
Breastfeeding
Low quantities of salicylates and of their metabolites are excreted into the breast milk. Since adverse effects for the infant have not been reported up to now, short-term use of the recommended dose does not require suspending lactation. In cases of long-term use and/or administration of higher doses, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
CLOPIDOGREL
Pregnancy
As no clinical data on exposure to clopidogrel during pregnancy are available, it is preferable not to use clopidogrel during pregnancy as a precautionary measure. Animal studies do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to pregnancy, embryonal/foetal development, parturition or postnatal development.
Breast-feeding
It is unknown whether clopidogrel is excreted in human breast milk. Animal studies have shown excretion of clopidogrel in breast milk. As a precautionary measure, breast-feeding should not be continued during treatment with Clopidogrel film-coated tablet.
Fertility
Clopidogrel was not shown to alter fertility in animal studies.
4.7. Effects on ability to drive and use machines
ROSUVASTATIN
Studies to determine the effect of rosuvastatin on the ability to drive and use machines have not been conducted. However, based on its pharmacodynamic properties, rosuvastatin is unlikely to affect this ability. When driving vehicles or operating machines, it should be taken into account that dizziness may occur during treatment.
ASPIRIN
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed with Aspirin 75mg Tablets.
Based on the pharmacodynamic properties and the side effects of acetylsalicylic acid, no influence on the reactivity and the ability to drive or use machines is expected.
CLOPIDOGREL
Clopidogrel has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
4.8. Undesirable effects
ROSUVASTATIN
The adverse reactions seen with rosuvastatin are generally mild and transient. In controlled clinical trials, less than 4% of rosuvastatin-treated patients were withdrawn due to adverse reactions.
Tabulated list of adverse reactions
Based on data from clinical studies and extensive post-marketing experience, the following table presents the adverse reaction profile for rosuvastatin. Adverse reactions listed below are classified according to frequency and system organ class (SOC).
The frequencies of adverse reactions are ranked according to the following convention: Common (≥1/100 to <1/10); Uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100); Rare (≥1/10,000 to <1/1000); Very rare (<1/10,000); Not known (cannot be estimated from the available data).
Table 2. Adverse reactions based on data from clinical studies and post-marketing experience
|
System organ class |
Common |
Uncommon |
Rare |
Very rare |
Not known |
|
Blood and lymphatic system disorders |
Thrombocytopenia |
||||
|
Immune system disorders |
Hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema |
||||
|
Endocrine disorders |
Diabetes mellitus1 |
||||
|
Psychiatric disorders |
Depression |
||||
|
Nervous system disorders |
Headache Dizziness |
Polyneuropathy Memory loss |
Peripheral neuropathy Sleep disturbances (including insomnia and nightmares) |
||
|
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders |
Cough Dyspnoea |
||||
|
Gastro-intestinal disorders |
Constipation Nausea Abdominal pain |
Pancreatitis |
Diarrhoea |
||
|
Hepatobiliary disorders |
Increased hepatic transaminases |
Jaundice Hepatitis |
|||
|
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders |
Pruritus Rash Urticaria |
Stevens-Johnson syndrome |
|||
|
Musculo-skeletal and connective tissue disorders |
Myalgia |
Myopathy (including myositis) Rhabdomyolysis Lupus-like syndrome Muscle rupture |
Arthralgia |
Tendon disorders, sometimes complicated by rupture Immune-mediated necrotising myopathy |
|
|
Renal and urinary disorders |
Haematuria |
||||
|
Reproductive system and breast disorders |
Gynaecomastia |
||||
|
General disorders and administration site conditions |
Asthenia |
Oedema |
|||
|
1 Frequency will depend on the presence or absence of risk factors (fasting blood glucose ≥ 5.6 mmol/L, BMI >30 kg/m2, raised triglycerides, history of hypertension). |
|||||
As with other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, the incidence of adverse drug reactions tends to be dose dependent.
Renal effects: Proteinuria, detected by dipstick testing and mostly tubular in origin, has been observed in patients treated with rosuvastatin. Shifts in urine protein from none or trace to ++ or more were seen in <1% of patients at some time during treatment with 10 and 20 mg, and in approximately 3% of patients treated with 40 mg. A minor increase in shift from none or trace to + was observed with the 20 mg dose. In most cases, proteinuria decreases or disappears spontaneously on continued therapy. Review of data from clinical trials and post-marketing experience to date has not identified a causal association between proteinuria and acute or progressive renal disease. Haematuria has been observed in patients treated with rosuvastatin and clinical trial data show that the occurrence is low.
Skeletal muscle effects: Effects on skeletal muscle e.g. myalgia, myopathy (including myositis) and, rarely, rhabdomyolysis with and without acute renal failure have been reported in rosuvastatin-treated patients with all doses and in particular with doses > 20 mg. A dose-related increase in CK levels has been observed in patients taking rosuvastatin; the majority of cases were mild, asymptomatic and transient. If CK levels are elevated (>5xULN), treatment should be discontinued.
Liver effects: As with other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, a dose-related increase in transaminases has been observed in a small number of patients taking rosuvastatin; the majority of cases were mild, asymptomatic and transient.
The following adverse events have been reported with some statins:
- Sexual dysfunction.
- Exceptional cases of interstitial lung disease, especially with long term therapy.
- The reporting rates for rhabdomyolysis, serious renal events and serious hepatic events (consisting mainly of increased hepatic transaminases) is higher at the 40 mg dose.
ASPIRIN
Side effects are grouped on the basis of System Organ Class. Within each system organ class the frequencies are defined as: very common (≥1/10), common (≥1/100 to <1/10), uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100), rare (≥1/10,000 to <1/1,000), very rare (<1/10,000) and not known (cannot be estimated from the available data)
|
Blood and lymphatic system disorders |
Common: Increased bleeding tendencies. Rare: Thrombocytopenia, granulocytosis, aplastic anaemia. Not known: Cases of bleeding with prolonged bleeding time such as epistaxis, gingival bleeding. Symptoms may persist for a period of 4–8 days after acetylsalicylic acid discontinuation. As a result there may be an increased risk of bleeding during surgical procedures. Existing (haematemesis, melaena) or occult gastrointestinal bleeding, which may lead to iron deficiency anaemia (more common at higher doses). |
|
Immune system disorders |
Rare: Hypersensitivity reactions, angio-oedema, allergic oedema, anaphylactic reactions including shock. |
|
Metabolism and digestive system disorders |
Not known: Hyperuricemia. |
|
Nervous system disorders |
Rare: Intracranial haemorrhage. Not known: Headache, vertigo. |
|
Ear and labyrinth disorders |
Not known: Reduced hearing ability; tinnitus. |
|
Vascular disorders |
Rare: Hemorrhagic vasculitis. |
|
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders |
Uncommon: Rhinitis, dyspnoea. Rare: Bronchospasm, asthma attacks. |
|
Reproductive systemand mammary disorders |
Rare: Menorrhagia. |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders |
Common: Dyspepsia. Rare: Severe gastrointestinal haemorrhage, nausea, vomiting. Not known: Gastric or duodenal ulcers and perforation. |
|
Hepatobiliary disorders |
Not known: Hepatic insufficiency. |
|
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders |
Uncommon: Urticaria. Rare: Steven-Johnsons syndrome, Lyells syndrome, purpura, erythema nodosum, erythema multiforme. |
|
Renal and urinary tract disorders |
Not known: Impaired renal function, salt and water retention. |
CLOPIDOGREL
Summary of the safety profile
Clopidogrel has been evaluated for safety in more than 44,000 patients who have participated in clinical studies, including over 12,000 patients treated for 1 year or more. Overall, clopidogrel 75 mg/day was comparable to ASA 325 mg/day in CAPRIE regardless of age, gender and race. The clinically relevant adverse reactions observed in the CAPRIE, CURE, CLARITY, COMMIT and ACTIVE-A studies are discussed below. In addition to clinical studies experience, adverse reactions have been spontaneously reported.
Bleeding is the most common reaction reported both in clinical studies as well as in post-marketing experience where it was mostly reported during the first month of treatment.
In CAPRIE, in patients treated with either clopidogrel or ASA, the overall incidence of any bleeding was 9.3%. The incidence of severe cases was similar for clopidogrel and ASA.
In CURE, there was no excess in major bleeds with clopidogrel plus ASA within 7 days after coronary bypass graft surgery in patients who stopped therapy more than five days prior to surgery. In patients who remained on therapy within five days of bypass graft surgery, the event rate was 9.6% for clopidogrel plus ASA, and 6.3% for placebo plus ASA.
In CLARITY, there was an overall increase in bleeding in the clopidogrel plus ASA group vs. the placebo plus ASA group. The incidence of major bleeding was similar between groups. This was consistent across subgroups of patients defined by baseline characteristics, and type of fibrinolytic or heparin therapy. In COMMIT, the overall rate of noncerebral major bleeding or cerebral bleeding was low and similar in both groups.
In ACTIVE-A, the rate of major bleeding was greater in the clopidogrel + ASA group than in the placebo + ASA group (6.7% versus 4.3%). Major bleeding was mostly of extracranial origin in both groups (5.3% in the clopidogrel + ASA group; 3.5% in the placebo +ASA group), mainly from the gastrointestinal tract (3.5% vs. 1.8%). There was an excess of intracranial bleeding in the clopidogrel + ASA treatment group compared to the placebo + ASA group (1.4% versus 0.8%, respectively). There was no statistically significant difference in the rates of fatal bleeding (1.1% in the clopidogrel + ASA group and 0.7% in the placebo +ASA group) and haemorrhagic stroke (0.8% and 0.6%, respectively) between groups.
Tabulated list of adverse reactions
Adverse reactions that occurred either during clinical studies or that were spontaneously reported are presented in the table below. Their frequency is defined using the following conventions: common (≥1/100 to <1/10); uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100); rare (≥1/10,000 to <1/1,000); very rare (<1/10,000), not known (cannot be estimated from the available data). Within each system organ class, adverse reactions are presented in order of decreasing seriousness.
|
System Organ Class |
Common |
Uncommon |
Rare |
Very rare, not known* |
|
Blood and the lymphatic system disorders |
Thrombocytopenia, leucopenia, eosinophilia |
Neutropenia, including severe neutropenia |
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), aplastic anaemia, pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, severe thrombocytopenia, acquired haemophilia A granulocytopenia, anaemia |
|
|
Cardiac disorders |
Kounis syndrome (vasospastic allergic angina / allergic myocardial infarction) in the context of a hypersensitivity reaction due to clopidogrel* |
|||
|
Immune system disorders |
Serum sickness, anaphylactoid reactions, cross reactive drug hypersensitivity among thienopyridines (such as ticlopidine, prasugrel)*, insulin autoimmune syndrome, which can lead to severe hypoglycemia, particularly in patients with HLA DRA4 subtype (more frequent in the Japanese population)* |
|||
|
Psychiatric disorders |
Hallucinations, confusion |
|||
|
Nervous system disorders |
Intracranial bleeding (some cases were reported with fatal outcome), headache, paraesthesia, dizziness |
Taste disturbances, ageusia |
||
|
Eye disorders |
Eye bleeding conjunctival, ocular, retinal) |
|||
|
Ear and labyrinth disorders |
Vertigo |
|||
|
Vascular disorders |
Haematoma |
Serious haemorrhage, haemorrhage of operative wound, vasculitis, hypotension |
||
|
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders |
Epistaxis |
Respiratory tract bleeding (haemoptysis, pulmonary haemorrhage), bronchospasm, interstitial pneumonitis, eosinophillic pneumonia |
||
|
Gastrointestinal disorders |
Gastrointestinal haemorrhage, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, dyspepsia |
Gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, gastritis, vomiting, nausea, constipation, flatulence |
Retroperitoneal haemorrhage |
Gastrointestinal and retroperitoneal haemorrhage with fatal outcome, pancreatitis, colitis (including ulcerative or lymphocytic colitis), stomatitis |
|
Hepato-biliary disorders |
Acute liver failure, hepatitis, abnormal liver function test |
|||
|
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders |
Bruising |
Rash, pruritus, Skin bleeding (purpura) |
Bullous dermatitis (toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens Johnson Syndrome, erythema multiforme, acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)), angioedema, drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS),rash erythematous or exfoliative, urticaria, eczema, lichen planus |
|
|
Reproductive systems and breast disorders |
Gynaecomastia |
|||
|
Musculoskeletal, connective tissue and bone disorders |
Musculo-skeletal bleeding (haemarthrosis), arthritis, arthralgia, myalgia |
|||
|
Renal and urinary disorders |
Haematuria |
Glomerulonephritis, blood creatinine increased |
||
|
General disorders and administration site conditions |
Bleeding at puncture site |
Fever |
||
|
Investigations |
Bleeding time prolonged, neutrophil count decreased, platelet count decreased |
*Information related to clopidogrel with frequency “not known”.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: Website: https://www.zuventus.co.in/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9. Overdose
ROSUVASTATIN
There is no specific treatment in the event of overdose. In the event of overdose, the patient should be treated symptomatically and supportive measures instituted as required. Liver function and CK levels should be monitored. Haemodialysis is unlikely to be of benefit.
ASPIRIN
Although considerable inter-individual variations are involved, it can be considered that the toxic dose is about 200 mg/kg in adults and 100 mg/kg in children. The lethal dose of acetylsalicylic acid is 25-30 grams. Plasma salicylate concentrations above 300 mg/l indicate intoxication. Plasma concentrations above 500 mg/l in adults and 300 mg/l in children generally cause severe toxicity. Overdose may be harmful for elderly patients and particularly for small children (therapeutic overdose or frequent accidental intoxications may be fatal).
Symptoms of moderate intoxications
Tinnitus, hearing disorders, headache, vertigo, confusion and gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain).
Symptoms of severe intoxications
Symptoms are related to severe disruption of the acid-base balance. In the first instance hyperventilation occurs, which results in respiratory alkalosis. Respiratory acidosis ensues due to suppression of the respiratory centre. In addition, metabolic acidosis occurs as a result of the presence of salicylate.
Since younger children are often not seen until they have reached a late stage of intoxication, they are usually in the stage of acidosis. Furthermore, the following symptoms may occur: hyperthermia and perspiration, resulting in dehydration: feelings of restlessness, convulsions, hallucinations and hypoglycaemia. Depression of the nervous system may lead to coma, cardiovascular collapse or respiratory arrest.
Treatment of overdose
If a toxic dose has been ingested, hospital admission is required. In the event of moderate intoxication, inducing the patient to vomit should be attempted. If this fails, gastric lavage may be attempted during the first hour after ingestion of a substantial amount of the medicine. Afterwards, administer activated carbon (adsorbent) and sodium sulfate (laxative).
Activated charcoal may be given as a single dose (50 g for an adult, 1 g/kg body weight for a child up to 12 years).
Alkalisation of the urine (250 mmol NaHCO3, for three hours) whilst checking urine pH levels. In the event of severe intoxication, haemodialysis is to be preferred. Other symptoms to be treated symptomatically.
CLOPIDOGREL
Overdose following clopidogrel administration may lead to prolonged bleeding time and subsequent bleeding complications. Appropriate therapy should be considered, if bleedings are observed. No antidote to the pharmacological activity of clopidogrel has been found. If prompt correction of prolonged bleeding time is required, platelet transfusion may reverse the effects of clopidogrel.
5. Pharmacological properties
1. Pharmacodynamic properties
ROSUVASTATIN
Mechanism of action
Rosuvastatin is a selective and competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme that converts 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A to mevalonate, a precursor for cholesterol. The primary site of action of rosuvastatin is the liver, the target organ for cholesterol lowering.
Rosuvastatin increases the number of hepatic LDL receptors on the cell-surface, enhancing uptake and catabolism of LDL and it inhibits the hepatic synthesis of VLDL, thereby reducing the total number of VLDL and LDL particles.
Pharmacodynamic effects
Rosuvastatin reduces elevated LDL-cholesterol, total cholesterol and triglycerides and increases HDL-cholesterol. It also lowers ApoB, non-HDL-C, VLDL-C, VLDL-TG and increases ApoA-I (see Table 3). Crestor also lowers the LDL-C/HDL-C, total C/HDL-C and non-HDL-C/HDL-C and the ApoB/ApoA-I ratios.
Table 3 Dose response in patients with primary hypercholesterolaemia (type IIa and IIb) (adjusted mean percent change from baseline)
|
Dose |
N |
LDL-C |
Total-C |
HDL-C |
TG |
nonHDL-C |
ApoB |
ApoA-I |
|
Placebo |
13 |
-7 |
-5 |
3 |
-3 |
-7 |
-3 |
0 |
|
5 |
17 |
-45 |
-33 |
13 |
-35 |
-44 |
-38 |
4 |
|
10 |
17 |
-52 |
-36 |
14 |
-10 |
-48 |
-42 |
4 |
|
20 |
17 |
-55 |
-40 |
8 |
-23 |
-51 |
-46 |
5 |
|
40 |
18 |
-63 |
-46 |
10 |
-28 |
-60 |
-54 |
0 |
A therapeutic effect is obtained within 1 week following treatment initiation and 90% of maximum response is achieved in 2 weeks. The maximum response is usually achieved by 4 weeks and is maintained after that.
Clinical efficacy and safety
Rosuvastatin is effective in adults with hypercholesterolaemia, with and without hypertriglyceridaemia, regardless of race, sex or age and in special populations such as diabetics or patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia.
From pooled phase III data, Rosuvastatin has been shown to be effective at treating the majority of patients with type IIa and IIb hypercholesterolaemia (mean baseline LDL-C about 4.8 mmol/L) to recognised European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS; 1998) guideline targets; about 80% of patients treated with 10 mg reached the EAS targets for LDL-C levels (<3 mmol/L).
In a large study, 435 patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia were given rosuvastatin from 20 mg to 80 mg in a force-titration design. All doses showed a beneficial effect on lipid parameters and treatment to target goals. Following titration to a daily dose of 40 mg (12 weeks of treatment), LDL-C was reduced by 53%. Thirty-three percent (33%) of patients reached EAS guidelines for LDL-C levels (<3 mmol/L).
In a force-titration, open label trial, 42 patients (including 8 paediatric patients) with homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia were evaluated for their response to rosuvastatin 20 – 40 mg. In the overall population, the mean LDL-C reduction was 22%.
In clinical studies with a limited number of patients, rosuvastatin has been shown to have additive efficacy in lowering triglycerides when used in combination with fenofibrate and in increasing HDL-C levels when used in combination with niacin.
In a multi-centre, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study (METEOR), 984 patients between 45 and 70 years of age and at low risk for coronary heart disease (defined as Framingham risk <10% over 10 years), with a mean LDL-C of 4.0 mmol/L (154.5 mg/dL), but with subclinical atherosclerosis (detected by Carotid Intima Media Thickness) were randomised to 40 mg rosuvastatin once daily or placebo for 2 years. Rosuvastatin significantly slowed the rate of progression of the maximum CIMT for the 12 carotid artery sites compared to placebo by -0.0145 mm/year [95% confidence interval -0.0196, -0.0093; p<0.0001]. The change from baseline was -0.0014 mm/year (-0.12%/year (non-significant)) for rosuvastatin compared to a progression of +0.0131 mm/year (1.12%/year (p<0.0001)) for placebo. No direct correlation between CIMT decrease and reduction of the risk of cardiovascular events has yet been demonstrated. The population studied in METEOR is low risk for coronary heart disease and does not represent the target population of rosuvastatin 40 mg. The 40 mg dose should only be prescribed in patients with severe hypercholesterolaemia at high cardiovascular risk.
In the Justification for the Use of Statins in Primary Prevention: An Intervention Trial Evaluating Rosuvastatin (JUPITER) study, the effect of rosuvastatin on the occurrence of major atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease events was assessed in 17,802 men (≥50 years) and women (≥60 years).
Study participants were randomly assigned to placebo (n=8901) or rosuvastatin 20 mg once daily (n=8901) and were followed for a mean duration of 2 years.
LDL-cholesterol concentration was reduced by 45% (p<0.001) in the rosuvastatin group compared to the placebo group.
In a post-hoc analysis of a high-risk subgroup of subjects with a baseline Framingham risk score >20% (1558 subjects) there was a significant reduction in the combined end-point of cardiovascular death, stroke and myocardial infarction (p=0.028) on rosuvastatin treatment versus placebo. The absolute risk reduction in the event rate per 1000 patient-years was 8.8. Total mortality was unchanged in this high-risk group (p=0.193). In a post-hoc analysis of a high-risk subgroup of subjects (9302 subjects total) with a baseline SCORE risk ≥5% (extrapolated to include subjects above 65 yrs) there was a significant reduction in the combined end-point of cardiovascular death, stroke and myocardial infarction (p=0.0003) on rosuvastatin treatment versus placebo. The absolute risk reduction in the event rate was 5.1 per 1000 patient-years. Total mortality was unchanged in this high-risk group (p=0.076).
In the JUPITER trial, there were 6.6% of rosuvastatin and 6.2% of placebo subjects who discontinued use of study medication due to an adverse event. The most common adverse events that led to treatment discontinuation were: myalgia (0.3% rosuvastatin, 0.2% placebo), abdominal pain (0.03% rosuvastatin, 0.02% placebo) and rash (0.02% rosuvastatin, 0.03% placebo). The most common adverse events at a rate greater than or equal to placebo were urinary tract infection (8.7% rosuvastatin, 8.6% placebo), nasopharyngitis (7.6% rosuvastatin, 7.2% placebo), back pain (7.6% rosuvastatin, 6.9% placebo) and myalgia (7.6% rosuvastatin, 6.6% placebo).
ASPIRIN
Acetylsalicylic acid inhibits the platelet activation: blocking the platelet cyclooxygenase by acetylation, it inhibits thromboxane A2 synthesis, a physiological activating substance released by the platelets and which would play a role in the complications of the atheromatosic lesions.
Inhibition of TXA2-synthesis is irreversible, because thrombocytes, which have no nucleus, are not capable (due to lack of protein synthesis capability) to synthesise new cyclooxygenase, which had been acetylated by acetylsalicylic acid.
The repeated doses from 20 to 325 mg involve an inhibition of the enzymatic activity from 30 to 95%.
Due to the irreversible nature of the binding, the effect persists for the lifespan of a thrombocyte (7-10 days). The inhibiting effect does not exhaust during prolonged treatments and the enzymatic activity gradually begins again upon renewal of the platelets 24 to 48 hours after treatment interruption.
Acetylsalicylic acid extends bleeding time on average by approximately 50 to 100%, but individual variations can be observed.
Experimental data suggest that ibuprofen may inhibit the effect of low dose acetylsalicylic acid on platelet aggregation when they are dosed concomitantly.
In one study, when a single dose of ibuprofen 400 mg was taken within 8 h before or within 30 min after immediate release acetylsalicylic acid dosing (81 mg), a decreased effect of acetylsalicylic acid on the formation of thromboxane or platelet aggregation occurred. However, the limitations of these data and the uncertainties regarding extrapolation of ex vivo data to the clinical situation imply that no firm conclusions can be made for regular ibuprofen use, and no clinically relevant effect is considered to be likely for occasional ibuprofen use.
CLOPIDOGREL
Mechanism of action
Clopidogrel is a prodrug, one of whose metabolites is an inhibitor of platelet aggregation. Clopidogrel must be metabolised by CYP450 enzymes to produce the active metabolite that inhibits platelet aggregation. The active metabolite of clopidogrel selectively inhibits the binding of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to its platelet P2Y12 receptor and the subsequent ADP-mediated activation of the glycoprotein GPIIb/IIIa complex, thereby inhibiting platelet aggregation. Due to the irreversible binding, platelets exposed are affected for the remainder of their lifespan (approximately 7-10 days) and recovery of normal platelet function occurs at a rate consistent with platelet turnover. Platelet aggregation induced by agonists other than ADP is also inhibited by blocking the amplification of platelet activation by released ADP.
Because the active metabolite is formed by CYP450 enzymes, some of which are polymorphic or subject to inhibition by other medicinal products, not all patients will have adequate platelet inhibition.
Pharmacodynamic effects
Repeated doses of 75 mg per day produced substantial inhibition of ADP-induced platelet aggregation from the first day; this increased progressively and reached steady state between Day 3 and Day 7. At steady state, the average inhibition level observed with a dose of 75 mg per day was between 40% and 60%. Platelet aggregation and bleeding time gradually returned to baseline values, generally within 5 days after treatment was discontinued.
Clinical efficacy and safety
The safety and efficacy of clopidogrel have been evaluated in 5 double-blind studies involving over 88,000 patients: the CAPRIE study, a comparison of clopidogrel to ASA, and the CURE, CLARITY, COMMIT and ACTIVE-A studies comparing clopidogrel to placebo, both medicinal products given in combination with ASA and other standard therapy.
Recent myocardial infarction (MI), recent stroke or established peripheral arterial disease
The CAPRIE study included 19,185 patients with atherothrombosis as manifested by recent myocardial infarction (<35 days), recent ischaemic stroke (between 7 days and 6 months) or established peripheral arterial disease (PAD). Patients were randomised to clopidogrel 75 mg/day or ASA 325 mg/day, and were followed for 1 to 3 years. In the myocardial infarction subgroup, most of the patients received ASA for the first few days following the acute myocardial infarction.
Clopidogrel significantly reduced the incidence of new ischaemic events (combined end point of myocardial infarction, ischaemic stroke and vascular death) when compared to ASA. In the intention to treat analysis, 939 events were observed in the clopidogrel group and 1,020 events with ASA (relative risk reduction (RRR) 8.7%, [95% CI: 0.2 to 16.4]; p=0.045), which corresponds, for every 1,000 patients treated for 2 years, to 10 [CI: 0 to 20] additional patients being prevented from experiencing a new ischaemic event. Analysis of total mortality as a secondary endpoint did not show any significant difference between clopidogrel (5.8%) and ASA (6.0%).
In a subgroup analysis by qualifying condition (myocardial infarction, ischaemic stroke, and PAD) the benefit appeared to be strongest (achieving statistical significance at p=0.003) in patients enrolled due to PAD (especially those who also had a history of myocardial infarction) (RRR = 23.7%; CI: 8.9 to 36.2) and weaker (not significantly different from ASA) in stroke patients (RRR = 7.3%; CI: -5.7 to 18.7 [p=0.258]). In patients who were enrolled in the trial on the sole basis of a recent myocardial infarction, clopidogrel was numerically inferior, but not statistically different from ASA (RRR = -4.0%; CI: -22.5 to 11.7 [p=0.639]). In addition, a subgroup analysis by age suggested that the benefit of clopidogrel in patients over 75 years was less than that observed in patients ≤75 years.
Since the CAPRIE trial was not powered to evaluate efficacy of individual subgroups, it is not clear whether the differences in relative risk reduction across qualifying conditions are real, or a result of chance.
Acute coronary syndrome
The CURE study included 12,562 patients with non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction), and presenting within 24 hours of onset of the most recent episode of chest pain or symptoms consistent with ischaemia. Patients were required to have either ECG changes compatible with new ischaemia or elevated cardiac enzymes or troponin I or T to at least twice the upper limit of normal. Patients were randomised to clopidogrel (300 mg loading dose followed by 75 mg/day, N=6,259) or placebo (N=6,303), both given in combination with ASA (75-325 mg once daily) and other standard therapies. Patients were treated for up to one year. In CURE, 823 (6.6%) patients received concomitant GPIIb/IIIa receptor antagonist therapy. Heparins were administered in more than 90% of the patients and the relative rate of bleeding between clopidogrel and placebo was not significantly affected by the concomitant heparin therapy.
The number of patients experiencing the primary endpoint [cardiovascular (CV) death, myocardial infarction (MI), or stroke] was 582 (9.3%) in the clopidogrel-treated group and 719 (11.4%) in the placebo-treated group, a 20% relative risk reduction (95% CI of 10%-28%; p=0.00009) for the clopidogrel-treated group (17% relative risk reduction when patients were treated conservatively, 29% when they underwent percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) with or without stent and 10% when they underwent coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)). New cardiovascular events (primary endpoint) were prevented, with relative risk reductions of 22% (CI: 8.6, 33.4), 32% (CI: 12.8, 46.4), 4% (CI: -26.9, 26.7), 6% (CI: -33.5, 34.3) and 14% (CI: -31.6, 44.2), during the 0-1, 1-3, 3-6, 6-9 and 9-12 month study intervals, respectively. Thus, beyond 3 months of treatment, the benefit observed in the clopidogrel + ASA group was not further increased, whereas the risk of haemorrhage persisted.
The use of clopidogrel in CURE was associated with a decrease in the need of thrombolytic therapy (RRR = 43.3%; CI: 24.3%, 57.5%) and GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors (RRR = 18.2%; CI: 6.5%, 28.3%).
The number of patients experiencing the co-primary endpoint (CV death, MI, stroke or refractory ischaemia) was 1,035 (16.5%) in the clopidogrel-treated group and 1,187 (18.8%) in the placebo-treated group, a 14% relative risk reduction (95% CI of 6%-21%, p=0.0005) for the clopidogrel-treated group. This benefit was mostly driven by the statistically significant reduction in the incidence of MI [287 (4.6%) in the clopidogrel treated group and 363 (5.8%) in the placebo treated group]. There was no observed effect on the rate of rehospitalisation for unstable angina.
The results obtained in populations with different characteristics (e.g. unstable angina or non-Q-wave MI, low to high risk levels, diabetes, need for revascularisation, age, gender, etc.) were consistent with the results of the primary analysis. In particular, in a post-hoc analysis in 2,172 patients (17% of the total CURE population) who underwent stent placement (Stent-CURE), the data showed that clopidogrel compared to placebo, demonstrated a significant RRR of 26.2% favouring clopidogrel for the co-primary endpoint (CV death, MI, stroke) and also a significant RRR of 23.9% for the second co-primary endpoint (CV death, MI, stroke or refractory ischaemia). Moreover, the safety profile of clopidogrel in this subgroup of patients did not raise any particular concern. Thus, the results from this subset are in line with the overall trial results.
The benefits observed with clopidogrel were independent of other acute and long-term cardiovascular therapies (such as heparin/LMWH, GPIIb/IIIa antagonists, lipid lowering medicinal products, beta blockers, and ACE-inhibitors). The efficacy of clopidogrel was observed independently of the dose of ASA (75-325 mg once daily).
In patients with acute ST-segment elevation MI, safety and efficacy of clopidogrel have been evaluated in 2 randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind studies, CLARITY and COMMIT.
The CLARITY trial included 3,491 patients presenting within 12 hours of the onset of a ST elevation MI and planned for thrombolytic therapy. Patients received clopidogrel (300 mg loading dose, followed by 75 mg/day, n=1,752) or placebo (n=1,739), both in combination with ASA (150 to 325 mg as a loading dose, followed by 75 to 162 mg/day), a fibrinolytic agent and, when appropriate, heparin. The patients were followed for 30 days. The primary endpoint was the occurrence of the composite of an occluded infarct-related artery on the predischarge angiogram, or death or recurrent MI before coronary angiography. For patients who did not undergo angiography, the primary endpoint was death or recurrent myocardial infarction by Day 8 or by hospital discharge. The patient population included 19.7% women and 29.2% patients ≥ 65 years. A total of 99.7% of patients received fibrinolytics (fibrin specific: 68.7%, non-fibrin specific: 31.1%), 89.5% heparin, 78.7% beta blockers, 54.7% ACE inhibitors and 63% statins.
Fifteen percent (15.0%) of patients in the clopidogrel group and 21.7% in the placebo group reached the primary endpoint, representing an absolute reduction of 6.7% and a 36 % odds reduction in favor of clopidogrel (95% CI: 24, 47%; p < 0.001), mainly related to a reduction in occluded infarct-related arteries. This benefit was consistent across all prespecified subgroups including patients' age and gender, infarct location, and type of fibrinolytic or heparin used.
The 2x2 factorial design COMMIT trial included 45,852 patients presenting within 24 hours of the onset of the symptoms of suspected MI with supporting ECG abnormalities (i.e. ST elevation, ST depression or left bundle-branch block). Patients received clopidogrel (75 mg/day, n=22,961) or placebo (n=22,891), in combination with ASA (162 mg/day), for 28 days or until hospital discharge. The co-primary endpoints were death from any cause and the first occurrence of re-infarction, stroke or death. The population included 27.8% women, 58.4% patients ≥ 60 years (26% ≥ 70 years) and 54.5% patients who received fibrinolytics.
Clopidogrel significantly reduced the relative risk of death from any cause by 7% (p=0.029), and the relative risk of the combination of re-infarction, stroke or death by 9% (p=0.002), representing an absolute reduction of 0.5% and 0.9%, respectively. This benefit was consistent across age, gender and with or without fibrinolytics, and was observed as early as 24 hours.
De-escalationofP2Y12 Inhibitor Agents in ACS
Switching from a more potent P2Y12 receptor inhibitor to clopidogrel in association with aspirin after acute phase in ACS has been evaluated in two randomized investigator-sponsored studies (ISS) - TOPIC and TROPICAL-ACS - with clinical outcome data.
The clinical benefit provided by the more potent P2Y12 inhibitors, ticagrelor and prasugrel, in their pivotal studies is related to a significant reduction in recurrent ischaemic events (including acute and subacute stent thrombosis (ST), myocardial infarction (MI), and urgent revascularization). Although the ischaemic benefit was consistent throughout the first year, greater reduction in ischaemic recurrence after ACS was observed during the initial days following the treatment initiation. In contrast, post-hoc analyses demonstrated statistically significant increases in the bleeding risk with the more potent P2Y12 inhibitors, occurring predominantly during the maintenance phase, after the first month post- ACS. TOPIC and TROPICAL-ACS were designed to study how to mitigate the bleeding events while maintaining efficacy.
TOPIC (Timing Of Platelet Inhibition after acute Coronary syndrome)
This randomized, open-label trial included ACS patients requiring PCI. Patients on aspirin and a more potent P2Y12 blocker and without adverse event at one month were assigned to switch to fixed-dose aspirin plus clopidogrel (de- escalated dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT)) or continuation of their drug regimen (unchanged DAPT).
Overall, 645 of 646 patients with STEMI or NSTEMI or unstable angina were analyzed (de-escalated DAPT (n=322); unchanged DAPT (n=323)). Follow-up at one year was performed for 316 patients (98.1%) in the de-escalated DAPT group and 318 patients (98.5%) in the unchanged DAPT group. The median follow-up for both groups was 359 days. The characteristics of the studied cohort were similar in the 2 groups.
The primary outcome, a composite of cardiovascular death, stroke, urgent revascularization, and BARC (Bleeding Academic Research Consortium) bleeding ≥2 at 1-year post ACS, occurred in 43 patients (13.4%) in the de-escalated DAPT group and in 85 patients (26.3%) in the unchanged DAPT group (p<0.01). This statistically significant difference was mainly driven by fewer bleeding events, with no difference reported in ischaemic endpoints (p=0.36), while BARC ≥2 bleeding occurred less frequently in the de-escalated DAPT group (4.0%) versus 14.9% in the unchanged DAPT group (p<0.01). Bleeding events defined as all BARC occurred in 30 patients (9.3%) in the de-escalated DAPT group and in 76 patients (23.5%) in the unchanged DAPT group (p<0.01).
TROPICAL-ACS (Testing Responsiveness to Platelet Inhibition on Chronic Antiplatelet Treatment for Acute Coronary Syndromes)
This randomized, open-label trial included 2,610 biomarker-positive ACS patients after successful PCI. Patients were randomized to receive either prasugrel 5 or 10 mg/d (Days 0-14) (n=1309), or prasugrel 5 or 10 mg/d (Days 0-7) then de- escalated to clopidogrel 75 mg/d (Days 8-14) (n=1309), in combination with ASA (<100 mg/day). At Day 14, platelet function testing (PFT) was performed. The prasugrel-only patients were continued on prasugrel for 11.5 months.
The de-escalated patients underwent high platelet reactivity (HPR) testing. If HPR≥46 units, the patients were escalated back to prasugrel 5 or 10 mg/d for 11.5 months; if HPR<46 units, the patients continued on clopidogrel 75 mg/d for 11.5 months. Therefore, the guided de-escalation arm had patients on either prasugrel (40%) or clopidogrel (60%). All patients were continued on aspirin and were followed for one year.
The primary endpoint (the combined incidence of CV death, MI, stroke and BARC bleeding grade ≥2 at 12 months) was met showing non-inferiority. Ninety-five patients (7%) in the guided de-escalation group and 118 patients (9%) in the control group (p non-inferiority=0.0004) had an event. The guided de-escalation did not result in an increased combined risk of ischemic events (2.5% in the de-escalation group vs 3.2% in the control group; p non-inferiority=0.0115), nor in the key secondary endpoint of BARC bleeding ≥2 ((5%) in the de-escalation group versus 6% in the control group (p=0.23)). The cumulative incidence of all bleeding events (BARC class 1 to 5) was 9% (114 events) in the guided de- escalation group versus 11% (137 events) in the control group (p=0.14).
Atrial fibrillation
The ACTIVE-W and ACTIVE-A studies, separate trials in the ACTIVE program, included patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) who had at least one risk factor for vascular events. Based on enrollment criteria, physicians enrolled patients in ACTIVE-W if they were candidates for vitamin K antagonist (VKA) therapy (such as warfarin). The ACTIVE-A study included patients who could not receive VKA therapy because they were unable or unwilling to receive the treatment.
The ACTIVE-W study demonstrated that anticoagulant treatment with vitamin K antagonists was more effective than with clopidogrel and ASA.
The ACTIVE-A study (N=7,554) was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study which compared clopidogrel 75 mg/day + ASA (N=3,772) to placebo + ASA (N=3,782). The recommended dose for ASA was 75 to 100 mg/day. Patients were treated for up to 5 years.
Patients randomized in the ACTIVE program were those presenting with documented AF, i.e., either permanent AF or at least 2 episodes of intermittent AF in the past 6 months, and had at least one of the following risk factors: age ≥ 75 years or age 55 to 74 years and either diabetes mellitus requiring drug therapy, or documented previous MI or documented coronary artery disease; treated for systemic hypertension; prior stroke, transient ischaemic attack (TIA), or non-CNS systemic embolus; left ventricular dysfunction with left ventricular ejection fraction <45%; or documented peripheral vascular disease. The mean CHADS2 score was 2.0 (range 0 -6).
The major exclusion criteria for patients were documented peptic ulcer disease within the previous 6 months; prior intracerebral hemorrhage; significant thrombocytopenia (platelet count < 50 x 109/l); requirement for clopidogrel or oral anticoagulants (OAC); or intolerance to any of the two compounds.
Seventy-three percent (73%) of patients enrolled into the ACTIVE-A study were unable to take VKA due to physician assessment, inability to comply with INR (international normalised ratio) monitoring, predisposition to falling or head trauma, or specific risk of bleeding; for 26% of the patients, the physician's decision was based on the patient's unwillingness to take VKA.
The patient population included 41.8 % women. The mean age was 71 years, 41.6% of patients were ≥75 years. A total of 23.0% of patients received anti-arrhythmics, 52.1% beta-blockers, 54.6% ACE inhibitors, and 25.4% statins.
The number of patients who reached the primary endpoint (time to first occurrence of stroke, MI, non-CNS systemic embolism or vascular death) was 832 (22.1%) in the group treated with clopidogrel + ASA and 924 (24.4%) in the placebo + ASA group (relative risk reduction of 11.1%; 95% CI of 2.4% to 19.1%; p=0.013), primarily due to a large reduction in the incidence of strokes. Strokes occurred in 296 (7.8%) patients receiving clopidogrel + ASA and 408 (10.8%) patients receiving placebo + ASA (relative risk reduction, 28.4%; 95% CI, 16.8% to 38.3%; p=0.00001).
Paediatric population
In a dose escalation study of 86 neonates or infants up to 24 months of age at risk for thrombosis (PICOLO), clopidogrel was evaluated at consecutive doses of 0.01, 0.1 and 0.2 mg/kg in neonates and infants and 0.15 mg/kg only in neonates. The dose of 0.2 mg/kg achieved the mean percent inhibition of 49.3% (5 µM ADP-induced platelet aggregation) which was comparable to that of adults taking Plavix 75 mg/day.
In a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group study (CLARINET), 906 paediatric patients (neonates and infants) with cyanotic congenital heart disease palliated with a systemic-to-pulmonary arterial shunt were randomised to receive clopidogrel 0.2 mg/kg (n=467) or placebo (n=439) along with concomitant background therapy up to the time of second stage surgery. The mean time between shunt palliation and first administration of study medicinal product was 20 days. Approximately 88% of patients received concomitant ASA (range of 1 to 23 mg/kg/day). There was no significant difference between groups in the primary composite endpoint of death, shunt thrombosis or cardiac-related intervention prior to 120 days of age following an event considered of thrombotic nature (89 [19.1%] for the clopidogrel group and 90 [20.5%] for the placebo group). Bleeding was the most frequently reported adverse reaction in both clopidogrel and placebo groups; however, there was no significant difference in the bleeding rate between groups. In the long-term safety follow-up of this study, 26 patients with the shunt still in place at one year of age received clopidogrel up to 18 months of age. No new safety concerns were noted during this long-term follow-up.
The CLARINET and the PICOLO trials were conducted using a constituted solution of clopidogrel. In a relative bioavailability study in adults, the constituted solution of clopidogrel showed a similar extent and slightly higher rate of absorption of the main circulating (inactive) metabolite compared to the authorised tablet.
2. Pharmacokinetic properties
ROSUVASTATIN
Absorption: Maximum rosuvastatin plasma concentrations are achieved approximately 5 hours after oral administration. The absolute bioavailability is approximately 20%.
Distribution: Rosuvastatin is taken up extensively by the liver which is the primary site of cholesterol synthesis and LDL-C clearance. The volume of distribution of rosuvastatin is approximately 134 L. Approximately 90% of rosuvastatin is bound to plasma proteins, mainly to albumin.
Metabolism: Rosuvastatin undergoes limited metabolism (approximately 10%). In vitro metabolism studies using human hepatocytes indicate that rosuvastatin is a poor substrate for cytochrome P450-based metabolism. CYP2C9 was the principal isoenzyme involved, with 2C19, 3A4 and 2D6 involved to a lesser extent. The main metabolites identified are the N-desmethyl and lactone metabolites. The N-desmethyl metabolite is approximately 50% less active than rosuvastatin whereas the lactone form is considered clinically inactive. Rosuvastatin accounts for greater than 90% of the circulating HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor activity.
Excretion: Approximately 90% of the rosuvastatin dose is excreted unchanged in the faeces (consisting of absorbed and non-absorbed active substance) and the remaining part is excreted in urine. Approximately 5% is excreted unchanged in urine. The plasma elimination half-life is approximately 19 hours. The elimination half-life does not increase at higher doses. The geometric mean plasma clearance is approximately 50 litres/hour (coefficient of variation 21.7%). As with other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, the hepatic uptake of rosuvastatin involves the membrane transporter OATP-C. This transporter is important in the hepatic elimination of rosuvastatin.
Linearity: Systemic exposure of rosuvastatin increases in proportion to dose. There are no changes in pharmacokinetic parameters following multiple daily doses.
Special populations:
Age and sex: There was no clinically relevant effect of age or sex on the pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin in adults. The exposure in children and adolescents with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia appears to be similar to or lower than that in adult patients with dyslipidaemia.
Race: Pharmacokinetic studies show an approximate 2-fold elevation in median AUC and Cmax in Asian subjects (Japanese, Chinese, Filipino, Vietnamese and Koreans) compared with Caucasians; Asian-Indians show an approximate 1.3-fold elevation in median AUC and Cmax. A population pharmacokinetic analysis revealed no clinically relevant differences in pharmacokinetics between Caucasian and Black groups.
Renal insufficiency: In a study in subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment, mild to moderate renal disease had no influence on plasma concentration of rosuvastatin or the N-desmethyl metabolite. Subjects with severe impairment (CrCl <30 ml/min) had a 3-fold increase in plasma concentration and a 9-fold increase in the N-desmethyl metabolite concentration compared to healthy volunteers. Steady-state plasma concentrations of rosuvastatin in subjects undergoing haemodialysis were approximately 50% greater compared to healthy volunteers.
Hepatic insufficiency: In a study with subjects with varying degrees of hepatic impairment, there was no evidence of increased exposure to rosuvastatin in subjects with Child-Pugh scores of 7 or below. However, two subjects with Child-Pugh scores of 8 and 9 showed an increase in systemic exposure of at least 2-fold compared to subjects with lower Child-Pugh scores. There is no experience in subjects with Child-Pugh scores above 9.
Genetic polymorphisms: Disposition of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, including rosuvastatin, involves OATP1B1 and BCRP transporter proteins. In patients with SLCO1B1 (OATP1B1) and/or ABCG2 (BCRP) genetic polymorphisms there is a risk of increased rosuvastatin exposure. Individual polymorphisms of SLCO1B1 c.521CC and ABCG2 c.421AA are associated with a higher rosuvastatin exposure (AUC) compared to the SLCO1B1 c.521TT or ABCG2 c.421CC genotypes. This specific genotyping is not established in clinical practice, but for patients who are known to have these types of polymorphisms, a lower daily dose of rosuvastatin is recommended.
ASPIRIN
Absorption
After oral administration, acetylsalicylic acid is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. However, a significant portion of the dosage is already hydrolysed to salicylic acid in the intestinal wall during the absorption process.
Distribution
Acetylsalicylic acid as well as the main metabolite salicylic acid, are extensively bound to plasma proteins, primarily albumin, and distributed rapidly into all parts of the body. Maximum plasma concentration is reached after 0.3 - 2 hours (total salicylate). The volume of distribution of acetylsalicylic acid is ca. 0.16 l/kg of body weight.
Biotransformation
Acetylsalicylic acid is rapidly metabolised to salicylic acid, with a half-life of 15-30 minutes. Salicylic acid is subsequently predominantly converted into glycine and glucuronic acid conjugates.
Elimination kinetics of salicylic acid is dose-dependent, because the metabolism is limited by liver enzyme capacity. Thus, elimination half-time varies and is 2-3 hours after low doses (75 mg – 160 mg).
Excretion
Salicylic acid and its metabolites are predominantly excreted via the kidneys.
CLOPIDOGREL
Absorption
After single and repeated oral doses of 75 mg per day, clopidogrel is rapidly absorbed. Mean peak plasma levels of unchanged clopidogrel (approximately 2.2-2.5 ng/ml after a single 75 mg oral dose) occurred approximately 45 minutes after dosing. Absorption is at least 50%, based on urinary excretion of clopidogrel metabolites.
Distribution
Clopidogrel and the main circulating (inactive) metabolite bind reversibly in vitro to human plasma proteins (98% and 94% respectively). The binding is non-saturable in vitro over a wide concentration range.
Biotransformation
Clopidogrel is extensively metabolised by the liver. In vitro and in vivo, clopidogrel is metabolised according to two main metabolic pathways: one mediated by esterases and leading to hydrolysis into its inactive carboxylic acid derivative (85% of circulating metabolites), and one mediated by multiple cytochromes P450. Clopidogrel is first metabolised to a 2-oxo-clopidogrel intermediate metabolite. Subsequent metabolism of the 2-oxo-clopidogrel intermediate metabolite results in formation of the active metabolite, a thiol derivative of clopidogrel. The active metabolite is formed mostly by CYP2C19 with contributions from several other CYP enzymes, including CYP1A2, CYP2B6 and CYP3A4. The active thiol metabolite which has been isolated in vitro, binds rapidly and irreversibly to platelet receptors, thus inhibiting platelet aggregation.
The Cmax of the active metabolite is twice as high following a single 300-mg clopidogrel loading dose as it is after four days of 75-mg maintenance dose. Cmax occurs approximately 30 to 60 minutes after dosing.
Elimination
Following an oral dose of 14C-labelled clopidogrel in man, approximately 50% was excreted in the urine and approximately 46% in the faeces in the 120-hour interval after dosing. After a single oral dose of 75 mg, clopidogrel has a half-life of approximately 6 hours. The elimination half-life of the main circulating (inactive) metabolite was 8 hours after single and repeated administration.
Pharmacogenetics
CYP2C19 is involved in the formation of both the active metabolite and the 2-oxo-clopidogrel intermediate metabolite. Clopidogrel active metabolite pharmacokinetics and antiplatelet effects, as measured by ex vivo platelet aggregation assays, differ according to CYP2C19 genotype.
The CYP2C19*1 allele corresponds to fully functional metabolism while the CYP2C19*2 and CYP2C19*3 alleles are nonfunctional. The CYP2C19*2 and CYP2C19*3 alleles account for the majority of reduced function alleles in Caucasian (85%) and Asian (99%) poor metabolisers. Other alleles associated with absent or reduced metabolism are less frequent and include CYP2C19*4, *5, *6, *7, and *8. A patient with poor metaboliser status will possess two loss-of-function alleles as defined above. Published frequencies for the poor CYP2C19 metaboliser genotypes are approximately 2% for Caucasians, 4% for Blacks and 14% for Chinese. Tests are available to determine a patient's CYP2C19 genotype.
A crossover study in 40 healthy subjects, 10 each in the four CYP2C19 metaboliser groups (ultrarapid, extensive, intermediate and poor), evaluated pharmacokinetic and antiplatelet responses using 300 mg followed by 75 mg/day and 600 mg followed by 150 mg/day, each for a total of 5 days (steady state). No substantial differences in active metabolite exposure and mean inhibition of platelet aggregation (IPA) were observed between ultrarapid, extensive and intermediate metabolisers. In poor metabolisers, active metabolite exposure was decreased by 63-71% compared to extensive metabolisers. After the 300 mg/75 mg dose regimen, antiplatelet responses were decreased in the poor metabolisers with mean IPA (5 μM ADP) of 24% (24 hours) and 37% (Day 5) as compared to IPA of 39% (24 hours) and 58% (Day 5) in the extensive metabolisers and 37% (24 hours) and 60% (Day 5) in the intermediate metabolisers. When poor metabolisers received the 600 mg/150 mg regimen, active metabolite exposure was greater than with the 300 mg/75 mg regimen. In addition, IPA was 32% (24 hours) and 61% (Day 5), which were greater than in the poor metabolisers receiving the 300 mg/75 mg regimen, and were similar to the other CYP2C19 metaboliser groups receiving the 300 mg/75 mg regimen. An appropriate dose regimen for this patient population has not been established in clinical outcome trials.
Consistent with the above results, in a meta-analysis including 6 studies of 335 clopidogrel-treated subjects at steady state, it was shown that active metabolite exposure was decreased by 28% for intermediate metabolisers, and 72% for poor metabolisers while platelet aggregation inhibition (5 μM ADP) was decreased with differences in IPA of 5.9% and 21.4%, respectively, when compared to extensive metabolisers.
The influence of CYP2C19 genotype on clinical outcomes in patients treated with clopidogrel has not been evaluated in prospective, randomised, controlled trials. There have been a number of retrospective analyses, however, to evaluate this effect in patients treated with clopidogrel for whom there are genotyping results: CURE (n=2721), CHARISMA (n=2428), CLARITY-TIMI 28 (n=227), TRITON-TIMI 38 (n=1477), and ACTIVE-A (n=601), as well as a number of published cohort studies.
In TRITON-TIMI 38 and 3 of the cohort studies (Collet, Sibbing, Giusti) the combined group of patients with either intermediate or poor metaboliser status had a higher rate of cardiovascular events (death, myocardial infarction, and stroke) or stent thrombosis compared to extensive metabolisers.
In CHARISMA and one cohort study (Simon), an increased event rate was observed only in poor metabolisers when compared to extensive metabolisers.
In CURE, CLARITY, ACTIVE-A and one of the cohort studies (Trenk), no increased event rate was observed based on metaboliser status.
None of these analyses were adequately sized to detect differences in outcome in poor metabolisers.
Special populations
The pharmacokinetics of the active metabolite of clopidogrel is not known in these special populations.
Renal impairment
After repeated doses of 75 mg clopidogrel per day in subjects with severe renal disease (creatinine clearance from 5 to 15 ml/min), inhibition of ADP-induced platelet aggregation was lower (25%) than that observed in healthy subjects, however, the prolongation of bleeding time was similar to that seen in healthy subjects receiving 75 mg of clopidogrel per day. In addition, clinical tolerance was good in all patients.
Hepatic impairment
After repeated doses of 75 mg clopidogrel per day for 10 days in patients with severe hepatic impairment, inhibition of ADP-induced platelet aggregation was similar to that observed in healthy subjects. The mean bleeding time prolongation was also similar in the two groups.
Race
The prevalence of CYP2C19 alleles that result in intermediate and poor CYP2C19 metabolism differs according to race/ethnicity (see Pharmacogenetics). From literature, limited data in Asian populations are available to assess the clinical implication of genotyping of this CYP on clinical outcome events.
6. Nonclinical properties
ROSUVASTATIN
Preclinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety pharmacology, genotoxicity and carcinogenicity potential. Specific tests for effects on hERG have not been evaluated. Adverse reactions not observed in clinical studies, but seen in animals at exposure levels similar to clinical exposure levels were as follows: In repeated-dose toxicity studies histopathologic liver changes likely due to the pharmacologic action of rosuvastatin were observed in mouse, rat, and to a lesser extent with effects in the gall bladder in dogs, but not in monkeys. In addition, testicular toxicity was observed in monkeys and dogs at higher dosages. Reproductive toxicity was evident in rats, with reduced litter sizes, litter weight and pup survival observed at maternally toxic doses, where systemic exposures were several times above the therapeutic exposure level.
ASPIRIN
The nonclinical safety profile of acetylsalicylic acid is well documented.
In experimental animal studies, salicylates have shown no other organ injury than renal damage. In rat studies, fetotoxicity and teratogenic effects were observed with acetylsalicylic acid at maternotoxic doses. Clinical relevance is unknown as the doses used in non-clinical studies are much higher (7 times at least) than the maximal recommended doses in targeted cardiovascular indications. Acetylsalicylic acid was extensively investigated with regard to mutagenic and carcinogenic effects. The results as a whole show no relevant signs for any mutagenic or carcinogenic effects in mice and rat studies.
CLOPIDOGREL
During non-clinical studies in rat and baboon, the most frequently observed effects were liver changes. These occurred at doses representing at least 25 times the exposure seen in humans receiving the clinical dose of 75 mg/day and were a consequence of an effect on hepatic metabolising enzymes. No effect on hepatic metabolising enzymes was observed in humans receiving clopidogrel at the therapeutic dose.
At very high doses, a poor gastric tolerability (gastritis, gastric erosions and/or vomiting) of clopidogrel was also reported in rat and baboon.
There was no evidence of carcinogenic effect when clopidogrel was administered for 78 weeks to mice and 104 weeks to rats when given at doses up to 77 mg/kg per day (representing at least 25 times the exposure seen in humans receiving the clinical dose of 75 mg/day).
Clopidogrel has been tested in a range of in vitro and in vivo genotoxicity studies, and showed no genotoxic activity.
Clopidogrel was found to have no effect on the fertility of male and female rats and was not teratogenic in either rats or rabbits. When given to lactating rats, clopidogrel caused a slight delay in the development of the offspring. Specific pharmacokinetic studies performed with radiolabelled clopidogrel have shown that the parent compound or its metabolites are excreted in the milk. Consequently, a direct effect (slight toxicity), or an indirect effect (low palatability) cannot be excluded.
7. Description
REVOSTAT GOLD® is a fixed dose combination of Rosuvastatin, Aspirin, and Clopidogrel. Rosuvastatin acts as a selective and competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme that converts 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A to mevalonate, a precursor of cholesterol. Aspirin [acetylsalicylic acid (ASA)] inhibits prostaglandin synthesis resulting in inhibition of platelet aggregation. Clopidogrel is an inhibitor of platelet activation and aggregation through the irreversible binding of its active metabolite to the P2Y12 class of ADP receptors on platelets. Each hard gelatin capsule contains Rosuvastatin (10 mg) + Aspirin (75 mg) + Clopidogrel (75 mg) IP + Excipient (q.s).
Chemical structure of Rosuvastatin
Chemical structure of Aspirin
Chemical structure of Clopidogrel
8. Pharmaceutical particulars
1. Incompatibilities
None
2. Shelf-life
Refer on pack
3. Packaging information
10 capsules per strip
4. Storage and handing instructions
Store below 300c. Protect from light.
Keep out of reach of children.
9. Patient Counselling Information
ROSUVASTATIN
Skeletal Muscle Effects
Patients should be advised to report promptly unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness, particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever.
Concomitant Use of Antacids
When taking CRESTOR with an aluminum and magnesium hydroxide combination antacid, the antacid should be taken at least 2 hours after CRESTOR administration.
Pregnancy
If the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus and the lack of known clinical benefit with continued use during pregnancy.
Liver Enzymes
It is recommended that liver enzymes be checked before and at 12 weeks following both the initiation of therapy and any elevation of dose, and periodically (e.g., semiannually) thereafter.
ASPIRIN
Bleeding
Inform patients that they may bruise or bleed more easily or that it may take longer to stop bleeding and to report to their physician any prolonged, unusual or excessive bleeding. Inform patients to notify their physician about blood in their stool or urine and the signs and symptoms of occult bleeding.
Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of GI side effects and seek medical advice when experiencing any of these signs and symptoms.
Hypersensitivity
Advise the patient to discontinue aspirin and seek immediate medical attention if any signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction occur.
Alcohol Consumption
Inform patients they should not take aspirin 2 hours before or 1 hour after consuming alcohol. Counsel patients who drink three or more alcoholic drinks every day about the risk of bleeding involved in chronic, heavy alcohol use while taking aspirin.
Administration Instructions
Advise patients to swallow aspirin capsules whole and not to chew or crush them.
Remind patients not to discontinue aspirin without first notifying and discussing with their physician. Advise patients not to use extra medicine to make up a missed dose. Advise patients not to take ibuprofen around the same time as aspirin.
Pregnancy and Lactation
Advise patients that ASA containing products such as aspirin cause harm to fetuses especially during the third trimester of pregnancy. Inform patients to notify their physician if they are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, breastfeed or are considering breastfeeding prior or during receiving treatment with aspirin.
CLOPIDOGREL
Benefits and Risks
Summarize the effectiveness features and potential side effects of Plavix.
Tell patients to take clopidogrel exactly as prescribed.
Remind patients not to discontinue clopidogrel without first discussing it with the physician who prescribed clopidogrel.
Bleeding
Inform patients that they:
- -will bruise and bleed more easily.
- -will take longer than usual to stop bleeding.
- -should report any unanticipated, prolonged, or excessive bleeding, or blood in their stool or urine.
Other Signs and Symptoms Requiring Medical Attention
Inform patients that TTP is a rare but serious condition that has been reported with clopidogrel and other drugs in this class of drugs.
Instruct patients to get prompt medical attention if they experience any of the following symptoms that cannot otherwise be explained: fever, weakness, extreme skin paleness, purple skin patches, yellowing of the skin or eyes, or neurological changes.
12. Date of revision
16th Jan 2025
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1. What REVOSTAT GOLD® is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you are given REVOSTAT GOLD®
3. How REVOSTAT GOLD® is given
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store REVOSTAT GOLD® capsules
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What REVOSTAT GOLD® is and what it is used for
REVOSTAT GOLD® is a capsule that contains:
Rosuvastatin which belongs to a group of medicines called statins, which act to decrease the blood cholesterol levels.
Aspirin contains acetylsalicylic acid, which in low doses belong to a group of medicines called anti-platelet agents. Platelets are tiny cells in the blood that cause the blood to clot and are involved in thrombosis. When a blood clot occurs in an artery it stops the blood flowing and cuts off the oxygen supply. When this happens in the heart it can cause a heart attack or angina; in the brain it can cause a stroke.
Clopidogrel belongs to a group of medicines called antiplatelet medicinal products. Platelets clump together during blood clotting. By preventing this clumping, antiplatelet medicinal products reduce the chances of blood clots forming (a process called thrombosis).
REVOSTAT GOLD® is used in adults to treat high cholesterol associated with atherosclerotic arterial disease with risk of heart attack, stroke and other problems.
Atherosclerosis is due to build-up of fatty deposits in your arteries.
2. What you need to know before you take REVOSTAT GOLD® Capsule
Do not take REVOSTAT GOLD®:
- If you have ever had an allergic reaction to any of its ingredients.
- If you are allergic to other salicylates or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAIDs are often used for arthritis or rheumatism and pain
- If you are pregnant or breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking REVOSTAT GOLD®, stop taking it immediately and tell your doctor. Women should avoid becoming pregnant while taking REVOSTAT GOLD® by using suitable contraception.
- If you have liver disease.
- If you have severe kidney problems.
- If you have repeated or unexplained muscle aches or pains.
- If you take a drug combination of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir (used for viral infection of the liver called hepatitis C).
- If you take a drug called ciclosporin (used, for example, after organ transplants).
- If you have had an asthma attack or swelling of some parts of the body e.g. face, lips, throat or tongue (angioedema) after taking salicylates or NSAIDs
- If you currently have or have ever had an ulcer in your stomach or small intestine or any other type of bleeding like a stroke
- If you have ever had the problem of your blood not clotting properly
- If you suffer from gout
If you are taking a medicine called methotrexate (e.g. for cancer or rheumatoid arthritis) in doses higher than 15mg per week.
If any of the above applies to you (or you are in doubt), please go back and see your doctor.
REVOSTAT GOLD® with alcohol
Drinking alcohol may possibly increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding and prolong bleeding time.
Other medicines and REVOSTAT GOLD® Capsule
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
ROSUVASTATIN
Tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following:
- ciclosporin (used for example, after organ transplants),
- warfarin or clopidogrel (or any other drug used for thinning the blood),
- fibrates (such as gemfibrozil, fenofibrate) or any other medicine used to lower cholesterol (such as ezetimibe),
- indigestion remedies (used to neutralise acid in your stomach),
- erythromycin (an antibiotic), fusidic acid (an antibiotic),
- an oral contraceptive (the pill),
- regorafenib (used to treat cancer),
- darolutamide (used to treat cancer),
- hormone replacement therapy,
- any of the following drugs used to treat viral infections, including HIV or hepatitis C infection, alone or in combination (please see Warnings and precautions): ritonavir, lopinavir, atazanavir, sofosbuvir, voxilaprevir, ombitasvir, paritaprevir, dasabuvir, velpatasvir, grazoprevir, elbasvir, glecaprevir, pibrentasvir.
The effects of these medicines could be changed by REVOSTAT GOLD® or they could change the effect of REVOSTAT GOLD®.
If you need to take oral fusidic acid to treat a bacterial infection you will need to temporarily stop using this medicine. Your doctor will tell you when it is safe to restart REVOSTAT GOLD®. Taking REVOSTAT GOLD® with fusidic acid may rarely lead to muscle weakness, tenderness or pain (rhabdomyolysis).
ASPIRIN
The effect of treatment may be influenced if acetylsalicylic acid is taken at the same time as some other medicines for:
- thinning of the blood/prevention of clots (e.g. warfarin, heparin, clopidogrel)
- rejection of organ after transplantation (ciclosporin, tacrolimus)
- high blood pressure (e.g. diuretics and ACE-inhibitors)
- regulation of the heart beat (digoxin)
- manic-depressive illness (lithium)
- pain and inflammation (e.g. NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or steroids)
- gout (e.g. probenecid)
- glaucoma (acetazolamide)
- cancer or rheumatoid arthritis (methotrexate; in doses lower than 15mg per week)
- diabetes (e.g. glibenclamide)
- depression (selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs) such as sertraline or paroxetine)
- use as hormone replacement therapy when the adrenal glands or pituitary gland have been destroyed or removed, or to treat inflammation, including rheumatic diseases and inflammation of the intestines (corticosteroids)
- antacids (indigestion medicine)
- metamizole (substance to decrease pain and fever) may reduce the effect of acetylsalicylic acid on platelet aggregation (blood cells sticking together and forming a blood clot), when taken concomitantly. Therefore, this combination should be used with caution in patients taking low dose aspirin for cardioprotection.
CLOPIDOGREL
You should specifically tell your doctor if you take
- medicines that may increase your risk of bleeding such as:
- oral anticoagulants, medicines used to reduce blood clotting,
- a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicine, usually used to treat painful and/or inflammatory conditions of muscle or joints,
- heparin or any other injectable medicine used to reduce blood clotting,
- ticlopidine, other antiplatelet agent,
- a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (including but not restricted to fluoxetine or fluvoxamine), medicines usually used to treat depression,
- rifampicin (used to treat severe infections)
- omeprazole or esomeprazole, medicines to treat upset stomach,
- fluconazole or voriconazole, medicines to treat fungal infections,
- moclobemide, medicines to treat depression,
- efavirenz, or other anti-retroviral medicines (used to treat HIV infections),
- carbamazepine, a medicine to treat some forms of epilepsy,
- repaglinide, medicine to treat diabetes,
- paclitaxel, medicine to treat cancer.
- opioids: while you are treated with clopidogrel, you should inform your doctor before being
- prescribed any opioid (used to treat severe pain).
If you have experienced severe chest pain (unstable angina or heart attack), you may be prescribed clopidogrel tablets in combination with aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid), a substance present in many medicines used to relieve pain and lower fever. An occasional use of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) (no more than 1,000 mg in any 24 hour period) should generally not cause a problem, but prolonged use in other circumstances should be discussed with your doctor.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Do not take REVOSTAT GOLD® if you are pregnant or breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking REVOSTAT GOLD® stop taking it immediately and tell your doctor. Women should avoid becoming pregnant while taking REVOSTAT GOLD® by using suitable contraception.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking REVOSTAT GOLD®:
- If you have problems with your kidneys.
- If you have problems with your liver.
- If you have had repeated or unexplained muscle aches or pains, a personal or family history of muscle problems, or a previous history of muscle problems when taking other cholesterol-lowering medicines. Tell your doctor immediately if you have unexplained muscle aches or pains, especially if you feel unwell or have a fever. Also, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you have a muscle weakness that is constant.
- If you regularly drink large amounts of alcohol.
- If your thyroid gland is not working properly.
- If you take other medicines called fibrates to lower your cholesterol. Please read this leaflet carefully, even if you have taken other medicines for high cholesterol before.
- If you take medicines used to treat the HIV infection e.g. ritonavir with Lopinavir and/or atazanavir.
- If you are taking or have taken in the last 7 days a medicine called fusidic acid (a medicine for bacterial infection), orally or by injection. The combination of fusidic acid and REVOSTAT GOLD® can lead to serious muscle problems (rhabdomyolysis).
- If you are over 70 (as your doctor needs to choose the right start dose of REVOSTAT GOLD® to suit you).
- If you have severe respiratory failure.
- If you are of Asian origin – that is Japanese, Chinese, Filipino, Vietnamese, Korean and Indian. Your doctor needs to choose the right start dose of REVOSTAT GOLD® to suit you.
- If you have or have ever had problems with your stomach or small intestine
- If you have high blood pressure
- If you are asthmatic, have hay fever, nasal polyps or other chronic respiratory diseases;
- acetylsalicylic acid may induce an asthma attack
- If you have ever had gout
- If you have heavy menstrual periods
- If you have a risk of bleeding such as
- a medical condition that puts you at risk of internal bleeding (such as a stomach ulcer)
- a blood disorder that makes you prone to internal bleeding (bleeding inside any tissues, organs or joints of your body).
- a recent serious injury
- a recent surgery (including dental)
- a planned surgery (including dental) in the next seven days
- If you have had a clot in an artery of your brain (ischaemic stroke) which occurred within the last seven days
In a small number of people, statins can affect the liver. This is identified by a simple test which looks for increased levels of liver enzymes in the blood. For this reason, your doctor will usually carry out this blood test (liver function test) before and during treatment with REVOSTAT GOLD®.
You must immediately seek medical advice, if your symptoms get worse or if you experience severe or unexpected side effects e.g. unusual bleeding symptoms, serious skin reactions or any other sign of serious allergy.
Inform your doctor if you are planning to have an operation (even a minor one, such as tooth extraction) since acetylsalicylic acid is blood-thinning there may be an increased risk of bleeding.
Acetylsalicylic acid may cause Reye’s syndrome when given to children. Reye’s syndrome is a very rare disease which affects the brain and liver and can be life threatening. For this reason, Aspirin Tablets should not be given to children aged under 16 years, unless on the advice of a doctor.
You should take care not to become dehydrated (you may feel thirsty with a dry mouth) since the use of acetylsalicylic acid at the same time may result in deterioration of kidney function. This medicinal product is not suitable as a pain killer or fever reducer.
While you are on this medicine your doctor will monitor you closely if you have diabetes or are at risk of developing diabetes. You are likely to be at risk of developing diabetes if you have high levels of sugars and fats in your blood, are overweight and have high blood pressure. If you are not sure if any of the above apply to you, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
Children and adolescents
- If the patient is under 6 years old: REVOSTAT GOLD® should not be given to children younger than 6 years.
- If the patient is below 18 years of age: The REVOSTAT GOLD® is not suitable for use in children and adolescents below 18 years of age.
Driving and using machines
Most people can drive a car and operate machinery while using REVOSTAT GOLD® – it will not affect their ability. However, some people feel dizzy during treatment with REVOSTAT GOLD®. If you feel dizzy, consult your doctor before attempting to drive or use machines.
3. How to take REVOSTAT GOLD® Capsule
Always take this medicine as your doctor has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
Regular cholesterol checks
It is important to go back to your doctor for regular cholesterol checks, to make sure your cholesterol has reached and is staying at the correct level.
If you take more REVOSTAT GOLD® than you should
Contact your doctor or nearest hospital for advice.
If you go into hospital or receive treatment for another condition, tell the medical staff that you’re taking REVOSTAT GOLD®.
If you forget to take REVOSTAT GOLD®
Don’t worry, just take your next scheduled dose at the correct time. Do not take a double dose
to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop taking REVOSTAT GOLD®
Talk to your doctor if you want to stop taking REVOSTAT GOLD®. Your cholesterol levels might increase again if you stop taking REVOSTAT GOLD®.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
It is important that you are aware of what these side effects may be. They are usually mild and disappear after a short time.
ROSUVASTATIN
Stop taking REVOSTAT GOLD® and seek medical help immediately if you have any of the following allergic reactions:
- Difficulty in breathing, with or without swelling of the face, lips, tongue and/or throat.
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue and/or throat, which may cause difficulty in swallowing.
- Severe itching of the skin (with raised lumps).
Also, stop taking REVOSTAT GOLD® and talk to your doctor immediately:
- If you have any unusual aches or pains in your muscles which go on for longer than you might expect. Muscle symptoms are more common in children and adolescents than in adults. As with other statins, a very small number of people have experienced unpleasant muscle effects and rarely these have gone on to become a potentially life threatening muscle damage known as rhabdomyolysis.
- If you experience muscle rupture.
- If you have lupus-like disease syndrome (including rash, joint disorders and effects on blood cells).
Common possible side effects (these may affect between 1 in 10 and 1 in 100 patients):
- Headache, stomach pain, constipation, feeling sick, muscle pain, feeling weak, dizziness.
- An increase in the amount of protein in the urine - this usually returns to normal on its own without having to stop taking your REVOSTAT GOLD®.
- Diabetes. This is more likely if you have high levels of sugars and fats in your blood, are overweight and have high blood pressure. Your doctor will monitor you while you are taking this medicine.
Uncommon possible side effects (these may affect between 1 in 100 and 1 in 1,000 patients):
- Rash, itching or other skin reactions.
- An increase in the amount of protein in the urine - this usually returns to normal on its own without having to stop taking your REVOSTAT GOLD®.
Rare possible side effects (these may affect between 1 in 1,000 and 1 in 10,000 patients):
- Severe allergic reaction – signs include swelling of the face, lips, tongue and/or throat, difficulty in swallowing and breathing, a severe itching of the skin (with raised lumps). If you think you are having an allergic reaction, then stop taking REVOSTAT GOLD® and seek medical help immediately.
- Muscle damage in adults – as a precaution, stop taking REVOSTAT GOLD® and talk to your doctor immediately if you have any unusual aches or pains in your muscles which go on for longer than expected.
- A severe stomach pain (inflamed pancreas).
- ncrease in liver enzymes in the blood.
- Bleeding or bruising more easily than normal due to low level of blood platelets.
- Lupus-like disease syndrome (including rash, joint disorders and effects on blood cells).
Very rare possible side effects (these may affect less than 1 in 10,000 patients):
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), hepatitis (an inflamed liver), traces of blood in your urine, damage to the nerves of your legs and arms (such as numbness), joint pain, memory loss and breast enlargement in men (gynaecomastia).
Side effects of unknown frequency may include:
- Diarrhoea (loose stools), Stevens-Johnson syndrome (serious blistering condition of the skin, mouth, eyes and genitals), cough, shortness of breath, oedema (swelling), sleep disturbances, including insomnia and nightmares, sexual difficulties, depression, breathing problems, including persistent cough and/or shortness of breath or fever, tendon injury and muscle weakness that is constant.
ASPIRIN
If you notice any of the following serious side effects, stop taking REVOSTAT GOLD® and contact a doctor immediately:
- Sudden wheezing, swelling of your lips, face or body, rash, fainting or difficulties swallowing (severe allergic reaction).
- Reddening of the skin with blisters or peeling and may be associated with a high fever and joint pains. This could by erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome or Lyell’s syndrome.
- Unusual bleeding, such as coughing up blood, blood in your vomit or urine, or black stools.
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Indigestion.
- Increased tendency for bleeding.
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Hives.
- Runny noses.
- Breathing difficulty.
Rare side effects (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people):
- Severe bleeding in the stomach or intestines, brain haemorrhage; altered number of blood cells.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Cramps in the lower respiratory tract, asthma attack.
- Inflammation in the blood vessels.
- Bruising with purple spots (cutaneous bleeding).
- Severe skin reactions such as rash known as erythema multiforme and it’s life threatening forms Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Lyell’s syndrome.
- Hypersensitivity reactions, such as swelling of e.g. lips, face or body, or shock.
- Abnormal heavy or prolonged menstrual periods.
Side effects with unknown frequency (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- Ringing in your ears (tinnitus) or reduced hearing ability.
- Headache.
- Vertigo.
- Ulcers in stomach or small intestine and perforation.
- Prolonged bleeding time.
- Impaired kidney function.
- Salt or water retention which may cause swelling of hands, feet, legs, stomach, breasts or face.
- Impaired liver function.
- High level of uric acid in the blood.
CLOPIDOGREL
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience:
- Fever, signs of infection or extreme tiredness. These may be due to rare decrease of some blood cells.
- Signs of liver problems such as yellowing of the skin and/or the eyes (jaundice), whether or not associated with bleeding which appears under the skin as red pinpoint dots and/or confusion.
- Swelling in the mouth or skin disorders such as rashes and itching, blisters of the skin. These may be the signs of an allergic reaction.
The most common side effect reported with Clopidogrel tablet is bleeding.
Bleeding may occur as bleeding in the stomach or bowels, bruising, haematoma (unusual bleeding or bruising under the skin), nose bleed, blood in the urine. In a small number of cases, bleeding in the eye, inside the head, the lung or the joints has also been reported.
If you experience prolonged bleeding when taking Clopidogrel tablets:
If you cut or injure yourself, it may take longer than usual for bleeding to stop. This is linked to the way your medicine works as it prevents the ability of blood clots to form. For minor cuts and injuries e.g., cutting yourself, shaving, this is usually of no concern. However, if you are concerned by your bleeding, you should contact your doctor straightaway.
Other side effects include:
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
Diarrhoea, abdominal pain, indigestion or heartburn.
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
Headache, stomach ulcer, vomiting, nausea, constipation, excessive gas in stomach or intestines, rashes, itching, dizziness, sensation of tingling and numbness.
Rare side effect (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people):
Vertigo, enlarged breasts in males.
Very rare side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
Jaundice; severe abdominal pain with or without back pain; fever, breathing difficulties sometimes associated with cough; generalised allergic reactions (for example, overall sensation of heat with sudden general discomfort until fainting); swelling in the mouth; blisters of the skin; skin allergy; sore mouth (stomatitis); decrease in blood pressure; confusion; hallucinations; joint pain; muscular pain; changes in taste or loss of taste of food.
Side effects with frequency not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
Hypersensitivity reactions with chest or abdominal pain, persistent low blood sugar symptoms.
In addition, your doctor may identify changes in your blood or urine test results.
Reporting of side effects
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions
via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: Website: https://www.zuventus.co.in/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store REVOSTAT GOLD® Capsule
Store below 30°C.
Store in the original package.
Keep this medicine in a safe place out of the sight and reach of children, preferably in a locked cupboard.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the box/blisters/label after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What REVOSTAT GOLD® Capsule contains
REVOSTAT GOLD® 10
- Each hard gelatin capsule contains Rosuvastatin (10 mg) + Aspirin (75 mg) + Clopidogrel (75 mg) IP + Excipient (q.s).
REVOSTAT GOLD® 20
- Each hard gelatin capsule contains Rosuvastatin (20 mg) + Aspirin (75 mg) + Clopidogrel (75 mg) IP + Excipient (q.s).