Rifaximax Suspension
Therapy Area
Anti Infective
1.0 Generic name
Rifaximin Oral Suspension
2.0 Quantitative and qualitative composition
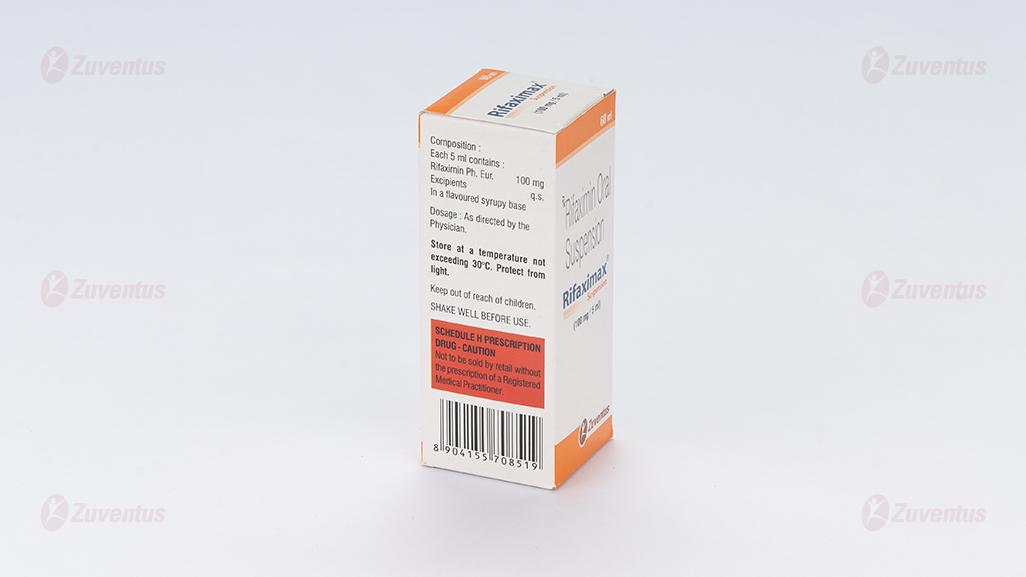
Each 5 ml contains :
Rifaximin IP 100 mg
Excipients q.s.
In a flavoured syrupy base
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Oral suspension (5 ml/100 mg)
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
Treatment of Infectious Diarrhoea in Adult and Children (>2years of age and above).
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Rifaximin suspension can be administered orally with or without food. It should be given in 2-4 divided dosage.
- For patients >12 years of age : The recommended dose is 200mg taken 3 times a day for 3 days.
- For patients 6-12 years of age : 400-800 mg/day for 3 days
- For patients 2-6 years of age : 20 ml/day for 3 days
Duration of the treatment should not exceed 7 days, [Ref: Robins GW, Wellington K. Rifaximin: a review of its use in the management of traveller's diarrhoea. Drugs. 2005;65(12):1697-713.
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to rifaximin, any of the rifamycin antimicrobial agents.
- Hypersensitivity reactions have included exfoliative dermatitis, angioneurotic edema, and anaphylaxis.
4.4 Warning and precautions
Rifaximin were not found to be effective in patients with diarrhea complicated by fever and/or blood in the stool or diarrhea due to pathogens other than Escherichia coli. Rifaximin suspension should not be used in patients where Campylobacter jejuni, Shigella spp., or Salmonella spp. may be suspected as causative pathogens. Rifaximin suspension should be discontinued if diarrhea symptoms get worse or persist more than 24-48 hours and alternative antibiotic therapy should be considered. Clostridium difficile -associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents including Rifaximin, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon which may lead to overgrowth of C. difficile. Studies indicate that a toxin produced by Clostridium difficile is the primary cause of CDAD. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhea subsequent to the administration of antibacterial agents. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over 2 months after the administration of antibacterial agents. If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
The use of antibiotics may promote the overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken. Rifaximin suspension should be discontinued if diarrhea persists more than 24-48 hours or worsens, or if patients have fever and/ or blood in the stool that they should seek medical care.
4.5 Drug interactions
In vitro studies have shown that Rifaximin did not inhibit cytochrome P450 isoenzymes 1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1 and CYP3A4 at concentrations ranging from 2 to 200 ng/mL. Rifaximin is not expected to inhibit these enzymes in clinical use. An in vitro study has suggested that Rifaximin induces CYP3A4. However, in patients with normal liver function, Rifaximin at the recommended dosing regimen is not expected to induce CYP3A4. It is unknown whether Rifaximin can have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of concomitant CYP3A4 substrates in patients with reduced liver function who have elevated Rifaximin concentrations. An in vitro study suggested that Rifaximin is a substrate of P-glycoprotein. It is unknown whether concomitant drugs that inhibit P-glycoprotein can increase the systemic exposure of Rifaximin. Two clinical drug-drug interaction studies using midazolam and an oral contraceptive containing ethinyl estradiol and norgestimate demonstrated that Rifaximin did not alter the pharmacokinetics of these drugs.
4.6 Special populations
Pregnancy category C
There are no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women. Rifaximin suspension should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
Lactation
It is not known whether Rifaximin is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for adverse reactions in nursing infants from Rifaximin suspension, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric use
The safety and effectiveness of Rifaximin suspension in pediatric patients less than 2 years of age have not been established.
Geriatric use
Clinical studies of Rifaximin suspension did not include sufficient number of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently than younger subjects.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Rifaximax suspension does not usually affect the ability to drive.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Some of the common side effects observed are : Nausea, Flatulence, Constipation, Vomiting, Pyrexia, Headache, Abdominal Pain, Rectal Tenesmus, Defecation Urgency etc. Some of the rare side effects (may or may not be associated with drug) observed in some patients are : lymphocytosis, neutropenia, tinnitus, motion sickness, loss of taste, hot flashes, edema, urticaria, pruritus etc.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com
Website : https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
No specific information is available on the treatment of overdosage with Rifaximin suspension. In clinical studies at doses higher than the recommended dose adverse events were similar to the recommended and to placebo. In the case of over-dosage, discontinue Rifaximin suspension, treat symptomatically, and institute supportive measures as required.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action / Pharmacodynamic properties
Rifaximin acts by binding to the beta-subunit of bacterial DNA dependent RNA polymerase resulting in inhibition of bacterial RNA synthesis. Escherichia coli have been shown to develop resistance to Rifaximin in vitro. However, the clinical significance of such an effect has not been studied. Rifaximin is a structural analog of rifampin. Organisms with high Rifaximin minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values also have elevated MIC values against rifampin. Cross-resistance between Rifaximin and other classes of antimicrobials has not been studied. Rifaximin has been shown to be active against the following pathogen in clinical studies of infectious diarrhea : Escherichia coli (enterotoxigenic and enteroaggregative strains).
Susceptibility Tests
In vitro susceptibility testing was performed according to the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS) agar dilution method M7-A6. However, the correlation between susceptibility testing and clinical outcome has not been determined.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption : Rifaximin can be administered with or without food. Systemic absorption of Rifaximin was low in both the fasting state and when administered within 30 minutes of a high-fat breakfast. Table 1 : Effect of Food on the Mean ± S.D. Pharmacokinetic Parameters Following a Single 400-mg Dose of Rifaximin
Systemic absorption of Rifaximin (200mg three times daily) was also evaluated in 13 subjects with shigellosis on Days 1 and 3 of a three-day course of treatment. Rifaximin concentrations and exposures were low and variable. There was no evidence of accumulation of Rifaximin following repeated administration for 3 days (9 doses). Peak plasma Rifaximin concentrations after 3 and 9 consecutive doses ranged from 0.81 to 3.4 ng/mL on Day 1 and 0.68 to 2.26 ng/mL on Day 3. Similarly, AUC0 last estimates were 6.95 ± 5.15 ngh/mL on Day1 and 7.83±4.94 ngh/mL on Day 3. Rifaximin is not suitable for treating systemic bacterial infections because less than 0.4% of the drug is absorbed after oral administration.
Distribution : Animals pharmacokinetic studies have demonstrated that 80% to 90% of orally administered Rifaximin is concentrated in the gut with less than 0.2% in the liver and kidney, and less than 0.01% in other tissues. In adults with infectious diarrhea treated with Rifaximin 800 mg daily for three days, concentrations of Rifaximin in stools averaged-8000 µg/g the day after treatment ended.
Metabolism and excretion : In a mass balance study, after administration of 400 mg 14C-Rifaximin orally to healthy volunteers, of the 96.94% total recovery, 96.62% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in feces almost exclusively as the unchanged drug and 0.32% was recovered in urine mostly as metabolites with 0.03% as the unchanged drug. Rifaximin accounted for 18% of radioactivity in plasma. This suggests that the absorbed Rifaximin undergoes metabolism with minimal renal excretion of the unchanged drug. The enzymes responsible for metabolizing Rifaximin are unknown.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
Carcinogenicity studies were not conducted. Rifaximin was not genotoxic in the bacterial reverse mutation assay, chromosomal aberration assay, rat bone marrow micronucleus assay, and the CHO/HGPRT mutation assay. There was no effect on fertility in male or female rats following the administration of Rifaximin at doses up to 300 mg/kg (approximately 5 times the clinical dose, adjusted for body surface area).
7.0 Description
Rifaximin, a non-aminoglycoside semi-synthetic, nonsystemic antibiotic derived from rifamycin SV. Rifaximin is a structural analog of rifampin.
Chemical name : (2S,16Z,18E,20S,21S,22R,23R,24R,25S,26S,27S, 28E)-5,6,21,23,25-pentahydroxy-27- methoxy2,4, 11,16,20,22,24, 26-octamethyl-2,7-(epoxypentadeca- [1,11,13] trienimino) benzofuro[4,5-e] pyrido[1,2-á] benzimidazole-1,15(2H)-dione, 25-acetate.
Molecular formula : C43H51N3O11
Molecular weight : 785.9 g/mol.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
A bottle of 60 ml.
8.4 Storage and handling instructions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30°C. Protect from light.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient counseling information
Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhea
Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including RIFAXIMAX SUSPENSION, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibiotics alters the normal flora of the colon which may lead to C. difficile. Patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If diarrhea occurs after therapy or does not improve or worsens during therapy, advise patients to contact a physician as soon as possible
Administration with Food
Inform patients that Rifaximax suspension may be taken with or without food.
Antibacterial Resistance
Counsel patients that antibacterial drugs including RIFAXIMAX SUSPENSION should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When RIFAXIMAX SUSPENSION is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by RIFAXIMAX SUSPENSION or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
12.0 Date of revision
26 August 2024
About Leaflet
Please read this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet
- What Rifaximin Oral Suspension is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you take Rifaximin Oral Suspension
- How to take Rifaximin Oral Suspension
- Possible side effects
- How to store Rifaximin Oral Suspension
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Rifaximin Oral Suspension is and what it is used for
Rifaximin Oral Suspension contains the active substance rifaximin, which is an antibiotic. It is used to treat infectious diarrhea caused by certain bacteria (Escherichia coli) in adults and children over 2 years of age.
2. What you need to know before you take Rifaximin Oral Suspension
Do not take Rifaximin Oral Suspension if:
- You are allergic to rifaximin, any of the rifamycin antibiotics, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
- You have a fever or blood in your stools.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Rifaximin Oral Suspension if:
- You have severe diarrhea with fever or blood in the stools.
- You have diarrhea caused by other bacteria such as Campylobacter, Shigella, or Salmonella.
- You have liver problems.
Other medicines and Rifaximin Oral Suspension
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines. This includes medicines obtained without a prescription and herbal medicines.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Rifaximin Oral Suspension is not expected to affect your ability to drive or use machines.
Warnings and precautions
- Effectiveness has been evaluated in patients with various gastrointestinal disorders including IBS, pouchitis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, hepatic disorders, and radiation-induced diarrhoea.
- Avoid taking Rifaximax suspension with antibiotics as they may inactivate some bacterial strains in Rifaximax suspension.
3. How to take Rifaximin Oral Suspension
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
The recommended dose is:
- Adults and children over 12 years: 200 mg (10 ml) three times a day for 3 days.
- Children 6-12 years: 400-800 mg/day for 3 days.
- Children 2-6 years: 20 ml/day for 3 days.
Shake the bottle well before use. You can take Rifaximin Oral Suspension with or without food.
If you use more Rifaximax suspension than you should
Tell your doctor if you accidentally use more than you were told.
If you forget to use Rifaximax suspension
If you forget to take at the right time, use it as soon as you remember, then carry on as before. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop using Rifaximax suspension
Do not stop your treatment even if you feel better unless told to do so by your doctor. If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Nausea
- Flatulence
- Constipation
- Vomiting
- Fever
- Headache
- Abdominal pain
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Drug Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page. Website link: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Rifaximax suspension
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- Store at a temperature not exceeding 30°C. Protect from light.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the bottle and carton after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
- Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Rifaximin Oral Suspension contains:
- The active substance is rifaximin. Each 5 ml of oral suspension contains 100 mg of rifaximin.
Revised on 11/24