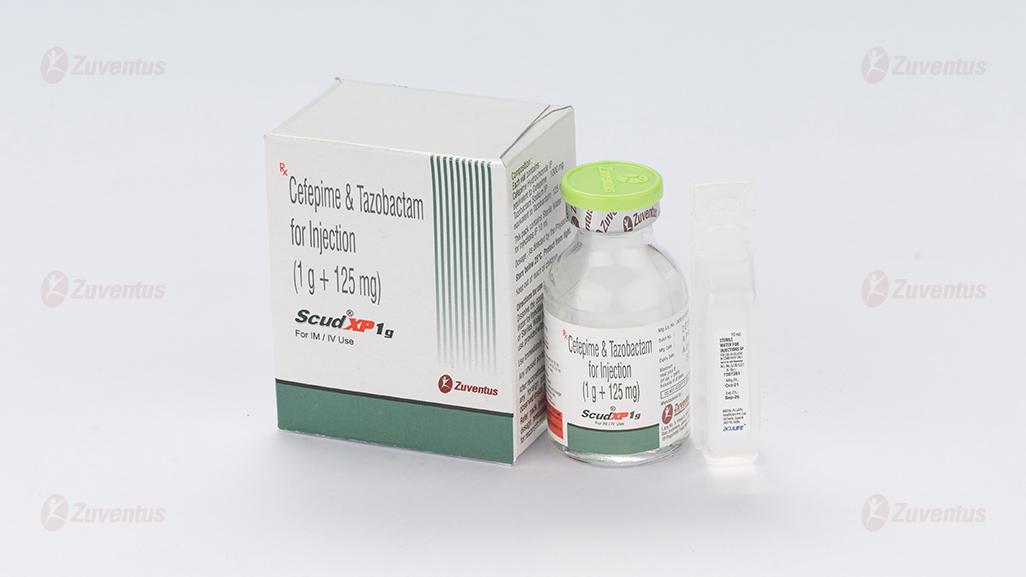
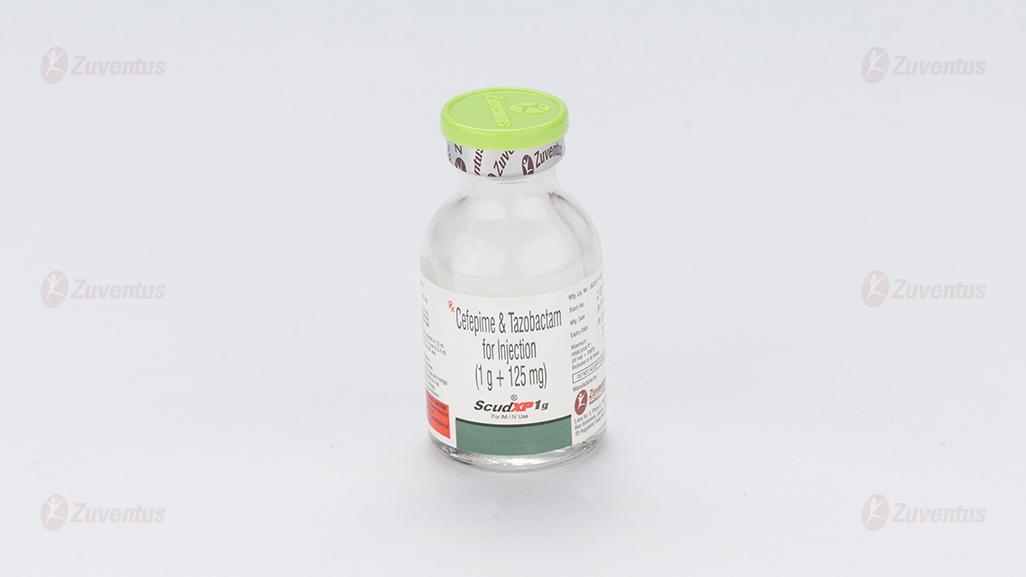
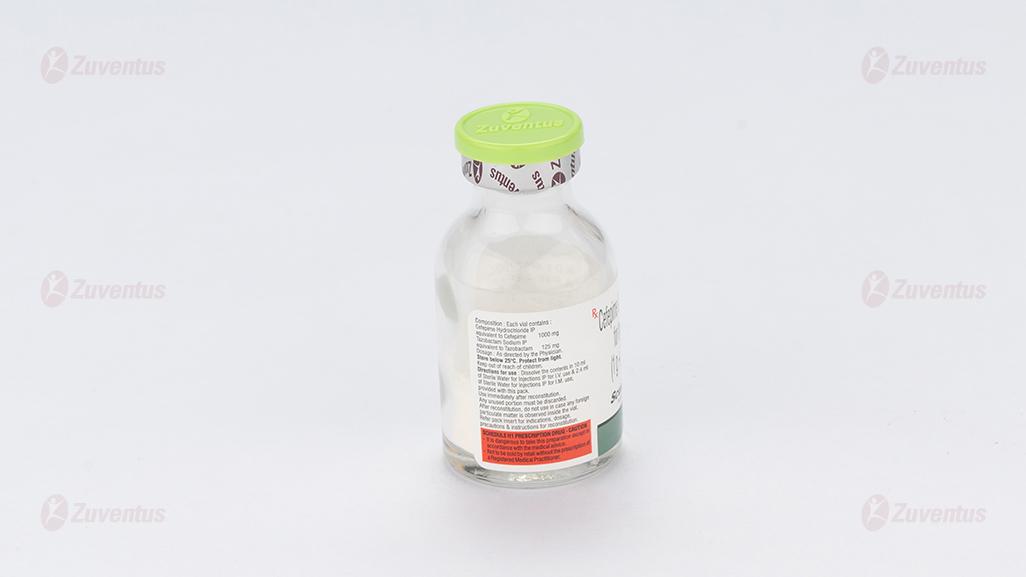
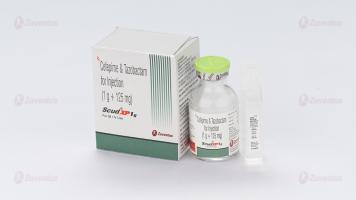
Scud XP 250 mg, 500 mg & 1g Injection
Therapy Area
Anti Infective
1.0 Generic Name
Cefepime & Tazobactam for Injection
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Scud XP 250 mg
Each vial contains :
Cefepime Hydrochloride IP equivalent to Cefepime 250 mg
Tazobactam Sodium IP equivalent to Tazobactam 31.25 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
Scud XP 500 mg
Each vial contains :
Cefepime Hydrochloride IP equivalent to Cefepime 500 mg
Tazobactam Sodium IP equivalent to Tazobactam 62.5 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
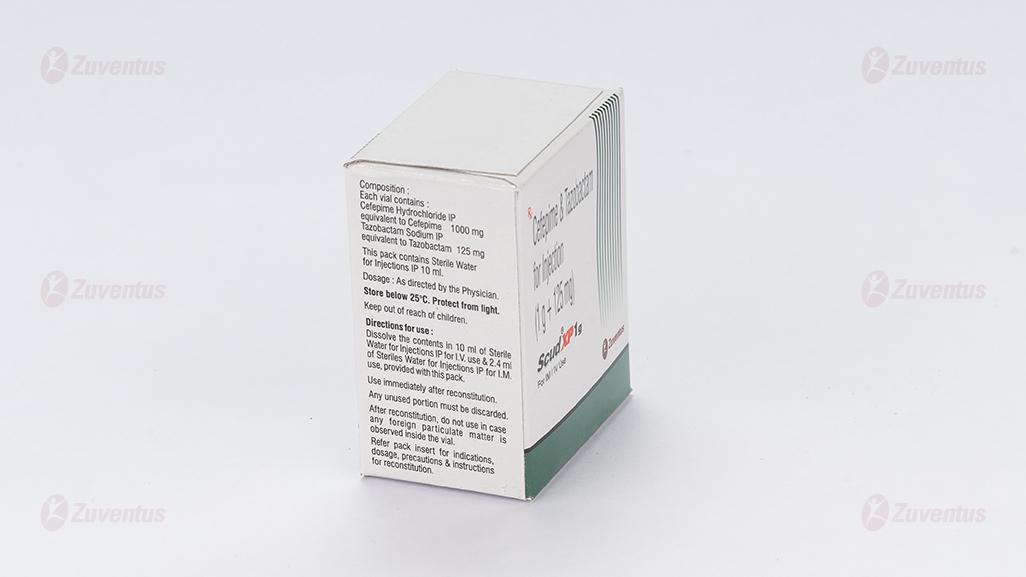
Scud XP 1 gm
Each vial contains :
Cefepime Hydrochloride IP equivalent to Cefepime 1000 mg
Tazobactam Sodium IP equivalent to Tazobactam 125 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 10 ml.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Injection, 250 mg/500 mg/1 gm
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
• uncomplicated and complicated urinary tract infections
• uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections
• complicated intra-abdominal infections
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Reconstitution:
IV Infusion: the contents of vials should be reconstituted with 5/10 ml of Sterile Water for Injections IP provided. The appropriate dose of the drug should then be added to a compatible IV solution. The resultant solutions are stable for 24 hours when stored at room temperature of 20°C to 25°C. Intermittent IV infusion is given over approximately 30 minutes. IM injection of Cefepime and Tazobactam is prepared by adding 2.4 ml Sterile Water for Injections IP.
| Type of infections in adult | Dose | Frequency | Durations (days) |
| Mild to Moderate Uncomplicated or Complicated Urinary Tract Infections | 0.5-1 g | Every 12 hours | 7-10 |
| Severe Uncomplicated or Complicated Urinary Tract Infections | 2 gm | Every 12 hours | 10 |
| Moderate to Severe Uncomplicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections | 2 gm | Every 12 hours | 10 |
| Complicated Intra-abdominal Infections | 2 gm | Every 8-12 hours | 7-10 |
Paediatric patients (2 months to 16 years): The maximum dose for pediatric patients should not exceed the recommended adult dose. The usual recommended dosage in pediatric patients up to 40 kg in weight is 50 mg per kg per dose, administered every 12 hours, for durations as given above.
4.3 Contraindications
Prior immediate hypersensitivity reactions to cefepime or the cephalosporin class of antibacterial drugs, penicillins, and other beta-lactam antibacterial drugs.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Before therapy with Cefepime Injection is instituted, careful inquiry should be made to determine whether the patient has had previous immediate hypersensitivity reactions to cefepime, cephalosporins, penicillins, or other beta-lactams. Exercise caution if this product is to be given to penicillin-sensitive patients because crosshypersensitivity among beta-lactam antibacterial drugs has been clearly documented and may occur in up to 10% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy. If an allergic reaction to Cefepime Injection occurs, discontinue the drug and institute appropriate supportive measures.
Neurotoxicity
Serious adverse reactions have been reported including life-threatening or fatal occurrences of the following: encephalopathy (disturbance of consciousness including confusion, hallucinations, stupor, and coma), aphasia, myoclonus, seizures, and nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Most cases occurred in patients with renal impairment who did not receive appropriate dosage adjustment. However, some cases of neurotoxicity occurred in patients receiving a dosage adjustment appropriate for their degree of renal impairment. In the majority of cases, symptoms of neurotoxicity were reversible and resolved after discontinuation of cefepime and/or after hemodialysis. If neurotoxicity associated with cefepime therapy occurs, discontinue cefepime and institute appropriate supportive measures.
Clostridioides difficile Associated Diarrhea
Clostridioides difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including Cefepime Injection, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin-producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibacterial drug use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibacterial drug use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibacterial treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated
Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
Prescribing cefepime in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria. As with other antimicrobials, prolonged use of cefepime may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible microorganisms. Repeated evaluation of the patient’s condition is essential. Should superinfection occur during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
Urinary Glucose
The administration of cefepime may result in a false-positive reaction for glucose in the urine when using some methods.
Coombs’ Tests
Positive direct Coombs’ tests have been reported during treatment with cefepime. In patients who develop hemolytic anemia, discontinue the drug and institute appropriate therapy. Positive Coombs’ test may be observed in newborns whose mothers have received cephalosporin antibacterials before parturition.
Prothrombin Time
Many cephalosporins, including cefepime, have been associated with a fall in prothrombin activity. Those at risk include patients with renal or hepatic impairment, or poor nutritional state, as well as patients receiving a protracted course of antibacterial therapy. Prothrombin time should be monitored in patients at risk, and exogenous vitamin K administered as indicated.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
The administration of cefepime may result in a false-positive reaction for glucose in the urine with certain methods. It is recommended that glucose tests based on enzymatic glucose oxidase reactions be used.
Aminoglycosides
Renal function should be monitored carefully if high doses of aminoglycosides are to be administered with Cefepime Injection because of the increased potential of nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity of aminoglycoside antibacterial drugs.
Diuretics
Nephrotoxicity has been reported following concomitant administration of other cephalosporins with potent diuretics such as furosemide.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
In what concerns cefepime there are no sufficient data on its exposure in pregnancy. Animal studies do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to pregnancy, embryonal/foetal development, labour or post-natal development. This medicinal product should only be prescribed to pregnant women with great caution.
Breastfeeding
Cefepime is excreted in human milk in very low quantities, so caution is recommended when administered to the breast-feeding woman
Fertility
There are no data on the use of cefepime in human fertility. Reproduction studies in animals did not reveal any effects on fertility.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The effects of the medicinal product on the ability to drive and use machines have not been studied. However, possible adverse reactions like altered state of consciousness, dizziness, confusional state or hallucinations may alter the ability to drive and use machines
4.8 Undesirable effects
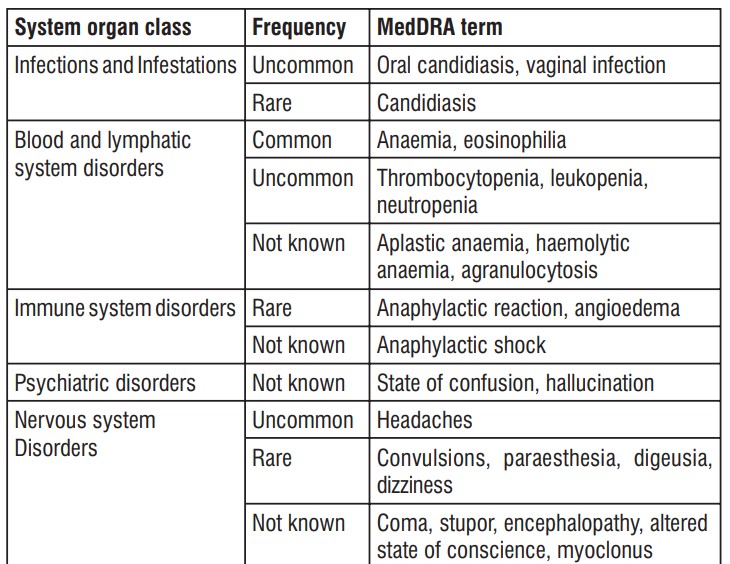
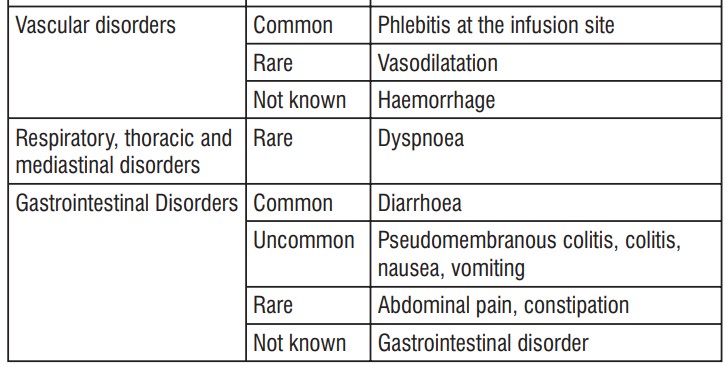
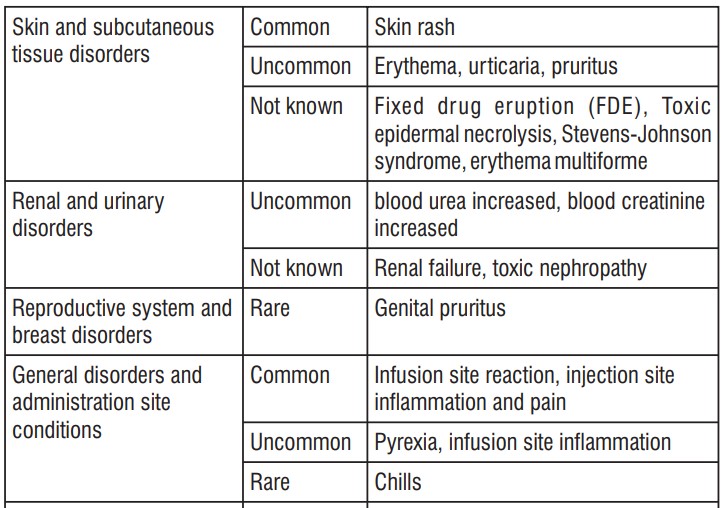
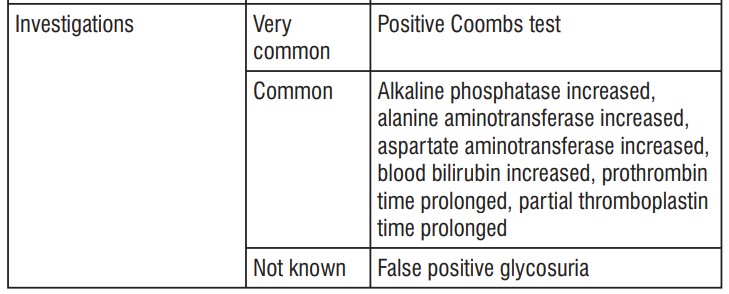
The safety profile of cefepime in infants and children is similar to that seen in the adult.
As with other drugs of the class of cephalosporins, encephalopathy (conscience disorder, including confusion, hallucinations, stupor and coma), convulsions, myoclonus and/or renal failure were reported. Most cases occurred in patients with renal impairment which received cefepime doses that exceeded those recommended.
Such as with other cephalosporins, anaphylaxis, including anaphylactic shock, transient leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis and thrombocytopenia were reported.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
In case of severe overdose, especially in patients with renal function impairment, haemodialysis can help remove cefepime from the body (peritoneal dialysis is not useful).
Accidental overdose occurred with the administration of high doses to patients with decreased renal function.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Cefepime is an antibacterial agent belonging to the cephalosporin class of antibacterials with in vitro antibacterial activity against facultative Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Tazobactam, a beta-lactam structurally related to penicillins, is an inhibitor of many beta-lactamases, which commonly cause resistance to penicillins and cephalosporins but it does not inhibit AmpC enzymes or metallo beta-lactamases.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Based on the spectrum of activity and decreased susceptibility to certain β – lactamases, Cefepime is classified as a 'FOURTH' generation cephalosporin. Its activity includes coverage against most gram negative bacteria which are susceptible to third generation cephalosporins. The drug is also active against some gram negative organisms including pseudomonas aeruginosa and certain enterobacteriaceae, that generally are resistant to most third generation cephalosporins. The activity of Cefepime against pseudomonas aeruginosa is similar to that of ceftazidime.
However, Cefepime is more active in- vitro against some strains of gram – positive bacteria e.g. staphylococcus, than some third generation cephalosporins. Emergence of drug resistance to Cefepime was considered as less of a problem till recently. Extended spectrum β – lactamases (ESBL) are capable of hydrolysing penicillins and broad and extended spectrum cephalosporins.
ESBL’s can be found in a variety of enterobacteriaceae species like, K. pneumonia, K. oxytoca, and E. coli. Other organisms to harbor ESBL’s are enterobacter spp., salmonella spp. Morganella morganil, proteus mirabilis, Serratia marcescens and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Cefepime is active against most ESBL producing organisms however susceptibility appears to decrease with increasing inoculum in-vitro susceptibility tests and in-vivo experimental models. Use of Cefepime alone has been associated with selection of ESBL producing organisms and outbreaks of infection.
Tazobactam acts as an irreversible inhibitor and inactivates both plasmid and chromosomally mediated β-lactamases. It neutralizes class A and D β-lactamases. ESBL are also inhibited by Tazobactam. Therefore, combination of Cefepime with tazobactam is a useful combination for the th treatment of infections due to ESBL producing organisms. Tazobactam augments and protects Cefepime, the powerful 4th generation cephalosporin.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Cefepime exhibits linear dose dependent pharmacokinetics over the dosage range from 250 mg to 2 g.
Cefepime is almost completely absorbed following IM administration. The single 500 mg, 1 g or 2 g IM doses of Cefepime attains peak plasma concentration 13.9, 29.6 or
57.5 mcg/ml respectively. Peak plasma concentration is attained within 1.4 to 1.6 hrs. After an hour the average plasma concentration averaged 12.5, 25.9 and 49.9 mcg/ml respectively.
Following IV Infusion over 30 min. of a single 500 mg, 1 g or 2 g dose of Cefepime, peak plasma concentrations of the drug averaged 39.1, 81.7 and 163.9 mcg/ml respectively, plasma concentrations one hour after the dose averaged 21.6, 44.5 and 85.5 mcg/ml respectively
Following parenteral administration, Cefepime is widely distributed into tissues and fluids, including blister fluid, bronchial mucosa, sputum, bile peritoneal fluid, appendix, gallbladder. Cefepime is distributed in to CSF following parenteral administration. It is also excreted in human milk.
Cefepime is approximately 20 % bound to serum proteins. Cefepime is partially metabolised in-vivo to N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP). The drug is eliminated principally unchanged in urine by glomerular filtration, approximately 85 % of a single dose Cefepime is excreted unchanged in urine.
Tazobactam 0.5 g when infused over 30 min as a single dose, the plasma concentration at 0.5 hour post injection is 13.7 -37.1 mcg/ml, and plasma elimination half-life is 0.94-1.5 hours.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
No animal carcinogenicity studies have been conducted with cefepime. In chromosomal aberration studies, cefepime was positive for clastogenicity in primary human lymphocytes, but negative in Chinese hamster ovary cells. In other in vitro assays (bacterial and mammalian cell mutation, DNA repair in primary rat hepatocytes, and sister chromatid exchange in human lymphocytes), cefepime was negative for genotoxic effects. Moreover, in vivo assessments of cefepime in mice (two chromosomalaberration and two micronucleus studies) were negative for clastogenicity. No untoward effects on fertility were observed in rats when cefepime was administered subcutaneously at doses up to 1,000 mg/kg/day (1.6 times the recommended maximum human dose calculated on a body surface area basis).
7.0 Description
Cefepime + Tazobactam is a combination of Cefepime, a semi - synthetic fourth generation cephalosporin antibiotic along with a β-Iactamase inhibitor Tazobactam. Tazobactam sodium, a derivative of the penicillin nucleus, is a penicillanic acid sulfone. Although Tazobactam has minimal antibacterial activity when used alone, the combined use of Cefepime with Tazobactam results in a synergistic effect that expands the spectrum of activity of Cefepime against many strains of β-lactamase producing bacteria.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
Scud XP 250 mg : A vial of 281.25 mg with SWFI IP 5 ml.
Scud XP 500 mg : A vial of 562.5 mg with SWFI IP 5 ml.
Scud XP 1 g : A vial of 1.125 g with SWFI IP 10 ml.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store below 25°C. Protect from light.
Keep out of reach of children.
After reconstitution, do not use in case any foreign particulate matter is observed inside the vial.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
• Counsel patients that antibacterial drugs, including cefepime-tazobactam for injection, should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g. the common cold). When cefepime-tazobactam for injection is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, tell patients that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment; and, (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by cefepime-tazobactam for injection or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
• Diarrhoea is a common problem caused by antibacterial drugs, which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Inform patient that they may develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) during treatment and as late as 2 or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. Inform patients that they should contact their physician as soon as possible if this occurs.
• Advise patients of neurological adverse events that could occur with the use of cefepime-tazobactam for injection. Instruct patients or their carers to inform their healthcare provider at once of any neurological signs and symptoms, including encephalopathy (disturbance of consciousness, including confusion, hallucinations, stupor and coma), aphasia (disturbance of speaking and understanding spoken and written language), myoclonus, seizures and nonconvulsive status epilepticus, for immediate treatment, dosage adjustment, or discontinuation of cefepime-tazobactam for injection.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1. What Scud XP is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you use Scud XP
3. How to use Scud XP
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store Scud XP
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Scud XP is and what it is used for
Scud XP contains Cefepime & Tazobactam and is used in the treatment of the following conditions:
- Urinary tract infections
- Skin infections
- Infection in the abdomen
2. What you need to know before you use Scud
Do not use Scud XP :
- if you are allergic to cefepime, any other cephalosporin antibiotics, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if you have a history of severe allergic reactions to any other type of beta-lactam antibiotics (penicillins, monobactams, and carbapenems).
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before using Scud XP.
Particular care should be taken when using Scud XP :
– Severe and occasionally fatal allergic reactions were reported. Please tell your doctor if you have a history of asthma or allergic reactions (skin rash, itching…). Severe allergic reactions may need epinephrine and other support therapy.
– Cefepime is not adequate for the treatment of certain types of infections. Your doctor has prescribed you this antibiotic because it is the best option for your illness.
– if you have kidney problems (such as reduced renal function) as the elimination of this medicine may be affected.
– if you suffer from persistent diarrhoea during or after using this medicine. Tell your doctor immediately so he can investigate whether the diarrhoea is the result of an intestinal inflammation caused by the use of the antibiotic; treatment with this medicine may need to be discontinued.
– If you suffer from allergies (such as hay fever, nettle rash) or have had an allergic reaction to medicines in the past. Cefepime must be discontinued on the appearance of any kind of hypersensitivity reaction and appropriate therapeutic measures initiated.
– Dosages for elderly patients should be chosen carefully and should take renal function into account, as there is a greater possibility to develop kidney disease.
Other medicines and Scud XP
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines, including medicines obtained without prescription.
Renal function should be carefully monitored when Scud XP is combined with drugs that may affect the kidneys (such as aminoglycosides and powerful diuretics).
The cephalosporins may enhance the effect of coumarin anticoagulants.
Interaction with diagnostic tests
Cefepime may produce a false positive reaction in some laboratory tests (urine glucose and Coombs test results).
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for
advice before using this medicine.
Do not use this medicine during pregnancy, unless absolutely necessary and specifically directed by your doctor. If you get pregnant during treatment with Scud XP tell your doctor.
Scud XP can be transferred to breast milk, therefore this medicine should be used during breast-feeding with great care and only after discussing with your doctor.
Driving and using machines
There have been no studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines.
However, you may experience disturbed consciousness, dizziness, confusion and hallucination, which may compromise the ability to drive and use machines.
3. How to use Scud XP
Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
Scud XP can be administered via intravenous use or intramuscular use.
The usual dose and the route of administration vary in accordance with the severity of the infection, the renal function and the general conditions of the patient.
The IV route of administration is preferable in patients with severe infections or in life-threatening situations, particularly if there is the possibility of shock.
| Type of infections in adult | Dose | Frequency | Duration (days) |
|
Mild to Moderate Uncomplicated or Complicated Urinary Tract Infections |
0.5-1 g of cefepime | Every 12 hours | 7-10 |
|
Severe Uncomplicated or Complicated Urinary Tract Infections |
2gm of cefepime | Every 12 hours | 10 |
|
Moderate to Severe Uncomplicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections |
2gm of cefepime | Every 12 hours |
10 |
|
Complicated Intra-abdominal Infections |
2gm of cefepime | Every 8-12 hours | 7-10 |
For Pediatric patients (Children)
Pediatric patients (2 months to 16 years): The maximum dose for pediatric patients should not exceed the recommended adult dose. The usual recommended dosage in pediatric patients up to 40 kg in weight is 50 mg per kg of cefepime per dose, administered every 12 hours, for durations as given above.
Elderly, patients with renal dysfunction, dialysis patients, and children with renal dysfunction:
The doctor will determine the dose to be administered.
If you use more Scud XP than you should
Contact your doctor or other healthcare professionals immediately, as you may experience more severe side effects under certain situations.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Scud XP may present one or more of the following side effects:
Very common (can affect more than 1 user in 10):
- Positive Coombs test without hemolysis (method of determining antibody levels);
Common (can affect up to 1 user in 10):
- Increased blood coagulation time (increased prothrombin or thromboplastin time);
- anaemia;
- an elevated level of certain blood cells (eosinophilia);
- infusion site phlebitis;
- diarrhoea;
- rashes;
- infusion site reaction;
- pain and inflammation on the injection site;
- an elevated level in certain blood counts (alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase).
Uncommon (can affect up to 1 user in 100)
- fungal infections of the mouth with white coating (oral candidiasis);
- vaginal infection;
- reduced levels of certain blood cells (thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, neutropenia)
- headaches;
- colitis (inflammation of the large intestine);
- pseudomembranous colitis; - nausea;
- vomiting;
- erythema (reddening of the skin);
- urticaria;
- itching;
- elevated blood urea;
- elevated serum creatinine;
- fever;
- inflammation on the infusion site.
Rare (can affect up to 1 user in 1,000):
- fungal infections (candidiasis);
- allergic reactions;
- angioedema (sudden swelling of the skin, subcutaneous tissue, mucosa or submucosa);
- convulsions;
- tingling;
- taste changes;
- dizziness;
- vascular dilation;
- shortness of breath;
- abdominal pain;
- constipation;
- genital itching;
- chills.
Not known (unknown frequency)
- aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia , agranulocytosis;
- confusion;
- hallucinations;
- coma;
- torpidity;
- encephalopathy (non-inflammatory brain disease)
- disturbed consciousness;
- myoclonus (muscle twitching);
- bleeding;
- gastrointestinal disease;
- severe skin reactions (as toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme);
- renal failure;
- toxic nephropathy (kidney damage);
- false positive urine glucose test results.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Scud XP
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the packaging and the container, after ‘EXP.’. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
This medicinal product does not require any special temperature storage conditions. Keep the container in the outer carton.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Scud XP contains
- The active substance is cefepime dihydrochloride monohydrate and Tazobactam.
Scud XP 250 mg
Each vial contains:
Cefepime Hydrochloride IP equivalent to Cefepime 250 mg
Tazobactam Sodium IP equivalent to Tazobactam 31.25 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
Scud XP 500 mg
Each vial contains:
Cefepime Hydrochloride IP equivalent to Cefepime 500 mg
Tazobactam Sodium IP equivalent to Tazobactam 62.5 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
Scud XP 1 gm
Each vial contains:
Cefepime Hydrochloride IP equivalent to Cefepime 1000 mg
Tazobactam Sodium IP equivalent to Tazobactam 125 mg
This pack contains Sterile Water for Injections IP 10 ml.
Pack size/ presentation:
Scud XP 250 mg: A vial of 281.25 mg with Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
Scud XP 500 mg: A vial of 562.5 mg with Sterile Water for Injections IP 5 ml.
Scud XP 1 g: A vial of 1.125 g with Sterile Water for Injections IP 10 ml.