Soventus®-dx Syrup
1.0 Generic Name
Chlorpheniramine Maleate & Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide syrup
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
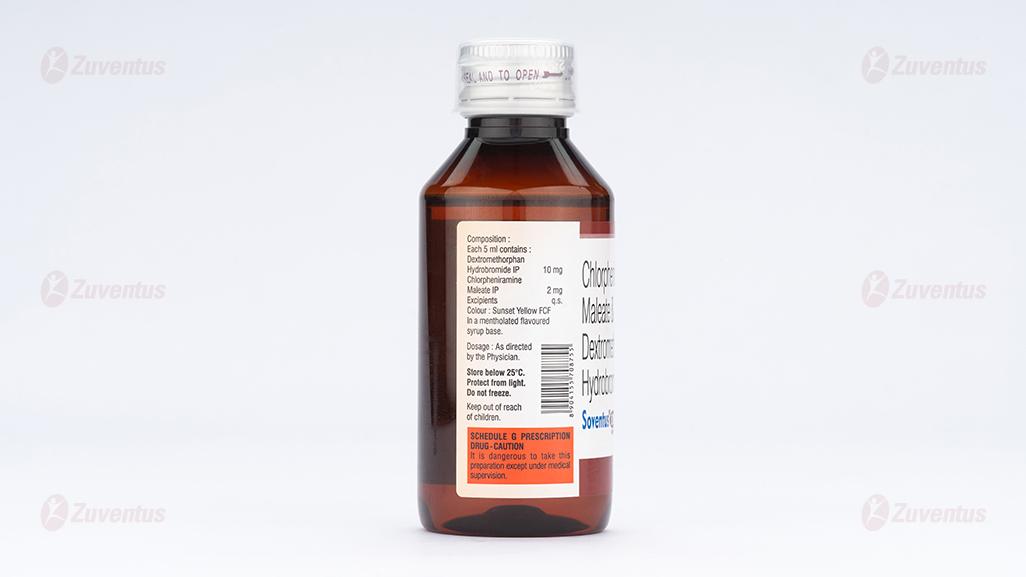
Each 5 ml Contains:
Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide IP 10 mg
Chlorpheniramine maleate IP 2 mg
Excipients q. s.
Colour: Sunset Yellow FCF
In a mentholated flavoured syrup base
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Syrup
100 ml bottle
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic Indication
For the temporary relief of cough due to throat irritation, sneezing & running nose.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
2 to 5 years of age: 2.5 ml (1/2 teaspoonful) 3 to 4 times a day.
6 to 12 years of age: 5 ml (1 teaspoonful) 3 to 4 times a day.
Adult (> 12 years of age): 10 ml (2 teaspoonful) 3 to 4 times a day.
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to Chlorpheniramine, Dextromethorphan or to any component of the formulation.
- Receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitors [MAOIs] (drugs for depression, psychiatric or emotional conditions, or Parkinson's disease) with or within 2 weeks.
- Patients with risk of developing respiratory failure
- Acute Asthma
- Patient with liver disease
- Persistent or chronic productive cough
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Chlorpheniramine maleate
This medicine should be given with caution to patients with epilepsy, severe cardiovascular disorders, liver disorders, renal impairment, glaucoma, urinary retention, prostatic enlargement, pyloroduodenal obstruction, asthma, bronchitis, bronchiectasis, thyrotoxicosis and severe hypertension.
Special care should be taken when using chlorpheniramine maleate in children and the elderly as they are more likely to experience the neurological anticholinergic effects and paradoxical excitation (e.g. Increased energy, restlessness, nervousness). Avoid use in elderly patients with confusion.
The anticholinergic properties of chlorphenamine may cause drowsiness, dizziness, blurred vision and psychomotor impairment in some patients which may seriously affect ability to drive and use machinery. The effects of alcohol may be increased and therefore concurrent use should be avoided.
Should not be used with other antihistamine containing products, including antihistamine containing cough and cold medicines.
Concurrent use with drugs which cause sedation such as anxiolytics and hypnotics may cause an increase in sedative effects, therefore medical advice should be sought before taking chlorphenamine concurrently with these medicines.
Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide
Dextromethorphan should not be given to patients at risk of developing respiratory failure. Caution is needed in patients with a history of asthma and it should not be given during an acute attack. Care is also advisable in patients with bronchitis, emphysema, or in other conditions where chronic or persistent cough occurs.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Chlorpheniramine maleate
This medicine may enhance the sedative effects of alcohol, hypnotics, anxiolytics, sedatives, opioid analgesics and neuroleptics.
The anti-muscarinic effects of chlorpheniramine are enhanced by other anti-muscarinic drugs and both anti-muscarinic and sedative effects are enhanced by monoamine oxidase inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants.
Metabolism of phenytoin may be inhibited by chlorpheniramine with the possible development of phenytoin toxicity.
Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): Dextromethorphan should not be used concurrently in patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or within 14 days of stopping treatment with MAOIs as there is a risk of serotonin syndrome (pyrexia, hallucinations, gross excitation or coma, hypertension, arrhythmias).
CYP2D6 inhibitors: Dextromethorphan is metabolized by CYP2D6 and has an extensive first-pass metabolism. Concomitant use of potent CYP2D6 enzyme inhibitors can increase the dextromethorphan concentrations in the body to levels multi-fold higher than normal. This increases the patient's risk for toxic effects of dextromethorphan (agitation, confusion, tremor, insomnia, diarrhoea and respiratory depression) and development of serotonin syndrome. Potent CYP2D6 enzyme inhibitors include SSRIs such as fluoxetine and paroxetine, quinidine and terbinafine. In concomitant use with quinidine, plasma concentrations of dextromethorphan have increased up to 20-fold, which has increased the CNS adverse effects of the agent. Amiodarone, flecainide and propafenone, sertraline, bupropion, methadone, cinacalcet, haloperidol, perphenazine and thioridazine also have similar effects on the metabolism of dextromethorphan. If concomitant use of CYP2D6 inhibitors and dextromethorphan is necessary, the patient should be monitored and the dextromethorphan dose may need to be reduced.
CNS depressants: Dextromethorphan might exhibit additive CNS depressant effects when co-administered with alcohol, antihistamines, psychotropics, and other CNS depressant drugs.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnant Women
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of this combination in pregnant women. There are no adequate controlled studies of chlorpheniramine in pregnant women and therefore should not be used during pregnancy. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of Dextromethorphan in pregnant women. Dextromethorphan should not be used during pregnancy or lactation unless the potential benefit of treatment to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the developing foetus or nursing infant.
Caution is advised when Soventus®-DX Syrup is used during pregnancy.
Lactating Women
Chlorpheniramine may be secreted in breast milk. Hence, it is not recommended in nursing mothers because of the risk of adverse effects, such as unusual excitement or irritability in infants. Chlorpheniramine may also inhibit lactation. It is not known whether dextromethorphan or its metabolites are excreted in breast milk. A decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Paediatric Patients
Safety and efficacy of this formulation in neonates and children below 2 years of age has not been established. Thus, Soventus®-DX Syrup is not recommended for use in paediatric patients below 2 years of age.
Geriatric Patients
The elderly patients taking Chlorpheniramine are more likely to experience neurological anticholinergic effects. Elderly patients with normal renal and hepatic function may be given the same dose as recommended for adults. Elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Renal Impairment Patients
Caution should be exercised while using Soventus®-DX syrup in patients with significant renal dysfunction. Dose should be reduced or the dosing interval must be extended in patients with severe renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment Patients
In hepatic impairment, Soventus®-DX syrup should be used with caution.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Soventus®-DX Syrup may cause side effects which could affect your ability to drive. Chlorpheniramine may cause blurred vision, dizziness, drowsiness and interfere with human performance and therefore may seriously influence the ability to drive and operate machinery. Dextromethorphan can impair cognitive function and can affect a patient's ability to drive safely.
4.8 Undesirable Effects
Chlorpheniramine maleate
Adverse reactions identified during post-marketing use with chlorphenamine are listed below. As these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, the frequency of some reactions is unknown but likely to be rare or very rare:
Children and the elderly are more susceptible to neurological anticholinergic effects and paradoxical excitation (e.g. increased energy, restlessness, nervousness)
Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide
ADRs are presented by frequency category based on 1) incidence in adequately designed clinical trials or epidemiology studies, if available, or 2) when incidence cannot be estimated, frequency category is listed as 'Not known’.



frequency category is listed as 'Not known’.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit / risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website : http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
The estimated lethal dose of chlorphenamine is 25 to 50mg/kg body weight. Symptoms and signs include sedation, paradoxical excitation of the CNS, toxic psychosis, convulsions, apnoea, anticholinergic effects, dystonic reactions and cardiovascular collapse including arrhythmias. Symptomatic and supportive measures should be provided with special attention to cardiac, respiratory, renal and hepatic functions and fluid and electrolyte balance. If overdosage is by the oral route, treatment with activated charcoal should be considered provided there are no contraindications for use and the overdose has been taken recently (treatment is most effective if given within an hour of ingestion.) Treat hypotension and arrhythmias vigorously. CNS convulsions may be treated with i.v. diazepam. Haemoperfusion may be used in severe cases.
Dextromethorphan is thought to be of low toxicity, but the effects in overdosage will be potentiated by simultaneous ingestion of alcohol and psychotropic drugs. Symptoms of overdose may include mydriasis, nausea and vomiting, CNS depression, excitation, lethargy, nystagmus, psychomotor hyperactivity, serotonin syndrome, somnolence (drowsiness), dizziness, dysarthria (slurred speech), mental confusion, psychotic disorder (psychosis), and respiratory depression. Treatment should be symptomatic and supportive. Gastric lavage may be of use. Naloxone has Patients should be kept under observation and symptomatic and supportive treatment is advised. been used successfully to reverse central or peripheral opioid effects of dextromethorphan in children (0.01mg/kg body weight).
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Chlorpheniramine maleate
Chlorpheniramine is a first-generation alkylamine antihistamine. It is a less sedating H1 blocker with autonomic effects (anti-cholinergic action), used in the prevention of the symptoms of allergic conditions such as rhinitis.
Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide
Dextromethorphan (D-3-methoxy-N-methylmorphinan) is the D-isomer of the codeine analog methorphan. It is an antitussive drug and one of the active ingredients used to prevent coughs.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Chlorpheniramine maleate
Chlorphenamine is a potent antihistamine (H1-antagonist). Antihistamines diminish or abolish the actions of histamine in the body by competitive reversible blockade of histamine H1-receptor sites on tissues. Chlorphenamine also has anticholinergic activity. Antihistamines act to prevent the release of histamine, prostaglandins and leukotrienes and have been shown to prevent the migration of inflammatory mediators. The actions of chlorphenamine include inhibition of histamine on smooth muscle, capillary permeability and hence reduction of oedema and wheal in hypersensitivity reactions such as allergy and anaphylaxis.
Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide
Dextromethorphan is the dextrorotatory isomer of 3-methoxy-N-methyl-morphinan. It is a synthetic morphine derivative that, in contrast to its levo-rotatory isomer, has no significant analgesic, respiratory depressant or physical dependency properties at recommended doses.
Dextromethorphan is a non-opioid antitussive drug. It exerts its antitussive activity by acting on the cough centre in the medulla oblongata, raising the threshold for the cough reflex. The onset of antitussive effects are realised within 15 to 30 minutes of oral administration, lasting for approximately 3 to 6 hours.
The major metabolite of dextromethorphan, dextrorphan, binds with high affinity to σ-receptors to produce its antitussive activity without exhibiting the classic opiate effects that occur from binding into μ- and δ-receptors. Dextrorphan also exhibits binding activity at serotonergic receptors and was shown to enhance serotonin activity by inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin. In larger than therapeutic doses, dextrorphan is also an antagonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Chlorpheniramine maleate
Chlorpheniramine maleate is almost completely absorbed after administration by mouth, peak plasma concentrations occurring at about 2.5 to 6 hours. The drug is widely distributed including passage into the CNS, with a volume of distribution of between 1 and 10L/KG. About 70% of chlorpheniramine in the circulation is protein-bound. Chlorpheniramine undergoes some first pass metabolism and enterohepatic recycling. Chlorpheniramine is extensively metabolised, principally to inactive desmethylated metabolites which are excreted primarily in the urine, together with about 35% unchanged drug. Only trace amounts are excreted in the faeces. The mean elimination half-life has been reported to be about 30 hours, with mean values ranging from 2 to 43 hours.
Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide
Absorption: Dextromethorphan is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract with peak plasma concentrations reached in approximately 2 to 2.5 hours. The low plasma levels of dextromethorphan suggest low oral bioavailability secondary to extensive first-pass (pre-systemic metabolism) in the liver. The maximum clinical effects occur 5 to 6 hours after ingestion of dextromethorphan.
Distribution: Dextromethorphan is widely distributed in the human body. Dextromethorphan and its active metabolite, dextrorphan, are actively taken up and concentrated in brain tissue. It is not known if dextromethorphan or dextrorphan are excreted in breast milk or cross the placenta.
Metabolism: Dextromethorphan undergoes rapid and extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver after oral administration. Genetically controlled O-demethylation (CYD2D6) is the main determinant of dextromethorphan pharmacokinetics in human volunteers. It appears that there are distinct phenotypes for this oxidation process resulting in highly variable pharmacokinetics between subjects. Unmetabolised dextromethorphan, together with the three demethylated morphinan metabolites dextrorphan (also known as 3-hydroxy-N-methylmorphinan), 3- hydroxymorphinan and 3-methoxymorphinan have been identified as conjugated products in the urine. Dextrorphan, which also has antitussive action, is the main metabolite. In some individuals metabolism proceeds more slowly and unchanged dextromethorphan predominates in the blood and urine.
Excretion: Dextromethorphan is primarily excreted via the kidney as unchanged parent drug and its active metabolite, dextrorphan. Dextrorphan and 3-hydroxy-morphinan are further metabolised by glucuronidation and are eliminated via the kidneys. The elimination half-life of the parent compound is between 1.4 to 3.9 hours; dextrorphan is between 3.4 to 5.6 hours. The half-life of dextromethorphan in poor metabolisers is extremely prolonged, in the range of 45 hours.
6.0 Nonclinical Properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Chlorpheniramine maleate
The antihistaminic potency of chlorpheniramine is confined mainly to its (+)-isomer. The racemate is similarly or slightly more toxic because of the contribution of (-)-isomer. The toxicity may therefore be non-specific, perhaps attributable to local anaesthetic action and the toxic effects (excitation/sedation, coma, convulsions and death) resemble those of other classic H1antihistamines. Toxic doses may cause hypotension attributable to myocardial depression, an effect which is clearer with the (-)-isomer. The experimental data on the carcinogenicity and mutagenicity of chlorpheniramine indicate lack of these adverse effects, but the racemate and the (+)-isomer have shown some embryotoxicity in fertility tests. Effective antihistaminic concentrations of chlorpheniramine in vitro are about 1-10µg/L and oral doses of 0.2-1 mg/kg antagonise histamine-induced bronchospasm in guinea pigs.
Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide
General toxicology: Acute oral toxicity studies conducted with Dextromethorphan report the following LD50 values (mg/kg): mouse, 210 and rat, 116. Acute subcutaneous toxicity with Dextromethorphan reports the LD50 value (mg/kg): mouse, 112. Acute intravenous toxicity with Dextromethorphan reports the LD50 value (mg/kg): rat, 16.3.
Repeat dose toxicity studies conducted in rats for 13-week duration at doses up to 100 mg/kg and 27 weeks at 10 mg/kg, and of 14 weeks in dogs by oral gavage at doses up to 4 mg/kg on five days per week. The only effect recorded was of reduced body weight gain in the rat 13-week study at the highest dose.
Genetic Toxicology: Dextromethorphan hydrobromide was negative in the bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test). Dextromethorphan 39 mg/kg is reported to be negative in in-vivo mouse micronucleus test and comet assay. Dextromethorphan was reported to be negative in in vitro chromosome aberration assay tested up to 200 μg/ml.
Carcinogenicity: There are no known reports of animal carcinogenicity studies for Dextromethorphan. The overall weight of evidence for Dextromethorphan and its structural analogues, support the conclusion that this class of phenanthrene-based chemicals, and Dextromethorphan, in particular, are not genotoxic in vitro or in vivo
Teratogenicity: There was no association between dextromethorphan and malformations.
Fertility: Mating, gestation, fertility, littering and lactation were studied in rats at doses up to 50 mg/kg and no adverse effects were found.
7.0 Description
Each 5 ml of Soventus®-DX syrup contains 10 mg of Dextromethorphan hydrobromide and 2 mg of chlorpheniramine maleate for oral administration.
Chlorpheniramine maleate
Chlorphenamine is a potent antihistamine (H1-antagonist). Antihistamines diminish or abolish the actions of histamine in the body by competative reversible blockade of histamine H1-receptor sites on tissues. Chlorphenamine also has anticholinergic activity. Molecular Weight: 390.9 g/mol Molecular Formula: C16H19ClN2.C4H4O4 Chemical Name: (Z)-but-2-enedioic acid;3-(4-chlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-3-pyridin-2-ylpropan-1-amine
Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide
Dextromethorphan is the dextrorotatory isomer of 3-methoxy-N-methyl-morphinan. It is a synthetic morphine derivative. Dextromethorphan is a non-opioid antitussive drug. It exerts its antitussive activity by acting on the cough centre in the medulla oblongata, raising the threshold for the cough reflex.
Molecular Weight: 352.3 g/mol
Molecular Formula: C18H26BrNO
Chemical Name:
(1S,9S,10S)-4-methoxy-17-methyl-17-azatetracyclo[7.5.3.01,10.02,7]heptadeca-2(7),3,5-triene;hydrobromide
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf life
Refer on Pack
8.3 Packaging information
100 ml bottle
8.4 Storage and handling information
Store in a cool & dark place. Keep out of reach of children
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
- Take exactly as directed by your doctor or on the label. Do not increase the dosage or take for longer than is recommended. Use a proper measuring cup or spoon to measure the dosage.
- If you are drowsy after taking Soventus®-DX Syrup, you should not drive or operate any machinery.
- Inform your doctor if you have a history of stomach ulcers or asthma.
- Inform your doctor if you are taking any other medications, e.g., anti-depressants.
- Consult your doctor if you do not see any improvement and have a cough for > 7 days.
- Avoid consuming alcohol while taking Soventus DX Syrup as it can cause excessive drowsiness.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet
1.What Soventus®-DX Syrup is and what it is used for
2.What you need to know before you take Soventus®-DX Syrup
3.How to take Soventus®-DX Syrup
4.Possible side effects
5.How to store Soventus®-DX Syrup
6.Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Soventus®-DX Syrup is and what it is used for
Soventus®-DX Syrup is a combination of Chlorpheniramine maleate & Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide. This medicine is used to help relieve dry, irritating coughs.
Dextromethorphan hydrobromide which is an antitussive to help stop persistent dry coughing. It works by reducing the activity of cough center in the brain. The other active ingredient is chlorphenamine maleate, an antihistamine which can help to relieve the symptoms of allergic reactions. It relieves allergic symptoms like runny nose, watery eyes, sneezing, throat irritation.
2. What you need to know before you take Soventus®-DX Syrup Do not take Soventus®-DX Syrup:
- If you are allergic to any of the ingredients of this medicine.
- If you are taking, or have taken in the last two weeks, drugs for depression known as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs).
- if you are taking selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (used to treat depression and anxiety such as fluoxetine, paroxetine and sertraline).
- If you have an acute asthma
- If you are taking other medicines containing antihistamines, including products for the relief of colds and coughs
- If you suffer from lung disease.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before taking Soventus®-DX Syrup.
- If you suffer from epilepsy, heart or circulatory disease, liver problems, kidney disease.
- If you high blood pressure or glaucoma.
- If you have chronic bronchitis, emphysema or asthma or have had a cough for a few weeks or a cough with a lot of mucus (phlegm).
- If you are taking any other cough and cold medicines.
- If your child is prone to developing certain allergic reactions (e.g. atopic reactions).
- If you are or have ever been addicted to opioids, alcohol, prescription medicines, or illegal drugs.
- If you have previously suffered from withdrawal symptoms such as agitation, anxiety, shaking or sweating, when you have stopped taking alcohol or drugs.
- If you have been told by your doctor that you are a slow metabolizer of CYP2D6.
- If you are taking medicines such as certain antidepressants or antipsychotics this medicine may interact with these medicines and you may experience mental status changes (e.g. agitation, hallucinations, coma), and other effects such as body temperature above 38°C, increase in heart rate, unstable blood pressure, and exaggeration of reflexes, muscular rigidity, lack of coordination and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g. nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea).
- If you are taking any other medicines, including: Certain drugs for depression such as norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRI), which include bupropion.
- If you are taking Antipsychotics (drugs used to treat mood disorders such as haloperidol, thioridazine, perphenazine).
- If you are taking anti-arrhythmic agents (drugs used to treat an irregular heartbeat such as amiodarone, propafenone, quinidine and flecainide).
- If you are taking calcimimetic agents (drugs used to treat secondary hyperparathyroidism, elevated parathyroid hormone levels such as cinacalcet).
- Antifungals (terbinafine).
- If you are taking opioid analgesics (drugs used to relieve pain e.g. codeine, tramadol, morphine, methadone). If using antihistamines (drugs used to treat the symptoms of allergic reactions).
- If you have an overactive thyroid.
- If you have difficulty passing urine.
- If you have an obstruction in their intestine.
- If you have a rare blood disease called porphyria.
If any of these points apply to you now or in the past, talk to a doctor or pharmacist.
Tell your doctor immediately if during treatment you suffer from
hypersensitivity reactions (itchiness, redness of the skin, hives, swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue or throat)
Other medicines and Soventus®-DX Syrup
Tell your doctor if you are taking or have taken the following medications.
Chlorpheniramine may enhance the sedative effects of alcohol, hypnotics, anti- anxiety, sedatives, opioid analgesics and neuroleptics.
Dextromethorphan should not be used concurrently in patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or within 14 days of stopping treatment with MAOIs as there is a risk of serotonin syndrome (pyrexia, hallucinations, gross excitation or coma, hypertension, arrhythmias).
Dextromethorphan might exhibit additive CNS depressant effects when co-administered with alcohol, antihistamines, psychotropics, and other CNS depressant drugs.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding
Do not take this medicine, if you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Geriatric Population
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before you take this syrup as you may be more likely to get side effects including confusion and you may need to take a lower daily dose.
Pediatric population
Not recommended for children below 2 years of age.
Renal Insufficiency
Caution should be exercised while using Soventus®-DX syrup in patients with significant renal dysfunction. Dose should be reduced or the dosing interval must be extended in patients with severe renal impairment.
Hepatic Insufficiency
Caution should be exercised in patients with moderate to severe and liver disease.
Driving and using machines
This medicine can affect your ability to drive. Do not drive whilst taking this medicine until you know how this medicine affects you. It may be an offence to drive when taking this medicine if your ability to drive safely is affected.
3. How to take Soventus®-DX Syrup
Check the seal is not broken before first use. If it is, do not give the medicine. Always use the measuring cup supplied with the pack.
2 to 5 years of age: 2.5 ml (1/2 teaspoonful) 3 to 4 times a day. 6 to 12 years of age: 5 ml (1 teaspoonful) 3 to 4 times a day. Adult (> 12 years of age): 10 ml (2 teaspoonful) 3 to 4 times a day. Do not take more than 4 doses in 24 hours. If symptoms persist or worsen, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
If you take more Soventus®-DX Syrup than you should
If anyone has too much intake, contact a doctor or your nearest accident and emergency department (casualty) taking this leaflet and pack with you. If you take more of this medicine than you should, you may experience the following symptoms: nausea and vomiting, involuntary muscle contractions, agitation, confusion, somnolence, disturbances in consciousness, involuntary and rapid eye movements, cardiac disorders (rapid heart beating), coordination disorders, psychosis with visual hallucinations, and hyperexcitability. Also, other types of hallucinations, psychotic disorders, seizures, clumsiness, dizziness, speech problems, lack of energy, high blood pressure, tremor, or constricted or dilated pupils. Tell your doctor or emergency department in hospital immediately.
If you forget to take Soventus®-DX Syrup
If you forget a dose, do not worry. Just wait until the next dose is due. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop taking Soventus®-DX Syrup
Unless your doctor instructs you to stop treatment, it is important to continue taking Soventus®-DX Syrup. If you stop and your original symptoms come back tell your doctor or pharmacist immediately.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them Tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist immediately if you notice any of these side effects during your treatment with Soventus®-DX Syrup:
- Drowsiness and sedation are very common side effects with chlorpheniramine. Other common side effects include disturbance in concentrating, un-coordination, dizziness, headaches, blurred vision, feeling or being sick, dry mouth, fatigue.
- Dextromethorphan may cause side effect such as swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue or throat which may cause difficulty in swallowing or breathing, fits.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Soventus®-DX Syrup
Store in a cool & dark place. Keep out of reach of children. Do not freeze.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Soventus®-DX Syrup contains:
Each 5 ml Contains: Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide IP 10 mg
Chlorpheniramine maleate IP 2 mg
Excipients q. s.
Colour: Sunset Yellow FCF In a mentholated flavoured syrup base
Pack size: 100 ml Bottle