Thaloric 6.25-12.5 Tablets
Therapy Area
Cardiology
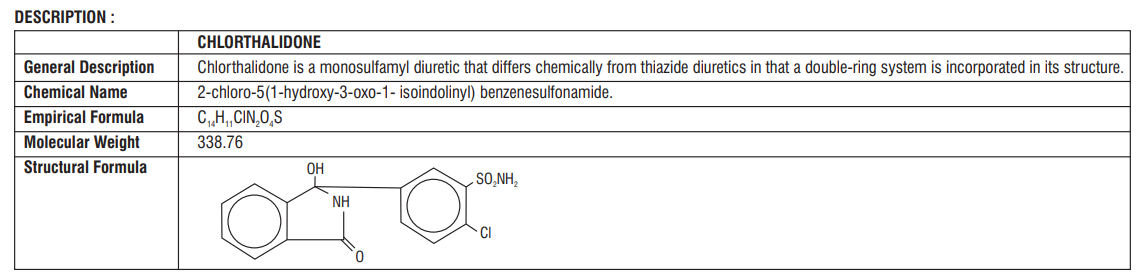
Composition
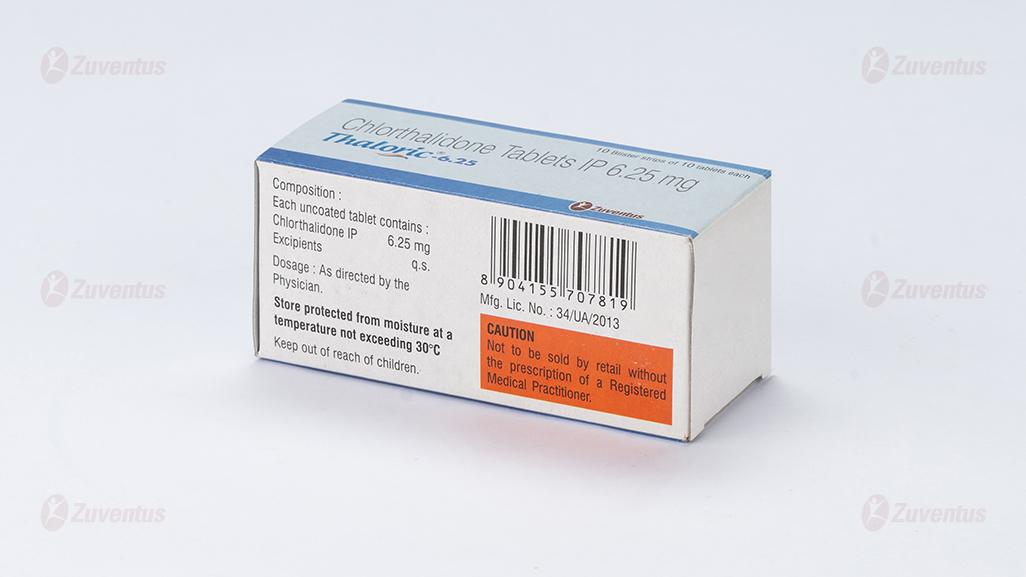
Thaloric-6.25
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Chlorthalidone IP 6.25 mg
Excipients q.s.
Thaloric-12.5
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Chlorthalidone IP 12.5 mg
Excipients q.s

Indications
For the treatment of mild to moderate hypertension in adults.
Contraindications
• Anuria, severe hepatic or renal failure (creatinine clearance <30ml/min),
• Hypersensitivity to Chlorthalidone and other sulphonamide derivatives,
• Refractory hypokalemia, hyponatremia and hypercalcemia, symptomatic hyperuricemia (history of gout or uric acid calculi),
• Hypertension during pregnancy,
• Untreated Addison's disease
• Concomitant lithium therapy
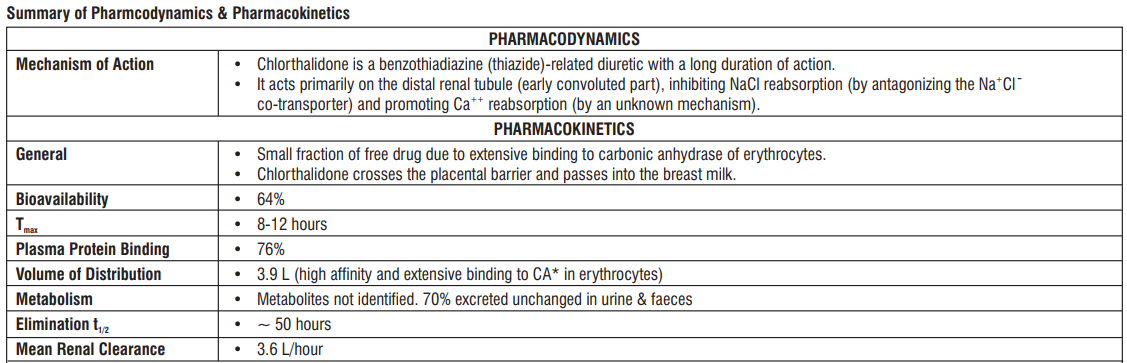
Dosage and method of administration
Chlorthalidone should be taken orally, preferably as a single daily dose at breakfast time.
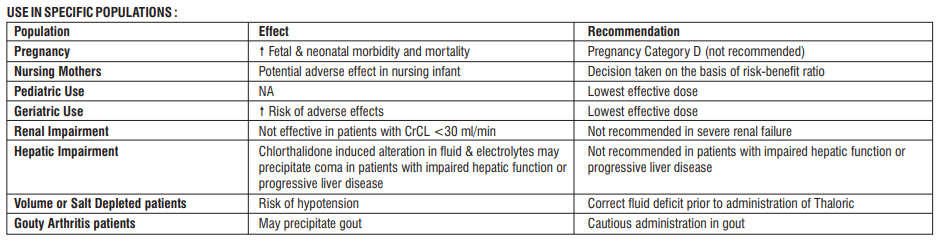
Pediatric Population
The lowest effective dose should be used in children. For example, an initial dose of 0.5 to 1mg/kg/48hours and a maximum dose of 1.7mg/kg/48hours have been used.
Geriatric Population
In elderly patients, the elimination of Chlorthalidone is slower than in healthy young adults, although absorption is the same. Therefore, a reduction in the recommended adult dosage may be needed. Close medical observation is indicated when treating patients of advanced age with Chlorthalidone.
Patients with Renal Impairment
Chlorthalidone loses its diuretic effect in patients with creatinine clearance <30 ml/min.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with hepatic impairment.
Overdosage
Signs and symptoms
In poisoning due to an overdosage the following signs and symptoms may occur: dizziness, nausea, somnolence, hypovolemia, hypotension and electrolyte disturbances associated with cardiac arrhythmias and muscle spasms.
Treatment
There is no specific antidote to Chlorthalidone. Gastric lavage, emesis or activated charcoal should be employed to reduce absorption. Blood pressure and fluid and electrolyte balance should be monitored and appropriate corrective measures taken. Intravenous fluid and electrolyte replacement may be indicated.
Adverse effects
| MedDRA System Organ Class | Adverse reactions |
| Electrolytes and metabolic disorders |
• Very common : hypokalemia, hyperuricemia, and rise in blood lipids mainly at higher doses • Common : hyponatremia, hypomagnesemia and hyperglycemia. |
| Skin | • Common : urticaria and other forms of skin rash. |
| Cardiovascular system | • Common : postural hypotension |
| Central nervous system | • Common : Dizziness. |
| Gastro-intestinal tract | • Common : loss of appetite and minor gastrointestinal distress. |
| Other effects | • Common : impotence |
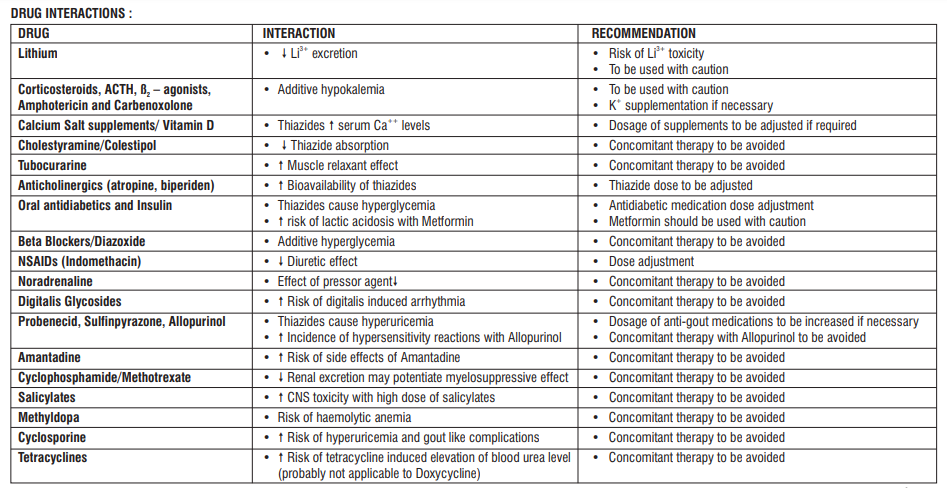
Drug interactions
Storage
Store protected from moisture at a temperature not exceeding 30°C
Keep out of reach of children.
Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
Presentation
Thaloric-6.25 : A blister strip of 10 tablets.
Thaloric-12.5 : A blister strip of 10 tablets.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1.What Thaloric Tablets are and what they are used for
2.What you need to know before you take Thaloric Tablets
3.How to take Thaloric Tablets
4.Possible side effects
5.How to store Thaloric Tablets
6.Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Thaloric Tablets are and what they are used for
Thaloric Tablets belong to a group of medicines called thiazide diuretics.
Thiazide diuretics help to reduce the amount of water in your body. They do this by increasing the amount of water that you pass as urine. They are sometimes called ‘water tablets’.
Thaloric Tablets are used to:
• treat high blood pressure (hypertension)
• treat heart failure
• help reduce the fluid retention that occurs with some kidney or liver diseases
• treat diabetes insipidus (a condition in which an individual produces large amounts of dilute urine and is constantly thirsty).
2. What you need to know before you take Thaloric Tablets
Do not take Thaloric Tablets:
• if you are allergic to Thaloric or sulphonamides such as sulfamethoxazole or any of the other ingredients of this medicine
• if you are not passing any urine at all
• if you have severe kidney or liver problems
• if you have low blood levels of potassium which can cause muscle weakness, muscle twitching or abnormal heartbeat
• if you have low blood levels of sodium which can cause tiredness, confusion, muscle twitching, fits or coma
• if you have high blood levels of calcium which can cause loss of appetite, tiredness or muscle weakness
• if you have ever had gout or kidney stones
• if you have Addison’s disease (which is a condition where your adrenal gland is not producing enough steroids)
• if you are taking lithium.
If any of the above applies to you, or if you are not sure, speak to your doctor or pharmacist before you take Thaloric Tablets.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before taking Thaloric Tablets:
• if you suffer from any other liver or kidney problems;
• if you are on a low-salt diet;
• if you suffer from diabetes mellitus (increased levels of sugar in the blood);
• if you have high cholesterol levels;
• if you have recently had an anaesthetic;
• if you are elderly.
• If you experience a decrease in vision or eye pain. These could be symptoms of fluid accumulation in the vascular layer of the eye (choroidal effusion) or an increase of pressure in your eye and can happen within hours to a week of taking Thaloric Tablets. This can lead to permanent vision loss, if not treated. If you earlier have had a penicillin or sulphonamide allergy, you can be at higher risk of developing this.
If any of the above applies to you, or if you are not sure, speak to your doctor or pharmacist before you take Thaloric Tablets.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines This applies to medicinal products subject to medical prescription or those obtained without a prescription, especially:
other treatments for high blood pressure or heart problems such as:
• ACE inhibitors (for example, lisinopril)
• beta blockers (for example propranolol hydrochloride)
• methyldopa
• vasodilators (for example bosentan)
• calcium channel blockers (for example amlodipine)
• guanethidine
corticosteroids such as prednisolone or betamethasone - used to treat allergic and inflammatory diseases and immune reactions
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) - used to treat a number of different conditions, including ulcerative colitis (a form of inflammatory bowel disease), Crohn’s disease (a form of chronic inflammatory bowel disease) and rheumatoid arthritis
corticosteroids such as prednisolone or betamethasone - used to treat allergic and inflammatory diseases and immune reactions
cytotoxic agents such as cyclophosphamide or methotrexate - used to treat cancer
asthma treatments such as salbutamol or formoterol
amphotericin - used to treat infections
carbenoxolone - used to treat ulcers
insulin and other treatments for diabetes such as chlorpropamide or glibenclamide
digoxin – for an irregular heartbeat
lithium - used to treat mental illness
anticholinergics such as atropine sulphate or hyoscine (butylbromide) - for abdominal or stomach spasms or cramps
colestyramine - used to reduce cholesterol levels and prevent heart disease
amantadine - used to treat Parkinson’s disease or viral infections
allopurinol - used to treat gout (a complex type of arthritis)
non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs) such as aspirin or indometacin - used for pain relief or rheumatism
ciclosporin - used to treat rheumatic disease or skin complaints or after a transplant
calcium salts or vitamin D - used for replacement therapy.
Please tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken/used any other medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription.
Thaloric Tablets with food, drink and alcohol
It is best to take Thaloric Tablets in the morning with food. Swallow your tablets whole with a drink of water. You should avoid low salt diets. Taking Thaloric Tablets may reduce the amount of salt in your body. If you are on a low salt diet check with your doctor first before taking Thaloric Tablets.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Pregnancy
Do not take Thaloric Tablets if you are pregnant or trying to become pregnant. Tell your doctor, immediately, if you become pregnant during treatment with Thaloric Tablets.
Breast-feeding
Do not take Thaloric Tablets if you are breast-feeding because the active substance of Thaloric Tablets passes into breast milk and could harm your baby.
Driving and using machines
Thaloric Tablets may cause dizziness. If you feel dizzy when you start taking these tablets, do not drive or work with machinery until these effects have worn off.
3. How to take Thaloric Tablets
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure. Your doctor will choose a suitable starting dose for your particular condition and monitor your progress. If necessary, this dose can be increased or reduced. Whilst you are taking Thaloric Tablets, your doctor may want to carry out a number of tests from time to time. This is quite usual and nothing to worry about. It is best to take Thaloric Tablets in the morning with food. Swallow your tablets whole with a drink of water.
Adults
The usual doses for adults are as follows:
• High blood pressure:
The starting dose is 25 mg (half a tablet) a day.
Your doctor may increase this to 50 mg (one tablet) a day if necessary.
• Heart failure:
The starting dose is 25 mg (half a tablet) a day.
Your doctor may increase this up to 200 mg (four tablets) a day if necessary.
• Fluid retention associated with kidney or liver disease:
Up to 50 mg (one tablet) a day.
• Diabetes insipidus (a disease in which an individual produces large amounts of dilute urine and is constantly thirsty):
The starting dose is 100 mg (two tablets) twice a day.
Your doctor may reduce your dose to 50 mg (one tablet) a day.
Children
Your doctor will choose a suitable dose based on your child’s age and weight.
Elderly patients or those with kidney problems
Your doctor may give you a lower dose because your body may not get rid of Thaloric Tablets as quickly as normal.
If you are not sure how many tablets to take, ask your doctor or pharmacist. Do not stop taking your tablets suddenly. Ask your doctor first.
If you take more Thaloric Tablets than you should
If you accidentally take more Thaloric Tablets than you should tell your doctor immediately or contact your nearest accident and emergency department. Show any left-over medicines or the empty packet to the doctor.
If you forget to take Thaloric Tablets
If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as possible, unless it is almost time to take the next dose. Do not take a double dose. Then go on as before. If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. If you get any of the following effects tell your doctor or pharmacist immediately:
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
• low blood levels of potassium which can cause muscle weakness, muscle twitching or abnormal heartbeat
• increased blood levels of uric acid
• increased blood levels of cholesterol.
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
• low levels of sodium which can cause tiredness, confusion, muscle twitching, fits or coma
• low levels of magnesium
• high blood sugar levels which can cause tiredness, weakness or feeling thirsty
• nettle rash
• skin rash
• low blood pressure which may make you feel dizzy when you stand up
• dizziness
• loss of appetite
• upset stomach
• impotence in men.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
• increased calcium in the blood which can cause agitation, sore eyes, abdominal pain
• sugar in the urine (this would show up when your doctor or nurse tests your urine)
• worsening of diabetes
• yellowing of the skin or eyes caused by liver or blood problems (jaundice)
• increased sensitivity of your skin to sunlight
• abnormal heartbeat the symptoms of which include palpitations and fainting
• pins and needles
• headache
• feeling or being sick
• stomach pain
• constipation
• diarrhoea
• reduction in blood platelets which increases the risk of bruising or bleeding
• severe reduction in the number of white blood cells which makes infection more likely
• an abnormally high amount of eosinophils (type of white blood cell) in the blood
• breathing problems
• problems with your kidneys.
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
• gout which causes pain and swelling in the joints.
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
• low levels of chloride in the blood, symptoms include dry mouth, thirst, gastrointestinal disturbances (including nausea, vomiting), weakness, lethargy, drowsiness, restlessness, seizures, confusion, headache, muscle pains or cramps, hypotension
• inflammation of the pancreas which causes severe stomach and back pain.
Frequency unknown:
• Decrease in vision or pain in your eyes due to high pressure (possible signs of fluid accumulation in the vascular layer of the eye (choroidal effusion) or acute angle-closure glaucoma).
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top right end of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Thaloric Tablets
This medicinal product does not require any special storage conditions. Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of Children. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton or container after “EXP”. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month. Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Thaloric Tablets contain
- The active substance is chlorthalidone:
Thaloric 6.25
Each uncoated tablet contains
Chlorthalidone IP 6.25 mg
Excipient q.s.
Thaloric 12.5
Each uncoated tablet contains
Chlorthalidone IP 12.5 mg
Excipient q.s.
Presentation/pack size
Thaloric - 6.25: A blister of 10 tablets
Thaloric - 12.5 A blister of 10 tablets