Tivibact Infusion
Therapy Area
Anti Infective
1. Generic Name
Ceftazidime 2 gm / Avibactam 0.5 gm Powder for Concentrate for Solution for Infusion
2. Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each vial contains :
Ceftazidime (As Ceftazidime
Pentahydrate) IP 2.0 gm
Avibactam Sodium
equivalent to Avibactam 0.5 gm
Excipients q.s.
3. Dosage form and strength
Powder for concentrate for solution for infusion, Ceftazidime 2 gm / Avibactam 0.5 gm
4. Clinical Particulars
4.1 Therapeutic Indication
- Complicated intra-abdominal infection (cIAI).
- Complicated urinary tract infection (cUTI), including pyelonephritis.
- Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP), including ventilator associated pneumonia (VAP) with susceptible gram negative microorganisms.
Treatment of patients with bacteremia that occurs in association with, or is suspected to be associated with, any of the infections listed above.
4.2 Posology & Method of Administration
It is recommended that Tivibact should be used to treat infections due to aerobic Gram-negative organisms in adults and paediatric patients aged 3 months and older with limited treatment options only after consultation with a physician with appropriate experience in the management of infectious diseases.
Posology
Dosage in adults with creatinine clearance (CrCL) > 50 mL/min Table 1 shows the recommended intravenous dose for adults with estimated creatinine clearance (CrCL) > 50 mL/min.
T 1 able : 1 Recommended dose for adults with estimated CrCL > 50 mL/min
| Type of infection | Dose of ceftazidime / avibactam | Frequency | Infusion time | Duration of treatment |
| cIAI2,3 | 2 g/0.5 g | Every 8 hours | 2 hours | 5-14 days |
| cUTI, including pyelonephritis3 | 2 g/0.5 g | Every 8 hours | 2 hours | 5-10 days4 |
| HAP/VAP3 | 2 g/0.5 g | Every 8 hours | 2 hours | 7-14 days |
| Bacteraemia associated with, or suspected to be associated with any of the above infections | 2 g/0.5 g | Every 8 hours | 2 hours | Duration of treatment should be in accordance with the site of infection. |
| Infections due to aerobic Gram-negative organisms in patients with limited treatment options2,3 | 2 g/0.5 g | Every 8 hours | 2 hours | Guided by the severity of the infection, the pathogen(s) and the patient's clinical and bacteriological progress5 |
1 CrCL estimated using the Cockcroft-Gault formula. 2 To be used in combination with metronidazole when anaerobic pathogens are known or suspected to be contributing to the infectious process. 3 To be used in combination with an antibacterial agent active against Gram-positive pathogens when these are known or suspected to be contributing to the infectious process. 4 The total duration shown may include intravenous Tivibact followed by appropriate oral therapy. 5 There is very limited experience with the use of Tivibact for more than 14 days. Dosage in paediatric patients with creatinine clearance (CrCL) >50 mL/min/1.73 m2 Table 2 shows the recommended intravenous doses for paediatric patients with estimated creatinine clearance 2 (CrCL) > 50 mL/min/1.73 m . T 1 2 able 2 : Recommended dose for paediatric patients with estimated CrCL > 50 mL/min/1.73 m
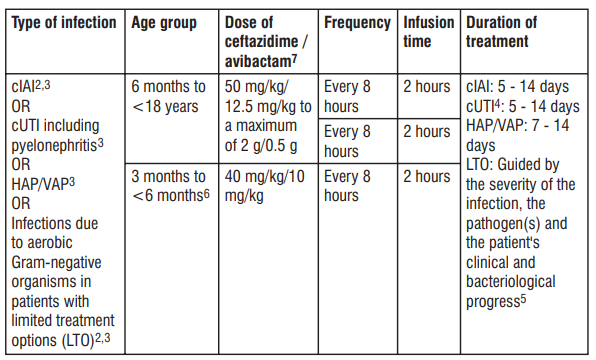
1 CrCL estimated using the Schwartz bedside formula. 2 To be used in combination with metronidazole when anaerobic pathogens are known or suspected to be contributing to the infectious process. 3 To be used in combination with an antibacterial agent active against Gram-positive pathogens when these are known or suspected to be contributing to the infectious process. 4 The total treatment duration shown may include intravenous Tivibact followed by appropriate oral therapy. 5 There is very limited experience with the use of Tivibact for more than 14 days. 6 There is limited experience with the use of Tivibact in paediatric patients 3 months to < 6 months. 7 Ceftazidime/avibactam is a combination product in a xed 4:1 ratio and dosage recommendations are based on the ceftazidime component only.
Special populations
Elderly
No dosage adjustment is required in elderly patients.
Renal impairment
No dosage adjustment is required in patients with mild renal impairment (estimated CrCL > 50 - ≤ 80 mL/min).
Table 3 shows the recommended dose adjustments for adults with estimated CrCL ≤ 50 mL/min.
Dosage in adults with CrCL ≤ 50 mL/min
Table 3: Recommended dose for adults with estimated CrCL ≤ 50 mL/min
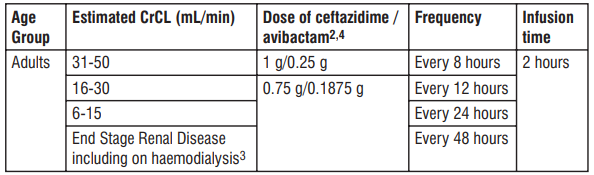
1 CrCL estimated using the Cockcroft-Gault formula. 2 Dose recommendations are based on pharmacokinetic modelling. 3 Ceftazidime and avibactam are removed by haemodialysis. Dosing of Tivibact on haemodialysis days should occur after completion of haemodialysis.
4 Ceftazidime/avibactam is a combination product in a xed 4:1 ratio and dosage recommendations are based on the ceftazidime component only. Table 4 and Table 5 show the recommended dose adjustments for paediatric patients with 2 estimated CrCL ≤ 50 mL/min/1.73 m according to different age groups. Dosage in paediatric patients ≥ 2 years of age with CrCl ≤ 50 mL/min/1.73 m2 T 1 2 able 4: Recommended dose for paediatric patients with estimated CrCL ≤ 50 mL/min/1.73 m
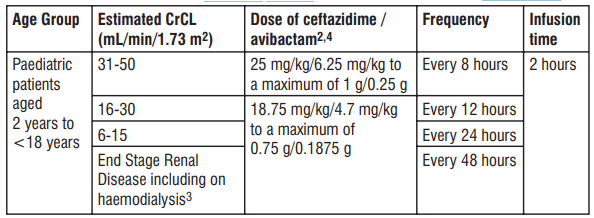
1 CrCL estimated using the Schwartz bedside formula. 2 Dose recommendations are based on pharmacokinetic modelling. 3 Ceftazidime and avibactam are removed by haemodialysis. Dosing of Tivibact on haemodialysis days should occur after completion of haemodialysis. 4 Ceftazidime/avibactam is a combination product in a xed 4:1 ratio and dosage recommendations are based on the ceftazidime component only. Dosage in paediatric patients <2 years of age with CrCl ≤ 50 mL/min/1.73 m2 T 1 2 able 5: Recommended dose for paediatric patients with estimated CrCL ≤ 50 mL/min/1.73 m
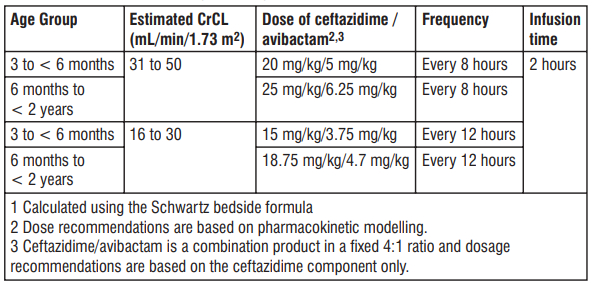
There is insufcient information to recommend a dosage regimen for paediatric patients < 2 2 years of age that have a CrCL < 16 mL/min/1.73 m .
Hepatic impairment
No dosage adjustment is required in patients with hepatic impairment
Paediatric population
The safety and efficacy of Tivibact in paediatric patients < 3 months old have not been established. No data are available.
Method of administration
Intravenous use.
Tivibact is administered by intravenous infusion over 120 minutes in an appropriate infusion
volume.
Reconstitution data
The powder must be reconstituted with water for injections and the resulting concentrate must then be immediately diluted prior to use. Tivibact (ceftazidime/avibactam) is a combination product; each vial contains 2 g of ceftazidime and 0.5 g of avibactam in a xed 4:1 ratio. Dosage recommendations are based on the ceftazidime component only.
Standard aseptic techniques should be used for solution preparation and administration. Doses may be prepared in an appropriately sized infusion bag or infusion syringe. Parenteral medicinal products should be inspected visually for particulate matter prior to administration.
Each vial is for single use only.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
The total time interval between starting reconstitution and completing preparation of the intravenous infusion should not exceed 30 minutes
Instructions for preparing adult and paediatric doses in INFUSION BAG or in INFUSION SYRINGE:
NOTE: The following procedure describes the steps to prepare an infusion solution with a nal concentration of 8-40 mg/mL of ceftazidime. All calculations should be completed prior to initiating these steps. For paediatric patients aged 3 to 12 months, detailed steps to prepare a 20 mg/mL concentration (sufcient for most scenarios) are also provided. 1. Prepare the reconstituted solution (167.3 mg/mL of ceftazidime): a) Insert the syringe needle through the vial closure and inject 10 mL of sterile water for injections. b) Withdraw the needle and shake the vial to give a clear solution. c) Insert a gas relief needle through the vial closure after the product has dissolved to relieve the internal pressure (this is important to preserve product sterility). 2. Prepare the nal solution for infusion (nal concentration must be 8-40 mg/mL of ceftazidime): a) Infusion bag: Further dilute the reconstituted solution by transferring an appropriately calculated volume of the reconstituted solution to an infusion bag containing any of the following: sodium chloride 9 mg/mL (0.9%) solution for injection, dextrose 50 mg/mL (5%) solution for injection, or Lactated Ringer's solution. b) Infusion syringe: Further dilute the reconstituted solution by transferring an appropriately calculated volume of the reconstituted solution combined with a sufficient volume of diluent (sodium chloride 9 mg/mL (0.9%) solution for injection or dextrose 50 mg/mL (5%) solution for injection) to an infusion syringe. Refer to Table 7 below. Table 7: Preparation of Tivibact for adult and paediatric doses in INFUSION BAG or in INFUSION
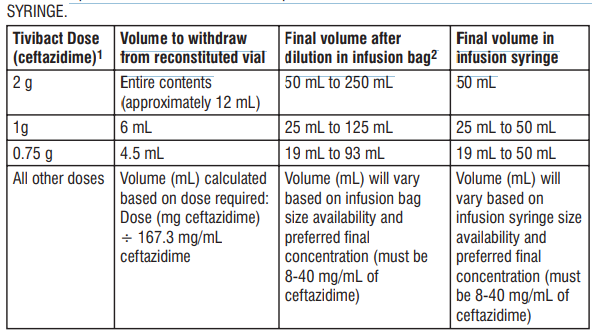
1 Based on ceftazidime component only. 2 Dilute to final ceftazidime concentration of 8 mg/mL for in-use stability up to 12 hours at 2 - 8°C, followed by up to 4 hours at not more than 25°C (i.e. dilute 2 g dose of ceftazidime in 250 mL, 1 g dose of ceftazidime in 125 mL, 0.75 g dose of ceftazidime in 93 mL, etc.). All other ceftazidime concentrations (> 8 mg/mL to 40 mg/mL) have in-use stability up to 4 hours at not more than 25°C.
Preparation of Tivibact for use in paediatric patients aged 3 to 12 months of age in INFUSION SYRINGE:
NOTE: The following procedure describes the steps to prepare an infusion solution with a nal concentration of 20 mg/mL of ceftazidime (sufficient for most scenarios). Alternative concentrations may be prepared, but must have a nal concentration range of 8-40 mg/mL of ceftazidime.
1. Prepare the reconstituted solution (167.3 mg/mL of ceftazidime): a) Insert the syringe needle through the vial closure and inject 10 mL of sterile water for injections. b) Withdraw the needle and shake the vial to give a clear solution. c) Insert a gas relief needle through the vial closure after the product has dissolved to relieve the internal pressure (this is important to preserve product sterility). 2. Prepare the nal solution for infusion to a nal concentration of 20 mg/mL of ceftazidime: a) Further dilute the reconstituted solution by transferring an appropriately calculated volume of the reconstituted solution combined with a sufcient volume of diluent (sodium chloride 9 mg/mL (0.9%) solution for injection or dextrose 50 mg/mL (5%) solution for injection) to an infusion syringe. b) Refer to Table 8, 9, or 10 below to conrm the calculations. Values shown are approximate as it may be necessary to round to the nearest graduation mark of an appropriately sized syringe. Note that the tables are NOT inclusive of all possible calculated doses but may be utilized to estimate the approximate volume to verify the calculation. Table 8: Preparation of Tivibact (final concentration of 20 mg/mL of ceftazidime) in paediatric patients 3 2 to 12 months of age with creatinine clearance (CrCL) > 50 mL/min/1.73 m
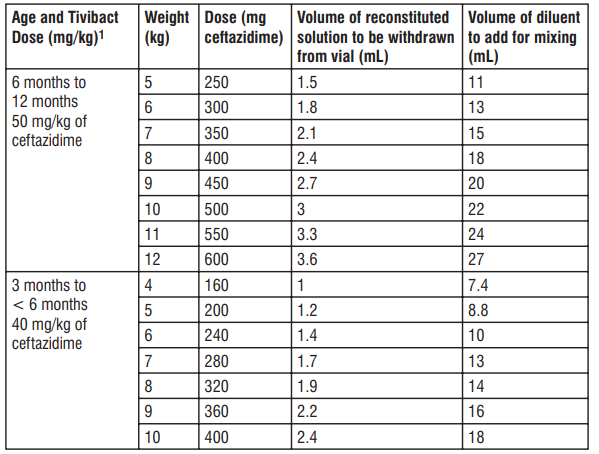
1 Based on ceftazidime component only. Table 9: Preparation of Tivibact (nal concentration of 20 mg/mL of ceftazidime) in paediatric patients 3 2 to 12 months of age with CrCL 31 to 50 mL/min/1.73 m
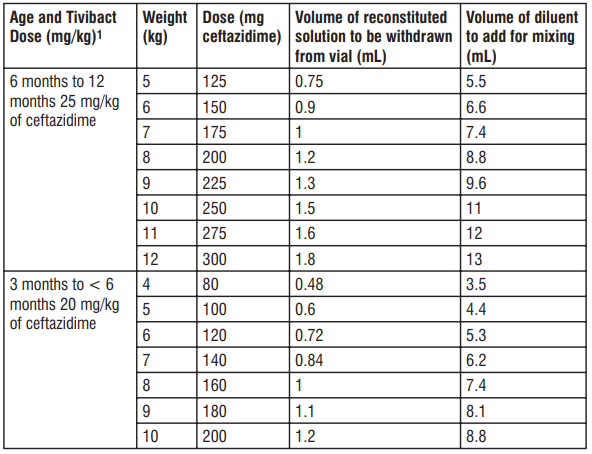
1 Based on ceftazidime component only. Table 10: Preparation of Tivibact (nal concentration of 20 mg/mL of ceftazidime) in paediatric patients 3 2 to 12 months of age with CrCL 16 to 30 mL/min/1.73 m
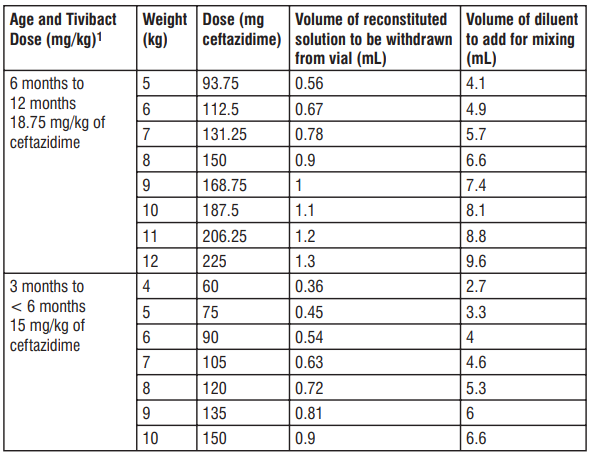
1 Based on ceftazidime component only.
4.3 Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to the active substances or to any of the excipients listed in the formulation. • Hypersensitivity to any cephalosporin antibacterial agent. • Severe hypersensitivity (e.g. anaphylactic reaction, severe skin reaction) to any other type of β-lactam antibacterial agent (e.g. penicillins, monobactams or carbapenems).
4.4 Warning & Precautions
Hypersensitivity reactions
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity reactions are possible. In case of hypersensitivity reactions, treatment with Tivibact must be discontinued immediately and adequate emergency measures must be initiated. Before beginning treatment, it should be established whether the patient has a history of hypersensitivity reactions to ceftazidime, to other cephalosporins or to any other type of β-lactam antibacterial agent. Caution should be used if ceftazidime/avibactam is given to patients with a history of non-severe hypersensitivity to penicillins, monobactams or carbapenems
Clostridioides difficile- associated diarrhoea
Clostridioides diffcile-associated diarrhoea has been reported with ceftazidime/avibactam, and can range in severity from mild to life-threatening. This diagnosis should be considered in patients who present with diarrhoea during or subsequent to the administration of Tivibact. Discontinuation of therapy with Tivibact and the administration of specic treatment for Clostridioides difcile should be considered. Medicinal products that inhibit peristalsis should not be given.
Renal impairment
Ceftazidime and avibactam are eliminated via the kidneys, therefore, the dose should be reduced according to the degree of renal impairment. Neurological sequelae, including tremor, myoclonus, non-convulsive status epilepticus, convulsion, encephalopathy and coma, have occasionally been reported with ceftazidime when the dose has not been reduced in patients with renal impairment. In patients with renal impairment, close monitoring of estimated creatinine clearance is advised. In some patients, the creatinine clearance estimated from serum creatinine can change quickly, especially early in the course of treatment for the infection.
Nephrotoxicity
Concurrent treatment with high doses of cephalosporins and nephrotoxic medicinal products such as aminoglycosides or potent diuretics (e.g. furosemide) may adversely affect renal function. Direct antiglobulin test (DAGT or Coombs test) seroconversion and potential risk of haemolytic anaemia Ceftazidime/avibactam use may cause development of a positive direct antiglobulin test (DAGT, or Coombs test), which may interfere with the cross-matching of blood and/or may cause drug induced immune haemolytic anaemia. While DAGT seroconversion in patients receiving Tivibact was very common in clinical studies (the estimated range of seroconversion across Phase 3 studies was 3.2% to 20.8% in patients with a negative Coombs test at baseline and at least one follow-up test), there was no evidence of haemolysis in patients who developed a positive DAGT on treatment. However, the possibility that haemolytic anaemia could occur in association with Tivibact treatment cannot be ruled out. Patients experiencing anaemia during or after treatment with Tivibact should be investigated for this possibility.
Complicated intra-abdominal infections in adults
In two studies in patients with cIAI, the most common diagnosis (approximately 42%) was appendiceal perforation or peri-appendiceal abscess. Approximately 87% of patients had
APACHE II scores of ≤ 10 and 4% had bacteraemia at baseline. Death occurred in 2.1% (18/857) of patients who received Tivibact and metronidazole and in 1.4% (12/863) of patients who received meropenem. Among a subgroup with baseline CrCL 30 to 50 mL/min death occurred in 16.7% (9/54) of patients who received Tivibact and metronidazole and 6.8% (4/59) of patients who received meropenem. Patients with CrCL 30 to 50 mL/min received a lower dose of Tivibact than is currently recommended for patients in this sub-group.
Complicated urinary tract infections in adults
In two studies in patients with cUTI, 381/1091 (34.9%) patients were enrolled with cUTI without pyelonephritis while 710 (65.1%) were enrolled with acute pyelonephritis (mMITT population). A total of 81 cUTI patients (7.4%) had bacteraemia at baseline. Hospital-acquired pneumonia (including ventilator-associated pneumonia) in adults. In a single study in patients with nosocomial pneumonia 280/808 (34.7%) had VAP and 40/808 (5%) were bacteraemic at baseline.
Patients with limited treatment options
The use of ceftazidime/avibactam to treat patients with infections due to Gram-negative aerobic pathogens who have limited treatment options is based on experience with ceftazidime alone and on analyses of the pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationship for ceftazidime/avibactam. Spectrum of activity of ceftazidime/avibactam Ceftazidime has little or no activity against the majority of Gram-positive organisms and anaerobes. Additional antibacterial agents should be used when these pathogens are known or suspected to be contributing to the infectious process. The inhibitory spectrum of avibactam includes many of the enzymes that inactivate ceftazidime, including Ambler class A β-lactamases and class C β-lactamases. Avibactam does not inhibit class B enzymes (metallo-β-lactamases) and is not able to inhibit many of the class D enzymes.
Non-susceptible organisms
Prolonged use may result in the overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms (e.g. enterococci, fungi), which may require interruption of treatment or other appropriate measures.
Interference with laboratory tests
Ceftazidime may interfere with copper reduction methods (Benedict's, Fehling's, Clinitest) for detection of glycosuria leading to false positive results. Ceftazidime does not interfere with enzyme-based tests for glycosuria.
Controlled sodium die
The maximum daily dose of this product is equivalent to 22% of the WHO recommended maximum daily intake for sodium. Tivibact is considered high in sodium. This should be considered when administering Tivibact to patients who are on a controlled sodium diet. Tivibact may be diluted with sodium-containing solutions and this should be considered in relation to the total sodium from all sources that will be administered to the patient.
Paediatric population
There is a potential risk of overdosing, particularly for paediatric patients aged from 3 to less than 12 months of age. Care should be taken when calculating the volume of administration of the dose.
4.5 Drug Interactions
In vitro, avibactam is a substrate of OAT1 and OAT3 transporters which might contribute to the active uptake of avibactam from the blood compartment and, therefore, affect its excretion. Probenecid (a potent OAT inhibitor) inhibits this uptake by 56% to 70% in vitro and, therefore, has the potential to alter the elimination of avibactam. Since a clinical interaction study of avibactam and probenecid has not been conducted, co-administration of avibactam with probenecid is n9ot recommended. Avibactam showed no signicant inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymes in vitro. Avibactam and ceftazidime showed no in vitro cytochrome P450 induction at clinically relevant concentrations. Avibactam and ceftazidime do not inhibit the major renal or hepatic transporters in the clinically relevant exposure range, therefore the interaction potential via these mechanisms is considered to be low. Clinical data have demonstrated that there is no interaction between ceftazidime and avibactam, and between ceftazidime/avibactam and metronidazole.
Other types of interaction
Concurrent treatment with high doses of cephalosporins and nephrotoxic medicinal products such as aminoglycosides or potent diuretics (e.g. furosemide) may adversely affect renal function. Chloramphenicol is antagonistic in vitro with ceftazidime and other cephalosporins. The clinical relevance of this nding is unknown, but due to the possibility of antagonism in vivo this drug combination should be avoided.
4.6 Special populations
Pregnancy
Animal studies with ceftazidime do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to pregnancy, embryonal/foetal development, parturition or postnatal development. Animal studies with avibactam have shown reproductive toxicity without evidence of teratogenic effects. Ceftazidime/avibactam should only be used during pregnancy if the potential benet outweighs the possible risk.
Breast-feeding
Ceftazidime is excreted in human milk in small quantities. It is unknown whether avibactam is excreted in human milk. A risk to newborns/infants cannot be excluded. A decision must be made whether to discontinue breast feeding or to discontinue/abstain from ceftazidime/avibactam therapy taking into account the benet of breast feeding for the child and the benet of therapy for the woman.
Fertility
The effects of ceftazidime/avibactam on fertility in humans have not been studied. No data are available on animal studies with ceftazidime. Animal studies with avibactam do not indicate harmful effects with respect to fertility.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Undesirable effects may occur (e.g. dizziness), which may inuence the ability to drive and use machines following administration of Tivibact.
4.8 Undesirable Effects
The most common adverse reactions were Coombs direct test positive, nausea, and diarrhoea. Nausea and diarrhoea were usually mild or moderate in intensity. Table 6: Frequency of adverse reactions by system organ class
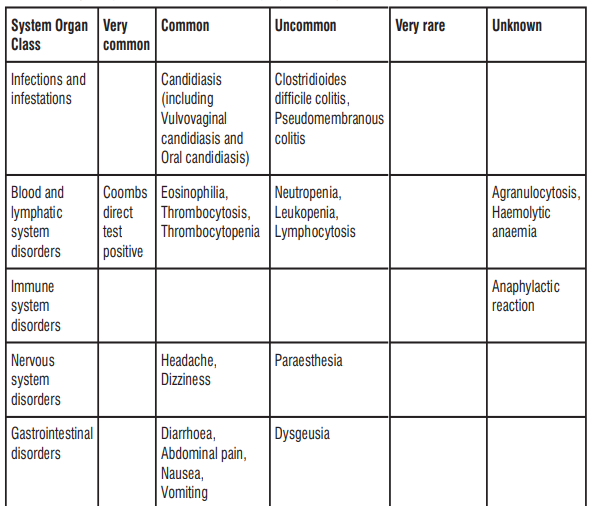
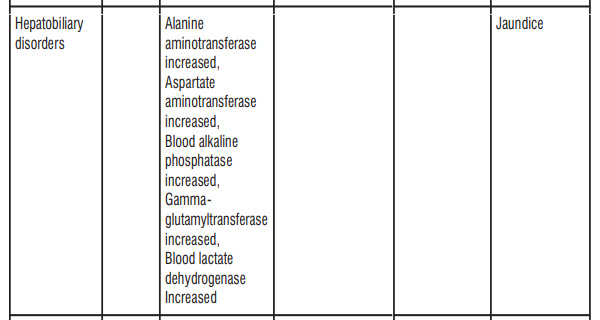
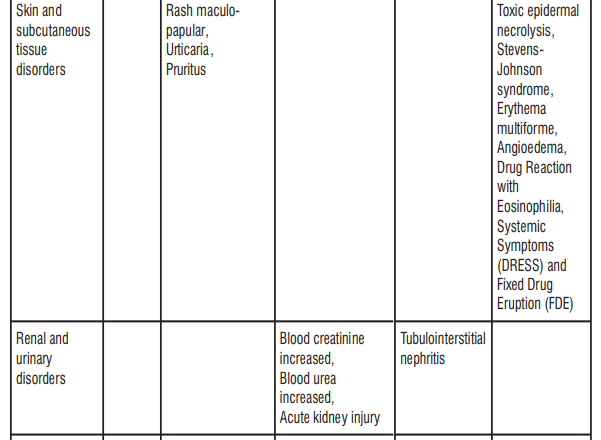

Paediatric population
The safety assessment in paediatric patients is based on the safety data from two trials in which 61 patients (aged from 3 years to less than 18 years) with cIAI and 67 patients with cUTI (aged from 3 months to less than 18 years) received Tivibact. Overall, the safety prole in these 128 paediatric patients was similar to that observed in the adult population with cIAI and cUTI.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benet/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com Website : http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Overdose with ceftazidime/avibactam can lead to neurological sequelae including encephalopathy, convulsions and coma, due to the ceftazidime component. Serum levels of ceftazidime can be reduced by haemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. During a 4-hour haemodialysis period, 55% of the avibactam dose was removed.
5. Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Ceftazidime inhibits bacterial peptidoglycan cell wall synthesis following binding to penicillin binding proteins (PBPs), which leads to bacterial cell lysis and death. Avibactam is a non β-lactam, β-lactamase inhibitor that acts by forming a covalent adduct with the enzyme that is stable to hydrolysis. It inhibits both Ambler class A and class C β-lactamases and some class D enzymes, including extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs), KPC and OXA-48 carbapenemases, and AmpC enzymes. Avibactam does not inhibit class B enzymes (metalloβ-lactamases) and is not able to inhibit many class D enzymes.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic Properties
Efficacy has been demonstrated in clinical studies against the following pathogens that were susceptible to ceftazidime/avibactam in vitro.
Complicated intra-abdominal infections
Gram-negative micro-organisms
• Citrobacter freundii
• Enterobacter cloacae
• Escherichia coli
• Klebsiella oxytoca
• Klebsiella pneumoniae
• Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Complicated urinary-tract infections
Gram-negative micro-organisms
• Escherichia coli
• Klebsiella pneumoniae
• Proteus mirabilis
• Enterobacter cloacae
• Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Hospital-acquired pneumonia including ventilator-associated pneumonia
Gram-negative micro-organisms
• Enterobacter cloacae
• Escherichia coli
• Klebsiella pneumoniae
• Proteus mirabilis
• Serratia marcescens
• Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Clinical efficacy has not been established against the following pathogens that are relevant to the approved indications although in vitro studies suggest that they would be susceptible to ceftazidime/avibactam in the absence of acquired mechanisms of resistance. Gram-negative micro-organisms
• Citrobacter koseri
• Enterobacter aerogenes
• Morganella morganii
• Proteus vulgaris
• Providencia rettgeri
In-vitro data indicate that the following species are not susceptible to ceftazidime/avibactam
• Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant)
• Anaerobes
• Enterococcus spp.
• Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
• Acinetobacter spp.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Distribution
The human protein binding of both ceftazidime and avibactam is approximately 10% and 8%, respectively. The steady-state volumes of distribution of ceftazidime and avibactam were about 17 L and 22 L, respectively in healthy adults following multiple doses of 2 g/0.5 g ceftazidime/avibactam infused over 2 hours every 8 hours. Both ceftazidime and avibactam penetrate into human bronchial epithelial lining uid (ELF) to the same extent with concentrations around 30% of those in plasma. The concentration time proles are similar for ELF and plasma. Penetration of ceftazidime into the intact blood-brain barrier is poor. Ceftazidime concentrations of 4 to 20 mg/L or more are achieved in the CSF when the meninges are inamed. Avibactam penetration of the blood brain barrier has not been studied clinically; however, in rabbits with inflamed meninges, CSF exposures of ceftazidime and avibactam were 43% and 38% of plasma AUC, respectively. Ceftazidime crosses the placenta readily, and is excreted in the breast milk.
Biotransformation
Ceftazidime is not metabolised. No metabolism of avibactam was observed in human liver preparations (microsomes and hepatocytes). Unchanged avibactam was the major drug-related component 14 in human plasma and urine following dosing with [ C]-avibactam.
Elimination
The terminal half-life (t½) of both ceftazidime and avibactam is about 2 h after intravenous administration. Ceftazidime is excreted unchanged into the urine by glomerular ltration; approximately 80-90% of the dose is recovered in the urine within 24 h. Avibactam is excreted unchanged into the urine with a renal clearance of approximately 158 mL/min, suggesting active tubular secretion in addition to glomerular ltration. Approximately 97% of the avibactam dose is recovered in the urine, 95% within 12 h. Less than 1% of ceftazidime is excreted via the bile and less than 0.25% of avibactam is excreted into faeces
6. Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
Ceftazidime
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, reproduction toxicity or genotoxicity. Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with ceftazidime.
Avibactam
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity or genotoxicity. Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with avibactam.
Reproduction toxicity
In pregnant rabbits administered avibactam at 300 and 1000 mg/kg/day, there was a dose-related lower mean foetal weight and delayed ossication, potentially related to maternal toxicity. Plasma exposure levels at maternal and foetal NOAEL (100 mg/kg/day) indicate moderate to low margins of safety.
In the rat, no adverse effects were observed on embryofetal development or fertility. Following administration of avibactam throughout pregnancy and lactation in the rat, there was no effect on pup survival, growth or development, however there was an increase in incidence of dilation of the renal pelvis and ureters in less than 10% of the rat pups at maternal exposures greater than or equal to approximately 1.5 times human therapeutic exposures.
7. Description
Tivibact is an antibacterial combination product consisting of the semisynthetic cephalosporin ceftazidime pentahydrate and the β-lactamases inhibitor avibactam sodium for IV administration.
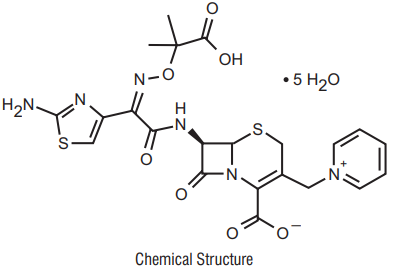
Ceftazidime
Ceftazidime pentahydrate is is the pentahydrate of (6R,7R,Z)-7-(2-(2aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(2- carboxypropan-2-yloxyimino)acetamido)-8-oxo-3-(pyridinium-1-ylmethyl)-5-thia-1azabicyclooct-2-ene-2-carboxylate. Its molecular weight is 636.6. The empirical formula is C22H32N6O12S2.
Avibactam
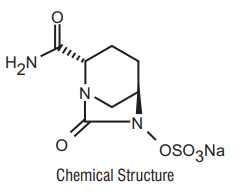
Avibactam sodium chemical name is sodium octan-6-yl] sulphate. Its molecular weight is 287.23. The empirical formula is C7H10N3O6SNa.
8 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
The compatibility of Tivibact with other medicines has not been established. Tivibact should not be mixed with or physically added to solutions containing other medicinal products.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack
8.3 Packaging information
20 ml USP Type - I glass vial containing 2.5 g Ceftazidim/Avibactam packed in carton along with pack insert.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions Store below 30°C. Protect from light
Keep out of reach of children.
9 Patient Counselling Information
Do not use Tivibact if
• you are allergic to ceftazidime, avibactam or any of the other ingredients of this medicine
• you are allergic to other cephalosporin antibiotics
• you have ever had a severe allergic reaction to other antibiotics belonging to the penicillin or carbapenem groups.
Do not use Tivibact if any of the above apply to you. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or nurse before using Tivibact
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or nurse before using Tivibact if:
• you have ever had any allergic reaction (even if only a skin rash) to other antibiotics belonging to the penicillin or carbapenem groups
• you have kidney problems - your doctor may give you a lower dose to make sure you don’t get too much medicine. This could cause symptoms such as fits (see section If you use more Tivibact than you should)
If any of the above apply to you (or you are not sure), talk to your doctor or nurse before using Tivibact.
Talk to your doctor or nurse if you suffer from diarrhoea during your treatment.
Other infections
There is a small possibility that you may get a different infection caused by another bacteria during or after treatment with Tivibact. These include thrush (fungal infections of the mouth or genital area).
Lab tests
Tell your doctor that you are taking Tivibact if you are going to have any tests. This is because you may get an abnormal result with a test called “DAGT” or “Coombs”. This test looks for antibodies that fight against your red blood cells. Tivibact can also affect the results of some urine tests for sugar. Tell the person taking the sample that you have been given Tivibact.
Paediatric patients
Tivibact should not be used in paediatric patients aged under 3 months. This is because it is not known if the medicine is safe to use in this age group.
Other medicines and Tivibact
Tell your doctor or nurse if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines. Talk to your doctor before using Tivibact if you are taking any of the following medicines:
• an antibiotic called chloramphenicol
• a type of antibiotic called an aminoglycoside - such as gentamicin, tobramycin
• a water tablet called furosemide
• a medicine for gout called probenecid
Tell your doctor before using Tivibact if any of the above apply to you.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Tivibact may make you feel dizzy. This may affect you being able to drive, use tools or machines.
Tivibact contains sodium
This medicine contains approximately 148 mg sodium in each vial. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you need 3 or more vials daily for a prolonged period, especially if you have been advised to have a low salt (sodium) diet.
How to use Tivibact
Tivibact will be given to you by a doctor or a nurse
If you use more Tivibact than you should
Tivibact will be given to you by a doctor or a nurse, so it is unlikely you will be given the wrong dose. However, if you have side effects or think you have been given too much Tivibact, tell your doctor or nurse straight away. If you have too much Tivibact it could have an effect on the brain and cause fits or coma.
If you miss a dose of Tivibact
If you think you have missed a dose, tell your doctor or nurse straight away. If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or nurse.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or nurse.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet:
- What is Tivibact and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Tivibact
- How to use Tivibact
- Possible side effects
- How to store Tivibact
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Tivibact is and what it is used for
What Tivibact is
Tivibact is an antibiotic medicine that contains two active substances ceftazidime and avibactam.
- Ceftazidime belongs to the group of antibiotics called “cephalosporins”. It can kill many types of bacteria.
- Avibactam is a “beta-lactamase inhibitor” that helps ceftazidime kill some bacteria that it cannot kill on its own.
What Tivibact is used for
Tivibact is used in adults and paediatric patients aged 3 months and over to treat:
- infections of the stomach and gut (abdomen)
- infections of the bladder or kidneys called “urinary tract infections”
- an infection of the lungs called “pneumonia”
- infections caused by bacteria that other antibiotics may not be able to kill
Tivibact is used in adults to treat infection of the blood associated with infections of the abdomen, urinary tract, or pneumonia.
How Tivibact works
Tivibact works by killing certain types of bacteria, which can cause serious infections.
2. What you need to know before you use Tivibact
Do not use Tivibact if:
you are allergic to ceftazidime, avibactam or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
you are allergic to other cephalosporin antibiotics
you have ever had a severe allergic reaction to other antibiotics belonging to the penicillin or carbapenem groups
Do not use Tivibact if any of the above apply to you. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or nurse before using Tivibact.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or nurse before using Tivibact if:
- you have ever had any allergic reaction (even if only a skin rash) to other antibiotics belonging to the penicillin or carbapenem groups
- you have kidney problems - your doctor may give you a lower dose to make sure you don’t get too much medicine. This could cause symptoms such as fits (see section If you use more Tivibact than you should)
If any of the above apply to you (or you are not sure), talk to your doctor or nurse before using Tivibact
Talk to your doctor or nurse if you suffer from diarrhoea during your treatment.
Other infections
There is a small possibility that you may get a different infection caused by another bacteria during or after treatment with Tivibact. These include thrush (fungal infections of the mouth or genital area).
Lab tests
Tell your doctor that you are taking Tivibact if you are going to have any tests. This is because you may get an abnormal result with a test called “DAGT” or “Coombs”. This test looks for antibodies that fight against your red blood cells.
Tivibact can also affect the results of some urine tests for sugar. Tell the person taking the sample that you have been given Tivibact.
Paediatric patients
Tivibact should not be used in paediatric patients aged under 3 months. This is because it is not known if the medicine is safe to use in this age group.
Other medicines and Tivibact
Tell your doctor or nurse if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines.
Talk to your doctor before using if you are taking any of the following medicines:
an antibiotic called chloramphenicol
a type of antibiotic called an aminoglycoside – such as gentamicin, tobramycin
a water tablet called furosemide
a medicine for gout called probenecid
Tell your doctor before using Tivibact if any of the above apply to you.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Tivibact may make you feel dizzy. This may affect you being able to drive, use tools or machines.
Tivibact contains sodium
This medicine contains approximately 146 mg sodium (main component of cooking/table salt) in each vial. This is equivalent to 7.3% of the recommended maximum daily dietary intake for sodium for an adult.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you need 3 or more vials daily for a prolonged period, especially if you have been advised to have a low salt (sodium) diet.
3. How to use Tivibact
Tivibact will be given to you by a doctor or a nurse.
How much to use
The recommended dose for adults is one vial (2 g of ceftazidime and 0.5 g of avibactam), every 8 hours. The dose for paediatric patients aged 3 months and over will be calculated by the doctor based on the weight and age of the child.
It is given as a drip into a vein – this will normally take about 2 hours.
A course of treatment usually lasts from 5 to up to 14 days, depending on the type of infection you have and how you respond to treatment.
People with kidney problems
If you have kidney problems your doctor may lower your dose. This is because Tivibact is removed from your body by the kidneys.
If you use more Tivibact than you should
Tivibact will be given to you by a doctor or a nurse, so it is unlikely you will be given the wrong dose. However, if you have side effects or think you have been given too much Tivibact, tell your doctor or nurse straight away. If you have too much Tivibact it could have an effect on the brain and cause fits or coma.
If you miss a dose of Tivibact
If you think you have missed a dose, tell your doctor or nurse straight away.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. The following side effects may happen with this medicine:
Serious side effects
Tell your doctor straight away if you notice any of the following serious side effects - you may need urgent medical treatment:
- severe allergic reactions – signs include sudden swelling of your lips, face, throat or tongue, a severe rash or other severe skin reactions, difficulty swallowing or breathing. This reaction may be life-threatening.
- diarrhoea that keeps getting worse or does not go away, or stools that contains blood or mucus – this may happen during or after treatment is stopped with Tivibact. If this happens do not take medicines that stop or slow bowel movement.
Tell your doctor straight away if you notice any of the serious side effects above.
Other side effects
Tell your doctor or nurse if you notice any of the following side effects:
Very common: (may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- abnormal result with a test called “DAGT” or “Coombs”. This test looks for antibodies that fight against your red blood cells. It is possible that this could cause anaemia (which may make you feel tired) and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Common: (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- fungal infections, including those of the mouth and vagina
- change in the number of some types of blood cells (called “eosinophils” and “thrombocytes”) – shown in blood tests
- headache
- feeling dizzy
- feeling sick (nausea) or being sick (vomiting)
- stomach pain
- diarrhoea
- increase in the amount of some enzymes produced by your liver - shown in blood tests
- raised itchy skin rash (“hives”)
- itchiness
- redness, pain or swelling where Tivibact was given into a vein
- fever
Uncommon: (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- increase in the number of a type of blood cell (called “lymphocytes”) – shown in blood tests
- decrease in the number of some types of blood cells (called “leucocytes”) - shown in blood tests
- tingling or numbness
- bad taste in your mouth an increase in the level of some types of substances in your blood (called “creatinine” and “urea”).
- These show how well your kidneys are working.
Very rare: (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- swelling in a part of the kidney that causes a reduction in its normal working function
Not known: (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- significant decrease in the type of white blood cells used to fight infection - shown in blood tests
- decrease in the number of red blood cells (haemolytic anaemia) – shown in blood tests
- severe allergic reaction (see Serious side effects, above)
- yellowing of the whites of the eyes or skin
- sudden onset of a severe rash or blistering or peeling skin, possibly accompanied by a high fever orjoint pain (these may be signs of more serious medical conditions such as toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme or a condition known as DRESS, Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms)
- swelling under the skin, particularly lips and around the eyes
Tell your doctor or nurse if you notice any of the side effects listed above.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top right end of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Tivibact
Store below 30°C. Protect from light.
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the container. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Tivibact contains
Ceftazidime (As Ceftazidime Pentahydrate) IP 2.0 gm
Avibactam Sodium equivalent to Avibactam 0.5 gm
Excipients q.s.