Vitanova-D3 Nano oral solution
Therapy Area
Vitamins/Minerals Supplements
1.0 Generic name
Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) Oral Solution 60000 IU
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
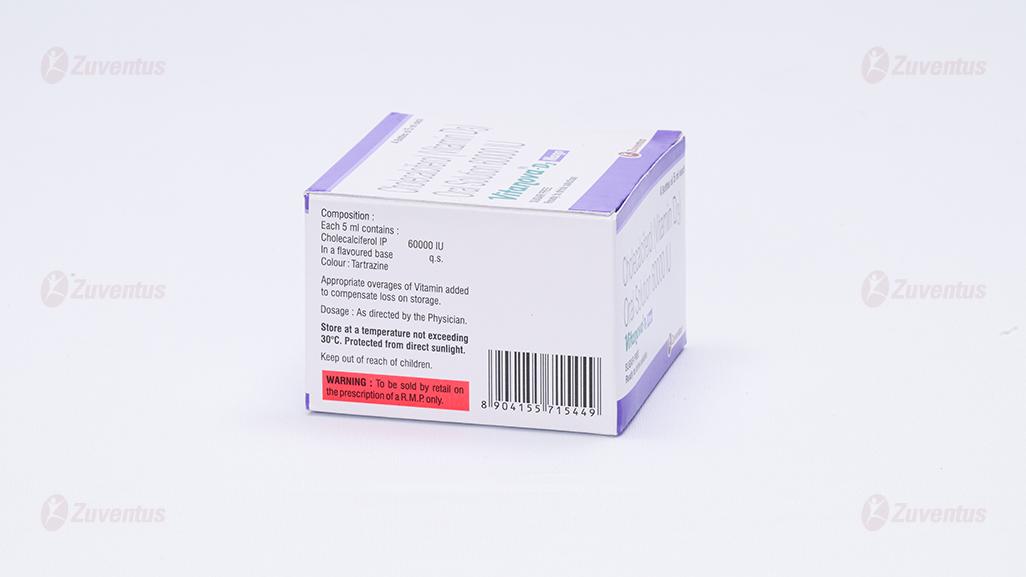
Each 5 ml syrup contains :
Cholecalciferol IP 60000 IU
In a flavoured base q.s.
Colour : Tartrazine
Appropriate overages of Vitamin added to compensate loss on storage.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Oral Solution, 60000 IU
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the treatment of Vitamin D3 deficiency.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Adults
Vitamin D3 60000 IU to be given once a week for a period of 8 weeks, followed by maintenance daily dose as directed by the Physician.
Pediatric use
As prescribed by the Physician only.
Hepatic insufficiency
The intestinal absorption of Cholecalciferol may be markedly impaired; conversion to Calcifediol may also be reduced significantly, with the requirement of high doses. Agents not requiring hepatic hydroxylation (e.g. Calcitriol, Alphacalcidol) are preferred.
Renal insufficiency
Although only small amounts of a Vitamin D dose are recovered in the urine, metabolic conversion to calcitriol is impaired and higher doses are generally required in most conditions. Agents not requiring hepatic hydroxylation (e.g. Calcitriol, Alphacalcidol) are preferred.
4.3 Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to Cholecalciferol, Ergocalciferol or Vitamin D metabolites (e.g. Calcitriol, Calcifediol, Alfacalcidol, Calcipotriol).
• Hypercalcemia or hypercalciuria.
• Diseases and/or conditions, which lead to hypercalcaemia (e.g. nephrocalcinosis, myeloma, bone metastases, primar y hyperparathyroidism, sarcoidosis, prolonged immobilisation accompanied by hypercalcaemia).
• Nephrolithiasis
• Hypervitaminosis D
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
The product should be prescribed with caution to patients suffering from sarcoidosis due to risk of increased metabolism of Vitamin D into its active form. These patients should be monitored with regard to the calcium content in serum and urine. During long-term treatment, serum calcium levels should be followed and renal function should be monitored through measurements of serum creatinine. Monitoring is especially important in elderly patients on concomitant treatment with cardiac glycosides or diuretics and in patients with a high tendency to calculus formation.
In case of hypercalciuria or signs of impaired renal function the dose should be reduced or the treatment discontinued. The product should be used with caution in patients with impairment of renal function and the effect on Calcium and Phosphate levels should be monitored. The risk of soft tissue calcification should be taken into account.
In patients with severe renal insufficiency, Vitamin D in the form of Cholecalciferol is not metabolised normally and other forms of Vitamin D should be used. The content of Vitamin D should be considered when prescribing other medicinal products containing Vitamin D.
Additional doses of Vitamin D should be taken under close medical supervision. In such cases it is necessary to monitor serum calcium levels and urinary Calcium excretion frequently.
Caution is required in patients suffering from cardiac conditions like arteriosclerosis due to the possible exacerbation related to hypercalcaemia and in patients with hyperlipidemia due to possibility of LDL elevation.
The content of this product should be considered when prescribing other medicinal products containing Vitamin D and preparation containing calcium. Prescription of this product with other Vitamin D supplements should be done under close medical supervision. In such cases serum calcium levels should be monitored.
In patients with compromised Calcium metabolism serum concentrations of phosphate should be checked during the Vitamin D therapy to reduce the risk of ectopic calcification.
Medical supervision is recommended for use of this product in children.
4.5 Drugs interactions
Thiazide diuretics reduce the urinary excretion of Calcium. Due to the increased risk of hypercalcaemia, serum calcium should be regularly monitored during concomitant use of Thiazide diuretics.
Concomitant use of phenytoin or barbiturates may reduce the effect of Vitamin D since the metabolism increases. Concomitant use of Vitamin D with Vitamin D analogues, is not recommended due to the additive effect and increased toxic potential. Excessive dosing of Vitamin D can induce hypercalcaemia, which may increase the risk of digitalis toxicity and serious arrhythimias due to the additive inotropic effects. The electrocardiogram (ECG) and serum calcium levels of patients should be closely monitored. Glucocorticoid steroids may increase Vitamin D metabolism and elimination. Systemic corticosteroids reduce calcium absorption. Moreover, the effect of Vitamin D may be decreased. Simultaneous treatment with ion exchange resins such as Cholestyramine or laxatives such as paraffin oil may reduce the gastrointestinal absorption of Vitamin D. Therefore, a time interval as long as possible between the intakes is recommended. The absorption and therefore the efficacy of Ketoconazole will be decreased by the concomitant intake of this product. Concomitant treatment with rifampicin can decrease the effect of Vitamin D3 because of metabolic activation.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
The product should be used during pregnancy only in case of a Vitamin D deficiency. It is not recommended during pregnancy in patients without a Vitamin D deficiency. Studies in animals have shown reproductive toxicity of high doses of Vitamin D. There are no indications that Vitamin D at therapeutic doses is teratogenic in humans. Overdose of Vitamin D has been associated with teratogenic effect in animals.
Lactation
Vitamin D can be used during breast feeding. Vitamin D3 passes into breast milk. This should be considered while giving additional Vitamin D to the child.
4.7 Effects on the ability to drive and use machines
There are no data on the effect of this product on driving capacity and use of machines. An effect is, however, unlikely.
4.8 Undesirable effects
High dose of cholecalciferol can cause weakness, fatigue, sleepiness, headache, loss of appetite, dry mouth, metallic taste, nausea and vomiting. Vitamin D toxicity, including nephrocalcinosis / renal failure, hypertension can occur with prolonged use of Cholecalciferol, relatively low doses can produce toxicity in hypersensitive infants and children.
Hypervitaminosis D is reversible upon discontinuation of treatment unless renal damage is severe. Metabolism and nutrition disorder like Hypercalcaemia and hypercalciuria is uncommon. Skin and subcutaneous disorders like pruritus, rash and urticaria are rarely observed.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit / risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via
email to : www.medico@zuventus.com
Website : http://www.zuventus.co.in/safety.aspx
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Treatment of hypercalcaemia
The treatment with Vitamin D must be discontinued. Treatment with Thiazide diuretics, Lithium, Vitamin A and Cardiac glycosides must also be discontinued.
Rehydration, and, according to severity, isolated or combined treatment with loop Diuretics, Bisphosphonates, Calcitonin and Corticosteroids should be considered. Serum electrolytes, renal function and diuresis must be monitored. In severe cases, ECG and CVP should be followed. In hypervitaminosis D cases of weakness, fatigue, muscle pain, polydipsia, polyuria, decreased appetite have been reported. Overdose can lead to hypervitaminosis and hypercalcemia.
Symptoms of hypercalcemia may include anorexia, thirst, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, muscle weakness, anorexia, nocturia, headache, fatigue, mental disturbances, polydipsia, polyuria, bone pain, nephrocalcinosis, renal calculi and in severe cases, cardiac arrhythmias. Extreme hypercalcaemia may result in coma and death.
Persistently high calcium levels may lead to irreversible renal damage and soft tissue calcification.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of 1,25(OH)2D(calcitriol) is mediated by the interaction of calcitriol with the Vitamin D receptor (VDR). Calcitriol binds to cytosolic VDRs within target cells, and the receptor-hormone complex translocates to the nucleus and interacts with DNA to modify gene transcription. The VDR belongs to the steroid and thyroid hormone receptor supergene family. Calcitriol also exerts nongenomic effects that may require the presence of a functional VDR.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Vitamin D3 is converted to 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 in the liver. Conversion to the active calcium-mobilizing hormone 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol) in the kidney is stimulated by both parathyroid hormone and hypophosphatemia. The principal action of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is to increase intestinal absorption of both calcium and phosphate as well as regulate serum calcium, renal calcium and phosphate excretion, bone formation and bone resorption.
Vitamin D is required for normal bone formation. Vitamin D insufficiency develops when both sunlight exposure and dietary intake are inadequate. Insufficiency is associated with negative calcium balance, increased parathyroid hormone levels, bone loss, and increased risk of skeletal fracture. In severe cases, deficiency results in more severe hyperparathyroidism, hypophosphatemia, proximal muscle weakness, bone pain and osteomalacia.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Vitamin D substances are well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The presence of bile is essential for adequate intestinal absorption; absorption may be decreased in patients with decreased fat absorption.
Distribution
Following absorption, Vitamin D3 enters the blood as part of chylomicrons. Vitamin D3 is rapidly distributed mostly to the liver where it undergoes metabolism to 25-hydroxyvitamin D3, the major storage form. Lesser amounts are distributed to adipose tissue and stored as Vitamin D3 at these sites for later release into the circulation. Circulating Vitamin D3 is bound to Vitamin D-binding protein.
Metabolism
Vitamin D3 is rapidly metabolized by hydroxylation in the liver to 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and subsequently metabolized in the kidney to 1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3, which represents the biologically active form. Further hydroxylation occurs prior to elimination. A small percentage of Vitamin D3 undergoes glucuronidation prior to elimination.
Excretion
When radioactive Vitamin D3was intravenously administered to healthy subjects, the mean urinary excretion of radioactivity after 48 hours was 2.4% of the administered dose, and the mean fecal excretion of radioactivity after 48 hours was 4.9% of the administered dose. In both cases, the excreted radioactivity was almost exclusively as metabolites of the parent. The mean half-life of Vitamin D3 in the serum following an oral dose is approximately 14 hours.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal toxicology or pharmacology
Non known animal toxicology data.
7.0 Description
Cholecalciferol is the naturally occurring form of Vitamin D. It is produced from 7- dehydrocholesterol, a sterol present in mammalian skin, by ultraviolet irradiation.
Chemical name : (5Z,7E)-9, 10-Secocholesta-5,7, 10(19)-trien-3β-ol
Synonyms : Vitamin D3, Cholecalciferol
Chemical formula : C27H44O
Molecular weight : 384.6 g/mol
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
None stated.
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
A bottle of 5 ml.
8.4 Storage and handling instructions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30°C. Protected from direct sunlight.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient Counselling Information
Take exactly as directed by your doctor or on the label. Do not increase the dosage or take for longer than is recommended. Instruct patients on the following points when administering the drug.
Inform the patient not to take Cholecalciferol if they have
• Allergic to Vitamin D or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
• High levels of Vitamin D in your blood.
• Kidney stones or serious kidney problems.
• High levels of calcium in your blood and/or urine.
Remind patients to inform their healthcare provider immediately before taking Cholecalciferol if they have
• Problems with kidneys
• Sarcoidosis
• They are already taking other medicines or supplements containing Vitamin D.
About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine, because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, or pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
1. What VITANOVA- D3 Nano oral solution is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you use VITANOVA- D3 Nano oral solution
3. How to use VITANOVA- D3 Nano oral solution
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store VITANOVA-D3 Nano oral solution
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What VITANOVA- D3 Nano oral solution is and what it is used for
VITANOVA- D3 Nano oral solution contains the active ingredient cholecalciferol (vitamin D 3 ). Vitamin D 3 , can be found in some foods and is also produced by the body when skin is exposed to sunlight. Vitamin D 3 helps the kidneys and intestine absorb calcium and it helps build bones. Vitamin D 3 deficiency is the predominant cause of rickets (defective mineralization of bones in children) and osteomalacia (inadequate mineralization of bones in adults).
Certain populations are at high risk of vitamin D deficiency, and may require higher doses and monitoring of serum 25 (OH)D:
- Institutionalised, foster homes or hospitalised individuals
- Dark skinned individuals - Individuals with limited effective sun exposure due to protective clothing or consistent use of sun screens
- Obese individuals
- Patients being evaluated for osteoporosis
- Use of certain concomitant medications (e.g., anticonvulsant medications, glucocorticoids)
- Patients with malabsorption, including inflammatory bowel disease and coeliac disease
- Those recently treated for vitamin D deficiency, and requiring maintenance therapy.
VITANOVA- D3 Nano oral solution is used for initial treatment of clinically relevant vitamin D deficiency in adults.
2. What you need to know before you use VITANOVA-D3 Nano oral solution
Do not use VITANOVA-D3 Nano oral solution:
• if you are allergic to vitamin D 3 or any of the other ingredients of this medicine;
• if you have high levels of calcium in your blood (hypercalcaemia) or urine (hypercalciuria);
• if you have kidney stones (renal calculi) or severe renal impairment;
• if you have high levels of vitamin D 3 in your blood (hypervitaminosis D)
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before using VITANOVA-D3 Nano oral solution if you:
• are undergoing treatment with certain medicines used to treat heart disorders (e.g., cardiac glycosides, such as digoxin);
• have sarcoidosis (an immune system disorder which may cause increased levels of vitamin D 3 in the body);
• are treated with diuretics (e.g. benzothiadiazine)
• are immobilized
• suffer from pseudo hypoparathyroidism
• are taking medicines containing vitamin D 3 , or eating foods or milk enriched with vitamin D 3 ;
• are likely to be exposed to a lot of sunshine whilst using VITANOVA- D3;
• take additional supplements containing calcium. Your doctor will monitor your blood levels of calcium to make sure they are not too high whilst you are using VITANOVA- D3;
• have kidney damage or disease and if you have a tendency for the formation of renal stones. Your doctor may want to measure the levels of calcium in your blood or urine.
• take a daily dose of vitamin D 3 exceeding 1,000 I.U. over a long period of time, your doctor should monitor the level of calcium in your blood by lab test.
Other medicines and VITANOVA- D3
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines. This is especially important if you are taking:
• medicines that act on the heart or kidneys, such as cardiac glycosides (eg, digoxin) or diuretics (e.g., bendroflumethiazide). When used at the same time as vitamin D 3 these medicines may cause a large increase in the level of calcium in the blood and urine;
• medicines containing vitamin D3 or eating food rich in vitamin D3 , such as, some types of vitamin D3 -enriched milk;
• actinomycin (a medicine used to treat some forms of cancer) and imidazole antifungals (e.g., clotrimazole and ketoconazole, medicines used to treat fungal disease). These medicines may interfere with the way your body process vitamin D3 ;
• medicines to treat tuberculosis e.g. rifampicin, isoniazid;
• the following medicines because they can interfere with the effect or the absorption of vitamin D3 :
- antiepileptic medicines (anticonvulsants), barbiturates;
- glucocorticoids (steroid hormones such as hydrocortisone or prednisolone). These can decrease the effect of vitamin D 3 ;
- medicines that lower the level of cholesterol in the blood (such as cholestyramine, or colestipol);
- certain medicines for weight loss that reduce the amount of fat your body absorbs (eg, orlistat);
- certain laxatives (such as liquid paraffin).
VITANOVA- D3 Nano oral solution with food, drink and alcohol
You should take this medicine preferably together with a meal to help your body absorb the vitamin D3 .
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine. The product should be used during pregnancy only in case of a Vitamin D deficiency. It is not recommended during pregnancy in patients without a Vitamin D deficiency.
Driving and using machines
VITANOVA- D3 Nano oral solution should not affect your ability to drive or operate machinery.
3. How to use VITANOVA- D3
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure. This medicine is taken orally.
You should take Vitanova-D3 Nano oral solution preferably together with a meal.
Adults and adolescent: Vitamin D3 60000 IU to be given once a week for a period of 8 weeks, followed by maintenance daily dose as directed by the Physician.
Your doctor will adjust the dose for you.
Pediatric population
Vitanova-D3 Nano oral solution 60000 I.U. should be used as prescribed by the Physician only.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Vitanova-D3 Nano oral solution should be used during pregnancy and lactation only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the mother and fetus.
If you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant or you are breast-feeding, you should talk to your doctor or pharmacist before you take Vitanova-D3 Nano oral solution.
If you take more VITANOVA- D3 Nano oral solution than you should
If you take more medicine than prescribed, stop using this medicine and contact your doctor. If it is not possible to talk to a doctor go to the nearest hospital emergency department and take the medicine package with you.
The most common symptoms of overdose are: nausea, vomiting, excessive thirst, the production of large amounts of urine over 24 hours, constipation and dehydration, high levels of calcium in the blood and in urine (hypercalcaemia and hypercalciuria) shown by lab test.
If you forget to take Vitanova- D3 Nano oral solution
If you forget to take a dose of Vitanova- D3, take the forgotten dose as soon as possible. Then take the next dose at the correct time. However, if it is almost time to take the next dose, do not take the dose you have missed; just take the next dose as normal. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Possible side effects may include:
Uncommon (affects less than 1 in 100 people)
- Too much calcium in your blood (hypercalcaemia)
- Too much calcium in your urine (hypercalciuria)
Rare (affects less than 1 in 1000 people)
- Skin rash
- Itching
- Hives
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store VITANOVA- D3
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and blister pack after "Exp". The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Do not store above 30° C.
Store in the original package in order to protect from light.
Do not freeze.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What VITANOVA- D3 contains
The active substance is cholecalciferol (vitamin D 3 ).
Each 5 ml syrup contains:
Cholecalciferol IP 60000 IU
In a flavoured base q.s.
Packaging
A bottle of 5 ml