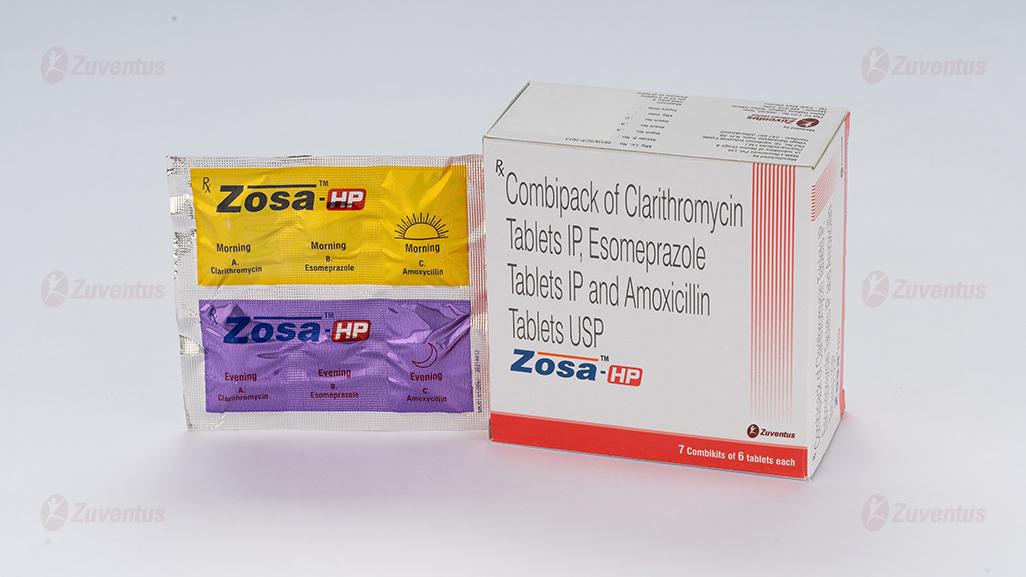
Zosa HP Kit Tablets
Therapy Area
Gastrointestinal
1.0 Generic name
Combipack of Clarithromycin Tablets IP, Esomeprazole Tablets IP and Amoxicillin Tablets USP
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
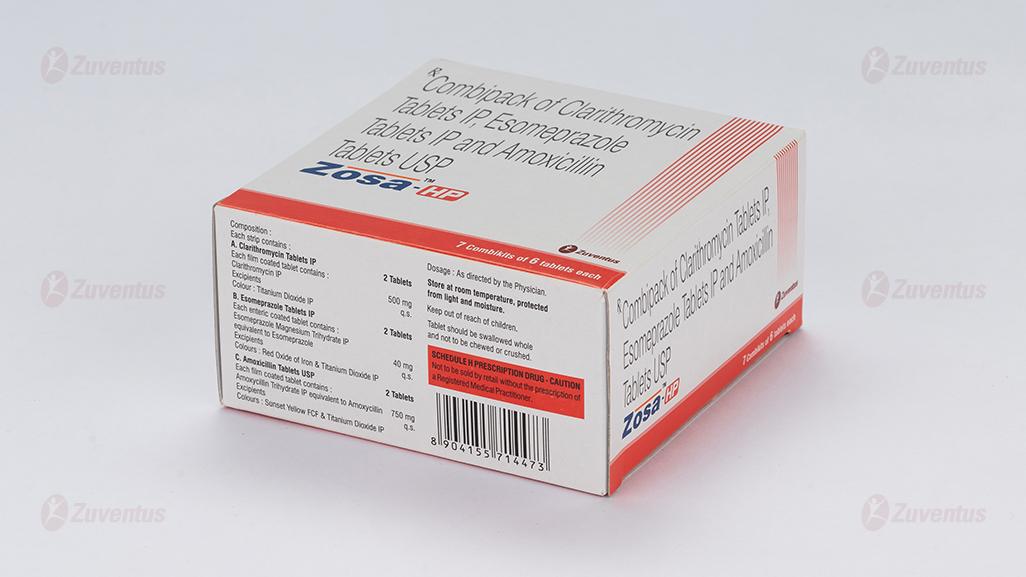
Each strip contains :
A. Clarithromycin Tablets IP 2 Tablets
Each film coated tablet contains :
Clarithromycin IP 500 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Titanium Dioxide IP
B. Esomeprazole Tablets IP 2 Tablets
Each enteric coated tablet contains :
Esomeprazole Magnesium Trihydrate IP
equivalent to Esomeprazole 40 mg
Excipients q.s
Colours : Red Oxide of Iron & Titanium Dioxide IP
C. Amoxicillin Tablets USP 2 Tablets
Each film coated tablet contains:
Amoxycillin Trihydrate IP
equivalent to Amoxycillin 750 mg
Excipients q.s
Colours : Sunset Yellow FCF & Titanium Dioxide IP
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Film Coated Tablet, Clarithromycin 500 mg and Amoxycillin 750 mg Enteric Coated Tablet, Esomeprazole 40 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For healing of duodenal ulcer associated with Helicobacter pylori and eradication of Helicobacter pylori in patients with active or healed peptic ulcer.
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Posology
The combipack contains two tablets of Clarithromycin (500 mg), two tablets of Esomeprazole (40 mg) and two tablets of Amoxicillin (750 mg). One pack is for 1 day of treatment. From this specially designed pack, one tablet of Clarithromycin, one tablet of Esomeprazole, and one tablet of Amoxicillin are to be taken in the morning and similarly one each in the evening. The duration of therapy recommended is for 7 days or as directed by the Physician.
Renal and hepatic impairment
Caution should be exercised while administering the combipack of Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin to patients with renal and hepatic impairment.
Method of administration
For oral administration only
4.3 Contraindications
• Contraindicated in patients with known severe hypersensitivity to any component of the formulation.
• Patients with history of QT prolongation (congenital or documented acquired QT prolongation) or ventricular cardiac arrhythmia, including torsades de pointes.
• Concomitant administration of Clarithromycin and Colchicine is contraindicated in patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
• Clarithromycin should not be used concomitantly with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) that are extensively metabolized by CYP3A4 (Lovastatin or Simvastatin), due to the increase risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis.
• Patients with hypokalaemia (risk of prolongation of QT-time).
• In patients who suffer from severe hepatic failure in combination with renal impairment.
• Concomitant Administration with any of the following drugs is contraindicated : Cisapride, Pimozide, Astemizole, Terfenadine and Ergotamine or Dihydroergotamine. There have been post marketing reports of drug interactions when Clarithromycin and/or Erythromycin are co-administered with Cisapride, Pimozide, Astemizole or Terfenadine, resulting in cardiac arrhythmias (QT prolongation, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and torsades de pointes), most likely due to inhibition of metabolism of these drugs by erythromycin and Clarithromycin. Fatalities have been reported.
• Should not be used concomitantly with Nelfinavir.
• History of a severe immediate hypersensitivity reaction (e.g. anaphylaxis) to another beta-lactam agent (e.g. a cephalosporin, carbapenem or monobactam).
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Embryo-fetal toxicity
Clarithromycin, a component of ZOSA HP KIT, has demonstrated adverse effects on pregnancy outcomes and/or embryo-fetal development in monkeys, rats, mice, and rabbits at doses that produced plasma concentrations 2 to 17 times the serum concentrations achieved in humans at the maximum recommended human dose. Based on findings in animal studies, ZOSA HP KIT is not recommended for use in pregnant women except in clinical circumstances where no alternative therapy is appropriate. If ZOSA HP KIT is used during pregnancy, or if pregnancy occurs while the patient is taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions
There have been post marketing reports of colchicine toxicity, some fatal, with concomitant use of Clarithromycin and colchicine, especially in the elderly, some of which occurred in patients with renal insufficiency. Monitor patients for clinical symptoms of colchicine toxicity
Myasthenia gravis
Exacerbation of symptoms of myasthenia gravis and new onset of symptoms of myasthenic syndrome have been reported in patients receiving Clarithromycin therapy. Monitor patients for symptoms.
Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea
Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of Clarithromycin and Amoxicillin, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile. C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin-producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents. If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis
Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) has been observed in patients taking PPIs, a component of ZOSA HP KIT. TIN may occur at any point during PPI therapy. Patients may present with varying signs and symptoms from symptomatic hypersensitivity reactions, to non-specific symptoms of decreased renal function (e.g., malaise, nausea, anorexia). In reported case series, some patients were diagnosed on biopsy and in the absence of extra-renal manifestations (e.g., fever, rash or arthralgia). Discontinue ZOSA HP KIT and evaluate patients with suspected acute TIN.
Cutaneous and systemic lupus
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have been reported in patients taking PPIs. These events have occurred as both new onset and an exacerbation of existing autoimmune disease. The majority of PPI-induced lupus erythematosus cases were CLE. The most common form of CLE reported in patients treated with PPIs was subacute CLE (SCLE) and occurred within weeks to years after continuous drug therapy in patients ranging from infants to the elderly. Generally, histological findings were observed without organ involvement. Systemic lupus erythematosus(SLE) isless commonly reported than CLE in patients receiving PPIs. PPI associated SLE is usually milder than non-drug induced SLE. Onset of SLE typically occurred within days to years after initiating treatment primarily in patients ranging from young adults to the elderly. The majority of patients presented with rash; however, arthralgia and cytopenia were also reported. Avoid administration of PPIs for longer than medically indicated. If signs or symptoms consistent with CLE or SLE are noted in patients receiving ZOSA HP KIT, discontinue the drug and refer the patient to the appropriate specialist for evaluation.
Most patients improve with discontinuation of the PPI alone in 4 to 12 weeks. Serological testing (e.g. ANA) may be positive and elevated serological test results may take longer to resolve than clinical manifestations.
Development of bacterial superinfections
The possibility of superinfections with mycotic or bacterial pathogens should be kept in mind during therapy with ZOSA HP KIT due to the Clarithromycin and Amoxicillin components. If superinfections occur, ZOSA HP KIT should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted.
Mononucleosis and Ampicillin
A high percentage of patients with mononucleosis who receive ampicillin develop an erythematosus skin rash. Thus, administration of ampicillin-class antibiotics is not recommended in patients with mononucleosis.
Development of drug resistant bacteria
Prescribing ZOSA HP KIT (Clarithromycin or Amoxicillin component) in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
4.5 Drug interaction
Colchicine
Concurrent use of Colchicine and ZOSA HP KIT may increase plasma Colchicine concentrations. Colchicine is a substrate for both CYP3A and the efflux transporter, P-glycoprotein (Pgp). The Clarithromycin component of ZOSA HP KIT is known to inhibit CYP3A and Pgp. When Clarithromycin and Colchicine are administered together, inhibition of Pgp and/or CYP3A by Clarithromycin may lead to increased plasma exposure to colchicine. Monitor patients for clinical symptoms of colchicine toxicity.
Ergotamine / Dihydroergotamine
Ergotamine / Dihydroergotamine plasma concentrations may increase when administered concomitantly with ZOSA HP KIT. Post-marketing reports indicate that co-administration of Clarithromycin with Ergotamine or Dihydroergotamine has been associated with acute ergot toxicity characterized by vasospasm and ischemia of the extremities and other tissues including the central nervous system. Concomitant administration of Clarithromycin with ergotamine or Dihydroergotamine is contraindicated.
Pimozide
The co-administration of Pimozide and ZOSA HP KIT may increase the Pimozide plasma concentrations due to an interaction with the Clarithromycin component of ZOSA HP KIT. Post-marketing reports indicate that coadministration of Clarithromycin with Pimozide has been associated with cardiac arrhythmias (QT prolongation, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and torsades de pointes). Two sudden deaths have been reported when Clarithromycin was added to ongoing Pimozide therapy. Pimozide is metabolized partly by CYP3A4. When Clarithromycin and Pimozide are administered together, inhibition of CYP3A4 by Clarithromycin may lead to increased plasma exposure to Pimozide. ZOSA HP KIT is contraindicated in patients receiving Pimozide.
Antiarrhythmics
Concurrent use of antiarrhythmic drugs and ZOSA HP KIT may potentiate the antiarrhythmic effects due to an interaction with the Clarithromycin component of ZOSA HP KIT. There have been post-marketing reports of torsades de pointes occurring with concurrent use of Clarithromycin and Quinidine or Disopyramide. Elevated digoxin serum concentrations in patients receiving Clarithromycin and Digoxin concomitantly have also been reported in post-marketing surveillance. Some patients have shown clinical signs consistent with digoxin toxicity, including potentially fatal arrhythmias. Monitor electrocardiograms for QTc prolongation during coadministration of ZOSA HP KIT with antiarrhythmic drugs. Serum concentrations of antiarrhythmics, including Digoxin, should also be monitored.
Anticoagulants
The simultaneous administration of anticoagulants and ZOSA HP KIT may alter the anticoagulant effects of Warfarin and other oral anticoagulants due to an interaction with the components of ZOSA HP KIT. Monitor prothrombin time and INR in patients receiving ZOSA HP KIT and oral anticoagulants simultaneously. There have been reports of increased INR and prothrombin time in patients receiving proton pump inhibitors, and Warfarin concomitantly. Increases in INR and prothrombin time may lead to abnormal bleeding and even death. Spontaneous reports in the post-marketing period suggest that concomitant administration of Clarithromycin and oral anticoagulants may potentiate the effects of the oral anticoagulants.
Antiretroviral drugs
Concurrent use of antiretroviral agents and ZOSA HP KIT may alter the antiretroviral effects due to interactions with the components of ZOSA HP KIT. Concomitant use of Atazanavir or Nelfinavir is not recommended unless the benefits of taking Atazanavir or nelfinavir with ZOSA HP KIT outweigh the risks. Co-administration of Atazanavir or Nelfinavir with proton pump inhibitors is expected to substantially decrease Atazanavir or nelfinavir plasma concentrations and thereby reduce the therapeutic effect of either of these drugs. Dose reduction of Saquinavir should be considered when co-administered with ZOSA HP KIT.
Cilostazol
Concomitant administration of ZOSA HP KIT and Cilostazol may increase systemic exposure of Cilostazol. Therefore, a dose reduction of Cilostazol by 50% should be considered when concomitantly administered with ZOSA HP KIT.
Tacrolimus
Concomitant administration of ZOSA HP KIT and Tacrolimus may increase the serum concentrations of Tacrolimus due to an interaction with the omeprazole component of ZOSA HP KIT. Frequent monitoring of whole blood trough concentrations of Tacrolimus is recommended when concomitantly administered with ZOSA HP KIT.
Theophylline
ZOSA HP KIT use in patients who are receiving Theophylline may be associated with an increase of serum Theophylline concentrations due to an interaction with the Clarithromycin component of ZOSA HP KIT. Monitoring of serum Theophylline concentrations should be considered for patients receiving high doses of Theophylline or with baseline concentrations in the upper therapeutic range.
Carbamazepine
The simultaneous administration of Carbamazepine and ZOSA HP KIT may alter the effect of carbamazepine due to an interaction with the Clarithromycin component of ZOSA HP KIT. Concomitant administration of single doses of Clarithromycin and Carbamazepine has been shown to result in increased plasma concentrations of Carbamazepine. Blood level monitoring of carbamazepine should be considered when administered concomitantly with ZOSA HP KIT.
Sildenafil
The systemic exposure of Sildenafil may increase when it is administered concomitantly with ZOSA HP KIT due to an interaction with the Clarithromycin component of ZOSA HP KIT; consider a reduction in sildenafil dosage.
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (Statins)
Concurrent use of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) and ZOSA HP KIT may alter the effect of HMG-CoA due to an interaction with the Clarithromycin component of ZOSA HP KIT. As with other macrolides, Clarithromycin has been reported to increase concentrations of statins (e.g., Lovastatin and Simvastatin). Rare reports of rhabdomyolysis have been reported in patients taking these drugs concomitantly.
Triazolobenzodiazepines (e.g. Triazolam and Alprazolam) and related Benzodiazepines (e.g. Midazolam)
The effect of Triazolobenzodiazepines / related Benzodiazepines may be altered when administered concomitantly with ZOSA HP KIT due to an interaction with the Clarithromycin component. There have been post-marketing reports of drug interactions and CNS effects (e.g., somnolence and confusion) with the concomitant use of Clarithromycin and Triazolam.
Probenecid
Probenecid decreases the renal tubular secretion of Amoxicillin. Concurrent use of ZOSA HP KIT and probenecid may result in increased and prolonged blood concentrations of the Amoxicillin component of ZOSA HP KIT.
Drugs for which gastric ph can affect bioavailability
Patients may need to be monitored when digoxin is taken concomitantly with ZOSA HP KIT. Use with caution in transplant patients receiving Mycophenolate Mofetil.
Drug-laboratory test interactions
High urine concentrations of Ampicillin may result in false-positive reactions when testing for the presence of glucose in urine using glucose tests based on the Benedict's copper reduction reaction that determines the amount of reducing substances like glucose in urine. Since this effect may also occur with Amoxicillin, it is recommended that glucose tests based on enzymatic glucose oxidase reactions be used. Following administration of Ampicillin to pregnant women, a transient decrease in plasma concentration of total conjugated estradiol, estriol-glucuronide, conjugated estrone, and estradiol has been noted. This effect may also occur with Amoxicillin.
4.6 Use in special population
Pregnancy
Use of ZOSA HP KIT during pregnancy may cause fetal harm. ZOSA HP KIT is not recommended for use in pregnant women except in clinical circumstances where no alternative therapy is appropriate. If ZOSA HP KIT is used during pregnancy, or if pregnancy occurs while taking ZOSA HP KIT, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Breast-feeding
The development and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for Esomeprazole or Clarithromycin or Amoxicillin and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed child from Clarithromycin or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric population
The safety and effectiveness of this combipack in pediatric patients infected with H. pylori have not been established.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed. However, undesirable effects may occur (e.g. allergic reactions, dizziness, confusion, vertigo, blurred vision (rarely), and or convulsions), which may influence the ability to drive and use machines.
4.8 Undesirable effects
The most frequent and common adverse reactions are abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting dysgeusia, acute kidney injury, headache. These adverse reactions are consistent with the known safety profile of macrolide antibiotics. There was no significant difference in the incidence of these gastrointestinal adverse reactions during clinical trials between the patient population with or without pre-existing mycobacterial infections.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Thrombocytopenia, Agranulocytosis, Pancytopenia.
Cardiac disorders
Torsades de pointes, Ventricular tachycardia, Ventricular arrhythmia.
Ear and labyrinth disorders
Deafness was reported chiefly in elderly women and was usually reversible, Blurred vision.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Pancreatitis acute, tongue discoloration, stomatitis, microscopic colitis was reported and was usually reversible with professional cleaning upon discontinuation of the drug. There have been reports of Clarithromycin tablets in the stool, many of which have occurred in patients with anatomic (including ileostomy or colostomy) or functional gastrointestinal disorders with shortened GI transit times. In several reports, tablet residues have occurred in the context of diarrhea. It is recommended that patients who experience tablet residue in the stool and no improvement in their condition should be switched to a different Clarithromycin formulation (e.g. suspension) or another antibacterial drug.
Hepatobiliary disorders
Hepatic failure, Jaundice hepatocellular. Adverse reactions related to hepatic dysfunction have been reported with Clarithromycin.
Immune system
disorders Anaphylactic reaction.
Infections and infestations
Pseudomembranous colitis, GI candidiasis, Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea, Hypomagnesemia, Gynecomastia, Interstitial nephritis, Bronchospasm, Mucocutaneous candidiasis
Investigations
Prothrombin time prolonged, WBC count decreased, INR increased. Abnormal urine color has been reported, associated with hepatic failure.
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Hypoglycemia has been reported in patients taking oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin, muscular weakness, Myalgia, Bone fracture.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Myopathy and rhabdomyolysis were reported and in some of the reports, Clarithromycin was administered concomitantly with statins, fibrates, colchicine or allopurinol, Muscular weakness, myalgia, bone fracture.
Nervous system disorders
Convulsion, Ageusia, Parosmia, Anosmia, Paresthesia, Hepatic encephalopathy, Taste disturbance.
Psychiatric disorders
Psychotic disorder, Confusional state, Depersonalization, Disorientation, Hallucination, Abnormal behavior, Abnormal dreams, Aggression, Agitation, Depression.
Renal and urinary disorders
Nephritis interstitial, Renal failure.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Toxic epidermal necrolysis, Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), Henoch-Schonlein purpura, Acne, Alopecia, Erythema multiforme, hyperhidrosis, Photosensitivity, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Toxic epidermal necrolysis (some fatal).
Reproductive system and breast
Gynaecomastia.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal
Bronchospasm.
Vascular disorders
Hemorrhage. There have been reports of colchicine toxicity with concomitant use of Clarithromycin and colchicine, especially in the elderly, some of which occurred in patients with renal insufficiency. Deaths have been reported in some such patients.
Haemic and lymphatic systems
Anaemia, including haemolytic anaemia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, eosinophilia, leucopenia, and agranulocytosis have been reported during therapy with penicillins. These reactions are usually reversible on discontinuation of therapy and are believed to be hypersensitivity phenomena.
Central nervous system
Reversible hyperactivity, agitation, anxiety, insomnia, confusion, convulsions, behavioral changes, and/or dizziness have been reported rarely.
Miscellaneous
Tooth discolouration (brown, yellow, or grey staining) has been rarely reported. Most reports occurred in pediatric patients. Discolouration was reduced or eliminated with brushing or dental cleaning in most cases.
Changes in laboratory values
Changes in laboratory values with possible clinical significance were as follows : Hepatic : Elevated SGPT (ALT) < 1%; SGOT (AST) < 1%; GGT < 1%; alkaline phosphatase < 1%; LDH < 1%; total bilirubin < 1%. Hematologic : Decreased WBC < 1%; elevated prothrombin time, 1%. Renal : Elevated BUN, 4%; elevated serum creatinine < 1%. Note : GGT, alkaline phosphatase, and prothrombin time data are from adult studies only.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorization of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit / risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com Website : https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
There is very limited experience to date with deliberate overdose. No specific antidote is known. As in any case of overdose, treatment should be symptomatic and general supportive measures should be utilized.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Esomeprazole belongs to a class of antisecretory compounds, the substituted Benzimidazoles, that suppress gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the H+/K+ ATPase enzyme system at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cell. Esomeprazole is protonated and converted in the acidic compartment of the parietal cell forming the active inhibitor, the achiral Sulphenamide. Because this enzyme system is regarded as the acid (proton) pump within the gastric mucosa, Esomeprazole has been characterized as a gastric acid-pump inhibitor, in that it blocks the final step of acid production. This effect is dose-related and leads to inhibition of both basal and stimulated acid secretion irrespective of the stimulus. Clarithromycin exerts its antibacterial activity by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit of susceptible microorganisms resulting in inhibition of protein synthesis. Amoxicillin acts through the inhibition of biosynthesis of cell wall mucopeptide.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Clarithromycin
Pharmacotherapeutic Group : Antibacterial for systemic use, macrolide. Clarithromycin is a semisynthetic derivative of erythromycin A. Clarithromycin is active in-vitro against a variety of aerobic and anaerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria as well as most Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) bacteria. Additionally, the 14-OH-Clarithromycin metabolite also has clinically significant antimicrobial activity. The 14-OH-Clarithromycin is twice as active against Hemophilus influenzae microorganisms as the parent compound. However, for Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) isolates the 14-OH-metabolite is 4 to 7 times less active than Clarithromycin. The clinical significance of this activity against Mycobacterium avium complex is unknown. Clarithromycin has bactericidal activity against several bacterial strains. The organisms include Hemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, H. pylori and Campylobacter spp.
Esomeprazole
Pharmacotherapeutic group : Drugs for acid-related disorders, proton pump inhibitor. Esomeprazole is a proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) that suppresses gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the H+/K+-ATPase in the gastric parietal cell. The S- and R-isomers of omeprazole are protonated and converted in the acidic compartment of the parietal cell forming the active inhibitor, the achiral Sulfenamide. By acting specifically on the proton pump, Esomeprazole blocks the final step in acid production, thus reducing gastric acidity. This effect is dose-related up to a daily dose of 20 to 40 mg and leads to inhibition of gastric acid secretion. Mechanism of action : Esomeprazole is a weak base and is concentrated and converted to the active form in the highly acidic environment of the secretory canaliculi of the parietal cell, where it inhibits the enzyme H+K+-ATPase – the acid pump and inhibits both basal and stimulated acid secretion.
Amoxicillin
Pharmacotherapeutic group : Penicillins with extended spectrum. Amoxicillin is semisynthetic penicillin (beta-lactam antibiotic) that inhibits one or more enzymes (often referred to as penicillin-binding proteins, PBPs) in the biosynthetic pathway of bactericidal peptidoglycan, which is an integral structural component of the bacterial cell wall. Inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis leads to weakening of the cell wall, which is usually followed by cell lysis and death. Amoxicillin is susceptible to degradation by beta-lactamases produced by resistant bacteria and therefore the spectrum of activity of Amoxicillin alone does not include organisms which produce these enzymes.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
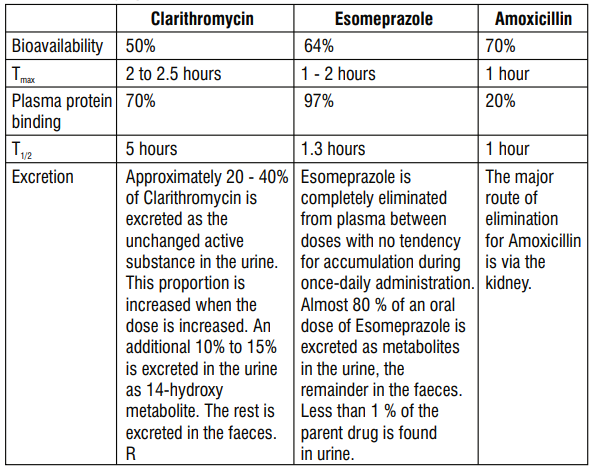
6.0 Nonclinical properties
Clarithromycin
Corneal opacity occurred in dogs at doses 12 times and in monkeys at doses 8 times greater than the maximum human daily dose (on a body surface area basis). Lymphoid depletion occurred in dogs at doses 3 times greater than and in monkeys at doses 2 times greater than the maximum human daily dose (on a body surface area basis).
Esomeprazole
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenic potential, toxicity to reproduction and development. Adverse reactions not observed in clinical studies, but seen in animals at exposure levels similar to clinical exposure levels and with possible relevance to clinical use were as follows : Carcinogenicity studies in the rat with the racemic mixture have shown gastric ECL-cell hyperplasia and carcinoids. These gastric effects in the rat are the result of sustained, pronounced hypergastrinaemia secondary to reduced production of gastric acid and are observed after long-term treatment in the rat with inhibitors of gastric acid secretion.
Amoxicillin
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on studies of safety pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity and toxicity to reproduction and development. Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with Amoxicillin.
7.0 Description
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is probably the most common bacterial infection, with a worldwide revalence of approximately 50%. H. pylori is implicated in the etiology of gastritis and peptic ulcers in humans. Newer triple therapies, including proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) such as Esomeprazole, Amoxicillin, and Clarithromycin, serve as a shorter, simpler and effective drug regimen for the eradication of H. pylori.
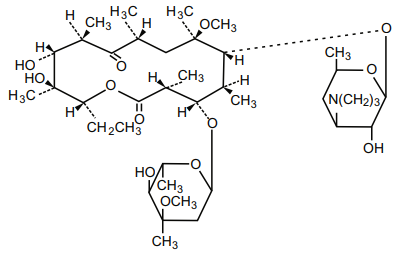
Clarithromycin is a semi-synthetic macrolide antimicrobial for oral use. Chemically, it is 6-0methylerythromycin. The molecular formula is C H NO , and the molecular weight is 747.96 38 69 13 gm/mol.
The structural formula is :
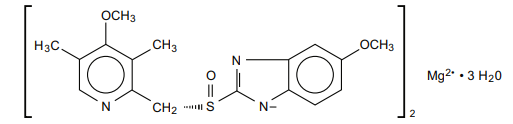
Esomeprazole is bis(5-methoxy-2sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole-1-yl) magnesium trihydrate. Esomeprazole is the S-isomer of omeprazole, which is a mixture of the S-and R-isomers. (Initial U.S. approval of Esomeprazole Magnesium : 2001). Its molecular formula is (C17 H18 N 3O 3S) Mg x 3 H2 O with molecular weight of 767.2 gm/mol as a trihydrate and 713.1 gm/mol on an anhydrous 2 basis.
The structural formula is :
Amoxicillin is one of the most commonly used antibiotics in the primary care setting. It is an amino-penicillin, created by adding an extra amino group to penicillin to battle antibiotic resistance.
The chemical name of Amoxicillin is (2S,5R,6R)-6--3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo heptane-2-carboxylic acid
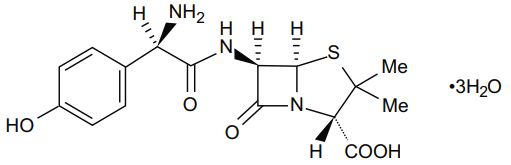
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack
8.3 Packaging information
Alu strip containing 2 Tablets of Clarithromycin Tablets IP, 2 Tablets of Esomeprazole Tablets IP and 2 Tablets of Amoxicillin Tablets USP.
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store at room temperature, protected from light and moisture.
Keep out of reach of children.
Tablet should be swallowed whole and not to be chewed or crushed.
9.0 Patient counselling information
Read this entire leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
• Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
• If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
• This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
• If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets and it is used for ?
Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets is a combination pack, which contains three different medicines. When taken together in the right doses, they will kill the bacteria in your stomach called Helicobacter pylori and let your peptic ulcer heal. Depending on the position of the ulcer it is called a gastric or duodenal ulcer. A gastric ulcer occurs in the stomach. A duodenal ulcer occurs in the duodenum which is the tube leading out from the stomach.
Most people who have a peptic ulcer also have a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori in their stomach. If the bacteria are killed it is unlikely that your ulcer will come back. Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets contains Esomeprazole, Amoxicillin and Clarithromycin. Amoxicillin and Clarithromycin are both types of antibiotic.
Before you take Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets When you must not take it
Do not take Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets if you have an allergy to :
• Any medicines containing Esomeprazole, Amoxicillin or Clarithromycin.
• Any ingredients listed at the end of the leaflet.
• Any other similar medicines such as proton pump inhibitors, penicillins, cephalosporins or macrolide antibiotics
Some of the symptoms of an allergic reaction may include shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing; swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body; rash, itching or hives on the skin.
Do not take Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets if you are taking any of the following medicines :
• Ergotamine
• Cisapride
• Pimozide
• Dihydroergotamine
• Astemizole
• Terfenadine
• Cilostazol
• Atazanavir
• Colchicine
• Simvastatin
• Lovastatin
• Ticagrelor
• Ranolazine
• Colchicine
• Oral midazolam
• Domperidone
Please check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any of these medicines. These medicines will be affected by the medicines in Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets and it is more likely you will get side effects. Do not take Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets if you have a history of heart conditions such as QT prolongation or ventricular cardiac arrhythmia. Do not take Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets if you have low potassium levels. Do not take Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets if you have both liver and kidney problems. Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets is not recommended for use in children. There is no information about the use of Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets in children. Do not take this medicine after the use by (expiry) date printed on the pack or if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering. If it has expired or is damaged, return it to your pharmacist for disposal. If you are not sure whether you should start taking this medicine, talk to your doctor.
Before you start to use it
Tell your doctor if you have allergies to any other medicines, foods, preservatives or dyes.
You must tell your doctor if you have :
• Problems with your blood.
• Problems with your liver or kidneys.
• Any heart conditions, such as QT prolongation or ventricular cardiac arrhythmia.
• You have glandular fever.
• Myasthenia gravis, a condition in which the muscles become weak and tire easily.
• Been diagnosed with osteoporosis.
• Low Potassium, low Magnesium or any other electrolyte imbalances.
• If you have ever had a skin reaction after treatment with a medicine similar to Esomeprazole that reduces stomach acid.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to be pregnant, are breast-feeding or plan to breastfeed
It is not known if it is safe for you to take Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets if you are pregnant. The medicines in Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets may affect the developing baby. Your baby can take in all the medicines in Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets from breast milk if you are breast-feeding. Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets is not recommended when breast-feeding. Your doctor can discuss with you the risks and benefits of using Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets if you are pregnant or breast-feeding. If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell them before you start taking Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets.
Taking other medicines
Do not take Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets if you are taking the following medicines :
• Ergotamine or Dihydroergotamine - medicines used to treat migraine headaches.
• Astemizole or Terfenadine – medicines used to treat hayfever and allergies
. • Atazanavir - a medicine used to treat Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
• Cilostazol - a medicine used to treat intermittent claudication.
• Colchicine - a medicine used to treat gout.
• Lovastatin or simvastatin – medicines used to treat high cholesterol.
• Ticagrelor - a medicine used to treat blood clots.
• Oral midazolam - a medicine used for surgical sedation.
• Domperidone - a medicine used for nausea.
Tell your doctor if you are taking any other medicines, including any that you buy without a prescription from a pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop. Some medicines and Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets may interfere with each other
These include :
• Diazepam, Triazolam or Alprazolam - medicines used as sedatives or to treat anxiety
• Ketoconazole, Itraconazole, Voriconazole or Fluconazole - medicines used to treat fungal infections
• Warfarin and Clopidogrel - medicines used to prevent blood clots.
• Allopurinol or probenecid - medicines used to treat gout.
• Phenytoin, Sodium valproate or Carbamazepine - medicines used to treat seizures.
• Atorvastatin or Rosuvastatin - medicines used to treat high cholesterol.
• Theophylline - a medicine used to treat asthma.
• Zidovudine, Saquinavir, Efavirenz, Etravirine, Nevirapine, Nelfinavir or Ritonavir - medicines used to treat HIV.
• Insulin, Repaglinide, Nateglinide, Pioglitazone or Rosiglitazone - medicines used to treat diabetes.
• Digoxin, Quinidine or Disopyramide - medicines used to treat heart conditions.
• Citalopram, Fluoxetine, Clomipramine and Imipramine - medicines used to treat depression.
• St John's wort - a herbal remedy used to treat mood disorders.
• Rifabutin, Rifapentine, Rifampicin or Erythromycin - medicines used to treat bacterial infections.
• Sildenafil, Tadalafil or Vardenafil - medicines used to treat impotence.
• Tolterodine - a medicine used to treat incontinence.
• Verapamil, Amlodipine or Diltiazem - medicines used to treat high blood pressure and some heart conditions. • Methylprednisolone - a corticosteroid.
• Vinblastine - a medicine used to treat cancer.
• Oral contraceptives or birth control pills.
Talk to your doctor about the need for an additional method of contraception while on Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets
• Tacrolimus or Ciclosporin - medicines used to prevent organ transplant rejection or to treat certain problems with the immune system.
• Methotrexate - a medicine used to treat arthritis and some types of cancer.
• Erlotinib or related medicines used to treat cancer.
• phenobarbitone - a medicine used to treat epilepsy.
• Tetracycline and aminoglycoside antibiotics - medicines used to treat certain infections.
• Atypical antipsychotics - medicines used to treat psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder (e.g. quetiapine).
• Ibrutinib - a medicine used to treat cancer.
These medicines may affect Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets or may affect how well it works. You may need different amounts of your medicines or you may need to take different medicines.
Your doctor and pharmacist have more information on medicines to be careful with or avoid while taking this medicine.
If you have not told your doctor about any of these things, tell them before you take any Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets.
How to take Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets ?
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure
Posology
The combipack contains two tablets of Clarithromycin (500 mg), two tablets of Esomeprazole (40 mg), and two tablets of Amoxicillin (750 mg). One pack is for 1 day of treatment. From this specially designed pack, one tablet of Clarithromycin, one tablet of Esomeprazole, and one tablet of Amoxicillin are to be taken in the morning and similarly one each in the evening. The duration of therapy recommended is for 7 days or as directed by the Physician.
Renal and hepatic impairment
Caution should be exercised while administering the combipack of Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin to patients with renal and hepatic impairment.
Method of administration
For oral administration only.
Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. If you notice any of the serious side effects, stop taking this medicine and contact a doctor immediately. Tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are taking Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets. Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets helps most people with peptic ulcer and Helicobacter pylori infection, but it may have unwanted side effects in a few people.
Tell your doctor if you notice any of the following and they worry you :
• Diarrhoea, nausea or vomiting
• Headache
• Dizziness
• Constipation
• Loss of appetite
• Stomach pain (e.g. cramps)
• Wind
• Dryness of the mouth or other body cavities
• Soreness of mouth or tongue
• "Pins and needles"
• Metallic taste or other change in taste or smell
• Chills
• Fatigue
• Excessive burping
These side effects are usually mild.
Tell your doctor immediately or go to emergency room at your nearest hospital if you notice the following :
• Muscle pain or weakness
• Increase in breast size (males)
• Fever
• Changes in sleep patterns
• Mood changes, hallucinations, confusion or depression
• Change in sexual function • Blurred vision, hearing disturbances
• Hair loss
• Bleeding or bruising more easily than normal
• Signs of frequent infections such as fever, severe chills, sore throat or mouth ulcers
• Skin rash
• Blood in urine
• Tremor
• Convulsions or fits
• Overgrowth of yeast infections (thrush)
• Fainting, irregular heart heat
• Yellowing of the eyes or skin
These may be serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention. If any of the following happen, stop taking Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets and tell your doctor immediately or go to emergency room at your nearest hospital :
• Shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing.
• Swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body.
• Chest pain.
• Severe skin reaction which may include rash, itching, redness, blistering or peeling of the skin
• Severe upper stomach pain, with nausea and vomiting.
• Signs of liver inflammation including yellowing of the skin or eyes, feeling generally unwell, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite.
• Skin reaction, especially in sun-exposed areas, with joint pain.
• Severe stomach or abdominal cramps, watery and severe diarrhoea, which may also be bloody (this may occur several weeks after you stop taking Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets).
Do not take any medicine to stop the diarrhoea unless advised by your doctor. These are very serious side effects. If you have them, you may have had a serious reaction to one of the medicines in Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets. You may need urgent medical attention or hospitalization. Tell your doctor if you notice anything else that is making you feel unwell. Some people may get other side effects while taking Clarithromycin, Esomeprazole and Amoxicillin Tablets. Do not be alarmed by this list of possible side effects. You may not experience any of them.
12.0 Date of issue
16 January 2023

About Leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet
1.What ZOSA HP KIT is and what it is used for
2.What you need to know before you take ZOSA HP KIT
3.How to take ZOSA HP KIT
4.Possible side effects of ZOSA HP KIT
5.How to store ZOSA HP KIT
6.Contents of the pack and other information
1. What ZOSA HP KIT is and what it is used for
ZOSA HP KIT is a combipack of three different tablets which are Clarithromycin 500 mg Film coated tablet, Amoxicillin 750 mg Film coated tablet and Esomeprazole 40 mg Enteric coated tablet. ZOSA HP KIT is used to treat and to prevent the stomach and peptic ulcers caused by bacteria known as Helicobacter pylori.
2. What you need to know before you take ZOSA HP KIT
Do not take ZOSA HP KIT
- if you are allergic to amoxicillin, penicillin, clarithromycin, esomeprazole or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
- if you have ever had an allergic reaction to any antibiotic. This can include a skin rash or swelling of the face or throat.
If you are taking the following medications. Consult your doctor for advice on alternative medicines or ask if you are not sure:
- Ergotamine or dihydroergotamine tablets or use ergotamine inhalers (medicines used to treat migraines).
- If you are allergic to other proton pump inhibitor medicines (e.g. pantoprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, omeprazole).
- If you are taking a medicine containing nelfinavir (used to treat HIV infection).
Combining the above drugs with ZOSA HP KIT may cause your blood vessels to narrow. This will lead to a decrease of blood supply to tissues.
- Cisapride (to treat stomach disorders), pimozide (to treat some mental illnesses), terfenadine or astemizole (to treat hay fever or allergy). Combining these medicines with ZOSA HP KIT can cause serious changes in your heart rhythm.
- Lovastatin or simvastatin (HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, commonly known as statins, used to lower levels of cholesterol (a type of fat) in the blood).
- If your potassium levels are low (hypokalaemia)
- If you have severe liver disease with kidney disease
- If you have an irregular heart rhythm.
Do not take ZOSA HP KIT if any of the above apply. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking ZOSA HP KIT.
Warnings and Precautions
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before taking ZOSA HP KIT, if you
- have glandular fever (fever, sore throat, swollen glands and extreme tiredness)
- have kidney problems, liver problems
- have, or are prone to, fungal infections (such as thrush)
- are not urinating regularly.
- are pregnant or breast feeding are due to have a specific blood test (Chromogranin A).
If you are not sure if any of the above apply to you, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking ZOSA HP KIT.
Blood and urine tests
If you are having:
Urine tests (glucose) or blood tests for liver function Oestriol tests (used during pregnancy to check the baby is developing normally)
Tell your doctor or pharmacist that you are taking ZOSA HP KIT. This is because ZOSA HP KIT can affect the results of these tests.
Other medicines and ZOSA HP KIT
Tell your doctor or pharmacist, if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
You should not take ZOSA HP KIT if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- Cisapride (to treat stomach disorders)
- Pimozide (to treat mental illness)
- Terfenadine or astemizole (to treat hay fever or allergies)
- Ergotamine or dihydroergotamine (to treat migraines) Lovastatin or simvastatin (to treat high cholesterol)
Tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following medicines. Because of the possibility of reactions your doctor will decide if you can still take ZOSA HP KIT tablets:
- Colchicine (usually taken for gout). This may increase your risk of side effects and lead to potential toxicity.
- Digoxin (to treat heart failure). It may cause irregular heart beat and may also increase your risk of side effects.
- Quinidine or disopyramide (to treat abnormal heart rhythm). This may cause you to experience seriously irregular heartbeat.
- Warfarin or acenocoumarol (to thin the blood). These medicines may change the rate at which your blood clots. This might result in toxic effects.
- Triazolam, alprazolam or midazolam (sedatives). These medicines may cause sleepiness and confusion.
- Rosuvastatin, atorvastatin (to treat high cholesterol). These medicines may lead to pain or weakness in muscles, or abnormal muscle breakdown. This can lead to kidney problems.
- Zidovudine (anti-viral agent). This may change the effectiveness of zidovudine.
- Rifabutin, rifampicin, rifapentin (to treat some infections). These medicines may change the effectiveness of ZOSA HP KIT.
- Efavirenz, nevirapine (HIV treatments). These medicines may change the effectiveness ZOSA HP KIT.
Taking the following medicines with ZOSA HP KIT may increase your risk of side effects. Tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following:
- Carbamazepine, valproate, phenobarbital or phenytoin (to treat epilepsy)
- Cilostazol (to treat poor circulation)
- Methylprednisolone (to treat inflammation)
- Sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil (to treat erection problems)
- Vinblastine (to treat cancer)
- Tolterodine (to treat urinary frequency)
- Omeprazole (to treat indigestion)
- Cyclosporin, tacrolimus, sirolimus (to help prevent rejection after a transplant)
- Theophylline (to treat asthma) Itraconazole or fluconazole (to treat fungal infections)
- Etavirine, ritonavir, atazanavir, saquinavir (anti-viral and anti-HIV medicines)
- Nateglinide, pioglitazone, repaglinide, rosiglitazone or insulin (to treat diabetes)
- Verapramil (to treat high blood pressure)
- Atazanavir (used to treat HIV infection). Clopidogrel (used to prevent blood clots).
- Ketoconazole, itraconazole or voriconazole (used to treat infections caused by a fungus).
- Erlotinib (used to treat cancer).
- Citalopram, imipramine or clomipramine (used to treat depression).
- Diazepam (used to treat anxiety, relax muscles or in epilepsy).
- Phenytoin (used in epilepsy). If you are taking phenytoin, your doctor will need to monitor you when you start or stop taking ZOSA HP KIT.
- Medicines that are used to thin your blood, such as warfarin. Your doctor may need to monitor you when you start or stop taking ZOSA HP KIT.
- Cilostazol (used to treat intermittent claudication – a pain in your legs when you walk which is caused by an insufficient blood supply).
- Cisapride (used for indigestion and heartburn).
- Digoxin (used for heart problems).
- Methotrexate (a chemotherapy medicine used in high doses to treat cancer) – if you are taking a high dose of methotrexate, your doctor may temporarily stop your ZOSA HP KIT treatment.
- Tacrolimus (organ transplantation).
- Rifampicin (used for treatment of tuberculosis).
- St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum) (used to treat depression).
- If you are taking allopurinol (used for gout) with ZOSA HP KIT, it may be more likely that you will have an allergic skin reaction.
- If you are taking probenecid (used for gout), your doctor may decide to adjust your dose of ZOSA HP KIT.
- If you are taking medicines to help stop blood clots (such as warfarin), you may need extra blood tests.
- If you are taking other antibiotics (such as tetracycline) ZOSA HP KIT may be less effective.
- If you are taking methotrexate (used for the treatment of cancer and severe psoriasis) ZOSA HP KIT may cause an increase in side effects.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Driving and using machines
ZOSA HP KIT can have side effects and the symptoms (such as allergic reactions, dizziness and convulsions) may make you unfit to drive. Do not drive or operate machinery unless you are feeling well.
3. How to take ZOSA HP KIT
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure. Kidney problems If you have kidney problems the dose might be lower than the usual dose.
If you take more ZOSA HP KIT than you should
If you have taken too much of ZOSA HP KIT or if a child accidentally swallows some tablets, seek medical advice immediately. Take the medicine to show the doctor.
If you forget to take ZOSA HP KIT
- If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as you remember.
- Do not take the next dose too soon, wait about 4 hours before taking the next dose.
- Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
How long should you take ZOSA HP KIT for?
Keep taking ZOSA HP KIT for as long as your doctor has told you to, even if you feel better. You need every dose to help fight the infection. If some bacteria survive they can cause the infection to come back.
Once you finish treatment, if you still feel unwell you should go back to see the doctor. Thrush (a yeast infection of moist areas of the body which causes soreness, itching and white discharge) may develop if ZOSA HP KIT is used for a long time. If this occurs tell your doctor.
If you take ZOSA HP KIT for a long time, your doctor may perform additional tests to check your kidneys, liver and blood are working normally. If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Stop taking ZOSA HP KIT and see a doctor straight away, if you notice any of the following serious side effects – you may need urgent medical treatment:
The following are very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- Allergic reactions, the signs may include: skin itching or rash, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, body or breathing difficulties. These can be serious and occasionally deaths have occurred
- Rash or pinpoint flat red round spots under the skin surface or bruising of the skin. This is due to inflammation of blood vessel walls due to an allergic reaction. It can be associated with joint pain (arthritis) and kidney problems
- A delayed allergic reaction can occur usually 7 to 12 days after having ZOSA HP KIT, some signs include: rashes, fever, joint pains and enlargement of the lymph nodes especially under the arms
- A skin reaction known as ‘erythema multiforme’ where you may develop: itchy reddish purple patches on the skin especially on the palms of the hands or soles of the feet, ‘hive-like’ raised swollen areas on the skin, tender areas on the surfaces of the mouth, eyes and genitals. You may have a fever and be very tired
- Other severe skin reactions can include: changes in skin colour, bumps under the skin, blistering, pustules, peeling, redness, pain, itching, scaling. These may be associated with fever, headaches and body aches
- Flu-like symptoms with a rash, fever, swollen glands, and abnormal blood test results (including increased white blood cells (eosinophilia) and liver enzymes) (Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)).
- Fever, chills, a sore throat or other signs of an infection, or if you bruise easily. These may be signs of a problem with your blood cells
- The Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction which occurs during treatment with Amoxicillin for Lyme disease and causes fever, chills, headache, muscle pain and skin rash
- Inflammation of the large bowel (colon) with diarrhoea (sometimes containing blood), pain and fever
- Serious liver side effects may occur. They are mainly associated with people having treatment over a long period, males and the elderly. You must tell your doctor urgently if you get:
- Severe diarrhoea with bleeding
- Blisters, redness or bruising of the skin
- Darker urine or paler stools
- Yellowing of the skin or the whites of the eyes (jaundice). See also anaemia below which might result in jaundice.
- Severe or prolonged diarrhoea, which may have blood or mucus in it (pseudomembranous colitis)
- Blistering of the skin, mouth, eyes or genitals (Stevens-Johnson syndrome) Henoch-Schonlein purpura (a rash which appears as purple spots on the skin)
These can happen when having the medicine or for up to several weeks after.
If any of the above happens stop taking the medicine and see your doctor straight away.
Sometimes you may get less severe skin reactions such as:
- A mildly itchy rash (round, pink-red patches), ‘hive-like’ swollen areas on forearms, legs, palms,
- hands or feet.
This is uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people). If you have any of these talk to your doctor as Amoxicillin will need to be stopped. The other possible side effects are:
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- headache
- skin rash
- feeling sick (nausea)
- diarrhoea
- increased levels of urea in the blood (detected in laboratory tests)
- change in sense of taste, headache
- abdominal pain, diarrhoea, indigestion, feeling sick, vomiting, bloating, stomach pain, constipation, wind (flatulence).
- difficulty sleeping
- increased sweating
- Benign polyps in the stomach
Other less common side effects
- Presence of protein, blood or white blood cells in the urine, changes in liver or kidney function tests or blood tests, prothrombin time prolongation (increased blood clotting time)
- Leucopenia (reduction in the number of white blood cells, which makes infections more likely), Anaemia (decrease in red blood cells, which can make the skin pale and cause weakness and breathlessness), eosinophilia (blood disorder), thrombocythaemia (increase in blood platelets, which increases the risk of bleeding or blood clots)
- Tremor (shaking)
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears) or hearing loss, vertigo (spinning sensation)
- Constipation, dry mouth, belching, flatulence (wind), bleeding from stomach and intestines
- Back, joint or muscle pain
- If you suffer from myasthenia gravis (a condition in which the muscles become weak and tire easily) clarithromycin may worsen these symptoms
- Gastroenteritis (inflammation of the stomach and intestines), oral thrush, vaginal bacterial or fungal infection
- Allergic reactions ranging from urticaria (nettle rash), mild skin eruptions and angioedema (swelling of the hands and face) to anaphylaxis (severe allergic reaction)
- Liver dysfunction or hepatitis (inflammation of the liver), cholestasis (obstruction of bile), jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes), hyperbilirubinaemia (increase of bilirubin in blood), liver failure
- sleepiness or difficulty in sleeping, nervousness
- Anorexia (loss of appetite)
- Widening of blood vessels
- Shortness of breath or other problems with breathing including asthma
- Feeling of weakness or discomfort, lethargy, fatigue, thirst, water retention in face (oedema), general feeling of being unwell, chest pain or any other pain
- Loss of taste or smell or inability to smell properly
- Discolouration of the tongue or teeth
- Inflammation of the mouth or tongue
- Heart rhythm disturbances or palpitations
- Hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar)
- Life-threatening irregular heart beat
- Tingling or numbness of limbs, convulsions (fits)
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), Pseudomembranous colitis (infection of the bowel)
- Kidney failure, interstitial nephritis (inflammation of the kidneys)
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis (severe peeling and blistering of the skin)
- Bad dreams, anxiety, confusion, depersonalisation (out of body feeling), disorientation (not knowing where you are), hallucinations, psychosis (mental illness)
- Acne
- Deafness
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Swelling of the feet and ankles
- Disturbed sleep (insomnia).
- Dizziness, feeling sleepy
- Spinning feeling (vertigo).
- Changes in blood tests that check how the liver is working.
- Skin rash, lumpy rash (hives) and itchy skin.
- Fracture of the hip, wrist or spine (if ZOSA HP KIT is used in high doses and over long duration).
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- Low levels of sodium in the blood. This may cause weakness, being sick (vomiting) and cramps.
- Feeling agitated, confused or depressed.
- Taste changes.
- Eyesight problems such as blurred vision.
- Suddenly feeling wheezy or short of breath (bronchospasm).
- An inflammation of the inside of the mouth.
- An infection called “thrush” which can affect the gut and is caused by a fungus.
- Hair loss (alopecia).
- Skin rash on exposure to sunshine.
- Joint pains (arthralgia) or muscle pains (myalgia).
- Generally feeling unwell and lacking energy. Increased sweating.
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- Thrush (a yeast infection of the vagina, mouth or skin folds), you can get treatment for thrush from your doctor or pharmacist
- Kidney problems
- Fits (convulsions), seen in patients on high doses or with kidney problems
- Dizziness
- Hyperactivity
- Crystals in the urine, which may be seen as cloudy urine, or difficulty or discomfort in passing urine. Make sure you drink plenty of fluids to reduce the chance of these symptoms
- Teeth may appear stained, usually returning to normal with brushing (this has been reported in children)
- The tongue may change to yellow, brown or black and it may have a hairy appearance
- An excessive breakdown of red blood cells causing a type of anaemia. Signs include: tiredness, headache, shortness of breath, dizziness, looking pale and yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes
- The blood may take longer to clot than it normally would. You may notice this if you have a nosebleed or cut yourself.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Drug Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store ZOSA HP KIT
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the blister and the carton after [Exp]. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
- Store below 30°C.
- Store in the original package in order to protect from moisture.
- Do not throw away medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
Combipack of Clarithromycin Tablets IP, Esomeprazole Tablets IP and Amoxicillin Tablets
Each strip contains:
A. Clarithromycin Tablets IP 2 Tablets
Each film coated tablet contains:
Clarithromycin IP 500 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Titanium Dioxide IP
B. Esomeprazole Tablets IP 2 Tablets
Each enteric coated tablet contains:
Esomeprazole Magnesium Trihydrate IP
equivalent to Esomeprazole 40 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colours: Red Oxide of Iron & Titanium Dioxide IP
C. Amoxicillin Tablets USP 2 Tablets
Each film coated tablet contains:
Amoxycillin Trihydrate IP
equivalent to Amoxycillin 750 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colours: Sunset Yellow FCF & Titanium Dioxide IP
Revised on 09/24