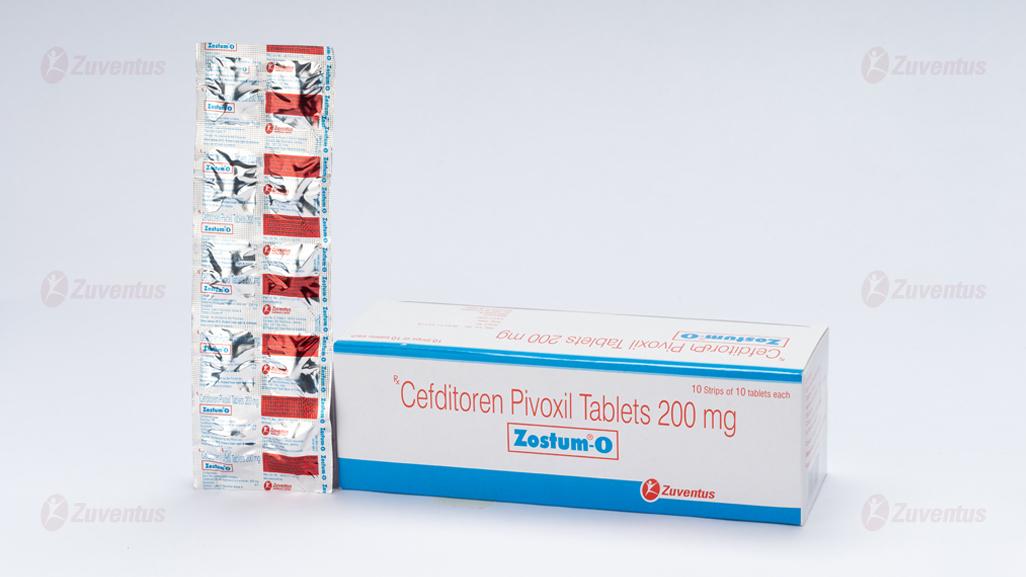
Zostum-O 200 Tablets
Therapy Area
Anti Infective
1.0 Name of the medicinal product
Cefditoren Pivoxil Tablets 200 mg
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
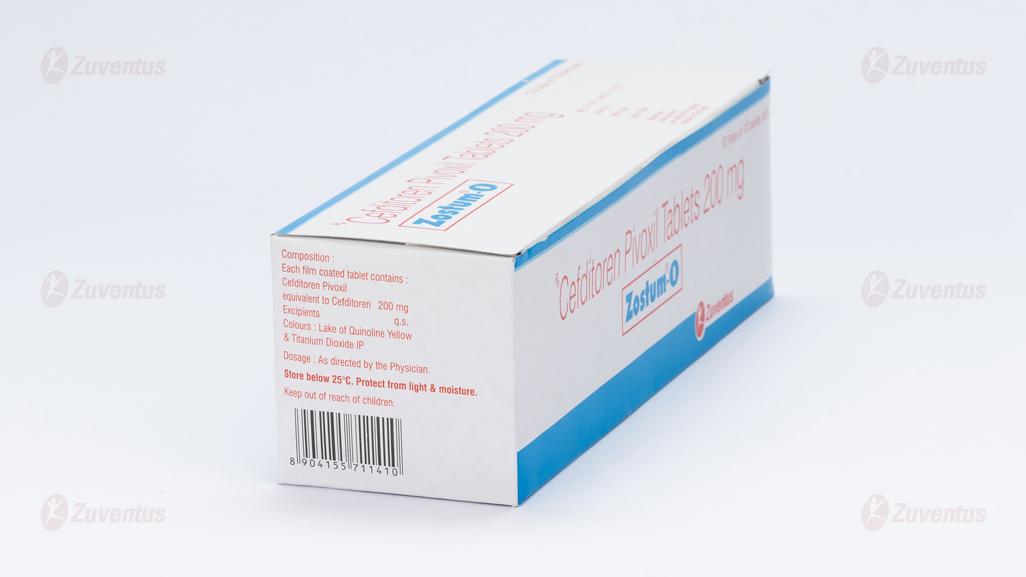
Each film coated tablet contains :
Cefditoren Pivoxil equivalent to Cefditoren 200 mg
Excipients q.s. Colours : Lake of Quinoline Yellow & Titanium Dioxide IP
3.0 Pharmaceutical form
Tablet 200 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Cefditoren pivoxil tablet is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate infections in adults and adolescents (12 years of age or older) which are caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed below.
- Acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis
- Pharyngitis /tonsillitis
- Uncomplicated skin and skin-structure infections
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis: 400 mg b.i.d. for 10 days
In Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis and Skin and Skin Structure infections: 200 mg b.i.d. for 10 days.
It is recommended to take dose with the meal.
Patients with Renal Insufficiency
No dose adjustment is necessary for patients with mild renal impairment (CLcr: 50-80 mL/min/1.73 m2). It is recommended that not more than 200 mg BID be administered to patients with moderate renal impairment (CLcr: 30-49 mL/min/1.73 m2) and 200 mg QD be administered to patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr: <30 mL/min/1.73 m2). The appropriate dose in patients with end-stage renal disease has not been determined.
Patients with Hepatic Disease
No dose adjustments are necessary for patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment
4.3 Contraindications
Cefditoren is contraindicated in patients with known allergy to the Beta-lactam class of antibiotics or any of the components of the formulations.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Before therapy with cefditoren pivoxil is instituted, careful inquiry should be made to determine whether the patient has had previous hypersensitivity reactions to cefditoren pivoxil, other cephalosporins, penicillins, or other drugs. If cefditoren pivoxil is to be given to penicillin- sensitive patients, caution should be exercised because cross- hypersensitivity among beta-lactam antibiotics has been clearly documented and may occur in up to 10% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy.
If an allergic reaction to cefditoren pivoxil occurs, the drug should be discontinued. Serious acute hypersensitivity reactions may require treatment with epinephrine and other emergency measures, including oxygen, intravenous fluids, intravenous antihistamines, corticosteroids, pressor amines, and airway management, as clinically indicated.
Cefditoren pivoxil is not recommended when prolonged antibiotic treatment is necessary, since other pivalate-containing compounds have caused clinical manifestations of carnitine deficiency when used over a period of months. With other antibiotics prolonged treatment may result in the possible emergence and overgrowth of resistant organisms. It should be taken with meals to enhance absorption. It may be taken concomitantly with oral contraceptives. It is not recommended when taken concomitantly with antacids or other drugs taken to reduce stomach acids
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Antacids – Antacids reduces the oral absorption of a single 400 mg dose of Cefditoren pivoxil administered following a meal, by a 14% decrease in mean Cmax and an 11% decrease in mean AUC. H2-Receptor Antagonists like Famotidine reduce the oral absorption of a single 400 mg dose of Cefditoren pivoxil administered following a meal, by a 27% decrease in mean Cmax and a 22% decrease in mean AUC. Probenecid increases the plasma concentration of cefditoren pivoxil, with a 49% increase in mean Cmax, a 122% increase in mean AUC, and a 53% increase in t1/2
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
The safety of Cefditoren has not been established. Cefditoren should not be used in pregnant women unless the potential benefits to the mother outweigh the risk to the fetus.
Nursing mothers:
Many drugs are excreted in human breast milk so caution should be exercised when cefditoren pivoxil is administered to nursing women. Geriatric use:
No clinically significant differences in effectiveness or safety were observed between older and younger patients. No dose adjustments are necessary in geriatric patients with normal (for their age) renal function.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Cefditoren has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive or use machines. However, cefditoren may cause side effects influencing the capacity of reaction and the ability to drive and use machines.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Fixed Drug Eruption (FDE) has been associated with Cefditoren pivoxil use
In clinical trials, 4834 adult and adolescent patients have been treated with the recommended doses of cefditoren pivoxil tablets (200 mg or 400 mg BID). Most adverse events were mild and self-limiting. No deaths or permanent disabilities have been attributed to cefditoren. The following adverse events were thought by the investigators to be possibly, probably, or definitely related to cefditoren tablets in multiple-dose clinical trials:
The overall incidence of adverse events, and in particular diarrhea, increased with the higher recommended dose of Cefditoren Pivoxil. Treatment related adverse events experienced by <1% but >0.1% of patients who received 200 mg or 400 mg BID of cefditoren pivoxil were abnormal dreams, allergic reaction, anorexia, asthenia, asthma, coagulation time increased, constipation, dizziness, dry mouth, eructation, face edema, fever, flatulence, fungal infection, gastrointestinal disorder, hyperglycemia, increased appetite, insomnia, leukopenia, leukorrhea, liver function test abnormal, myalgia, nervousness, oral moniliasis, pain, peripheral edema, pharyngitis, pseudomembranous colitis, pruritus, rash, rhinitis, sinusitis, somnolence, stomatitis, sweating, taste perversion, thirst, thrombocythemia, urticaria, and vaginitis. Pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may begin during or after antibiotic treatment.
Sixty-one of 2675 (2%) patients who received 200 mg BID and 69 of 2159 (3%) patients who received 400 mg BID of cefditoren pivoxil discontinued medication due to adverse events thought by the investigators to be possibly, probably, or definitely associated with cefditoren therapy. The discontinuations were primarily for gastrointestinal disturbances, usually diarrhea or nausea. Diarrhea was the reason for discontinuation in 19 of 2675 (0.7%) patients who received 200 mg BID and in 31 of 2159 (1.4%) patients who received 400 mg BID of cefditoren pivoxil.
Changes in laboratory parameters of possible clinical significance, without regard to drug relationship and which occurred in ≥1% of patients who received cefditoren pivoxil 200 mg or 400 mg BID, were hematuria (3.0% and 3.1%), increased urine white blood cells (2.3% and 2.3%), decreased hematocrit (2.1% and 2.2%), and increased glucose (1.8% and 1.1%). Those events which occurred in <1% but >0.1% of patients included the following: increased/decreased white blood cells, increased eosinophils, decreased neutrophils, increased lymphocytes, increased platelet count, decreased hemoglobin, decreased sodium, increased potassium, decreased chloride, decreased inorganic phosphorus, decreased calcium, increased SGPT/ALT, increased SGOT/AST, increased cholesterol, decreased albumin, proteinuria, and increased BUN. It is not known if these abnormalities were caused by the drug or the underlying condition being treated.
Cephalosporin Class Adverse Reactions
In addition to the adverse reactions listed above which have been observed in patients treated with cefditoren pivoxil, the following adverse reactions and altered laboratory test results have been reported for cephalosporin class antibiotics: Adverse Reactions: Allergic reactions, anaphylaxis, drug fever, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, serum sickness-like reaction, erythema multiforme, toxic epidermal necrolysis, colitis, renal dysfunction, toxic nephropathy, reversible hyperactivity, hypertonia, hepatic dysfunction including cholestasis, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia, hemorrhage, and superinfection. Altered Laboratory Tests: Prolonged prothrombin time, positive direct Coombs’ test, false-positive test for urinary glucose, elevated alkaline phosphatase, elevated bilirubin, levated LDH, increased creatinine, pancytopenia, neutropenia, and agranulocytosis. Several cephalosporins have been implicated in triggering seizures, particularly in patients with renal impairment when the dosage was not reduced. If seizures associated with drug therapy occur, the drug should be discontinued. Anticonvulsant therapy can be given if clinically indicated
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorization of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com
Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Treat over-dosage symptomatically and institute supportive measures as required. In animals diarrhea and soft stool lasting for few days were observed. Gastric Lavage may be done to remove the excess drug from the stomach.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of action
Cefditoren is bactericidal in nature and its activity results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis via affinity for penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). It has high affinity for penicillin binding protein (PBP) of various bacteria.
5.2 Pharmacodynamic properties
Antibacterial activity Cefditoren pivoxil is metabolized into cefditoren on absorption in the intestinal wall and shows its antibacterial activity. Cefditoren exerts broad spectrum antibacterial activity in vitro against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Especially it showed strong antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococcus sp., Streptococcus sp. and Streptococcus pneumoniae, and gram-negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis, Klebsiella sp., Proteus sp. and Haemophilus influenzae, and against anaerobic bacteria such as Peptostreptococcus sp., Propionibacterium acnes, Bacteroides sp. and Prevotella sp. Cefditoren also showed antibacterial activity against -lactamase-non producing ampicillin resistant Haemophilus influenzae (BLNAR). In vitro, cefditoren was stable against -lactamases producing strains.
5.3 Pharmacokinetic Properties
Absorption
Following oral administration, cefditoren pivoxil is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and hydrolyzed to cefditoren by esterases. Maximal plasma concentrations (Cmax) of cefditoren under fasting conditions average 1.8 ± 0.6 µg/mL following a single 200 mg dose and occur 1.5 to 3 hours following dosing. Less than dose-proportional increases in Cmax and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) were observed at doses of 400 mg and above. Cefditoren does not accumulate in plasma following twice daily administration to subjects with normal renal function. Under fasting conditions, the estimated absolute bioavailability of cefditoren pivoxil is approximately 14%. Administration of cefditoren pivoxil following a high fat meal resulted in a 70% increase in mean AUC and a 50% increase in mean Cmax compared to administration of cefditoren pivoxil in the fasted state.
Distribution
The mean volume of distribution at steady state (Vss) of cefditoren is 9.3 ± 1.6 L. Binding of cefditoren to plasma proteins averages 88% from in vitro determinations, and is concentration-independent at cefditoren concentrations ranging from 0.05 to 10 µg/mL.
Metabolism and Excretion
Cefditoren is eliminated from the plasma, with a mean terminal elimination half-life (t1/2) of 1.6 ± 0.4 hours in young healthy adults. Cefditoren is not appreciably metabolized. After absorption, cefditoren is mainly eliminated by excretion into the urine, with a renal clearance of approximately 4-5 L/h. Cefditoren renal clearance is reduced in patients with renal insufficiency.
6.0 Nonclinical Properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
No known animal toxicology data.
7.0 Description
Zostum-O contains cefditoren pivoxil, a semi-synthetic cephalosporin antibiotic for oral administration. It is a prodrug which is hydrolyzed by esterases during absorption, and the drug is distributed in the circulating blood as active cefditoren.
Chemical name: 2, 2-Dimethylpropanoyloxymethyl (6R, 7R)-7-[(Z)-2- (2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino) acetylamino]-3-[(1Z)- 2-(4-methylthiazol-5-yl) ethenyl]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0] oct-2-ene -2-carboxylate.
Molecular formula: C25H28N6O7S3
Molecular weight: 620.72
8.0 Pharmaceutical Particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicable.
8.2 Shelf Life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging Information
A strip of 6 tablets / A strip of 10 tablets.
8.4 Storage and handing Instructions
Store below 25°C. Protect from light & moisture.
Keep out of reach of children.
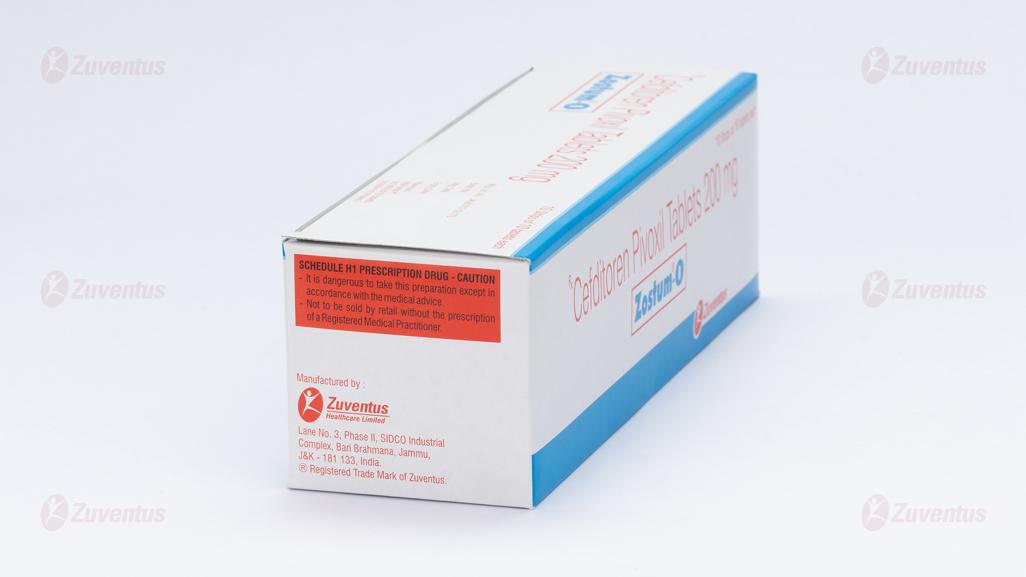
9.0 Details of manufacturer
- Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including Cefditoren Pivoxil should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold).
- When Cefditoren Pivoxil is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Cefditoren Pivoxil or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
- Cefditoren Pivoxil should be taken with meals to enhance absorption.
- Cefditoren Pivoxil may be taken concomitantly with oral contraceptives.
- It is not recommended that Cefditoren Pivoxil be taken concomitantly with antacids or other drugs taken to reduce stomach acids
12.0 Date of Issue
07 April 2023
About leaflet
- Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any more questions, please ask your doctor or your pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you personally and you should not pass it on to anyone else. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects that are not listed in the leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
In this leaflet:
1. What ZOSTUM-O tablets are and what they are used for
2. What you need to know before you take ZOSTUM-O Tablets
3. How to take ZOSTUM-O Tablets
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store ZOSTUM-O Tablets
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Zostum-o Tablets are and what they are used for
ZOSTUM-O Tablets contains cefditoren Pivoxil, a broad-spectrum third generation cephalosporin class antibiotic. Cefditoren tablets may be used to treat mild to moderate infections in adults and adolescents (12 years of age or older):
- inflammation and irritation of the bronchial tubes (acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis)
- sore throat, swollen tonsils, difficulty in swallowing, Sinus infection and tender lymph nodes on the sides of the neck (pharyngitis, tonsillitis, rhino-sinusitis)
- bacterial skin infections (uncomplicated skin and skin-structure infections)
Cefditoren is bactericidal in nature and its activity results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis via affinity for penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). It is stable in the presence of a variety of beta-lactamases, including penicillinases and some cephalosporinases. It is active against aerobic gram-positive pathogens like Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes and aerobic gram-negative pathogens like Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis.
2. What you Nned to know before you take Zostum-o Tablets
Do not take ZOSTUM-O Tablets if you are:
- allergic to the Beta-lactam class of antibiotics or any of the components of the formulations.
Warnings and Precautions
- Before therapy with cefditoren pivoxil is instituted, careful inquiry should be made to determine whether the patient has had previous hypersensitivity reactions to cefditoren pivoxil, other cephalosporins, penicillins, or other drugs.
- If cefditoren pivoxil is to be given to penicillin-sensitive patients, caution should be exercised because cross-hypersensitivity among ß-lactam antibiotics has been clearly documented and may occur in up to 10% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy.
- If an allergic reaction to cefditoren pivoxil occurs, the drug should be discontinued. Serious acute hypersensitivity reactions may require treatment with epinephrine and other emergency measures, including oxygen, intravenous fluids, intravenous antihistamines, corticosteroids, pressor amines, and airway management, as clinically indicated.
- Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents, including cefditoren pivoxil, and may range in severity from mild to life-threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhea subsequent to the administration of antibacterial agents.
- Treatment with antibacterial agents alters normal flora of the colon and may permit overgrowth of clostridia. Studies indicate that a toxin produced by Clostridium difficile is a primary cause of antibiotic-associated colitis.
- After the diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis has been established, appropriate therapeutic measures should be initiated. Mild cases of pseudomembranous colitis usually respond to drug discontinuation alone. In moderate to severe cases, consideration should be given to management with fluids and electrolytes, protein supplementation, and treatment with an antibacterial drug clinically effective against C. difficile colitis.
- Prescribing cefditoren pivoxil in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
- Cefditoren pivoxil is not recommended when prolonged antibiotic treatment is necessary. since other pivalate-containing compounds have caused clinical manifestations of carnitine deficiency when used over a period of months. No clinical effects of carnitine decrease have been associated with short-term treatment.
- Community-acquired pneumonia clinical trials demonstrated no adverse events attributable to decreases in serum carnitine concentrations. However, some sub-populations (e.g., patients with renal impairment, patients with decreased muscle mass) may be at increased risk for reductions in serum carnitine concentrations during cefditoren pivoxil therapy.
- As with other antibiotics, prolonged treatment may result in the possible emergence and overgrowth of resistant organisms. Careful observation of the patient is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate alternative therapy should be administered.
- Prothrombin time should be monitored in patients at risk and exogenous vitamin K administered as indicated.
Pregnancy Category B
Cefditoren pivoxil was not teratogenic up to the highest doses tested in rats and rabbits. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproductive studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Labor and Delivery
Cefditoren pivoxil has not been studied for use during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
Because many drugs are excreted in human breast milk, caution should be exercised when cefditoren pivoxil is administered to nursing women.
Geriatric Use
No dose adjustments are necessary in geriatric patients with normal (for their age) renal function. This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines, in particular
Antacids: Co-administration of an antacid reduces the oral absorption of cefditoren pivoxil. Therefore, it is not recommended that cefditoren pivoxil be taken concomitantly with antacids.
H2-Receptor Antagonists: Co-administration of H2-Receptor antagonists with cefditoren reduces the oral absorption of cefditoren. Although the clinical significance is not known, it is not recommended that cefditoren pivoxil be taken concomitantly with H2 receptor antagonists.
Probenecid: Co-administration of probenecid with cefditoren resulted in an increase in the plasma exposure of cefditoren.
Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Cefditoren has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive or use machines. However, cefditoren may cause side effects influencing the
capacity of reaction and the ability to drive and use machines.
3. How to take Zostum-o Tablets
Follow your doctor’s instructions. Check the pharmacy label to see how many tablets to take and how often to take them. If you are still not sure, ask your pharmacist or doctor. The usual doses are described below.
Adults and Adolescents (12 years of age or older)
- inflammation and irritation of the bronchial tubes (acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis): 400 mg (2 tablets) two times daily for 10 days
- sore throat, swollen tonsils, difficulty in swallowing, Sinus infection and tender lymph nodes on the sides of the neck (pharyngitis, tonsillitis, rhino-sinusitis): 200 mg (one tablet) two times daily for 10 days.
- bacterial skin infections (uncomplicated skin and skin-structure infections): 200 mg (one tablet) two times daily for 10 days.
Patients with Renal Insufficiency
No dose adjustment is necessary for patients with mild renal impairment (CLcr: 50-80 mL/min/1.73 m2). It is recommended that not more than 200 mg two times daily be administered to patients with moderate renal impairment (CLcr: 30-49 mL/min/1.73 m2) and 200 mg once daily be administered to patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr: <30 mL/min/1.73 m2). The appropriate dose in patients with end-stage renal disease has not been determined.
Patients with Hepatic Disease
No dose adjustments are necessary for patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment
Method of administration
The tablets can be taken after food. Always continue with the course even if you feel better. If your infection gets worse or you do not start to feel better within a few days or a new infection develops, go back and see your doctor.
If you take more cefditoren than you should
If you have taken too much cefditoren, contact your doctor, pharmacist or go to your nearest hospital immediately. In case of overdose admission into hospital may be necessary.
If you forget to take ZOSTUM-O TABLETS
If you forget to take ZOSTUM-O TABLETS, take your dose as soon as possible. If it is almost time for the next dose, just skip that dose and take the next one when it is due. If in doubt, please contact your doctor or pharmacist. If you have to skip a dose, still take all of your tablets. This means that you will finish your course a day later. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you stop taking ZOSTUM-O TABLETS
Never stop the treatment with cefditoren on your own, but first discuss this with your doctor. If you stop taking cefditoren too soon, the infection may return. Take the tablets for the full time of treatment, even when you begin to feel better.
4. Possible side effects
In clinical trials, 4834 adult and adolescent patients have been treated with the recommended doses of cefditoren Pivoxil. Most adverse events were mild and self-limiting. No deaths or permanent disabilities have been attributed to cefditoren.
The following adverse events were thought related to cefditoren tablets in multiple-dose clinical trials:
Treatment-Related Adverse Events in Trials in Adults and Adolescent Patients ≥ 12 Years of age
The overall incidence of adverse events, and in particular diarrhea, increased with the higher recommended dose of cefditoren.
Cephalosporin Class Adverse Reactions
In addition to the adverse reactions listed above which have been observed in patients treated with cefditoren Pivoxil, the following adverse reactions and altered laboratory test results have been reported for cephalosporin class antibiotics:
Adverse Reactions: Allergic reactions, drug fever, colitis, renal dysfunction, reversible hyperactivity, liver dysfunction including cholestasis, anemia, hemorrhage, and superinfection.
Altered Laboratory Tests results: Prolonged prothrombin time, liver enzyme levels, elevated bilirubin, kidney dysfunction etc.
Several cephalosporins have been implicated in triggering seizures, particularly in patients with renal impairment when the dosage was not reduced. If seizures associated with drug therapy occur, the drug should be discontinued. Anticonvulsant therapy can be given if clinically indicated.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice any other effects not listed.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Drug Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store Zostum-o Tablets
Do not use the tablets after the end of the expiry month (use-by date) shown on the product packaging. Store below 25oC. Store in a cool and dry place. Protect from light & moisture. Store in the original package.
KEEP THIS MEDICINE OUT OF THE SIGHT AND REACH OF CHILDREN
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
Composition of ZOSTUM-O TABLETS
Each film coated tablet contains:
Cefditoren Pivoxil
equivalent to Cefditoren 200 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colours: Lake of Quinoline Yellow & Titanium Dioxide IP
Package information
- A strip of 6 tablets or
- A strip of 10 tablets.