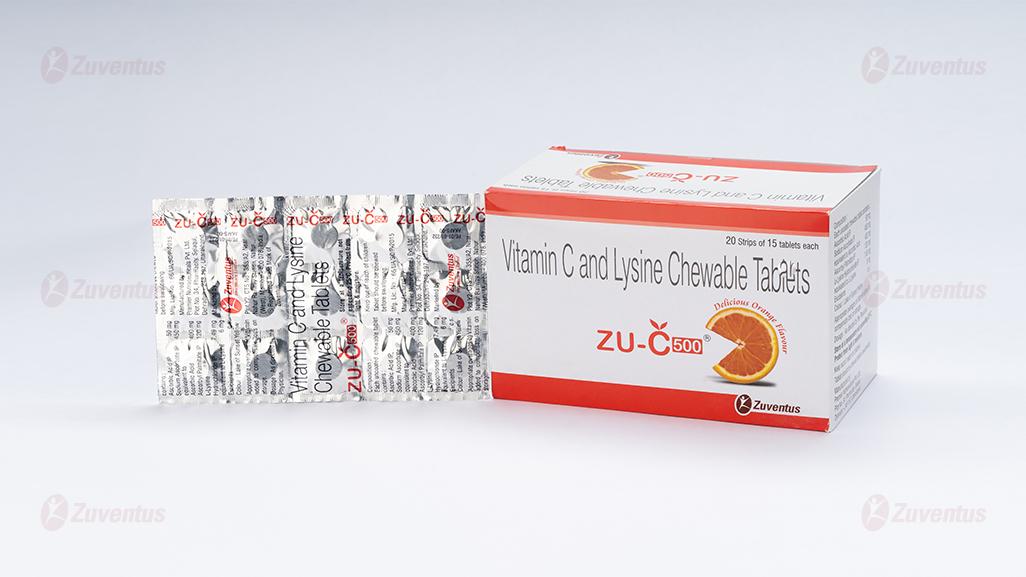
ZU-C 500
Therapy Area
Vitamins/Minerals Supplements
1.0 Generic name
Vitamin C Chewable Tablets 500
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
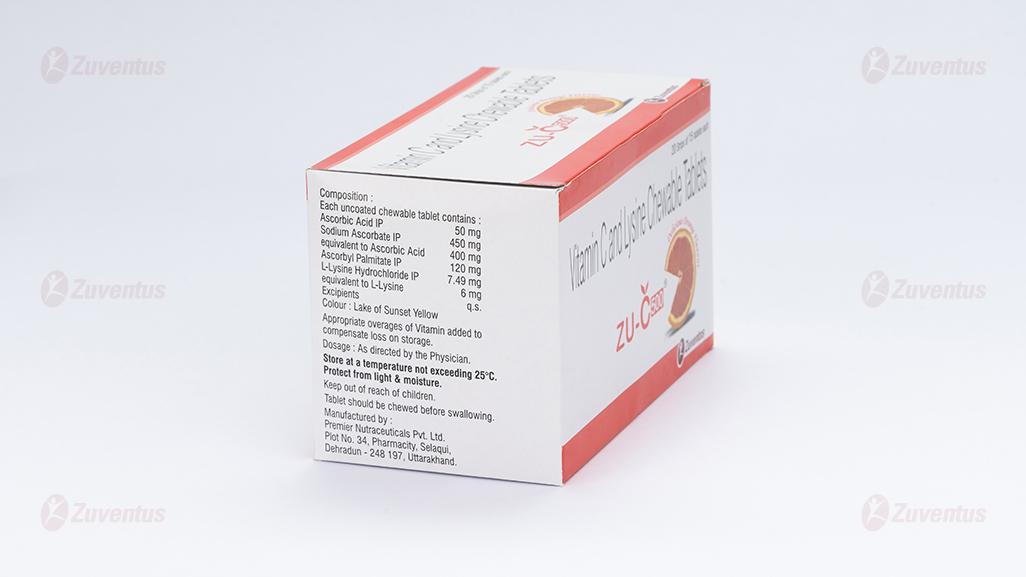
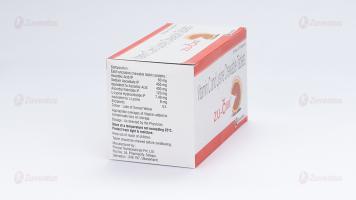
Each uncoated chewable tablets contains:
Ascorbic Acid IP 50 mg
Sodium Ascorbate IP equivalent to Ascorbic Acid 400 mg '
Ascorbyl Palmitate IP 120 mg '
L- Lysine Hydrochloride USP 7.49 mg
'equivalent to L- Lysine 6 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Sunset of Yellow FCF
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Oral, Chewable Tablets, 500 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic indication
For the prevention and treatment of Vitamin C deficiency
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Method of administration
Vitamin C Chewable Tablets are to be chewed before swallowing.
Posology
- Adults and Children > 12 years: 1-2 tablets per day (equivalent to 500 or 1000 mg/day) until symptoms subside.
- Children 6-12 years: 1 tablet per day (equivalent to 500 mg/day) until symptoms subside.
- Vitamin C Chewable Tablets are not recommended for children under 6 years.
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
- Ascorbic acid should not be given to patients with hyperoxaluria.
- Oxalate urolithiasis and iron storage diseases (thalassaemia, haemochromatosis, sideroblastic anaemia) or other medical conditions that predispose individuals to iron overload.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
a. Increased intake of ascorbic acid over a prolonged period may result in an increased renal clearance of ascorbic acid, and deficiency may result if the intake is reduced or withdrawn rapidly.
b. Exceeding the recommended dose should be avoided as there have been isolated reports of severe haemolysis in patients with erythrocytic glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency when taking high doses (> 4000 mg/day) of ascorbic acid. Do not exceed the recommended dose.
c. Caution is required and use the minimum recommended dose in patients with renal impairment.
d. Patients with rare hereditary fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption or sucraseisomaltase deficiency should not take ascorbic acid.
e. Interference with serological testing
- Ascorbic acid may interfere with tests and assays for urinary glucose, giving false-negative results with methods utilising glucose oxidase with indicator and false-positive results with neocuproine methods.
- Estimation of uric acid by phosphotungstate or uricase with copper reduction and measurement of creatinine in non-deproteinised serum may also be affected.
- High doses of ascorbic acid may give false-negative readings in faecal occult blood tests.
- Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, total lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine.
4.5 Drugs interactions
- Ascorbic acid increases the renal excretion of amphetamine.
- The plasma concentration of ascorbate is decreased by smoking and oral contraceptives.
- Ascorbic acid increases the absorption of iron. This should be borne in mind in the case of iron replacement.
- Concomitant administration of aspirin and ascorbic acid may interfere with absorption of ascorbic acid. Renal excretion of salicylate is not affected and does not lead to reduced anti-inflammatory effects of aspirin.
- Concomitant administration of aluminium-containing antacids may increase urinary aluminium elimination. Concurrent administration of antacids and ascorbic acid is not recommended, especially in patients with renal insufficiency.
- Co-administration with amygdalin (a complementary medicine) can cause cyanide toxicity.
- Concurrent administration of ascorbic acid with desferrioxamine enhances urinary iron excretion. Cases of cardiomyopathy and congestive heart failure have been reported in patients with idiopathic haemochromatosis and thalassaemias receiving desferrioxamine who were subsequently given ascorbic acid. Ascorbic acid should be used with caution in these patients and cardiac function monitored.
- Ascorbic acid may interfere with biochemical determinations of creatinine, uric acid and glucose in samples of blood and urine.
4.6 Use in special populations
Pregnancy
For ascorbic acid no clinical data on exposed pregnancies are available. Animal studies do not indicate direct or harmful effects with respect to pregnancy, embryonal/foetal development, parturition or postnatal development. Pregnant women should exercise caution.
Breast-feeding
Ascorbic acid is excreted in breast milk. Though again caution should be exercised, no evidence exists suggesting such excretion is hazardous to the infant.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
On the basis of the product's pharmacodynamic profile and reported adverse events, ascorbic acid has no known effect on an individual's ability to drive or operate machinery.
4.8 Undesirable effects
- Nervous system disorders: headache.
- Vascular disorders: flushing.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, vomiting and stomach cramps. Large doses of ascorbic acid may cause diarrhoea.
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: redness of skin.
- Renal and urinary disorders: Patients known to be at risk of hyperoxaluria should not ingest ascorbic acid doses exceeding 1g daily as there may be increased urinary oxalate excretion. However, such risk has not been demonstrated in normal, non-hyper oxaluric individuals. Ascorbic acid has been implicated in precipitating haemolytic anaemia in certain individuals deficient of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Increased intake of ascorbic acid over a prolonged period may result in increased renal clearance of ascorbic acid, and deficiency may result if the intake is reduced or withdrawn rapidly. Doses of more than 600mg daily have a diuretic effect.
- Reporting of suspected adverse reactions Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to: medico@zuventus.com Website: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
Symptoms: At doses of over 3g per day unabsorbed ascorbic acid is mainly excreted unmetabolised in the faeces. Absorbed ascorbic acid additional to the body's needs is rapidly eliminated. Large doses of ascorbic acid may cause diarrhoea and the formation of renal oxalate calculi. Symptomatic treatment may be required. Ascorbic acid may cause acidosis or haemolytic anaemia in certain individuals with a deficiency of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Renal failure can occur with massive ascorbic acid overdosage.
Management: Gastric lavage may be given if ingestion is recent otherwise general supportive measure should be employed as required.
5.0 Pharmacological properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Vitamins – Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) ATC code: A11GA01
5.1 Mechanism of Action
Ascorbic acid, coupled with dehydroascorbic acid to which it is reversibly oxidised, has a variety of functions in cellular oxidation processes.
5.2 Pharmacodynamicproperties
5.3 Pharmacodynamic properties
Ascorbic acid is required in several important hydroxylations, including the conversion of proline to hydroxyproline (and thus collagen formation e.g. for intercellular substances and during wound healing); the formation of the neurotransmitters 5-hydroxytryptamine from tryptophan and noradrenaline from dopamine, and the biosynthesis of carnitine from lysine and methionine. Ascorbic acid appears to have an important role in metal ion metabolism, including the gastrointestinal absorption of iron and its transport between plasma and storage organs. There is evidence that ascorbic acid is required for normal leucocyte functions and that it participates in the detoxification of numerous foreign substances by the hepatic microsomal system. Deficiency of ascorbic acid leads to scurvy, which may be manifested by weakness, fatigue, dyspnoea, aching bones, perifollicular hyperkeratosis, petechia and ecchymosis, swelling and bleeding of the gums, hypochromic anaemia and other haematopoietic disorders, together with reduced resistance to infections and impaired wound healing. In addition, an ascorbic acid deficiency impairs the immune defence reactions, especially chemotaxis, complement activation and interferon production. Ascorbic acid improves the absorption of iron salts by reducing ferric ions and forming iron chelates. It blocks the chain reactions triggered by oxygen radicals in aqueous compartments of the body. The anti-oxidative functions form a close biochemical interaction with those of vitamin E, vitamin A and carotenoids.
5.4 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Ascorbic acid is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. As the unit dose increases the bioavailability falls to 60-75% after 1 g, to approximately 40% after 3 g and down to 16% after 12 g. The unabsorbed proportion is broken down by the flora in the large intestine, predominantly to CO2 and organic acids.
Distribution
Ascorbic acid is widely distributed to all tissues. Body stores of ascorbic acid normally are about 1.5g. The concentration is higher in leucocytes and platelets than in erythrocytes and plasma.
Metabolism
In healthy adults the maximum metabolic turnover of 40 to 50 mg/day is achieved at plasma concentrations of 0.8 to 1.0 mg/dl. The total daily turnover is about 1 mg/kg. At extremely high oral doses plasma concentrations of up to 4.2 mg/dl are achieved for a short time after about 3 hours
Elimination
Ascorbic acid additional to the body's needs, generally amounts above 200mg daily, is rapidly eliminated; unmetabolised ascorbic acid and its inactive metabolic products are chiefly excreted in the urine. The amount of ascorbic acid excreted unchanged in the urine is dose-dependent and may be accompanied by mild diuresis.
6.0 Nonclinical properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
There are no other preclinical data of relevance to the prescriber which are additional to that already included in other sections of the prescribing information.
7.0 Description
Vitamin C Chewable Tablets 500 is a blend of water soluble ascorbic acid (450mg) along with 120 mg Ascorbyl palmitate, a fat-soluble derivative of ascorbic acid. Ascorbyl palmitate is approximately 42.5% of Vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Considering this 120 mg Ascorbyl palmitate will provide approximately 50 mg of ascorbic acid. Therefore, each Vitamin C Chewable 500 Tablets provide tablet provides total 500 mg of ascorbic acid (Vitamin C).
Ascorbyl Palmitate (120 mg):
- Ascorbyl palmitate is also known as "vitamin C ester" because it is an ester formed from ascorbic acid and palmitic acid. It is used either as a fat-soluble form of vitamin C, or as an antioxidant food additive.
- Ascorbyl palmitate possesses all the benefits of vitamin C. Ascorbyl palmitate is highly bioavailable, fat-soluble derivative of ascorbic acid and is able to be stored in the lipid cell membrane until the body is ready to put it to use.
- Ascorbyl palmitate is an amphipathic molecule (fat as well as water soluble form of vitamin C) which is better absorbed than ascorbic acid (water-soluble form). This dual solubility allows it to be incorporated into cell membranes.
- The fat-soluble aspect of ascorbyl palmitate extends vitamin C free radical protection (free radical protection) into the fat parts of the body.
- When incorporated into the cell membranes of human red blood cells, ascorbyl palmitate has been found to protect them from oxidative damage and to protect alpha-tocopherol (a fat-soluble antioxidant) from oxidation by free radicals.
L-Lysine:
L-Lysine is an essential amino acid, necessary building block for all proteins in the body. Amino acids such as L-lysine and vitamin C are crucial for the body’s production of collagen and the protection of the endothelium of the artery walls.
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
None.
8.2 Shelf-life
18 months
8.3 Packaging information
20 strips of 15 tablets in each strip
1 strip of 15 chewable tablets
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Protect from Light.
Keep out of reach of children.
9.0 Patient counselling information
Chew the tablets carefully before swallowing. Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Do not take Ascorbic Acid Tablets if:
- You are allergic to Ascorbic Acid or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
- You suffer from hyperoxaluria (excretion of urine containing large amounts of calcium oxalate crystals).
Talk to your doctor before taking Ascorbic Acid Tablets:
- If you are to undergo any blood or urine tests as ascorbic acid can interfere with some blood and urine tests.
- If you are a regular smoker.
- If you have kidney failure as ascorbic acid enhances aluminium absorption (present in antacids) which may reach toxic levels.
Tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. This is particularly important if you are taking any of the following:
- Amphetamines.
- Contraceptives.
- Aspirin.
- Iron-containing medicines.
- Amygdalin (Vitamin B17) - can cause cyanide toxicity
Ascorbic Acid Tablets should not be taken for the first month after starting desferrioxamine treatment
If you stop taking Ascorbic Acid Tablets:
Keep taking this medicine until your doctor tells you to stop. You may need to stop taking the tablets slowly as they may alter your kidney function.
About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or nurse
- This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours
- If you get any side-effects talk to your doctor, this includes any possible side effects not included in this leaflet.
In this leaflet:
- What ZU-C 500 is and what they are used for?
- What you need to know before you are given ZU-C 500
- How to take ZU-C 500
- Possible side effects
- How to store ZU-C 500
- Content of pack and other information.
1. What ZU-C 500 is and what they are used for?
ZU-C 500 contains ascorbic acid. Ascorbic acid is a nutritional supplement commonly called Vitamin C. It is used to prevent and treat Vitamin C deficiency (e.g. scurvy) or other conditions requiring extra vitamin C.
2. What you need to know before you are given ZU-C 500?
Do not use ZU-C 500 if:
- If you are allergic to ascorbic acid or any of the other ingredient of this medicine.
- You have a condition called hyperoxaluria, where you have too much calcium oxalate crystals in your urine. This can lead to kidney stones.
If this applies to you talk to your doctor or nurse.
Warnings and Precautions
Check with your doctor before taking ZU-C 500 if:
- You have kidney problems
- You smoke
- You have an enzyme deficiency called G6PD deficiency. Large doses of ascorbic acid can cause your blood cells to break up.
- If you have undergone any blood or urine test as Vitamin-c interfere with the results.
Tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- Aspirin
- Desferrioxamine used to treat iron overload
- Medicines used to treat epilepsy (e.g. phenytoin)
- Appetite suppressants (e.g. fenfluramine)
- Oral contraceptives which contains oestrogen (e.g. “the pill”)
- antibiotics (e.g. tetracycline)
- iron supplement
- oral anticoagulants (e.g. Warfarin)
- fluphenazine for mental disorders
- Any other medicine, including medicines obtained without a prescription.
If any of the above applies to you talk to your doctor or nurse. Ascorbic acid tablets should not be taken for the first month after starting Desferrioxamine treatment.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, trying to become pregnant or breastfeeding. Large doses of ascorbic acid, i.e. greater than 1g daily, should not be taken during pregnancy since the effect of large doses on the foetus is unknown. Ascorbic acid is excreted in breast milk but there is no evidence of any hazard to the baby.
Driving and using machines.
This medicine doesn’t affect the ability to drive or operate the machinery. If you think it you are affected, you should not drive or operate machinery until you feel better.
3. How to take ZU-C 500 tablets
Always take ZU-C 500 exactly as your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure. Tablet should be chewed before swallowing.
Unless otherwise prescribed by your doctor, the usual dose is as follows:
- Adults and Children > 12 years: 1-2 tablets per day (equivalent to 500 or 1000 mg/day) until symptoms subside.
- Children 6-12 years: 1 tablet per day (equivalent to 500 mg/day) until symptoms subside.
- Vitamin C Chewable Tablets are not recommended for children under 6 years.
If you take more ZU-C 500 tablets than you should
If you have taken a lot of tablet at the same time or you think your child may have swallowed any, contact nearest hospital casualty department and tell the doctor immediately.
Large doses of ascorbic acid may cause diarrhoea and kidney stones may form if your urine is acidic. Doses of 600 mg or more may lead to more frequent passing water.
If you forget to take ZU-C 500 tablets
Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose, as you would not substitute the missing amount but you risk overdosing. Continue the treatment according to the instructions.
If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines ZU-C 500 can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
- Diarrhoea, stomach cramps, nausea (feeling sick), vomiting, headache etc.
- Flushing, redness of skin
- Haemolytic anemia (body’s own immune system breaks the Red blood cells), signs may include fatigue and paleness.
- Increased urination (passing water) due to diuretic effect
- Formation of kidney stones if your urine is acidic.
If any of the side effects gets serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or nurse. Reporting of side effects If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.com and click the tab “Drug Safety Reporting” located on the top of the home page.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store ZU-C 500 tablets
Keep out of the reach and sight of children. Do not use ZU-C 500 tablets after the expiry date which is stated on the outer carton/container. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month. Do not store above 25°C.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Content of the pack and other information
What ZU-C 500 tablets contain:
Each uncoated chewable tablets contains: Ascorbic Acid IP 50 mg
Sodium Ascorbate IP equivalent to Ascorbic Acid 400 mg
Ascorbyl Palmitate IP 120 mg
L- Lysine Hydrochloride USP equivalent to L- Lysine 6 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour: Sunset of Yellow FCF
Packaging information: 20 strips of 15 tablets each.