Zuglimin 500 Tablets
Therapy Area
Anti-diabetic
1.0 Generic name
Imeglimin Hydrochloride Tablets 500 mg / 1000 mg
2.0 Qualitative and quantitative composition
Each film coated tablet contains :
Imeglimin Hydrochloride 500 mg / 1000 mg
Excipients q.s.
3.0 Dosage form and strength
Film-coated tablets; 500 mg and 1000 mg
4.0 Clinical particulars
4.1 Therapeutic Indication
Zuglimin is indicated for the treatment of Type II diabetes
4.2 Posology & Method of Administration
For adults, 1000 mg of Imeglimin is orally administered twice daily in the morning and evening.
4.3 Contraindications
- Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to the ingredients of this drug
- Patients with severe ketosis, diabetic coma or precoma, type 1 diabetes.
- Patients with severe infections, before and after surgery, and with serious trauma.
4.4 Warning & Precautions
The usage of this drug should be considered only when the blood glucose control is insufficient after dietary control and exercise therapy, which are the basics of diabetes treatment. For patients with renal dysfunction, it is recommended to perform renal function checks regularly, as the excretion of this drug may be delayed and the blood concentration of this drug may increase. Clinical trials 2 have not been conducted on efficacy and safety measures in patients with moderate or severe renal dysfunction (eGFR<45 mL/min/1.73m ) using efficacy and safety as indicators, and administration is not recommended.
Before using this drug, patients should be fully informed of hypoglycemic symptoms and how to deal with them. Since hypoglycemic symptoms may occur, care should be taken when administering to patients engaged in work at heights, driving a car, etc. The mechanism of action of this drug may be partly in common with biguanide drugs, in addition, because co-administration of both drugs may increase gastrointestinal symptoms, care should be taken when selecting concomitant drugs.
Hypoglycemia may occur when used concomitantly with insulin preparations, sulfonylureas, or rapid-acting insulin secretagogues. If hypoglycemic symptoms (initial symptoms : weakness, severe hunger, sweating, etc.) are observed, take appropriate measures such as ingesting food containing carbohydrates. However, if hypoglycemic symptoms are observed due to concomitant use with an α-glucosidase inhibitor, glucose should be administered.
In non-clinical studies using rats, no clear effects of this drug on blood lactate levels were observed, and in clinical studies, the development of lactic acidosis was not observed. The mechanism of action of Imeglimin is partially in common with biguanide drugs. It has been reported that biguanide drugs cause rare and serious lactic acidosis, and risk factors include renal dysfunction, liver dysfunction, conditions that are likely to accompany hypoxia, and dehydration (including concomitant use of drugs with diuretic effects), excessive alcohol intake, infectious diseases and the elderly.
4.5 Drug Interactions
Imeglimin is mainly excreted as an unchanged drug from the kidney. Following precautions should be taken when Zuglimin is combined with other drugs.
| Drug name, etc. | Clinical symptoms / measures | Mechanism / risk factors |
| Diabetes medications : Insulin preparations, Sulfonylureas, Fast-acting insulin secretagogues, α-glucosidase inhibitor, Thiazolidine drug, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors, etc. | Be aware of the development of hypoglycemia. In particular, when used in combination with insulin preparations, sulfonylureas or fast-acting insulin secretagogues, the risk of hypoglycemia may increase. To reduce the risk of hypoglycemia caused by these drugs, consider reducing the dose of insulin preparations, sulfonylureas, or fast-acting insulin secretagogues. | The hypoglycemic effect may be enhanced. |
| Biguanide drugs | Be aware of the development of hypoglycemia and gastrointestinal symptoms. | For hypoglycemia, the hypoglycemia effect may be enhanced. Gastrointestinal symptoms tend to occur more often, especially in the early stages of concomitant use. |
| Drugs that enhance the hypoglycemic effect : β-blockers, Salicylic acid, Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, etc | Administer while carefully observing blood glucose level and other patient conditions. | The hypoglycemic effect may be enhanced. |
| Drugs that reduce hypoglycemic effects : Adrenaline adrenocortical hormone, thyroid hormone, etc. | Administer while carefully observing blood glucose level and other patient conditions. | The hypoglycemic effect may be enhanced. |
4.6 Special populations
The following patients or conditions may cause hypoglycemia :
- Pituitary dysfunction or adrenal dysfunction.
- Malnutrition, starvation, irregular dietary intake, lack of dietary intake or weakness.
- Intense muscle exercise.
- Excessive alcohol intake.
- Patients with renal dysfunction
The administration of Imeglimin is not recommended in patients with renal dysfunction with eGFR <45 mL/min/1.73 m (including dialysis patients). The blood concentration of this drug may increase significantly
The pharmacokinetics parameters comparing the single oral dose of Imeglimin in subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment (classified based on eGFR measurements) with a single oral dose of Imeglimin with 2 normal renal function (eGFR 90 mL/min/1.73m or more) are as follows :
|
Renal function |
Dosage (mg) |
Number of subjects |
Cmax |
AUC0-last |
|
|
|
|
Geometric mean ratio [90% confidence interval] |
Geometric mean [90% confidence interval] |
|
Mild (60 ≤ eGFR <90) |
1000 |
6 |
1.42 [1.05, 1.91] |
1.49 [1.03, 2.17] |
|
Moderate (30 ≤ eGFR <60) |
1000 |
6 |
1.52 [1.13, 2.05] |
1.81 [1.25, 2.63] |
|
Severe (15 ≤ eGFR <30) |
500 |
6 |
1.50 [1.11, 2.02] |
2.49 [1.71, 3.61] |
The pharmacokinetics of repeated oral administration twice a day in subjects with varying degrees of renal dysfunction (classified based on CLcr (creatinine clearance) are as follows
|
Renal function (CLcr*) |
Number of |
Cmax |
AUCτ |
|
|
|
Geometric mean ratio [90% confidence interval] |
Geometric mean [90% confidence interval] |
|
Mild (50 ≤ CLcr ≤ 80) |
4 |
1.28 [1.03, 1.59] |
1.50 [1.16, 1.94] |
|
Moderate(30≤ CLcr<50) |
6 |
1.95 [1.61, 2.35] |
2.32 [1.85, 2.92] |
|
Severe(CLcr<30) |
5 |
2.86 [2.08, 3.94] |
3.56 [2.51,5.06] |
*Creatinine clearance (mL/min)
Pregnant woman
Do not administer this drug to pregnant women or women who may be pregnant, and use insulin preparations. Transfer to the fetus has been observed in animal experiments (rats). In animal experiments in which this drug was administered during the fetal organogenesis period, when 1500 mg/kg/day (corresponding to an exposure dose of about 17 times the maximum clinical dose of 2000 mg/day) was orally administered to rats. Low surviving fetal body weight and delayed ossification have been observed. After implantation, when rabbits are orally administered at 200 mg/kg/day (corresponding to an exposure dose of about 1.4 times the maximum clinical dose of 2000 mg/day), total embryo absorption and the number of surviving foetus tend to be low. An increasing tendency of mortality and a low tendency of living fetal weight have been observed.
Lactating women
During treatment, consider continuing or discontinuing breastfeeding, taking into account the therapeutic benefits and benefits of breastfeeding. Transfer to milk has been observed in animal experiments (rats).
Children
No clinical trials have been conducted on children.
Elderly
Carefully administer while observing the patient’s condition. In general, the physiological function is often reduced.
4.7 Effects on the ability to drive and use machines
Since hypoglycemic symptoms may occur due to Imeglimin, if you feel dizzy while taking this medicine, do not drive or use machines.
4.8 Undesirable Effects
The clinical trial evidence shows that the incidences of hypoglycemia observed for Imeglimin are similar to that of placebo (as shown in clinical trials TIMES 1* and TIMES 3**). *Dubourg J, et al. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(4):952-959. DOI: 10.2337/dc20-0763. ** Reilhac C, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022;24(5):838-848. DOI: 10.1111/dom.14642. Hypoglycemia may occur when used in combination with an insulin preparation, a sulfonylurea agent, or fast-acting insulin secretagogues. If hypoglycemic symptoms (initial symptoms : weakness, severe hunger, sweating, etc.) are observed, take appropriate measures such as ingesting foods containing sugar. However, if hypoglycemic symptoms are observed in combination with an α-glucosidase inhibitor, glucose should be administered.
Other side effects
| 1 % to 5 % | Less than 1 % | |
| Infectious diseases and parasites | - | Cystitis |
| Metabolic and malnutrition | - | Loss of appetite |
| Eye disorders | - | Diabetic retinopathy, retinal edema / macular edema |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Nausea, diarrhoea, constipation | Vomiting, abdominal discomfort, dyspepsia, upper abdominal pain, loose stools, abdominal distension, gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| Laboratory test | - | Increased blood lactate, increased lipase, weight loss |
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued side monitoring and benefit/risk ratio of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via email to : medico@zuventus.com
Website :https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
4.9 Overdose
There is no specific antidote for Imeglimin. In case of an overdose event, the stomach should be immediately emptied by gastric lavage. Treatment should be symptomatic and supportive, especially observing and treating hypoglycemia. There is no data on the removal of the Imeglimin by dialysis (hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis or hemofiltration).
5.0 Pharmacological properties
5.1 Mechanism of Action /Pharmacodynamic Properties
Imeglimin is a drug that exerts a hypoglycemic effect by glucose concentration-dependent insulin secretion promoting action and improving insulin resistance. Its mechanism of action is assumed to be mediated by an action on mitochondria.
Glucose Concentration-Dependent Insulin Secretion Promoting Effects
Imeglimin increased insulin secretion in the presence of high glucose in an in-vitro study using pancreatic islets from Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rats. In addition, blood insulin concentrations were increased in glucose tolerance tests in streptozotocin-induced diabetes model rats, GK rats, and high-fat diet-loading rats. The glucose clamp test also increased blood insulin levels. When patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were given 1500 mg of the drug once a day or placebo orally twice a day for 7 days, and a high glucose clamp test was performed 2 hours after the last dose, the AUC of 0-45 min in blood insulin concentration immediately after glucose administration and 45 minutes after glucose administration increased in the Imeglimin group as compared to the placebo group. When patients with type 2 diabetes were given 1500 mg or placebo twice a day for 18 weeks, and an oral glucose tolerance test was performed 2 hours after the last dose, the insulinogenic index increased in the drug group as compared to the placebo.
Improving Insulin Resistance
Imeglimin has an inhibitory effect on gluconeogenesis and an action on increasing glucose uptake in in-vitro studies using primary cultured hepatocytes and in-vitro tests using muscle cell lines. It also increased steady-state glucose infusion rates in a euglycemic hyperinsulin clamp study in a streptozotocin-induced diabetes model. When patients with type 2 diabetes were given 1500 mg of this drug twice a day for 18 weeks, and an oral glucose tolerance test was performed 2 hours after the last dose, the Stumvoll index [calculated from plasma glucose (mmol/l) and insulin (pmol/l concentrations during OGTT)], which is one of the indices of insulin resistance in the drug group, improved compared to the placebo group.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Single Dose
When 1000 mg of the drug was administered orally on an empty stomach to healthy adults, the plasma concentration transition and pharmacokinetic parameters were as follows.
| Dose | Tmax (hr) | Cmax (ng/mL) | AUC0-24 (ng.hr/mL) | T1/2 (hr) |
| 1000 mg (n=6) | 2.5 (1.5-3.0) | 1393 (40.3) | 9780 (36.1) | 12.0 (113.0) |
Data are expressed in Geometric mean (% geometric CV), Tmax : median (range)
Effect of diet
The pharmacokinetic parameters of a single oral dose of 1000 mg of this drug to healthy adult males on an empty stomach and after meals were as follows. No clinically significant dietary effects were observed.
| Dosing time | Tmax (hr) | Cmax (ng/ mL) | AUC0-48 (ng·hr/ mL) | T1/2 (hr) |
| On an empty stomach (n = 12) | 3.0 (1.0- 4.0) | 1681 (27.5) | 12970 (30.6) | 7.2 (56.4) |
| After meal (n = 12) | 4.0 (3.0 - 4.0) | 1424 (26.1) | 11960 (29.9) | 6.1 (59.9) |
Data are expressed in Geometric mean (% geometric CV), Tmax : median (range)
Repeated Doses
When 6 healthy adults were given repeated oral administration of 1000 mg twice a day for 7 days, plasma concentrations reached steady state on day 5, and the accumulation ratios of Cmax and AUC0-12 on day 7 were 1.43 and 1.57 times, respectively. As a result of population PK analysis based on plasma concentrations obtained from 867 patients who received the drug, the exposure dose (AUC0-12,SS) was estimated to be 18.0 mcg·hr/mL (geometric mean).
Distribution
The protein binding rate of Imeglimin in human plasma ranged from 1.2% to 6.4%.
Metabolism
Imeglimin does not induce/inhibit CYP450. When a single oral dose of 14C-labelled Imeglimin 1000 mg was given to 6 healthy adult males, Imeglimin was hardly metabolized, and the main radioactive components in plasma and urine were unchanged. Imeglimin does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, CYP3A4 / 5 (IC50 > 100 μ.mol/ L, CYP1A2, CYP2 at concentrations up to 120 μ.mol/L, CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 / 5 were not induced.
Excretion
When a single oral dose of 14 C-labelled Imeglimin 1000 mg was given to 6 healthy adult men, the cumulative excretion rate of urinary radioactivity and unchanged drug up to 144 hours after administration was 43.2% and 42.0% of the administered radioactivity, and feces. The cumulative excretion rate of medium radioactivity was 54.8% of the administered radioactivity.
Drug interactions
In an in-vitro study, Imeglimin was a substrate for organic cation transporter 1 (OCT1), OCT2, multidrug and toxin extrusion protein 1 (MATE1) and MATE2-K, but not for P-glycoprotein, Breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1) and OAT3. Imeglimin showed no inhibitory effect on P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3 and MATE2-K (IC50>1000 μ.mol/L). On the other hand, it showed an inhibitory effect on OCT1 (K : 154 μ.mol/L), OCT2 (IC : 146 μ.mol/L) and MATE1 (IC : 19.24 μ.mol/ L). It was considered unlikely that a drug interaction would be observed.
6.0 Nonclinical Properties
6.1 Animal Toxicology or Pharmacology
The acute oral median lethal dose (LD50) of Imeglimin HCL in Wistar rats & Swiss Albino mice was concluded as >2000.0 mg/kg body weight. The repeated oral administration of Imeglimin HCl to male and female Wistar rats for a period of 28 days with 50.0 mg/kg, 100.0 mg/kg and 200.0 mg/kg body weight doses did not show any significant differences in the body weight, feed consumption and other parameters (male and female) as compared to the vehicle control group. Hence, high dose of Imeglimin HCl (200.0 mg/kg, body weight) was concluded as NOAEL (No Observed Adverse Effect Level) in both male and female rats. The repeated oral administration of Imeglimin HCl to New Zealand White Rabbits following a period of 28-days with 25.0 mg/kg, 50.0 mg/kg and 100.0 mg/kg body weight, doses did not show any significant differences in the body weight, feed consumption and other parameters of male and female rabbits as compared with vehicle control animals. Therefore, a high dose of Imeglimin HCl (100.0 mg/kg, body weight) has been considered as NOAEL (No Observed Adverse Effect Level) in both male and female rabbits.
7.0 Description
Imeglimin is the first of the group of oral tetrahydrotriazine compounds, glimin, class of oral antidiabetic agents for Type II diabetes.
Chemical name : (R)-6-imino-N,N,4-trimethyl-1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-1,3,5-triazin-2-amine hydrochloride.
IUPAC Name : (R)-N2,N2,6-trimethyl-1,6-dihydro-1,3,5-triazine-2, 4-diamine hydrochloride.
Molecular formula : C6H13N・HCl
Molecular weight : 191.66
Structural formula :
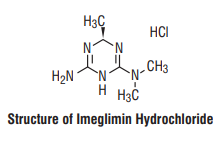
8.0 Pharmaceutical particulars
8.1 Incompatibilities
Not applicables
8.2 Shelf-life
Refer on the pack.
8.3 Packaging information
Zuglimin 500 : PVC-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets
Zuglimin 1000 : PVC-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets
8.4 Storage and handing instructions
Store below 30°C.
Keep out of reach of children
9.0 Patient counselling information
What are Zuglimin Tablets?
Zuglimin Tablets are used to treat type 2 diabetes. This is also known as non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. People with type 2 diabetes are not able to make enough insulin or respond normally to the insulin their bodies make. When this happens, sugar (glucose) builds up in the blood. This can lead to serious medical problems including kidney damage, amputations, and blindness. Diabetes is also closely linked to heart disease. The main goal of treating diabetes is to lower your blood sugar to a normal level. Zuglimin Tablets contain Imeglimin hydrochloride which is a first-in-class drug with a unique dual mechanism of action for the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes, both as a monotherapy or as an add-on to other glucose-lowering therapies.
How should I take Zuglimin Tablets?
Zuglimin Tablets must be swallowed whole and never crushed or chewed. Your doctor will tell you how much medicine to take and when to take it. If you miss a dose of Zuglimin Tablets, take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular schedule. Do not double the dose. If you have taken too many tablets, contact your doctor immediately.
Tell your doctor if you :
- have allergic to Imeglimin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
- are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. Your doctor may wish to alter your dose of Imeglimin Tablets if you are taking other diabetes drugs such as : Insulin preparations, Sulfonylurea, Fast-acting insulin secretagogues, α-glucosidase inhibitors, Thiazolidine drugs, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists SGLT2 inhibitors, etc.
- are taking the drugs that enhance the hypoglycemic effect (β-blockers Salicylic acid agents, Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, etc.) or reduce hypoglycemic effects (Adrenaline adrenocortical hormone thyroid hormone, etc.)
- have severely reduced kidney function.
- are breastfeeding, pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
What should I avoid while taking Zuglimin Tablets?
If you feel dizzy while taking this medicine, do not drive, use machines, or work at heights.
Can Zuglimin Tablets be used in children?
Zuglimin Tablets have not been studied in children.
General advice about prescription medicines
If you have questions or problems, talk with your doctor or other healthcare providers. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about Zuglimin Tablets. Do not use Zuglimin Tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed.
12.0 Date of issue
10 December 2022

About leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
What is in this leaflet
1. What ZugliminTM is and what it is used for
2. What you need to know before you use ZugliminTM
3. How to use ZugliminTM
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store ZugliminTM
6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What ZugliminTM is and what it is used for
ZugliminTM tablets contains Imeglimin hydrochloride, is a first-in-class drug that belongs to a new class of antidiabetic medication known as the "glimins." It is designed to target the key defects of type 2 diabetes mellitus by improving insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues, enhancing insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells, and inhibiting hepatic glucose production.
Imeglimin works through a unique mechanism involving the mitochondria, which helps to improve the metabolic function and energy balance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
This multifaceted approach helps to regulate blood glucose levels more effectively.
2. What you need to know before you take ZugliminTM
Do not take ZugliminTM:
If you are allergic to Imeglimin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine & If you think you may be allergic to Imeglimin or any of the other ingredients of Imeglimin.
Patients with complications / medical history
- The following patients or conditions that may cause hypoglycemia
- Pituitary dysfunction or adrenal dysfunction
- Malnutrition, starvation, irregular dietary intake, lack of dietary intake or weakness
- Intense muscle exercise
- Excessive alcohol intake
Patients with renal dysfunction
Patients with renal dysfunction with eGFR < 45 mL/min/1.73m2 (including dialysis patients)-administration is not recommended. The blood concentration of this drug may increase significantly.
Patients with hepatic dysfunction
The blood concentration of this drug may increase. In addition, clinical trials have not been conducted in patients with severe (Child-Pugh classification C) liver dysfunction.
Other medicines and Imeglimin Tablets:
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. Your doctor may wish to alter your dose of Imeglimin Tablets if you are taking other medicines such as:
- Diabetes drugs, Insulin preparations, etc.
- Drugs that enhance the hypoglycemic effect: β-blockers, Salicylic acid agents, Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, etc.
- Drugs that reduce hypoglycaemic effects: Adrenaline, adrenocortical hormone, thyroid hormone, etc.
Pregnancy, breast feeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, don’t take this medication.
Driving and using machines
If you feel dizzy while taking this medicine, do not drive or use machines.
3. How to take ZugliminTM tablets
Adults: generally recommended dosage is 1000 mg of Imeglimin is orally administered twice daily in the morning and evening.
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure. Swallow the tablet whole with some water.
If you take more Imeglimin Tablets than you should
If you have taken too many tablets, contact your doctor immediately or go to the nearest hospital casualty department taking any remaining medication and this patient information leaflet with you.
If you forget to take Imeglimin Tablets
If you miss a dose of Imeglimin Tablets, take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular schedule. Do not double the dose.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Stop taking this medicine and consult your doctor immediately if any of the following occur:
Hypoglycemia, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, dyspepsia, upper abdominal pain, loose stools, abdominal distension, gastroesophageal reflux disease, urinary bladder infection, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic retinal edema / macular edema, increased blood lactate, increased lipase and weight loss you may need medical treatment.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly: Website: www.zuventus.co.in and click the tab “Safety Reporting” located on the top end of the home page.
Website link: https://www.zuventus.com/drug-safety-reporting
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
You can also report the side effect with the help of your treating physician.
5. How to store ZugliminTM tablets
Store below 30°C. Keep out of reach of children.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
Zuglimin 500: PVC-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets
Zuglimin 1000: PVC-Alu blister strip of 10 tablets
7. Date of revision
27th June 2024